Simulating the Effect of Climate Change on Vegetation Zone Distribution on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
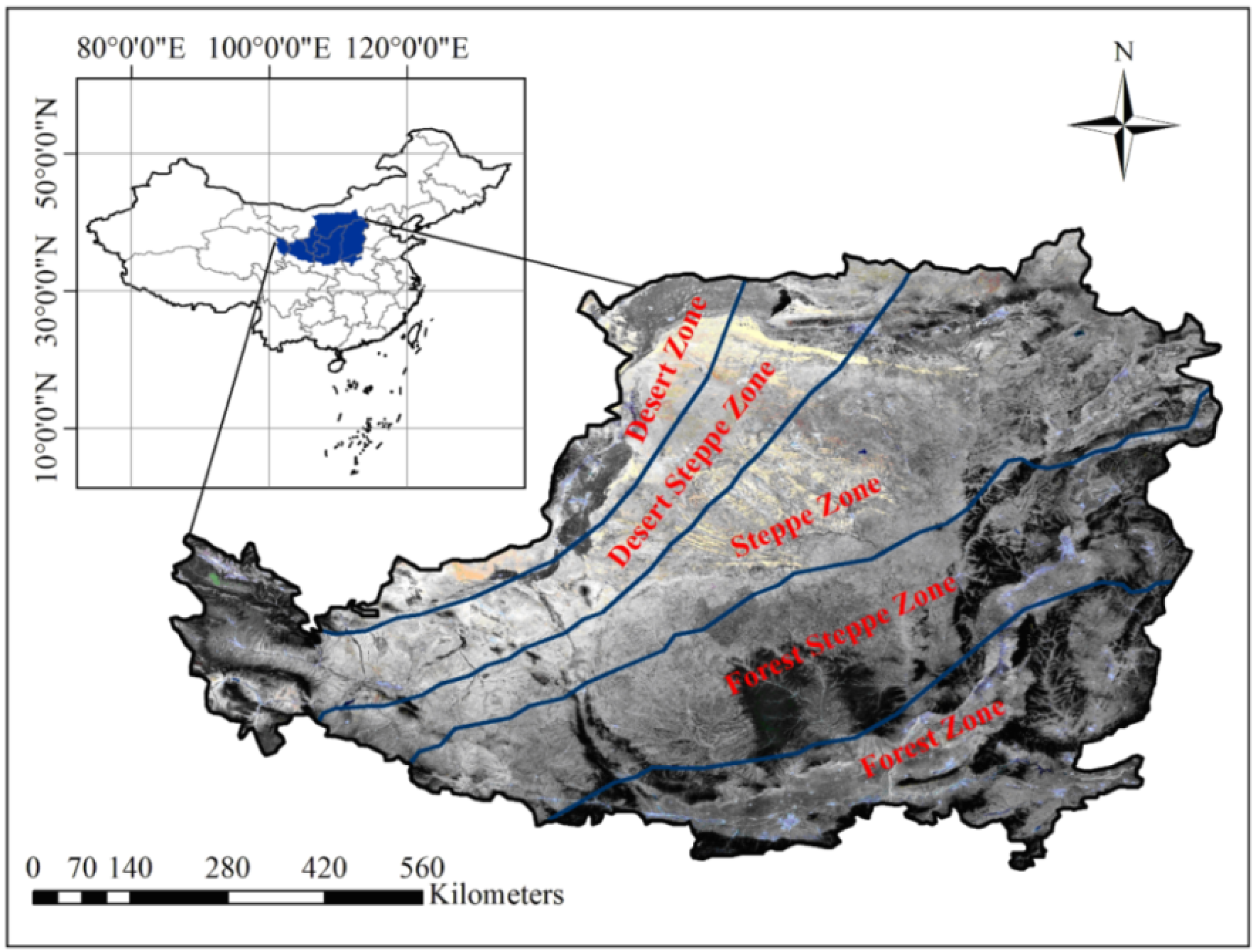
2.1. Study Region
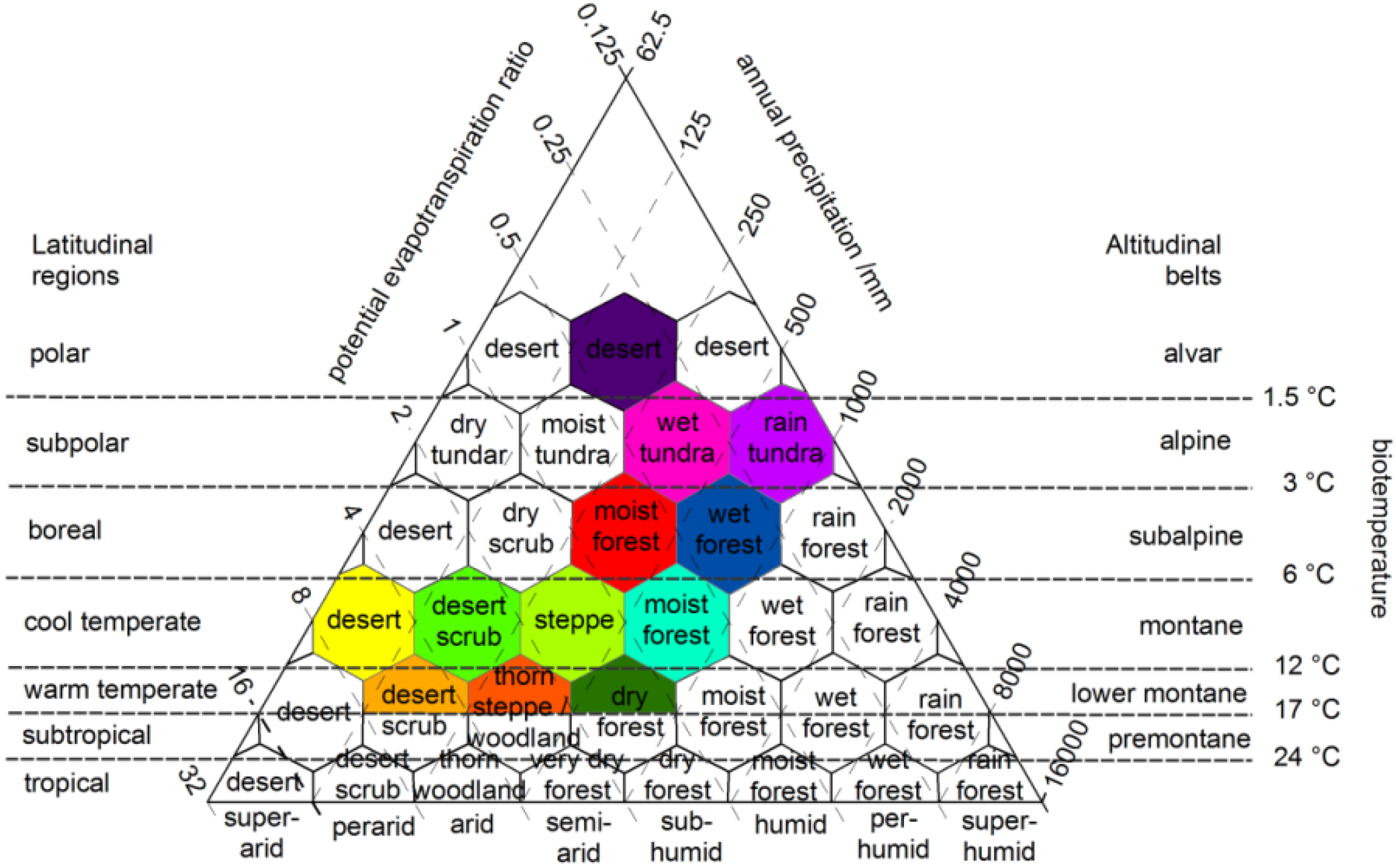
2.2. Holdridge Life Zone Model
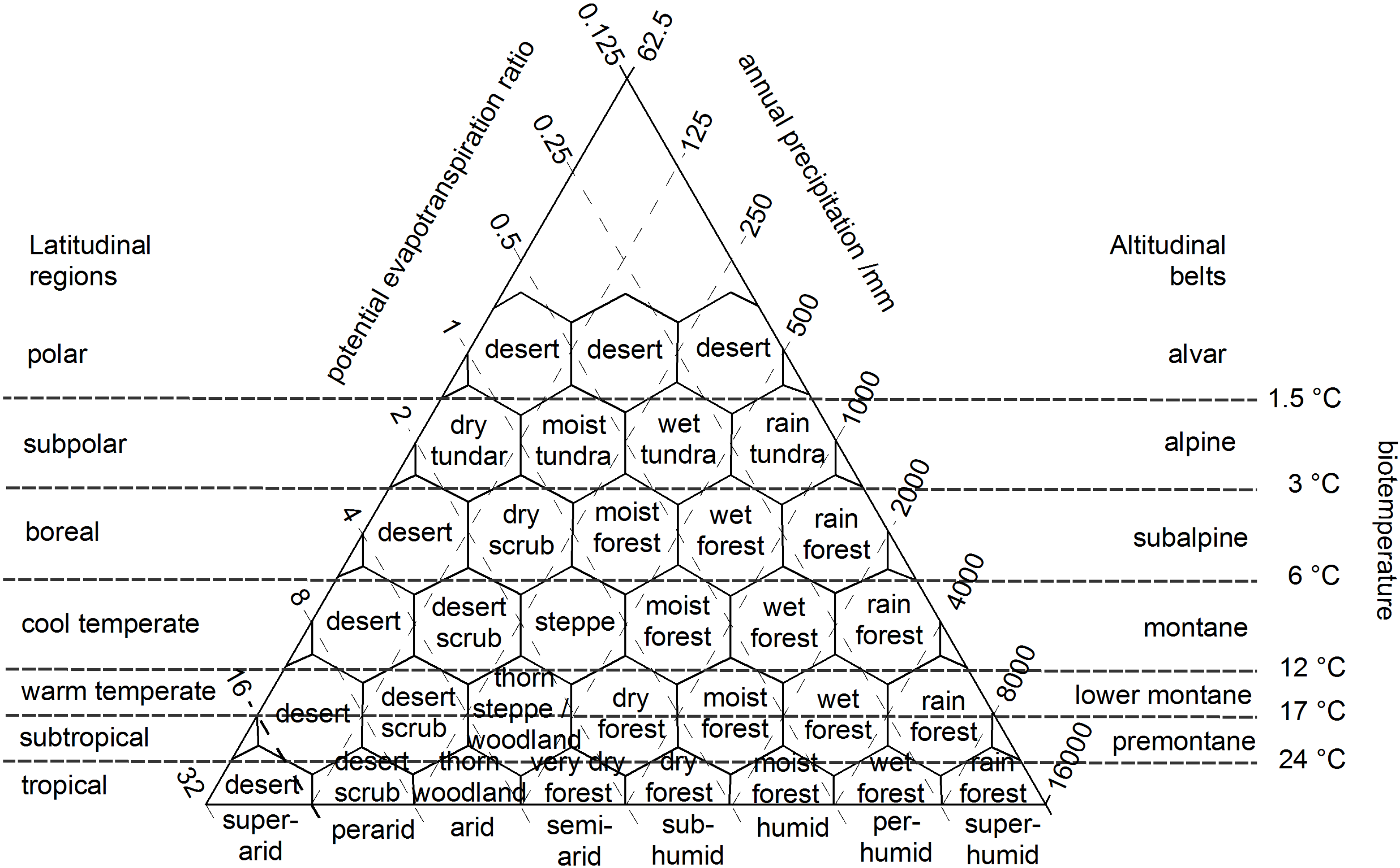
2.3. Current Climate Layers and Future Climate Scenarios
| GCMs | Simulation of Temperature (°C) | Simulation of Precipitation (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCP2.6 | RCP4.5 | RCP6.0 | RCP8.5 | RCP2.6 | RCP4.5 | RCP6.0 | RCP8.5 | |
| BCC-CSM1-1 a | 9.6 | 10.2 | 10.5 | 11.7 | 449 | 467 | 454 | 475 |
| CCSM4 b | 9.2 | 10.1 | 10.3 | 11.5 | 444 | 467 | 460 | 491 |
| GISS-E2-R c | 9.0 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 455 | 485 | 463 | 498 |
| HadGEM2-AO d | 9.9 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 12.5 | 475 | 550 | 466 | 524 |
| IPSL-CM5A-LR e | 10.0 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 13.0 | 489 | 485 | 456 | 490 |
| MIROC-ESM-CHEM f | 10.0 | 11.4 | 11.1 | 13.1 | 499 | 480 | 484 | 492 |
| NorESM1-M g | 9.9 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 11.8 | 481 | 480 | 459 | 472 |
| Model Ensemble h | 9.7 | 10.6 | 10.6 | 12.1 | 470 | 488 | 463 | 492 |
2.4. Simulation Process and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Spatial Distribution Patterns of Vegetation Zones
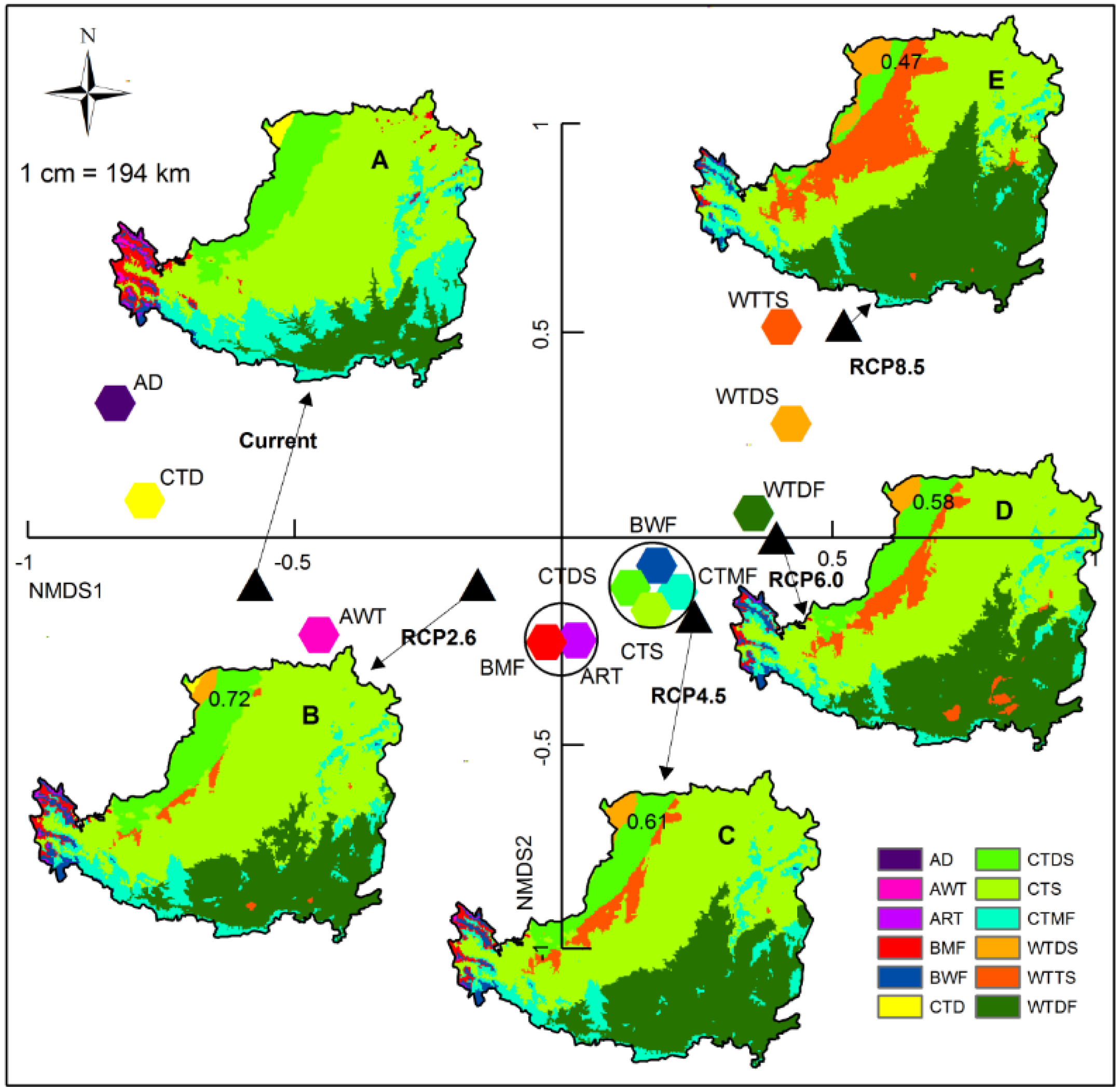
3.2. Change Distribution Area of Vegetation Zones
| Vegetation Zone | Current Climate Area (Percent) | Future Climate Scenarios (2070s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCP2.6 Area (Percent) | RCP4.5 Area (Percent) | RCP6 Area (Percent) | RCP8.5 Area (Percent) | ||
| Alvar desert | 1 (0.2) | - | - | - | - |
| Alpine wet tundra | 4 (0.7) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.2) | - | - |
| Alpine rain tundra | 2 (0.3) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.2) | 1 (0.2) | - |
| Boreal moist forest | 18 (3.0) | 8 (1.3) | 7 (1.1) | 4 (0.7) | 1 (0.2) |
| Boreal wet forest | 8(1.3) | 9 (1.5) | 7 (1.1) | 8 (1.3) | 6 (1.0) |
| Cool temperate desert | 5(0.8) | 2 (0.3) | - | - | - |
| Cool temperate desert scrub | 68(11.2) | 63 (10.3) | 51 (8.4) | 48 (7.9) | 22 (3.6) |
| Cool temperate steppe | 317(51.8) | 314 (51.6) | 274 (44.9) | 279 (46.0) | 210 (34.5) |
| Cool temperate moist forest | 114 (18.5) | 58 (9.5) | 56 (9.2) | 49 (8.0) | 42 (6. 9) |
| Warm temperate desert scrub | - | 6 (1.0) | 8 (1.3) | 8 (1.3) | 17 (2.8) |
| Warm temperate thorn steppe | - | 8 (1.3) | 24 (3.9) | 39 (6.4) | 84 (13.8) |
| Warm temperate dry forest | 74 (12.2) | 139 (22.8) | 181 (29.7) | 172 (28.2) | 227 (37.2) |
3.3. Zonal, Meridional and Vertical Shift of Domain Vegetation Zones
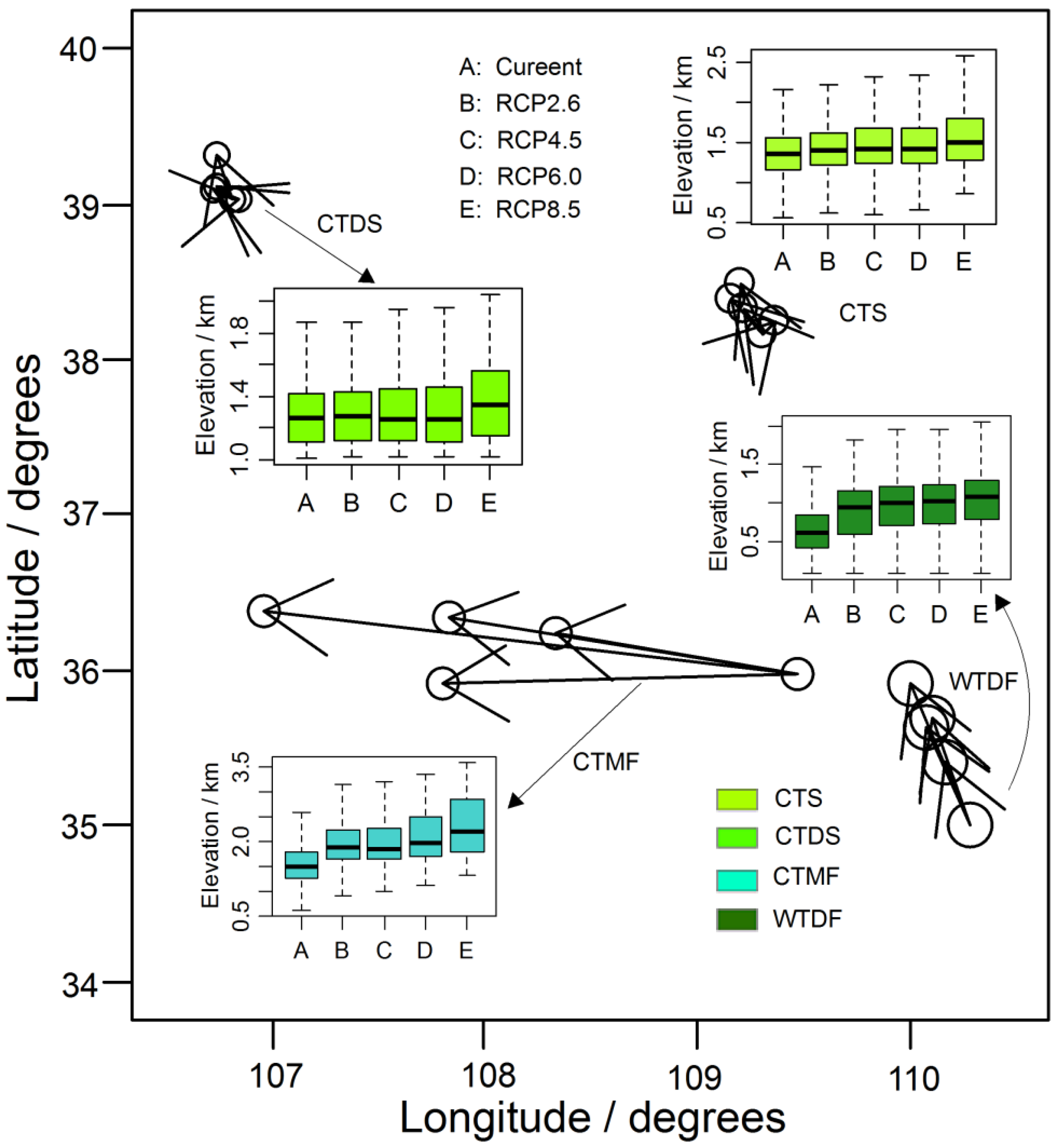
4. Discussion
4.1. Vegetation Zone Response to Climate Change and Its Explanation
4.2. Potentials and Limitations of HLZ Model and Its Applications
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC. Climate change 2013: The physical science basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.-K., Tigno, M.R., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for plicymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Mitigation of Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Edenhofer, O., Pichs-Madruga, R., Sokona, Y., Farahani, E., Kadner, S., Seyboth, K., Adler, A., Baum, I., Brunner, S., Eickemeier, P., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for policymakers. In Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part A: Global and Sectoral Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Field, C.B., Barros, V.R., Dokken, D.J., Mach, K.J., Mastrandrea, M.D., Bilir, T.E., Chatterjee, M., Ebi, K.L., Estrada, Y.O., Genova, R.C., et al., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, R.G.; Phillips, S.J.; Loranty, M.M.; Beck, P.S.A.; Damoulas, T.; Knight, S.J.; Goetz, S.J. Shifts in arctic vegetation and associated feedbacks under climate change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2013, 3, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, J.; Gegout, J.C.; Marquet, P.A.; de Ruffray, P.; Brisse, H. A significant upward shift in plant species optimum elevation during the 20th century. Science 2008, 320, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felde, V.A.; Kapfer, J.; Grytnes, J.A. Upward shift in elevational plant species ranges in sikkilsdalen, central norway. Ecography 2012, 35, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.D.; Franco, A.M.A.; Hill, J.K. Range retractions and extinction in the face of climate warming. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2006, 21, 415–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massot, M.; Clobert, J.; Ferriere, R. Climate warming, dispersal inhibition and extinction risk. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, R.J.; Blanckenhorn, W.U.; Berger, D. Forecasting extinction risk of ectotherms under climate warming: An evolutionary perspective. Funct. Ecol. 2012, 26, 1324–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IGBP. International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme. Available online: http://www.igbp.net/ (accessed on 12 February 2015).
- Peng, C.H. From static biogeographical model to dynamic global vegetation model: A global perspective on modelling vegetation dynamics. Ecol. Model. 2000, 135, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Zhang, X.S.; Li, B.L. The possible response of life zones in china under global climate change. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2003, 38, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Joshi, P.K.; Ghosh, A.; Areendran, G. Assessing biome boundary shifts under climate change scenarios in India. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, W.M.; Emanuel, W.R.; Zinke, P.J.; Sangenberger, A.G. Soil carbon pools and world life zones. Nature 1982, 298, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, K.; Imbach, P.; Zamora, J.C. An assessment of climate change impacts on the tropical forests of central America using the holdridge life zone (HLZ) land classification system. iForest 2013, 6, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.X.; Fan, Z.M.; Liu, J.Y.; Wei, B.X. Scenarios of major terrestrial ecosystems in China. Ecol. Model. 2006, 199, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, A.E.; Brown, S.L.; Dodson, R.; Smith, T.S.; Shugart, H.H. The holdridge life zones of the conterminous United States in relation to ecosystem mapping. J. Biogeogr. 1999, 26, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotelov, N.V.; Bogatyrev, B.G.; Kirilenko, A.P.; Venevsky, S.V. Modelling of time-dependent biome shifts under global climate changes. Ecol. Model. 1996, 87, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Jorgensen, S.E.; Gao, Z.Q.; Zhang, S.H.; Deng, X.Z. Changes of Holdridge life zone diversity in all of China over half a century. Ecol. Model. 2001, 144, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F. Research on impacts of global climate change to holdridge’s life zones of china by geo-information system. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 1, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, F.Z.; Jin, Y.H.; Liu, J.P.; Shang, L.N.; Zhao, D.S. Response of vegetation distribution to global climate change in northeast china. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2003, 23, 564–570. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, J.M.; Lv, G.F. Life zones determination and their responds to climate changes in neimongol. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. NeiMonggol 1999, 30, 360–366. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, F.L. Effects of accelerated soil erosion on soil nutrient loss after deforestation on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 2005, 15, 707–715. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.B.; Qi, J.G.; Feng, Z.D.; Yin, R.S.; Guo, B.Y.; Zhang, F.; Zou, S.B. Quantifying the effect of ecological restoration on soil erosion in China’s Loess Plateau region: An application of the mmf approach. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, B.J.; Wang, Y.F.; Lu, Y.H.; He, C.S.; Chen, L.D.; Song, C.J. The effects of land-use combinations on soil erosion: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, A.; Liu, G.; Yamanaka, N.; Du, S. Restoration and Development of the Degraded Loess Plateau, China; Springer Verlag: Tokyo, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission; Ministry of Water Resources; Ministry of Agriculture; State Forestry Administration. The Integrated Management Planning of the Loess Plateau from 2010 to 2030. Available online: http://www.ndrc.gov.cn/zcfb/zcfbtz/2010tz/t20110117_391043.htm (accessed on 11 December 2014).
- Du, S.; Wang, Y.L.; Kume, T.; Zhang, J.G.; Otsuki, K.; Yamanaka, N.; Liu, G.B. Sapflow characteristics and climatic responses in three forest species in the semiarid Loess Plateau region of China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, N.G.; Luo, W.X. Sylviculture on the Loess Plateau; China Forestry Press: Beijing, China, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, M.A.; Guo, Z.S.; Xia, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.P. Vegetation Carrying Capacity of Soil Water in the Loess Plateau; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Worldclim. Global Climate Data—Free Climate Data for Ecological Modeling and gis. Available online: http://www.worldclim.org/ (accessed on 12 November 2014).
- Chen, J.M.; Wan, H.E. Vegetation Construction and Soil and Water Conservation in the Loess Plateau of China; China Forestry Press: Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Holdridge, L.R. Determination of world plant formations from simple climatic data. Science 1947, 105, 367–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climat. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, C.H. Preliminary assessment of simulations of climate changes over China by CMIP5 multi-models. Atmos. Oceanic Sci. Lett. 2012, 5, 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.B.; Wang, Y.R.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, X.Y. Climate warming and drying and its environmental effects in the Loess Plateau. Resour. Sci. 2005, 27, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.W.; Song, L.C.; Li, W.P.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, H.; Xin, X.G.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.L.; Wu, F.H.; et al. An overview of bcc climate system model development and application for climate change studies. J. Meteorol. Res. 2014, 28, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.G.; Wu, T.W.; Li, J.L.; Wang, Z.Z.; Li, W.P.; Wu, F.H. How well does bcc_csm1.1 reproduce the 20th century climate change over china? Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett. 2013, 6, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Faith, D.P.; Minchin, P.R.; Belbin, L. Compositional dissimilarity as a robust measure of ecological distance. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, P.R. An evaluation of relative robustness of techniques for ecologcial ordinations. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.J.; Shi, Y.; Giorgi, F. A high resolution simulation of climate change over china. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 462–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Wang, B. Future change of global monsoon in the CMIP5. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 42, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M. A coupled model study on the intensification of the asian summer monsoon in ipccsres scenarios. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 22, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Yu, E.T. Simulation and projection of changes in rainy season precipitation over China using the wrf model. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2013, 27, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Committee for Physical Geography of China. Physical Geography of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.Y.; Kato, T.; Guo, Z.D.; Yang, Y.H.; Hu, H.F.; Shen, H.H.; Zhao, X.; Kishimoto-Mo, A.W.; Tang, Y.H.; Houghton, R.A. Evidence for environmentally enhanced forest growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9527–9532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.H.; Tong, X.J.; Xing, L.M. Assessing the impacts of climate change on the potential evapotranspiration in the upper middle reach of Yellow River. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 11, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, D.P.; Xu, Z.X.; Li, J.Y.; Liu, Z.F. Spatiotemporal characteristics of potential evapotranspiration in the weihe river basin under future climate change. Adv. Water Sci. 2011, 22, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Q.J. Analysis of variation of climate and potential evapotranspiration and its influencing factors in the loess area in last 50 years. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2012, 30, 270–278. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Su, Z.X.; Yang, D.A. Simulation of influence on life zone in Sichuan Basin under the change of climate in the future. Chin. J. Ecol. 2004, 23, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Deng, J.L.; Guan, D.X.; Jin, C.J.; Wang, A.Z.; Wu, J.B.; Yuan, F.H. Spatiotemporal changes of potential evapotranspiration in songnen plain of northeast china. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 22, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.P.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W. Variation and tendency of surface aridity index from 1960 to 2005 in three provinces of northeast china. Adv. Earth Sci. 2008, 23, 619–627. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.F.; Jiang, L.X.; Wang, L.L. Variation characteristics of water budget condition of heilongjiang province in recent 50 years. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2012, 40, 14391–14396. [Google Scholar]
- Raunkiaer, C. Plant Life Forms; The Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1937. [Google Scholar]
- Prentice, I.C.; Cramer, W.; Harrison, S.P.; Leemans, R.; Monserud, R.A.; Solomon, A.M. A global biome model based on plant physiology and dominance, soil properties and climate. J. Biogeogr. 1992, 19, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.N.; Kittel, T.G.F.; Cannon, R.F. Comparing the correlative holdridge model to mechanistic biogeographical models for assessing vegetation distribution response to climatic change. Clim. Chang. 2000, 44, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enquist, C.A.F. Predicted regional impacts of climate change on the geographical distribution and diversity of tropical forests in costa rica. J. Biogeogr. 2002, 29, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Liao, J.; Hsing, Y.T.; Huang, C.H.; Liu, F.M. Policies, land use, and water resource management in an arid oasis ecosystem. Environ. Manag. 2015, 55, 1036–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takanose, Y.; Ishida, S.; Kudo, N.; Kamitani, T. Effects of tillage and irrigation on the occurrence and establishment of native wetland plant species in fallow paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 11, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josa, R.; Jorba, M.; Vallejo, V.R. Opencast mine restoration in a mediterranean semi-arid environment: Failure of some common practices. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, T.D.; Aide, T.M.; Thomlinson, J.R. Urban expansion and the loss of prime agricultural lands in puerto rico. Ambio 2001, 30, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Wang, J.F.; Liu, M.L.; Meng, B. Spatial heterogeneity of the driving forces of cropland change in china. Sci. China Ser. D 2005, 48, 2231–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, W.G.; Sinclair, A.R.E.; Odarkor-Lanquaye, N.; Klinkenberg, B. Stable forest cover under increasing populations of swidden cultivators in central laos: The roles of intrinsic culture and extrinsic wildlife trade. Ecol. Soc. 2009, 14, 33. Available online: http://www.ecologyandsociety.org/vol14/iss1/art33/ (1 April 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Bahadur, K.C.K. Linking physical, economic and institutional constraints of land use change and forest conservation in the hills of nepal. For. Policy Econ. 2011, 13, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdridge, L.R.; Grenke, W.C.; Hatheway, W.H.; Liang, T.; Tosi, J.A. Forest Environments in Tropical Life Zones: A Pilot Study; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Villers-Ruiz, L.; Trejo-Vazquez, I. Climate change on mexican forests and natural protected areas. Glob. Environ. Chang. 1998, 8, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Wen, Z.; Guo, K.; Du, S. Simulating the Effect of Climate Change on Vegetation Zone Distribution on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Forests 2015, 6, 2092-2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062092
Li G, Wen Z, Guo K, Du S. Simulating the Effect of Climate Change on Vegetation Zone Distribution on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Forests. 2015; 6(6):2092-2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062092
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guoqing, Zhongming Wen, Ke Guo, and Sheng Du. 2015. "Simulating the Effect of Climate Change on Vegetation Zone Distribution on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China" Forests 6, no. 6: 2092-2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062092
APA StyleLi, G., Wen, Z., Guo, K., & Du, S. (2015). Simulating the Effect of Climate Change on Vegetation Zone Distribution on the Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Forests, 6(6), 2092-2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062092