Identification and Target Prediction of MicroRNAs in Ulmus pumila L. Seedling Roots under Salt Stress by High-Throughput Sequencing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Salt Stress Treatment
2.2. Small RNA Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Identification of Conserved and Novel miRNAs
2.4. Prediction of miRNA Target Genes
2.5. Expression Analysis of miRNAs between Libraries
2.6. Verification of miRNAs by qRT-PCR
3. Results
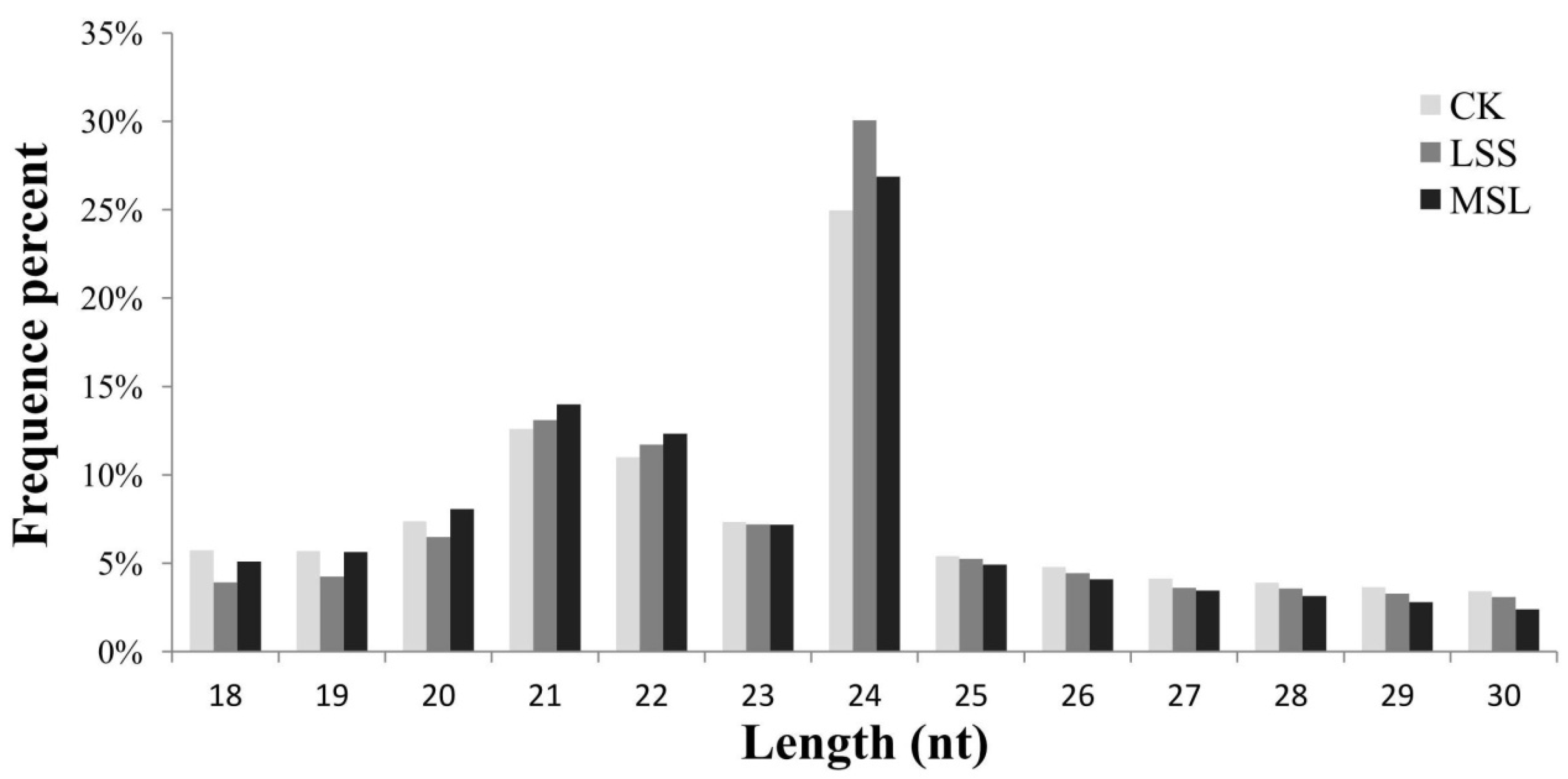
3.1. Deep Sequencing of U. pumila Small RNAs
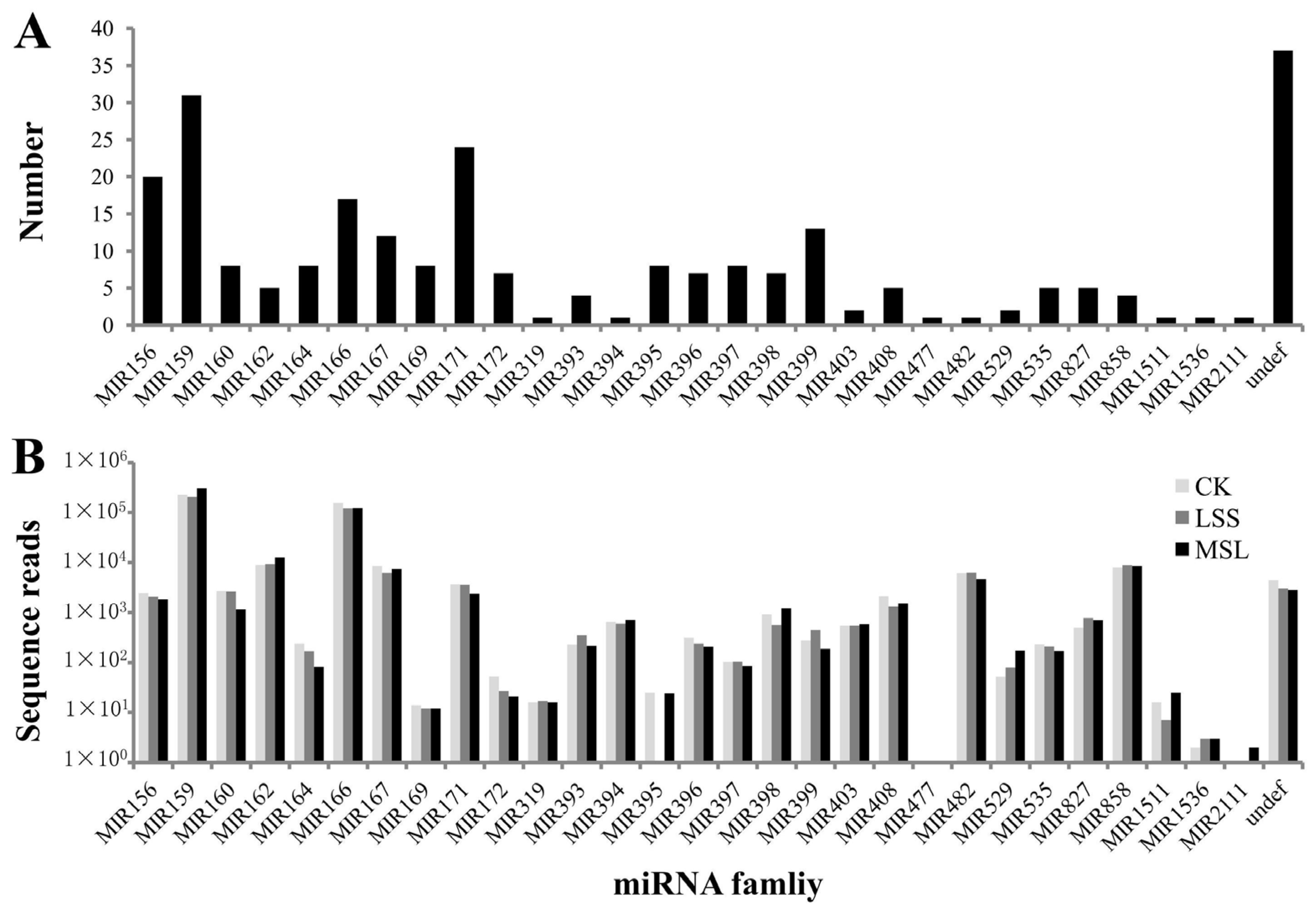
3.2. Identification of Conserved miRNAs in U. pumila
3.3. Discovery of Novel miRNA in U. pumila
3.4. Prediction of Potential miRNAs Targets in U. pumila
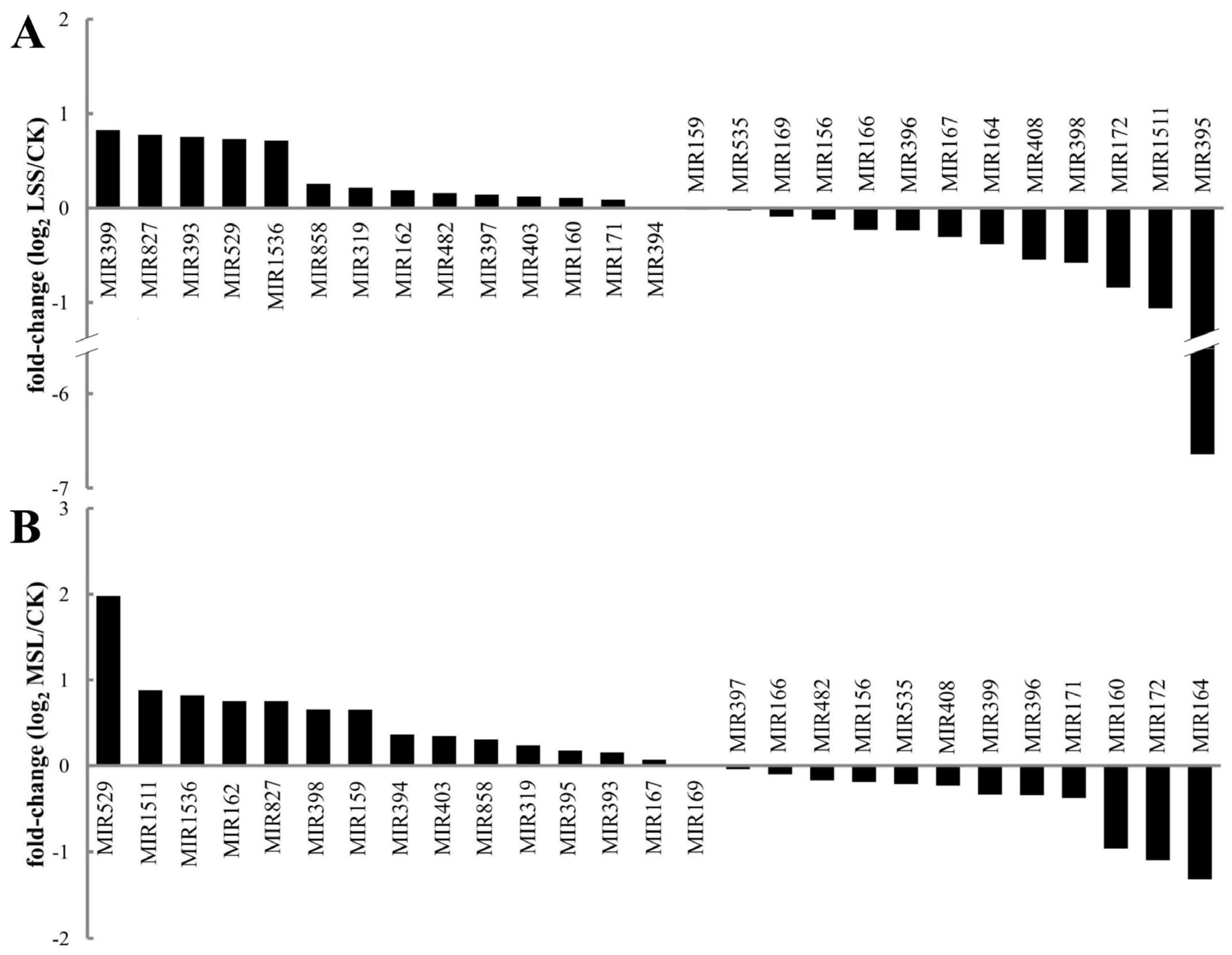
3.5. miRNA Expression Profiles Between Libraries
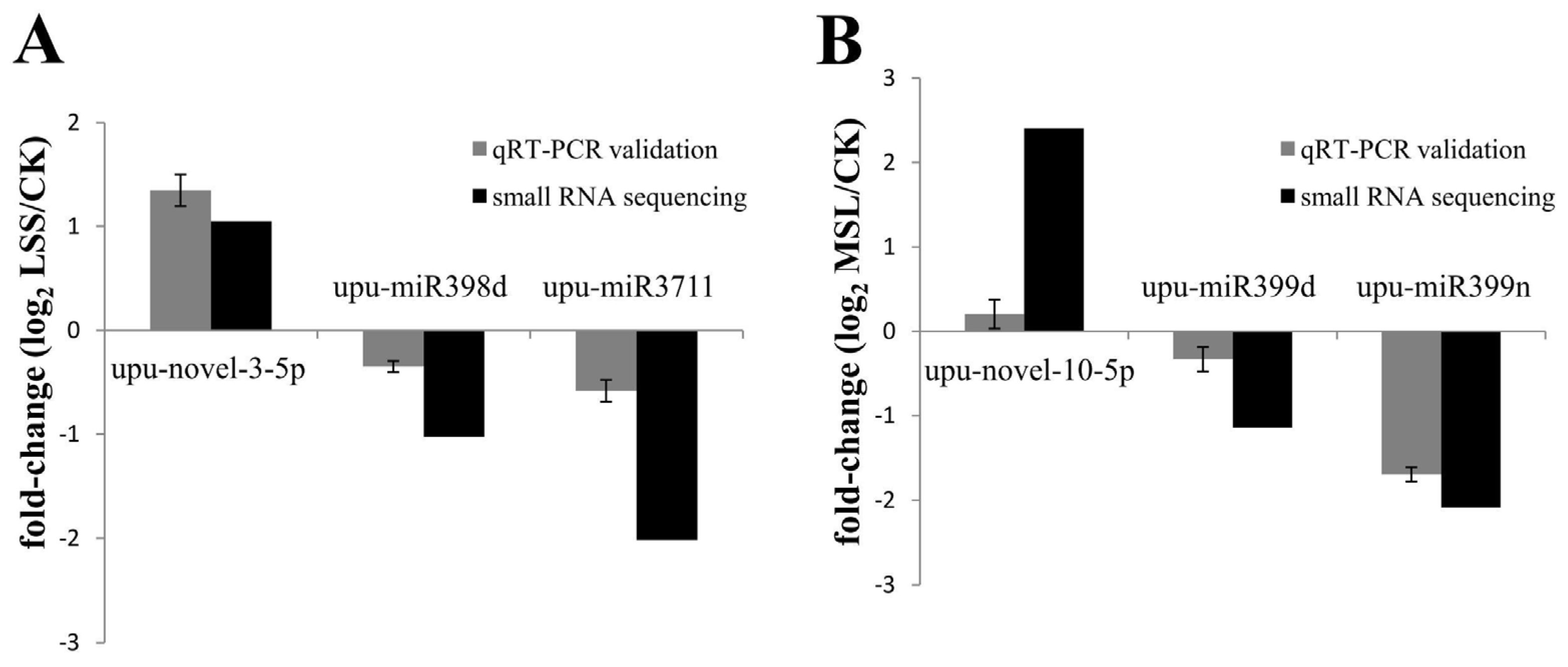
3.6. Validation of Deep Sequencing Results by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, J.C.; Ambros, V. Role of microRNAs in plant and animal development. Science 2003, 301, 336–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2006, 57, 19–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X. MicroRNA biogenesis and function in plants. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5923–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, A.C.; Vaucheret, H. Functions of microRNAs and related small RNAs in plants. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, M.; Liu, R.; Niu, S.; Fan, G. Identification and functional analysis of microRNAs and their targets in Platanus acerifolia under lead (Pb) stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7098–7111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Shen, F. Identification of miRNAs and their targets in cotton inoculated with Verticillium dahliae by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 14749–14768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Gong, S.; Hao, Z.; Tao, J. Identification of miRNAs responsive to Botrytis cinerea in herbaceous peony (Paeonia lactiflora pall.) by high-throughput sequencing. Genes 2015, 6, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. MicroRNA: A new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Li, D.; Li, Z.; Hu, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhu, L.; Luo, H. Constitutive expression of a miR319 gene alters plant development and enhances salt and drought tolerance in transgenic creeping bentgrass. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1375–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Bai, X.; Yang, L.; Lv, D.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Ji, W.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, Y. Osa-MIR393: A salinity- and alkaline stress-related microRNA gene. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kwak, K.J.; Jung, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, H. MicroRNA402 affects seed germination of Arabidopsis thaliana under stress conditions via targeting DEMETER-LIKE Protein3 mRNA. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, Z.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zhang, J.Z. Effects of sand burial on survival, growth, gas exchange and biomass allocation of Ulmus pumila seedlings in the hunshandak sandland, China. Ann. Bot. 2004, 94, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, L. Phenological responses of Ulmus pumila (siberian elm) to climate change in the temperate zone of China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2012, 56, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MA, C.G. A provenance test of white elm (Ulmus pumila L.) in China. Silvae. Genet. 1989, 38, 2. [Google Scholar]
- You, Y.O.; Choi, N.Y.; Kim, K.J. Ethanol extract of Ulmus pumila root bark inhibits clinically isolated antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 269874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, C.; Chung, H.Y.; Nandre, R.M.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, T.I.; Kim, I.S.; Yang, S.H.; Hwang, S.G. An active extract of Ulmus pumila inhibits adipogenesis through regulation of cell cycle progression in 3T3-L1 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalapa, J.E.; Brunet, J.; Guries, R.P. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite markers for red elm (Ulmus rubra Muhl.) and cross-species amplification with siberian elm (Ulmus pumila L.). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2008, 8, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, H.; Pritchard, H.W.; Wang, X. Reactive oxygen species-provoked mitochondria-dependent cell death during ageing of elm (Ulmus pumila L.) seeds. Plant J. 2015, 81, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, G.; Camposeo, S.; Fracchiolla, M.; Vivaldi, G.; De Lucia, B.; Cazzato, E. Salinity differentially affects growth and ecophysiology of two mastic tree (Pistacia lentiscus L.) accessions. Forests 2016, 7, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Khan, S.; Hussain, N.; Hanjra, M.A.; Akbar, S. Characterizing soil salinity in irrigated agriculture using a remote sensing approach. Phys. Chem. Earth 2013, 55–57, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.X.; Wang, Z.G.; Liang, H.Y.; Yang, M.S. Effects of salt stress on physiological characters and salt-tolerance of Ulmus pumila in different habitats. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 23, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.G.; Liu, Z.X.; Zhang, H.X. Effect of NaCl stress on seed germination and seedling growth in different families of Ulmus pumila. Seed 2016, 35, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- Shavrukov, Y. Salt stress or salt shock: Which genes are we studying? J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, D.H.; Lippold, F.; Redestig, H.; Hannah, M.A.; Erban, A.; Kramer, U.; Kopka, J.; Udvardi, M.K. Integrative functional genomics of salt acclimatization in the model legume Lotus japonicus. Plant J. 2008, 53, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedlander, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRdeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaldun, A.B.; Huang, W.; Liao, S.; Lv, H.; Wang, Y. Identification of microRNAs and target genes in the fruit and shoot tip of Lycium chinense: A traditional chinese medicinal plant. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, M.; Shen, Y.; Shi, S.; Tang, T. miREvo: An integrative microRNA evolutionary analysis platform for next-generation sequencing experiments. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Li, W.; Yang, W.; Qi, L.; Han, S. Identification of microRNAs in Caragana intermedia by high-throughput sequencing and expression analysis of 12 microRNAs and their targets under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekimler, S.; Sahin, K. Computational methods for microRNA target prediction. Genes 2014, 5, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.J.; Ma, Y.K.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.J. psRobot: A web-based plant small RNA meta-analysis toolbox. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, W22–W28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paola, D.; Cattonaro, F.; Pignone, D.; Sonnante, G. The miRNAome of globe artichoke: Conserved and novel microRNAs and target analysis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, F.; Frazier, T.P.; Zhang, B. Identification and characterization of microRNAs and their targets in the bioenergy plant switchgrass (Panicum virgatum). Planta 2010, 232, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: MicroRNAs located on Xq27.3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saminathan, T.; Bodunrin, A.; Singh, N.V.; Devarajan, R.; Nimmakayala, P.; Jeff, M.; Aradhya, M.; Reddy, U.K. Genome-wide identification of microRNAs in pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) by high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhotia, N.; Joshi, G.; Bhardwaj, A.R.; Katiyar-Agarwal, S.; Agarwal, M.; Jagannath, A.; Goel, S.; Kumar, A. Identification and characterization of miRNAome in root, stem, leaf and tuber developmental stages of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) by high-throughput sequencing. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Axtell, M.J.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Baulcombe, D.; Bowman, J.L.; Cao, X.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Green, P.J.; et al. Criteria for annotation of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 3186–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cannon, C.H.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. Conservation and divergence of plant microRNA genes. Plant J. 2006, 46, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Marshall, M.; et al. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 2003, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stief, A.; Altmann, S.; Hoffmann, K.; Pant, B.D.; Scheible, W.R.; Baurle, I. Arabidopsis miR156 regulates tolerance to recurring environmental stress through SPL transcription factors. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1792–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achard, P.; Herr, A.; Baulcombe, D.C.; Harberd, N.P. Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development 2004, 131, 3357–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.S.; Xie, Q.; Fei, J.F.; Chua, N.H. MicroRNA directs mRNA cleavage of the transcription factor NAC1 to downregulate auxin signals for Arabidopsis lateral root development. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Li, Q.; Wei, H.; Chang, M.J.; Tunlaya-Anukit, S.; Kim, H.; Liu, J.; Song, J.; Sun, Y.H.; Yuan, L.; et al. Ptr-miR397a is a negative regulator of laccase genes affecting lignin content in Populus trichocarpa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10848–10853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopalan, R.; Vaucheret, H.; Trejo, J.; Bartel, D.P. A diverse and evolutionarily fluid set of microRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene Dev. 2006, 20, 3407–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Yang, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Pan, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Liang, X.; Yu, S. Identification and characterization of microRNAs from peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) by high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, S.; Nie, X.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Biradar, S.S.; Jia, X.; Weining, S. Identification and characterization of microRNAs from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) by high-throughput sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Ma, R.; Yu, M.; Guo, S.; Guo, L.; Korir, N.K. Identification of known and novel microRNAs and their targets in peach (Prunus persica) fruit by high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Ge, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, L.; Hou, D.; Hou, C. Identification and characterization of microRNAs at different flowering developmental stages in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) by high-throughput sequencing. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 2335–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lertpanyasampatha, M.; Gao, L.; Kongsawadworakul, P.; Viboonjun, U.; Chrestin, H.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Narangajavana, J. Genome-wide analysis of microRNAs in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis L.) using high-throughput sequencing. Planta 2012, 236, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baksa, I.; Nagy, T.; Barta, E.; Havelda, Z.; Varallyay, E.; Silhavy, D.; Burgyan, J.; Szittya, G. Identification of Nicotiana benthamiana microRNAs and their targets using high throughput sequencing and degradome analysis. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Nan, F.; Feng, J.; Lv, J.; Liu, Q.; Xie, S. Identification and characterization of microRNAs in Eucheuma denticulatum by high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analysis. RNA. Biol. 2016, 13, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulcheski, F.R.; de Oliveira, L.F.V.; Molina, L.G.; Almerão, M.P.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Marcolino, J.; Barbosa, J.F.; Stolf-Moreira, R.; Nepomuceno, A.L.; Marcelino-Guimarães, F.C.; et al. Identification of novel soybean microRNAs involved in abiotic and biotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axtell, M.J.; Snyder, J.A.; Bartel, D.P. Common functions for diverse small RNAs of land plants. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1750–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, X.; Gong, Y.; Yu, R.; Limera, C.; Liu, L. Genome-wide identification and characterization of cadmium-responsive microRNAs and their target genes in radish (Raphanus sativus L.) roots. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 4271–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Wilen, R.W.; Robertson, A.J.; Gusta, L.V. Isolation, chromosomal localization, and differential expression of mitochondrial manganese superoxide dismutase and chloroplastic copper/zinc superoxide dismutase genes in Wheat. Plant Physiol. 1999, 120, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadeeswaran, G.; Saini, A.; Sunkar, R. Biotic and abiotic stress down-regulate miR398 expression in Arabidopsis. Planta 2009, 229, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, R.; Datt Pant, B.; Stitt, M.; Scheible, W.R. PHO2, MicroRNA399, and PHR1 define a phosphate-signaling pathway in plants. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, B.D.; Buhtz, A.; Kehr, J.; Scheible, W.R. MicroRNA399 is a long-distance signal for the regulation of plant phosphate homeostasis. Plant J. 2008, 53, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, T.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Identification of rapeseed microRNAs involved in early stage seed germination under salt and drought stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sample Names | The Time Points of Salt Treatment and Sample Collection | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −102 h | −72 h | −48 h | −24 h | −6 h | 0 h | |
| CK (0) | sample collection | |||||
| LSS (50 mM) | 50 mM | sample collection | ||||
| MSL (200 mM) | 50 mM | 50 mM | 50 mM | 50 mM | sample collection | |
| Category | CK | LSS | MSL | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Small RNAs (%) | Unique Small RNAs (%) | Total Small RNAs (%) | Unique Small RNAs (%) | Total Small RNAs (%) | Unique Small RNAs (%) | |
| Raw reads | 11,073,886 | 8,469,247 | 9,159,614 | |||
| Clean reads (18–30 nt) | 7,655,641 | 3,162,254 | 6,291,043 | 2,930,417 | 7,153,780 | 2,877,526 |
| Clean reads mapping to transcriptome of Ulmus pumila L. | 4,175,143 (100%) | 748,789 (100%) | 2,953,860 (100%) | 602,673 (100%) | 3,893,883 (100%) | 676,645 (100%) |
| rRNA, snRNA, snoRNA, and tRNA | 802,856 (19.23%) | 44,528 (5.95%) | 527,510 (17.86%) | 38,240 (6.35%) | 644,135 (16.54%) | 37,383 (5.52%) |
| Known miRNA | 218,706 (5.24%) | 824 (0.11%) | 202,718 (6.86%) | 820 (0.14%) | 274,876 (7.06%) | 774 (0.11%) |
| Unannotated | 3,153,581 (75.53%) | 703,437 (93.94%) | 2,223,632 (75.28%) | 563,613 (93.52%) | 2,974,872 (76.40%) | 638,488 (94.36%) |
| miRNA family | Ulmus pumila L. * | Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. | Populus trichocarpa Torr. & Gray | Malus domestica Borkh. | Oryza sativa L. | Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench | Predicted Targets # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIR156 | 20 | 14 | 12 | 29 | 12 | 9 | 49 |
| MIR159 | 31 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 34 |
| MIR160 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 1 |
| MIR162 | 5 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| MIR164 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 3 |
| MIR166 | 17 | 9 | 17 | 9 | 13 | 11 | 2 |
| MIR167 | 12 | 4 | 8 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 3 |
| MIR169 | 8 | 14 | 33 | 6 | 18 | 17 | 6 |
| MIR171 | 24 | 4 | 13 | 15 | 9 | 11 | 2 |
| MIR172 | 7 | 5 | 9 | 15 | 4 | 6 | 16 |
| MIR319 | 1 | 3 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| MIR393 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
| MIR394 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| MIR395 | 8 | 6 | 11 | 9 | 25 | 12 | 12 |
| MIR396 | 7 | 2 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 14 |
| MIR397 | 8 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5 |
| MIR398 | 7 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 |
| MIR399 | 13 | 6 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 9 |
| MIR403 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MIR408 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 |
| MIR477 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MIR482 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| MIR529 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 11 |
| MIR535 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| MIR827 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| MIR858 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| MIR1511 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| MIR1536 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| MIR2111 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Identification and Target Prediction of MicroRNAs in Ulmus pumila L. Seedling Roots under Salt Stress by High-Throughput Sequencing. Forests 2016, 7, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7120318
Zhu J, Yang X, Liu Z, Zhang H. Identification and Target Prediction of MicroRNAs in Ulmus pumila L. Seedling Roots under Salt Stress by High-Throughput Sequencing. Forests. 2016; 7(12):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7120318
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jianfeng, Xiuyan Yang, Zhengxiang Liu, and Huaxin Zhang. 2016. "Identification and Target Prediction of MicroRNAs in Ulmus pumila L. Seedling Roots under Salt Stress by High-Throughput Sequencing" Forests 7, no. 12: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7120318
APA StyleZhu, J., Yang, X., Liu, Z., & Zhang, H. (2016). Identification and Target Prediction of MicroRNAs in Ulmus pumila L. Seedling Roots under Salt Stress by High-Throughput Sequencing. Forests, 7(12), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/f7120318






