Wireless Wave Attenuation in Forests: An Overview of Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methods
4. Results
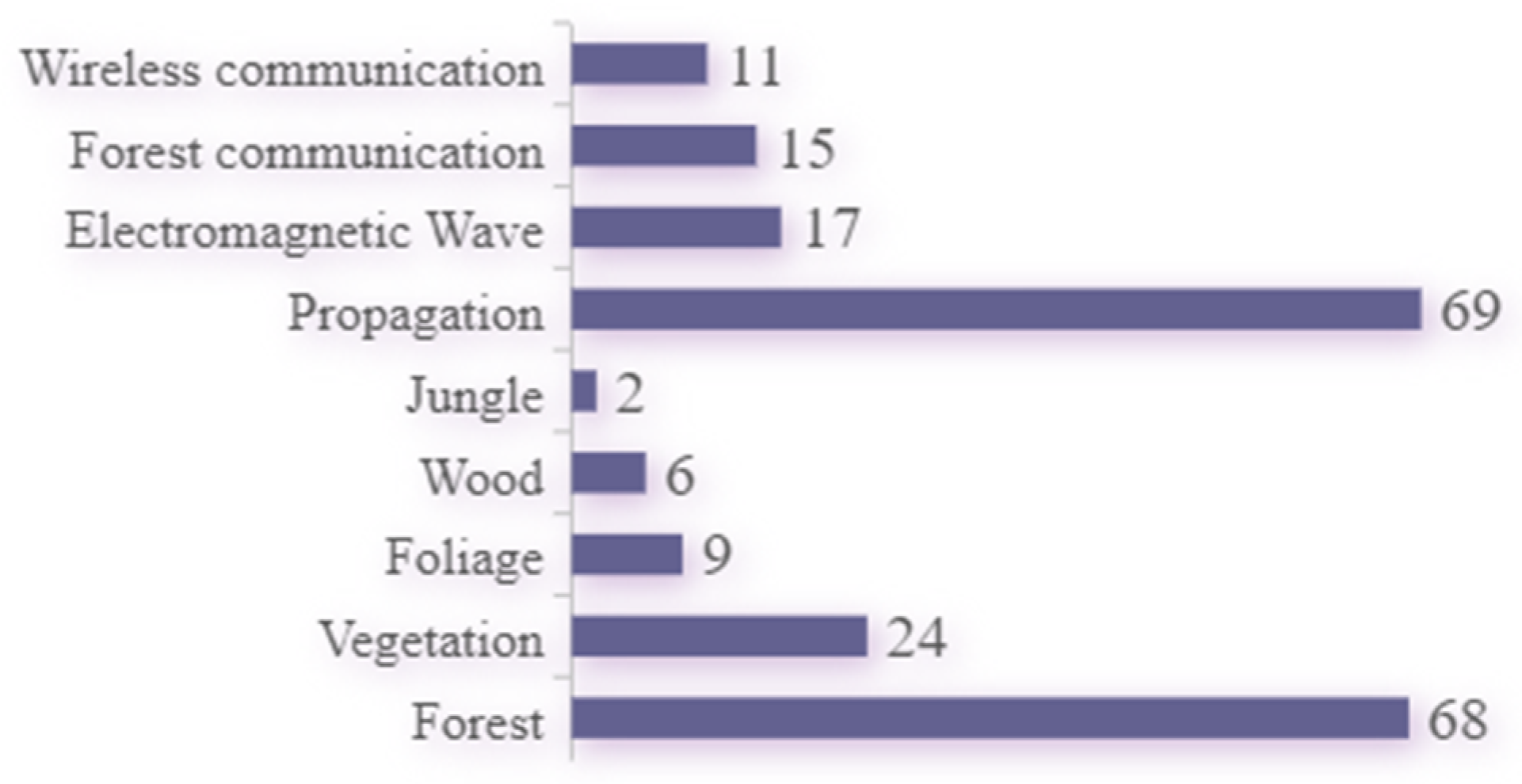
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
- -
- The term “Jungle” was mentioned only twice, indicating that it is not a commonly used keyword in current literature, and research on jungle-specific forest communication, prediction, and electromagnetic wave transmission is relatively scarce.
- -
- “Propagation” and “Forest” are the most frequently occurring keywords, mentioned 69 and 68 times, respectively. This suggests that they are central concepts in the field of forest electromagnetic wave propagation. “Electromagnetic Wave” appeared 17 times and “Forest communication” 15 times, indicating their relative importance in the research, though not as primary focuses. By contrast, “Wireless communication” (eleven mentions), “Foliage” (nine mentions), and “Wood” (six mentions) are less frequently mentioned, possibly indicating a lower focus on these terms in forest electromagnetic wave propagation research.
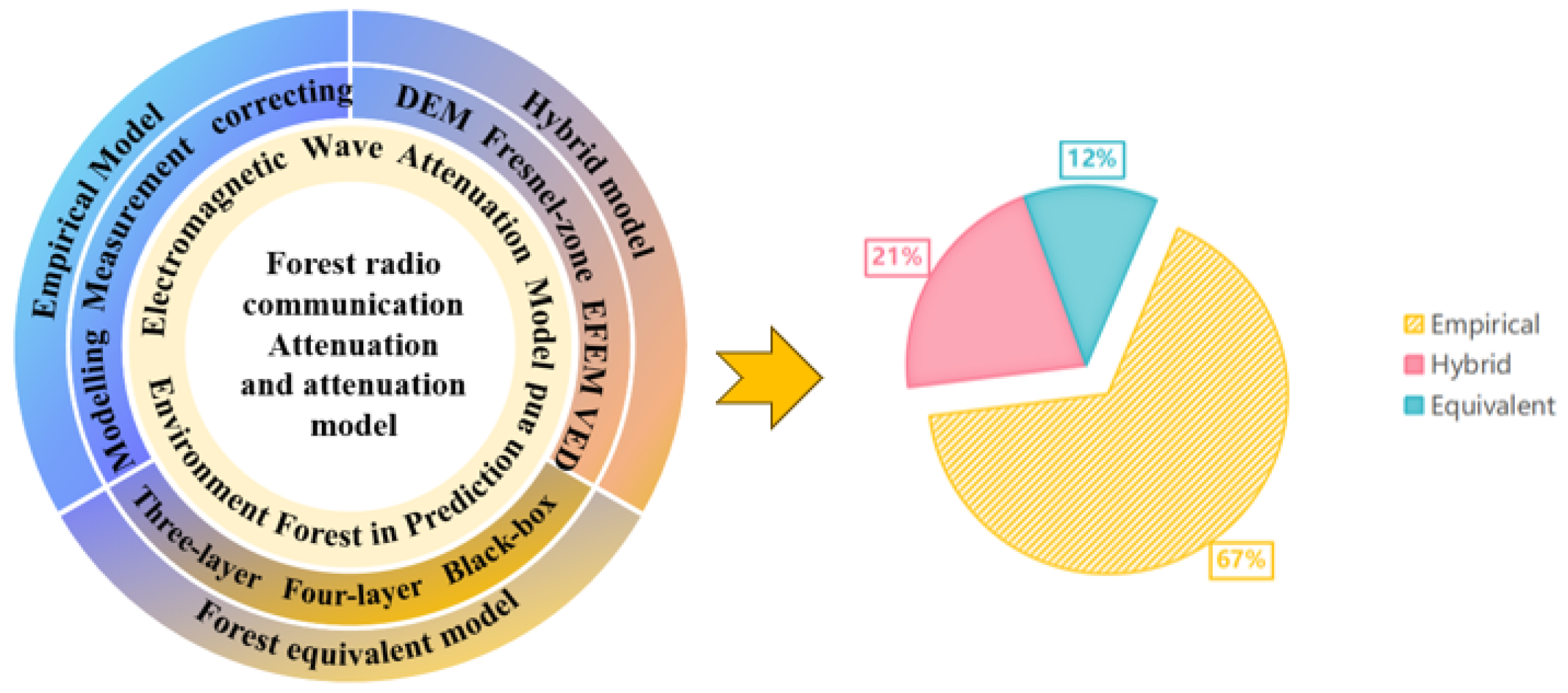
4.2. Thematic Analysis
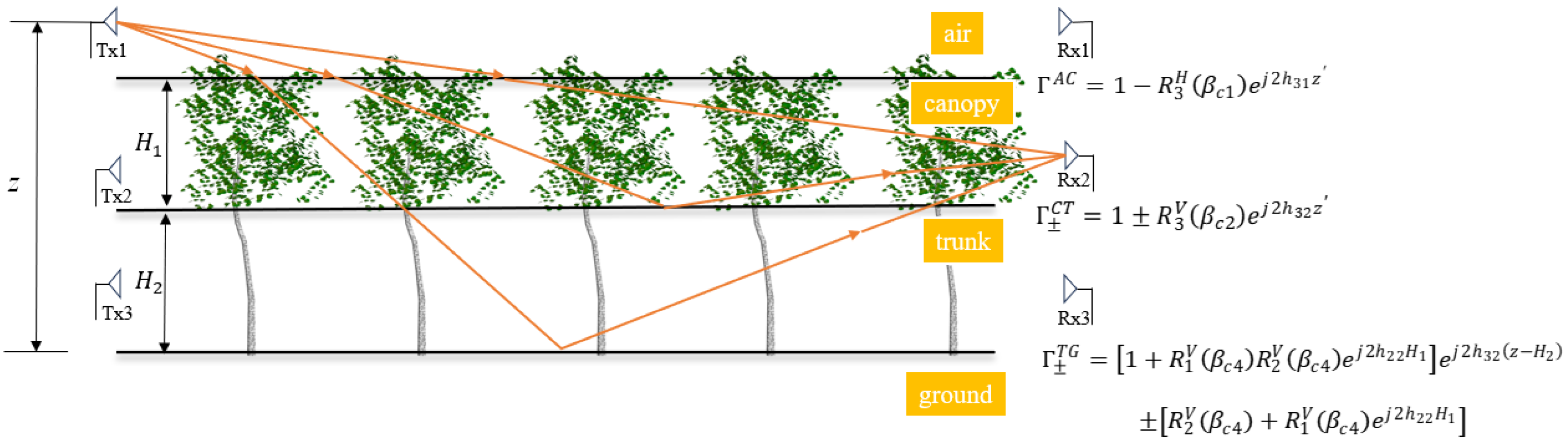
4.2.1. Forest Equivalent Model Research
4.2.2. Empirical Formulas and Models
4.2.3. Hybrid Formulas and Models
5. Discussion
5.1. Model Characteristics and Practical Applications
5.2. Complex and Adverse Forest Environments
5.3. Main Research Bands for Electromagnetic Wave Transmission in Forests
5.4. Applications of Electromagnetic Attenuation Principles in Forestry Operations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, H.; Qu, D.; Ding, J.; Wang, Z.; He, H.; Chen, H. Enabling LPWAN Massive Access: Grant-Free Random Access with Massive MIMO. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2022, 29, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X.; Huo, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J. Durable Superhydrophobic Coatings for Prevention of Rain Attenuation of 5G/Weather Radomes. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labelle, E.R.; Hansson, L.; Högbom, L.; Jourgholami, M.; Laschi, A. Strategies to Mitigate the Effects of Soil Physical Disturbances Caused by Forest Machinery: A Comprehensive Review. Curr. For. Rep. 2022, 8, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Forest Service. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/United_States_Forest_Service (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- World Atlas of Ground Conductivities. Available online: https://hamwaves.com/ground/doc/ground-conductivity-atlas.vlf&mf.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Phillips, C.; Sicker, D.; Grunwald, D. A Survey of Wireless Path Loss Prediction and Coverage Mapping Methods. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Atlas of Electrical Conductivity. Available online: https://hamwaves.com/ground/en/index.html (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Olasupo, T.O.; Otero, C.E. The Impacts of Node Orientation on Radio Propagation Models for Airborne-Deployed Sensor Networks in Large-Scale Tree Vegetation Terrains. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2020, 50, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, J.R.; Yao, S.; Kroeger, T.; Carducci, C.; Murphy, C. Drone-Based Forest Propagation Measurements for Ground-to-Air EMI Applications. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2019, 18, 2627–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, S.; Picco, G.P.; Bruzzone, L. LaPS: LiDAR-Assisted Placement of Wireless Sensor Networks in Forests. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. (TOSN) 2019, 15, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetri, S.; Picco, G.P.; Bruzzone, L. Estimating Low-Power Radio Signal Attenuation in Forests: A LiDAR-Based Approach. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Distributed Computing in Sensor Systems, Fortaleza, Brazil, 10–12 June 2015; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Bazezew, M.N.; Hussin, Y.A.; Kloosterman, E.H.; Hasmadi, I.M.; Soromessa, T.; Adan, M.S. Factual Approach for Tropical Forest Parameters Measurement and Monitoring: Future Option with a Focus on Synergetic Use of Airborne and Terrestrial LiDAR Technologies. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3219–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimbelman, E.G.; Keefe, R.F. Lost in the Woods: Forest Vegetation, and Not Topography, Most Affects the Connectivity of Mesh Radio Networks for Public Safety. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchette, D.; Fournier, R.A.; Luther, J.E.; Côté, J.-F. Predicting Wood Fiber Attributes Using Local-Scale Metrics from Terrestrial LiDAR Data: A Case Study of Newfoundland Conifer Species. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 347, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.; Jaeger, D.; Hanewinkel, M. Digitization in Wood Supply—A Review on How Industry 4.0 Will Change the Forest Value Chain. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 206–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.W.; Jiao, P.N. Solving the Field of a Four-Layer Jungle Model Using the Vector Green Function Method. J. Radio Sci. (China) 1986, 2, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.W.; Jiao, P.N. Mixed Path Propagation of Radio Waves in Jungle Communication. J. Commun. (China) 1988, 6, 1–6+41. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.W.; Yeo, T.S.; Kooi, P.S.; Leong, M.S.; Koh, J.H. Analysis of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation in Forest Environment Along Multiple Paths. PIER 1999, 23, 137–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, L.W.; Koh, J.H.; Yeo, T.S.; Leong, M.S.; Kooi, P.-S. Analysis of Radiowave Propagation in a Four-Layered Anisotropic Forest Environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1967–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-W.; Lee, C.-K.; Yeo, T.-S.; Leong, M.-S. Radio Wave Propagation along Earth-Space Paths in the Presence of a Multilayered Anisotropic Forest. Electromagnetics 2002, 22, 235–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-W.; Lee, C.-K.; Yeo, T.-S.; Leong, M.-S. Wave Mode and Path Characteristics in a Four-Layered Anisotropic Forest Environment. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2004, 52, 2445–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ng, B.C. Study of Propagation Loss Prediction in Forest Environment. Prog. Electromagn. Res. B 2009, 17, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbstreit, J.W.; Crichlow, W.Q. Measurement of the Attenuation of Radio Signals by Jungles. J. Res. NBS/USNC-URSI 1964, 68D, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamir, T. On Radio-Wave Propagation in Forest Environments. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1967, 15, 806–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dence, D.; Tamir, T. Radio Loss of Lateral Waves in Forest Environments. Radio Sci. 1969, 4, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Cavalcante, G.P. Radio Loss in Forests Using a Model with Four Layered Media. Radio Sci. 1983, 18, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myagmardulam, B.; Tadachika, N.; Takahashi, K.; Miura, R.; Ono, F.; Kagawa, T.; Shan, L.; Kojima, F. Path Loss Prediction Model Development in a Mountainous Forest Environment. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2021, 2, 2494–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.P.; Messier, G.G.; Wasson, M.W. Boreal Forest Low Antenna Height Propagation Measurements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2016, 64, 4004–4011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejselbaek, J.; Odum Nielsen, J.; Fan, W.; Pedersen, G.F. Empirical Study of Near Ground Propagation in Forest Terrain for Internet-of-Things Type Device-to-Device Communication. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 54052–54063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijun, Z.; Yushu, T. Theory and Experiment Validation of Radio Wave Propagation in the Forest and Its Application for Extended Frequency. In Proceedings of the ISAPE 2012, Xi’an, China, 22–26 October 2012; pp. 531–534. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, G.; Tian, G.; Liu, W. A Model with Leaf Area Index and Trunk Diameter for LoRaWAN Radio Propagation in Eastern China Mixed Forest. J. Sens. 2020, 2020, 2687148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ng, B.C. Empirical Near Ground Path Loss Modeling in a Forest at VHF and UHF Bands. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2009, 57, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wesenbeeck, B.K.; Wolters, G.; Antolínez, J.A.A.; Kalloe, S.A.; Hofland, B.; De Boer, W.P.; Çete, C.; Bouma, T.J. Wave Attenuation through Forests under Extreme Conditions. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, K.; Koh, I.-S. Effect of Canopy-Air Interface Roughness on HF-VHF Wave Propagation in Forest. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2002, 50, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee, K.L.; Torrico, S.A.; Kurner, T. Foliage Attenuation Over Mixed Terrains in Rural Areas for Broadband Wireless Access at 3.5 GHz. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2011, 59, 2698–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufemi, A.; Oluwole, F.; Olajide, O. UHF Band Radio Wave Propagation Mechanism in Forested Environments for Wireless Communication Systems. J. Inf. Eng. Appl. 2013, 3, 2224–5782. [Google Scholar]
- Vougioukas, S.; Anastassiu, H.T.; Regen, C.; Zude, M. Influence of Foliage on Radio Path Losses (PLs) for Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Planning in Orchards. Biosyst. Eng. 2013, 114, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krraoui, H.; Mejri, F.; Aguili, T. Dielectric Constant Measurement of Materials by a Microwave Technique: Application to the Characterization of Vegetation Leaves. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2016, 30, 1643–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sarabandi, K. A Physics-Based Statistical Model for Wave Propagation Through Foliage. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2007, 55, 958–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Kuo, Y. Calculation of Radio Loss in Forest Environments by an Empirical Formula. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2001, 31, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaunstein, N.; Kovacs, I.Z.; Ben-Shimol, Y.; Bach Andersen, J.; Katz, D.; Eggers, P.C.F.; Giladi, R.; Olesen, K. Prediction of UHF Path Loss for Forest Environments: PREDICTION OF UHF PATH LOSS. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 25-1–25-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atutov, E.B.; Lomukhin, Y.L. Average Field in a Forest Medium. J. Commun. Technol. Electron. 2007, 52, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picallo, I.; Klaina, H.; Lopez-Iturri, P.; Aguirre, E.; Celaya-Echarri, M.; Azpilicueta, L.; Eguizábal, A.; Falcone, F.; Alejos, A. A Radio Channel Model for D2D Communications Blocked by Single Trees in Forest Environments. Sensors 2019, 19, 4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabihi, R.; Vaughan, R.G. Simplifying Through-Forest Propagation Modelling. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 2020, 1, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, Q. Environment Features-Based Model for Path Loss Prediction. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2022, 11, 2010–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, R.K.; Swarup, S.; Roy, M.N. Radio Wave Propagation through Rain Forests of India. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 1990, 38, 433–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissberger, M.A. An Initial Critical Summary of Models for Predicting the Attenuation of Radio Waves by Trees; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 1982.
- Goldman, J.; Swenson, G.W. Radio Wave Propagation through Woods. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 1999, 41, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, I.Z.; Eggers, P.C.F.; Olesen, K. Radio Channel Characterisation for Forest Environments in the VHF and UHF Frequency Bands. In Proceedings of the Gateway to 21st Century Communications Village. VTC 1999-Fall. IEEE VTS 50th Vehicular Technology Conference (Cat. No.99CH36324), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 19–22 September 1999; Volume 3, pp. 1387–1391. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ng, B.C. Path Loss Modeling for Near-Ground VHF Radio-Wave Propagation through Forests with Tree-Canopy Reflection Effect. Prog. Electromagn. Res. M 2010, 12, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitirgan, M.; Yoruk, Y.E.; Celik, S.; Kurnaz, O.; Helhel, S.; Ozen, S. Generation of an Empiric Propagation Model for Forest Environment at GSM900/GSM1800/CDMA2100. In Proceedings of the 2011 XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–20 August 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, C.R.; Volos, H.I.; Buehrer, R.M. Characterization of Low-Antenna Ultrawideband Propagation in a Forest Environment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2013, 62, 2878–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, J.A.; Santos, F.E. A Model to Estimate the Path Loss in Areas with Foliage of Trees. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 71, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibdah, Y.; Ding, Y. Path Loss Models for Low-Height Mobiles in Forest and Urban. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2017, 92, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougerie, S.; Israel, J.; Kan, T. Validation of ITU-R P.833-9 Tree Attenuation Model for Land Mobile Satellite Propagation Channel at Ku/Ka Band. In Proceedings of the 2021 15th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), Dusseldorf, Germany, 22–26 March 2021; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Oestges, C.; Villacieros, B.M.; Vanhoenacker-Janvier, D. Radio Channel Characterization for Moderate Antenna Heights in Forest Areas. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 4031–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masking Angle for Satellite Paths. Available online: https://www.itu.int/md/R07-WP3M-C-0164 (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- Hall, M.P.M. Background to COST Project 235 [MM Wave Radio Propagation]. In Proceedings of the 1995 SBMO/IEEE MTT-S International Microwave and Optoelectronics Conference, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 24–27 July 1995; Volume 1, pp. 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Nuaimi, M.O.; Stephens, R.B.L. Measurements and Prediction Model Optimisation for Signal Attenuation in Vegetation Media at Centimetre Wave Frequencies. IEE Proc.-Microw. Antennas Propag. 1998, 145, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, J.A.R.; Santos, F.E.S. An Empirical Propagation Model for Forest Environments at Tree Trunk Level. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2011, 59, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay-Fernandez, J.A.; Cuinas, I. Peer to Peer Wireless Propagation Measurements and Path-Loss Modeling in Vegetated Environments. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2013, 61, 3302–3311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoraishi, M.; Takada, J.-i.; Imai, T. Radio Wave Propagation Through Vegetation. In Wave Propagation Theories and Applications; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.E.; Ortiz, F.M.; Costa, L.H.M.K.; Foubert, B.; Amadou, I.; Mitton, N. A Study of the LoRa Signal Propagation in Forest, Urban, and Suburban Environments. Ann. Telecommun. 2020, 75, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Beelde, B.; De Beelde, R.; Tanghe, E.; Plets, D.; Verheyen, K.; Joseph, W. Vegetation Loss at D-Band Frequencies and New Vegetation-Dependent Exponential Decay Model. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2022, 70, 12092–12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.-J.; Li, W.-B. Propagation Path Loss Prediction Model of Multi-Sensor Network in Forest. Procedia Eng. 2011, 15, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Azevedo, J.A.; Santos, F.E.; Sousa, T.A.; Agrela, J.M. Impact of the Antenna Directivity on Path Loss for Different Propagation Environments. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2015, 9, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios-Ulloa, A.; Ariza-Colpas, P.; Sánchez-Moreno, H.; Quintero-Linero, A.; De La Hoz-Franco, E. Modeling Radio Wave Propagation for Wireless Sensor Networks in Vegetated Environments: A Systematic Literature Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, G.P.N.; Habaebi, M.H.; Toha, S.F.; Islam, M.R.; Yusoff, S.H.B.; Adesta, E.Y.T.; Anzum, R. Near Ground Pathloss Propagation Model Using Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System for Wireless Sensor Network Communication in Forest, Jungle and Open Dirt Road Environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.2108-1—Prediction of Clutter Loss. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-P.2108/recommendation.asp?lang=en&parent=R-REC-P.2108-1-202109-I (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- RECOMMENDATION ITU-R P.833-10—Attenuation in Vegetation. Available online: https://www.itu.int/rec/R-REC-P.833-10-202109-I/en (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Zhang, W.; Lo, T.; Litva, J. Fractal Modeling of Forest Surfaces for Electromagnetic Wave Scattering Research. Proceedings of 6th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications, Toronto, ON, Canada, 27–29 September 1995; Volume 1, pp. 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ng, B.C. The Effects of Tropical Weather on Radio-Wave Propagation Over Foliage Channel. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2009, 58, 4023–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chymitdorzhiev, T.N.; Dagurov, P.N.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Mironov, V.L. Electromagnetic Wave Attenuation for Propagation through a Forest Belt. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; IGARSS ’04. Proceedings. Volume 3, pp. 2091–2094. [Google Scholar]
- Torabi, A.; Zekavat, S.A. Near-Ground Channel Modeling for Distributed Cooperative Communications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2016, 64, 2494–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Portillo-Quintero, C.; Sanchez-Azofeifa, A.; MacGregor, M.H. Predicting RF Path Loss in Forests Using Satellite Measurements of Vegetation Indices. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks Workshops, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 8–11 September 2014; pp. 592–596. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, P. Comprehensive Measurement and Modeling in Foliage Environments Using UHF UWB Ground-Based Radar. J. Electromagn. Waves Appl. 2019, 33, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawhly, T.; Chandra Tiwari, R. Loss Exponent Modeling for the Hilly Forested Region in the VHF Band III. Radio Sci. 2021, 56, e2020RS007201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonor, N.R.; Caldeirinha, R.F.S.; Fernandes, T.R.; Ferreira, D.; Sanchez, M.G. A 2D Ray-Tracing Based Model for Micro- and Millimeter-Wave Propagation Through Vegetation. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propagat. 2014, 62, 6443–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.D.; Silva, D.K.N.D.; Eras, L.E.C.; Souza, N.W.P.D.; Cruz, A.F.S.D.; Costa, E. Broadband Channel Characterization in Wooded Environment in the 26 GHz Band. J. Microw. Optoelectron. Electromagn. Appl. 2021, 20, 726–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.-J.; Yin, H.; He, Z.; Chen, R.-S. Radio Wave Propagation Prediction for Forests in Rainy Environment. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society (ACES-China) Symposium, Chengdu, China, 28–31 July 2021; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Arshad, K.; Katsriku, F.; Lasebae, A. Radiowave VHF Propagation Modelling in Forest Using Finite Elements. In Proceedings of the 2006 2nd International Conference on Information & Communication Technologies, Damascus, Syria, 24–28 April 2006; Volume 2, pp. 2146–2149. [Google Scholar]
- De Souza, J.F.; Magno, F.N.B.; Valente, Z.A.; Costa, J.C.; Cavalcante, G.P.S. Mobile Radio Propagation along Mixed Paths in Forest Environment Using Parabolic Equation. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2009, 51, 1133–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.-W.; Guo, L.-X.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, Q.-L. Parabolic Equation Modeling of Propagation over Terrain Using Digital Elevation Model. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2018, 2018, 1878307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, M.S.; Malevich, E.S.; Permyakov, V.A. Modeling of Radio-Wave Propagation in Forest by the Method of Parabolic Equation. Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malevich, E.S.; Mikhailov, M.S.; Volkova, A.A. Comparison of the Results of an Experimental Research of the Radio Wave Propagation in the Forest with Numerical Simulation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Radiation and Scattering of Electromagnetic Waves (RSEMW), Divnomorskoe, Russia, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 364–367. [Google Scholar]
- Malevich, E.S.; Mikhailov, M.S.; Volkova, A.A.; Permyakov, V.A. The Research of Radio Wave Propagation Mechanisms in the Forest Vegetation with the Complex Landscape. In Proceedings of the 2019 Antennas Design and Measurement International Conference (ADMInC), St. Petersburg, Russia, 16–18 October 2019; pp. 87–89. [Google Scholar]
- Shehadeh, H.A.; Idris, M.Y.I.; Ahmedy, I.; Hassen, H.R. Optimal Placement of Near Ground VHF/UHF Radio Communication Network as a Multi Objective Problem. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 110, 1169–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.M.D.; Ramirez, L.A.R.; Dias, M.H.C. On the Use of UTD-Based Models for RF Path Loss Prediction Due to Diffraction on a Forest-Covered Ridge. J. Microw. Optoelectron. Electromagn. Appl. 2021, 20, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gans, M.J.; Amitay, N.; Yeh, Y.S.; Damen, T.C.; Valenzuela, R.A.; Cheon, C.; Lee, J. Propagation Measurements for Fixed Wireless Loops (FWL) in a Suburban Region with Foliage and Terrain Blockages. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2002, 1, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H. Temporal Variations Investigation over a Forested Channel in VHF and UHF Hands. In Proceedings of the 2006 7th International Symposium on Antennas, Propagation & EM Theory, Guilin, China, 26–29 October 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Phaiboon, S.; Somkuarnpanit, S. Mobile Path Loss Characteristics for Low Base Station Antenna Height in Different Forest Densities. In Proceedings of the 2006 1st International Symposium on Wireless Pervasive Computing, Phuket, Thailand, 16–18 January 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, M.H.C.; Rotava, A.; Andrade, F.G.; Alem, R.A.; Melo, M.A.K.; Santos, J.C.A. Path Loss Measurements of HF/VHF Land Links in a Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest Urban Site. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2011, 10, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, P.; Sharma, R.P.; Tripathi, S.; Kumar, C.; Ramesh, D. 2.4 GHz RF Received Signal Strength Based Node Separation in WSN Monitoring Infrastructure for Millet and Rice Vegetation. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 18298–18306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Yao, Y.; Han, X.; He, X. Measurement, Data Analysis and Modeling of Electromagnetic Wave Propagation Gain in a Typical Vegetation Environment. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Ng, B.C. Investigation of Rainfall Effect on Forested Radio Wave Propagation. IEEE Antennas Wirel. Propag. Lett. 2008, 7, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Regional Description | Ground Quality | Conductivity σ (S/m) | Regional Description Ea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban, Industrial Areas | Very Poor | 0.001 | 5 |
| Sandy, Dry, Flat, Coastal Areas | Poor | 0.002 | 10 |
| Rocky Soil, Steep Hills, Typical Mountains | Poor | 0.002 | 13 |
| Pastoral, Mid-Hills, Plantations, Heavy Clay | Good | 0.005 | 13 |
| Pastoral Idyll, Low Hills, Fertile Soil | Very Good | 0.0303 | 20 |
| Saltwater | Very Good | 5.0 | 81 |
| Model | Empirical Formula | Frequency Band | Data |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. A. Weissberger [47] | LF MF HF VHF UHF | 1982 | |
| ITU-R [50] | VHF UHF SHF | 1986 | |
| R. K. Tewari [46] | UHF | 1990 | |
| COST235 [58] | VHF UHF SHF | 1995 | |
| FITU-R [59] | VHF UHF SHF | 1998 | |
| J. Goldman [48] | VHF UHF | 1999 | |
| Z. Kovacs [49] | VHF UHF | 1999 | |
| H. Chen [40] | UHF | 2001 | |
| N. Blaunstein [41] | VHF UHF | 2003 |
| Model | Empirical Formula | Frequency Band | Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meng [22] | VHF UHF | 2009 | |
| C. Oestges [56] | UHF | 2009 | |
| LITU [32] | VHF | 2009 | |
| M. Bitirgan+Friis [51] | UHF | 2011 | |
| J. A. R. Azevedo [60] | UHF | 2011 | |
| C. R. Anderson [52] | UHF SHF | 2013 | |
| J. A. Azevedo [66] | UHF | 2015 | |
| J. A. Azevedo [53] | SHF UHF | 2016 | |
| ITU-R P.833-9 [55] | VHF UHF SHF | 2016 | |
| ITU-RP.833-9 MA [55] | VHF UHF SHF | 2016 | |
| NZG [55] | VHF UHF SHF | 2016 | |
| Y. Ibdah [54] | UHF | 2017 | |
| J. Hejselbaek [29] | UHF | 2018 | |
| J. R. Hampton [9] | UHF | 2019 | |
| B. Myagmardulam [27] | UHF | 2021 | |
| ITU-R P.2108 [69] | VHF UHF SHF | 2021 | |
| ITU-R P.833-10 [70] | VHF UHF SHF | 2021 |
| Name | Frequency Range | Terrain | Citations | Reported Loss/Attenuation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herbstreit | VHF | Jungle | [23] | Up to 100 dB, especially in areas with dense jungle vegetation |
| Weissberger | Various | Jungle | [47] | Loss values ranging from 10–60 dB, depending on frequency and forest density |
| Tewari | VHF | Jungle | [46] | 60–70 dB in dense rainforest conditions, with significant variations based on foliage density |
| Gans | VHF/UHF | Mountain forest | [89] | 30–50 dB, with higher losses in more rugged terrains |
| Meng | 40 MHz to 1400 MHz | Jungle | [90] | 100–120 dB for different frequencies, with higher losses at higher frequencies |
| Phaiboon | 1.8 GHz | Suburban forest | [91] | 50–60 dB with higher losses in denser tree environments |
| Meng | Near-ground, 40 MHz to 2.4 GHz | rainforest | [32] | 50–80 dB, with lower frequencies showing better penetration |
| Olufemi | UHF Band | Jungle | [36] | Up to 20 dB higher loss in the wet season compared to the dry season |
| Ibdah | VHF/UHF | Suburban forest | [54] | Losses around 30–40 dB for low-height antennas in denser forests |
| Dias | 25, 60, 81 MHz | rainforest | [92] | 50–120 dB depending on frequency; mean error: ≤3.0 dB. Standard deviation: ≤4.3 dB |
| Pal | 2.4 GHz | Farm | [93] | 40–50 dB depending on tree density and foliage conditions |
| Zhang | 200 to 2600 (MHz) | Suburban forest | [94] | Shadow fading std dev: 4.8–10.1 dB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Li, W.; Han, D.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Bai, X.; Xu, D. Wireless Wave Attenuation in Forests: An Overview of Models. Forests 2024, 15, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091587
Ma Y, Li W, Han D, He Y, Li Q, Bai X, Xu D. Wireless Wave Attenuation in Forests: An Overview of Models. Forests. 2024; 15(9):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091587
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuewei, Wenbin Li, Dongtao Han, Yuan He, Qingsong Li, Xiaopeng Bai, and Daochun Xu. 2024. "Wireless Wave Attenuation in Forests: An Overview of Models" Forests 15, no. 9: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091587
APA StyleMa, Y., Li, W., Han, D., He, Y., Li, Q., Bai, X., & Xu, D. (2024). Wireless Wave Attenuation in Forests: An Overview of Models. Forests, 15(9), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15091587






