Increased Soil Moisture in the Wet Season Alleviates the Negative Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forest
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Measurement of Indicators
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
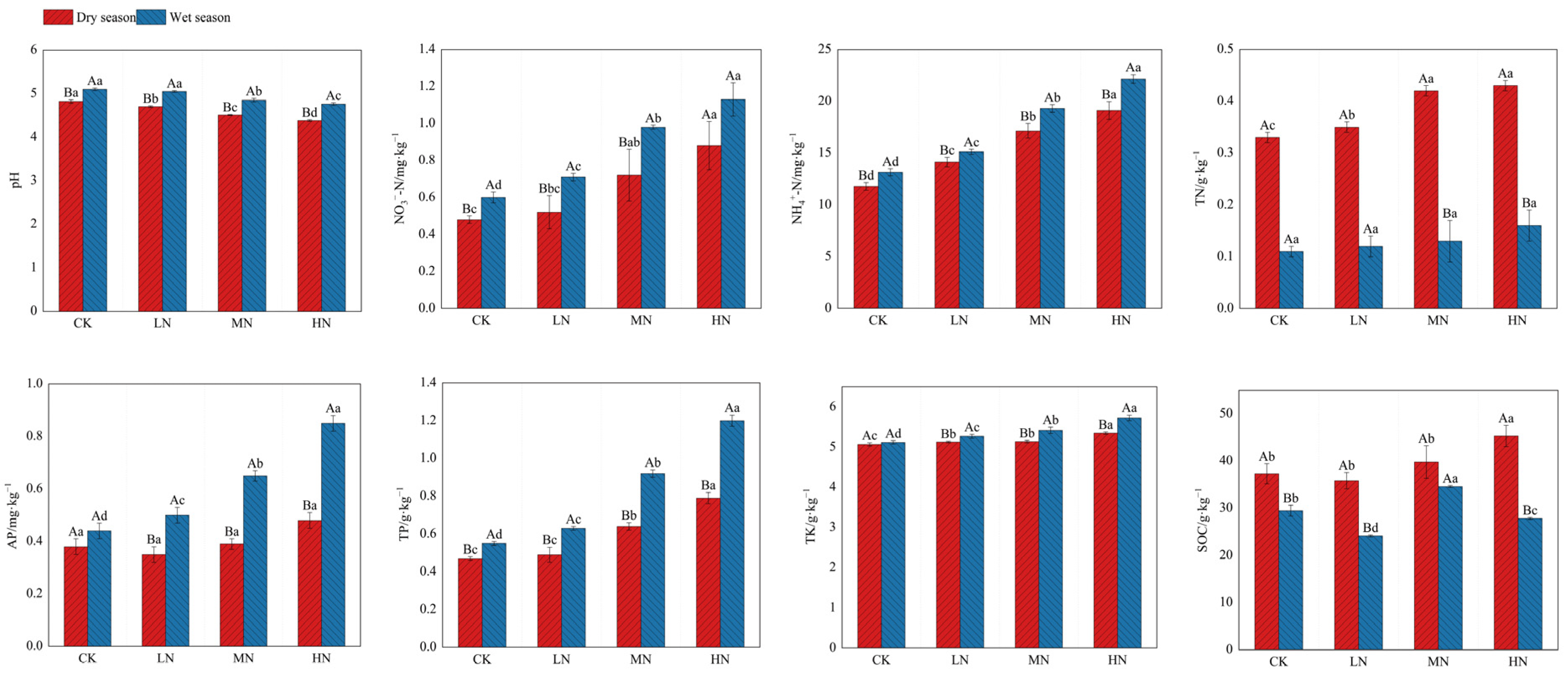
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties under N Deposition
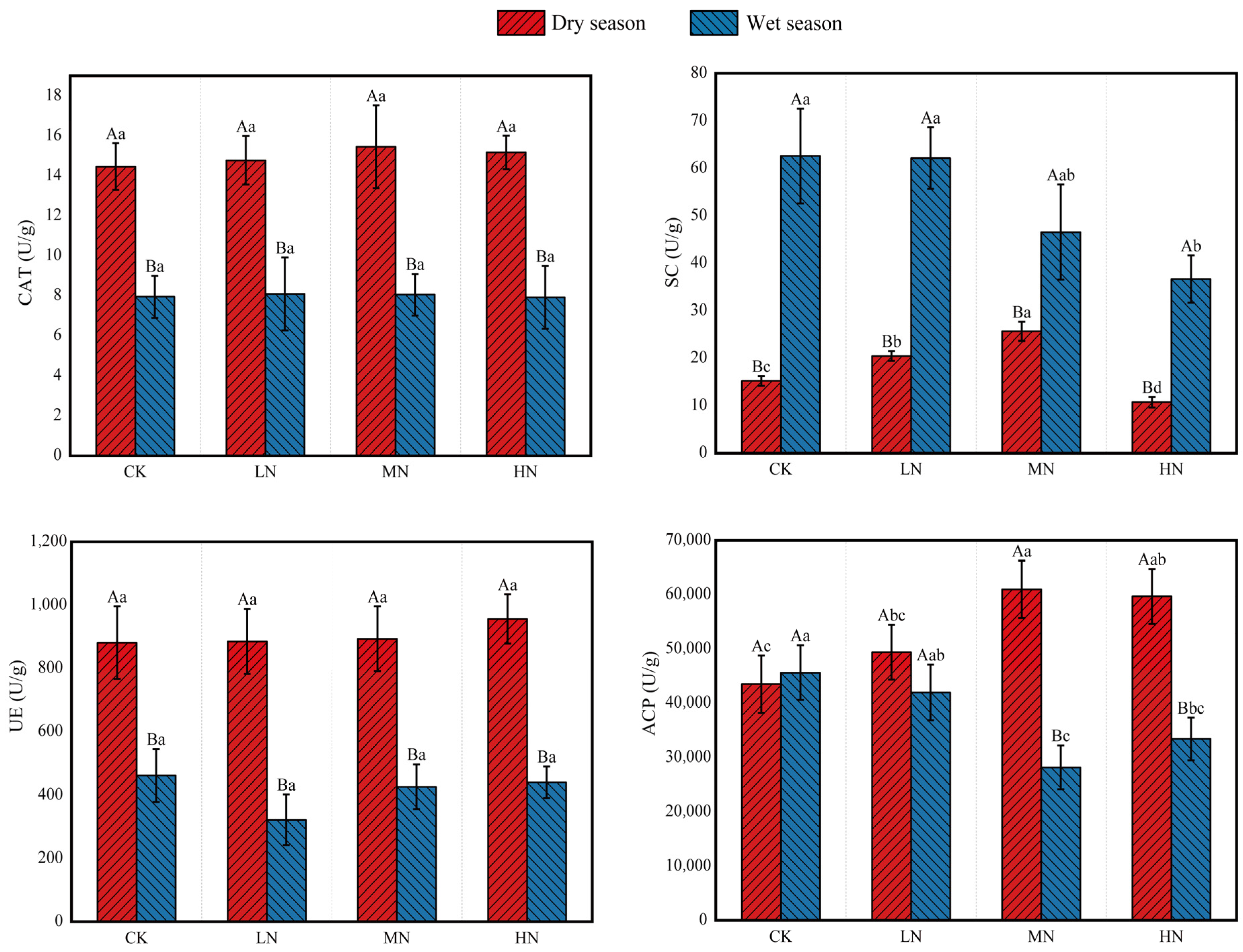
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activities under N Deposition
3.3. Soil Microbial Community Structure under N Deposition
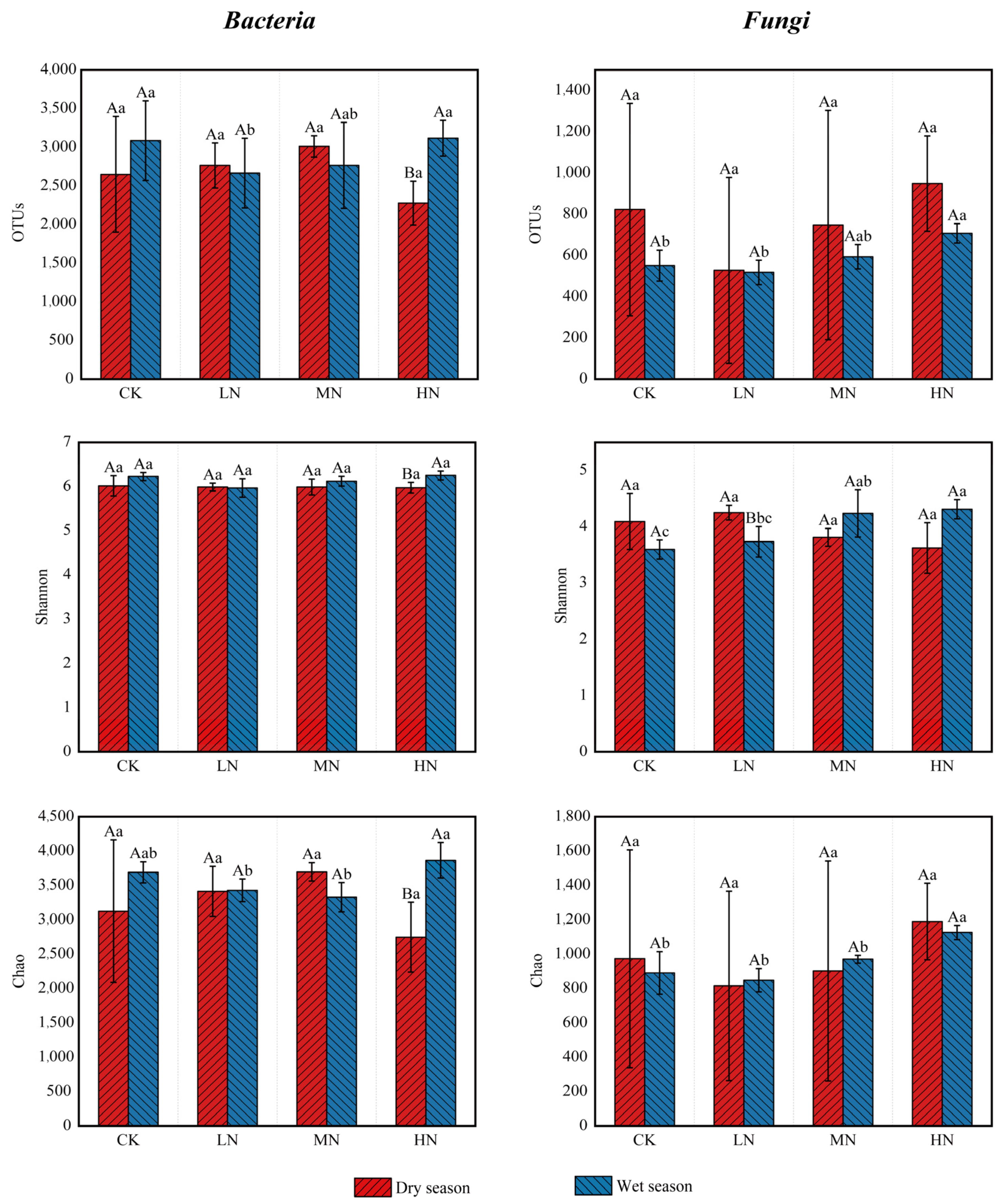
3.3.1. Soil Microbial α-Diversity
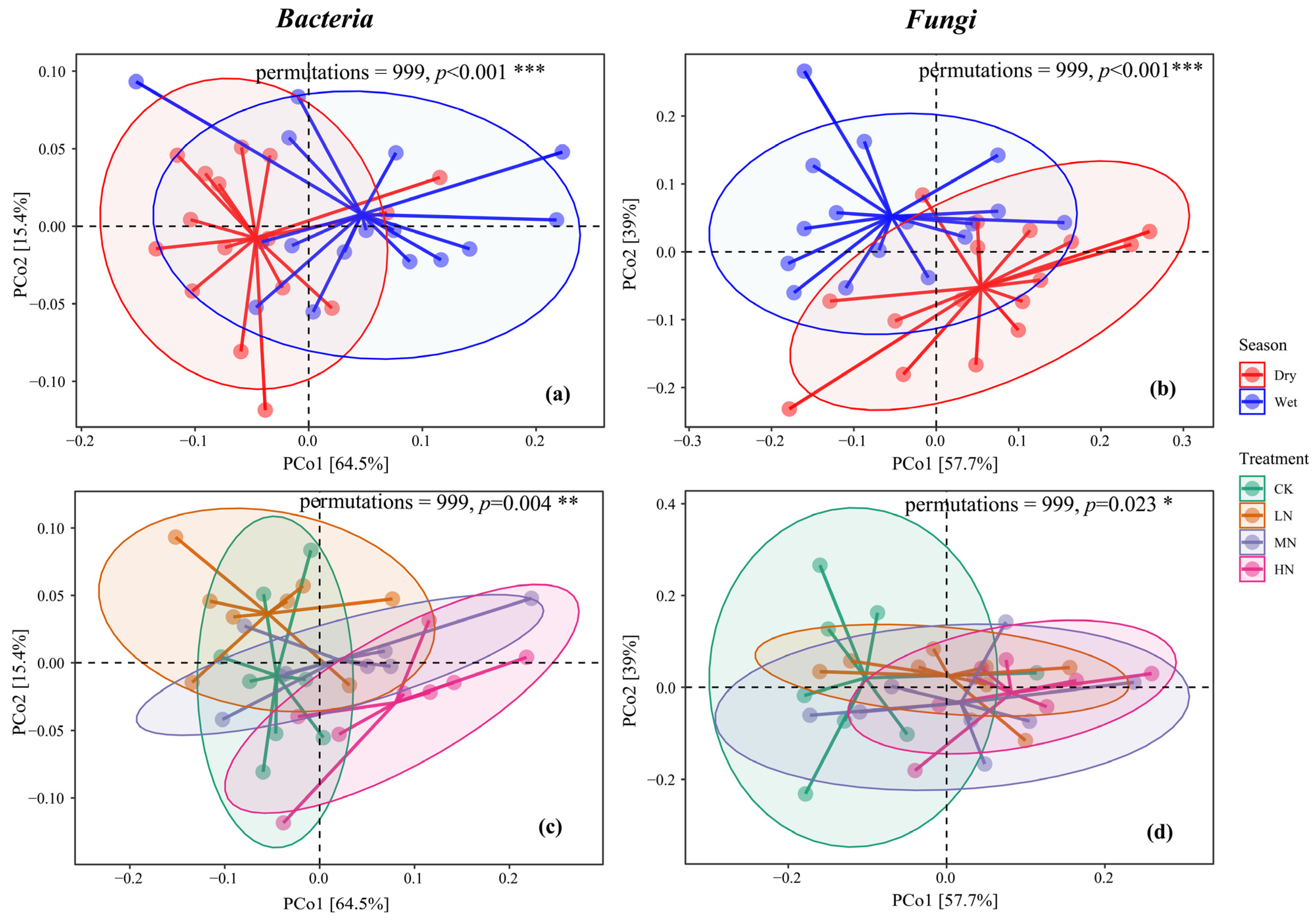
3.3.2. Soil Microbial β-Diversity
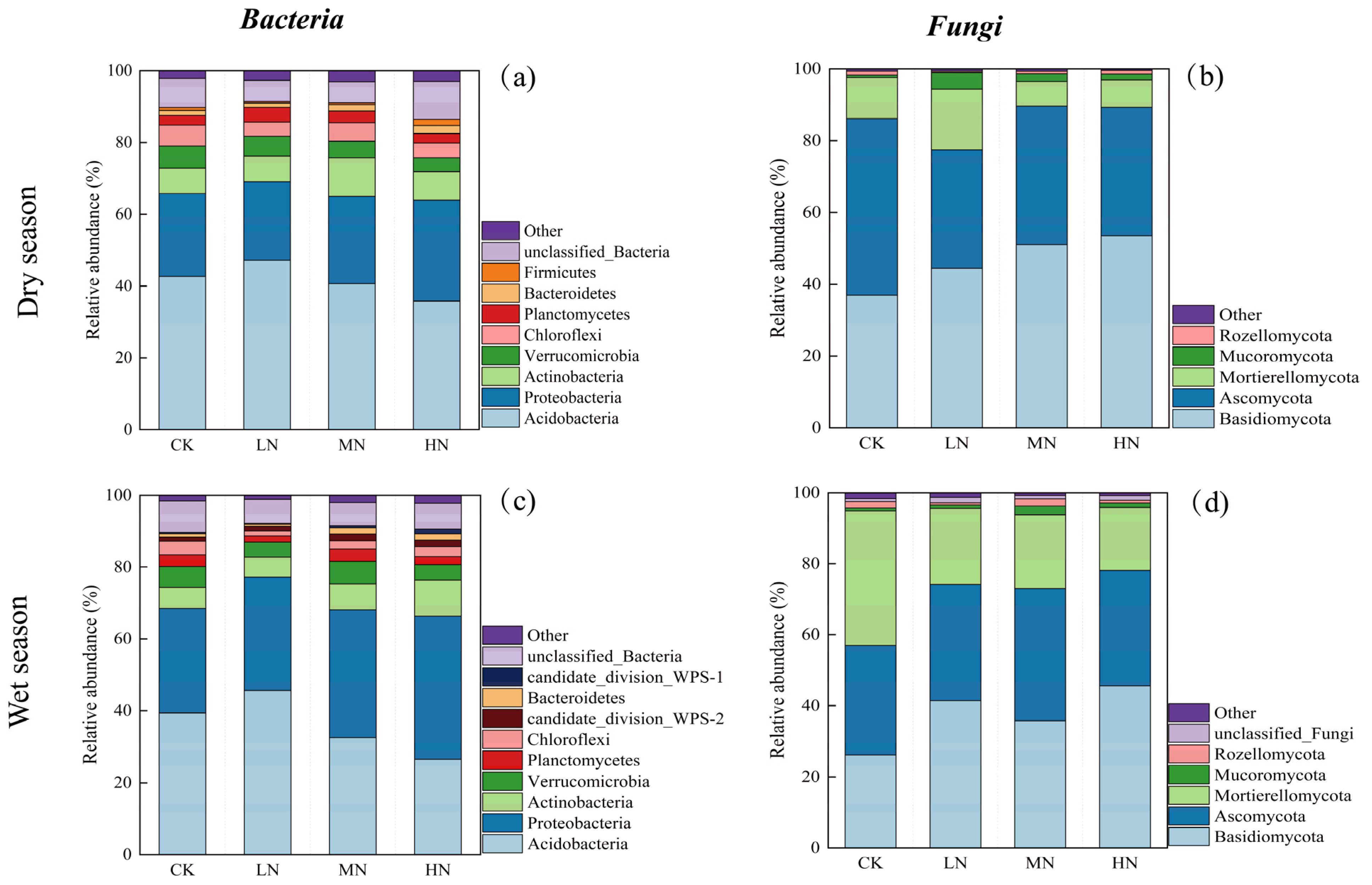
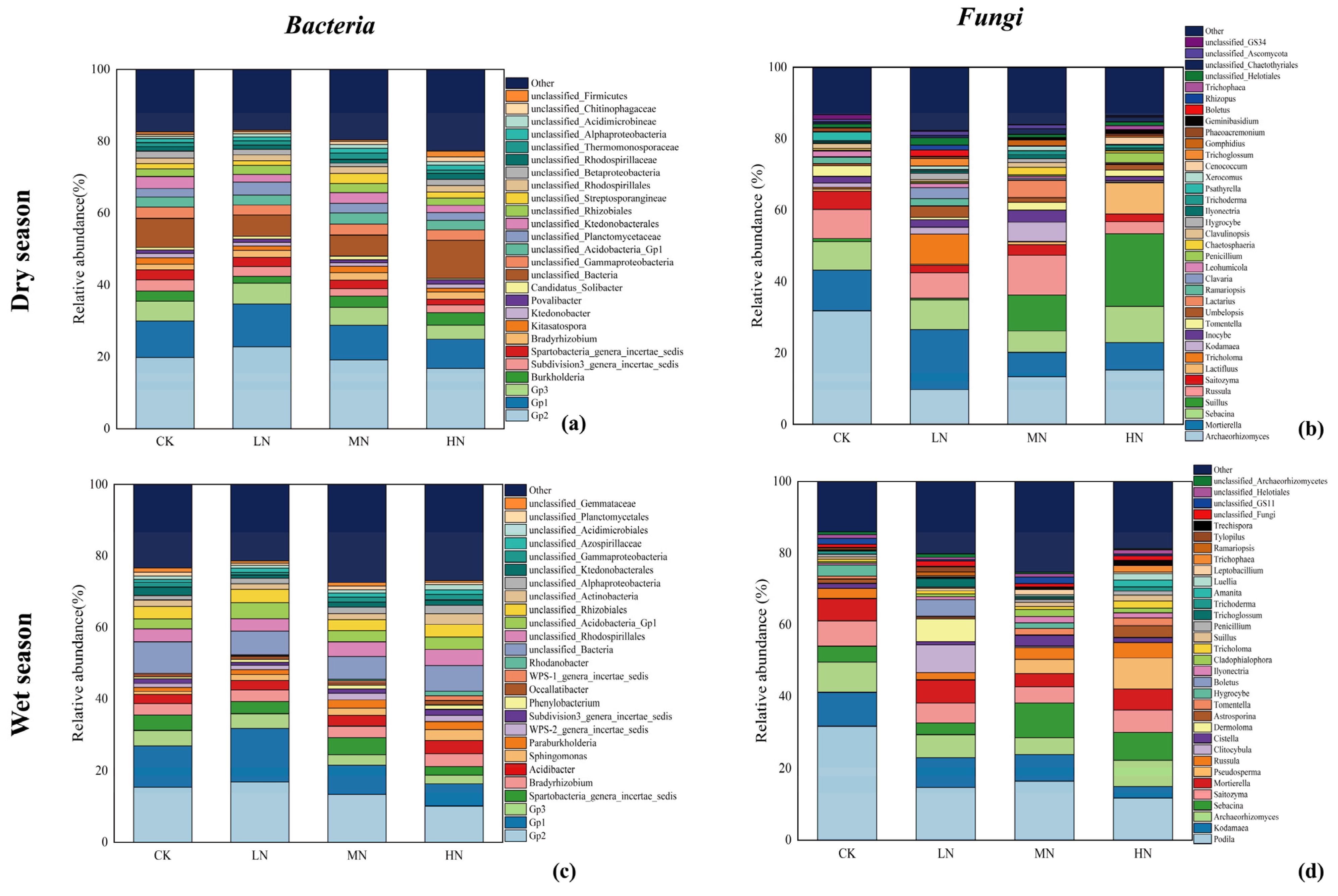
3.4. Soil Microbial Community Composition
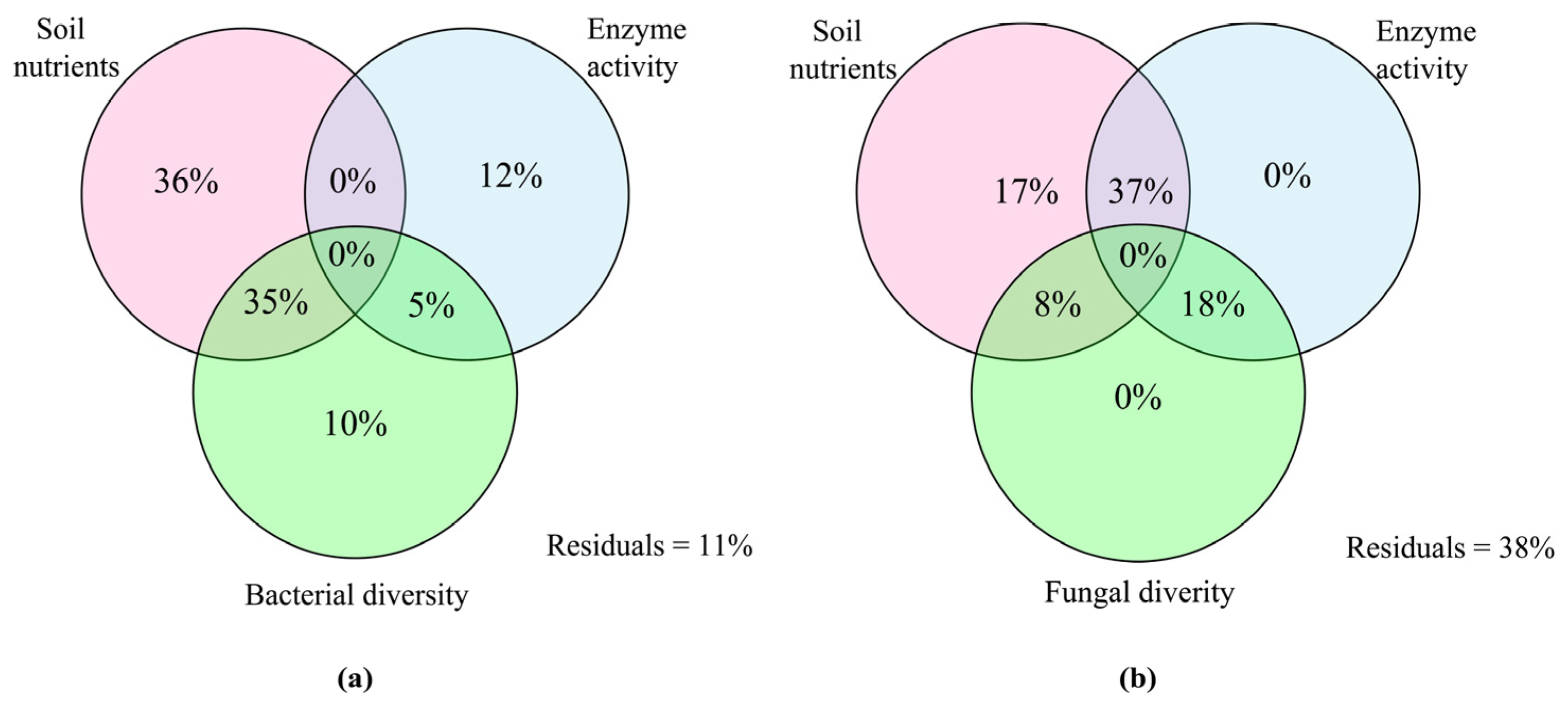
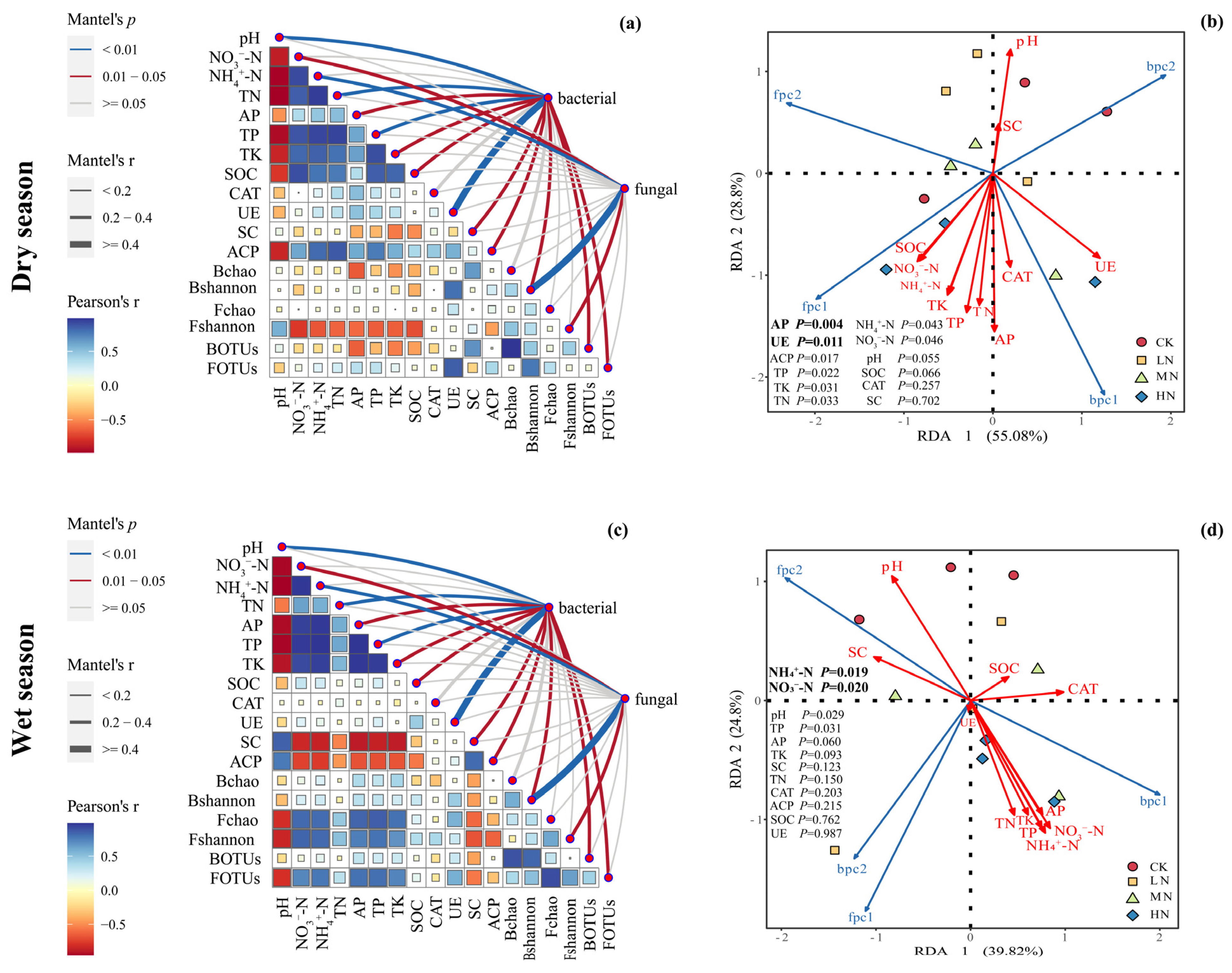
3.5. Correlation between Microbial Community Structure and Soil Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of N Deposition on Soil Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activities
4.2. Effects of N Deposition on the Structure and Composition of Soil Microbial Communities
4.3. Correlation of Soil Microbial Communities with Environmental Factors
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.; Luo, T.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Z.Y. Research advances in nitrogen deposition effects on microbial processes involved in soil nitrogen cycling in tropical and subtropical forests. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 8528–8538. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J. Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, S.; Shi, Y.; Groffman, P.M.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Zhu, Y.-G. Centennial-scale analysis of the creation and fate of reactive nitrogen in China (1910–2010). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA. 2013, 110, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.-N.; Yang, D.-X.; Duan, L. Response of Forest Ecosystems to Decreasing Atmospheric Nitrogen Deposition. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2023, 44, 2681–2693. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lü, X.-T.; Li, M.-H.; Wu, T.; Jin, G. N limitation increases along a temperate forest succession: Evidences from leaf stoichiometry and nutrient resorption. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 15, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Tian, P.; Wang, Q. Forest conversion induces seasonal variation in microbial β-diversity. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Jia, Y.; He, N.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Piao, S.; Liu, X.; He, H.; Guo, X. Stabilization of atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China over the past decade. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 424–429. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, J.; Djukic, I.; Bloem, J.; Lehtinen, T.; Hemerik, L.; De Ruiter, P.; Lair, G. Effects of land use on soil microbial biomass, activity and community structure at different soil depths in the Danube floodplain. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 79, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Meena, M.; Yadav, G.; Sonigra, P.; Nagda, A.; Mehta, T.; Swapnil, P.; Harish; Marwal, A.; Kumar, S. Multifarious responses of forest soil microbial community toward climate change. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 49–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Nie, C.; Liu, Y.; Du, W.; He, P. Soil microbial community composition closely associates with specific enzyme activities and soil carbon chemistry in a long-term nitrogen fertilized grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 264–274. [Google Scholar]
- Erdel, E.; Şimşek, U.; Kesimci, T.G. Effects of fungi on soil organic carbon and soil enzyme activity under agricultural and pasture land of Eastern Türkiye. Sustainability 2023, 15, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.A.; Scelza, R.; Acevedo, F.; Diez, M.; Gianfreda, L. Enzymes as useful tools for environmental purposes. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Y.; Duan, H.; Chen, B.; Wei, X.; Fan, H. Long-term nitrogen addition changes soil microbial community and litter decomposition rate in a subtropical forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Lin, K.; Xu, J.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zeng, Q. Nutrient availability is a dominant predictor of soil bacterial and fungal community composition after nitrogen addition in subtropical acidic forests. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246263. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.; Zheng, C.; Suter, H.; Huang, Z. Different responses of soil bacterial and fungal communities to nitrogen deposition in a subtropical forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y. Meta-analysis of the impacts of global change factors on soil microbial diversity and functionality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3072. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Song, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Zhu, D.; Zhao, J.; Fu, S. Chronic enhanced nitrogen deposition and elevated precipitation jointly benefit soil microbial community in a temperate forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 193, 109397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Long, Z.; Ding, L.; Zhang, W.; Tang, H.; Liu, J. Research progress of soil microorganism application based on high-throughput sequencing technology. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; Volume 692, p. 042059. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Long, Y.; Li, H.; Da, W.; Hu, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, X.; Kong, W. Microbial diversity in saline alkali soil from Hexi Corridor analyzed by Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing system. Microbiol. China 2017, 44, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, Q.; Cui, J.; Zhou, F.; Du, K.; Zhang, L.; Fu, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Shi, G.; Gao, M. Wet-only deposition of atmospheric inorganic nitrogen and associated isotopic characteristics in a typical mountain area, southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Liang, Z.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Y. Differential Responses of Bacterial and Fungal Community Structure in Soil to Nitrogen Deposition in Two Planted Forests in Southwest China in Relation to pH. Forests 2024, 15, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Gui-Sen, Y.; Zhi-Shan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Ya-Fei, S.; Rui, H.U. Litter decomposition and its effects on soil microbial community in Shapotou area, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 1810–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Gui-Yao, L.; Li-Li, C.; Zhi-You, Y. Effects of nitrogen addition on the structure of rhizosphere microbial community in Pinus tabuliformis plantations on Loess Plateau, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Guan-Tao, C.; Yong, P.; Jun, Z.; Shun, L.I.; Li-Hua, T. Effects of short-term nitrogen addition on fine root biomass, lifespan and morphology of Castanopsis platyacantha in a subtropical secondary evergreen broad-leaved forest. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Britton, A.J.; Helliwell, R.C.; Fisher, J.M.; Gibbs, S. Interactive effects of nitrogen deposition and fire on plant and soil chemistry in an alpine heathland. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, A.; Sarma, S. The impact of carbon and nitrogen catabolite repression in microorganisms. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 251, 126831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Sun, Q.-Y.; Mao, B.; Zeng, D.-H. Understory vegetation interacts with nitrogen addition to affect soil phosphorus transformations in a nutrient-poor Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 507, 120026. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, P.; Xiao, H.; Yuxin, W.; Chen, J. Changes in the soil microbial communities of alpine steppe at Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under different degradation levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Yang, J.; Sang, C.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Jiang, P.; Wang, C.; Bai, E. Phosphorus reduces negative effects of nitrogen addition on soil microbial communities and functions. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuscu, I.K.; Cetin, M.; Yigit, N.; Savaci, G.; Sevik, H. Relationship between Enzyme Activity (Urease-Catalase) and Nutrient Element in Soil Use. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2018, 27, 2107–2112. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, C.; Nevison, G.B.; Hughes, S.; Reynolds, B.; Hudson, J. Enzymic involvement in the biogeochemical responses of a Welsh peatland to a rainfall enhancement manipulation. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1998, 27, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Xing, Y.; Yan, G.; Liu, G.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q. Long-Term Nitrogen Addition Could Modify Degradation of Soil Organic Matter through Changes in Soil Enzymatic Activity in a Natural Secondary Forest. Forests 2023, 14, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Xue, S.; Wang, G. Soil bacterial community dynamics reflect changes in plant community and soil properties during the secondary succession of abandoned farmland in the Loess Plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 40–49. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, S.D.; Hanson, C.A.; Treseder, K.K. Nitrogen fertilization reduces diversity and alters community structure of active fungi in boreal ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Mori, T.; Mao, Q.; Zhou, K.; Zhou, G.; Nie, Y.; Mo, J. Responses of soil microbial community to continuous experimental nitrogen additions for 13 years in a nitrogen-rich tropical forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Drabek, O.; Boruvka, L.; Mladkova, L.; Kocarek, M. Possible method of aluminium speciation in forest soils. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 97, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Z.; Hashidoko, Y.; Shen, W. Ammonium nitrogen content is a dominant predictor of bacterial community composition in an acidic forest soil with exogenous nitrogen enrichment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Demoling, F.; Nilsson, L.O.; Bååth, E. Bacterial and fungal response to nitrogen fertilization in three coniferous forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 370–379. [Google Scholar]
- Fierer, N.; Leff, J.W.; Adams, B.J.; Nielsen, U.N.; Bates, S.T.; Lauber, C.L.; Owens, S.; Gilbert, J.A.; Wall, D.H.; Caporaso, J.G. Cross-biome metagenomic analyses of soil microbial communities and their functional attributes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21390–21395. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, D.B.; Kennedy, N.M.; Clipson, N.; Melville, K.; Gadd, G.M.; McDermott, F.P. Characterization of bacterial community structure on a weathered pegmatitic granite. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 51, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jumpponen, A. Soil fungal community assembly in a primary successional glacier forefront ecosystem as inferred from rDNA sequence analyses. New Phytol. 2003, 158, 569–578. [Google Scholar]
- Morrison, E.W.; Frey, S.D.; Sadowsky, J.J.; van Diepen, L.T.; Thomas, W.K.; Pringle, A. Chronic nitrogen additions fundamentally restructure the soil fungal community in a temperate forest. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 23, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, C.F.; Vilgalys, R.; Kuske, C.R. Changes in fungal community composition in response to elevated atmospheric CO2 and nitrogen fertilization varies with soil horizon. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 78. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, S.J.; Matson, P.A. Nutrient status of tropical rain forests influences soil N dynamics after N additions. Ecol. Monogr. 2003, 73, 107–129. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Hu, H.-W.; Wang, J.; He, J.-Z.; Zheng, C.; Wan, X.; Huang, Z. Niche separation of comammox Nitrospira and canonical ammonia oxidizers in an acidic subtropical forest soil under long-term nitrogen deposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 126, 114–122. [Google Scholar]
- Högberg, M.N.; Högberg, P.; Myrold, D.D. Is microbial community composition in boreal forest soils determined by pH, C-to-N ratio, the trees, or all three? Oecologia 2007, 150, 590–601. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, L.; Lin, Q.; Yuan, M.; Xu, D.; Yu, H.; Hu, Y.; Duan, J.; Li, X.; He, Z. Responses of the functional structure of soil microbial community to livestock grazing in the T ibetan alpine grassland. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 637–648. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, M.; Rui, J.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Bai, Y.; Heděnec, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Pei, K.; Liu, C. Rate-specific responses of prokaryotic diversity and structure to nitrogen deposition in the Leymus chinensis steppe. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 79, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Lladó, S.; López-Mondéjar, R.; Baldrian, P. Forest soil bacteria: Diversity, involvement in ecosystem processes, and response to global change. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00063-16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Guo, Z.; Shen, W.; Ren, L.; Sun, D.; Yao, Q.; Zhu, H. Fungal communities are more sensitive to the simulated environmental changes than bacterial communities in a subtropical forest: The single and interactive effects of nitrogen addition and precipitation seasonality change. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Marshall, R.; Lag-Brotons, A.J.; Semple, K.T.; Stutter, M. Phosphorus solubility changes following additions of bioenergy wastes to an agricultural soil: Implications for crop availability and environmental mobility. Geoderma 2021, 401, 115150. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, C.; Wu, M.; Li, Z. Shifts in bacterial and fungal diversity in a paddy soil faced with phosphorus surplus. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 259–267. [Google Scholar]

| Stand | Altitude/m | Age/a | H/m | DBH/cm | Canopy Density | Slope/(o) | Aspect | Soil Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2130 | 17 | 9.6 | 14.5 | 0.87 | 23 | NE | Argi-udic Ferrosols |
| 2 | 2132 | 15 | 12.1 | 20.7 | 0.90 | 28 | NE | Argi-udic Ferrosols |
| 3 | 2133 | 17 | 10.8 | 18.3 | 0.85 | 30 | NE | Argi-udic Ferrosols |
| Abbreviation | Full Name | Unit | Abbreviation | Full Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Control | 0 g·N·m−2·a−1 | OTUs | Operational taxonomic units |
| LN | Low nitrogen | 10 g·N·m−2·a−1 | Chao | Chao 1 index |
| MN | Medium nitrogen | 20 g·N·m−2·a−1 | Shannon | Shannon index |
| HN | High nitrogen | 25 g·N·m−2·a−1 | BOTUs | Number of bacterial OUT items |
| pH | Acidity and alkalinity | FOTUs | Number of fungal OUT items | |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon | g·kg−1 | Bchao | Bacterial chao1 index |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate nitrogen | mg·kg−1 | Fchao | Fungal chao1 index |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen | mg·kg−1 | Bshannon | Bacterial Shannon index |
| TN | Total nitrogen | g·kg−1 | Fshannon | Fungal Shannon index |
| TK | Total potassium | g·kg−1 | bpc1 | Bacterial community |
| AP | Available phosphorus | mg·kg−1 | bpc2 | Bacterial community |
| TP | Total phosphorus | g·kg−1 | fpc1 | Fungi community |
| CAT | Catalase | U/g | fpc2 | Fungi community |
| SC | Sucrase | U/g | EBLFs | Evergreen broad-leaved forests |
| UE | Urease | U/g | SMCs | Soil microbial communities |
| ACP | Acid phosphatase | U/g |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Wang, K.; Song, Y. Increased Soil Moisture in the Wet Season Alleviates the Negative Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forest. Forests 2024, 15, 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081473
Chen W, Hou Z, Zhang D, Chen L, Wang K, Song Y. Increased Soil Moisture in the Wet Season Alleviates the Negative Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forest. Forests. 2024; 15(8):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081473
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wen, Zheng Hou, Donghui Zhang, Leixi Chen, Keqin Wang, and Yali Song. 2024. "Increased Soil Moisture in the Wet Season Alleviates the Negative Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forest" Forests 15, no. 8: 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081473
APA StyleChen, W., Hou, Z., Zhang, D., Chen, L., Wang, K., & Song, Y. (2024). Increased Soil Moisture in the Wet Season Alleviates the Negative Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Microbial Communities in Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forest. Forests, 15(8), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15081473






