Abstract
Haploids are a valuable tool for genomic studies in higher plants, especially those with huge genome size and long juvenile periods, such as conifers. In these species, megagametophyte cultures have been widely used to obtain haploid callus and somatic embryogenic lines. One of the main problems associated with tissue culture is the potential genetic instability of the regenerants. Because of this, chromosomal stability of the callus and/or somatic embryos should also be assessed. To this end, chromosome counting, flow cytometry and genotyping using microsatellites have been reported. Here, we present an overview of the work done in conifers, with special emphasis on the production of a haploid cell line in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster L.) and the use of a set of molecular markers, which includes Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and microsatellites or Single Sequence Repeats (SSRs), to validate chromosomal integrity confirming the presence of all chromosomic arms.
1. Introduction
Haploid tissues are valuable for genomic studies and breeding purposes in higher plants, especially those with huge genomes and long juvenile periods, such as conifers. To this end, megagametophytes and, to a lesser extent, microsporophylls (i.e., pollen grains), have been used as a source of material.
In the last few years, development of next-generation sequencing technologies has made genomes and transcriptomes available from non-model species such as conifers [1]. To date, different conifer genome sequencing projects have been performed from diploid tissue and also from haploid megagametophytes, since they offer a major reduction in sequence complexity [2,3,4]. However, the reduced amount DNA that can be obtained from a single megagametophyte may be insufficient to sequence these large genomes [5]. To follow this approach, it is essential to generate a genetically stable haploid cell line derived from in vitro grown tissues for each targeted species.
The generation of haploid lines relies on the proliferative capability of initial haploid tissue. The latest review on this subject [6] reported limited success when male haploid tissues were used as explants, whereas haploid cell lines exhibiting different degrees of morphogenesis have been reported from megagametophyte cultures of several conifers. An updated overview of what has been reported from megagametophyte cultures in conifers is depicted in Table 1. Briefly, proliferating calli were obtained from Picea sitchensis [7] and organogenic and/or embryogenic cultures of Pices abies [8,9], Larix decidua, Larix leptolepsis, and their reciprocal crosses [10,11,12,13,14]. In addition, putative L. decidua haploid plants were obtained [15]. Chromosome counting of this material showed that haploid cultures sometimes produced a diversity of chromosome complements ([12,16] and references therein) and that the plant regenerated from L. decidua haploid somatic embryos was mixoploid with predominant diploid cells [15,16]. More recently, mass production of pollen protoplast has been reported for Pinus bungeana and Picea wilsonii [17], but their haploid status was not analyzed.

Table 1.
Haploid tissue obtained from megagametophyte cultures of conifer species.
In the last decade, advances in genome sequencing have prompted the development of protocols to generate true haploid cell lines to be used as a DNA source for massive genome analyses of conifer species. As a result of these efforts, haploid cell lines from megagametophytes of Pinus pinaster [19] and Larix sibirica [18] have been obtained and the haploid status studied using DNA markers. The developmental stage of the megagametophyte is an important factor in these studies, although the optimal stage for the induction of haploid cultures may differ among species and genotypes [6,7,18,19]. Modified Murashige and Skoog [20] or Litvay (as described in [21]) media, supplemented with different concentrations of 2,4-D with or without cytokinins, have been widely used to initiate callus formation and for further proliferation in conifers [6,7,18,19]. However, is well documented that long-term cultures may induce instability of the regenerants [22]. This instability can be genomic (affecting ploidy level), chromosomic (inversions, deletions…), genic (mutation), or epigenetic [16,18,23,24,25,26,27]. Since in vitro variation in chromosome sets has been recorded [12,13,16,18,19], it is crucial to validate the suitability of the starting material when approaching de novo whole genome sequencing based on a single haploid tissue. Different strategies can be used to confirm the presence of all chromosomes in a haploid state and the absence of large deletions involving the loss of chromosome arms [18], including chromosome counting, cytometry, and genotyping using molecular markers [26]. Karyological analysis enables unfailing detection of all modifications in chromosome number, but it is sometimes difficult to obtain a high enough number of cells containing metaphases with chromosomes sufficiently contracted and separated to provide a reliable chromosome count [19]. Flow cytometry allows an indirect evaluation, but hardly detects aneuploidy involving the presence of only one extra or missing chromosome, or important chromosome rearrangements.
Pinus pinaster (maritime pine) is an important conifer in Mediterranean regions with a high ecological and socio-economical value [28], but is also one of the most advanced models for conifer research. As a result, several collaborative initiatives to sequence the genome of this species have been launched in the last few years [29]. In previous work, Arrillaga et al. generated some maritime pine haploid cell lines [19], one of which (L5) was considered a good candidate to be used as a template for maritime pine genome sequencing [30]. The haploid status of the L5 callus line was initially checked using flow cytometry and seven microsatellite markers [19]. Therefore, a more in-depth analysis of chromosome integrity was needed to ensure its suitability for massive sequencing. Here, we describe the selection and use of a set of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) and microsatellites or Single Sequence Repeats (SSRs) to assess the presence of all chromosome arms in the DNA extracted from all L5 haploid callus line samples used for Pinus pinaster genome sequencing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
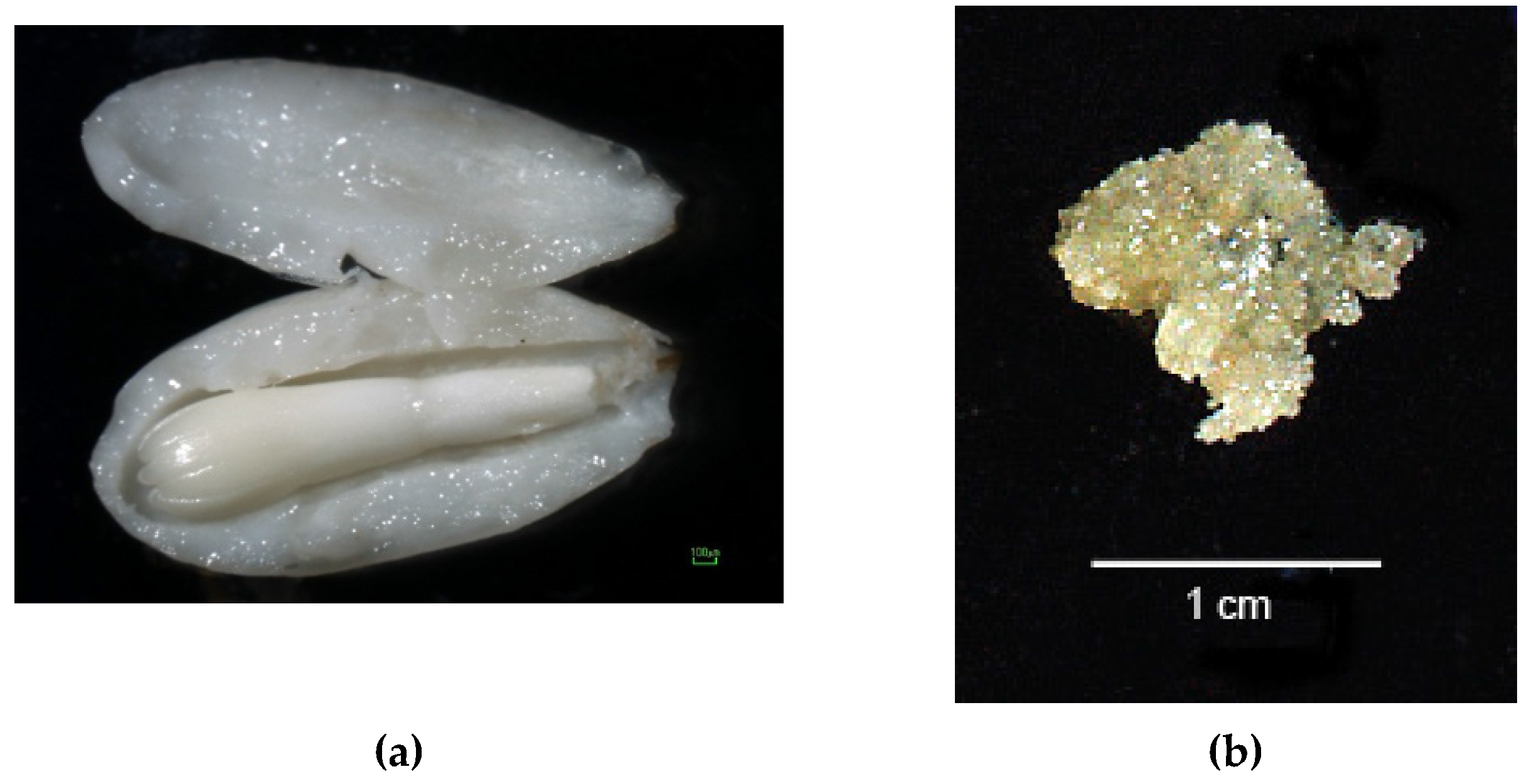
As starting plant material, we used the putative haploid maritime pine L5 line previously generated by Arrillaga et al. [19]. Briefly, this line was obtained from a megagametophyte isolated from a cone of the Oria 6 genotype (Oria, Almeria, Spain) collected before seed dehydration. After embryo removal, the isolated megagametophyte was cultured on modified Litvay’s medium (mLV) [21] for callus induction (Figure 1). The generated L5 line was maintained by transference to the same medium every 3 weeks.

Figure 1.
(a) Developmental stage of the megagametophyte used to initiate maritime pine haploid cultures. The zygotic embryo was removed before culture initiation; (b) callus from Line L5.
2.2. Chromosome Integrity Analysis
Total DNA from L5 cell line samples, derived from a single megagametophyte preselected as a template for genome sequencing, as well as from needles of the mother tree (Oria 6) was extracted using the Qiagen DNeasy® Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol. SNP and SSR molecular markers covering all chromosome arms were identified based on their positions on the Oria 6 genetic map [28] (Figure 2). Allelic composition of the SSR loci was determined by electrophoresis in acrylamide gels according to de Miguel et al. [28]. SNPs were genotyped by sequencing a region of 200–400 bp flanking each targeted site amplified by PCR using specific primers. Primers (available as Supplementary Material Table S1) were designed based on a BLAST search of the sequences used to build the genotyping array, which was used to construct the Oria 6 genetic map [29]. PCRs were performed in 25 μL containing 10 ng of DNA; 1× Pfu buffer (Fermentas, Burlington, ON, Canada), 0.2 mM of each dNTP, 1.5 mM MgSO4, 1.25 U Pfu DNA polymerase (Fermentas, Burlington, ON, Canada), and 0.2 μM of each primer. A Perkin-Elmer GenAmp 9700 thermal cycler (Perkin Elmer Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) was used to carry out the PCR reactions. The thermocycler parameters were: 95 °C for 1 min, 20 touchdown cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, (Tm + 3) °C, 45 s (−0.5 °C/cycle), 72 °C for 1 min; 20 cycles of 95 °C for 30 s, (Tm − 5) °C for 30 s, 72 °C for 1 min and a final extension step of 72 °C for 7 min. After PCR, an aliquot of each amplified product was checked by electrophoresis on 1% agarose gels, and the visualized band was purified using a QiaquickTM gel extraction kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and sequenced. The haploid/diploid state of the targeted SNP was evaluated by aligning the sequences obtained for the callus and the mother tree with that of the reference transcriptome using the software SeqMan 7.1 from DNAStar (Lasergene, GATC Biotech, Konstanz, Germany).
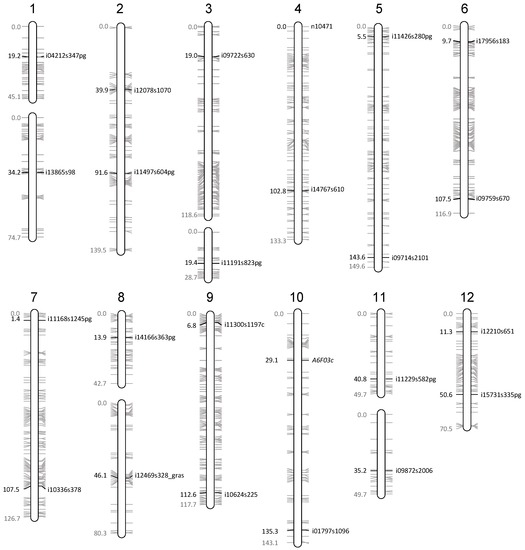
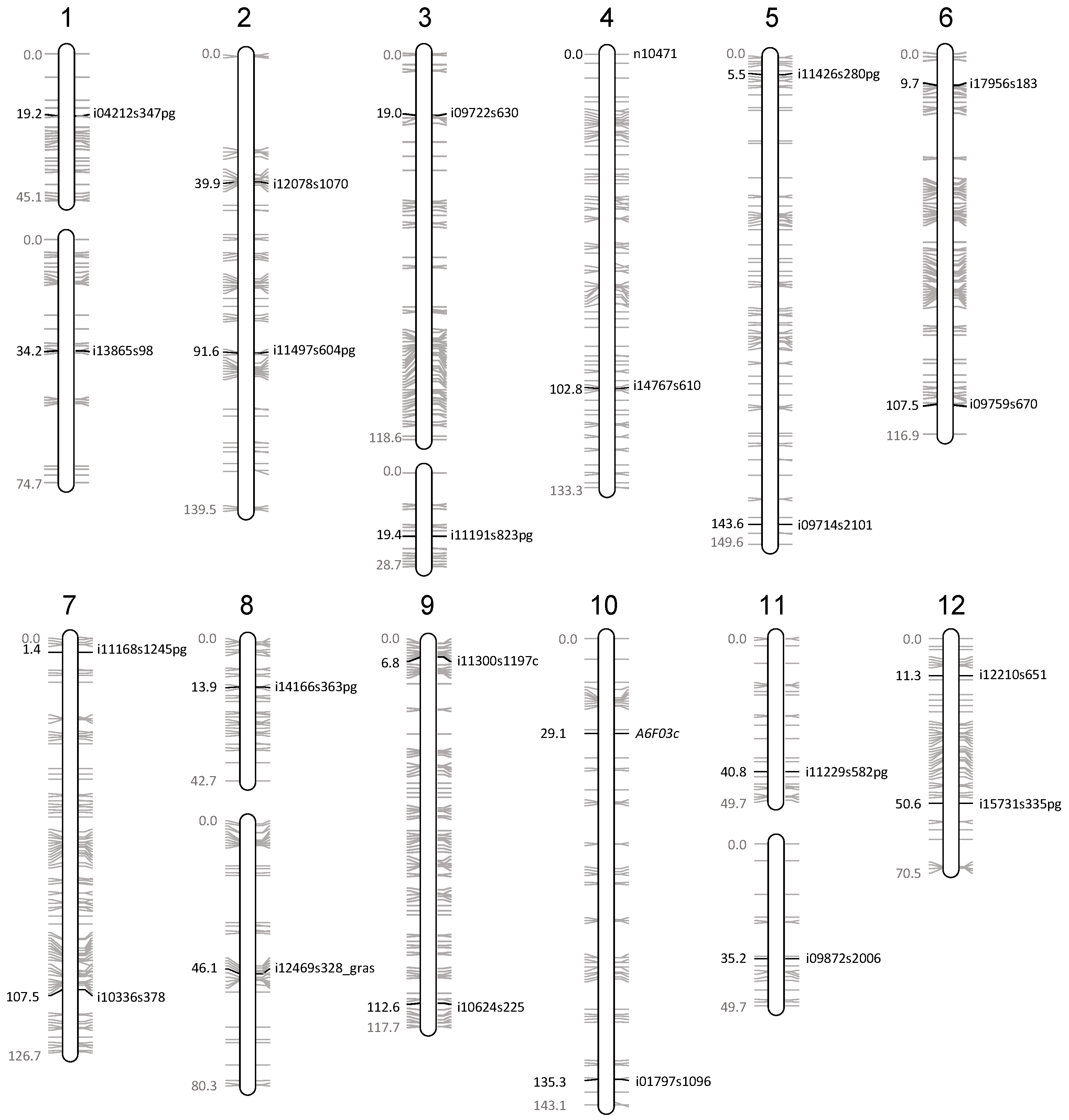
Figure 2.
Location of the molecular markers on the Oria 6 genetic map. The position of the markers used to confirm the presence of all chromosome arms, as well as the size of each linkage group is indicated in centimorgans according to [28].
3. Results
In previous work, the ploidy level of the L5 line was tested by karyological, flow cytometry analyses and 7 SSR markers [19]. In order to have the most appropriate material for maritime pine DNA sequencing, the chromosome integrity should be demonstrated.
The genotyping of the single SSR locus studied (A6F03) confirmed the presence of the upper arm of chromosome 10 in a haploid state by detecting one and two alleles on the DNA from L5 callus line and needle samples of the mother tree, respectively (Table 2). In addition, a set of 64 SNPs located on the 23 remaining chromosome arms of the Oria 6 genetic map [28] was selected to further analyze chromosome integrity. Thus, new primers were designed flanking these selected 64 SNPs. The analysis of the sequences obtained with 23 of them confirmed the presence and the haploid status of their respective chromosome arms by detecting two alleles in the diploid DNA and one allele in the haploid samples at the targeted SNP position (Table 2). Regarding the remaining 41 primer pairs, 24 led to poor or no amplification, probably because of the presence of mismatched nucleotides in the primer sequences; six amplified more than two DNA fragments on agarose gels or sequences with high levels of variation, even in the L5 sample, pointing towards the amplification of unspecific or duplicated sequences; four amplified DNA fragments had no homology with the reference sequence used to design the primers; and seven amplified monomorphic DNA fragments were observed in the diploid sample.

Table 2.
Molecular markers used to validate the presence of all chromosome arms. The position of each marker on the Oria 6 genetic map [29] as well as the allelic state of the mother tree (Oria 6) and L5 line (callus) are shown.
4. Discussion
Different molecular marker technologies have been used to study the genetic stability of cell lines or regenerated plants. Thus, random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers have been used in peach [31] cedar [32], lemon [33] and chestnut [34], whereas amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) has been used in kiwifruit [35], grape [36] and apple [37]. In the last few years, microsatellites have been widely used to analyze many plant species, including arabian coffee [38], cork oak [39] and trembling aspen [40]. In conifers, genetic stability of in vitro-derived diploid cultures has been widely studied. Embryogenic cells lines and cotyledonary embryos of Pinus sylvestris showed high mutation rates in SSR sequences [25]. In contrast, the stability of RAPD markers and nuclear microsatellite sequences has been reported at successive stages of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies, including plants regenerated from somatic embryos [41,42,43]. In Pinus pinaster, the genetic stability of embryogenic cultures and derived plantlets has been studied by flow cytometry [44], microsatellites [45] and DNA methylation [27]. Flow cytometry analysis was unable to detect genetic changes whereas both microsatellites and DNA methylation studies allowed identifying genetic variation in embryogenic lines [27,44,45]. These results pointed to the use of DNA markers as the most appropriate method to detect genetic/epigenetic instability compared with flow cytometry techniques.
The use of molecular markers to detect genomic instability attains special relevance when approaching de novo whole genome sequencing based on a single haploid tissue. To the best of our knowledge, only two studies have previously used molecular markers to assess the genetic stability of conifer haploid cultures. In Larix sibirica, mutations in one or more of the 11 microsatellite loci were detected in all the megagametophyte-derived calli tested [18]. In Pinus pinaster, the seven microsatellites used to genotype 16 megagametophyte-haploid lines showed expected allele composition, amplifying a single allele from the mother tree [19]. Microsatellites are robust, highly variable and codominant markers. Despite these benefits, however, the main drawbacks of using microsatellites in pine species are the large proportion of amplification failure, inconsistencies in the amplification, multibanding patterns, and lack of polymorphism [46], probably due to the complexity of their genomes. For these reasons, a limited number of SSR markers have been located on the existing P. pinaster genetic maps [47,48,49], and only one of them that showed clear amplification profiles and was informative in terms of the position on one of the chromosome arms (locus A6F03) and was used in this study. However, the analysis of specific regions of the conifer genome can be performed using markers based on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Although they are less polymorphic than SSR markers, SNPs are abundant, ubiquitous and amenable for high-throughput detection. In this line, identification of specific heterozygous SNP loci located on the remaining chromosome arms of the Oria 6 genome allowed validation of their presence in the L5 cell line. Although several SNPs initially targeted were discarded because of inconsistencies in the amplification, scoring or sequencing process, 23 SNPs were finally selected based on their usefulness to validate the presence of their corresponding chromosome arms (Table 2). Therefore, the molecular marker analysis described allowed the detection of a single allele at each studied loci (one SSR and 23 SNPs), confirming the presence of all chromosomes in a haploid state in the P. pinaster cell line L5 and the absence of deletions involving the loss of chromosome arms. Thus, the present work represents not only a step forward in validating the suitability of the L5 cell line samples for massive sequencing of the P. pinaster genome but also provides a set of markers that could be used for similar purposes in this species.
5. Conclusions
The availability of haploid cell lines or plants is important to facilitate genome sequencing of plant species with large genomes, such as conifers. In most haploid in vitro cultures, genetic instability has been described by karyologial and, later, by flow cytometry analyses. Therefore, when starting a de novo whole genome sequencing project based on single haploid tissue, the validation of the suitability of the starting material is highly desirable. In this work, we validated the L5 cell line, which is being used as a template for genome sequencing of Pinus pinaster, by genotyping molecular markers located on each chromosome arm, a strategy that may be extended to other species.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/1999-4907/7/11/274/s1, Table S1: Primer sequences and reference sequence. Sequences of primers used to genotype the plant material for the microsatellite and to amplify and sequence the region around the targeted SNPs, and reference sequence from Oria 6 transcriptome with the SNP indicated using parentheses.
Acknowledgments
Research funds were provided by Spanish National projects (BIO2007-29814 and BIO2010-12302-E) and the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under Grant Agreement No. 289841 (ProCoGen). We have not received any funds for covering the costs to publish in open access.
Author Contributions
J.A.C.; J.S.; M.T.C. and I.A. conceived and designed the experiments; J.A.C.; M.M.; M.D.V. and L.D. performed the experiments; J.A.C.; M.T.C. and I.A. analyzed the data; J.A.C.; J.S.; M.T.C. and I.A. contributed materials/analysis tools; J.A.C.; J.S.; M.T.C. and I.A. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Uddenberg, D.; Akhter, S.; Ramachandran, P.; Sundström, J.F.; Carlsbecker, A. Sequenced genomes and rapidly emerging technologies pave the way for conifer evolutionary developmental biology. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birol, I.; Raymond, A.; Jackman, S.D.; Pleasance, S.; Coope, R.; Taylor, G.A.; Yuen, M.M.S.; Keeling, C.I.; Brand, D.; Vandervalk, B.P.; et al. Assembling the 20 Gb white spruce (Picea glauca) genome from whole-genome shot gun sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1492–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nystedt, B.; Street, N.R.; Wetterbom, A.; Zuccolo, A.; Lin, Y.C.; Scofield, D.G.; Vezzi, F.; Delhomme, N.; Giacomello, S.; Alexeyenko, A.; et al. The Norway spruce genome sequence and conifer genome evolution. Nature 2013, 497, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neale, D.B.; Wegrzyn, J.L.; Stevens, K.A.; Zimin, A.V.; Puiu, D.; Crepeau, M.W.; Cardeno, C.; Koriabine, M.; Holtz-Morris, A.E.; Liechty, J.D.; et al. Decoding the massive genome of loblolly pine using haploid DNA and novel assembly strategies. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimin, A.; Stevens, K.A.; Crepeau, M.W.; Holtz-Morris, A.; Koriabine, M.; Marçais, G.; Puiu, D.; Roberts, M.; Wegrzyn, J.L.; de Jong, P.J.; et al. Sequencing and assembly of the 22-gb loblolly pine genome. Genetics 2014, 196, 875–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, R. State of development of technology for haploid production from gymnosperm microgametophyte and megagametophyte culture. Propag. Ornam. Plants 2004, 4, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Baldursson, S.; Nørgaard, J.; Krogstrup, P. Factors influencing haploid callus initiation and proliferation in megagametophyte cultures of Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis). Silvae Gene 1993, 42, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Simola, L.K.; Honkanen, J. Organogenesis and fine structure in megagametophyte callus lines of Picea abies. Physiol. Plant 1983, 59, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simola, L.K.; Santanen, A. Improvement of nutrient medium for growth and embryogenesis of megagametophyte and embryo callus lines of Picea abies. Physiol. Plant 1990, 80, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Aderkas, P.; Bonga, J.M.; Nagmani, R. Promotion of embryogenesis in cultured megagametophytes of Larix decidua. Can. J. For. Res. 1987, 7, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Von Aderkas, P.; Bonga, J.M. Morphological definition of phenocritical period for initiation of haploid embryogenic tissues from explants of Larix decidua. In Somatic Cell Genetics of Woody Plants; Ajuha, M.R., Ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Von Aderkas, P.; Klimaszewska, K.; Bonga, J.M. Diploid and haploid embryogenesis in Larix leptolepis L. decidua, and their reciprocal hybrids. Can. J. For. Res. 1990, 20, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Aderkas, P.; Pattanavibool, R.; Hristoforoglu, K.; Ma, Y. Embryogenesis and genetic stability in long term megagametophyte derived cultures of larch. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2003, 75, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Aderkas, P. Embryogenesis from protoplasts of haploid European larch. Can. J. For. Res. 1992, 22, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Aderkas, P.; Bonga, J.M. Plants from haploid tissue of Larix decidua. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 87, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Aderkas, P.; Anderson, P. Aneuploidy and polyploidization in haploid tissue cultures of Larix decidua. Physiol. Plant 1993, 88, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Zhang, L.; Lin, J. A rapid, efficient method for the mass production of pollen protoplast from Pinus bungeana Zucc. ex Endl and Picea wilsonii Mast. Flora 2006, 201, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutovsky, K.V.; Tretyakova, I.N.; Oreshkova, N.V.; Pak, M.E.; Kvitko, O.V.; Vaganov, E.A. Somaclonal variation of haploid in vitro tissue culture obtained from Siberian larch (Larix sibirica Ledeb.) megagametophytes for whole genome de novo sequencing. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol.-Plant 2014, 50, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrillaga, I.; Guevara, M.A.; Muñoz-Bertomeu, J.; Lázaro-Gimeno, D.; Sáez-Laguna, E.; Díaz, L.M.; Torralba, L.; Mendoza-Poudereux, I.; Segura, J.; Cervera, M.T. Selection of haploid cell lines from megagametophyte cultures of maritime pine as a DNA source for massive sequencing of the species. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2014, 118, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelu-Walter, M.A.; Bernier-Cardou, M.; Klimaszewska, K. Simplified and improved somatic embriogenesis for clonal propagation or Pinus pinaster (Ait.). Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, P.J.; Scowcroft, W.R. Somaclonal variation—A novel source of variability from cell cultures for plant improvement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1981, 60, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tulecke, W. Somatic embryogenesis in woody perennials. In Cell and Tissue Culture in Forestry; Bonga, J.M., Durzan, D.J., Eds.; Martinus Nijhoff: Dordrecht, Germany, 1987; Volume 2, pp. 61–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bhojwani, S.S.; Dantu, P.K. Somaclonal variation. In Plant Tissue Culture: An Introductory Text; Springer: New Delhi, Indian, 2013; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Burg, K.; Helmersson, A.; Bozhkov, P.; von Arnold, S. Developmental and genetic variation in nuclear microsatellite stability during somatic embryogenesis in pine. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leva, A.; Petruchelli, R. Monitoring of cultivar identity in micropropagated olive plants using RAPD and ISSR markers. Biol. Plantarum. 2012, 56, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, C.; Marum, L. An epigenetic view of plant cells cultured in vitro: Somaclonal variation and beyond. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3713–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel, M.; Cabezas, J.A.; de María, N.; Sánchez-Gómez, D.; Guevara, M.Á.; Vélez, M.D.; Sáez-Laguna, E.; Díaz, L.M.; Mancha, J.A.; Barbero, M.C.; et al. Genetic control of functional traits related to photosynthesis and water use efficiency in Pinus pinaster Ait. drought response: Integration of genome annotation, allele association and QTL detection for candidate gene identification. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, J.; Dean, J.F.D.; Plomion, C.; Peterson, D.G.; Cánovas, F.M.; Pavy, N.; Ingvarsson, P.K.; Savolainen, O.; Guevara, M.A.; Fluch, S.; et al. Towards decoding the conifer giga-genome. Plant Mol. Biol. 2012, 80, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promoting a Functional and Comparative Understanding of the Conifer Genome Implementing Applied Aspects for More Productive and Adapted Forests (ProCoGen). Available online: http://www.procogen.eu/ (accessed on 10 November 2016).
- Hashmi, G.; Huettel, R.; Meyer, R.; Krusberg, L.; Hammerschlag, F. RAPD analysis of somaclonal variants derived from embryo callus cultures of peach. Plant Cell Rep. 1997, 16, 624–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renau-Morata, B.; Arrillaga, I.; Segura, J. In vitro storage of cedar shoot cultures under minimal growth conditions. Plant Cell Rep. 2006, 25, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orbovic, V.; Calovic, M.; Viloria, Z.; Nielsen, B.; Gmitter, F.; Castle, W.; Grosser, J. Analysis of genetic variability in various tissue culture-derived lemon plant populations using RAPD and flow cytometry. Euphytica 2008, 161, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.C.; Goulao, L.; Oliveira, C.; Gonçalves, J.C.; Amancio, S. RAPD assessment for identification of clonal identity and genetic stability of in vitro propagated chestnut hybrids. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2004, 77, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, M.J.; Herrera, M.T.; Vázquez, R.A.; Romo, S.; González, M.V. Micropropagation of two selected male kiwifruit and analysis of genetic variation with AFLP markers. HortSci 2005, 40, 740–746. [Google Scholar]
- Popescu, C.F.; Flak, A.; Glimelius, K. Application of AFLPs to characterize somaclonal variation in anther-derived grapevines. Vitis 2002, 41, 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- Xiangqian, Li.; Mingliang, Xu.; Schuyler, S.; Korban, S. DNA methylation profiles differ between field- and in vitro grown leaves of apple. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar]
- Etienne, H.; Bertrand, B. Somaclonal variation in Coffea arabica: Effects of genotype and embryogenic cell suspension age on frequency and phenotype of variants. Tree Physiol. 2003, 23, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, T.; Pinto, G.; Loureiro, J.; Costa, A.; Santos, C. Determination of genetic stability in long-term somatic embryogenic cultures and derived plantlets of cork oak using microsatellite markers. Tree Physiol. 2006, 26, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Rajora, O. Microsatellite DNA somaclonal variation in micropropagated trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides). Plant Cell Rep. 2001, 20, 531–536. [Google Scholar]
- Hanacek, P.; Havel, L.; Truksa, M. Characterisation and determination of genetic stability of early somatic embryo culture clones of Norway spruce using RAPD markers. Biologia 2002, 57, 517–521. [Google Scholar]
- Harvengt, L.; Trontin, J.F.; Reymond, I.; Canlet, F.; Pâques, M. Molecular evidence of true-to-type propagation of a 3-year-old Norway spruce through somatic embryogenesis. Planta 2001, 213, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmersson, A.; von Arnold, S.; Burg, K.; Bozhkov, P.V. High stability of nuclear microsatellite loci during the early stages of somatic embryogenesis in Norway spruce. Tree Physiol. 2004, 24, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marum, L.; Loureiro, J.; Rodriguez, E.; Oliveira, M.; Miguel, C. Flow cytometric and morphological analyses of Pinus pinaster somatic embryogenesis. Biotech 2009, 143, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marum, L.; Rocheta, M.; Maroco, J.; Oliveira, M.M.; Miguel, C. Analysis of genetic stability at SSR loci during somatic embryogenesis in maritime pine (Pinus pinaster). Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariette, S.; Changné, D.; Decroocq, S.; Vendramin, G.; Lalanne, C.; Madur, D.; Plomion, C. Microsatellite markers for Pinus pinaster Ait. Ann. For. Sci. 2001, 58, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagné, D.; Brown, G.R.; Lalanne, C.; Madur, D.; Pot, D.; Plomion, C. Comparative genome and QTL mapping between maritime and loblolly pines. Mol. Breed. 2003, 12, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancerel, E.; Lepoittevin, C.; Le Provost, G.; Lin, Y.C.; Jaramillo-Correa, J.P.; Eckert, A.J.; Wegrzyn, J.L.; Zelenika, D.; Boland, A.; Frigerio, J.M.; et al. Development and implementation of a highly-multiplexed SNP array for genetic mapping in maritime pine and comparative mapping with loblolly pine. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Miguel, M.; de Maria, N.; Guevara, M.A.; Diaz, L.; Sáez-Laguna, E.; Sánchez-Gómez, D.; Chancerel, E.; Aranda, I.; Collada, C.; Plomion, C.; et al. Annotated genetic linkage maps of Pinus pinaster Ait. from a Central Spain population using microsatellite and gene based markers. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).