Response of the Stability of Soil Aggregates and Erodibility to Land Use Patterns in Wetland Ecosystems of Karst Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
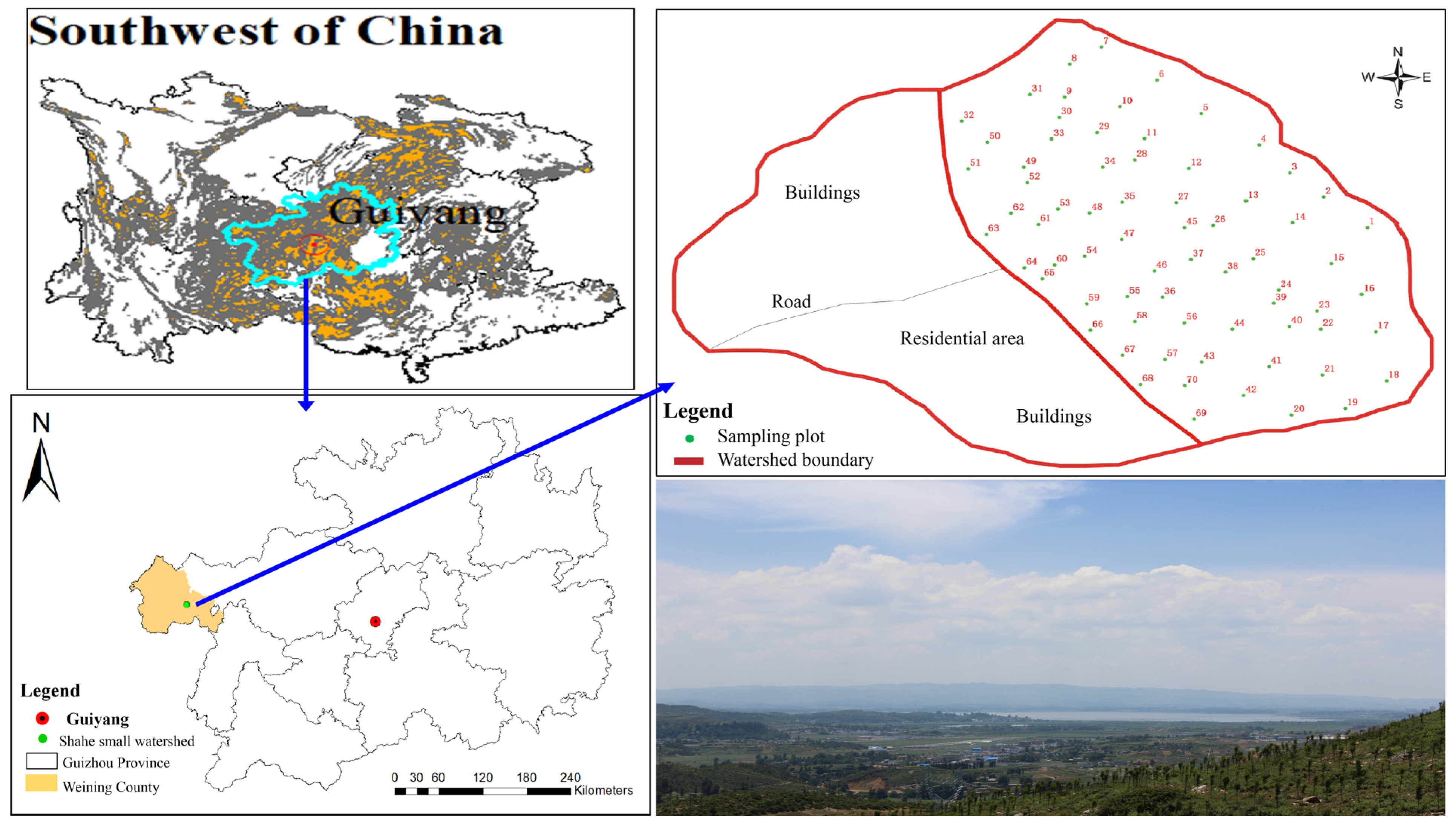
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Soil Sampling and Treatments
2.2.1. Experimental Design and Field Sampling
2.2.2. Calculation of Soil Index
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil in Different Land Use Patterns
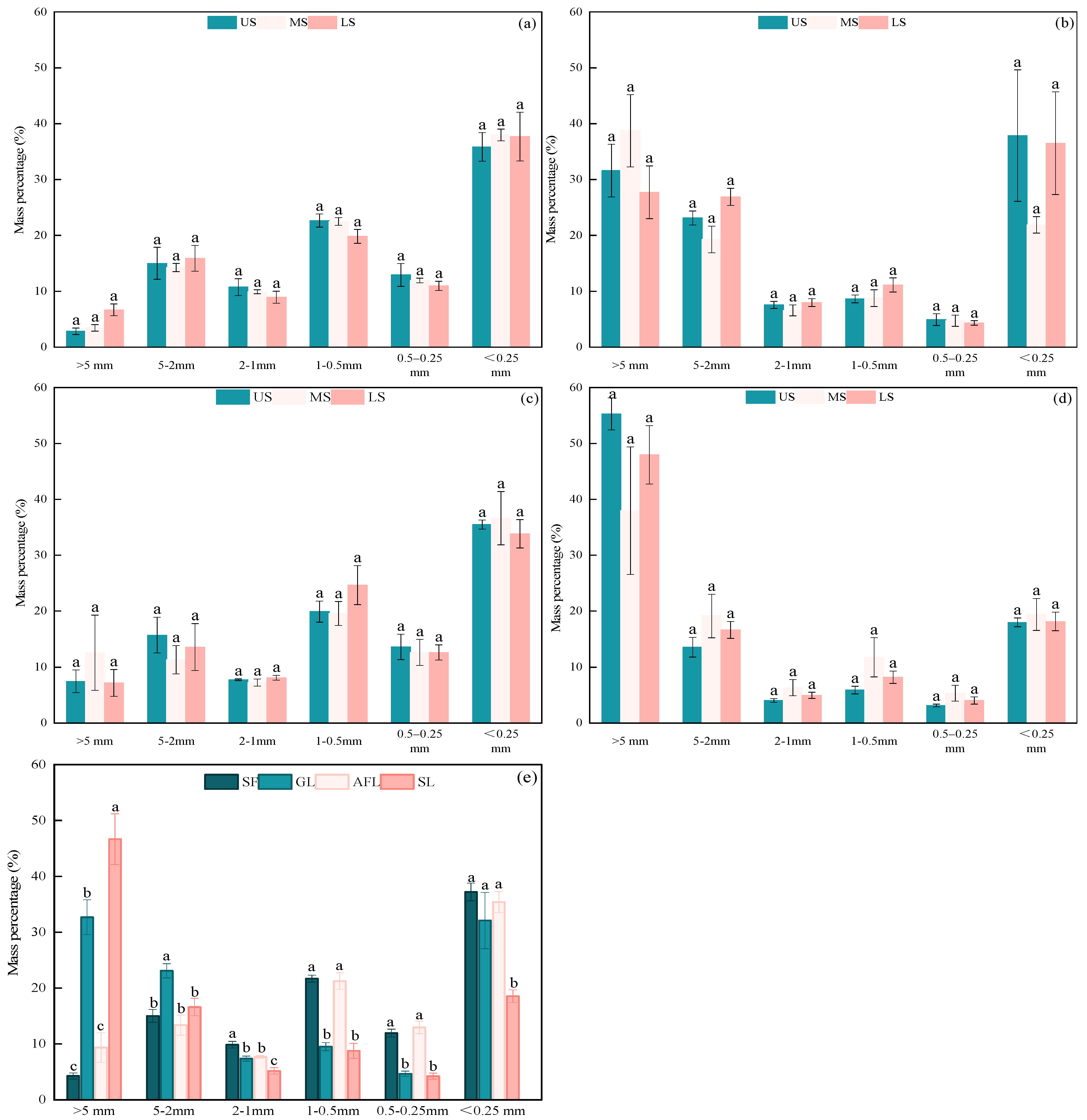
3.2. Distribution of Soil Water Stable Aggregate Fractions in Soils
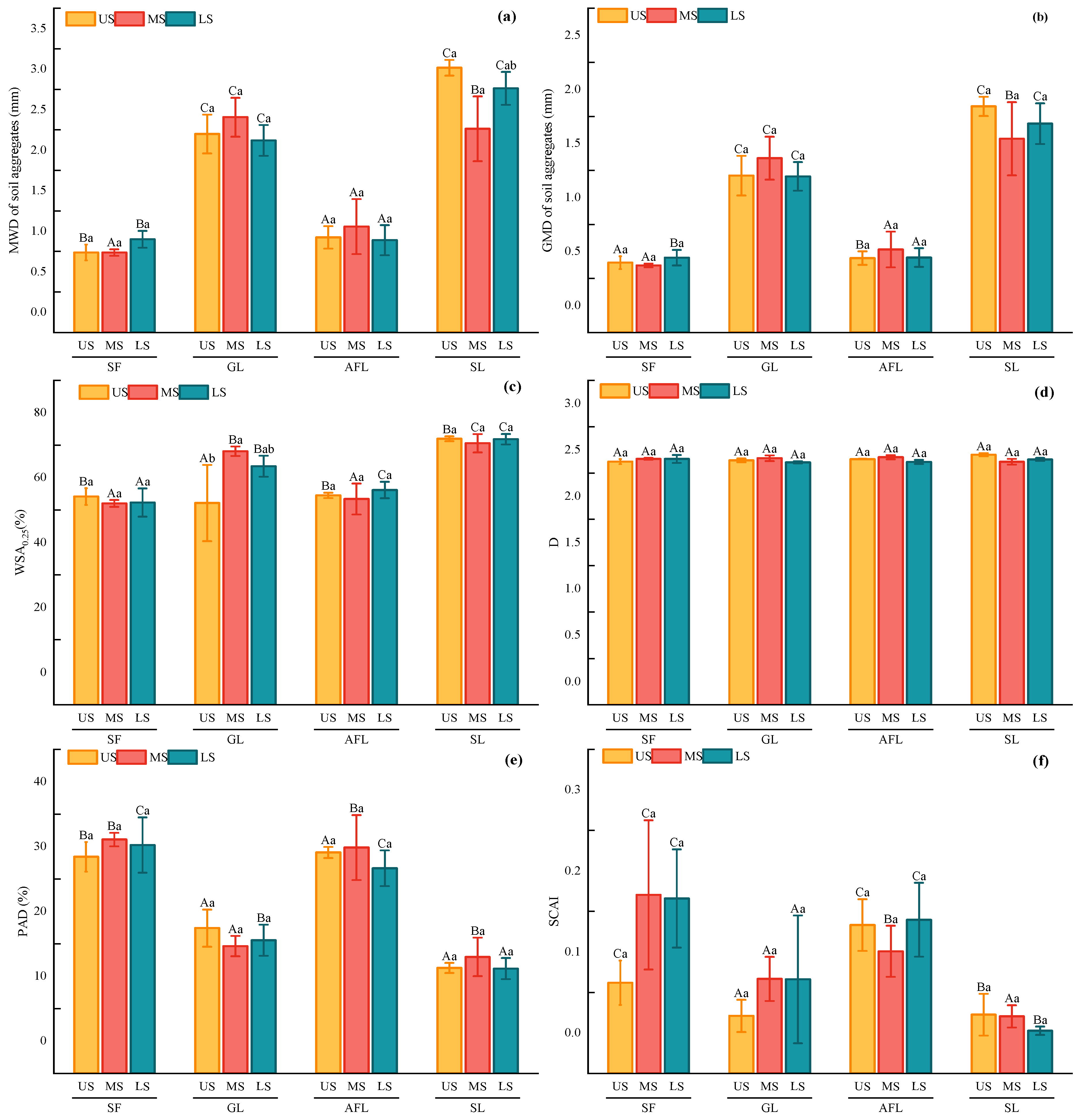
3.3. The Water Stability of Soil Aggregates under Different Land Uses
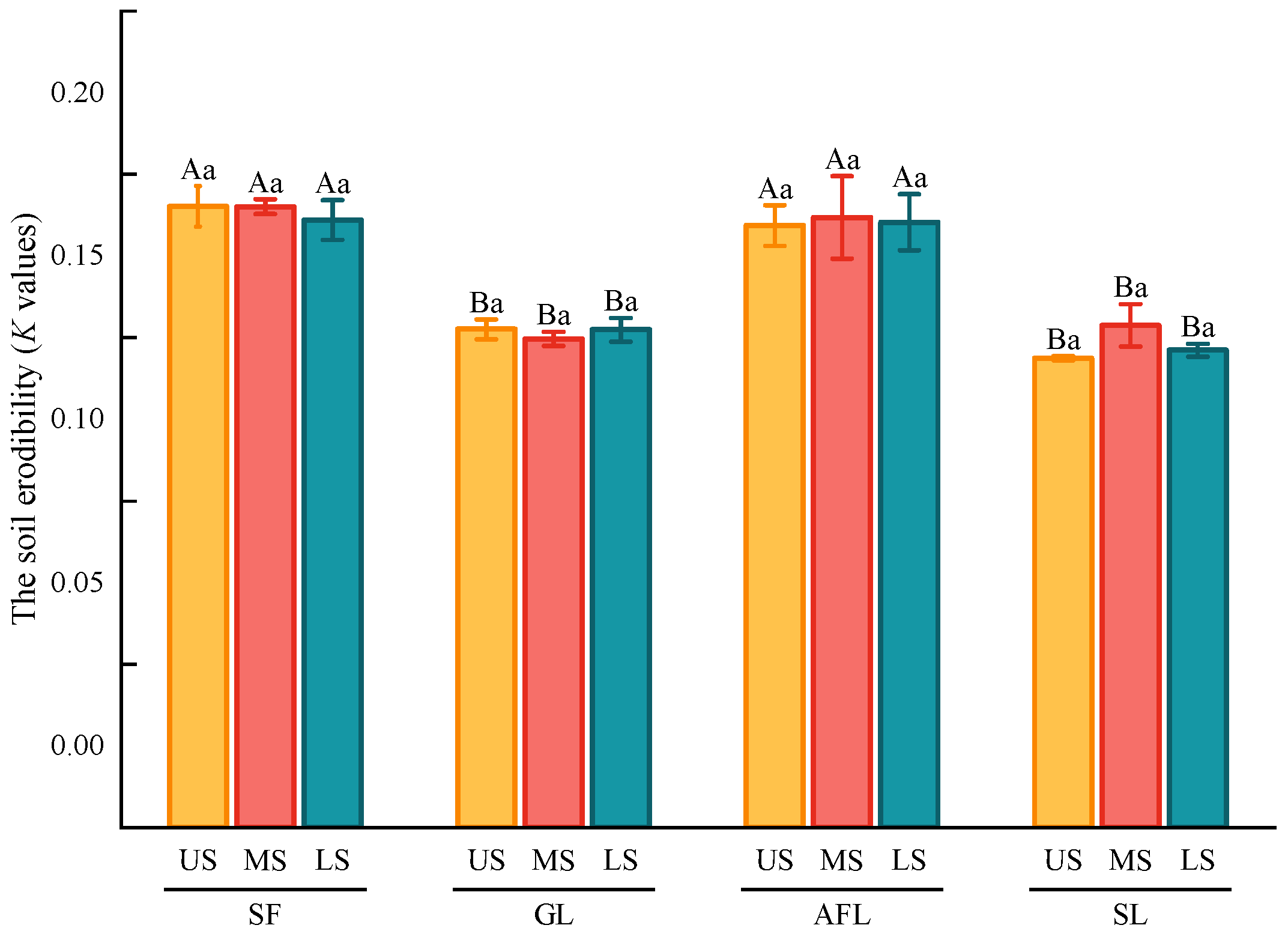
3.4. The Comparison of the Soil Erodibility
3.5. Correlation between Soil Properties and Soil Water Stable Aggregate Fraction
3.6. Comprehensive Evaluation of Soil Aggregate Stability
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Different Land Use Patterns on the Particle Size Distribution of Aggregates
4.2. Response of the Stability of Soil Aggregates to Different Land Use Patterns
4.3. Effects of the Pattern of Land Use on the Soil Erodibility
4.4. Correlation between Soil Aggregate Stability Index and Soil Properties
4.5. The Limit of Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fluet-Chouinard, E.; Stocker, B.D.; Zhang, Z.; Malhotra, A.; Melton, J.R.; Poulter, B.; Kaplan, J.O.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Siebert, S.; Minayeva, T.; et al. Extensive Global Wetland Loss over the Past Three Centuries. Nature 2023, 614, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schütt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. An Assessment of the Global Impact of 21st Century Land Use Change on Soil Erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devátý, J.; Dostál, T.; Hösl, R.; Krása, J.; Strauss, P. Effects of Historical Land Use and Land Pattern Changes on Soil Erosion—Case Studies from Lower Austria and Central Bohemia. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zhang, K.; He, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z. Linking Rocky Desertification to Soil Erosion by Investigating Changes in Soil Magnetic Susceptibility Profiles on Karst Slopes. Geoderma 2021, 389, 114949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X. Distribution and Migration Characteristics of Microplastics in Farmland Soils, Surface Water and Sediments in Caohai Lake, Southwestern Plateau of China. J. Cleaner Prod. 2022, 366, 132912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Tan, W.; Fang, L.; Ji, L.; Deng, H. Spatial Analysis of Soil Aggregate Stability in a Small Catchment of the Loess Plateau, China: I. Spatial Variability. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Qiu, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, B.; Shao, M. Response of Soil OC, N and P to Land-Use Change and Erosion in the Black Soil Region of the Northeast China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 302, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Paustian, K. Aggregate-Associated Soil Organic Matter as an Ecosystem Property and a Measurement Tool. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, A4–A9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, Y.; Yang, Y.; An, S.; Zhu, Z. Effects of Different Vegetation Restoration Measures on Soil Aggregate Stability and Erodibility on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2020, 185, 104294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounirou, L.A.; Yonaba, R.; Tazen, F.; Ayele, G.T.; Yaseen, Z.M.; Karambiri, H.; Yacouba, H. Soil Erosion across Scales: Assessing Its Sources of Variation in Sahelian Landscapes under Semi-Arid Climate. Land 2022, 11, 2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaca, F.; Lax, A.; Albaladejo, J. Soil Aggregate Stability and Organic Matter in Clay and Fine Silt Fractions in Urban Refuse-amended Semiarid Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, L.; Zhang, Z.; Carlson, K.M.; MacDonald, G.K.; Brauman, K.A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Zhao, X.; et al. Progress towards Sustainable Intensification in China Challenged by Land-Use Change. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweizer, S.A.; Fischer, H.; Häring, V.; Stahr, K. Soil Structure Breakdown Following Land Use Change from Forest to Maize in Northwest Vietnam. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delelegn, Y.T.; Purahong, W.; Blazevic, A.; Yitaferu, B.; Wubet, T.; Göransson, H.; Godbold, D.L. Changes in Land Use Alter Soil Quality and Aggregate Stability in the Highlands of Northern Ethiopia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melese, T.; Senamaw, A.; Belay, T.; Bayable, G. The Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Land Use Land Cover Change, and Its Impact on Soil Erosion in Tagaw Watershed, Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Glob. Chall. 2021, 5, 2000109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrends Kraemer, F.; Hallett, P.D.; Morrás, H.; Garibaldi, L.; Cosentino, D.; Duval, M.; Galantini, J. Soil Stabilisation by Water Repellency under No-till Management for Soils with Contrasting Mineralogy and Carbon Quality. Geoderma 2019, 355, 113902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorji, T.; Field, D.J.; Odeh, I.O.A. Soil Aggregate Stability and Aggregate–associated Organic Carbon under Different Land Use or Land Cover Types. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 36, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, H.; Xie, Y.; Lu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Ma, J. Response of Soil Aggregate Stability and Erodibility to Different Treatments on Typical Steppe in the Loess Plateau, China. Restor. Ecol. 2022, 30, e13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z. Effects of Soil Aggregate Stability on Soil N Following Land Use Changes under Erodible Environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S.; Liu, W.; Ren, C.; Yang, G.; Ren, G. Effects of Land Use Change on Organic Carbon Dynamics Associated with Soil Aggregate Fractions on the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J. Changes of Soil Aggregate Stability and Erodibility After Cropland Conversion in Degraded Karst Region. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 3333–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wan, F.; Zhang, B. Evaluation of Soil Antierodibility of Different Forests in Volcanic Hilly Land of Xuyi County. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 7–11. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madenoglu, S.; Atalay, F.; Erpul, G. Uncertainty Assessment of Soil Erodibility by Direct Sequential Gaussian Simulation (DSIM) in Semiarid Land Uses. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H. Variation in Soil Erodibility under Five Typical Land Uses in a Small Watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 174, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, P.; Wang, C.; Wan, Y. Impact of Land Use Type on Soil Erodibility in a Small Watershed of Rolling Hill Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 227, 105597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, G. Assessing Soil Degradation under Land-Use Change: Insight from Soil Erosion and Soil Aggregate Stability in a Small Karst Catchment in Southwest China. PeerJ 2020, 8, e8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jin, R.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X. Impacts of Land Use Changes on Wetland Ecosystem Services in the Tumen River Basin. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Lin, C. The Distribution Characteristics of Soil Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Under Different Land Use Patterns in Caohai Plateau Wetland. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 199–204. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Lin, C. Pollution Characteristics and Potential Ecological Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Caohai in Guizhou Province, China. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 2236–2241. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Ji, Y.; Chen, Y. Distribution Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Total Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Total Phosphorus in Sediments of Caohai Lake, China. Earth Environ. 2016, 44, 297–303. (in Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Ma, L.; Sun, R.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Yan, D.; Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Y. Evaluation of Potential Ecological Risk, Possible Sources and Controlling Factors of Heavy Metals in Surface Sediment of Caohai Wetland, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastola, S.; Dialynas, Y.G.; Bras, R.L.; Noto, L.V.; Istanbulluoglu, E. The Role of Vegetation on Gully Erosion Stabilization at a Severely Degraded Landscape: A Case Study from Calhoun Experimental Critical Zone Observatory. Geomorphology 2018, 308, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Y. Aggregate Stability and Size Distribution of Red Soils under Different Land Uses Integrally Regulated by Soil Organic Matter, and Iron and Aluminum Oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Soil Chemical and Physical Analysis; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Keeney, D.R. Determination and Isotope-Ratio Analysis of Different Forms of Nitrogen in Soils: 3. Exchangeable Ammonium, Nitrate, and Nitrite by Extraction-Distillation Methods. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1966, 30, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zheng, F.; Wen, L.; Shen, H. Effects of Sheet and Rill Erosion on Soil Aggregates and Organic Carbon Losses for a Mollisol Hillslope under Rainfall Simulation. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Pendall, E.; Bell, C.; Wallenstein, M.D. Soil Aggregate Size Distribution Mediates Microbial Climate Change Feedbacks. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 68, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Zhang, W.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, K. Soil Aggregate Mediates the Impacts of Land Uses on Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Microbial Activity in a Karst Ecosystem. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Long, J.; Li, J. Conversion of Cropland to Chinese Prickly Ash Orchard Affects Soil Organic Carbon Dynamics in a Karst Region of Southwest China. Nutr. Cycling Agroecosyst. 2016, 104, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelaw, A.M.; Singh, B.R.; Lal, R. Organic Carbon and Nitrogen Associated with Soil Aggregates and Particle Sizes Under Different Land Uses in Tigray, Northern Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Han, X.; Zhang, Y.; Long, J.; Li, N. 31-Year Contrasting Agricultural Managements Affect the Distribution of Organic Carbon in Aggregate-Sized Fractions of a Mollisol. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoubi, S.; Mokhtari Karchegani, P.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Honarjoo, N. Soil Aggregation and Organic Carbon as Affected by Topography and Land Use Change in Western Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 121, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Carbon and Nitrogen Distribution in Aggregates from Cultivated and Native Grassland Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1993, 57, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Xu, C.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; He, X. Particles Interaction Forces and Their Effects on Soil Aggregates Breakdown. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 147, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Tang, Z.; Shangguan, Z.; Peng, C.; Deng, L. Factors Affecting the Spatial and Temporal Variations in Soil Erodibility of China. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padbhushan, R.; Rakshit, R.; Das, A.; Sharma, R.P. Effects of Various Organic Amendments on Organic Carbon Pools and Water Stable Aggregates under a Scented Rice–Potato–Onion Cropping System. Paddy Water Environ. 2016, 14, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, I. Land-Use Effects on Organic Matter and Physical Properties of Soil in a Southern Mediterranean Highland of Turkey. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 83, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.-L.; Ding, G.-D.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Qin, S.-G.; Bao, Y.-F.; Yu, M.-H.; Liu, Y.-D. Fractal Approach to Estimating Changes in Soil Properties Following the Establishment of Caragana Korshinskii Shelterbelts in Ningxia, NW China. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 43, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhu, H.; Fu, W.; Shao, M. Responses of Soil Aggregate Stability, Erodibility and Nutrient Enrichment to Simulated Extreme Heavy Rainfall. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, T.; Liu, W.; Xia, D.; Xia, L.; Guo, T.; Ma, Y.; Xu, W.; Hu, Y. Effects of Land Use Types on Soil Erodibility in a Small Karst Watershed in Western Hubei. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaezi, A.R.; Sadeghi, S.H.R.; Bahrami, H.A.; Mahdian, M.H. Modeling the USLE K-Factor for Calcareous Soils in Northwestern Iran. Geomorphology 2008, 97, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K. Filling the European Blank Spot—Swiss Soil Erodibility Assessment with Topsoil Samples. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ruiz, J.M.; Beguería, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.; González-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Sanjuán, Y. A Meta-Analysis of Soil Erosion Rates across the World. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Xiao, H.; Ning, K.; Tang, C. Effects of Land Use and Land Cover on Soil Erosion Control in Southern China: Implications from a Systematic Quantitative Review. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 282, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-W.; Zhang, G.-H.; Geng, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.C. Land Use Impacts on Soil Detachment Capacity by Overland Flow in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2015, 124, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Peng, X.; Peth, S.; Xiao, T.Q. Effects of Vegetation Restoration on Soil Aggregate Microstructure Quantified with Synchrotron-Based Micro-Computed Tomography. Soil Tillage Res. 2012, 124, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérès, G.; Cluzeau, D.; Menasseri, S.; Soussana, J.F.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Habekost, M.; Gleixner, G.; Weigelt, A.; Weisser, W.W.; et al. Mechanisms Linking Plant Community Properties to Soil Aggregate Stability in an Experimental Grassland Plant Diversity Gradient. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erktan, A.; Cécillon, L.; Graf, F.; Roumet, C.; Legout, C.; Rey, F. Increase in Soil Aggregate Stability along a Mediterranean Successional Gradient in Severely Eroded Gully Bed Ecosystems: Combined Effects of Soil, Root Traits and Plant Community Characteristics. Plant Soil 2016, 398, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikary, P.P.; Tiwari, S.P.; Mandal, D.; Lakaria, B.L.; Madhu, M. Geospatial Comparison of Four Models to Predict Soil Erodibility in a Semi-Arid Region of Central India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 5049–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesodun, J.; Adeyemi, E.; Oyegoke, C. Distribution of Nutrient Elements within Water-Stable Aggregates of Two Tropical Agro-Ecological Soils under Different Land Uses. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 92, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sheng, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, L. Effects of Land Use Change on Constitution, Stability, and C, N, P Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Aggregates in Southwest China. Environm. Sci. 2022, 43, 3752–3762. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Types | Slope | SOC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (mg kg−1) | AN (g kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | SWC (%) | BD (g cm−3) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | |||||||||
| Sloping farmland | US | 23.56 ± 5.16 Aa | 0.28 ± 0.02 ABa | 0.52 ± 0.06 Aa | 112.63 ± 11.80 ABa | 14.05 ± 3.01 ABa | 17.23 ± 1.13 Aa | 1.38 ± 0.06 Cb | 7.17 ± 0.34 Aa |
| MS | 17.74 ± 2.88 Aab | 0.28 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.37 ± 0.06 ABa | 106.76 ± 12.38 Aa | 9.18 ± 2.20 Ab | 19.17 ± 1.17 Aa | 1.63 ± 0.07 Aa | 6.77 ± 0.34 Aa | |
| LS | 22.45 ± 1.85 Aa | 0.30 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.45 ± 0.05 Aa | 111.49 ± 6.11 Aa | 13.21 ± 2.16 Aa | 15.77 ± 1.87 Aa | 1.53 ± 0.05 Cab | 7.05 ± 0.43 Aa | |
| Grassland | US | 25.10 ± 4.10 Aa | 0.32 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.52 ± 0.08 Aa | 126.70 ± 14.93 Aa | 9.36 ± 1.73 ABa | 17.07 ± 1.09 Aa | 1.73 ± 0.07 ABa | 7.35 ± 0.26 Aa |
| MS | 19.07 ± 4.59 Aab | 0.29 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.53 ± 0.12 Aa | 142.98 ± 9.55 Aa | 9.51 ± 2.67 Aa | 17.30 ± 0.97 Aa | 1.79 ± 0.04 Aa | 7.27 ± 0.22 Aa | |
| LS | 20.68 ± 3.45 Aa | 0.24 ± 0.01 Aa | 0.33 ± 0.03 Ba | 95.69 ± 6.95 Ab | 4.68 ± 1.10 Bb | 19.72 ± 1.87 Aa | 1.92 ± 0.04 Aa | 7.58 ± 0.11 Aa | |
| Artificial forest land | US | 19.44 ± 4.69 Aab | 0.23 ± 0.03 Ba | 0.21 ± 0.02 Bb | 77.76 ± 16.49 Ba | 2.77 ± 1.79 Ba | 19.31 ± 1.23 Aab | 1.84 ± 0.06 Da | 7.72 ± 0.10 Aa |
| MS | 13.12 ± 4.61 Ab | 0.24 ± 0.04 Aa | 0.25 ± 0.02 Bab | 83.11 ± 21.56 Ba | 1.87 ± 0.98 Ba | 15.39 ± 2.17 Ab | 1.63 ± 0.13 Aa | 6.33 ± 0.43 Ab | |
| LS | 24.48 ± 9.35 Aa | 0.23 ± 0.07 Aa | 0.29 ± 0.03 Ba | 83.92 ± 19.63 Aa | 2.57 ± 0.69 Ba | 20.91 ± 1.17 Aa | 1.80 ± 0.05 ABa | 6.96 ± 0.53 Aab | |
| Shrubland | US | 22.23 ± 5.17 Aa | 0.27 ± 0.03 ABa | 0.29 ± 0.03 Ba | 109.63 ± 12.53 ABa | 4.03 ± 0.89 Ba | 17.66 ± 2.18 Aa | 1.63 ± 0.07 Ba | 7.56 ± 0.15 Aa |
| MS | 26.30 ± 7.72 Aa | 0.28 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.28 ± 0.03 Ba | 126.54 ± 28.56 Aa | 2.378 ± 0.43 Ba | 19.76 ± 1.87 Aa | 1.70 ± 0.06 Aa | 6.78 ± 0.47 Aa | |
| LS | 22.61 ± 6.59 Aa | 0.28 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.27 ± 0.02 Ba | 106.54 ± 21.63 Aa | 2.94 ± 0.88 Ba | 18.65 ± 1.55 Aa | 1.73 ± 0.04 Ba | 7.25 ± 0.33 Aa |
| Indexes | PCs | Coefficient Matrix | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| X1 | 0.096 | −0.124 | 0.662 | 0.239 | −0.134 | 0.210 | 0.548 | 0.003 |
| X2 | 0.365 | −0.502 | 0.385 | 0.191 | −0.019 | 0.029 | 0.397 | 0.059 |
| X3 | 0.369 | 0.470 | 0.291 | −0.004 | 0.033 | 0.204 | 0.179 | −0.105 |
| X4 | 0.081 | 0.795 | 0.301 | 0.24 | −0.047 | 0.338 | 0.188 | 0.077 |
| X5 | 0.208 | 0.826 | −0.039 | 0.061 | 0.066 | 0.212 | −0.092 | 0.031 |
| X6 | 0.089 | 0.827 | 0.033 | 0.123 | 0.019 | 0.245 | −0.034 | 0.061 |
| X7 | −0.467 | 0.534 | −0.293 | 0.066 | −0.042 | 0.060 | −0.282 | 0.120 |
| X8 | −0.331 | 0.656 | −0.235 | −0.036 | −0.013 | 0.087 | −0.269 | 0.017 |
| X9 | 0.947 | 0.079 | −0.172 | 0.136 | 0.244 | 0.010 | −0.043 | 0.158 |
| X10 | 0.945 | 0.100 | −0.146 | 0.172 | 0.236 | 0.031 | −0.019 | 0.179 |
| X11 | 0.754 | 0.193 | 0.014 | −0.229 | 0.189 | 0.012 | −0.015 | −0.195 |
| X12 | 0.010 | −0.215 | −0.300 | 0.906 | −0.004 | 0.056 | 0.012 | 0.825 |
| X13 | −0.933 | −0.174 | 0.056 | 0.234 | −0.245 | 0.012 | 0.054 | 0.177 |
| X14 | 0.564 | −0.527 | −0.352 | −0.046 | 0.196 | −0.237 | −0.17 | 0.085 |
| Eigenvalue | 2.697 | 2.938 | 0.205 | 2.053 | ||||
| Variance (%) | 39.500 | 31.387 | 17.319 | 11.794 | ||||
| Cumulative variance (%) | 28.642 | 51.401 | 63.958 | 72.511 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cen, L.; Peng, X.; Dai, Q. Response of the Stability of Soil Aggregates and Erodibility to Land Use Patterns in Wetland Ecosystems of Karst Plateau. Forests 2024, 15, 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040599
Cen L, Peng X, Dai Q. Response of the Stability of Soil Aggregates and Erodibility to Land Use Patterns in Wetland Ecosystems of Karst Plateau. Forests. 2024; 15(4):599. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040599
Chicago/Turabian StyleCen, Longpei, Xudong Peng, and Quanhou Dai. 2024. "Response of the Stability of Soil Aggregates and Erodibility to Land Use Patterns in Wetland Ecosystems of Karst Plateau" Forests 15, no. 4: 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040599
APA StyleCen, L., Peng, X., & Dai, Q. (2024). Response of the Stability of Soil Aggregates and Erodibility to Land Use Patterns in Wetland Ecosystems of Karst Plateau. Forests, 15(4), 599. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15040599








