Abstract
Timely and accurate information on tree species is of great importance for the sustainable management of natural resources, forest inventory, biodiversity detection, and carbon stock calculation. The advancement of remote sensing technology and artificial intelligence has facilitated the acquisition and analysis of remote sensing data, resulting in more precise and effective classification of tree species. A review of the remote sensing data and deep learning tree species classification methods is lacking in its analysis of unimodal and multimodal remote sensing data and classification methods in this field. To address this gap, we search for major trends in remote sensing data and tree species classification methods, provide a detailed overview of classic deep learning-based methods for tree species classification, and discuss some limitations of tree species classification.
1. Introduction and Review Approach
1.1. Significance of Tree Species Information
Timely and accurate information on the spatial distribution of tree species (TS) has immeasurable value. In forest management, information on TS classification is required for forest inventory [1], biodiversity assessment and monitoring [2], invasive species monitoring [3], and forest sustainable management. In ecology, large-scale spatial information on tree species improves the understanding of the ecology of tree species [4,5]. In the environmental field, tree species information facilitates the estimation of wildlife habitat [6] and forest insect abundance [7,8].
In recent decades, remote sensing technology has made great progress in spatial and spectral resolution, and a variety of remote sensing data has made it possible to classify TS. The interest of practitioners in remote sensing-derived tree species information is reflected in the survey conducted by Felbermeier et al. [9]. They analyzed 347 questionnaires sent to professionals working in the forestry sector. Two-thirds of the interviewees reported deficiencies in forest information, and 90% of them expected improvements through the application of remote sensing. When asked which parameters should be addressed by remote sensing applications, tree species were ranked first out of 63 parameters [10]. Additionally, in the sustainable management of urban trees, remote sensing methods have been an effective alternative to field surveys [11].
1.2. Objectives
This review of tree species classification includes species groups, dominant species, stands, and individual trees, but does not include forest type. The main objectives of this review on TS classification are as follows:
- Analysis of the literature on the classification of tree species by remote sensing in the past 25 years and quantifying general trends.
- A statistical analysis of the unimodal and multimodal remote sensing data in TS classification is conducted by reading and analyzing each paper. Subsequently, the remote sensing data trends are studied.
- Provide a detailed overview of the classic deep learning-based methods that solely utilize convolutional neural networks (CNN) for classifying tree species.
- Identification of research gaps in TS classification and description of future trends in TS classification using remote sensing data.
1.3. Review Approach
In this review, we browsed the literature from Web of Science (WOS) Core Collection and Google Scholar databases for the last 35 years, in the period of January 1988–June 2023, using the following keywords: remote sensing OR LiDAR OR UAV OR tree species OR clsssifi* OR map* OR indenti* OR discriminat* OR detect*. Given the fact that there were fewer qualified papers published in 1988–1998, this review is focused on papers published after 1998, especially after 2013. The studies that were found to satisfy the above conditional search were then further filtered based on the following criteria:
- TS classification objects must be group tree species OR main tree species OR dominant tree species OR stand tree species OR individual tree.
- The research must report on the corresponding specific remote sensing data.
- The research must report the tree species classification methods.
- The research must report the assessment of the classification result.
A total of 300 papers met the review criteria for this study. Each paper was read and analyzed manually. The methods and data with the highest classification accuracy were recorded and subsequently summarized and analyzed for general trends. Additionally, classic deep learning-based methods for TS classification methods were recorded and analyzed with summary statistics.
The remainder of the study is organized as follows: Section 2 analyzes the literature on TS classification by remote sensing in the past 25 years and the quantification of general trends. Section 3 provides a detailed overview of classic deep learning-based methods for tree species classification. Limitations and future work in TS classification are discussed in Section 4, and in Section 5 conclusions are drawn.
2. Trends in Tree Species Classification
2.1. Remote Sensing Data for TS Classification
The four primary categories of remote sensing data utilized for the TS classification include passive optical remote sensing data, active remote sensing data, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) data, and auxiliary data. Passive optical remote sensing data offer a valuable means of distinguishing between tree species by measuring the spectral response of directional electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun and reflected by the canopy (and other surfaces) in sensor-specific wavelength regions [10]. Active remote sensing sensors emit energy pulses and record the return time and amplitude to derive information about the TS structure. Fassnacht et al. [10] and Ruiliang Pu [12] provide a detailed overview of the four primary categories of remote sensing data. This article offers only a cursory overview of the remote sensing data for TS classification. Passive optical data encompass multispectral images (MSIs), very high spatial resolution (VHR) images, and hyperspectral images (HSIs). Active data include light detection and ranging (LiDAR) and synthetic aperture radar (SAR). The primary UAV data are LiDAR [13,14,15], HIS [16,17], MSI [7,18], and the red, green, and blue image (RGB) [19,20,21,22]. Auxiliary data encompass a range of variables, including elevation, slope, slope direction, temperature, and precipitation.
Passive optical remote sensing measures the spectral response of the tree canopy to provide useful information for TS classification [23,24]. This information can be obtained from the moderate spatial resolution satellite MSI sensors, including Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), Landsat-5 TM, Landsat-7 ETM+, Landsat-8 OLI/TIRS, Landsat-9 OLI-2/TIRS-2, Sentinel-2A MSI, Compact Airborne Spectrographic Imager (CASI), Advanced Himawari Imager (AHI), and Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre High-Resolution Visible (SPOT) series [25,26,27,28,29]. It is not possible to achieve individual TS classification using single sensor data at such resolutions, and MSI sensors achieve TS classification by coupling with other sensor data. MSI sensors have an auxiliary role in the improvement of individual TS classification accuracy [12]. Since 2000, data from VHR commercial satellite sensors have had the potential to create digital base maps [30]. Furthermore, images acquired by VHR sensors have enabled the successful classification of tree species [31,32,33,34,35]. Typical VHR satellite sensors include GeoEye-1, Gaofen-2, IKONOS, Quickbird, Plé-aides, RapidEye, and WorldView-2/3/4 (WV2/3/4). The most common HSI sensors used for TS classification include airborne sensors (AVIRIS, CASI, HYDICE, and HyMAP) and satellite sensors (Hyperion, Gaofen-5, and CHRIS). The researchers used the subtle spectral information of HSI to successfully classify tree species. Due to the small number of satellite HSI sensors in operation, only a few satellite HSI sensor data are currently available to classify TS [36], of which airborne HSI data are more useful and important for the classification of tree species [37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44].
Active remote sensing LiDAR data measure the reflected energy from the target surface and record features of the reflected spectrum, such as amplitude, frequency, and phase, which allows for the extraction of tree structural parameters and vertical structural properties [45]. LiDAR sensors calculate parameters such as tree height, forest density, and leaf area index at the single wood and stand level from the recorded intensities [46,47,48], which are mainly determined by the structural morphology of the tree foliage, so there are differences in the parameters of different tree species, so LiDAR-derived information allows for the classification of tree species [49,50,51,52,53]. But TS classification accuracy is limited. LiDAR data are usually combined with passive optical remote sensing data [14,15,18,54,55,56], and it has been shown that the combination of LiDAR data and passive optical remote sensing data for TS classification can significantly improve accuracy [46,57], because passive optical remote sensing data provide rich spectral, spatial, and textural information of tree species, and LiDAR data provide a vertical profile and structural information, which form a useful complement to each other and can more comprehensively describe the characteristics of tree species and achieve better classification results. SAR is primarily used to classify forest types because forest information by SAR relates mainly to canopy structure and water content [58]. Alberto Udali et al. used the Sentinel-1 C-Band SAR data in southern Sweden to classify TS, and yielded an overall accuracy (OA) of 0.66 [59]. Sasan S. Saatchi and Eric Rignot acquired synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data during the Boreal Ecosystem Atmospheric Study’s intensive field campaigns over the southern study area near Prince Albert, Canada. They employed SAR images to classify the dominant forest types present, including jack pine, black spruce, trembling aspen, clearing, open water, and three categories of mixed strands, achieving a classification accuracy of greater than 90% [60]. Y W Kee et al. employed the L-band ALOS PALSAR-2 dataset and open-source C-band Sentinel-1 SAR datasets to distinguish between oil palm trees and weeds [61].
UAV remote sensing systems are adaptable and can fly freely in unrestricted areas. Additionally, they are affordable, devoid of cloud infrastructure, and capable of obtaining data at a precise temporal, spatial, and spectral level [62,63]. UAV data can be used to accurately classify tree species and even individual trees [22,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72], as different data provide different quantitative features for TS classification. UAV remote sensing systems are limited in the application of large-scale TS classification due to short flight endurance and unstable conditions such as high winds.
Ancillary data are mainly the topographic and meteorological information obtained, such as elevation, slope, slope direction, temperature, and precipitation [73,74]. Shirazinejad employed multi-temporal Sentinel-2 and DEM data to classify ten tree species within the Hyrcanian region of northern Iran. The results demonstrated that the incorporation of DEM data enhanced classification accuracy by 3% in comparison to Sentinel-2 data alone [73]. Qi et al. utilized Landsat data to delineate the distribution of bamboo forests in China. The findings indicated that elevation facilitated the enhancement of the classification accuracy of bamboo forests [74]. Fang et al. employed the Sentinel-2 imagery, SRTM elevation data, and WorldClim bioclimatic data to classify 19 dominant tree species in Yunnan Province. The resulting classification exhibited an OA of 72.03% and a Kappa coefficient of 0.69 [25].
2.2. Literature Trends in Remote Sensing Data
Multimodal remote sensing data are currently considered mainstream due to their availability at low cost, and the emergence of multimodal deep learning methods for image classification. In this paper, to study trends in tree species classification from the perspective of remote sensing data use, we statistically analyze the literature on tree species classification from a data-driven perspective.
Detailed statistical analyses were performed on the 300 papers. The number of studies focusing on TS classification has increased constantly over the past 25 years (in Figure 1), which indicates that TS classification is a hot topic in current research. This growth is closely linked to the development of remote sensing technology and its corresponding computer science and technology. Remote sensing technology has advanced significantly since 2010, particularly for UAV, hyperspectral data, and LiDAR data. Advances in computer science and technology have brought about the evolution of classifiers for TS classification. The employment of high-resolution spatial and spectral remote sensing data, along with sophisticated classification algorithms, has resulted in further facilitation of TS classification research. Figure 1 shows that there is no advantage in tree classification between unimodal and multimodal remote sensing data.
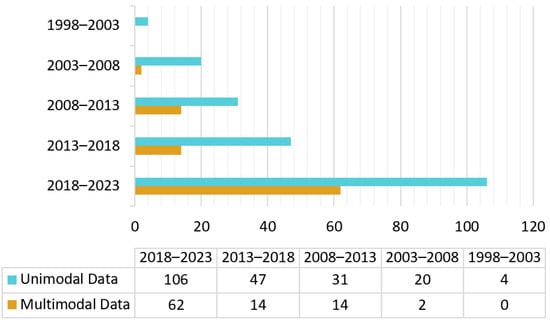
Figure 1.
Number of papers published per five-year interval for unimodal and multimodal data, respectively.
A total of 208 papers were analyzed on the use of unimodal remote sensing data for tree species classification over the last 25 years. Among them, four papers were published from 1 January 1998 to 1 January 2003, three of which used colored infrared aerial photographs and one used MSI. Additionally, a total of 92 papers were analyzed on the use of multimodal remote sensing data for tree species classification over the last 20 years. Multimodal data tree species classification literature before 2003 was not found. Figure 2 shows the number of papers per five-year interval for various modal data.
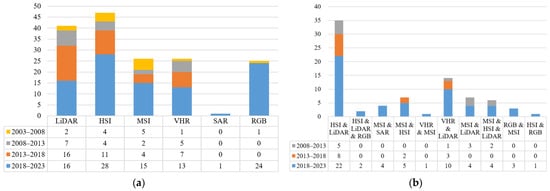
Figure 2.
Number of papers per five-year interval for various modal data. (a) Number of the unimodal data studies. (b) Number of the multimodal data studies.
Focusing on unimodal remote sensing data in Figure 2a, the most used unimodal data are HIS. In the 2 January 2018 and 1 January 2023 time span, the main unimodal data used for tree species classification were HIS (total of 28 cases), and RGB (24 cases). Since 2018, deep learning algorithms have dominated digital image processing. These algorithms rely on RGB images as input data, and the proliferation of drones has made it easier to obtain small-scale RGB images of tree species. Consequently, a vast amount of tree species classification literature on CNN and RGB has emerged within this timeframe. In the 2 January 2013 and 1 January 2018 time span, the main unimodal data were LiDAR (total of 16 cases) and HSI (total of 11 cases). In the 2 January 2008 and 1 January 2013 time span, the main unimodal data were LiDAR (seven cases), HIS (four cases), and VHR (five cases). In the 2 January 2003 and 1 January 2008 time span, the main unimodal data were HSI (four cases) and MSI (five cases). So, the main unimodal data for tree species classification were HSI, LiDAR, RGB, and VHR.
Focusing on multimodal remote sensing data in Figure 2b, regardless of the time frame, the most used multimodal data were HIS and LiDAR; in the 2 January 2018 and 1 January 2023 time span, the main multimodal data used for tree species classification were HIS and LiDAR (total 26 cases), VHR and LiDAR (total 10 cases), and MSI and HSI (total 6 cases). In the 2 January 2013 and 1 January 2018 time span, the main multimodal data were HIS and LiDAR (total nine cases). In the 2 January 2008 and 1 January 2013 time span, the main multimodal data were HIS and LiDAR (total five cases).
2.3. Methods for TS Classification
Firstly, the classification methods and corresponding data with the highest accuracy rate for tree species classification in each paper were recorded. Thereafter, the classification methods and corresponding data for tree species classification were statistically analyzed according to a time period of every five years. Finally, the classification methods and corresponding data for every five years were statistically displayed in a graph.
2.3.1. Classification Methods of Unimodal Remote Sensing Data
A total of 208 papers with unimodal data were statistically analyzed using the classification method that yielded the highest classification accuracy (Figure 3). A total of 13 papers, for which the corresponding unimodal data and classification methods yielded a frequency of 1, were not included in Figure 3. This was due to the fact that they were not statistically significant. In addition to the primary classifier depicted in Figure 3, the remaining 30 papers employed a variety of other classifiers, including logistic regression classifiers, linear discriminant analysis (LDA), maximum likelihood classifiers (MLC), fractal geometry, and quantitative structure models, among others.
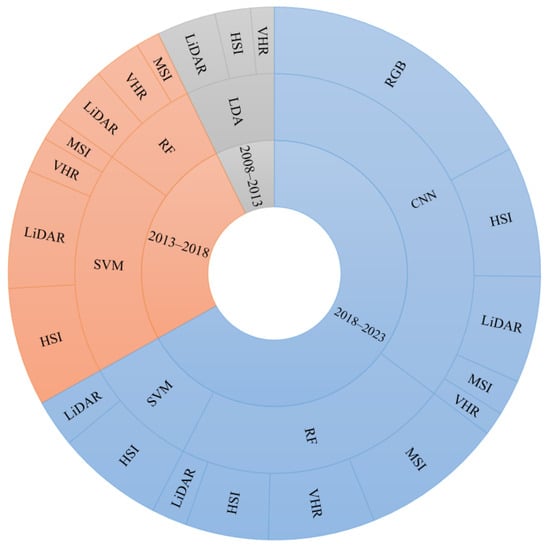
Figure 3.
Frequency of studies about the unimodal remote sensing data and their most efficient classifier per five-year time interval. Abbreviations are HIS = hyperspectral image; VHR = Very high (high) spatial resolution; LiDAR = Light detection and ranging; MSI = Multispectral image; RGB = Red, Green, and Blue image; SAR = synthetic aperture radar; SVM = Support vector machine; RF = Random forest; CNN = convolutional neural network; MLC = maximum likelihood classifiers; LDA = linear discriminant analysis.
Focusing on unimodal remote sensing data and their most efficient classifier in Figure 3, in the 2 January 2018 and 1 January 2023 time span, the main classifiers were CNN, SVM, and RF. In the 2 January 2013 and 1 January 2018 time span, the main classifiers were RF and SVM, In the 2 January 2008 and 1 January 2013 time span, the main classifier used for optimal classification results was LDA. With the development of remote sensing and computer science and technology, the main classification methods of unimodal remote sensing were CNN, RF, and SVM.
2.3.2. Classification Methods of Multimodal Remote Sensing Data
A total of 92 papers with multimodal data were statistically analyzed using the classification method that produced the best results. The literature on tree species classification using multimodal data prior to the year 2003 was not retrieved. Two papers, one using HIS and LiDAR data and nearest neighbor rules classifier and another using MSI and SAR data and Bayes rule classifier were published from 2 January 2003 to 1 January 2008. The statistical analysis results of the multimodal data and the main classifiers from 2 January 2008 to 1 January 2023 are shown in Figure 4. In addition to the main classifier in Figure 4, the remaining 12 papers used other classifiers such as spectrum angle mapper classifiers, nearest neighbor classifiers, and so on.
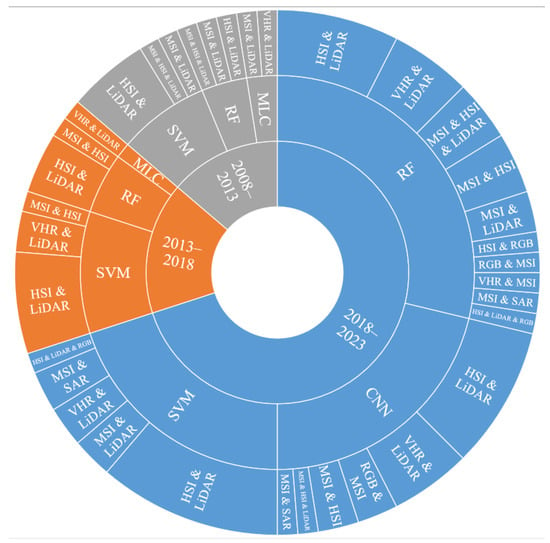
Figure 4.
Frequency of studies about the multimodal remote sensing data and their most efficient classifier per five-year time interval.
Focusing on multimodal remote sensing data and their most efficient classifier in Figure 4, in the 2 January 2018 and 1 January 2023 time span, the main classifiers were CNN, SVM, and RF. In the 2 January 2008 and 1 January 2018 time span, the main classifiers were SVM and RF. In all, the most used classification method was SVM, followed by RF and CNN.
2.4. Literature Trends in TS Classification Methods
Figure 3 and Figure 4 present the trends of the TS classification methods. Currently, there are two main types of methods, traditional machine learning methods and classic deep learning-based methods. The former’s classifiers include RF, SVM, LDA, and MLC, among others. The latter refers specifically to CNNs and excludes methods such as transformers. Figure 5 depicts the tree classification process of these two methods.
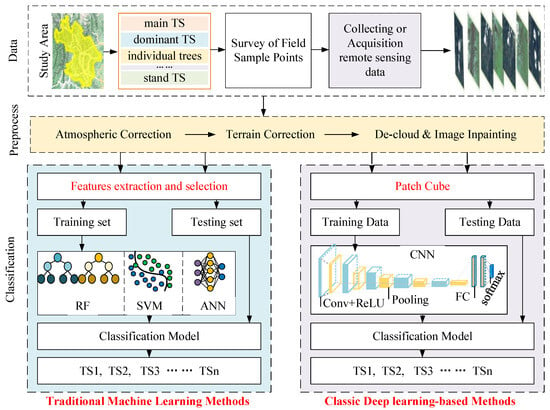
Figure 5.
The TS classification process of traditional machine learning methods and classic deep learning-based methods.
Scales and categories for TS classification were determined based on a study of the natural variability and tree species composition of the study area. Remote sensing data for TS classification were collected and acquired based on data accessibility. The data underwent preprocessing, including atmospheric and terrain correction, de-clouding, and image inpainting. The tree samples were then labeled based on the complete ground inventory data, as the tree species categories in the remotely sensed data were not easily identifiable through visual interpretation alone.
The classification process for tree species using traditional machine learning methods involves preprocessing, extracting and selecting features, classifying the species using classifiers, and evaluating the results. The process of classic deep learning-based methods involves preprocessing, and cutting the remote sensing image data with labels into a patch cube, dividing the patch cube into a training set and a test set, using the data from the training set to train the CNN, storing the parameters of the best classified CNN model, and finally testing the network with the data from the test set to obtain the final TS classification result. The main difference between these two methods is whether or not the feature extraction is automated.
In Figure 6a, the study areas are categorized by size. Red dots represent areas larger than 10,000 hectares, green rectangles represent areas between 1000 and 10,000 hectares, blue triangles represent areas between 100 and 1000 hectares, and magenta hexagrams represent areas smaller than 100 hectares. In Figure 6b, the size of study areas for traditional machine learning methods is represented by green bubbles and classic deep learning-based methods are represented by orange bubbles. Meanwhile, a larger bubble indicates a larger study area.
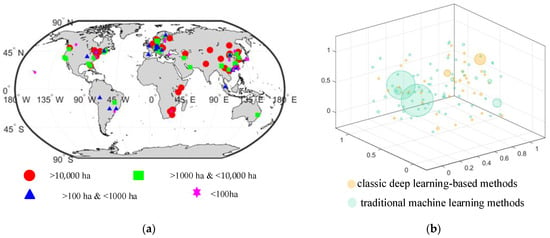
Figure 6.
The area size of the study site. (a) The study areas are categorized by size. (b) Size of the study area for the two primary classification methods.
Figure 6 only statistically analyzes the literature that presents the area and latitude/longitude range of the study area. In cases where multiple papers cover the same study area, only one area is counted. Figure 6a indicates that tree classification studies are typically conducted on a larger scale. Additionally, Figure 6b demonstrates that traditional machine learning methods are utilized for tree classification in large study areas, while classic deep learning-based methods are employed for tree classification in small study areas. It is worth noting that there are larger orange bubbles in Figure 6b, where the classic deep learning-based methods are also beginning to be used for tree classification in large study areas. A multi-sensor, multi-label dataset for tree species classification using CNN was created by Steve Ahlswede et al. [75] using aerial images, Sentinel-1 images, and Sentinel-2 images. The study area, which covers approximately 47,710 km2, is located in the federal state of Lower Saxony, Germany. Xueliang Wang and Honge Ren [76] used HSI from the HJ-1A satellite and MSI from the Sentinel-2 satellite to classify tree species using CNN. The study was conducted in the Tahe Forestry Bureau, which is situated in the center of the Daxing’an Mountains in the northwest of China’s Heilongjiang Province. The total area covered by the study was 14,420 km2.
Fassnacht et al. [10] and Ruiliang Pu [12] provide a detailed overview of traditional machine learning methods for TS classification. This thesis only covers classic deep learning-based methods for TS classification.
3. Literature Review on Classic Deep Learning-Based Methods
In 2015, the article “Deep Learning” was published in Nature, in which LeCun Y and others predicted that the future application of deep learning in images, video, audio, and other aspects will break through [77], and deep learning algorithms based on a big data platform is the direction of the future development of artificial intelligence, and also the mainstream of modern artificial intelligence research. Image recognition is one of the important research components of deep learning, and they predicted that research on classic deep learning (convolutional neural network, CNN) applied to TS classification in remote sensing images will be conducted more and more in 2018 and beyond.
The classic deep learning structure consists of a convolutional layer, a pooling layer, and a fully connected layer, and the activation function (commonly used as Relu) is typically used after the convolutional layer. The basic structure is shown in Figure 7, the convolutional layer and the pooling layer are used to extract TS features, and the fully connected layer is used to classify TS. The whole classification process is an automatic process, which is an end-to-end process, only the corresponding data of the input layer need to be given, and features are automatically extracted from the network. It is more time-consuming and labor-intensive to create the samples (labels).
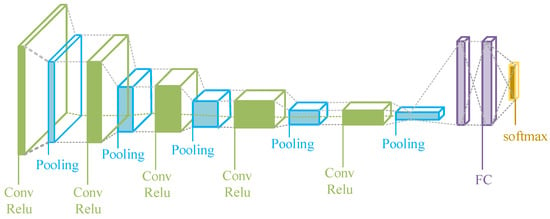
Figure 7.
The Basic Structure of CNN. Abbreviations are as follows: Conv = the convolutional layer, and FC = the fully connected layer. Relu is the activation function. Pooling is max-pooling or average-pooling.
A total of 71 research papers were filtered. These papers focused on classic deep learning-based methods for tree species classification. Seventy papers were published between 2 January 2018 and 1 January 2023, highlighting the rapid development of deep learning-based methods for TS classification, which is a relatively new field.
3.1. Patch Size
After preprocessing the remote sensing data, the images must be divided into patches of size m × n. These patches will form the CNN dataset, also known as the patch cube. The size of the patches is the size of the CNN input image and is crucial for the classification object, such as individual TS, dominant TS, and the design of the classification CNN network structure. Out of all the literature, 62 papers provided a description of patch size, while 9 papers did not mention the size of the input image (patch size) for the CNN. Table 1 shows some patch sizes used for various data.

Table 1.
Patch sizes.
In Table 1, bold patch size indicates a higher frequency of occurrence in the literature, and “3 × 3~15 × 15” means that patch size was tested from 3 × 3 to 15 × 15 in Step 2.
After analyzing and summarizing the literature on patch size, we concluded that there are five ways to introduce patch size. (1) Patch size is the same as the input image size of the CNN model itself in some papers, such as 224 × 224, and 227 × 227. (2) The optimal patch size for classification results is given in some papers, while other patch sizes used for comparison are not mentioned. (3) Some papers used multiple patch sizes without final analytical interpretation. (4) In three research papers, a variety of patch sizes were tried and some analytical interpretations were made. Long Chen et al. [42] used prototypical networks and HSI data to classify TS. They experimented with 3 × 3~31 × 31 patch sizes and found that under the same conditions, a patch size of 17 × 17 resulted in significantly improved classification accuracy. This suggests that the spatial and channel feature extraction of prototypical networks for this patch size meets the requirements for high-precision classification. As patch size increases, more noise may be introduced, potentially causing fluctuations in classification accuracy. Janne Mäyrä et al. [54] utilized a 3D CNN network and HSI data to classify individual TS. The patch sizes used were 9 × 9, 13 × 13, 17 × 17, and 21 × 21 (square patches with diameters of 4, 6, 8, and 10 m, respectively). The results showed that the 9 × 9 patch size had the highest producer accuracy of 0.84. The classification accuracy was not significantly affected by the different patch sizes throughout the experiment. The paper demonstrates that larger image patches contain multiple trees of different species. Ying Sun et al. [78] utilized RGB to classify individual TS, and demonstrated the best performance for TS classification. RGB and CHM and RGB and VHR were also utilized but did not perform as well. The patch sizes used were 32 × 32, 48 × 48, and 64 × 64, with ResNet50 performing best in the 64 × 64 patch size. The study concluded that larger patch sizes are more effective in deep learning-based methods, while smaller patch sizes lead to higher overall accuracy in traditional machine learning methods. When using traditional machine learning methods, larger patch sizes may mix other information and influence the features of the tree species if the mean feature value was used. (5) Six research papers provided information on patch size and its corresponding spatial resolution (Table 2).

Table 2.
Patch size and its corresponding spatial resolution.
3.2. Reference Data
Classic deep learning-based methods belong to the supervised modeling approach. These datasets require remote sensing images and reference data, also known as annotations, samples, or labels. The most commonly used method for acquiring reference data was through field plot surveys (79%). A small percentage of the literature used forest management inventory data (7%), while 6% relied on visual interpretation. The remaining studies used public datasets with their own data labels.
3.3. TS Classification Scales
Determining the appropriate scale for TS classification depends on the needs of the application. The scale can range from dominant tree species to individual trees, and it is important to consider the required data resolution and labeling process. Based on classic deep learning-based methods, 51% of the research papers achieved the individual tree classification, 25% were focused on tree species classification, 19% on the dominant TS of main TS classification, and the remaining papers used public datasets. The classification of individual trees relies mainly on LiDAR and RGB data. In most cases, the crowns of individual trees are segmented and used for classification. In some literature, each image contains only one tree, and therefore, individual tree classification is performed directly.
3.4. CNN Architectures and Application
3.4.1. CNN from the Functional Perspective
Depending on the specific use, classic deep learning-based methods can be categorized into four main groups. The main function, representative networks, labeling structure, resulting output, and usage of these four groups in TS classification are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The four main groups of classic deep learning-based methods in TS classification.
CNNs can be classified into four categories: classic CNN, object detection, semantic segmentation, and instance segmentation based on their functions. Classic CNN, object detection, and instance segmentation have the function of classification, so classic CNN, object detection, and instance segmentation can be used to classify TS, while object detection and instance segmentation, which have additional functions such as localization, require more complex and time-consuming labeling. Before TS classification, semantic segmentation is performed to obtain the tree’s canopy.
The statistical analysis results of the 71 papers categorized by the function of CNNs are presented in Figure 8.
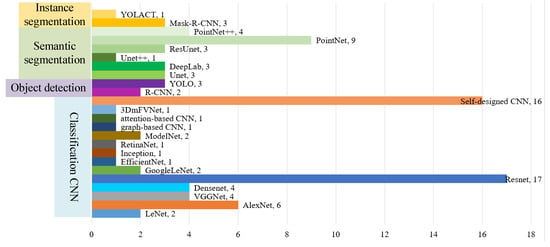
Figure 8.
CNN networks for TS classification.
Figure 8 shows that ResNet is the most commonly used classic CNN network for TS classification. In TS classification, the input image size to the network is relatively small, which limits the use of some classic networks. Self-designed shallower CNN networks are more common due to the feature extraction problems that arise in the convolutional and pooling layers when using classic CNN networks. The PointNet network is often preferred when segmenting individual trees for TS classification using LiDAR point cloud data (Figure 8). The infrequent use of object detection and instance segmentation in TS classification is shown in Figure 8; the labels can be complex, the bounding box often does not explicitly define crown/canopy boundaries, and the crown/canopy is not rectangular. Natural canopies often have smooth transitions or overlapping crowns, which limits the object detection and instance segmentation that can be applied in TS classification. But for certain tree species with non-overlapping crowns, it is important to try object detection and instance segmentation so that the tree transformation can be easily tracked afterward.
3.4.2. CNN from the Input Data Perspective
Depending on the input remote sensing data, classic deep learning-based methods can be categorized into 1DCNN, 2DCNN, and 3DCNN, where the number refers to the dimensions of the convolutional kernel. The multi-temporal remote sensing data use Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) or 1DCNN. Other input data can use 1DCNN, 2DCNN, or 3DCNN. Among them, 2DCNN is the most commonly used in the TS classification (75%). 3DCNN was used most often for LiDAR and HSI data (19%), and the model was self-designed.
Yanbiao Xi et al. [95] utilized 1DCNN in conjunction with spectral and crown texture features of HIS to classify 7 TS, resulting in an overall accuracy of 85.04%. The features were used to generate a vector as the input layer for the 1DCNN network, which comprised two convolutional layers, one max-pooling layer, and fully connected layers. Research papers on 3DCNN tree classifications are concentrated between 2019 and 2021. Haiyan Guan et al. [96] and Maohua Liu et al. [53] utilized a self-designed 3DCNN and LiDAR data to achieve a TS classification with an overall accuracy of 96.4% and 92.5%, respectively. Somayeh Nezami et al. [97] achieved a TS classification using a self-designed 3DCNN, and RGB and HIS data, with a producer accuracy of 99.6%. Bin Zhang et al. [43] and Janne Mäyrä et al. [54] employed a self-designed 3DCNN and HSI data to classify the TS, achieving classification accuracy of 93.14% and 87%, respectively. The two studies utilized the canopy height model derived from LiDAR data to match ground reference data to aerial imagery.
3.4.3. Multimodal Remote Sensing Data Fusion
Multimodal data fusion is generally categorized into three types: input-stack fusion, feature-stack fusion, and decision-level fusion. In the literature on TS classification based on classic deep learning-based methods, only two types of fusion were found: input-stack fusion (six papers) and feature-stack fusion (three papers).
Bingjie Liu et al. [98] utilized PointMLP to extract features from LiDAR point cloud data and 2DCNN to extract features from UAV RGB images for tree species classification with 98.52% accuracy. Xueliang Wang et al. [76] proposed the double-branch multi-source fusion (DBMF) method. One branch utilized the CNN network to abstract the spatial features for the MSI, while the other branch employed the bidirectional long short-term memory (Bi-LSTM) to abstract the spectral features for the HSI. The resulting features were concatenated to classify TS, achieving an overall accuracy of 92%. Ira Harmon et al. [99] and Sean Hartling et al. [100] utilized input-stack fusion. They used the HCM, DEM, and RGB/HSI data, VHR and LiDAR data to classify TS, respectively.
3.5. CNN Model Assessment and Operational Framework in TS Classification
3.5.1. CNN Model Assessment
The TS classification results were evaluated based on the OA, precision, recall, F1 score, and kappa [50,57,80,84,91,94,101], and these metrics are defined as follows:
The variables used in this study include TP (true positives), FP (false positives), FN (false negatives), TN (true negatives), (expected proportion of agreement), and N (total sample size). TP represents the number of positive samples correctly predicted by the CNN model, while FP represents the number of negative samples incorrectly predicted as positive. FN represents the number of positive samples incorrectly predicted as negative, while TN represents the number of negative samples correctly predicted by the model. is calculated by dividing the sum of the product of the actual sample size and the predicted sample size by the square of the total number of samples. The user’s accuracy (UA), producer’s accuracy (PA), and Dice similarity coefficient are equivalent to precision, Recall, and F1, respectively. UA measures the proportion of relevant positive predictions, while PA measures the proportion of correctly classified positive results. F1 is the weighted average of UA and PA, with a best value of one and a worst value of zero. The kappa coefficient and OA measure the overall consistency between the identification result and the reference data. The OA value ranges from 0 to 1, while the kappa coefficient value ranges from −1 to 1 and is typically greater than zero. Equations (1)–(5) compute their values based on the confusion matrix, ranging from 0 to 1. A value of one indicates the highest similarity between the predicted TS and reference data, while zero indicates no similarity. Each of these five evaluation indicators has its own limitations. However, from a theoretical perspective, there is no combination of evaluation indicators that can be used to evaluate the optimal classification result of the models.
In semantic and instance segmentation, the intersection over union (IoU, also known as the Jaccard Index) is used to evaluate the performance of the differently trained models on independent testing datasets [94].
The crown polygons from the test set () and the predicted crown polygons from the segment CNN algorithm () are compared using the intersection and union operations to determine their common and combined areas, respectively.
3.5.2. CNN Model Operational Framework
Figure 9 shows the statistical results of the CNN operational framework for TS classification. There are lots of frameworks for deep learning. Based on the development of deep learning in artificial intelligence, the most popular framework in the past few years was Google’s TensorFlow, but in the past two years, the most popular framework has been Facebook’s PyTorch. Our statistical results from the literature are consistent with the development of deep learning artificial intelligence. Currently, the use of the PyTorch framework is gradually increasing and replacing TensorFlow.
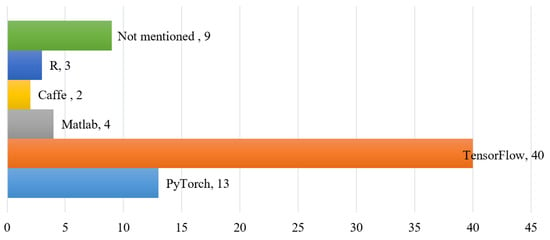
Figure 9.
The statistical results of CNN operational framework for TS classification. Where TensorFlow (https://www.tensorflow.org/), Pytorch (https://pytorch.org/), Matlab (https://www.mathworks.com/), and R (https://www.r-project.org/), Caffe has been merged into PyTorch.
4. Limitations and Future Work
There are still many factors that limit the accuracy and precision of TS classification, such as spatial resolution, temporal resolution, spectral resolution, phenological transformation information, forest environments, shadows, cloud shading, small canopies, spectral shapes of different canopies, and canopy overlap, and so on [102]. At the same time, the current TS classification used in different study areas has some limitations because the algorithms themselves have prerequisites for using them, and the data may not always be able to meet the prerequisites of the algorithms perfectly. Thus, TS classification based on remote sensing is full of challenges, and there are many aspects worth our efforts in the future.
4.1. Data Fusion
- Spatially sharpened data fusion method
Pan-sharpening is a pixel-level fusion that can be applied to both single-sensor data and multi-sensor images. Single-sensor fusion produces a high-resolution multispectral image by fusing a pan-band and a low-resolution multispectral image. Such a sharpened image has a nominal pan high resolution but its MS property may be slightly different from the original MS property. Compared to the direct use of low-resolution MS images, sharpened images improve the quality of individual canopy object segmentation for optimal canopy object segmentation. Spatial sharpening of multi-sensor images is performed using different optical sensor data, one high-resolution and one low-resolution multispectral data. The low-resolution multispectral band image is then resampled to a higher resolution to make the images from both sensors the same size, and finally, the spatially sharpened data are obtained by using a spatial sharpening algorithm. No studies have been found in the literature reporting the direct use of spatial sharpened methods to improve TS classification, but spatial sharpening improves the spatial resolution and maintains the spectral properties of MSI [103], and spatial sharpened fusion methods should be useful in practice for TS classification [12].
- Feature-level data fusion method
Feature-level fusion is the fusion of features extracted from different sensors, which is a simple overlapping of multi-source features to increase the number of features for TS classification, not true fusion.
- Spatiotemporal Data Fusion method
At present, the spatiotemporal fusion algorithm of remote sensing data has matured. The spatiotemporal fused time series data have a high temporal and spatial resolution, which can respond well to the information on phenological changes in tree species. However, so far, spatiotemporal fusion has not been directly applied to the research of TS classification.
Multi-source remote sensing data fusion has developed rapidly in recent years. The fusion of homogeneous remote sensing data has achieved the fusion of multi-sensor data in the three dimensions of time, space, and spectra, and obtained high-quality data with multi-temporal phase, high-spectral, and high-spatial and temporal resolution. The fusion of heterogeneous remote sensing data is mainly the fusion of optical remote sensing data and active remote sensing data, of which the fusion of SAR images and optical remote sensing data is more sophisticated. In the future, to effectively improve the accuracy and precision of TS classification, the real fusion algorithm of multimode remote sensing data will be applied to TS classification, or the existing multimode remote sensing data fusion algorithm will be improved to study TS classification.
4.2. Phenology Information
Multi-temporal remote sensing data have great significance in improving the classification accuracy of tree species [23,85,104,105,106], as current research has shown that time series images can correspond to the phonological and seasonal characteristics of tree species, and the characteristics change differently for different tree species throughout the year [107]. However, the seasonal division of the series is currently not uniform; some literature divides the multi-temporal data into four seasons (Spring, Summer, Fall, and Winter), some in two seasons (Wet/Dry, Dry/Rainy, Growing/Non-Growing, and so on), and some in multiple seasons (Early Spring, Late Spring, and Midsummer). How to extract the valuable features from the multi-temporal data and how to use the features has not yet been completed, and it has not yet been concluded which combination of two-season, one-season, or multi-season time series images is most effective for the classification accuracy of tree species. For example, Li et al. [104] used two seasons of WV2 (14 September 2012) and WV3 (18 October 2014) data to classify five tree species in Beijing, China, and Karlson et al. [108] used two seasons of WV2 images to classify five dominant species in West Africa and found that TS classification using two seasons of time series data was better than that using single or multiple seasons. Ferreira et al. [35] investigated whether using wet and dry seasons separately or in combination improved tree classification accuracy, and the study concluded that the two-season combination did not have higher tree classification accuracy than the single-season. Pu et al. [23] tested combinations of two-, three-, four-, and five-season multi-temporal images for a study on TS classification ability, and they found that combining more than two combinations of seasonal images did not produce better TS classification results than combinations of two seasonal images (dry/wet season images).
Most current studies select the best seasonal time-series images and do not fully utilize images from all seasons when classifying tree species. In the literature, R. Pu and S. Landry [109] proposed a seasonal trajectory difference index, which integrates the possible contributions of all seasons as a feature for classifying tree species and can help improve the accuracy and precision of classifying tree species. How to take full advantage of the phonological and seasonal information, and combine the algorithms in the fields of time series processing and digital signal processing to create a characteristic or method with an explicit physical meaning of phenological variation, to improve the accuracy of TS classification, still needs to be resolved.
4.3. Data Label
The remote sensing data label is directly related to the usefulness of the final TS classification product. Currently, data are labeled through plot surveys, and it is generally difficult for someone familiar enough with the study area to accurately identify all the tree species through remote sensing data, so visual interpretation is essentially not used. For large-scale TS classification, the plot survey is very difficult and takes several years or more, resulting in a temporal mismatch between remote sensing data and labels. In some primary forests or parts of forests with complex terrain and difficult transportation, it is impossible to conduct field surveys, so it is even more difficult to solve the labeling problem.
Weakly supervised learning labels can be used at the image level or sparsely at the pixel level, reducing the cost of manual labeling. Even when results from other data studies are available and ground truth data are scarce, the method can help solve the labeling problem [110,111]. Semi-supervised learning lies between supervised and weakly supervised learning. It has been shown that robust CNNs with a small number of high-quality labels can be trained [112]. In the future, weakly supervised learning or semi-supervised learning can be used to support data labeling when large datasets are constructed.
4.4. Patch Size
When utilizing remote sensing for tree species classification, it is important to consider the optimal ground sampling density and spatial unit. Specifically, it is necessary to determine the spatial unit for obtaining tree species information and the optimal ground sampling density for deriving such information using a given sensor [9]. The size detailed statistics and analysis reveal that out of 71 papers on classic deep learning-based methods of tree species classification, only three provide rough explanations of different patch sizes, and only six offer information on patch size and its corresponding spatial resolution.
Fromm et al. [113] have shown that the accuracy of detection of tree seedlings can vary by up to 20% based on the resolution of the UAV image (0.3–6.3 cm). Similarly, when the pixel size was reduced from 40 cm to 60 cm, Neupane et al. [114] found a 17% decrease in detection accuracy for banana trees in plantations. So, when selecting the patch size for the TS classification, it is important to consider the spatial unit and optimal ground sampling density. This can contribute to the criteria for selecting patch size. This is a very interesting problem, and it is worth trying to solve in the future.
4.5. CNN Model Optimization Approaches
Due to the increasing performance of computer hardware, CNN models now have billions of parameters. This gives them incredible fitting ability but also makes them highly susceptible to overfitting for a particular dataset. To improve the generalization ability of CNN models and alleviate the overfitting problem, the following strategies can be employed: To improve the dataset, consider using data augmentation procedures. To improve the CNN model, add regularization techniques to the weights. To improve the training process, consider stopping the model early. To improve the model structure, add the Dropout layer and the normalization layer.
When a CNN model experiences overfitting, the first network structure typically considered for use is Dropout. Dropout reduces the coupling between nodes during training by replacing some nodes with masks to achieve regularity. There are also other improved versions of Dropout, such as Spatial Dropout, DropBlock, and Max-pooling Dropout. Normalization is a rapidly growing set of algorithms in deep learning. Batch normalization (BN) is a classical normalization algorithm that is frequently used to mitigate overfitting in deep learning. It normalizes features from the same channel of different samples and effectively solves the exploding gradient problem, making the CNN network model more stable.
4.6. Outlook on New Technologies
Vision transformers (ViTs) have been trending in image classification tasks due to their promising performance when compared to convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Multimodal deep learning can fuse different modalities of remote sensing data to achieve richer information representation and more accurate TS classification. We believe that the transformer and multimodal-based methods will be applied to TS classification shortly. The methods will comprehensively improve the effect of TS classification and create a new situation of TS classification by mining and fusing the data information of each modality.
5. Conclusions
In this study, a total of 300 publications related to the study of classifying and mapping TS using images from different remote sensing sensors were analyzed. In this regard, a review of the unimodal and multimodal remote sensor data and the classic deep learning-based methods for TS classification was carried out. After carrying out the review and summary, some conclusions with remarks and recommendations will be summarized in the following paragraphs.
- From the number of publications, tree species classification has become a hot topic in current research. From the unimodal and multimodal remote sensor data utilization, the main unimodal data for TS classification were HSI, LiDAR, RGB, and VHR, and the most used multimodal data were HIS and LiDAR.
- According to the literature analysis of TS classification methods, the most commonly used classifiers for remote sensing data, whether unimodal or multimodal, were CNN, RF, and SVM. Therefore, this article summarizes the process of remote sensing TS classification and condenses the two major current TS classification methods: traditional machine learning methods and classic deep learning-based methods.
- Traditional machine learning methods are utilized for tree classification in large study areas, while classic deep learning-based methods are employed for tree classification in small study areas. The classic deep learning-based methods are beginning to be used for tree classification in large study areas.
- The classic deep learning-based methods for TS classification are reviewed in detail in terms of patch size, reference data, TS classification scales, CNN architectures and applications, CNN operational framework, and CNN model assessment.
- Six limitations and future work are discussed below, and suggestions are made to overcome potential issues in the future. (a) Data fusion. A spatial-temporal fusion algorithm and real fusion algorithm of multimodal remote sensing data can be applied to TS classification, or the existing multimodal remote sensing data fusion algorithm should be improved to study TS classification. (b) Phenology information. A feature or method was created with an explicit physical meaning of the phenological variation used to improve the accuracy of TS classification. (c) Data label. Label production is very labor-intensive, and field surveys for TS classification labeling are time-consuming and laborious. It is recommended that field surveys with weakly supervised and semi-supervised learning for labeling are combined. (d ) Patch size. When utilizing remote sensing data for tree species classification, it is important to consider the optimal ground sampling density and spatial unit. Specifically, it is necessary to determine the spatial unit for obtaining tree species information and the optimal ground sampling density for deriving such information using a given sensor. Patch size has not been studied enough, and it may depend on the spatial resolution of the classification target, the distribution and size of the forest stand area, or other factors, which is an interesting problem to study. (e) CNN model optimization. To improve the generalization ability of CNN models and alleviate the overfitting problem, some strategies were given. (f) New technologies, such as transformer and multimodal-based methods will be applied to TS classification shortly.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.Z. and P.F.; methodology, L.Z. and Y.C.; literature analysis, L.Z. and Z.D.; investigation, L.Z. and Z.D.; resources, L.Z. and Z.D.; data curation, Y.C.; writing—original draft preparation, L.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.C., P.F. and. L.W.; visualization, Z.D.; supervision, L.W.; project administration, L.Z.; funding acquisition, L.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Forestry Innovation Programs of Southwest Forestry University, grant number LXXK-2023Mxx; the Key Development and Promotion Project of Yunnan Province under Grant 202102AE090051; Scientific Research Fund Project of Yunnan Provincial Education Department, grant number 2024J0685; the Key Laboratory of State Forestry and Grassland Administration on Forestry and Ecological Big Data, Southwest Forestry University, grant number 2022-BDG-02; and in part by Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology’s Basic Research Program, grant number 202401AT070271.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| AHI | Advanced Himawari imager |
| ASTER | Advanced spaceborne thermal emission and reflection radiometer |
| Bi-LSTM | Bidirectional long short-term memory |
| CASI | Compact airborne spectrographic imager |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| Conv | The convolutional layer |
| DBMF | Double-branch multi-source fusion |
| FC | The fully connected layer |
| HSI | Hyperspectral image |
| IoU | Intersection over union |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LiDAR | Light detection and ranging |
| MLC | Maximum likelihood classifiers |
| MSI | Multispectral image |
| OA | Overall accuracy |
| PA | Producer’s accuracy |
| RF | Random forest |
| RGB | The red, green, and blue image |
| RNN | Recurrent neural network |
| SAR | Active remote sensing synthetic aperture radar |
| SPOT | Satellite Pour l’Observation de la Terre HighResolution Visible |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| TS | Tree species |
| UA | User’s accuracy |
| UAV | Unmanned aerial vehicle |
| VHR | Very high spatial resolution |
| ViTs | Vision transformers |
| WOS | Web of Science |
References
- Fang, F.; McNeil, B.E.; Warner, T.A.; Maxwell, A.E.; Dahle, G.A.; Eutsler, E.; Li, J. Discriminating Tree Species at Different Taxonomic Levels Using Multi-Temporal WorldView-3 Imagery in Washington DC, USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, J.; Ao, Z.; Lao, D.; Xin, Q.; Fang, F.; McNeil, B.E.; Warner, T.A.; Maxwell, A.E.; Dahle, G.A.; et al. Deep Learning Approaches for the Mapping of Tree Species Diversity in a Tropical Wetland Using Airborne LiDAR and High-Spatial-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Forests 2019, 10, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasumani, M.; Bunyan, M.; Robin, V.V. Opportunities and Challenges in Using Remote Sensing for Invasive Tree Species Management, and in the Identification of Restoration Sites in Tropical Montane Grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, D.; Périé, C.; Casajus, N.; De Blois, S. Challenges in Modelling the Abundance of 105 Tree Species in Eastern North America Using Climate, Edaphic, and Topographic Variables. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 291, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, S.; Weinstein, B.G.; Zou, S.; Bohlman, S.A.; Zare, A.; Singh, A.; Stewart, D.; Harmon, I.; Steinkraus, A.; White, E.P. Continental-Scale Hyperspectral Tree Species Classification in the United States National Ecological Observatory Network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, Á.; García, M.; Siegel, R.B.; Koltunov, A.; Ramírez, C.; Ustin, S. Burned Forest Characterization at Single-Tree Level with Airborne Laser Scanning for Assessing Wildlife Habitat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahnejad, A.; Panagiotidis, D. Tree Species Classification and Health Status Assessment for a Mixed Broadleaf-Conifer Forest with UAS Multispectral Imaging. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, K.M.; Escanferla, M.E.; Jetton, R.M.; Man, G.; Crane, B.S. Prioritizing the Conservation Needs of United States Tree Species: Evaluating Vulnerability to Forest Insect and Disease Threats. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 18, e00622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felbermeier, B.; Hahn, A.; Schneider, T. Study on User Requirements for Remote Sensing Applications in Forestry. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Symposium Technical Commission VII, Vienna, Austria, 5–7 July 2010; pp. 210–212. [Google Scholar]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Latifi, H.; Stereńczak, K.; Modzelewska, A.; Lefsky, M.; Waser, L.T.; Straub, C.; Ghosh, A. Review of Studies on Tree Species Classification from Remotely Sensed Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.R.; Hardin, P.J.; Hardin, A.J. Classification of Urban Tree Species Using Hyperspectral Imagery. Geocarto Int. 2012, 27, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R. Mapping Tree Species Using Advanced Remote Sensing Technologies: A State-of-the-Art Review and Perspective. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 2021, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Zhou, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, W. Individual Tree Segmentation and Tree Species Classification in Subtropical Broadleaf Forests Using UAV-Based LiDAR, Hyperspectral, and Ultrahigh-Resolution RGB Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Li, M.; Hao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, B. Tree Species Classification in a Typical Natural Secondary Forest Using UAV-Borne LiDAR and Hyperspectral Data. GISci. Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2171706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, K.; Zhuo, L.; Liu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, L. Combining UAV-Based Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data for Mangrove Species Classification Using the Rotation Forest Algorithm. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothe, C.; La Rosa, L.E.C.; De Almeida, C.M.; Gonsamo, A.; Schimalski, M.B.; Castro, J.D.B.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Dalponte, M.; Lima, C.L.; Liesenberg, V.; et al. Evaluating a Convolutional Neural Network for Feature Extraction and Tree Species Classification Using Uav-Hyperspectral Images. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2020, 5, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.A.; Marcato Junior, J.; Araújo, M.S.; Di Martini, D.R.; Tetila, E.C.; Siqueira, H.L.; Aoki, C.; Eltner, A.; Matsubara, E.T.; Pistori, H.; et al. Assessment of CNN-Based Methods for Individual Tree Detection on Images Captured by RGB Cameras Attached to UAVS. Sensors 2019, 19, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartling, S.; Sagan, V.; Maimaitijiang, M. Urban Tree Species Classification Using UAV-Based Multi-Sensor Data Fusion and Machine Learning. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 1250–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, M.; Ise, T. Explainable Identification and Mapping of Trees Using UAV RGB Image and Deep Learning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, X.; Cao, L. Tree Species Classification in Subtropical Natural Forests Using High-Resolution UAV RGB and SuperView-1 Multispectral Imageries Based on Deep Learning Network Approaches: A Case Study within the Baima Snow Mountain National Nature Reserve, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onishi, M.; Watanabe, S.; Nakashima, T.; Ise, T. Practicality and Robustness of Tree Species Identification Using UAV RGB Image and Deep Learning in Temperate Forest in Japan. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xia, K.; Feng, H.; Yang, Y.; Du, X. Tree Species Classification Using Deep Learning and RGB Optical Images Obtained by an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle. J. For. Res. 2021, 32, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S.; Yu, Q. Assessing the Potential of Multi-Seasonal High-Resolution Pléiades Satellite Imagery for Mapping Urban Tree Species. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 71, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asner, G.P.; Jones, M.O.; Martin, R.E.; Knapp, D.E.; Hughes, R.F. Remote Sensing of Native and Invasive Species in Hawaiian Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1912–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, P.; Ou, G.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, W.; Dai, Q.; Huang, X. Regionalized Classification of Stand Tree Species in Mountainous Forests by Fusing Advanced Classifiers and Ecological Niche Model. GISci. Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2211881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, V.; Beloiu, M.; Darvishsefat, A.A.; Griess, V.C.; Maftei, C.; Waser, L.T. Mapping Tree Species Composition in a Caspian Temperate Mixed Forest Based on Spectral-Temporal Metrics and Machine Learning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Guo, S.; Ye, Z.; Deng, H.; Hou, X.; Zhang, H. Urban Tree Classification Based on Object-Oriented Approach and Random Forest Algorithm Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (Uav) Multispectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, A.; Lindberg, E.; Reese, H.; Olsson, H. Tree Species Classification Using Sentinel-2 Imagery and Bayesian Inference. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 100, 102318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Ren, C.; Tian, Q.; Ren, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, Z. Exploitation of Time Series Sentinel-2 Data and Different Machine Learning Algorithms for Detailed Tree Species Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 7589–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.H.; Wang, X. Planimetric Accuracy of Ikonos 1 m Panchromatic Orthoimage Products and Their Utility for Local Government GIS Basemap Applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4267–4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, B.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C. Identifying Leading Species Using Tree Crown Metrics Derived from Very High Spatial Resolution Imagery in a Boreal Forest Environment. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 36, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deventer, H.; Cho, M.A.; Mutanga, O. Improving the Classification of Six Evergreen Subtropical Tree Species with Multi-Season Data from Leaf Spectra Simulated to WorldView-2 and RapidEye. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 4804–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, E.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Xu, E.; Hou, Y.; Sun, R. An End-to-End Deep Fusion Model for Mapping Forests at Tree Species Levels with High Spatial Resolution Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, H.J.; Axelsson, C.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Huo, L.; Holmgren, J. Comparison of Single Tree Species Classification Using Very Dense ALS Data or Dual-Wave ALS Data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2023—2023 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Pasadena, CA, USA, 16–21 July 2023; pp. 3066–3069. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, M.P.; Wagner, F.H.; Aragão, L.E.O.C.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; de Souza Filho, C.R. Tree Species Classification in Tropical Forests Using Visible to Shortwave Infrared WorldView-3 Images and Texture Analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 149, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceballos, A.; Hernández, J.; Corvalán, P.; Galleguillos, M. Comparison of Airborne LiDAR and Satellite Hyperspectral Remote Sensing to Estimate Vascular Plant Richness in Deciduous Mediterranean Forests of Central Chile. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2692–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.L.; Roberts, D.A. Species-Level Differences in Hyperspectral Metrics among Tropical Rainforest Trees as Determined by a Tree-Based Classifier. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1820–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Pang, Y.; Meng, S.; Ju, H.; Li, Z. Tree Species Classification Using Airborne Hyperspectral Data in Subtropical Mountainous Forest. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 2284–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Modzelewska, A.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Stereńczak, K. Tree Species Identification within an Extensive Forest Area with Diverse Management Regimes Using Airborne Hyperspectral Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 84, 101960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, F.; Zhang, Y. Spectral--Spatial and Cascaded Multilayer Random Forests for Tree Species Classification in Airborne Hyperspectral Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Cao, L. Tree-Species Classification in Subtropical Forests Using Airborne Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Tian, X.; Chai, G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, E. A New CBAM-P-Net Model for Few-Shot Forest Species Classification Using Airborne Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Three-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network Model for Tree Species Classification Using Airborne Hyperspectral Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wietecha, M.; Modzelewska, A.; Stereńczak, K. Airborne Hyperspectral Data for the Classification of Tree Species a Temperate Forests. Sylwan 2017, 161, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Dalla Mura, M.; Chanussot, J.; Zhang, G. Soft-Then-Hard Super-Resolution Mapping Based on Pansharpening Technique for Remote Sensing Image. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 12, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonzo, M.; Bookhagen, B.; Roberts, D.A. Urban Tree Species Mapping Using Hyperspectral and Lidar Data Fusion. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Skidmore, A.K.; Premier, J.; Heurich, M. A Voxel Matching Method for Effective Leaf Area Index Estimation in Temperate Deciduous Forests from Leaf-on and Leaf-off Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowska, M.; Rapiński, J. A Review of Tree Species Classification Based on Airborne LiDAR Data and Applied Classifiers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, Z.; Yastikli, N. The Use of Machine Learning Algorithms in Urban Tree Species Classification. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, H.; Su, Y.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, E.; Tian, X. Tree Species Classification Using Ground-Based LiDAR Data by Various Point Cloud Deep Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, M.; Brandmeier, M.; Briechle, S.; Krzystek, P. Classification of Tree Species and Standing Dead Trees with Lidar Point Clouds Using Two Deep Neural Networks: Pointcnn and 3dmfv-Net. PFG–J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2022, 90, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinelli, D.; Paris, C.; Bruzzone, L. An Approach Based on Deep Learning for Tree Species Classification in LiDAR Data Acquired in Mixed Forest. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y. Tree Species Classification of LiDAR Data Based on 3D Deep Learning. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2021, 177, 109301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäyrä, J.; Keski-Saari, S.; Kivinen, S.; Tanhuanpää, T.; Hurskainen, P.; Kullberg, P.; Poikolainen, L.; Viinikka, A.; Tuominen, S.; Kumpula, T.; et al. Tree Species Classification from Airborne Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Using 3D Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 256, 112322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Skidmore, A.K.; Holzwarth, S.; Heiden, U.; Heurich, M. Mapping Individual Silver Fir Trees Using Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data in a Central European Mixed Forest. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 98, 102311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jombo, S.; Adam, E.; Tesfamichael, S. Classification of Urban Tree Species Using LiDAR Data and WorldView-2 Satellite Imagery in a Heterogeneous Environment. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 9943–9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Coops, N.C.; Aven, N.W.; Pang, Y. Mapping Urban Tree Species Using Integrated Airborne Hyperspectral and LiDAR Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapin, A.; Pettinato, S.; Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Fontanelli, G.; Garzelli, A. Comparison of Machine Learning Methods Applied to SAR Images for Forest Classification in Mediterranean Areas. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udali, A.; Lingua, E.; Persson, H.J. Assessing Forest Type and Tree Species Classification Using Sentinel-1 C-Band SAR Data in Southern Sweden. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saatchi, S.S.; Rignot, E. Classification of Boreal Forest Cover Types Using SAR Images. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, Y.W.; Shariff, A.R.M.; Sood, A.M.; Nordin, L. Application of SAR Data for Oil Palm Tree Discrimination. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 169, 12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned Aerial Systems for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing: A Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothe, C.; Dalponte, M.; de Almeida, C.M.; Schimalski, M.B.; Lima, C.L.; Liesenberg, V.; Miyoshi, G.T.; Tommaselli, A.M.G. Tree Species Classification in a Highly Diverse Subtropical Forest Integrating UAV-Based Photogrammetric Point Cloud and Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiefer, F.; Kattenborn, T.; Frick, A.; Frey, J.; Schall, P.; Koch, B.; Schmidtlein, S. Mapping Forest Tree Species in High-Resolution UAV-Based RGB-Imagery by Means of Convolutional Neural Networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 170, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brede, B.; Lau, A.; Bartholomeus, H.M.; Kooistra, L. Comparing RIEGL RiCOPTER UAV LiDAR Derived Canopy Height and DBH with Terrestrial LiDAR. Sensors 2017, 17, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Shen, X.; Cao, L.; Wang, G.; Cao, F. Estimating Forest Structural Attributes Using UAV-LiDAR Data in Ginkgo Plantations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 146, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Leng, W.; Liu, K.; Liu, L.; He, Z.; Zhu, Y. Object-Based Mangrove Species Classification Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Hyperspectral Images and Digital Surface Models. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevalainen, O.; Honkavaara, E.; Tuominen, S.; Viljanen, N.; Hakala, T.; Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Saari, H.; Pölönen, I.; Imai, N.N.; et al. Individual Tree Detection and Classification with UAV-Based Photogrammetric Point Clouds and Hyperspectral Imaging. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisein, J.; Michez, A.; Claessens, H.; Lejeune, P. Discrimination of Deciduous Tree Species from Time Series of Unmanned Aerial System Imagery. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michez, A.; Piégay, H.; Jonathan, L.; Claessens, H.; Lejeune, P. Mapping of Riparian Invasive Species with Supervised Classification of Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 44, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.J.; Tarasoff, C.; Whitworth, G.E.; Baron, J.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Church, J.S. Utility of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for Mapping Invasive Plant Species: A Case Study on Yellow Flag Iris (Iris pseudacorus L.). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2083–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, S.E.; Ahmed, O.S. Deciduous Tree Species Classification Using Object-Based Analysis and Machine Learning with Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Multispectral Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5236–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazinejad, G.; Javad Valadan Zoej, M.; Latifi, H. Applying Multidate Sentinel-2 Data for Forest-Type Classification in Complex Broadleaf Forest Stands. Forestry 2022, 95, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Song, B.; Liu, C.; Gong, P.; Luo, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, T. Bamboo Forest Mapping in China Using the Dense Landsat 8 Image Archive and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlswede, S.; Schulz, C.; Gava, C.; Helber, P.; Bischke, B.; Förster, M.; Arias, F.; Hees, J.; Demir, B.; Kleinschmit, B. TreeSatAI Benchmark Archive: A Multi-Sensor, Multi-Label Dataset for Tree Species Classification in Remote Sensing. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2023, 15, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, H. DBMF: A Novel Method for Tree Species Fusion Classification Based on Multi-Source Images. Forests 2022, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xin, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, H. Characterizing Tree Species of a Tropical Wetland in Southern China at the Individual Tree Level Based on Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4415–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhou, H.; Xu, C.; Hu, J.; Xue, X.; Xu, L.; Lou, X.; Zeng, K.; Wang, Q. Deep Learning in Forest Tree Species Classification Using Sentinel-2 on Google Earth Engine: A Case Study of Qingyuan County. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jing, L.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Chen, F. Individual Tree Species Identification Based on a Combination of Deep Learning and Traditional Features. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.R.; Baek, W.K.; Jung, H.S. Mapping Tree Species Using CNN from Bi-Seasonal High-Resolution Drone Optic and LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Jing, L.; Wang, H. A New Individual Tree Species Recognition Method Based on a Convolutional Neural Network and High-spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egli, S.; Höpke, M. Cnn-Based Tree Species Classification Using High-Resolution Rgb Image Data from Automated Uav Observations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, S.; Armenakis, C.; Vepakomma, U. Resnet-Based Tree Species Classification Using Uav Images. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2019, 42, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lu, Y. Establishing a Citywide Street Tree Inventory with Street View Images and Computer Vision Techniques. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2023, 100, 101924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Lim, W.; Chang, B.; Jeong, J.; Kim, I.; Park, C.R.; Ko, D.W. An Automatic Approach for Tree Species Detection and Profile Estimation of Urban Street Trees Using Deep Learning and Google Street View Images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloiu, M.; Heinzmann, L.; Rehush, N.; Gessler, A.; Griess, V.C. Individual Tree-Crown Detection and Species Identification in Heterogeneous Forests Using Aerial RGB Imagery and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.P.; de Almeida, D.R.A.; de Almeida Papa, D.; Minervino, J.B.S.; Veras, H.F.P.; Formighieri, A.; Santos, C.A.N.; Ferreira, M.A.D.; Figueiredo, E.O.; Ferreira, E.J.L. Individual Tree Detection and Species Classification of Amazonian Palms Using UAV Images and Deep Learning. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 475, 118397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veras, H.F.P.; Ferreira, M.P.; da Cunha Neto, E.M.; Figueiredo, E.O.; Corte, A.P.D.; Sanquetta, C.R. Fusing Multi-Season UAS Images with Convolutional Neural Networks to Map Tree Species in Amazonian Forests. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 71, 101815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyn, C.; Lejeune, P.; Michez, A.; Latte, N. Mapping Tree Species Proportions from Satellite Imagery Using Spectral–Spatial Deep Learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 280, 113205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibril, M.B.A.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Shanableh, A.; Al-Ruzouq, R.; Wayayok, A.; Hashim, S.J. Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Large-Scale Date Palm Tree Mapping from Uav-Based Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadwick, A.J.; Coops, N.C.; Bater, C.W.; Martens, L.A.; White, B. Species Classification of Automatically Delineated Regenerating Conifer Crowns Using RGB and Near-Infrared UAV Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Dong, R.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Multispecies Individual Tree Crown Extraction and Classification Based on BlendMask and High-Resolution UAV Images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2023, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Hao, Z.; Post, C.J.; Mikhailova, E.A.; Lin, L.; Zhao, G.; Tian, S.; Liu, J. Comparison of Classical Methods and Mask R-CNN for Automatic Tree Detection and Mapping Using UAV Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.; Bai, J.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, H.; Chen, L. Mapping Tree Species Composition Using OHS-1 Hyperspectral Data and Deep Learning Algorithms in Changbai Mountains, Northeast China. Forests 2019, 10, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Yan, W.; Li, D.; Li, J. 3D-Cnn Based Tree Species Classification Using Mobile Lidar Data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci.-ISPRS Arch. 2019, 42, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezami, S.; Khoramshahi, E.; Nevalainen, O.; Pölönen, I.; Honkavaara, E. Tree Species Classification of Drone Hyperspectral and RGB Imagery with Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Hao, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, S.; Li, Z.; Chen, E.; Tian, X.; Ren, M. TSCMDL: Multimodal Deep Learning Framework for Classifying Tree Species Using Fusion of 2-D and 3-D Features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, I.; Marconi, S.; Weinstein, B.; Bai, Y.; Wang, D.Z.; White, E.; Bohlman, S. Improving Rare Tree Species Classification Using Domain Knowledge. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartling, S.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Carron, J. Urban Tree Species Classification Using a Worldview-2/3 and LiDAR Data Fusion Approach and Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briechle, S.; Krzystek, P.; Vosselman, G. Silvi-Net—A Dual-CNN Approach for Combined Classification of Tree Species and Standing Dead Trees from Remote Sensing Data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 98, 102292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technology Application Center, University of New Mexico. Remote Sensing of Natural Resources; Technology Application Center, University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Aburaed, N.; Alkhatib, M.Q.; Marshall, S.; Zabalza, J.; Al Ahmad, H. A Review of Spatial Enhancement of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imaging Techniques. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 2275–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ke, Y.; Gong, H.; Li, X. Object-Based Urban Tree Species Classification Using Bi-Temporal WorldView-2 and WorldView-3 Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16917–16937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madonsela, S.; Cho, M.A.; Mathieu, R.; Mutanga, O.; Ramoelo, A.; Kaszta, Ż.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Wolff, E. Multi-Phenology WorldView-2 Imagery Improves Remote Sensing of Savannah Tree Species. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszta, Ż.; Van De Kerchove, R.; Ramoelo, A.; Cho, M.A.; Madonsela, S.; Mathieu, R.; Wolff, E. Seasonal Separation of African Savanna Components Using Worldview-2 Imagery: A Comparison of Pixel-and Object-Based Approaches and Selected Classification Algorithms. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheeren, D.; Fauvel, M.; Josipović, V.; Lopes, M.; Planque, C.; Willm, J.; Dejoux, J.-F. Tree Species Classification in Temperate Forests Using Formosat-2 Satellite Image Time Series. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, M.; Ostwald, M.; Reese, H.; Bazié, H.R.; Tankoano, B. Assessing the Potential of Multi-Seasonal WorldView-2 Imagery for Mapping West African Agroforestry Tree Species. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Landry, S. Mapping Urban Tree Species by Integrating Multi-Seasonal High Resolution Pléiades Satellite Imagery with Airborne LiDAR Data. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 53, 126675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, M.; Prexl, J.; Ebel, P.; Liebel, L.; Zhu, X.X. Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation of Satellite Images for Land Cover Mapping--Challenges and Opportunities. arXiv, 2020; arXiv:2002.08254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattenborn, T.; Leitloff, J.; Schiefer, F.; Hinz, S. Review on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) in Vegetation Remote Sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 24–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, B.G.; Marconi, S.; Bohlman, S.; Zare, A.; White, E. Individual Tree-Crown Detection in RGB Imagery Using Semi-Supervised Deep Learning Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromm, M.; Schubert, M.; Castilla, G.; Linke, J.; McDermid, G. Automated Detection of Conifer Seedlings in Drone Imagery Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, B.; Horanont, T.; Hung, N.D. Deep Learning Based Banana Plant Detection and Counting Using High-Resolution Red-Green-Blue (RGB) Images Collected from Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).