A Bayesian Spatial Model Highlights Distinct Dynamics in Deforestation from Coca and Pastures in an Andean Biodiversity Hotspot
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area

3. Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Land Use Change Spatial Model

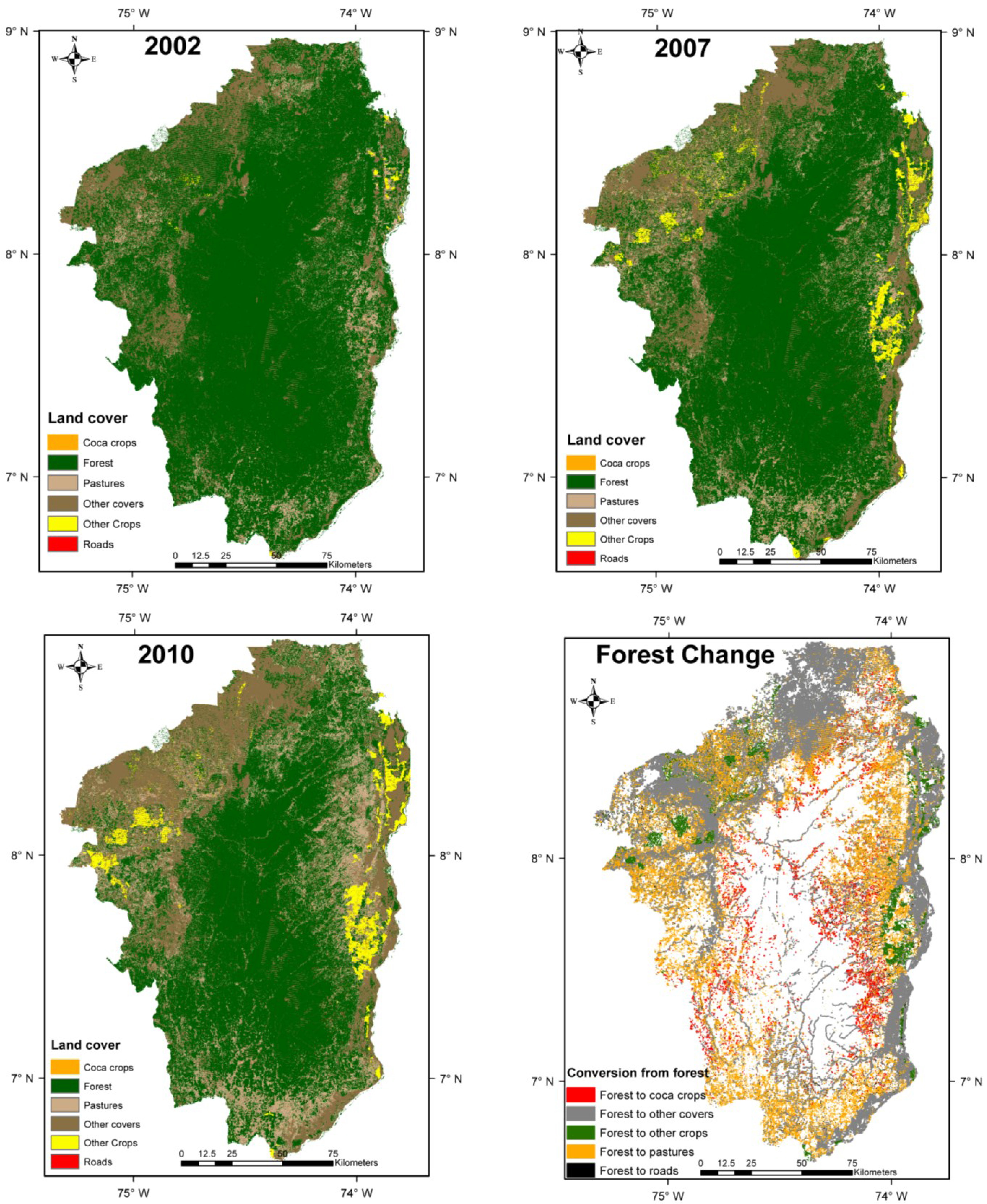
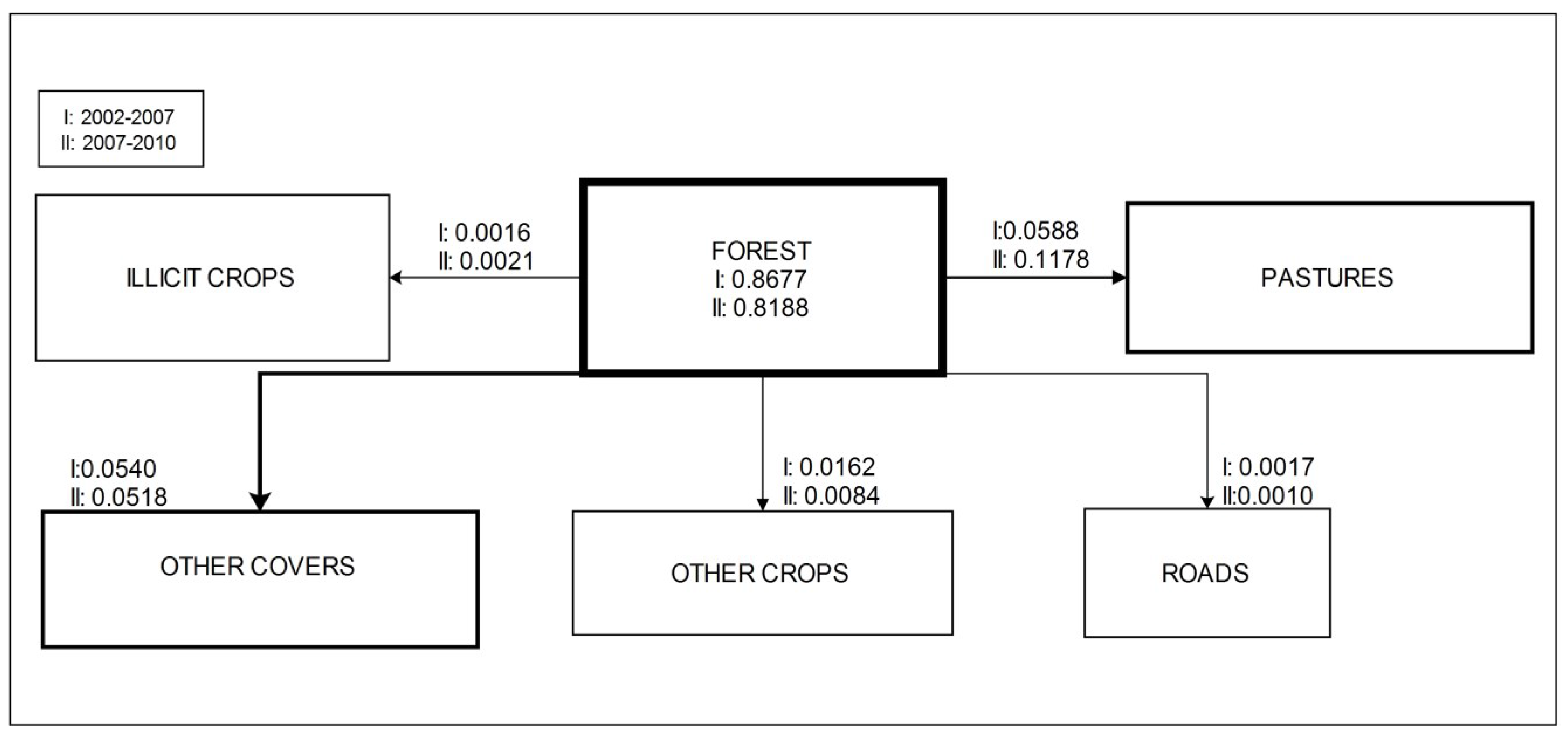
4. Results
| Land Use/Ha per Year | 2002 | 2007 | 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | 2,227,931 | 1,915,913 | 1,574,470 |
| Coca crops | 941 | 5379.5 | 6013 |
| Pastures | 228,558 | 270,638 | 495,917 |
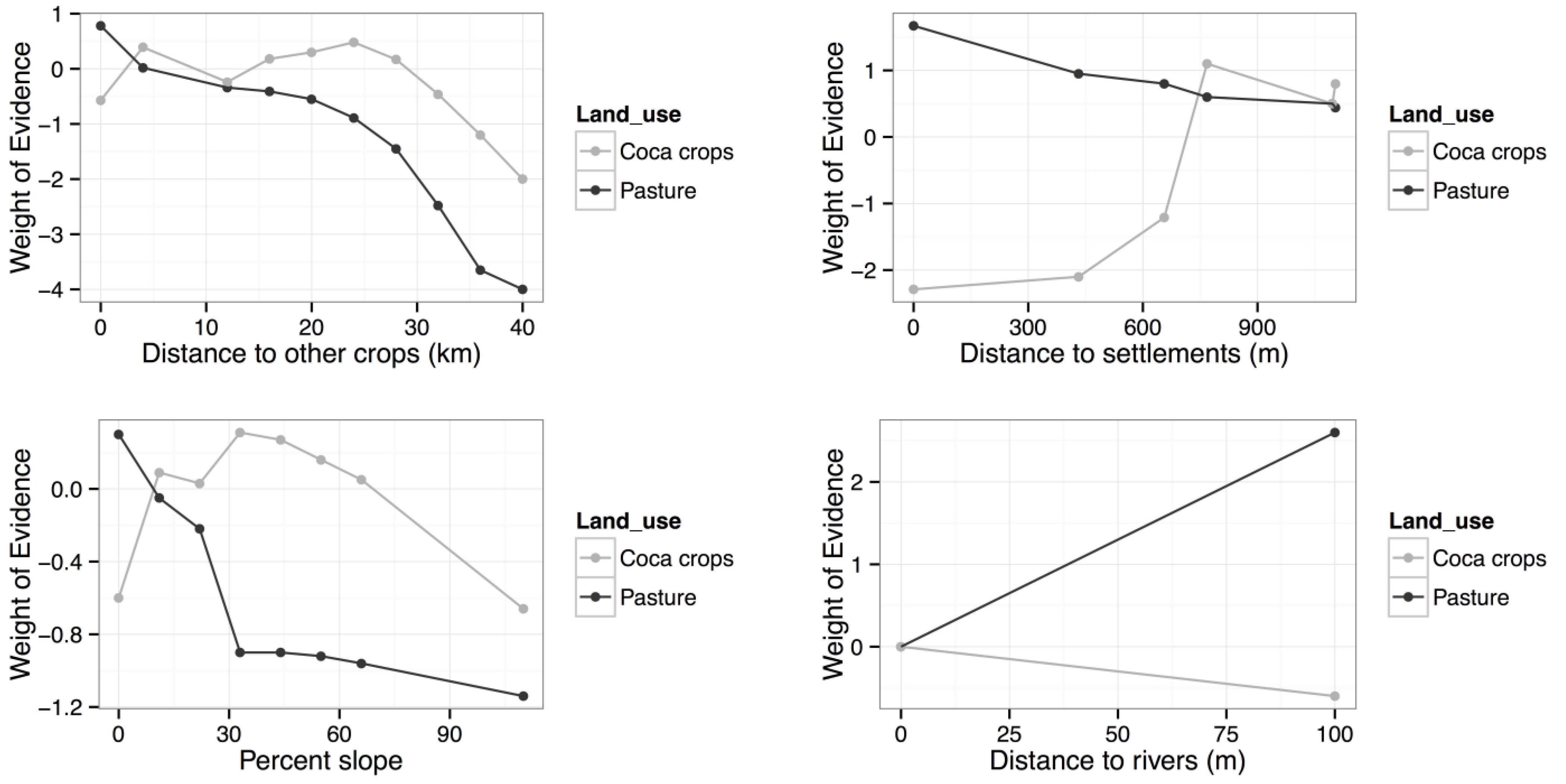
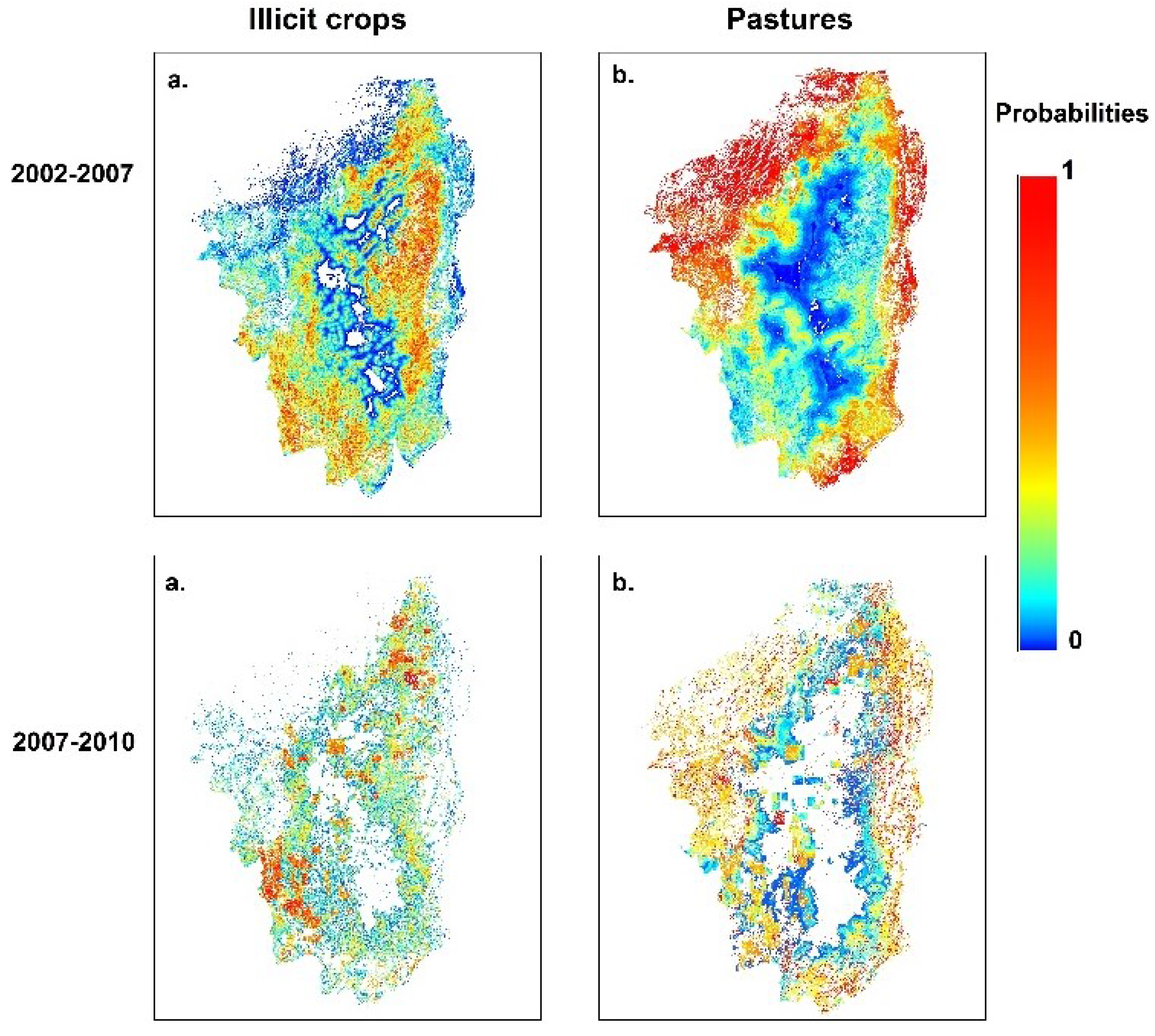
Model Calibration and Validation
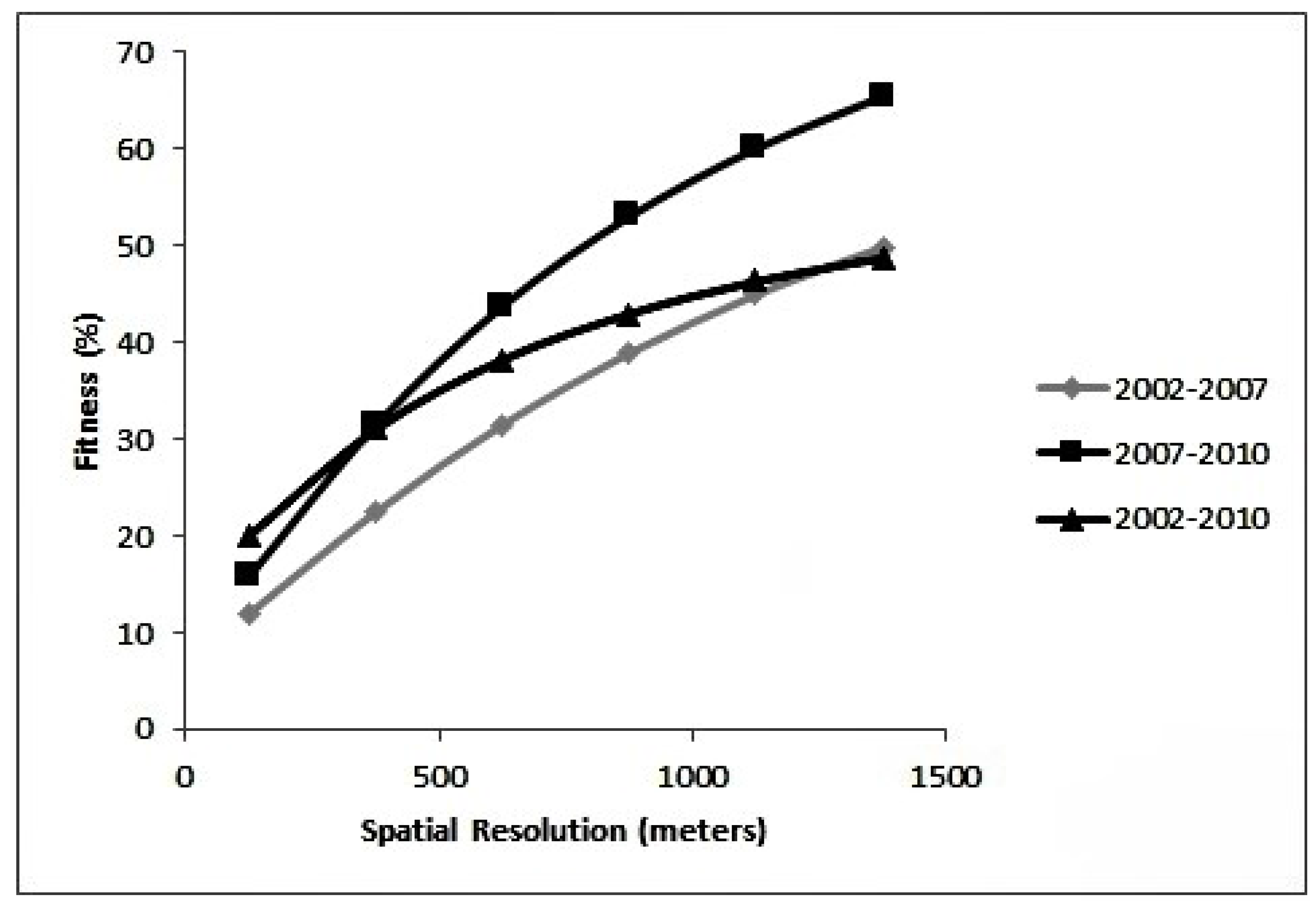
5. Discussion
5.1. Model Calibration and Distinct Dynamic
5.2. Model Validation and Future Improvements
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wright, S.J. Tropical forests in a changing environment. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arroyo-Rodríguez, V.; Mandujano, S. The importance of tropical rain forest fragments to the conservation of plant species diversity in Los Tuxtlas, Mexico. Biodivers. Conserv. 2006, 15, 4159–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, S.; Tilman, D.; Fargione, J.; Chapin, F.S.; Dirzo, R.; Kitzberger, T.; Gemmill, B.; Zobel, M.; Vilá, M.; Mitchell, C.; et al. Biodiversity regulation of ecosystem services. In Ecosystems and Human Well-Being: Current State and Trends; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; pp. 297–329. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st-century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudel, T.K. Changing agents of deforestation: From state-initiated to enterprise driven processes, 1970–2000. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geist, H.J.; Lambin, E.F. What Dirves Tropical Deforestation? A Meta-Analysis of Proximate and Underlying Causes of Deforestation Based on Subnational Case Study Evidence; International Human Dimensions Programme on Global Environ.: Louvain, Belgium, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Geist, H.J. Lambin proximate causes and underlying driving forces of tropical deforestation. Bioscience 2002, 52, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudel, T.K. Shrinking tropical forests, human agents of change, and conservation policy. Conserv. Biol. 2006, 20, 1604–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteras Pascual, D.; Villa García, C.M. Deforestación y Fragmentación de Ecosistemas Naturales en el Escudo Guayanés Colombiano; Grey Comercializadora Ltda: Bogotá, Colombia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Foley, J.A.; Defries, R.; Asner, G.P.; Barford, C.; Bonan, G.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chapin, F.S.; Coe, M.T.; Daily, G.C.; Gibbs, H.K.; et al. Global consequences of land use. Science 2005, 309, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenteras, D.; Rodríguez, N.; Retana, J.; Morales, M. Understanding deforestation in montane and lowland forests of the Colombian Andes. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenteras, D.; Cabrera, E.; Rodríguez, N.; Retana, J. National and regional determinants of tropical deforestation in Colombia. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaman, P.; Donegan, T.; Cuervo, A. New distributional bird records from Serrania de San Lucas and adjacent central cordillera of colombia. Br. Ornithol. Club 2002, 122, 285–303. [Google Scholar]
- Dávalos, L.M. The San Lucas mountain range in Colombia : How much conservation is owed to the violence ? Biodivers. Conserv. 2001, 10, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaman, P.; Donegan, T.; Gonzalez, C.; Bustos, X.; Cuervo, A. Presenting the first biological assessment of Serranía San Lucas.; Colombian EBA Project Report Series No. 3; Fundación ProAves: Bogotá, Colombia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fundacion Colibri Evaluación ecológica rápida de la Serranía de San Lucas. Available online: http://www.thc-fc.org/PDF/SerraniaSanLucas.pdf (accessed on 15 Mar 2013).
- Álvarez, M.D. Forests in the Time of Violence. J. Sustain. For. 2003, 16, 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, M. Dinámica del uso del Suelo y Cambio Climático en la Planeación Sistemática Para la Conservación: un caso de Estudio en la Cuenca Grijalva-Usumacinta; Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México: México, DF, México, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Soares Filho, B.S.; Rodrigues, H.O.; Costa, W.L. Modeling Environmental Dynamics with Dinamica EGO; Centro de Sensoriamento Remoto. Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais: Belo Hotizonte, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadística Sistema de Consulta Información Censal; DANE: Bogotá, Colombia, 2005. Available online: http://systema59.dane.gov.co/cgibin/RpWebEngine.exe/PortalAction?&MODE=MAIN&BASE=CG2005BASICO&MAIN=WebServerMain.inl (accessed on 15 September 2015).
- Rodriguez, N.; Armenteras, D.; Morales, M.; Romero, M. Ecosistemas de los Andes Colombianos; Segunda.; Instituto de Investigación de Recursos Biológicos Alexander von Humboldt: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- UNODC. Análisis Multitemporal de Cultivos de Coca Periodo 2001–2006; Oficina de las Naciones Unidas contra la droga y el delito: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- SIMCI II-UNODC Norma Técnica de Metadatos. Available online: http://www.biesimci.org/Satelital/Original/Landsat/indices/B071L11-S009055E006.html (accessed on 1 January 2015).
- UNODC. Monitoreo de Cultivos de Coca 2010; Oficina de las Naciones Unidas contra la droga y el delito: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- UNODC. Monitoreo de Cultivos de Coca 2014; Oficina de las Naciones Unidas contra la droga y el delito: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soares-Filho, B.S.; Coutinho Cerqueira, G.; Lopes Pennachin, C. Dinamica—A stochastic cellular automata model designed to simulate the landscape dynamics in an Amazonian colonization frontier. Ecol. Modell. 2002, 154, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinali, F.; Alesheikh, A.A. Weighting Spatial Information in GIS for Copper Mining Exploration. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2008, 5, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, C.M.; Vieira Monteiro, A.M.; Câmara, G.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Coutinho Cerqueira, G.; Lopes Pennachin, C.; Batty, M. GIS and remote sensing as tools for the simulation of urban land-use change. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 759–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, A.M.; Fearnside, P.M.; de Alencastro Graça, P.M.L.; Nogueira, E.M. Avoided deforestation in Brazilian Amazonia: Simulating the effect of the Juma Sustainable Development Reserve. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 282, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.E.; Ferreira, L.G.; Miziara, F.; Soares-Filho, B.S. Modeling landscape dynamics in the central Brazilian savanna biome: Future scenarios and perspectives for conservation. J. Land Use Sci. 2013, 8, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, E.E.; de Almeida, C.M.; de Carvalho Ximenes, A.; Formaggio, A.R.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Pellikka, P. Dynamic modeling of forest conversion: Simulation of past and future scenarios of rural activities expansion in the fringes of the Xingu National Park, Brazilian Amazon. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, E.E.; Clark, B.J.F.; Pellikka, P.; Siljander, M. Modelling agricultural expansion in Kenya’s Eastern Arc Mountains biodiversity hotspot. Agric. Syst. 2010, 103, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamusoko, C.; Wada, Y.; Furuya, T.; Tomimura, S.; Nasu, M.; Homsysavath, K. Simulating Future Forest Cover Changes in Pakxeng District, Lao People’s Democratic Republic (PDR): Implications for Sustainable Forest Management. Land 2013, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanly, J. Los Factores de la Deforestación y de la Degradación de los Bosques; XII Congreso Forestal Mundial: Quebéc, City, 2003; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, J.; Kolb, M.; Houet, T.; Paegelow, M.; Camacho Olmeda, M.T. Éclairer le choix des outils de simulation des changements des modes d’occupation et d’usages des sols. Une approche comparative. Rev. Int. Géomatique 2011, 21, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westen, C.J. Use of Weights of Evidence Modeling for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping; International Institute for Geoinformation Science and Earth Observation: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- De Maria Almeida, C.; Batty, M.; Vieira Monteiro, A.M.; Câmara, G.; Soares-Filho, B.S.; Cerqueira, G.C.; Pennachin, C.L. Stochastic cellular automata modeling of urban land use dynamics: empirical development and estimation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2003, 27, 481–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávalos, L.M.; Bejarano, A.C.; Hall, M.A.; Correa, H.L.; Corthals, A.; Espejo, O.J. Forests and drugs: Coca-driven deforestation in tropical biodiversity hotspots. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávalos, L.M.; Holmes, J.S.; Rodríguez, N.; Armenteras, D. Demand for beef is unrelated to pasture expansion in northwestern Amazonia. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 170, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, G.I. Selvas sin Ley. Conflicto, drogas y globalización de la deforestación de Colombia. In Guerra, Sociedad y Medio Ambiente; Fescol: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2004; pp. 107–173. [Google Scholar]
- García Romero, H. Deforestación en Colombia : Retos y perspectivas; Fededesarrollo: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sabogal, A. Levantamiento de una Línea de Base Sobre Minería Ilegal de oro en Colombia; Fededesarrollo: Bogotá D.C., Colombia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, C.P.; Cochrane, M.A.; Souza, C.M.; Laurance, W.F. Roads, deforestation, and the mitigating effect of protected areas in the Amazon. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 177, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC. Monitoreo de Cultivos de coca 2012; Oficina de las Naciones Unidas contra la droga y el delito: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Armenteras, D.; Rudas, G.; Rodriguez, N.; Sua, S.; Romero, M. Patterns and causes of deforestation in the Colombian Amazon. Ecol. Indic. 2006, 6, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mas, J. Modelling deforestation using GIS and artificial neural networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 2004, 19, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahecha, L.; Gallego, L.A.; Peláez, F.J. Situación actual de la ganadería de carne en Colombia y alternativas para impulsar su competitividad y sostenibilidad. Rev. Colomb. Ciencias Pecu. 2002, 15, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Redo, D.J.; Aide, T.M.; Clark, M.L. The relative importance of socioeconomic and environmental variables in explaining land change in Bolivia, 2001–2010. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2012, 102, 778–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, E.; Costa, S.; Aguiar, A.P.; Câmara, G.; Carneiro, T. Dynamical coupling of multiscale land change models. Landsc. Ecol. 2009, 24, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.D. Roads, Development and Deforestation: A Review; Development Research Group, World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mas, J.-F.; Kolb, M.; Paegelow, M.; Camacho Olmedo, M.T.; Houet, T. Inductive pattern-based land use/cover change models: A comparison of four software packages. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 51, 94–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieilledent, G.; Grinand, C.; Vaudry, R. Forecasting deforestation and carbon emissions in tropical developing countries facing demographic expansion: A case study in Madagascar. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 1702–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, M.; Mas, J.-F.; Galicia, L. Evaluating drivers of land-use change and transition potential models in a complex landscape in Southern Mexico. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2013, 27, 1804–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, Ž.; Boerboom, L.; Glade, T. Future Forest Cover Change Scenarios with Implications for Landslide Risk: An Example from Buzau Subcarpathians, Romania. Environ. Manag. 2015, 56, 1228–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares-Filho, B.; Alencar, A.; Nepstad, D.; Cerqueira, G.; Vera Diaz, M.D.C.; Rivero, S.; Solorzano, L.; Voll, E. Simulating the response of land-cover changes to road paving and governance along a major Amazon highway: The Santarem-Cuiaba corridor. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC. Cultivos de Coca: Estadísticas Municipales Censo 31 de Diciembre de 2012; Oficina de las Naciones Unidas contra la droga y el delito: Bogotá, DC, Colombia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rincón Ruiz, A.; Pascual, U.; Romero, M. An exploratory spatial analysis of illegal coca cultivation in Colombia using local indicators of spatial association and socioecological variables. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 34, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chadid, M.A.; Dávalos, L.M.; Molina, J.; Armenteras, D. A Bayesian Spatial Model Highlights Distinct Dynamics in Deforestation from Coca and Pastures in an Andean Biodiversity Hotspot. Forests 2015, 6, 3828-3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6113828
Chadid MA, Dávalos LM, Molina J, Armenteras D. A Bayesian Spatial Model Highlights Distinct Dynamics in Deforestation from Coca and Pastures in an Andean Biodiversity Hotspot. Forests. 2015; 6(11):3828-3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6113828
Chicago/Turabian StyleChadid, Maria Alejandra, Liliana M. Dávalos, Jorge Molina, and Dolors Armenteras. 2015. "A Bayesian Spatial Model Highlights Distinct Dynamics in Deforestation from Coca and Pastures in an Andean Biodiversity Hotspot" Forests 6, no. 11: 3828-3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6113828
APA StyleChadid, M. A., Dávalos, L. M., Molina, J., & Armenteras, D. (2015). A Bayesian Spatial Model Highlights Distinct Dynamics in Deforestation from Coca and Pastures in an Andean Biodiversity Hotspot. Forests, 6(11), 3828-3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/f6113828






