Comparison of Suspended Branch and Direct Infestation Techniques for Artificially Infesting Hemlock Seedlings with the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid for Resistance Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Crawler Dispersal Experiments
2.2. Artificial Infestation Experiments
2.2.1. Source Material
2.2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.3. March 2012 Progrediens Infestation
2.2.4. May 2012 Sistens Infestation
2.2.5. March 2013 Progrediens Infestation
2.2.6. Assessment of Adelgid Densities on Seedlings
2.2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Crawler Dispersal Experiments

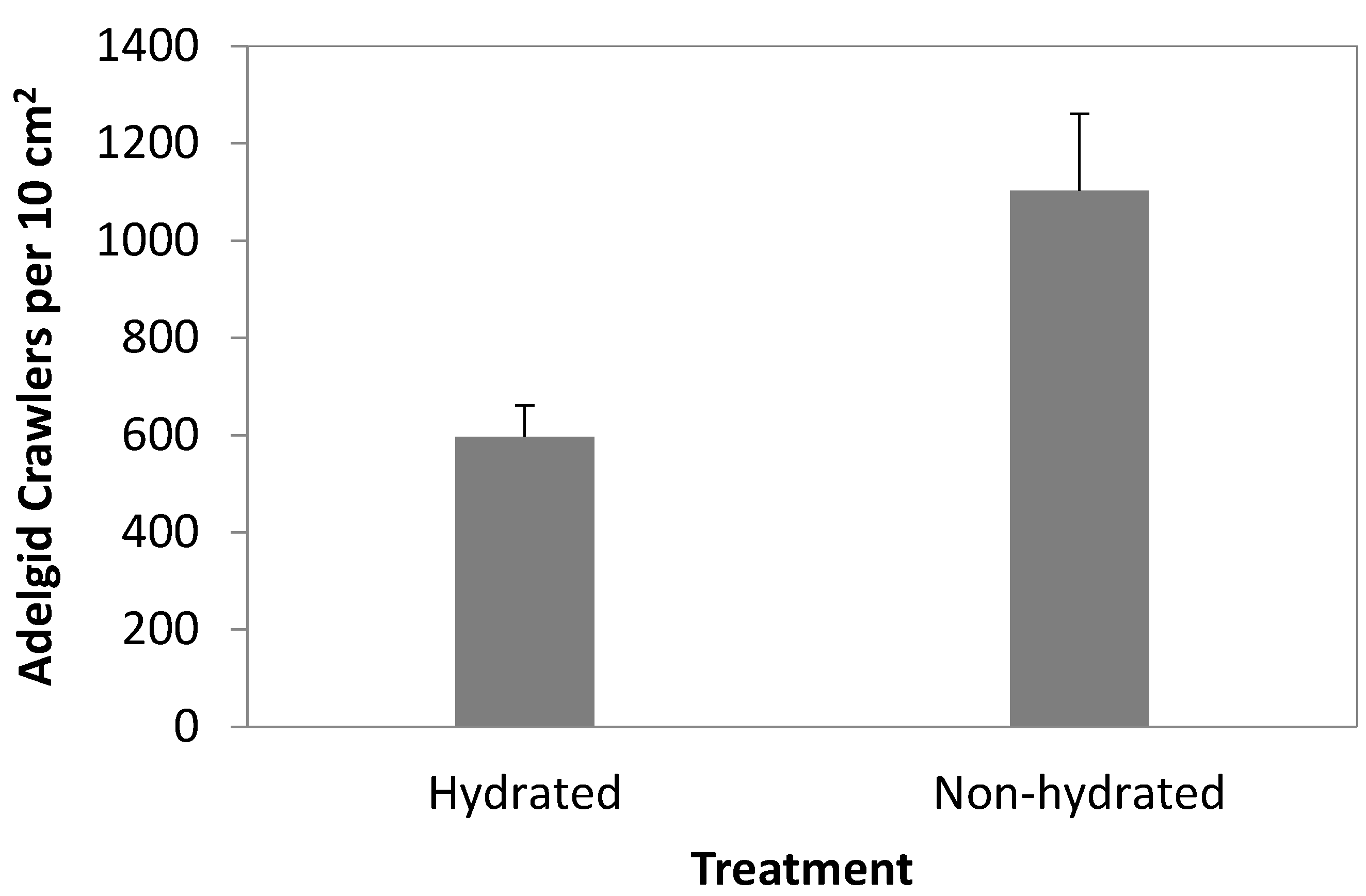
3.2. 2012 Artificial Infestation Experiments
3.3. 2013 Artificial Infestation Experiment
| Main Effect | Main Effect × Month | Main Effect × Hemlock Species | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Effect | Alone | March | May | Eastern | Carolina | Western |
| Treatment | ||||||
| Control | 0.09 (± 0.03) * | 0.09 (± 0.03) * | 0.09 (± 0.03) * | 0.10 (± 0.06) * | 0.13 (± 0.08) * | 0.05 (± 0.02) * |
| Direct Low | 0.40 (± 0.08) a | 1.01 (± 0.16) b | 0.16 (± 0.06) a | 0.26 (± 0.09) a | 0.61 (± 0.16) a | 0.41 (± 0.13) a |
| Direct High | 0.65 (± 0.11) a | 1.76 (± 0.22) a | 0.23 (± 0.07) a | 0.55 (± 0.16) a | 0.75 (± 0.18) a | 0.65 (± 0.17) a |
| Suspended Branch | 0.43 (± 0.07) a | 0.53 (± 0.12) c | 0.34 (± 0.10) a | 0.48 (± 0.14) a | 0.61 (± 0.15) a | 0.27 (± 0.10) a |
| Hemlock Species | ||||||
| Eastern | 0.41 (± 0.09) a | 1.11 (± 0.18) a | 0.15 (± 0.06) a | |||
| Carolina | 0.65 (± 0.10) a | 1.22 (± 0.18) a | 0.35 (± 0.09) a | |||
| Western | 0.41 (± 0.08) a | 0.69 (± 0.14) a | 0.25 (± 0.08) a | |||
| Month | ||||||
| March | 0.98 (± 0.10) a | |||||
| May | 0.24 (± 0.05) b | |||||
4. Discussion
4.1. Crawler Dispersal
| June 2013 Adelgid Density (Progrediens) | November 2013 Adelgid Density (Sistens) | |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment | ||
| Control | 0.0002 (± 0.03) * | 0.05 (± 0.05) * |
| Direct Low | 7.77 (± 0.46) b | 3.96 (± 0.46) a |
| Direct High | 10.22 (± 0.57) a | 2.94 (± 0.39) a |
| Suspended Branch | 12.13 (± 0.67) a | 1.76 (± 0.29) b |
| Hemlock Species | ||
| Eastern | 12.71 (± 0.52) a | 2.75 (± 0.26) a |
| Carolina | 7.68 (± 0.40) b | 2.74 (± 0.32) a |
| Treatment*Species | ||
| Eastern hemlock | ||
| Control | 0.02 (± 0.05) * | 0.04 (± 0.04) * |
| Direct Low | 9.57 (± 0.79) b | 3.99 (± 0.57) a |
| Direct High | 12.10 (± 0.86) a | 3.38 (± 0.45) a |
| Suspended Branch | 17.71 (± 1.02) a | 1.54 (± 0.31) a |
| Carolina hemlock | ||
| Control | 0.0001 (± 0.03) * | 0.08 (± 0.08) * |
| Direct Low | 6.31 (± 0.60) b | 4.00 (± 0.77) a |
| Direct High | 8.63 (± 0.73) a | 1.56 (± 0.77) a |
| Suspended Branch | 8.31 (± 0.74) a | 2.67 (± 0.76) a |
4.2. 2012 Infestations
4.3. 2013 Infestations
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Souto, D.; Luther, T.; Chianese, B. Past and current status of HWA in eastern and Carolina hemlock stands. In Proceedings of the First Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Review, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 12 October 1995; Salom, S.M., Tigner, T.C., Reardon, R.C., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1996; pp. 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Counties with Established HWA Populations 2012. Available online: http://na.fs.fed.us/fhp/hwa/maps/2011.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2015).
- Evans, R.A.; Johnson, E.; Shreiner, J.; Ambler, A.; Battles, J.; Cleavitt, N.; Fahey, T.; Sciascia, J.; Pehek, E. Potential impacts of hemlock woolly adelgid (Adelges tsugae) on eastern hemlock (Tsuga canadensis) ecosystems. In Proceedings of the First Hemlock Woolly Adelgid Review, Charlottesville, VA, USA, 12 October 1995; Salom, S.M., Tigner, T.C., Reardon, R.C., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 1996; pp. 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, A.M.; Bank, M.S.; Clinton, B.D.; Colburn, E.A.; Elliott, K.J.; Ford, C.R.; Foster, D.R.; Kloeppel, B.D.; Knoepp, J.D.; Lovett, G.M.; et al. Loss of foundation species: Consequences for the structure and dynamics of forested ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vose, J.M.; Wear, D.N.; Mayfield III, A.E.; Nelson, C.D. Hemlock woolly adelgid in the southern Appalachians: Control strategies, ecological impacts, and potential management responses. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 291, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.S. Evidence of a polymorphic life cycle in the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1989, 82, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClure, M.S. Role of wind, birds, deer, and humans in the dispersal of hemlock woolly adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae). Environ. Entomol. 1990, 19, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.F.; Shields, K.S.; Berlyn, G.P. Hemlock woolly adelgid (Homoptera: Adelgidae): Stylet bundle insertion and feeding sites. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1995, 88, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havill, N.P.; Vieira, L.C.; Salom, S.M. Biology and Control of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2014; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Onken, B.P.; Reardon, R.C. An overview and outlook for biological control of hemlock woolly adelgid. In Implementation and Status of Biological Control of the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid; Onken, B., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2011; pp. 222–228. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, J.S.; Montgomery, M.E.; Cheah, C.A.S.J.; Onken, B.; Cowles, R.S. Eastern Hemlock Forests: Guidelines to Minimize the Impacts of Hemlock Woolly Adelgid; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2004; p. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Jetton, R.M.; Whittier, W.A.; Dvorak, W.S.; Rhea, J. Conserved ex situ genetic resources of eastern and Carolina hemlock: Eastern North American conifers threatened by the hemlock woolly adelgid. Tree Plant. Notes 2013, 56, 59–71. [Google Scholar]
- Oten, K.L.F.; Merkle, S.A.; Jetton, R.M.; Smith, B.C.; Talley, M.E.; Hain, F.P. Understanding and developing resistance in hemlocks to the hemlock woolly adelgid. Southeast. Nat. 2014, 13, 147–167. [Google Scholar]
- Bentz, S.E.; Riedel, L.G.H.; Pooler, M.R.; Townsend, A.M. Hybridization and self-compatibility in controlled pollination of eastern North American and Asian hemlock (Tsuga) species. J. Arboric. 2002, 28, 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, M.E.; Bentz, S.E.; Olsen, R.T. Evaluation of hemlock (Tsuga) species and hybrids for resistance to Adelges tsugae (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) using artificial infestation. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caswell, T.; Casagrande, R.; Maynard, B.; Preisser, E. Production and evaluation of eastern hemlocks potentially resistant to the hemlock woolly adelgid. In Proceedings of the Fourth Symposium on Hemlock Woolly Adelgid in the Eastern United States, Hartford, CT, USA, 12–14 February 2008; Onken, B., Reardon, R., Eds.; USDA Forest Service: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2008; pp. 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Butin, E.; Preisser, E.; Elkinton, J. Factors affecting settlement rate of the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae, on eastern hemlock, Tsuga canadensis. Agric. For. Entomol. 2007, 9, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetton, R.M.; Hain, F.P.; Dvorak, W.S.; Frampton, J. Infestation rate of hemlock woolly adelgid (Hemiptera: Adelgidae) among three North American hemlock (Tsuga) species following artificial inoculation. J. Entomol. Sci. 2008, 43, 438–442. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, L.; Frampton, J.; Monahan, J.; Goldfarb, B.; Hain, F. Two novel techniques to screen Abies seedlings for resistance to the balsam woolly adelgid, Adelges piceae. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jetton, R.M.; Mayfield III, A.E.; Powers, Z.L. Development of a rain down technique to artificially infest hemlocks with the hemlock woolly adelgid, Adelges tsugae. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS Version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McClure, M.S. Density-dependent feedback and population cycles in Adelges tsugae (Homoptera: Adelgidae) on Tsuga canadensis. Environ. Entomol. 1991, 20, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.; Jetton, R. A shady situation: Evaluating the effect of shade on hemlock woolly adelgid densities on potted hemlock seedlings. In Proceedings of the 55th Southern Forest Insect Work Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–26 July 2013; p. 43.
- Oten, K.L.F. Host-Plant Selection by the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid, Adelges Tsugae Annand: Sensory Systems and Feeding Behavior in Relatizon to Physical and Chemical Host-Plant Characteristics. Ph.D. Thesis, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, USA, October 2012. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Powers, Z.L.; Mayfield, A.E., III; Frampton, J.; Jetton, R.M. Comparison of Suspended Branch and Direct Infestation Techniques for Artificially Infesting Hemlock Seedlings with the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid for Resistance Screening. Forests 2015, 6, 2066-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062066
Powers ZL, Mayfield AE III, Frampton J, Jetton RM. Comparison of Suspended Branch and Direct Infestation Techniques for Artificially Infesting Hemlock Seedlings with the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid for Resistance Screening. Forests. 2015; 6(6):2066-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062066
Chicago/Turabian StylePowers, Zaidee L., Albert E. Mayfield, III, John Frampton, and Robert M. Jetton. 2015. "Comparison of Suspended Branch and Direct Infestation Techniques for Artificially Infesting Hemlock Seedlings with the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid for Resistance Screening" Forests 6, no. 6: 2066-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062066
APA StylePowers, Z. L., Mayfield, A. E., III, Frampton, J., & Jetton, R. M. (2015). Comparison of Suspended Branch and Direct Infestation Techniques for Artificially Infesting Hemlock Seedlings with the Hemlock Woolly Adelgid for Resistance Screening. Forests, 6(6), 2066-2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6062066





