Variation in the Concentrations of Major Secondary Metabolites in Ginkgo Leaves from Different Geographical Populations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Extraction
2.3. HPLC Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
- Total flavonoid = (quercetin + kaempferol + isorhamnetin) × 2.51 [18];
- Ginkgolide = ginkgolide A + ginkgolide B + ginkgolide C;
- Total lactone = ginkgolide + bilobalide.
3. Results and Discussion
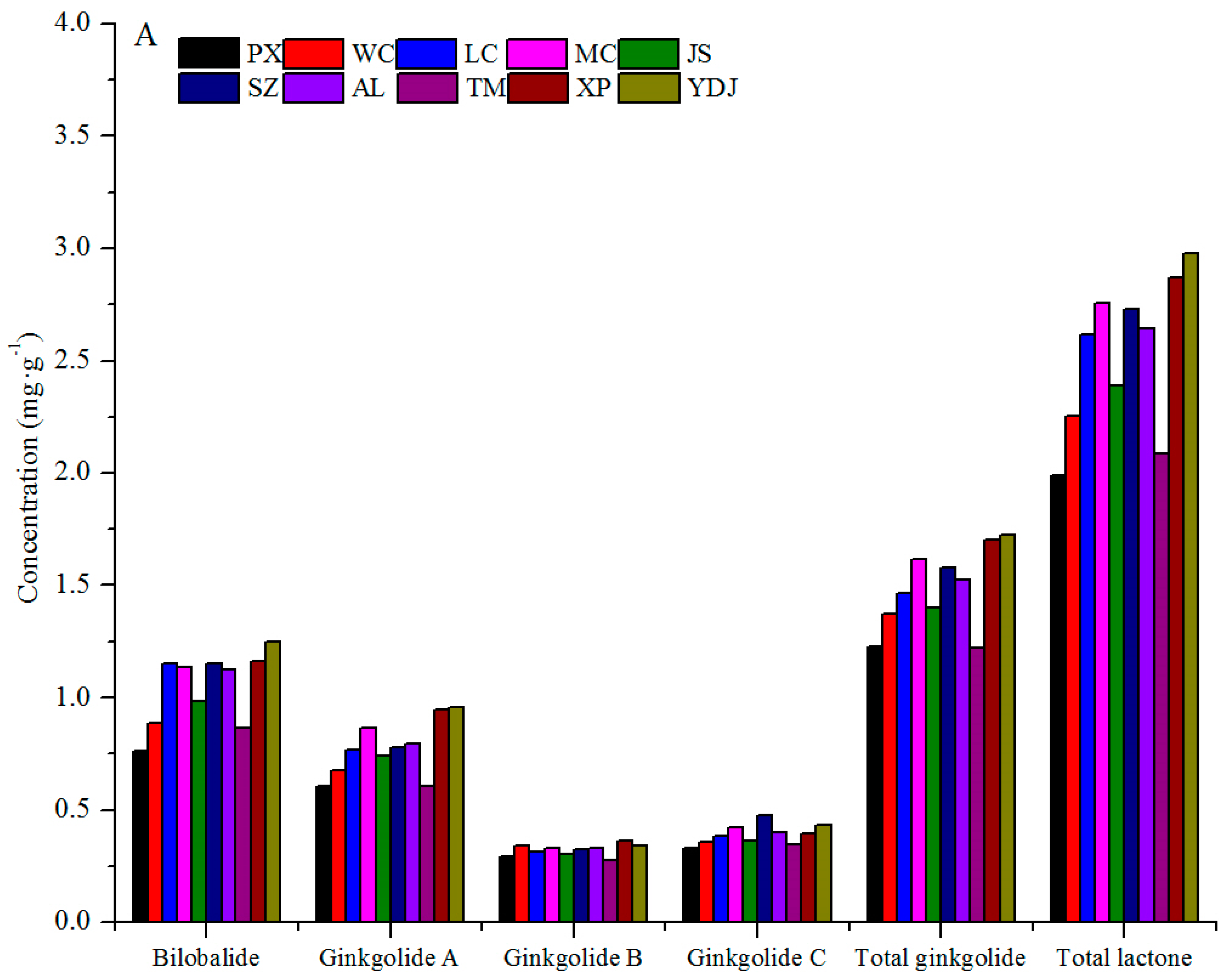
3.1. Variation among Geographical Populations
3.2. Correlations between Pairs of Concentrations and Geographical Climate Factors
3.3. Variation within Geographical Populations
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Zheng, S.L. Palaeobiology: The missing link in Ginkgo evolution. Nature 2003, 423, 821–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yao, X.; Cheng, Z.Q. Rapid and sensitive determination of major active ingredients and toxic components in Ginkgo biloba leaves extract (EGb 761) by a validated UPLC–MS-MS Method. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 4, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.C.; Lai, S.M.; Suen, S.Y. Extraction of flavonoid glycosides from Ginkgo biloba leaves and their adsorption separations using hydrophobic and anion-exchange membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2003, 5, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.M.; Tian, H.J.; Zhang, G.Y.; Dai, Y.R. Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on hydroxyl radical-induced thymocyte apoptosis and on age-related thymic atrophy and peripheral immune dysfunctions in mice. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2003, 8, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Kelly, G.E.; Husband, A.J. Flavonoid compounds in maintenance of prostate health and prevention and treatment of cancer. Mol. Biotechnol. 2005, 3, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.J.; Wang, X.D.; Morris, M.E. Dietary flavonoids: Effects on xenobiotic and carcinogen metabolism. Toxicol. In Vitro 2006, 2, 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niering, P.; Michels, G.; Wätjen, W.; Ohler, S.; Steffan, B.; Chovolou, Y.; Kampkotter, A.; Proksch, P.; Kahl, R. Protective and detrimental effects of kaempferol in rat H4IIE cells: Implication of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2005, 2, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim, K.E.; Tagliaferro, A.R.; Bobilya, D.J. Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 10, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufi, A.M.; Ibrahim, S.S.; Elmaghraby, T.K.; Hafez, E.E. Preventive effect of the flavonoid, quercetin, on hepatic cancer in rats via oxidant/antioxidant activity: Molecular and histological evidences. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmaillzadeh, A.; Azadbakht, L. Dietary flavonoid intake and cardiovascular mortality. Brit. J. Nutr. 2008, 4, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Beek, T.A. Chemical analysis of Ginkgo biloba leaves and extracts. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 1, 21–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratskaya, E.L.; Krishtal, O.A. Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract constituents on glycine-activated strychnine-sensitive receptors in hippocampal pyramidal neurons of the rat. Neurophysiology 2002, 2, 155–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Zhu, X.L.; Geng, Q.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Shao, J.H. Change of peripheral blood monocytes derived macrophage scavenger receptors activity in patients with coronary heart disease, and the intervention effect of Ginkgo biloba extract. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2004, 12, 1069–1072, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, S. Constituents of Ginkgo biloba L. leaves. Sci. Papers Inst. Phys. Chem. Res. 1932, 19, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Itokawa, H.; Totsuka, N.; Nakahara, K.; Takeya, K.; Lepoittevin, J.P.; Asakawa, Y. Antitumor principles from Ginkgo biloba L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3016–3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, H.; Johannisson, R.; Koch, E.; Siegers, C.P. In vitro evaluation of the cytotoxic potential of alkylphenols from Ginkgo biloba L. Toxicology 2002, 177, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Ruppert, G.; Luepke, N.P. Evidence for toxic effects of alkylphenols from Ginkgo biloba in the hen’s egg test (HET). Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese, P.C. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; China Medico-Pharmaceutical Science & Technology Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.J.; Xu, Y.Q.; Wei, G.Y.; Liao, S.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Huang, W.J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y. Chemotypic and genetic diversity in Epimedium sagittatum from different geographical regions of China. Phytochemistry 2015, 116, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinckmann, J.A. Emerging importance of geographical indications and designations of origin–authenticating geo-authentic botanicals and implications for phytotherapy. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Guo, P.; Brand, E. The formation of daodi medicinal materials. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 140, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kliebenstein, D.J.; Lambrix, V.M.; Reichelt, M.; Gershenzon, J.; Mitchell-Olds, T. Gene duplication in the diversification of secondary metabolism: Tandem 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases control glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlag, E.M.; McIntosh, M.S. The relationship between genetic and chemotypic diversity in American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.). Phytochemistry 2013, 93, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suhre, K.; Gieger, C. Genetic variation in metabolic phenotypes: Study designs and applications. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Chen, C.; Dobeš, C.; Fu, C.X.; Koch, M.A. Phylogeography of a living fossil: Pleistocene glaciations forced Ginkgo biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae) into two refuge areas in China with limited subsequent postglacial expansion. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 48, 1094–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.Y.; Fu, C.X.; Qiu, Y.X. Genetic variation of Ginkgo biloba L. (Ginkgoaceae) based on cpDNA PCR-RFLPs: Inference of glacial refugia. Heredity 2005, 94, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, D.K.; Tang, D.R.; He, J.L.; Chen, D. Correlation analysis between growth indices and contents of of ginkgolides in the leaves of Ginkgo biloba in Shaanxi. J. NW For. Univ. 2009, 3, 49–53, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xue, P.; Li, B.H.; Xiao, X.H.; Zhang, Y.Y. Genetic variation of the chemical constituents in Ginkgo leaves. Econ. Forest Res. 2000, 3, 31–33, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.W.; Liu, X.L.; Cao, F.L.; Wang, G.B.; Zhang, W.X. Cluster analysis on the main medicinal components in differential leaves of Ginkgo clones. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2014, 3, 292–305, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, L.; Cao, F.L.; Chen, T.C.; Yan, Y.H.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, G.B.; Wang, G.B. Optimization of homogenization conditions for the extraction of proanthocyanidin from Ginkgo biloba leaves using response surface methodology. Food Sci. 2012, 22, 12–16, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.J.; Zu, Y.G.; Fu, Y.J.; Li, C.Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Hou, C.L. Homogenated extraction of total flavonoids from fruits of sea buckthom (Hippophae rhamnoides L.). Chem. Ind. For. Prod. 2006, 2, 38–40, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.C.; Mani, A.; Cai, Y.L.; Thomson, J.; Ma, J.; Peudru, F.; Chen, S.; Luo, M.; Zhang, J.Z.; Chapman, R.G.; et al. An effective identification and quantification method for Ginkgo biloba flavonol glycosides with targeted evaluation of adulterated products. Phytomedicine 2016, 4, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasler, A.; Sticher, O.; Meier, B. Identification and determination of the flavonoids from Ginkgo biloba by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1992, 1, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobstein, A.; Rietsch-Jako, L.; Haag-Berrurier, M.; Anton, R. Seasonal variations of the flavonoid content from Ginkgo biloba leaves. Planta Med. 1991, 5, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.L.; Zhou, J.C.; Long, H.P.; Han, L.L. Total flavonol glucoside and lactone content changes of flavonol glucoside in different growing seasons. Cent. South Pharm. 2009, 8, 564–567, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Duan, H.J.; Cao, S.; Zheng, H.Q.; Hu, D.H.; Lin, J.; Lin, H.Z.; Hu, R.Y.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, Y. Variation in the Growth Traits and Wood Properties of Chinese Fir from Six Provinces of Southern China. Forests 2016, 7, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.Q.; Hu, D.H.; Wang, R.H.; Wei, R.P.; Yan, S. Assessing 62 Chinese Fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) breeding parents in a 12-year grafted clone test. Forests 2015, 6, 3799–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.X.; She, C.Q.; Fang, S.Z. Geographic variation of flavonoid compounds in Cyclocarya paliurus leaves. J. Zhejiang For. Coll. 2009, 4, 522–527, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gosztola, B.; Németh-Zámbori, É. Variability of total flavonoid and mucilage content of wild growing chamomile (Matricaria recutita L.) populations. Julius-Kühn-Archiv 2016, 453, 112–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.D.; Wang, H.T. Effects of light spectrum and photoperiod on contents of flavonoid and terpene in leaves of Ginkgo biloba L. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2006, 2, 51–54, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Elmastaş, M.; Demir, A.; Genx, N.; Dölek, Ü.; Gxneş, M. Changes in flavonoid and phenolic acid contents in some Rosa species during ripening. Food Chem. 2017, 235, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, R.J. Phenolic acids in foods: An overview of analytical methodology. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 10, 2866–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schijlen, E.G.; De Vos, C.R.; Van Tunen, A.J.; Bovy, A.G. Modification of flavonoid biosynthesis in crop plants. Phytochemistry 2004, 19, 2631–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.G.; Shen, Q.; Wang, N.; Qi, L.W.; Li, P. Combining metabolic profiling and gene expression analysis to reveal the biosynthesis site and transport of ginkgolides in Ginkgo biloba L. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Liu, S.B. Study on leaf shape variation and total flavonoids in different populations of Gynostemma pentagynum Z.P. Wang. Amino Acids Biot. Res. 2015, 4, 53–56, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]


| Population | Location | Longitude (East) | Latitude (North) | Elevation (m) | Frost-Free Period (Day) | Annual Rainfall (mm) | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.PX | Panxian, Guizhou | 104°31′ | 25°36′ | 1619 | 271 | 1390 | 32 |
| 2.WC | Wuchuan, Guizhou | 108°8′ | 28°38′ | 994 | 280 | 1272 | 22 |
| 3.LC | Lingchuan, Guangxi | 110°33′ | 25°18′ | 323 | 318 | 1926 | 28 |
| 4.MC | Mochuan, Guangxi | 110°48′ | 25°29′ | 325 | 293 | 1842 | 29 |
| 5.JS | Jingshan, Hubei | 113°3′ | 31°16′ | 238 | 230 | 1085 | 32 |
| 6.SZ | Suizhou, Hubei | 113°18′ | 31°26′ | 235 | 230 | 968 | 31 |
| 7.AL | Anlu, Hubei | 113°20′ | 31°24′ | 120 | 246 | 1100 | 33 |
| 8.TM | Mt. Tianmu, Zhejiang | 119°26′ | 30°19′ | 481 | 234 | 956 | 34 |
| 9.XP | Xiaopu, Zhejiang | 119°47′ | 31°1′ | 64 | 240 | 1309 | 31 |
| 10.YDJ | Yingdianjie, Zhejiang | 120°5′ | 28°49′ | 166 | 236 | 1374 | 26 |
| Total | 298 |
| SMs | PX | WC | LC | MC | JS | SZ | AL | TM | XP | YDJ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q ** | e (C) | cde (BC) | bc (AB) | cd (BC) | de (C) | de (C) | a (A) | cde (BC) | cde (BC) | ab (A) |
| K ** | e (E) | a (A) | cd (CDE) | de (E) | de (E) | de (DE) | bc (ABC) | bc (BCD) | ab (AB) | bc (BCD) |
| I ** | bcd (ABC) | a (A) | a (A) | ab (AB) | cd (BC) | cd (BC) | abc (ABC) | d (C) | bcd (ABC) | ab (AB) |
| TF ** | e (C) | a (A) | ab (AB) | bcd (ABC) | e (C) | de (C) | a (A) | cde (BC) | abc (AB) | a (A) |
| B ** | c (D) | bc (CD) | a (AB) | a (AB) | b (BC) | a (AB) | a (AB) | bc (CD) | a (AB) | a (A) |
| GA ** | d (F) | cd (DEF) | bc (BCD) | ab (ABC) | bc (CDE) | bc (BCD) | a (ABCD) | d (EF) | a (AB) | a (A) |
| GB ** | de (CD) | ab (AB) | bcd (BCD) | abc (ABC) | cd (BCD) | abc (ABC) | abc (ABC) | e (D) | a (A) | abc (AB) |
| GC ** | e (D) | cde (BCD) | bcd (ABC) | ab (A) | cde (BCD) | a (A) | ab (AB) | de (CD) | abc (ABC) | a (A) |
| TG ** | g (E) | ef (DE) | cde (BCD) | abc (ABC) | de (CDE) | abcd (ABCD) | bcde (ABCD) | fg (E) | ab (AB) | a (A) |
| TL ** | f (E) | de (CDE) | bc (ABC) | ab (AB) | cd (BCD) | ab (AB) | abc (AB) | ef (DE) | ab (A) | a (A) |
| G ** | abc (AB) | bc (B) | bc (AB) | bc (B) | a (A) | c (B) | bc (B) | ab (AB) | c (B) | e (C) |
| SMs | Q | K | I | TF | B | GA | GB | GC | TG | TL | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | 1 | ||||||||||
| K | 0.451 | 1 | |||||||||
| I | 0.509 | 0.303 | 1 | ||||||||
| TF | 0.826 ** | 0.791 ** | 0.727 * | 1 | |||||||
| B | 0.618 | 0.140 | 0.321 | 0.445 | 1 | ||||||
| GA | 0.524 | 0.211 | 0.335 | 0.445 | 0.904 ** | 1 | |||||
| GB | 0.371 | 0.519 | 0.541 | 0.607 | 0.640 * | 0.780 ** | 1 | ||||
| GC | 0.325 | −0.044 | 0.114 | 0.156 | 0.833 ** | 0.680 * | 0.535 | 1 | |||
| TG | 0.499 | 0.212 | 0.339 | 0.437 | 0.930 ** | 0.979 ** | 0.821 ** | 0.800 ** | 1 | ||
| TL | 0.566 | 0.181 | 0.337 | 0.449 | 0.981 ** | 0.960 ** | 0.748 * | 0.830 ** | 0.984 ** | 1 | |
| G | −0.586 | −0.437 | −0.476 | −0.634 * | −0.652 * | −0.695 * | −0.701 * | −0.635 * | −0.744 * | −0.713 * | 1 |
| SMs | Longitude | Latitude | Altitude | Annual Rainfall | Mean Annual Temperature | Frost-Free Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q | 0.362 | 0.039 | −0.504 | 0.219 | 0.367 | 0.092 |
| K | 0.398 | 0.34 | −0.206 | −0.172 | −0.204 | −0.074 |
| I | −0.335 | −0.6 | 0.047 | 0.762 * | 0.565 | 0.760 * |
| TF | 0.224 | −0.035 | −0.295 | 0.285 | 0.259 | 0.28 |
| B | 0.512 | 0.153 | −0.833 ** | 0.278 | 0.456 | −0.047 |
| GA | 0.537 | 0.131 | −0.708 * | 0.29 | 0.277 | −0.117 |
| GB | 0.186 | 0.133 | −0.382 | 0.216 | 0.019 | 0.046 |
| GC | 0.327 | 0.232 | −0.638 * | 0.027 | 0.186 | −0.188 |
| TG | 0.483 | 0.17 | −0.708 * | 0.238 | 0.241 | −0.123 |
| TL | 0.506 | 0.165 | −0.781 ** | 0.263 | 0.35 | −0.088 |
| G | −0.369 | 0.006 | 0.291 | −0.164 | −0.027 | 0.051 |
| SMs | PX | WC | LC | MC | JS | SZ | AL | TM | XP | YDJ | Mean CV% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Min | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 0.18 | 0.32 | 37.37 | |
| Q | Max | 0.76 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.83 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.25 | 0.95 | 0.83 | 1.20 | |
| CV% | 32.77 | 41.79 | 27.15 | 33.77 | 46.13 | 50.43 | 31.44 | 45.57 | 32.04 | 32.63 | ||
| Min | 0.10 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 40.38 | |
| K | Max | 0.67 | 1.34 | 1.11 | 0.73 | 0.70 | 0.88 | 1.27 | 1.11 | 1.34 | 1.23 | |
| CV% | 39.69 | 48.88 | 37.16 | 30.48 | 41.92 | 48.61 | 39.53 | 44.28 | 37.92 | 35.35 | ||
| I | Min | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.17 | 0.24 | 41.33 |
| Max | 0.69 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.49 | 0.60 | 0.81 | 0.60 | 0.69 | 0.71 | ||
| CV% | 42.35 | 46.60 | 39.11 | 39.02 | 37.25 | 42.55 | 40.38 | 57.53 | 40.72 | 27.82 | ||
| TF | Min | 1.08 | 1.63 | 1.54 | 1.59 | 1.14 | 1.25 | 1.83 | 1.44 | 1.67 | 2.21 | 34.37 |
| Max | 5.33 | 6.73 | 6.59 | 5.76 | 4.74 | 5.58 | 7.98 | 5.83 | 6.04 | 7.24 | ||
| CV% | 36.23 | 41.04 | 29.33 | 31.32 | 36.87 | 38.43 | 31.75 | 42.09 | 27.78 | 28.90 | ||
| B | Min | 0.60 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.70 | 0.63 | 0.70 | 0.82 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.65 | 21.41 |
| Max | 1.08 | 1.26 | 2.03 | 1.84 | 1.37 | 1.71 | 1.63 | 1.18 | 2.00 | 2.20 | ||
| CV% | 14.54 | 19.87 | 28.82 | 25.54 | 18.67 | 22.22 | 18.58 | 15.06 | 25.41 | 25.38 | ||
| GA | Min | 0.43 | 0.44 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.44 | 0.43 | 0.52 | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.52 | 26.49 |
| Max | 0.86 | 1.36 | 1.28 | 1.62 | 1.49 | 1.33 | 1.20 | 0.89 | 1.92 | 1.39 | ||
| CV% | 17.20 | 29.99 | 25.93 | 31.37 | 26.54 | 29.18 | 24.15 | 21.63 | 35.95 | 23.00 | ||
| GB | Min | 0.23 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.25 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 18.46 |
| Max | 0.40 | 0.61 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.39 | 0.54 | 0.55 | 0.34 | 0.60 | 0.56 | ||
| CV% | 12.51 | 23.68 | 19.21 | 20.04 | 14.41 | 20.32 | 20.35 | 11.13 | 21.25 | 21.71 | ||
| GC | Min | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.31 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 15.74 |
| Max | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.79 | 0.70 | 0.46 | 0.58 | 0.54 | 0.62 | 0.68 | 0.68 | ||
| CV% | 6.76 | 12.18 | 25.10 | 19.73 | 11.31 | 14.25 | 12.51 | 15.23 | 20.14 | 20.19 | ||
| TG | Min | 0.98 | 1.02 | 1.02 | 1.05 | 0.96 | 1.02 | 1.19 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 1.07 | 19.41 |
| Max | 1.64 | 2.32 | 2.31 | 2.55 | 2.31 | 2.24 | 2.16 | 1.53 | 3.20 | 2.60 | ||
| CV% | 12.20 | 21.58 | 21.84 | 22.28 | 18.44 | 20.90 | 17.26 | 12.79 | 27.40 | 19.44 | ||
| TL | Min | 1.63 | 1.63 | 1.77 | 1.76 | 1.59 | 1.72 | 1.86 | 1.64 | 1.61 | 1.74 | 20.36 |
| Max | 2.67 | 3.12 | 4.34 | 4.73 | 3.68 | 5.72 | 3.97 | 2.71 | 5.90 | 4.80 | ||
| CV% | 12.51 | 18.34 | 22.35 | 24.66 | 17.71 | 27.81 | 17.81 | 12.41 | 29.10 | 20.91 | ||
| G | Min | 13.25 | 10.67 | 11.36 | 10.36 | 11.87 | 8.76 | 9.70 | 9.21 | 8.13 | 8.18 | 27.48 |
| Max | 29.20 | 26.74 | 35.10 | 24.81 | 36.89 | 24.92 | 25.65 | 29.09 | 28.00 | 22.08 | ||
| CV% | 24.50 | 25.01 | 34.84 | 22.73 | 26.77 | 22.93 | 23.16 | 27.28 | 40.90 | 26.71 | ||
| Mean CV% | 22.84 | 29.90 | 28.26 | 27.36 | 26.91 | 30.69 | 25.17 | 27.73 | 30.78 | 25.64 | 27.53 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Mu, K.; Xu, M.; Ma, X.; Ni, Z.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.-a. Variation in the Concentrations of Major Secondary Metabolites in Ginkgo Leaves from Different Geographical Populations. Forests 2017, 8, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8080266
Zhou Q, Mu K, Xu M, Ma X, Ni Z, Wang J, Xu L-a. Variation in the Concentrations of Major Secondary Metabolites in Ginkgo Leaves from Different Geographical Populations. Forests. 2017; 8(8):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8080266
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qi, Kemin Mu, Meng Xu, Xueying Ma, Zhouxian Ni, Jianwen Wang, and Li-an Xu. 2017. "Variation in the Concentrations of Major Secondary Metabolites in Ginkgo Leaves from Different Geographical Populations" Forests 8, no. 8: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8080266
APA StyleZhou, Q., Mu, K., Xu, M., Ma, X., Ni, Z., Wang, J., & Xu, L.-a. (2017). Variation in the Concentrations of Major Secondary Metabolites in Ginkgo Leaves from Different Geographical Populations. Forests, 8(8), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/f8080266





