The Effects of Forest Gaps on the Physical and Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Area and Methods
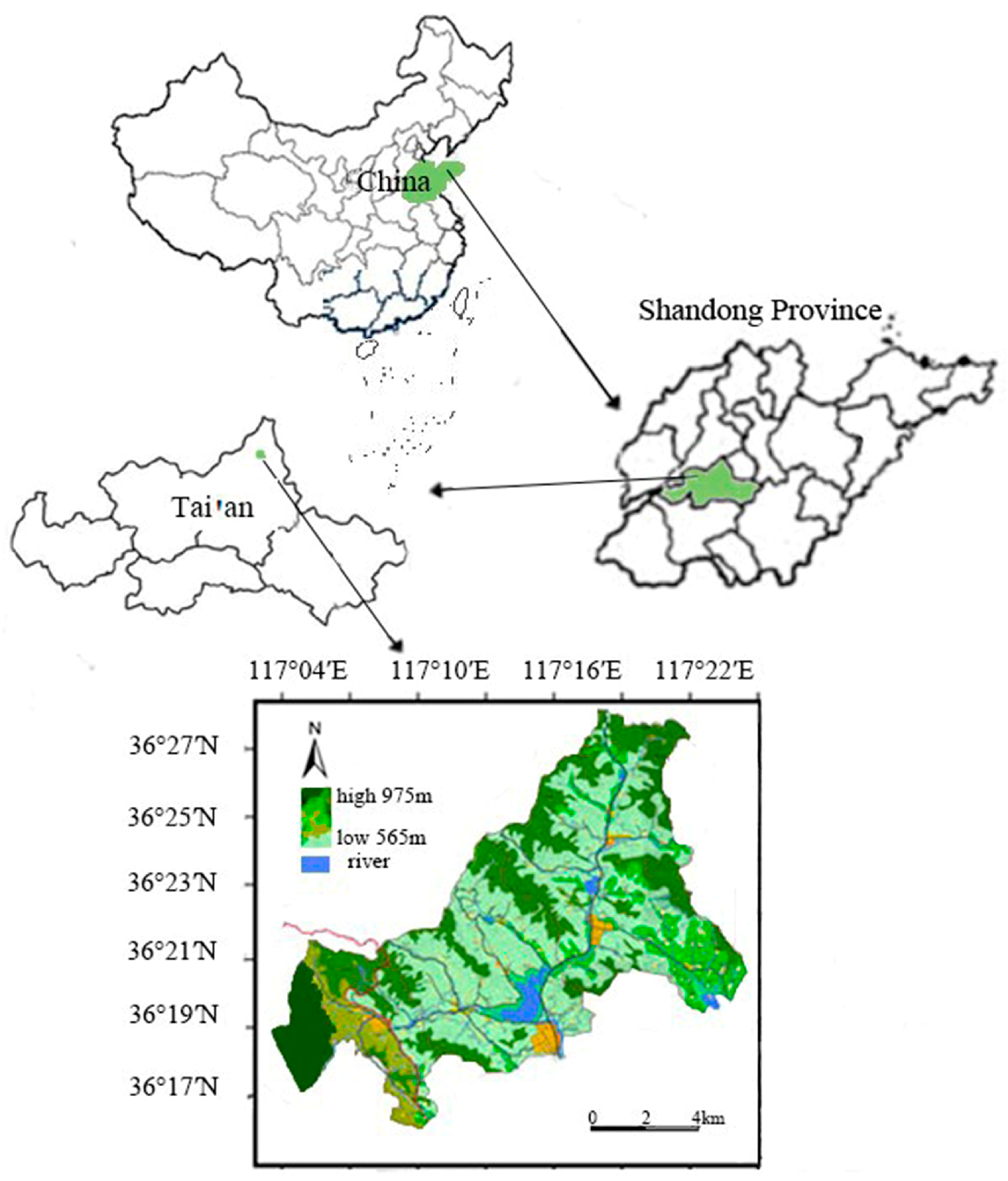
2.1. Introduction to the Study Area
2.2. Sample Plot Setting and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Processing and Determination
2.4. Data Analysis and Processing
2.4.1. Soil Fractal Dimension
2.4.2. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Physical Properties of Soil in Gap and Non-Gap Forests of Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L.
3.1.1. Soil Physical Indicators
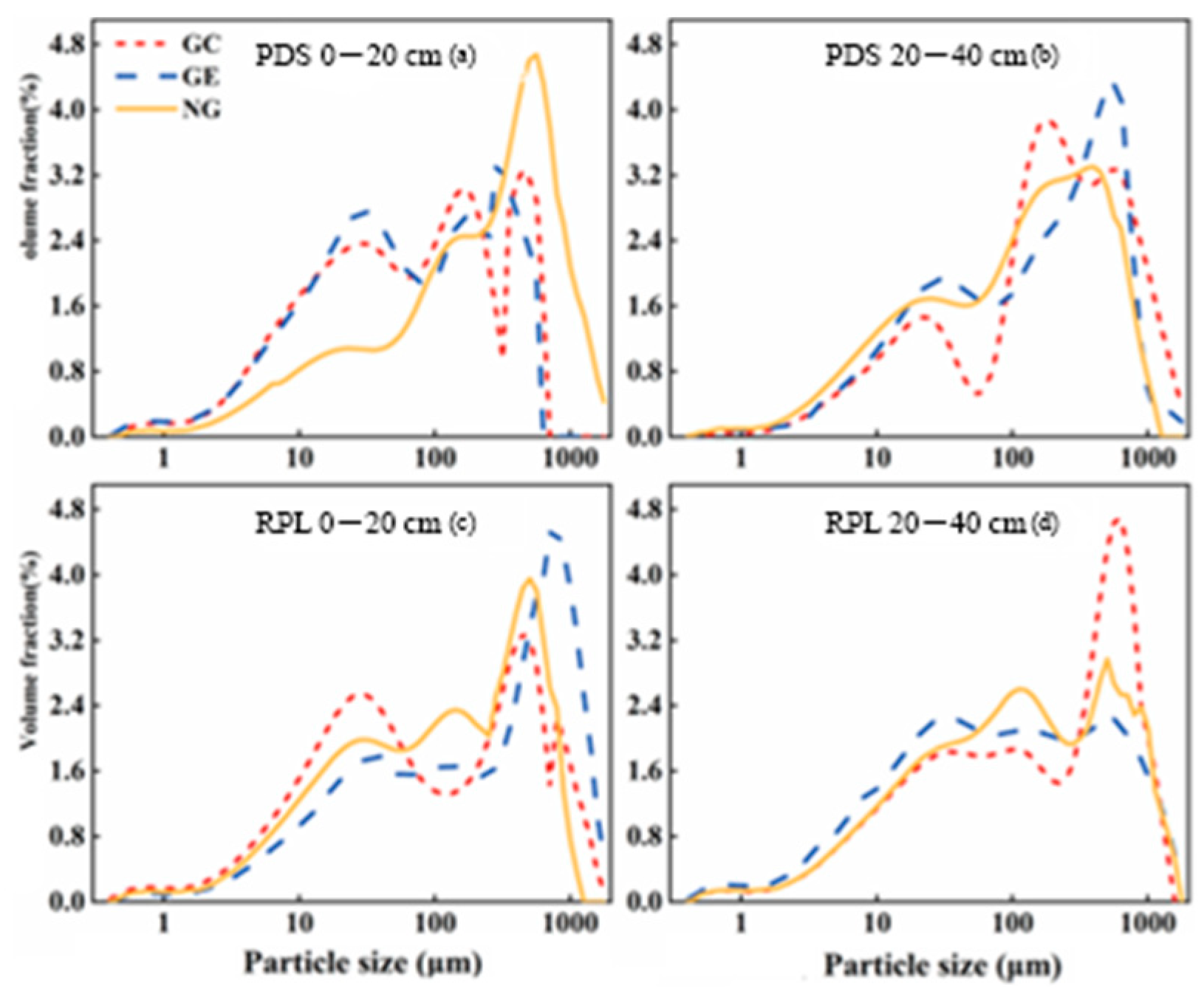
3.1.2. Soil Particle Composition and Distribution Characteristics
3.2. Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Forest Gaps and Non-Gaps of Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests
3.2.1. Soil Chemical Indicators and C, N, and P Contents
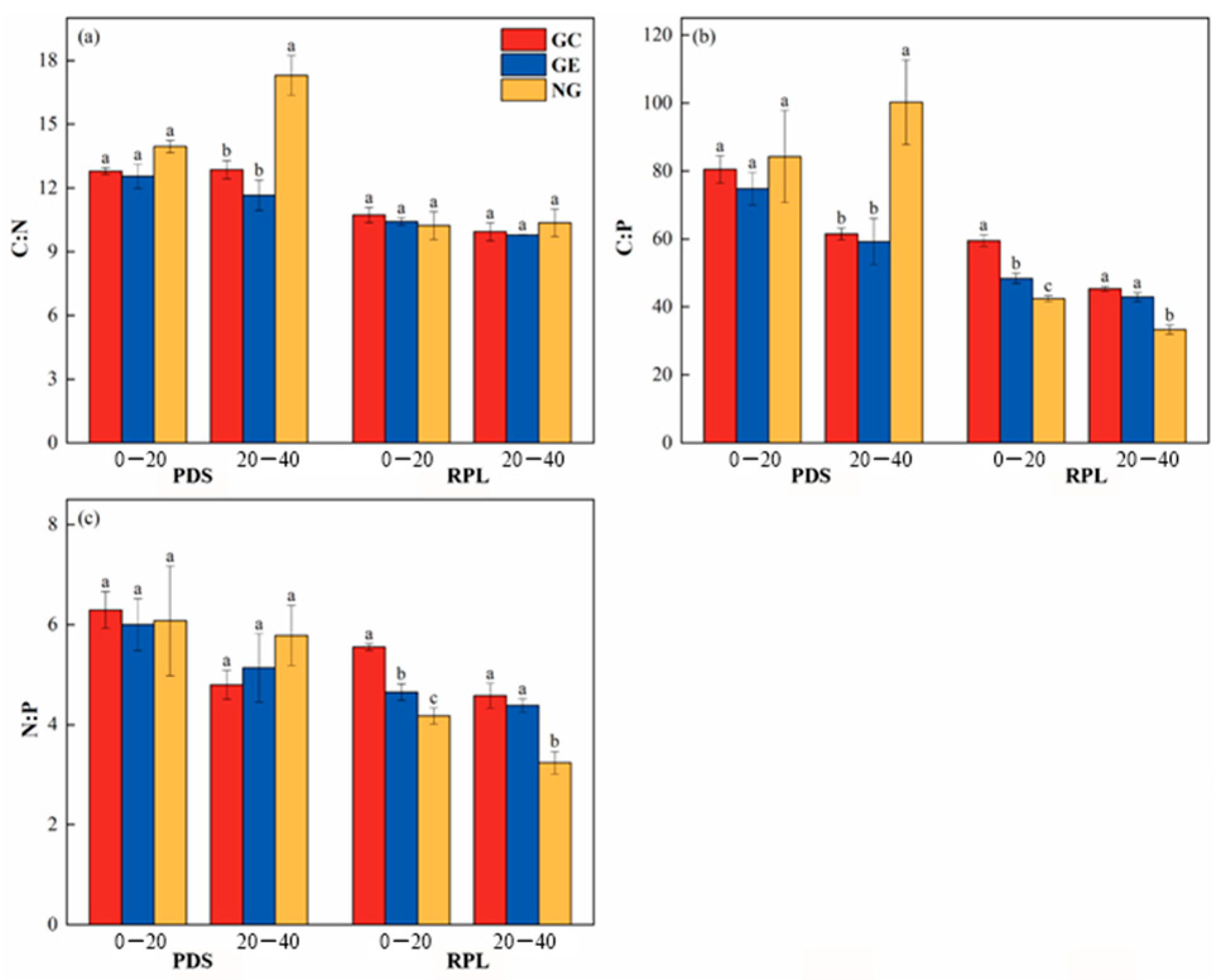
3.2.2. Characteristics of Soil’s Ecological Stoichiometry
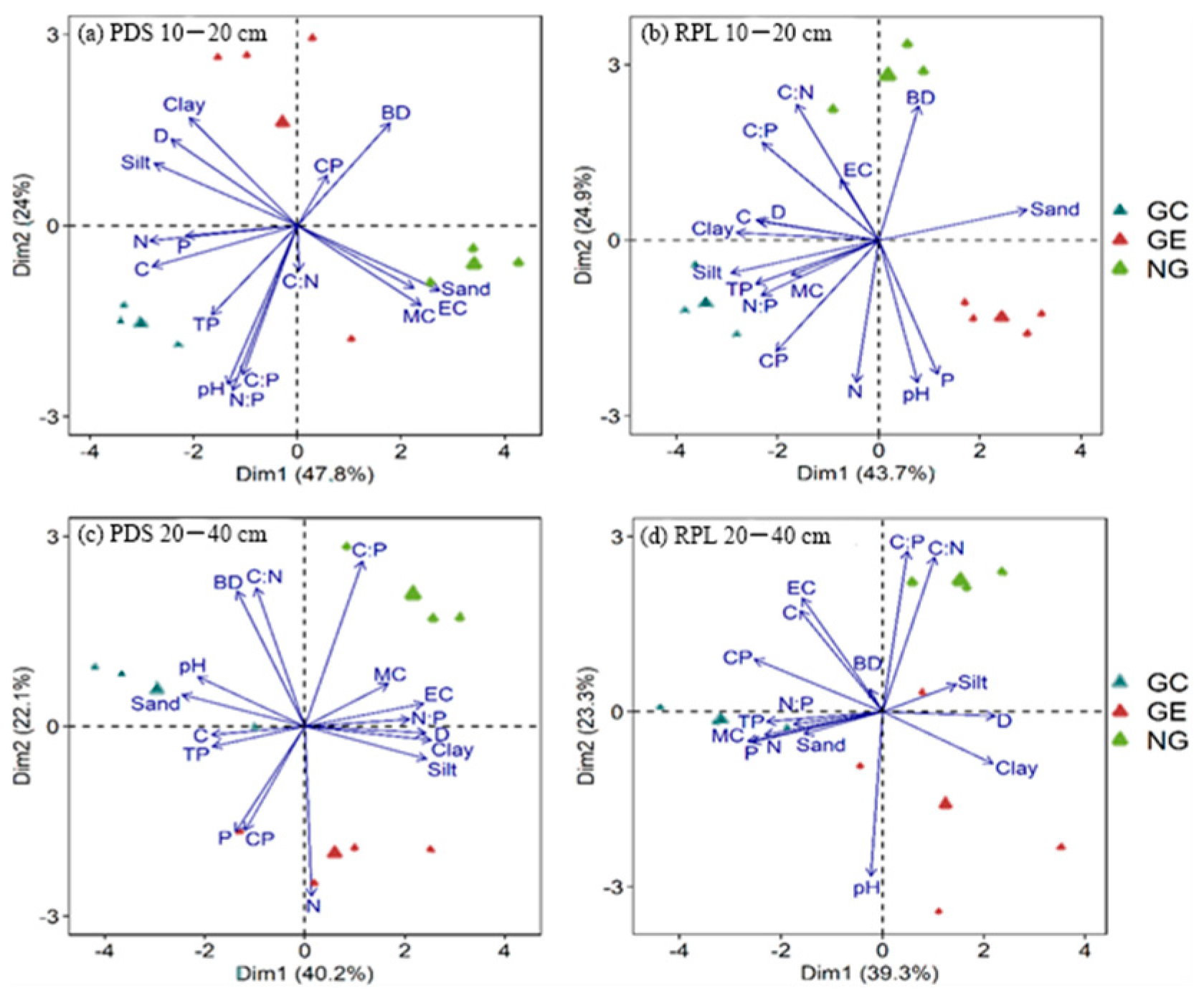
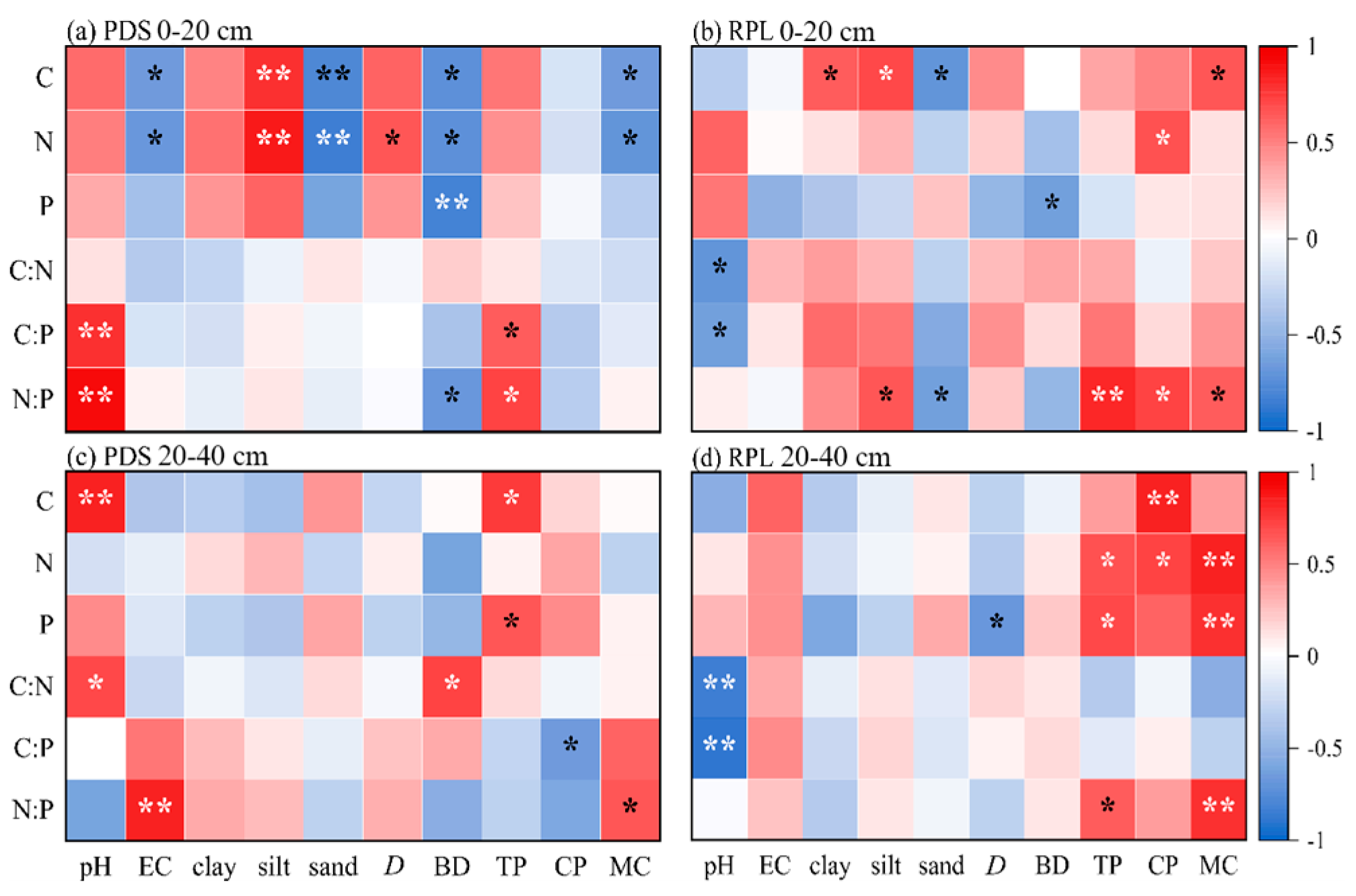
3.3. Correlation Analysis between Soil’s Ecological Stoichiometry and Soil-Related Properties in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forest Gaps
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Forest Gaps on the Soil Physical Properties of Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests
4.2. Effects of Forest Gaps on the Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Factors | df | C | N | P | C:N | C:P | N:P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forest | 1 | F | 0.121 | 65.457 ** | 48.241 ** | 216.750 ** | 232.887 ** | 3.840 |
| P | 0.731 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.060 | ||
| Forest Gap | 2 | F | 54.350 ** | 71.941 ** | 31.574 ** | 91.134 ** | 85.589 ** | 0.259 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.773 | ||
| Soil layer | 1 | F | 278.481 ** | 291.262 ** | 68.698 ** | 2.354 | 87.922 ** | 21.844 ** |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.136 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| F × G | 2 | F | 36.935 ** | 13.531 ** | 9.334 ** | 28.402 ** | 11.768 ** | 2.379 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.111 | ||
| F × S | 1 | F | 8.689 * | 2.594 | 1.184 | 4.633 * | 0.067 | 0.071 |
| P | 0.006 | 0.119 | 0.286 | 0.040 | 0.797 | 0.792 | ||
| G × S | 2 | F | 23.718 ** | 18.701 ** | 4.176 * | 10.388 ** | 26.159 ** | 10.172 ** |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.026 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| F × G × S | 2 | F | 17.694 ** | 25.387 ** | 3.390 * | 19.851 ** | 10.791 ** | 8.034 * |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.048 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
References
- Tian, A.; Halik, Ü.; Fu, W.; Sawirdin, S.; Cheng, S.; Lei, J. Research History of Forest Gap as Small-Scale Disturbances in Forest Ecosystems. Forests 2023, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandpré, L.; Boucher, D.; Bergeron, Y.; Gagnon, D. Effects of small canopy gaps on boreal mixedwood understory vegetation dynamics. Community Ecol. 2011, 12, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebe, S.A.; Morris, D.M.; Luckai, N.J.; Reid, D.E.B. The influence of coarse woody debris on soil carbon and nutrient pools 15 years after clearcut harvesting in black spruce—Dominated stands in northwestern Ontario, Canada. Écoscience 2014, 21, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Wang, C.; Yuan, X.; Tao, L.; Li, P.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of Different Forest Gap Ages on Soil Physical Properties and Stoichiometric Characteristics in Cryptomeria japonica plantations (L.f.) D.Don, 1839. Forests 2022, 13, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B.; Liu, K.; Dong, K.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y. Effects of thinning on growth and soil organic carbon of Cryptomeria fortunei Plantation in Western Sichuan. For. Resour. Manag. 2020, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Liu, J.; Su, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, D.; Wu, Z.; Hong, W.; Wang, J.L.-M. Effects of Forest Gaps on Soil Properties in Castanopsis kawakamii Nature Forest. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, N.; Zhang, B.; Yang, H. Variation in soil erodibility under five typical land uses in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 174, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Latif, Z.; Blackburn, G.A. The effects of gap size on some microclimate variables during late summer and autumn in a temperate broadleaved deciduous forest. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2010, 54, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L. Effects of Different Reform Modes on Soil Quality of Low-Efficiency Forests in Low Mountain and Hilly Areas of Sichuan Province; Sichuan Agricultural University: Yaan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco, J.A.; Bosco Imbert, J.; Castillo, F.J. Effects of thinning on nutrient content pools in two Pinus sylvestris forests in the western Pyrenees. Scand. J. For. Res. 2006, 21, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzgall, K.; Vidal, A.; Schubert, D.I.; Höschen, C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Buegger, F.; Pouteau, V.; Chenu, C.; Mueller, C.W. Particulate organic matter as a functional soil component for persistent soil organic carbon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y. Non-structural carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus between black locust and chinese pine plantations along a precipitation gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Trees 2018, 32, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Du, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Wu, Q. Effects of Forest Gaps on Abies faxoniana Rehd. Leaf Litter Mass Loss and Carbon Release along an Elevation Gradient in a Subalpine Forest. Forests 2022, 13, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X. A Review on Effects of Forest Gap. World For. Res. 2016, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ye, W. Adcances in study on forest gaps. J. Trop. Subtrop. Bot. 2001, 9, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, X.; Yang, W.; Tan, B.; Li, H.; He, J.; Xu, L.; Wu, F. Forest gaps slow the sequestration of soil organic matter: A humification experiment with six foliar litters in an alpine forest. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharenbroch, B.C.; Bockheim, J.G. Impacts of forest gaps on soil properties and processes in old growth northern hardwood-hemlock forests. Plant Soil 2007, 294, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Pieristè, M.; Liu, C.; Kenta, T.; Robson, T.M.; Kurokawa, H. The contribution of photodegradation to litter decomposition in a temperate forest gap and understorey. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 2625–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Chen, G.; Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, X. Effects of Forest Gaps on the Structure and Diversity of Soil Bacterial Communities in Weeping Cypress Forest Plantations. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 882949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Tong, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Linkages of C:N:P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, K.; Yang, Q.; Lu, R.; Yan, L.; Wang, X.; Xia, J. Depth-dependent soil C-N-P stoichiometry in a mature subtropical broadleaf forest. Geoderma 2020, 370, 114357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Gao, P.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Niu, X. Decomposition dynamics and ecological stoichiometry of Quercus acutissima and Pinus densiflora litter in the Grain to Green Program Area of northern China. J. For. Res. 2019, 31, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Gao, P.; Li, C.; Dong, X.; Zhou, R.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Dun, X. Characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus loss in runoff from Quercus acutissima Carr. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. under simulated rainfall. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Gao, P.; Zhou, R.; Li, C.; Dun, X.; Niu, X. Changing characteristics and influencing factors of the soil microbial community during litter decomposition in a mixed Quercus acutissima Carruth. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. forest in Northern China. Catena 2021, 196, 104811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ni, R.; Lv, C.; Xue, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Shen, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y. The effect of Robinia pseudoacacia expansion on the soil particle size distribution on Mount Tai, China. Catena 2022, 208, 105774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logsdon, S.D.; Reneau, R.B.; Parker, J.C. Corn Seedling Root Growth as Influenced by Soil Physical Properties1. Agron. J. 1987, 79, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, M.; Bosch-Serra, N.; Estudillos, G.; Poch, R.M. Rehabilitation of Semi-Arid Coal Mine Spoil Bank Soils with Mine Residues and Farm Organic By-Products. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2009, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, J.L.; Lázaro, R. Seasonal changes in bulk density under semiarid patchy vegetation: The soil beats. Geoderma 2014, 235–236, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, M.; Sharma, K.L.; Indoria, A.K.; Reddy, K.S.; Charry, G.R.; Srinivas, K.; Prabhakar, M.; Parmar, B.; Chandrika, D.S.; Vasavi, M.; et al. Long-term effects of soil management practices on soil Zn chemical fractions and their availability to grain sorghum {Sorghum vulgare (L.)} grown in a yearly rotation with castor (Ricinus communis) in rainfed red Alfisol soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2019, 51, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, G.; Zhao, K.; Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Li, X. Response of plant diversity and soil physicochemical properties to different gap sizes in a Pinus massoniana plantation. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Concilio, A.; Oakley, B.; North, M.; Chen, J. Spatial variability in microclimate in a mixed-conifer forest before and after thinning and burning treatments. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 904–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Tang, M.; Shi, B.; Jin, G. Effect of canopy gap size on soil respiration in a mixed broadleaved-Korean pine forest: Evidence from biotic and abiotic factors. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 99, 103194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.Y.; Huang, J.S.; Zhao, G.J.; Bao, W.K.; Li, G.Q.; Pang, X.Y. Effects of afforestation with different tree species on soil enzyme activities and nutrient content in eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 32, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, G.; Pokorný, J.; Mueller, C.W.; Prater, I.; Preusser, S.; Kandeler, E.; Meador, T.; Straková, P.; Hájek, T.; van Buiten, G.; et al. Soil texture affects the coupling of litter decomposition and soil organic matter formation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 159, 108302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguid, M.C.; Frey, B.R.; Ellum, D.S.; Kelty, M.; Ashton, M.S. The influence of ground disturbance and gap position on understory plant diversity in upland forests of southern New England. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 303, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleghe, E.; Naveed, M.; Baggs, E.M.; Hallett, P.D. Plant exudates improve the mechanical conditions for root penetration through compacted soils. Plant Soil 2017, 421, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, Z.; Li, P. Fractal features of soil particle-size distribution and total soil nitrogen distribution in a typical watershed in the source area of the middle Dan River, China. Catena 2013, 101, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumert, V.L.; Vasilyeva, N.A.; Vladimirov, A.A.; Meier, I.C.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Mueller, C.W. Root Exudates Induce Soil Macroaggregation Facilitated by Fungi in Subsoil. Front. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkai, K.; Tóth, B.; Barna, G.; Hernádi, H.; Kocsis, M.; Makó, A. Particle-size and organic matter effects on structure and water retention of soils. Biologia 2015, 70, 1456–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C. Effects of different meadow use types on the fractal characteristics of soil particle in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Su, Y.; Li, X.; Yin, H.; Li, X.; Guo, M.; He, Y. Forest gaps influence fungal community assembly in a weeping cypress forest. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3215–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, L.; Forrester, J.A.; Wurzburger, N.; Mladenoff, D.J. Emergent properties of downed woody debris in canopy gaps: A response of the soil ecosystem to manipulation of forest structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 108053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Yin, H.; Li, W. Effeects of gap locations on the decomposition of fine root of Toona sinensis and soil fungal community diversity in cypress plantation forest. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 2784–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, J.; Ma, Z.-W.; Li, L.-H. Soil nutrient contents and stoichiometry as affected by land-use in an agro-pastoral region of northwest China. Catena 2017, 150, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessen, D.O.; Ågren, G.I.; Anderson, T.R.; Elser, J.J.; de Ruiter, P.C. Carbon Sequestration in Ecosystems: The Role of Stoichiometry. Ecology 2004, 85, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.A. Soil Microbiology, Ecology, and Biochemistry; Academic Press: Boston, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Rui, Y.; Gunina, A.; He, X.; Ge, T.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; et al. Stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil: Effects of agricultural land use and climate at a continental scale. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Matthews, B.; Rosinger, C.; Sandén, H.; Godbold, D.L.; Katzensteiner, K. Tree regeneration retards decomposition in a temperate mountain soil after forest gap disturbance. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaarakka, L.; Tamminen, P.; Saarsalmi, A.; Kukkola, M.; Helmisaari, H.-S.; Burton, A.J. Effects of repeated whole-tree harvesting on soil properties and tree growth in a Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.) stand. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 313, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egnell, G.; Leijon, B. Effects of different levels of biomass removal in thinning on short-term production of pinus sylvestris and picea abies stands. Scand. J. For. Res. 2008, 12, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nord-Larsen, T. Stand and site productivity response following whole-tree harvesting in early thinnings of Norway spruce (Picea abies (L.) Karst.). Biomass Bioenergy 2001, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitousek, P.M.; Porder, S.; Houlton, B.Z.; Chadwick, O.A. Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: Mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen–phosphorus interactions. Ecol. Appl. 2010, 20, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, E.N.; Henderson, B.L. C:N:P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güsewell, S. N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Tian, D.; Han, W.; Tang, Z.; Fang, J. An assessment on the uncertainty of the nitrogen to phosphorus ratio as a threshold for nutrient limitation in plants. Ann. Bot. 2017, 120, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, A.; Li, X.; Ni, X.; Ji, C. Responses of tree growth to nitrogen addition in Quercus wutaishanica forests in Mount Dongling, Beijing, China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2019, 43, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Hui, D. Responses of Nutrient Resorption to Human Disturbances in Phoebe bournei Forests. Forests 2022, 13, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, K.; Liang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, C. Effects of leaf litter decomposition on bacterial community structure in the leaf litter of four dominant tree species in Mount Tai. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 3175–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, D.; Song, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, Z. Forest Gaps Size on Pinus massoniana Plantation of Three Natural Regeneration Herb N and P Stoichiometry. Bull. Bot. Rse. 2017, 37, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Stand | Sample Plot | Forest Gap Size (m2) | Elevation (m) | Slope (°) | Slope Aspect | Longitude–Latitude | Average Tree Height of Border Trees (m) | Average Mean Diameter of Border Trees (cm) | Average Age of Border Trees (a) | Crown Density | Stand Density (tree•hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | G | 209.42 | 802.0 | 21 | Southwest | N 36°20′2″ E 117°6′46″ | 7.19 | 22.16 | 54 | / | / |
| NG | / | 784.0 | 25 | West | N 36°19′5″ E 117°6′4″ | / | / | / | 0.6 | 621 | |
| RPL | G | 351.86 | 768.1 | 22 | West | N 36°20′2″ E 117°5′4″ | 13.89 | 18.98 | 51 | / | / |
| NG | / | 771.4 | 27 | Northwest | N 36°20′24″ E 117°5′42″ | / | / | / | 0.65 | 760 |
| Stand | Soil Layer (cm) | Gap Position | Soil Bulk Density (g•cm−3) | Soil Total Porosity (%) | Capillary Porosity (%) | Non-Capillary Porosity (%) | Soil Moisture Content (%) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | 0–20 | GC | 1.21 ± 0.00 b | 50 ± 1 a | 42 ± 0 a | 8 ± 1 a | 16 ± 1 b | 2 ± 0 ab | 47 ± 4 a | 51 ± 4 b |
| GE | 1.30 ± 0.05 ab | 48 ± 1 a | 43 ± 1 a | 5 ± 1 b | 19 ± 3 ab | 2 ± 0 a | 45 ± 6 a | 53 ± 7 b | ||
| NG | 1.38 ± 0.02 a | 48 ± 1 a | 43 ± 1 a | 5 ± 0 b | 23 ± 0 a | 1 ± 0 b | 20 ± 2 b | 79 ± 2 a | ||
| 20–40 | GC | 1.39 ± 0.03 a | 47 ± 2 a | 40 ± 0 a | 7 ± 2 a | 13 ± 0 a | 1 ± 0 a | 23 ± 6 a | 76 ± 6 a | |
| GE | 1.32 ± 0.05 b | 45 ± 1 ab | 40 ± 0 a | 5 ± 1 a | 14 ± 1 a | 1 ± 0 a | 30 ± 3 a | 69 ± 3 a | ||
| NG | 1.48 ± 0.00 a | 44 ± 0 b | 39 ± 0 a | 4 ± 0 b | 15 ± 0 b | 1 ± 0 a | 31 ± 4 a | 68 ± 4 a | ||
| RPL | 0–20 | GC | 1.07 ± 0.01 b | 55 ± 2 a | 49 ± 0 a | 6 ± 2 a | 24 ± 0 a | 2 ± 0 a | 41 ± 2 a | 57 ± 3 c |
| GE | 1.08 ± 0.02 b | 51 ± 1 b | 47 ± 1 b | 3 ± 1 b | 22 ± 1 b | 1 ± 0 b | 31 ± 1 c | 68 ± 2 a | ||
| NG | 1.27 ± 0.00 a | 48 ± 2 b | 44 ± 0 c | 4 ± 2 b | 19 ± 1 c | 2 ± 0 b | 23 ± 1 b | 76 ± 1 b | ||
| 20–40 | GC | 1.25 ± 0.05 a | 49 ± 1 a | 45 ± 1 a | 3 ± 1 a | 20 ± 0 a | 2 ± 0 b | 30 ± 3 a | 68 ± 3 a | |
| GE | 1.14 ± 0.05 a | 47 ± 2 b | 43 ± 0 b | 3 ± 1 a | 18 ± 1 b | 2 ± 0 a | 38 ± 4 a | 59 ± 4 a | ||
| NG | 1.32 ± 0.01 a | 47 ± 1 b | 43 ± 0 b | 3 ± 1 b | 16 ± 0 c | 2 ± 0 b | 31 ± 3 a | 67 ± 3 a |
| Stand | Soil Layer (cm) | Gap Position | Organic Carbon (g·kg−1) | Total Nitrogen (g·kg−1) | Total Phosphorus (g·kg−1) | pH | Electric Conductivity (μs·cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDS | 0–20 | GC | 35.2 ± 1.8 a | 2.8 ± 0.2 a | 0.4 ± 0.0 a | 6.1 ± 0.0 a | 96.6 ± 3.1 c |
| GE | 28.2 ± 1.1 b | 2.3 ± 0.1 b | 0.4 ± 0.0 a | 5.8 ± 0.0 b | 130.3 ± 5.0 b | ||
| NG | 15.3 ± 0.7 c | 1.1 ± 0.0 c | 0.2 ± 0.0 b | 5.8 ± 0.0 b | 150.0 ± 4.0 a | ||
| 20–40 | GC | 16.6 ± 0.6 a | 1.3 ± 0.0 a | 0.3 ± 0.0 a | 6.4 ± 0.0 a | 74.2 ± 3.9 b | |
| GE | 16.1 ± 1.7 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | 0.3 ± 0.02 a | 6.0 ± 0.0 b | 112.5 ± 5.1 a | ||
| NG | 10.3 ± 0.76 b | 0.6 ± 0.1 b | 0.1 ± 0.02 b | 6.0 ± 0.0 b | 104.2 ± 5.1 a | ||
| RPL | 0–20 | GC | 26.2 ± 0.9 a | 2.5 ± 0.2 a | 0.5 ± 0.03 a | 5.9 ± 0.0 a | 67.4 ± 2.2 b |
| GE | 24.6 ± 1.4 b | 2.0 ± 0.2 a | 0.4 ± 0.02 a | 5.8 ± 0.1 ab | 65.6 ± 2.2 b | ||
| NG | 21.5 ± 0.2 b | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 0.3 ± 0.01 b | 5.7 ± 0.0 b | 75.0 ± 1.4 a | ||
| 20–40 | GC | 16.3 ± 0.6 a | 1.6 ± 0.1 a | 0.4 ± 0.01 a | 6.1 ± 0.1 a | 55.9 ± 4.4 a | |
| GE | 13.4 ± 1.3 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | 0.3 ± 0.04 a | 5.9 ± 0.1 ab | 52.2 ± 4.1 a | ||
| NG | 14.5 ± 0.5 a | 1.4 ± 0.1 a | 0.2 ± 0.00 b | 5.8 ± 0.0 b | 62.9 ± 2.1 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dun, X.; Liu, Y.; Lian, F.; Zhao, W.; Su, W.; Zhao, W.; Tian, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Z. The Effects of Forest Gaps on the Physical and Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests. Forests 2024, 15, 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101784
Dun X, Liu Y, Lian F, Zhao W, Su W, Zhao W, Tian Z, Qiao Y, Gao P, Zhang Z. The Effects of Forest Gaps on the Physical and Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests. Forests. 2024; 15(10):1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101784
Chicago/Turabian StyleDun, Xingjian, Yuchen Liu, Fengjie Lian, Wentai Zhao, Wei Su, Wei Zhao, Zhihao Tian, Yanhui Qiao, Peng Gao, and Zhenxiang Zhang. 2024. "The Effects of Forest Gaps on the Physical and Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests" Forests 15, no. 10: 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101784
APA StyleDun, X., Liu, Y., Lian, F., Zhao, W., Su, W., Zhao, W., Tian, Z., Qiao, Y., Gao, P., & Zhang, Z. (2024). The Effects of Forest Gaps on the Physical and Ecological Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil in Pinus densiflora Sieb. and Robinia pseudoacacia L. Forests. Forests, 15(10), 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15101784






