Effects of a Heat Wave on Nocturnal Stomatal Conductance in Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plants and Growing Conditions
2.2. Measurements and Statistical Analyses
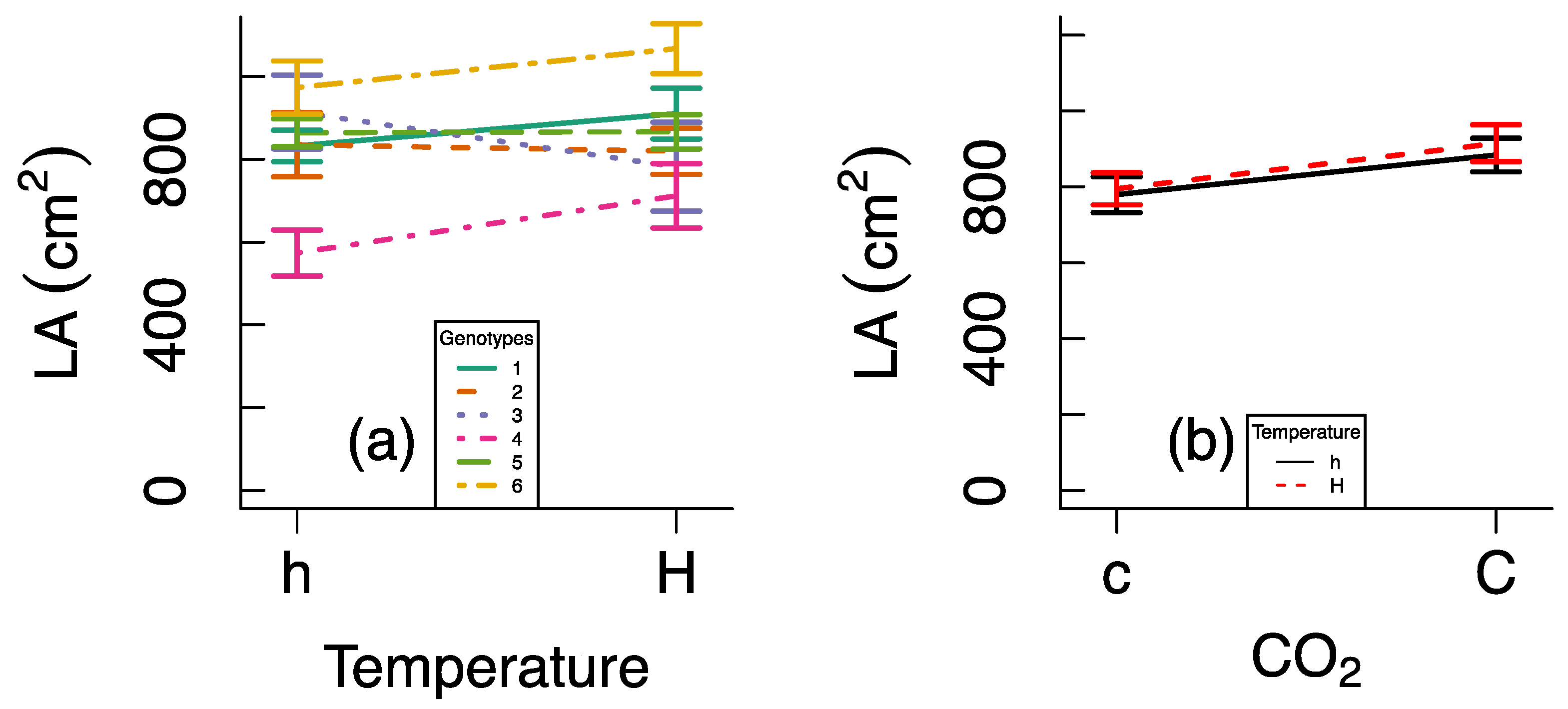
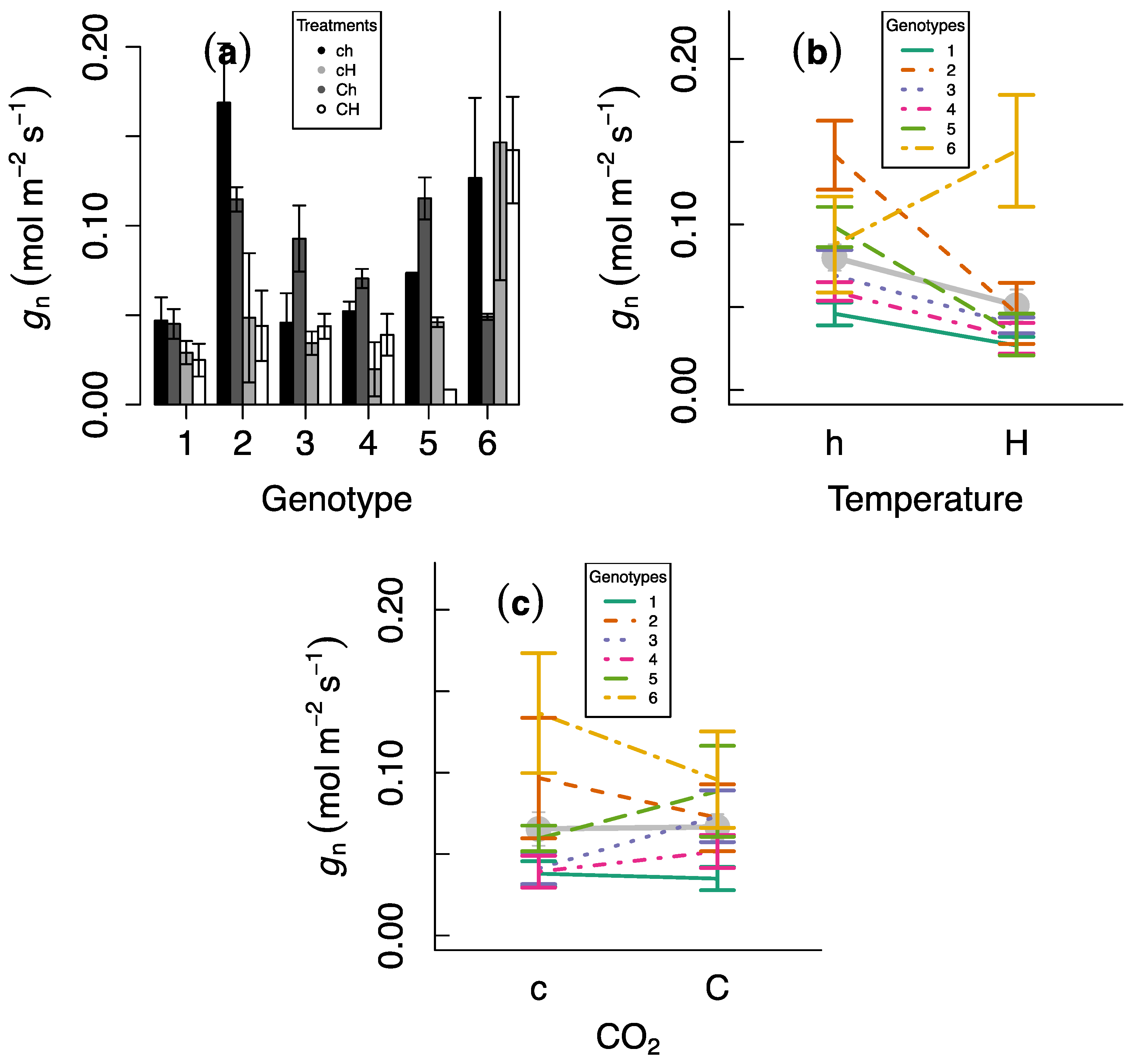
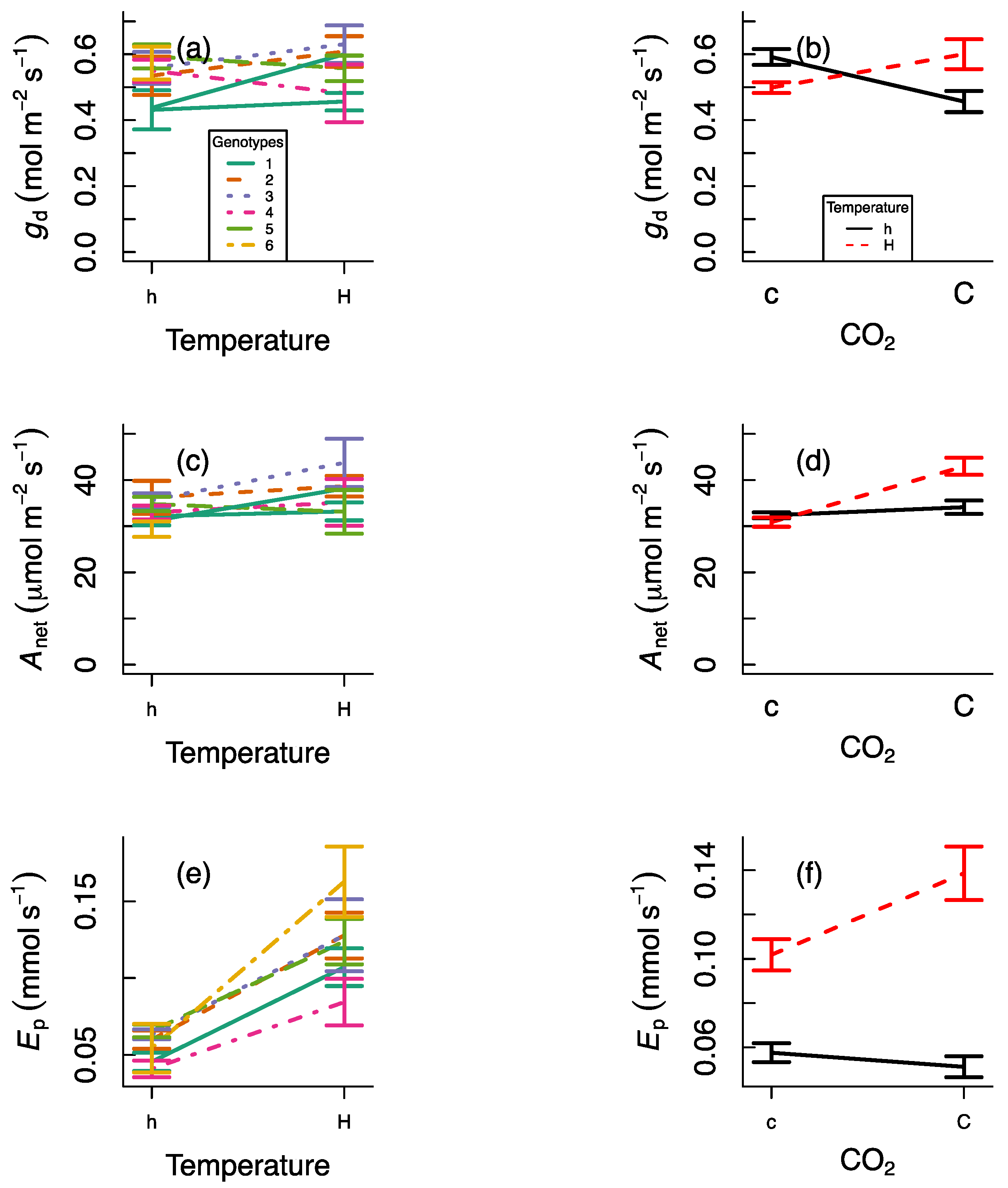
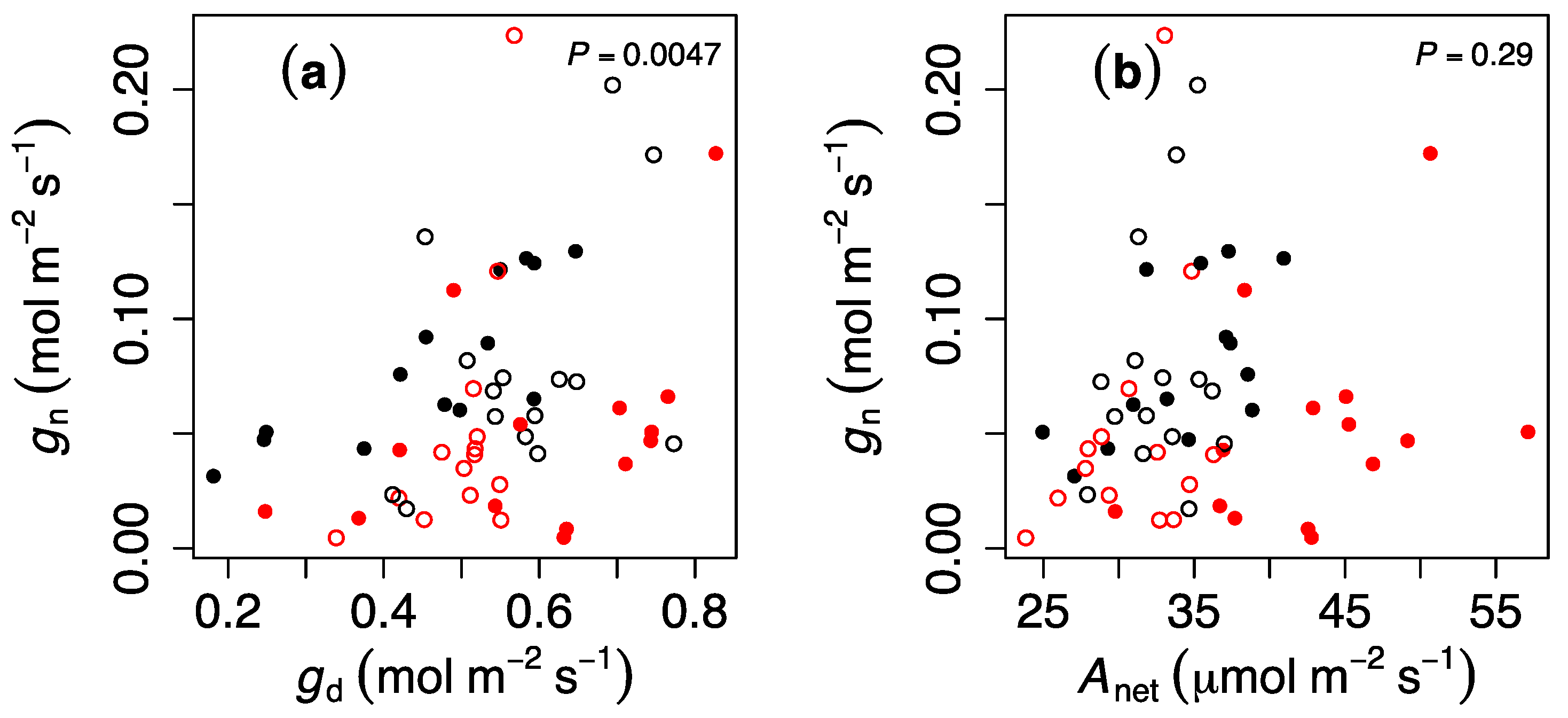
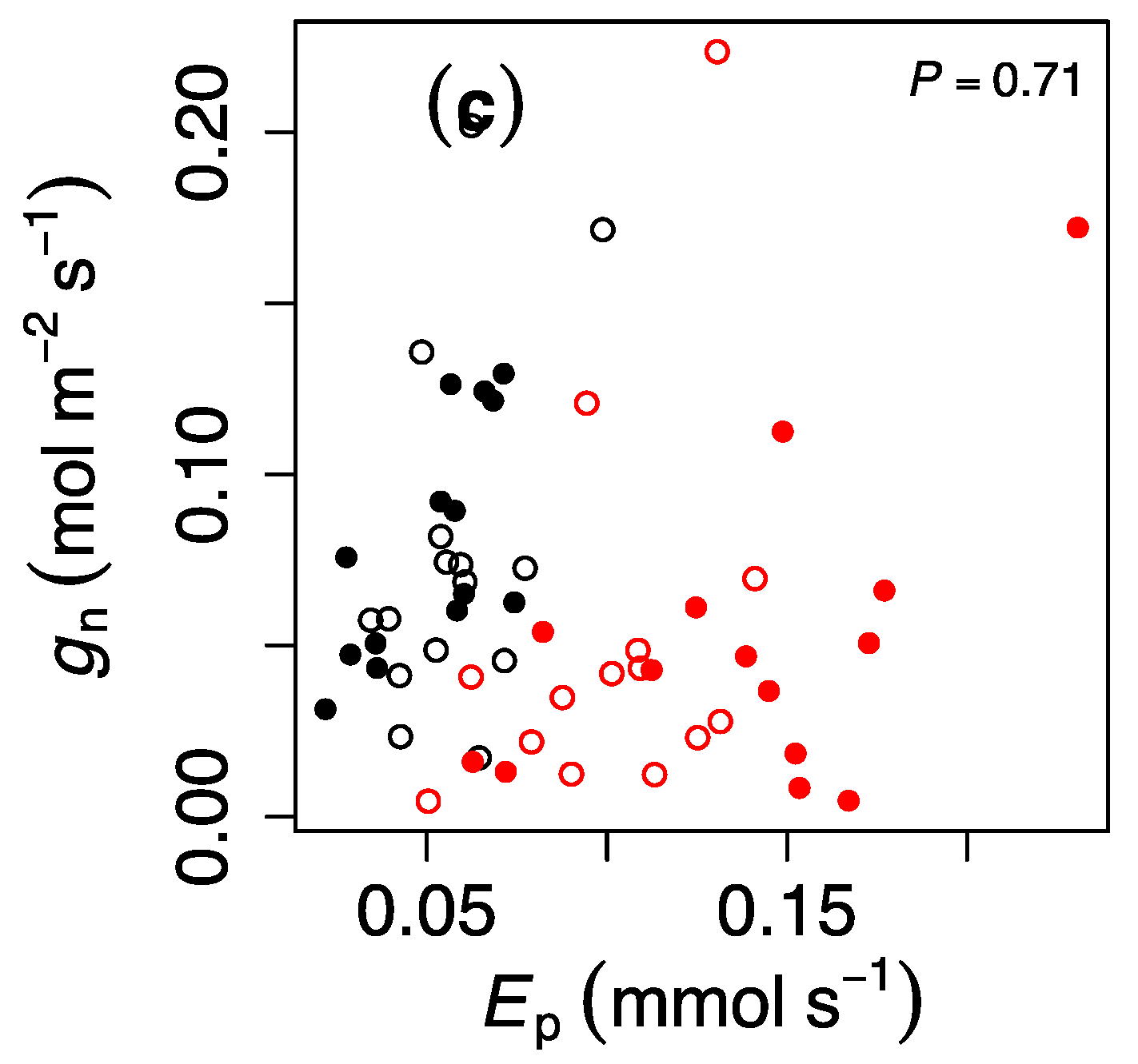
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Genotype | Location | Latitude | Longitude | MAP (mm) | MAT (°C) | MXT (°C) | ATR (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | YASS RIVER | 34.53 | 149.02 | 675 | 14.0 | 28.4 | 25.8 |
| 2 | OVENS VALLEY | 36.36 | 146.47 | 653 | 15.0 | 30.5 | 26.8 |
| 3 | COONAWARRAW | 37.2 | 140.42 | 646 | 14.5 | 30.0 | 24.0 |
| 4 | NYNGAN | 31.33 | 147.11 | 481 | 19.2 | 34.2 | 27.6 |
| 5 | CONDOBOLIN | 33.06 | 147.09 | 459 | 17.6 | 33.9 | 28.9 |
| 6 | BARMAH SF | 35.5 | 145.07 | 403 | 16.4 | 33.0 | 28.2 |
References
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E. A review of global terrestrial evapotranspiration: Observation, modeling, climatology, and climatic variability. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, M.A. How significant is nocturnal sap flow? Tree Physiol. 2014, 34, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardozzi, D.L.; Zeppel, M.J.B.; Fisher, R.A.; Tawfik, A. Representing nighttime and minimum conductance in clm4.5: Global hydrology and carbon sensitivity analysis using observational constraints. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, I.R.; Farquhar, G.D. Stomatal function in relation to leaf metabolism and environment. In Integration of Activity in the Higher Plant; Jennings, D.H., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Caird, M.A.; Richards, J.H.; Donovan, L.A. Nighttime stomatal conductance and transpiration in C3 and C4 plants. Plant Physiol. 2007, 143, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppel, M.J.; Lewis, J.D.; Phillips, N.G.; Tissue, D.T. Consequences of nocturnal water loss: A synthesis of regulating factors and implications for capacitance, embolism and use in models. Tree Physiol. 2014, 34, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musselman, R.C.; Minnick, T.J. Nocturnal stomatal conductance and ambient air quality standards for ozone. Atm Env. 2000, 34, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogle, K.; Lucas, R.W.; Bentley, L.P.; Cable, J.M.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Griffith, A.; Ignace, D.; Jenerette, G.D.; Tyler, A.; Huxman, T.E.; et al. Differential daytime and night-time stomatal behavior in plants from North American deserts. New Phytol. 2012, 194, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeppel, M.J.B.; Lewis, J.D.; Chaszar, B.; Smith, R.A.; Medlyn, B.E.; Huxman, T.E.; Tissue, D.T. Nocturnal stomatal conductance responses to rising [CO2], temperature and drought. New Phytol. 2012, 193, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, M.M.; Cernusak, L.A.; Whitehead, D.; Griffin, K.; Turnbull, M.; Tissue, D.T.; Farquhar, G.D. Nocturnal stomatal conductance and implications for modelling δ 18O of leaf-respired CO2 in temperate tree species. Funct. Plant Biol. 2005, 32, 1107–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resco de Dios, V.; Diaz-Sierra, R.; Goulden, M.L.; Barton, C.V.; Boer, M.M.; Gessler, A.; Ferrio, J.P.; Pfautsch, S.; Tissue, D.T. Woody clockworks: Circadian regulation of night-time water use in eucalyptus globulus. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easlon, H.M.; Richards, J.H. Photosynthesis affects following night leaf conductance in vicia faba. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resco de Dios, V.; Roy, J.; Ferrio, J.P.; Alday, J.G.; Landais, D.; Milcu, A.; Gessler, A. Processes driving nocturnal transpiration and implications for estimating land evapotranspiration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, A.G.; Katata, G.; Hoshika, Y.; Hossain, M.; Kreuzwieser, J.; Arneth, A.; Ruehr, N.K. Immediate and potential long-term effects of consecutive heat waves on the photosynthetic performance and water balance in douglas-fir. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 205, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, M.M.; Buckley, T.N. The stomatal response to evaporative demand persists at night in ricinus communis plants with high nocturnal conductance. Plant Cell Environ. 2007, 30, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.B.; Barros, V.; Stocker, T.F.; Dahe, Q.; Dokken, D.J.; Ebi, K.L.; Mastrandrea, M.D.; Mach, K.J.; Plattner, G.-K.; Allen, S.K.; et al. Managing the Risks of Extreme Events and Disasters to Advance Climate Change Adaptation—Special Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012; p. 582. [Google Scholar]
- De Dios, V.R.; Loik, M.E.; Smith, R.A.; Aspinwall, M.J.; Tissue, D.T. Genetic variation in circadian regulation of nocturnal stomatal conductance enhances plant fitness. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milcu, A.; Puga-Freitas, R.; Ellison, A.M.; Blouin, M.; Scheu, S.; Freschet, G.T.; Rose, L.; Barot, S.; Cesarz, S.; Eisenhauer, N.; et al. Genotypic variability enhances the reproducibility of an ecological study. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H. Plants and Microclimate: A Quantitative Approach to Environmental Plant Physiology, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; p. 423. [Google Scholar]
- Loik, M.E.; Resco de Dios, V.; Smith, R.; Tissue, D.T. Relationships between climate of origin and photosynthetic responses to an episodic heat wave depend on growth CO2 concentration for eucalyptus camaldulensis var. Camaldulensis. Funct. Plant Biol. 2017, 44, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pury, D.G.G.; Farquhar, G.D. Simple scaling of photosynthesis from leaves to canopies without the errors of big-leaf models. Plant Cell Environ. 1997, 20, 537–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Lme4: Linear mixed-effects models using eigen and s4. R package version 1.1-7. 2014. Available online: Http://cran.R-project.Org/package=lme4 (accessed on 20 February 2018).
- Buckley, T.N. Modeling stomatal conductance. Plant Physiol. 2017, 174, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Dios, V.R.; Gessler, A.; Ferrio, J.P.; Alday, J.G.; Bahn, M.; del Castillo, J.; Devidal, S.; García-Muñoz, S.; Kaylerd, Z.; Landais, D.; et al. Circadian rhythms have significant effects on leaf-to-canopy gas exchange under field conditions. GigaScience 2016, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfautsch, S.; Adams, M.A. Water flux of eucalyptus regnans: Defying summer drought and a record heat wave in 2009. Oecologia 2013, 172, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupper, P.; Ivanova, H.; Sõber, A.; Rohula-Okunev, G.; Sellin, A. Night and daytime water relations in five fast-growing tree species: Effects of environmental and endogenous variables. Ecohydrology 2017, e1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, C.J.; Aspinwall, M.J.; Resco de Dios, V.; Smith, R.; Tissue, D.T. Leaf photosynthetic, economics and hydraulic traits are decoupled among genotypes of a widespread species of eucalypt grown under ambient and elevated CO2. Funct. Ecol. 2016, 30, 1491–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, N.G.; Lewis, J.D.; Logan, B.A.; Tissue, D.T. Inter- and intra-specific variation in nocturnal water transport in eucalyptus. Tree Physiol. 2010, 30, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucci, S.J.; Scholz, F.G.; Goldstein, G.; Meinzer, F.C.; Hinojosa, J.A.; Hoffmann, W.A.; Franco, A.C. Processes preventing nocturnal equilibration between leaf and soil water potential in tropical savanna woody species. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoppach, R.; Claverie, E.; Sadok, W. Genotype-dependent influence of night-time vapour pressure deficit on night-time transpiration and daytime gas exchange in wheat. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christman, M.A.; Richards, J.H.; McKay, J.K.; Stahl, E.A.; Juenger, T.E.; Donovan, L.A. Genetic variation in arabidopsis thaliana for night-time leaf conductance. Plant Cell Environ. 2008, 31, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogle, K.; Barber, J.J.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Bentley, L.P.; Young, J.M.; Huxman, T.E.; Loik, M.E.; Tissue, D.T. Quantifying ecological memory in plant and ecosystem processes. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| gn | gd | Anet | Ep | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| χ2 | P | χ2 | P | χ2 | P | χ2 | P | |
| CO2 | 0.001 | 0.99 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 27.42 | <0.001 | 1.560 | 0.21 |
| Genotype | 41.01 | <0.001 | 19.83 | 0.003 | 17.92 | 0.006 | 30.72 | <0.001 |
| Heat wave | 11.85 | <0.001 | 1.66 | 0.20 | 6.23 | 0.01 | 116.88 | <0.001 |
| C × G | 8.67 | 0.12 | 7.68 | 0.26 | 4.99 | 0.54 | 4.33 | 0.50 |
| C × H | 0.07 | 0.79 | 13.45 | <0.001 | 17.02 | <0.001 | 16.97 | <0.001 |
| G × H | 28.63 | <0.001 | 6.45 | 0.26 | 6.04 | 0.30 | 10.41 | 0.06 |
| C × G × H | 6.99 | 0.22 | 4.63 | 0.46 | 2.39 | 0.79 | 5.44 | 0.56 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Resco de Dios, V.; Loik, M.E.; Smith, R.A.; Tissue, D.T. Effects of a Heat Wave on Nocturnal Stomatal Conductance in Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Forests 2018, 9, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060319
Resco de Dios V, Loik ME, Smith RA, Tissue DT. Effects of a Heat Wave on Nocturnal Stomatal Conductance in Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Forests. 2018; 9(6):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060319
Chicago/Turabian StyleResco de Dios, Víctor, Michael E. Loik, Renee A. Smith, and David T. Tissue. 2018. "Effects of a Heat Wave on Nocturnal Stomatal Conductance in Eucalyptus camaldulensis" Forests 9, no. 6: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060319
APA StyleResco de Dios, V., Loik, M. E., Smith, R. A., & Tissue, D. T. (2018). Effects of a Heat Wave on Nocturnal Stomatal Conductance in Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Forests, 9(6), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9060319






