Abstract
Castanopsis hystrix, a dominant canopy species in the subtropical forests of south China, is renowned for its high natural regeneration ability. Therefore, this paper took C. hystrix as the subject of study. Examining the variations in microbial diversity and community composition within the soil rhizosphere of C. hystrix across different elevation gradients, we explored how this community-forming species impacts soil microbial diversity and community structure and how soil microorganisms respond to changes in soil physicochemical properties due to altitude gradients. The results show: (1) soil samples from five altitudes established 1078 fungal OTU and 5595 bacterial OTUs. (2) Basidiomycota and ascomycota are dominant fungal groups in the soil, with Acidobacteria being the predominant bacteria for C. hystrix. (3) As altitude increases, fungal communities’ richness and diversity index peaks at 849 m; for bacterial communities, the richness index peaks at 387 m and the diversity index at 670 m. (4) Total phosphorus (TP), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), hydrolyzed nitrogen (HN), total nitrogen (TN), and organic matter (SOM) are significant environmental factors affecting fungal community structure. At the same time, available potassium (AK) significantly influences the composition of bacterial communities. The study underscores the intricate relationship between altitude, soil properties, and microbial diversity, offering insights into how C. hystrix contributes to ecosystem resilience. Recommendations include enhancing phosphorus supplementation and controlling nitrogen deposition to maintain forest ecological integrity, additionally, the supply of potassium in the soil should also be a key consideration. Further research is necessary to understand the broader implications for biodiversity conservation and adaptive management strategies in the face of climate change.
1. Introduction
Soil microorganisms are crucial for soil ecosystems, influencing soil structure and quality through their involvement in material cycling and carbon transformation. Investigations have indicated that the diversity within soil microbial populations can signify the functional steadiness of soil ecosystems and their environmental impacts [1]. The rich diversity of microbial communities contributes significantly to the resilience and adaptability of ecosystems, enhancing soil fertility and promoting robust plant growth [2]. Diverse microbial populations facilitate a range of soil functions, including nutrient recycling, organic matter decomposition, and pathogen suppression, leading to more resilient and productive soil systems [3]. The rhizosphere, influenced by plant root activity, is a microenvironment where complex interactions occur among plants, soil, and microorganisms [4]. Rhizosphere soil microorganisms mediate the transfer and transport of nutrients between roots and soil, significantly enhancing plant growth and regulating resource allocation [5]. As essential participants in nutrient cycling and soil fertility changes in forest ecosystems, bacteria exhibit sensitive responses to soil physiological and biochemical processes. They are highly correlated with changes in soil nutrient effectiveness [6]. Soil bacteria, a dominant category among soil microbes, play roles in nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, and the breaking down of organic matter, thereby directly influencing soil fertility and plant well-being. The varied activities of these bacteria not only aid plant development but also bolster the sustainability and productivity of forest ecosystems [7]. Soil fungi, another essential part of soil microorganisms, play vital roles in decomposing forest litter, transforming organic matter, and improving soil environments, acting as primary decomposers in forest soils [8,9]. Ectomycorrhizal fungi form symbiotic mycorrhizal relationships with higher plant roots, and multiple individual host plants and mycorrhizal fungi can form mycorrhizal symbiotic networks [10,11,12], facilitating water and nutrient absorption for host plants and enhancing their stress tolerance [13]. Some soil fungi are pathogens, significantly affecting the health of forest communities [14]. Generally, the species composition of a community determines its ecological function, and the functionality of forest ecosystems heavily depends on soil microbial communities [15]. Research shows a significant positive correlation between soil microbial diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality, with more prosperous and functionally diverse microbial communities having more excellent resistance to pathogen invasion and disturbances [16,17]. Therefore, exploring the diversity and spatial distribution patterns of soil microorganisms provides a theoretical basis for the healthy and sustainable development of forest ecosystems and is of great significance for understanding the microbial mechanisms driving soil element cycles.
Soil microbes are highly sensitive to shifts in their environment, with even small alterations in environmental conditions resulting in substantial changes in the diversity of the microbial community [18]. Investigations suggest that elements like precipitation, altitude, soil pH, organic matter, and the functional traits of vegetation all play roles in shaping the diversity of bacterial populations within the soil [19]. Changes in altitudinal gradients can lead to variations in precipitation and temperature over short geographic distances, impacting vegetation types and soil properties and consequently affecting soil microbial diversity and community structure [20]. However, current research on the relationship between soil microbial community diversity and altitude is inconclusive. For instance, research conducted by Li Ji found that altitude had a stronger influence on soil bacterial and fungal communities than soil depth and that bacterial and fungal communities showed divergent patterns with altitude and soil depth [21]. Research from the Yu Ge observations indicated that samples gathered from lower elevations were more nutrient-poor and acidic compared to those collected at medium to high elevations. Additionally, there was an increase in the Proteobacteria-to-Acidobacteria ratio as one moved from lower to medium–high altitudes [22]. Meng Zhao Yun’s research [23] revealed that as altitude rose, the diversity of fungi associated with Picea crassifolia gradually diminished, although there was no notable variation in the richness of the fungi. Shen et al.’s research on Mount Kilimanjaro found a concave pattern in soil bacterial diversity with increasing altitude [24], while Ren et al.’s study on different altitudinal gradients in the Taibai mountains observed a hump-shaped relationship between soil bacterial diversity and altitude [25].
Castanopsis hystrix Miq, a member of the Fagaceae family and Castanopsis genus, is commonly referred to as spiny tannin. This species is a distinguished evergreen hardwood, notable for its rarity and significance in timber production [26]. As a leading constituent of the forests in the southern subtropics, it is highly regarded for its dominant position in these ecosystems. C. hystrix is characterized by its lofty, erect trunks and a robust capacity to adapt to a wide range of environmental conditions [27]. It flourishes across diverse elevations from thirty to one thousand six hundred meters, especially in the southern regions of China. C. hystrix wood is greatly esteemed for its long-lasting nature, decay resistance, the attractive light-red color of its heartwood, and its workability. These traits render it a preferred choice for timber in its native regions [28]. The potential for its application in interior decor, carpentry, and ship construction is quite promising. Recent studies on the rhizosphere microorganisms of C. hystrix have been conducted, such as by Wang Qian [29], who selected C. hystrix and Pinus massoniana from a mixed forest in Pingxiang, Guangxi, collecting ectomycorrhizal roots and rhizosphere soil. The findings indicated that the rhizospheres of C. hystrix and Pinus massoniana predominantly harbored fungi from the Amanita, Lactarius, Russula, Clavulinopsis, Mortierella, Inocybe, Trichoderma, and Clavulina genera, with Russula being the most prevalent. Ectomycorrhizal fungi were the primary symbiotic fungi in both mycorrhizal and rhizosphere environments. RDA analysis of dominant fungal groups and soil environmental factors indicated that soil pH, total phosphorus, and total potassium were the main factors affecting the mycorrhizal fungal community structure. The research conducted by Yuanyuan Cheng [30] indicated that soil microbial diversity and richness are greater in natural forests compared to plantations. In the rhizosphere of C. henryi, Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Acidobacteria were identified as the predominant groups. Notably, Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria were found to be significantly more abundant in natural forests, whereas Acidobacteria was more prevalent in plantations. Zishu Xue [31] conducted an examination and comparison of the rhizosphere microbiomes of S. miltiorrhiza and S. castanea. Additionally, to assess the potential geographic spread of S. castanea, MaxEnt models were utilized to forecast the future suitable habitat areas for S. castanea within China. All these studies on the rhizosphere microorganisms of C. hystrix were conducted within the same altitudinal range, and there are no reports on the diversity and community structure of these microorganisms in response to microclimates, vegetation, and soil physicochemical properties caused by altitude gradients. Investigating how subtropical community-forming plants in south Asia affect the ecosystem structure and their response to environmental changes will contribute significantly to understanding the ecological effects of future climate change and developing coping strategies. Therefore, this paper took C. hystrix as the subject of study. By analyzing the differences in soil rhizosphere microbial diversity and community structure of C. hystrix at various altitudinal gradients, we investigated the influence of this community-forming species on soil microbial diversity and community composition, as well as the response of soil microorganisms to alterations in soil physicochemical characteristics resulting from altitude variations. This research was the inaugural effort to elucidate the intricate interplay among various altitudes within C. hystrix, offering fresh perspectives on the adaptive strategies of plant and microbial communities to environmental gradients. Additionally, it established a theoretical basis for predicting the responses of soil microbial communities to changes in the environment. Our goals were: (1) to clarify the diversity and community composition of soil microorganisms around the roots of C. hystrix; (2) to identify the main drivers of microbial diversity and community composition under different altitudinal gradients. We hypothesized that: (1) microbial communities respond to changes in altitude; (2) soil characteristics are crucial in forming microbial communities. The findings from this research deepen our knowledge of the soil microbial community structure associated with C. hystrix and furnish a theoretical framework for anticipating how soil microbial populations will react to shifts in the environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Site and Experimental Materials
The study area was situated along the southern edge of the south subtropical zone (Figure 1), bordering the northern tropics, and is characterized by a south subtropical monsoon climate [32]. It spans from 21°57′47″ N to 22°19′27″ N and from 106°39′50″ E to 106°59′30″ E. The average annual temperature is 21.5 °C, with January averaging 13.5 °C as the coldest month and July averaging 27.6 °C as the warmest month. The region receives around 1400 mm of rainfall annually. Daqing Mountain, with its central peak reaching 1045 m and valley elevations of 130 to 150 m, exhibits a complex topography. In terms of soil classification, the zonal soil is primarily classified as Ferralsols (red soil) in the Chinese system, as Oxisols in the soil taxonomy, or Ferralsols in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources. These soils are typically formed from medium-acid volcanic rocks and granite, with an average depth of 0.5 to 1.0 m. The geological consistency across the elevation gradient suggests that variations in soil and microbial properties are predominantly due to elevation changes rather than differences in parent material or topography.
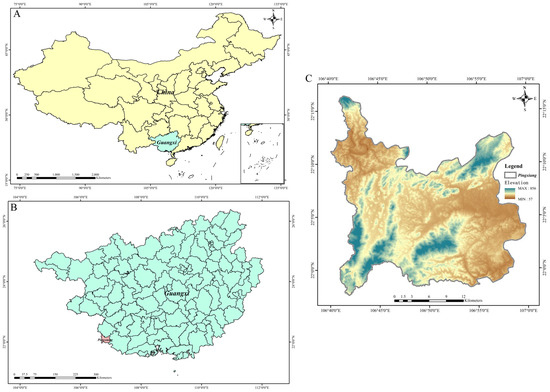
Figure 1.
(A) The location of Guangxi in China. (B) Pingxiang city’s geographical position within Guangxi. (C) A topographic depiction of Pingxiang city.
2.2. Sampling Method
C. hystrix was selected from altitudes of 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m. At each altitude, three plots of 50 m × 50 m were chosen as replicates, with the three replicates situated adjacent to each other. Each replicate collected soil samples from around 10 healthy C. hystrix trees. After removing the surface layer of dead branches and leaves, soil around the roots was gently collected from the end of the roots at a depth of 10 to 40 cm. The soil was then placed into sterile plastic bags, labeled, and returned to the laboratory for mixing and sieving through a 1 mm mesh. The mixed soil samples were divided into two parts: one for determining soil physicochemical properties and the other stored in sterilized tubes at −80 °C for high-throughput sequencing.
2.3. Assessment of Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics
The pH was determined through a potentiometric approach. Organic matter content was determined via external heating with potassium dichromate oxidation and volumetric analysis. Total nitrogen (TN) content was measured using H2SO4-HClO4 digestion, followed by analysis with a SmartChem200 automatic chemical element analyzer (Kepu Man Analytical Instrument (Beijing) Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The contents of soil nitrate-nitrogen (NO3−-N) and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N) were measured using the SmartChem200 automatic analyzer (Kepu Man Analytical Instrument (Beijing) Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The content of soil total phosphorus (TP) was determined through acid dissolution and subsequent molybdenum-antimony anti-colorimetric method. The available phosphorus (AP) content was measured via the hydrochloric acid-ammonium fluoride method, total potassium (TK) content through sodium hydroxide alkali melting followed by flame photometry, and available potassium (AK) content was assessed using ammonium acetate extraction coupled with flame photometry. Soil available nitrogen (AN) content was the sum of nitrate and ammonium nitrogen contents [33].
2.4. Total DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing of Soil Microorganisms
DNA was isolated from 0.5 g of dry weight rhizospheric soil employing a soil DNA extraction kit. The V4–V5 regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA genes underwent amplification through PCR, utilizing primers 338F (ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA) and 806R (GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT). The ITS2 segments of the fungal rRNA genes were amplified via PCR employing primers ITS3-F (GCATCGATGAAGAACGCAGC) and ITS4-R (TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC). High-throughput sequencing and OTU clustering: quantification, normalization, library preparation for sequencing, and (Guangdong Meigene Biotech Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) performed the data quality control for the PCR products. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina Nova 6000 platform using PE250 sequencing of the constructed amplicon library. Optimized sequences were clustered into operational taxonomic units (OTUs) with 97% similarity. OTUs possessing abundance levels below 0.001% of the total sequencing volume across all samples were eliminated. The abundance matrix, omitting infrequent OTUs, was employed for further sequential analysis. The UNITE database (Release 5.0, https://unite.ut.ee/, accessed on 10 March 2023) served as the reference for taxonomic classification of OTUs.
2.5. Data Analysis
Statistical evaluations were performed utilizing SPSS 22.0 along with the R package, “vegan”. Alpha diversity measures were utilized for evaluating microbial diversity and richness and sequencing depth. This was represented through various indices: ACE, Observed_OTUs, Shannon, Chao1, Goods_coverage and Simpson. These metrics illuminate aspects of richness and evenness, with Observed_OTUs assessing the diversity of operational taxonomic units (OTUs) within bacterial and fungal communities. Chao1 and ace indices are critical for assessing microbial richness, while Shannon and Simpson indices quantify diversity. Goods_coverage provides an estimate of the extent of microbial coverage. Conversely, beta diversity was employed to examine the differences in microbial communities among various samples, illustrated through principal coordinate analysis and nonmetric multidimensional scaling.
3. Result and Analysis
3.1. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties
Differences in the physicochemical properties of the rhizospheric soil of C. hystrix at different altitudes are illustrated in Figure 2. Soil organic matter (SOM), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), hydrolyzed nitrogen (HN), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) showed a “V-shaped” trend with increasing altitude, with a decrease observed between 554 and 670 m, and then an increase at 849 m where the values of SOM, TN, TP, HN, and NO3−-N were significantly higher than at 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, and 670 m (p < 0.01) (Figure 2A–C,F,G). Total potassium (TK) displayed an “M-shaped” trend with increasing altitude, significantly decreasing between 387 and 554 m, with little change between 554 and 849 m. The value of TK at 387 m was significantly different from those at 198 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m (p < 0.01) (Figure 2D). Available nitrogen (AN) followed an “N-curve” pattern, significantly decreasing at 198 to 387 m, then increasing, followed by a gradual decrease from 554 to 849 m. The value of AN at 198 m was significantly different from those at 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m (p < 0.01) (Figure 2E). Available potassium (AK) and available phosphorus (AP) both showed an “inverted U-shaped” curve with increasing altitude, initially increasing, and then decreasing before rising again. The AK value at 387 m was significantly different from those at 198 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m (p < 0.01), and the AP value at 554 m was significantly different from those at 198 m, 387 m, 670 m, and 849 m (p < 0.01). Soil pH decreased with increasing altitude, with the pH value at 387 m significantly different from those at 198 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m (p < 0.01).
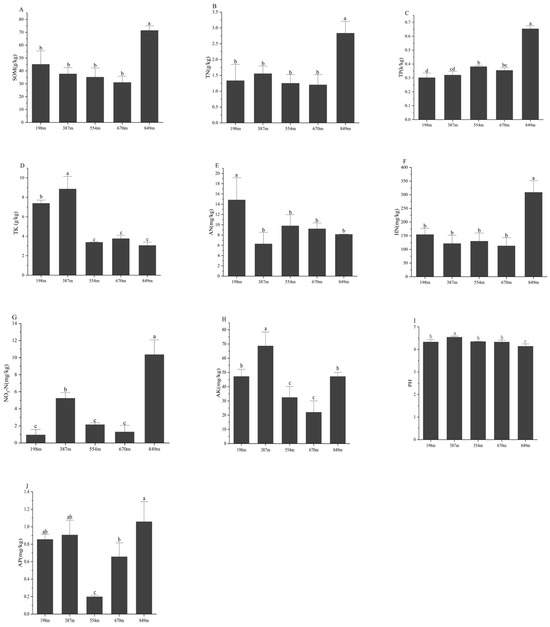
Figure 2.
Physical and chemical characteristics of C. hystrix rhizospheric soil across various elevations. (A) SOM: soil organic matter; (B) TN: total nitrogen; (C) TP: total phosphorus; (D) TK: total potassium; (E) AN: NH4+-N (ammonium nitrogen); (F) HN: alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen; (G) NO3−-N: nitrate nitrogen; (H) AK: available potassium; (I) PH: potential of hydrogen; (J) AP: available phosphorous. Note: distinct lowercase letters signify significant disparities among various treatments (p < 0.05).
3.2. Microbial Community Characteristics
A total of 1078 fungal operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were established, with the OTUs at altitudes of 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m being 440, 503, 453, 454, and 605 OTUs, respectively. The distribution of OTUs from the highest to the lowest number by altitude was as follows: 849 m > 387 m > 670 m > 554 m > 198 m. Additionally, there were 152 fungal OTUs standard across the five altitudinal regions, accounting for 14.10% of the total fungal OTUs. Thus, fungal communities have significant differences across these five altitudes (Figure 3A). A sum of 5595 bacterial OTUs was identified, with counts at altitudes of 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m being 2204, 3354, 2906, 2797, and 3328 OTUs, respectively. Moreover, there were 1246 bacterial OTUs standards across the five altitudinal regions, accounting for 22.27% of the total bacterial OTUs. Therefore, bacterial communities have significant differences across these five altitudes (Figure 3B).
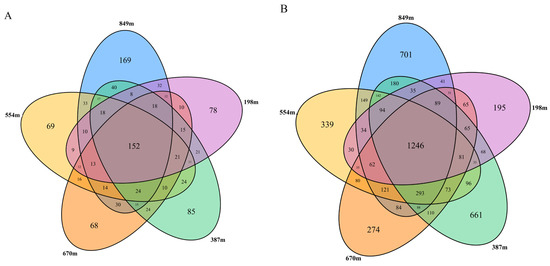
Figure 3.
Illustrative Venn diagrams of fungal (A) and bacterial (B) OTUs present at different altitudes within the rhizospheric soil of C. hystrix. The figure indicates the altitudes of the rhizosphere soil sample collection sites (198, 387, 554, 670, and 849 m).
To achieve a more detailed analysis of fungal OTUs, the ITS2 region of fungal rRNA genes in 15 soil samples was evaluated. This resulted in the identification of 7 phyla, 19 classes, 37 orders, 66 families, 99 genera, and 163 species. Focusing on the phylum level, the study across the five altitudinal gradients detected 19 fungal phyla (Figure 4A). The predominant phyla, each having a relative abundance exceeding 1% were Basidiomycota, Ascomycota, and Rozellomycota, with relative abundances of 74.37%, 22.29%, and 1.06%, respectively. The dominant groups with relative abundance greater than 5.0% were two phyla, accounting for 10.53% of the total but with a relative abundance of 96.66%. With increasing altitude, Basidiomycota’s relative abundance showed a trend of initially decreasing, then increasing, and eventually decreasing again, being highest at 198 m (89.91%), significantly higher than at 387 m (42.58%) and 849 m (69.36%), and not significantly different from 554 m (87.33%) and 670 m (82.69%). As the altitude increased, Ascomycota’s relative abundance first increased, then decreased, and eventually increased again, highest at 387 m (53.44%), significantly higher than at other altitudes. Among the identified dominant species with lower relative abundance, Rozellomycota’s relative abundance at different altitudes was 849 m > 387 m > 554 m > 670 m > 198 m, with 670 m and 198 m significantly lower than the other three altitudes. Mortierellomycota’s relative abundance was 849 m > 554 m > 387 m > 670 m > 198 m, with the 849 m altitude showing a notably higher count than 198 m. There were considerable variations in the abundance of most identified fungal categories across different elevations. Considering the family level, there were differences in soil fungal community composition under different treatments (Figure 4B). The study detected 99 fungal families across the five altitudinal gradients. The dominant families with relative abundance greater than 1% were 10, namely Russulaceae, Thelephoraceae, Elaphomycetaceae, Sebacinaceae, Atheliaceae, Inocybaceae, Agaricaceae, Helotiaceae, Tricholomataceae, Cortinariaceae, with relative abundances of 19.46%, 16.44%, 7.37%, 6.32%, 2.96%, 3.00%, 1.97%, 1.64%, 1.61%, 1.02%, respectively. The dominant groups with relative abundance greater than 5.0% were four families, accounting for 4.04% of the total, but with a relative abundance of 49.59%. With increasing altitude, Russulaceae’s relative abundance showed a trend of initially decreasing, then increasing, and eventually decreasing again, being highest at 198 m (55.80%), significantly higher than at other altitudes; Thelephoraceae’s relative abundance showed an “N-shaped” trend, being highest at 670 m (50.86%), significantly higher than at other altitudes; Elaphomycetaceae’s relative abundance first increased and then gradually decreased, being highest at 387 m (34.85%), significantly higher than at other altitudes; Sebacinaceae’s relative abundance showed an “N-shaped” trend, being highest at 849 m (26.45%), significantly higher than at other altitudes. Significant differences existed in the abundance of most identified fungal groups between different altitudes. At the genus level, the study detected 114 fungal genera across the five altitudinal gradients (Figure 4C). The dominant genera with relative abundance greater than 1% were seven, namely Russula, Sebacina, Byssocorticium, Inocybe, Elaphomyces, Tomentella, and Phaeocollybia, with relative abundances of 19.12%, 6.31%, 2.96%, 2.94%, 1.34%, 1.07%, 1.02%, respectively. The dominant groups with relative abundance greater than 5.0% were two genera, accounting for 1.75% of the total, but with a relative abundance of 25.43%. With increasing altitude, Russula’s relative abundance showed a trend of initially decreasing, then increasing, and eventually decreasing again, being highest at 198 m (54.14%), significantly higher than at other altitudes; Sebacina’s relative abundance showed a gradually increasing trend, being highest at 849 m (26.44%), significantly higher than at other altitudes.
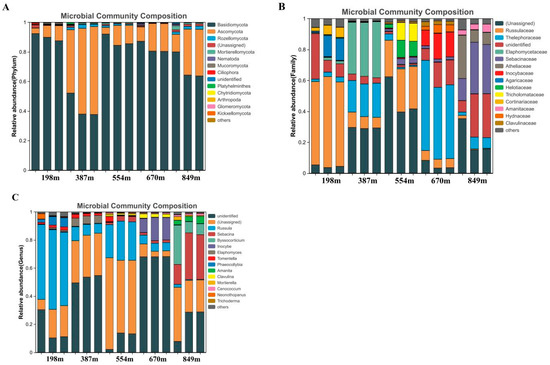
Figure 4.
Structure and composition of fungal communities within the rhizospheric soil samples of C. hystrix at different altitudes. (A) Top 10 fungal phyla. (B) Top 10 Fungal Family. (C) Top 10 fungal genus. Relative abundance was determined as the percentage of total effective fungal sequences within a sample. Classifications utilized the SILVA database. Phyla, families, and genera not ranking in the top 10 for both libraries were categorized as “other”. Information is provided for rhizospheric soil samples gathered at altitudes of 198, 387, 554, 670, and 849 m.
To deepen our understanding of the bacterial community traits in five rhizospheric soil samples, we evaluated the V4–V5 region of the 16S RNA gene. In the 15 soil samples, we detected 2 domains, 32 phyla, 72 classes, 155 orders, 193 families, 266 genera, and 143 species. In the study areas across the five altitudinal gradients, 32 bacterial phyla were detected (Figure 5A), with six dominant bacterial phyla having a relative abundance greater than 1%, namely Acidobacteria, Proteobacteria, Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobia, Actinobacteria, and Planctomycetes, with relative abundances of 62.83%, 20.44%, 4.28%, 3.53%, 2.07%, and 1.88%, respectively. The prevailing groups, each having a relative abundance above 5.0%, encompassed two phyla. These accounted for 6.25% of the total count but represented 83.27% in terms of relative abundance. Relative abundance of Acidobacteria showed no significant difference across different altitudinal gradients. With increasing altitude, the relative abundance of Proteobacteria first decreased, then increased, and significantly decreased again, being highest at 670 m (30.35%), significantly higher than at 849 m. There were differences in soil bacterial community composition at the family level under different treatments (Figure 5B), with 193 bacterial families detected across the five altitudinal gradients. The dominant bacterial families with relative abundance greater than 1% included eight families, namely Solibacteraceae_Subgroup_3, Xanthobacteraceae, Acidobacteriaceae_Subgroup_1, Chthoniobacteraceae, Pedosphaeraceae, Koribacteraceae, Burkholderiaceae, and Gemmataceae, with relative abundances of 9.67%, 2.59%, 2.49%, 1.79%, 1.76%, 1.74%, 1.72%, and 1.42%, respectively. The dominant groups with a relative abundance greater than 5.0% included one family, accounting for 0.52% of the total number, but with a relative abundance of 9.67%. With increasing altitude, the relative abundance of Solibacteraceae_Subgroup_3 first significantly increased, then markedly decreased, highest at 387 m (16.07%), significantly higher than at other altitudes. At the genus level, 266 genera were detected across the five altitudinal gradients (Figure 5C). The predominant bacterial genera, each with a relative abundance exceeding 1%, encompassed six genera, namely Candidatus_Solibacter, Candidatus_Koribacter, Candidatus_Udaeobacter, Bryobacter, Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia, and Bradyrhizobium, with relative abundances of 6.95%, 1.74%, 1.66%, 1.62%, 1.25%, and 1.17%, respectively. The dominant groups with relative abundance greater than 5.0% included one genus, accounting for 0.38% of the total, but with a relative abundance of 6.95%. With increasing altitude, the relative abundance of Candidatus_Solibacter showed a trend of first significantly increasing, then markedly decreasing, and then increasing again, highest at 387 m (12.48%), significantly higher than at other altitudes.
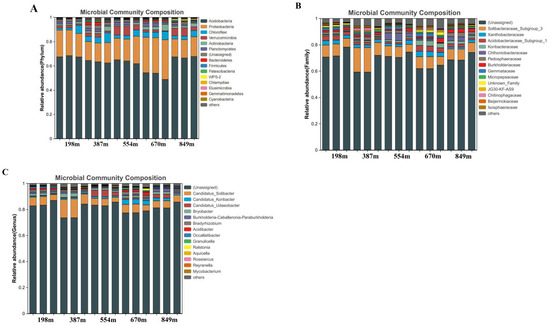
Figure 5.
The composition and structure of bacterial communities in the rhizospheric soil of C. hystrix at varying altitudes were examined. (A) This included an analysis of the top 10 bacterial phyla. (B) The investigation extended to the top 10 bacterial families. (C) Additionally, the study identified the top 10 bacterial genera. Relative abundance was determined as a percentage of each sample’s total effective bacterial sequences. Classifications were based on the SILVA database. Phyla, families, and genera that did not make the top 10 in either library were collectively categorized as “other”. The presented data correspond to rhizospheric soil samples collected from altitudes of 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m.
3.3. Microbial Biodiversity
3.3.1. α Diversity Index Analysis
The diversity of fungal communities in rhizospheric soil samples was revealed using α diversity indices, including Observed_OTUs, Chao1, ACE, Shannon, Simpson, and Goods_coverage indices (Figure 6). The results indicated specific differences in the diversity, evenness, and richness of the fungal communities in the rhizosphere of Pinus tabuliformis at different altitudes. With increasing altitude, the richness indices of the fungal community (ACE, richness, and Chao1 indices) showed a trend of initially increasing, then decreasing, then increasing again, reaching the maximum at an altitude of 849 m, with the minimum at 554 m. The fungal community’s evenness index (Pielou index) increased, then decreased, and gradually increased again with altitude, with the highest at 387 m and the lowest at 554 m. The diversity index (Shannon index) for the fungal community initially rose and then fell, and gradually increased with altitude, reaching the maximum at 849 m and the minimum at 554 m. The Goods_coverage fluctuated, initially decreasing, and then increasing with altitude. These data indicate that the results accurately represent the actual conditions of each sample. The statistical probability of detecting new fungi in the samples was zero.
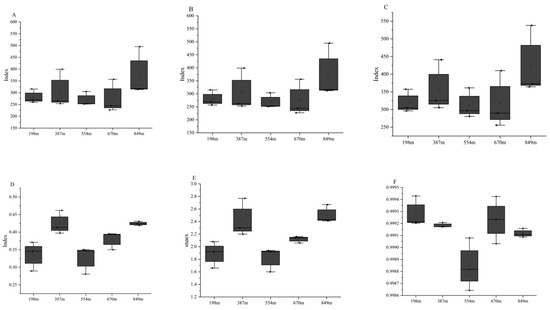
Figure 6.
α diversity metrics for fungal communities based on ITS regions in the rhizospheric soil of C. hystrix at different altitudes are detailed. The data corresponds to rhizospheric soil samples collected from altitudes of 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m. Specifically, the indices include: (A) CHAO1; (B) Richness; (C) ACE; (D) Pielou; (E) Shannon; and (F) Goods-coverage.
The diversity within bacterial communities from rhizospheric soil samples was unveiled through α diversity metrics (specifically Observed_OTUs, Chao1, ACE, Shannon, Simpson, and Goods_coverage) (Figure 7). The results indicated specific differences in the diversity, evenness, and richness of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of C. hystrix at different altitudes. With increasing altitude, the richness indices of the bacterial community (ACE, richness, and Chao1 indices) showed a trend of initially increasing, then decreasing, and then increasing again, reaching the maximum at an altitude of 387 m, with the minimum at 198 m. The bacterial community’s evenness index (Pielou index) exhibited an “M-shaped” trend with increasing altitude, the highest at 670 m and the lowest at 198 m. Similarly, the bacterial community’s diversity index (Shannon index) displayed an “M-shaped” trend with altitude, peaking at 670 m and the lowest at 198 m. The Goods_coverage fluctuated, initially increasing, then decreasing, and increasing again with altitude. These data indicate that the results accurately represent the actual conditions of each sample. The statistical probability of detecting new fungi in the samples was zero.
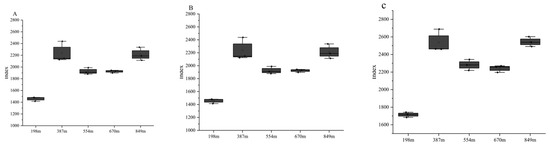
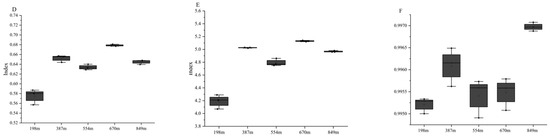
Figure 7.
The alpha diversity indices for bacterial communities (derived from 16S rRNA genes) within the rhizospheric soil of C. hystrix at different elevations are presented. The data represent rhizospheric soil samples collected from altitudes of 198 m, 387 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m. The indices are as listed: (A) CHAO1; (B) Richness; (C) ACE; (D) Pielou; (E) Shannon; and (F) Goods-coverage.
3.3.2. Beta Diversity Indices of the Microbial Communities
Figure 8A illustrates the dispersal of fungal communities in rhizospheric soil samples of C. hystrix at five distinct altitudes, as deduced from the principal coordinates analysis (PCoA). Considering the first principal coordinate, which represents 24.7% of the overall variance, the fungal communities in rhizospheric soil at four altitudes (198 m, 554 m, 670 m, and 849 m) were grouped together and clearly distinguished from the community at 387 m. Similarly, non-metric multidimensional scaling analysis, known as NMDS, also divided the rhizospheric soil samples into two separate groups, as shown in Figure 8B. Bacterial communities in the rhizosphere of C. hystrix at altitudes of 198 m, 554 m, and 849 m were markedly distinct from those at 387 m and 670 m, as shown by the PCoA results for the first principal coordinate, depicted in Figure 8C, with the first principal coordinate accounting for 37.5% of the total variance. NMDS analysis suggested that the bacterial community structures at 198 m, 387 m, and 554 m were similar at these altitudes. However, there was a noticeable distinction exists between the rhizospheric bacterial community structure at 670 m and that at 849 m (Figure 8D).
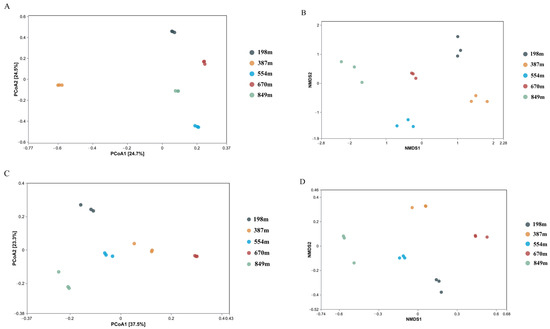
Figure 8.
Analysis of bacterial and fungal communities in the C. hystrix rhizospheric soil samples at various altitudes using principal coordinate analysis (PCOA) and nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS). (A) PCoA for the fungal community. (B) NMDS for analyzing the fungal community. (C) PCoA for the bacterial community. (D) NMDS for the bacterial community. Information relates to rhizospheric soil samples collected at altitudes of 198, 387, 554, 670, and 849 m.
3.4. The Influence of Soil Physicochemical Properties on the Soil Microbial Community in the Rhizosphere of C. hystrix
The correlation analysis between soil chemical properties and the alpha diversity of fungal communities (depicted in Figure 9A) revealed significant associations. Notably, soil NO3−-N values exhibited a positive correlation with CHAO1, ACE, Pielou, and Shannon indices, indicating an increase in diversity and evenness with higher NO3−-N levels. Conversely, NH4+-N values showed a negative correlation with the Shannon index, suggesting a decrease in diversity with higher NH4+-N levels. Additionally, AP (available phosphorus) and TN (total nitrogen) values were positively correlated with the Shannon index, demonstrating their positive impact on fungal diversity. These results indicated that soil NO3−-N, NH4+-N, AP, and TN values had a significant impact on the diversity of fungal communities within the rhizospheric soil of C. hystrix. Furthermore, the analysis of the correlation between soil physicochemical properties and the alpha diversity of bacterial communities (illustrated in Figure 9B) highlights that soil NH4+-N values were significantly negatively correlated with CHAO1, ACE, Pielou, and Shannon indices. This suggests that higher NH4+-N levels in the soil may detrimentally affect the diversity of bacterial communities. Overall, these findings emphasize the significant impact of specific soil nutrients, notably NO3−-N and NH4+-N, concerning diversity in fungal as well as bacterial populations within rhizospheric soil from C. hystrix.
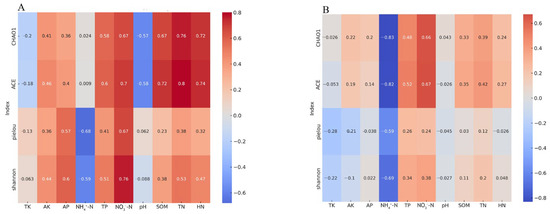
Figure 9.
Pearson correlation between soil chemical properties and microbial community α diversity. (A) Pearson correlation between soil chemical properties and fungus community α diversity. (B) Pearson correlation between soil chemical properties and bacterial community α diversity is depicted. The intensity of the color and the sign (positive or negative) represent the strength and direction of the correlation, with blue hues indicating positive correlations and red hues indicating negative correlations. TK: total potassium; AK: available potassium; AP: available phosphorous; NH4+-N: NH4+-N; TP: total phosphorus; NO3−-N: nitrate nitrogen; PH: potential of hydrogen potential of hydrogen; SOM: soil organic matter; TN: total nitrogen; HN: alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) concentrated on ten leading fungal groups along with environmental factors from rhizospheric soil, uncovered substantial alterations in fungal community structure within C. hystrix soil across five different altitude levels. The initial two axes of the RDA, RDA1 and RDA2, represented 15.11% and 12.62% of the total variance, respectively, underscoring the most impactful environmental gradients affecting the fungal communities. The soil physicochemical properties were categorized into two distinct groups (as depicted in Figure 10A). One group included TP, TN, NO3−-N, HN, SOM, AP, and AK, indicating a set of properties that might interact or influence each other and the fungal community in a similar manner. The other cluster consisted of the remaining soil elements, indicating varying or more subtle influences on the fungal genera. The impact of rhizospheric soil physical and chemical properties on the fungal genera was quantitatively assessed, with TP being the most significant, followed by NO3−-N, HN, TN, SOM, pH, NH4+-N, TK, AK, and ultimately AP. This ranking signifies the relative impact each property has on shaping the fungal community structure. Notably, TP, NO3−-N, TN, and HN emerged as the primary environmental factors affecting the dominant fungal community. Specifically, TP exhibited a significant positive correlation with the abundance of specific fungal genera such as Sebacina, Amanita, and Byssocorticlum, indicating that higher levels of total phosphorus in the soil might promote the growth or presence of these genera. This analysis sheds light on the complex interplay between soil environment and fungal biodiversity, providing valuable insights for understanding and managing C. hystrix ecosystems.
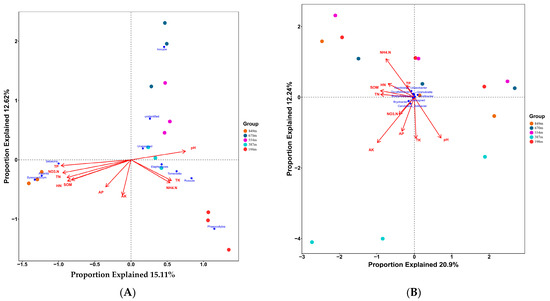
Figure 10.
Associations between microbial phyla and soil physical and chemical characteristics. (A) Redundancy analysis (RDA) for the top five fungal phyla and soil physical and chemical properties. (B) RDA for the top five bacterial phyla and soil physical and chemical properties. Information is provided for rhizospheric soil samples gathered at altitudes of 198, 387, 554, 670, and 849 m. SOM: soil organic matter; TN: total nitrogen; TP: total phosphorus; TK: total potassium; AN: NH4+-N (ammonium nitrogen); HN: alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen; NO3−-N: nitrate nitrogen; AK: available potassium; PH: potential of hydrogen; AP: available phosphorous.
Redundancy analysis (RDA), examining ten leading bacterial groups along with environmental factors in rhizospheric soil, indicated relatively minor shifts in bacterial community structure within C. hystrix soil over five different elevation zones. RDA1 and RDA2, constituting the first two axes, together accounted for 33.34% of the overall variance, with 20.9% and 12.44% respectively, indicating the significant environmental gradients impacting bacterial communities. Soil physicochemical properties were bifurcated into two distinct groups (illustrated in Figure 10B). The first group comprised AK (available potassium), AP (available phosphorous), NH4+-N (ammonium nitrogen), TP (total phosphorus), NO3−-N (nitrate nitrogen), SOM (soil organic matter), TN (total nitrogen), and HN (alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen). These properties likely have a similar or interrelated impact on the bacterial community. Conversely, the remaining soil properties formed another group, suggesting a different set of influences on bacterial structures. The extent of influence of these soil physicochemical properties on the bacterial community structure was quantitatively determined. AK was identified as having the most significant impact, followed by SOM, TN, pH, NH4+-N, HN, TK (total potassium), AP, NO3−-N, and TP. This ranking reveals the relative importance of each property on shaping the bacterial community structure. At the genus level, soil AK emerged as a principal environmental factor influencing the bacterial community composition. Notably, soil AK values showed a positive correlation with the abundance of the genera Bryobacter and Candidatus_Solibacter. This suggests that higher levels of available potassium in the soil might favor the growth or prevalence of these bacterial genera. The analysis provides insights into the nuanced relationship between soil physicochemical conditions and bacterial diversity, aiding in the ecological understanding and management of C. hystrix habitats.
4. Discussion
4.1. Physical and Chemical Characteristics and Microbial Community Structure of C. hystrix Rhizospheric Soil
Li Yun-Chou et al. [34] discovered that altitude was a critical factor influencing the natural regeneration distribution patterns of C. hystrix in the subtropical regions of south Asia. Similarly, Lu Li-Hua and colleagues [35] found that altitude significantly affects the growth of C. hystrix. Under identical parent rock, soil, and site index conditions, C. hystrix demonstrated superior growth at lower altitudes than at higher altitudes. Nonetheless, additional studies are required to clarify the connection between altitude and the rhizospheric soil characteristics of C. hystrix. Altitudinal gradients are considered an ideal method for exploring variations and patterns in rhizospheric effects, representing a powerful “natural experiment” to observe how rhizospheric effects respond to changes in climate and biological traits [36].
In this research, the physical and chemical properties of C. hystrix rhizospheric soil at various elevations exhibited intricate response behaviors. Soil organic matter (SOM), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), hydrolyzable nitrogen (HN), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) exhibited a significant “V-shaped” trend, correlating with increasing altitude. Huo et al. [37] noted that carbon and nitrogen mineralization processes in temperate forests along altitudinal gradients are tightly coupled in rhizospheric soils. These soil properties decreased at medium altitudes and then increased at higher altitudes, likely linked to changes in microbial activity in the rhizosphere. The diversity and function of rhizospheric microbial communities might change with elevation, potentially exhibiting stronger positive interactions at higher elevations, thereby influencing soil nutrient cycling [38]. The “M-shaped” trend of total potassium (TK) might relate to complex biogeochemical interactions within the soil, playing a pivotal role in nutrient cycling in the rhizosphere. The “N-curve” trend of ammonium nitrogen (AN) and the decline in pH values further emphasize the impact of altitudinal changes on soil acidity and its interaction with microbial communities, aligning with Zhao et al.’s [39] findings in their study on soil organic carbon processes. Additionally, the “inverted U-shaped” trends of available potassium (AK) and available phosphorus (AP) reveal potential effects of altitude on soil fertility and plant nutrient uptake. This may be associated with the nutrient absorption efficiency of plant roots at lower altitudes and environmental factors (such as temperature) limiting nutrient cycling processes at mid-altitudes, as reflected in a 2022 study along the altitudinal gradient of Changbai Mountain [40], which found a strong link between soil carbon and nitrogen mineralization in rhizospheric soils.
Using high-throughput sequencing technology, the soil fungi of C. hystrix were classified into 1078 operational taxonomic units (OTUs), belonging to 19 phyla, 37 classes, 66 orders, 99 families, 114 genera, and 163 species. In C. hystrix, Basidiomycota fungi were the most prevalent, accounting for 74.37% relative abundance, succeeded by Ascomycota fungi, which had a relative abundance of 22.29%. Studies showed that Basidiomycota fungi can decompose complex lignocellulosic components with widespread mycelial propagation, thus becoming the dominant fungal group in soil [41]. Ascomycota fungi are highly adaptable and can rapidly metabolize organic substrates, decomposing plant residues and degrading organic matter [42,43]. At the genus level, seven leading fungal genera, each with a relative abundance exceeding 1%, were identified: Russula, Sebacina, Byssocorticium, Inocybe, Elaphomyces, Tomentella, and Phaeocollybia, with respective abundances of 19.12%, 6.31%, 2.96%, 2.94%, 1.34%, 1.07%, and 1.02%. Two dominant genera with a relative abundance greater than 5.0% accounted for 25.43% of the total. C. hystrix is a typical ectomycorrhizal tree, capable of forming ectomycorrhizae with various fungi. The diversity and abundance of ectomycorrhizal fungi are of significant importance for maintaining plant diversity and the stability and productivity of ecosystems [44]. Dominant genera such as Russula, Inocybe, Byssocorticium, Elaphomyces, Tomentella, and Phaeocollybia can all form ectomycorrhizae with C. hystrix. Wang Qian [29] showed that ectomycorrhizae formed between C. hystrix and Russula fungi promote root growth and nutrient absorption in plants, improving plant stress resistance, survival rates during cultivation and transplantation, and producing edible fruiting bodies, thus playing an essential part in ecosystems [45,46]. The genus Phaeocollybia is widespread in various forest ecosystems and exhibits almost no host specificity [47]. The Byssocorticium and Inocybe fungi are highly competitive in harsh environments, occupying dominant positions [48], with the former possessing saprotrophic functions, facilitating nutrient cycling in plants by decomposing forest litter [49], and the latter supplying host plants with water and mineral nutrients, playing a crucial ecological role in forest succession [50]. Species in the Tomentella genus are known to form ectomycorrhizae (ECM) with higher plants, absorbing host carbohydrates while supplying nitrogen and water, a symbiotic relationship critical for forest ecosystem succession and biodiversity maintenance [51]. In the case of Phaeocollybia, one study has suggested a root parasitic lifestyle [52], whereas recent work from Abies forests in Mexico suggested that Phaeocollybia is ECM [53].
The soil bacteria of C. hystrix were divided into 5595 OTUs, belonging to 32 phyla, 72 classes, 155 orders, 193 families, 266 genera, and 143 species. Acidobacteria was the dominant bacteria in C. hystrix, with a relative abundance of 62.83%, followed by Proteobacteria, with a relative abundance of 20.44%. Studies indicate that Acidobacteria possess acidophilic and oligotrophic characteristics and participate in the soil iron cycle [54]. Pankratov et al. [55] noted that the capacity of Acidobacteria to degrade cellulose is less prominent compared to other bacteria renowned for their cellulose decomposition abilities; its resilience maintains essential ecological functions of soil bacteria in harsh habitats. Proteobacteria, the largest phylum of bacteria [56], perform a crucial function in the cycling of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur [57]. At the genus level, this study detected 266 genera across five altitudinal gradients, with six dominant bacterial genera having a relative abundance greater than 1%, namely Candidatus_Solibacter, Candidatus_Koribacter, Candidatus_Udaeobacter, Bryobacter, Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia, and Bradyrhizobium, with respective abundances of 6.95%, 1.74%, 1.66%, 1.62%, 1.25%, and 1.17%. One dominant genus with a relative abundance greater than 5.0% was Candidatus Solibacter, known for decomposing organic matter to obtain a carbon source [58] and widely present in organic-rich soils [59].
In conclusion, this study provides a comprehensive analysis of C. hystrix rhizospheric soil properties and microbial communities across different altitudes, utilizing advanced high-throughput sequencing technology. It reveals complex response patterns in soil physicochemical properties, the diversity and functionality of microbial communities, and their significant roles in biogeochemical interactions, nutrient cycling, and ecosystem health. The research underscores the importance of microbial diversity in maintaining ecosystem structure and function, offering a deeper understanding of ecological dynamics and the influence of altitude and local biodiversity.
4.2. The Impact of Altitude on the Microbial Community Structure in the Rhizosphere Soil of C. hystrix
Comprehensive studies have emphasized that the physical and chemical characteristics of rhizosphere soil, along with plant traits, significantly affect the diversity and richness of microbial communities in the rhizosphere [60,61,62]. Nonetheless, the impact of environmental factors, like altitude, on the diversity and richness of microbial communities is still less investigated. Understanding the spatial distribution patterns of rhizosphere soil microbial communities is vital for anticipating how forest ecosystems might respond to global changes. It is well-established that the composition and concentration distribution of microbial groups vary across different environments, and even in similar conditions, the compositions and functions of microbial communities can differ regionally [63]. In our study, this was exemplified by the observed notable changes in the relative abundance of various microbial groups as the altitude increased.
In this study, the dominant fungal genera identified can form ectomycorrhizae with C. hystrix. These ectomycorrhizal fungi can also form mycorrhizal networks [11], connecting multiple individual plant hosts and mycorrhizal fungi [64], enhancing water and nutrient absorption in C. hystrix, and improving its tolerance to adverse conditions. Therefore, these ectomycorrhizal fungi species and functional diversity are crucial for maintaining the stability of C. hystrix forest ecosystems [65]. Notably, the abundance fluctuation of the seven dominant genera along the altitudinal gradient indicates their differential adaptation to various ecological niches and a strong correlation between altitude and fungal distribution [66,67]. Across different altitudes, Proteobacteria and Acidobacteria remained dominant in the rhizosphere soil bacterial communities, contributing significantly to community composition variation. However, their relative abundance peaked at different altitudes, which is consistent with many studies on forest ecosystems, which show that soils in different habitats have similar bacterial compositions but also distinct dominant groups [68]. This is primarily due to the broad ecological niches and strong adaptability of Proteobacteria and Acidobacteria to various environments [69]. Furthermore, the differential adaptability of microbial groups to microenvironments is a reason for the varied peak abundances of these two phyla in different vegetation zones or altitudes. Studies have shown that Acidobacteria can improve soil nutrient content by degrading complex lignin and cellulose [55]. In our study, their relative abundance increased at an altitude of 849 m, which could explain the increase in rhizosphere soil nutrients SOM, N, and P at these altitudes. Bacteria from the phyla Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria, known for their symbiotic nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilization abilities [70], are crucial for improving rhizosphere soil environments and the material cycling of forest ecosystems.
Alpha diversity metrics additionally indicated that altitude indeed impacts the diversity, evenness, and richness of the microbial community in the C. hystrix rhizosphere. In our study, as altitude increased, the richness indices of the fungal community (ACE index, richness index, and Chao1 index) showed a trend of initially increasing, then decreasing, then increasing again, peaking at 849 m and reaching the lowest at 554 m. The diversity index (Shannon index) for the fungal community first increased, then decreased, and gradually increased again, peaking at 849 m and hitting the lowest at 554 m. The richness indices for the bacterial community (ACE index, richness index, and Chao1 index) followed a similar trend, peaking at 387 m and lowest at 198 m. The bacterial community’s diversity index (Shannon index) showed an “M-shaped” trend, peaking at 670 m and lowest at 198 m. The peaks and troughs of microbial fungal community diversity did not coincide with those of the bacterial community, indicating a complex ecological issue. Different microorganisms respond differently to environmental factors, which might be the main reason for this phenomenon. Research has demonstrated that the relationship between plants and microbial communities is influenced by abiotic factors, including soil nutrients, pH, and altitude [71]. Since soil bacteria and fungi compete for similar resources [72], their differences in decomposition ability, environmental preferences, and related functions might lead to differing responses to the same ecological processes [73]. Fungi can strengthen their dominance by altering the soil to favor specific species, while bacterial diversity is mainly determined by environmental factors, with species diversity regulated by pH and nutrients and functional diversity influenced by annual precipitation; fungal diversity exhibits trends contrary to these factors, suggesting a notable antagonistic relationship between bacteria and fungi. Distribution patterns for bacterial resistance genes echo impacts from bacterial-fungal interactions within soil microbial communities [8].
In conclusion, this study enhances the knowledge of microbial communities in rhizospheric soil by concentrating on the lesser-examined effect of altitude on microbial diversity and richness. It identified dominant fungal genera forming ectomycorrhizae with C. hystrix and highlighted their adaptability to different ecological niches along the altitudinal gradient. The research also observed significant dominance and adaptability of Proteobacteria and Acidobacteria, with their abundance varying at different altitudes. Detailed α-diversity indices revealed the complex influence of altitude on fungal and bacterial communities. Additionally, it discussed the complex interactions and antagonism between bacteria and fungi, reflecting the multifaceted nature of soil microbial communities influenced by environmental factors like altitude, soil nutrients, and pH.
4.3. Impact of Soil Physical and Chemical Characteristics on Bacterial and Fungal Community Configurations in the Rhizospheric Soil of C. hystrix
Soil physicochemical properties significantly impact fungal diversity and community structure. Studies of fungal communities in the broadleaf forests of northern Michigan, USA, indicated that soil moisture content and pH were the primary environmental factors affecting soil fungi [74]. Liu et al. [75] suggested that soil pH serves as a key determinant for soil fungal diversity in southwest China. Zhou Yujie et al. [76], in their study on the diversity of soil fungal communities in Wuyi Mountain’s Hevea brasiliensis forests, also found that soil nutrients significantly influenced soil fungi, with fungal abundance positively correlated with potassium content, suggesting a potential activating role of potassium on soil fungi. The PCoA and NMDS evaluations of rhizosphere soil microbial populations across five distinct elevation zones in our study indicated that variations in altitude can substantially modify the microbial community composition of C. hystrix rhizosphere soil. Soil physical and chemical properties had a significant impact on the structure of fungal communities in the rhizosphere soil of C. hystrix, ranked in order of importance: TP > NO3−-N > HN > TN > SOM > pH > NH4+-N > TK > AK > AP. Soil TP, NO3−-N, TN, and HN are the four main environmental factors affecting the dominant fungal phylum communities. TP displayed a notable positive correlation with the abundance of Sebacina, Amanita, and Byssocorticlum. The sequence of impact of rhizospheric soil physical and chemical properties on the bacterial community composition was AK > SOM > TN > pH > NH4+-N > HN > TK > AP > NO3−-N > TP. At the genus level, soil AK was the primary environmental factor affecting the bacterial community composition. Additionally, AK showed a positive correlation with the abundance of Bryobacter and Candidatus_Solibacter.
In the forests of the south Asian subtropical region of China, due to intense soil weathering, global warming, and atmospheric N deposition, the soils exhibit characteristics of “rich N” and “lacking P” [77]. JIAN [78] demonstrated that soil P limitation significantly correlates with soil pH, while N deposition leads to soil acidification. Nitrogen, a crucial energy and nutrient source for microbes, is essential for their growth and metabolic activities [79]. Studies have indicated that soil nitrogen accumulation impacts the structure of soil microbial communities beneath vegetation by influencing plant community diversity, productivity, and stability [80]. This explains why changes in NO3−-N and TN significantly affect the fungal community structure. Wang et al. [81], in their study on the impact of nitrogen on fungal communities in northern coniferous forests, found that increased nitrogen content reduces fungal diversity, leading to changes in fungal community composition. Nitrogen and phosphorus are key factors determining the growth and infection of mycorrhizal fungi, and nitrogen-fixing bacteria in C. hystrix forests convert molecular N to organic N, improving plant N nutrition and secreting auxins to promote plant growth [82]. In this study, TP was identified as the primary influencing factor on the structure of the fungal community in C. hystrix rhizosphere soil, suggesting that the growth of C. hystrix plantations might also be limited by phosphorus. Soil total nitrogen content exhibited a positive correlation with soil fungal diversity and was significantly associated with the abundance of Sebacina, Amanita, and Byssocorticlum, indicating a significant impact of soil nitrogen elements on the composition of soil fungal communities.
Potassium, one of the three essential plant elements, significantly influences plant growth, development, metabolism, and resistance. Although soil potassium content generally ranges between 1% and 3%, significantly higher than nitrogen and phosphorus, most is not readily available for plant absorption within a single season, with plant-available potassium typically not exceeding 2% of the total potassium. Soil potassium levels influence soil microbial growth [83], and some ectomycorrhizal fungi can activate potassium in the surrounding soil through their extraradical mycelium, supplying it to their host plants and promoting plant potassium absorption [84]. Available potassium is a crucial indicator of soil potassium supply capacity, with plants absorbing potassium through soil microbes that convert insoluble potassium into soluble forms [85]. Consistent with previous studies [86], soil AK was identified as the main environmental factor affecting the composition of the bacterial community.
In summary, this study enhances our understanding of how soil physicochemical properties, particularly nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, impact fungal and bacterial communities in C. hystrix rhizosphere soil. It highlighted the significant influence of altitude on microbial structure and detailed the crucial roles of TP, NO3−-N, and AK as primary environmental factors affecting microbial composition. The research revealed the complex interactions between soil nutrients and microbial diversity, providing nuanced insights into their collective impact on forest ecosystem structure and function.
5. Conclusions
In summary, this study clearly demonstrates that altitude significantly impacts the physicochemical properties of the soil and soil microbial interactions in the rhizosphere of C. hystrix. Soil properties and microbial communities respond complexly to altitude, with key nutrients showing a “V-shaped” trend as altitude increases. This trend, indicative of microbial activity changes, affects soil acidity and microbial interactions. Predominantly, Basidiomycota and Ascomycota fungi, crucial for the plant’s growth and ecosystem stability, dominate these communities. Their abundance and diversity, along with that of bacterial communities, are influenced by soil nutrient content, especially phosphorus, nitrogen, and potassium. Considering the altitude’s influence on soil and microbial properties is crucial for forest management, particularly in subtropical China with its “rich N” and “lacking P” soil characteristics. Future research should focus on the ecological roles and strategies for managing C. hystrix rhizosphere microbial communities at different altitudes for sustainable forest management.
Author Contributions
Methodology, G.X. and X.Z.; Formal analysis, G.X.; Investigation, G.X. and X.Z., J.X., Q.Z., L.T., S.D., J.Z. and C.Z.; Data curation, G.X., J.X. and X.Z.; Writing—review & editing, G.X., J.W. and X.Z.; Supervision, X.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Scientific Program Project of the Experimental Centre of Tropical Forestry, Chinese Academy of Forestry (RL2020-05). Chinese Academy of Forestry Special Funds in 2023 for Basic Research Operating Expenses Project (CAFYBB2023MA024). The Scientific Program Project of the Experimental Centre of Tropical Forestry, Chinese Academy of Forestry (RLSF-2023-04). The National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31971655).
Data Availability Statement
The information detailed in this study can be obtained upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ma, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Niu, Y.; Cai, L. Characteristics and ecological function prediction of alfalfa soil bacterial community in rain-fed areas of the Loess Plateau with different planting years. J. Grass Ind. 2021, 30, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The Interplay between Microbial Communities and Soil Properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cheng, J.; Franks, A.E.; Huang, X.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ma, B.; Xu, J.; He, Y. Loss of Microbial Diversity Weakens Specific Soil Functions, but Increases Soil Ecosystem Stability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Gao, D.; Liu, J.; Qiao, P.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.; Jin, X.; Wu, F. Changes in Rhizosphere Soil Microbial Communities in a Continuously Monocropped Cucumber (Cucumis Sativus L.) System. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 60, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, W.; Janda, T.; Molnár, Z. Unveiling the Significance of Rhizosphere: Implications for Plant Growth, Stress Response, and Sustainable Agriculture. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 206, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, D.; Mondal, R.; Khoshru, B.; Senapati, A.; Radha, T.K.; Mahakur, B.; Uniyal, N.; Myo, E.M.; Boutaj, H.; Sierra, B.E.G.; et al. Actinobacteria-Enhanced Plant Growth, Nutrient Acquisition, and Crop Protection: Advances in Soil, Plant, and Microbial Multifactorial Interactions. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 149–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Balser, T.C.; Firestone, M.K. Linking Microbial Community Composition to Function in a Tropical Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and Function of the Global Topsoil Microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.; Sun, H. Soil Fungal Community and Potential Function in Different Forest Ecosystems. Diversity 2022, 14, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genre, A.; Lanfranco, L.; Perotto, S.; Bonfante, P. Unique and Common Traits in Mycorrhizal Symbioses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Zobel, M. How Mycorrhizal Associations Drive Plant Population and Community Biology. Science 2020, 367, eaba1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahanovitc, R.; Livne-Luzon, S.; Angel, R.; Klein, T. Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Mediate Belowground Carbon Transfer between Pines and Oaks. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Van Bodegom, P.M.; Terrer, C.; Zelfde, M.V.; McCallum, I.; Luke McCormack, M.; Fisher, J.B.; Brundrett, M.C.; De Sá, N.C.; Tedersoo, L. Global Mycorrhizal Plant Distribution Linked to Terrestrial Carbon Stocks. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Chang, J.; Chang, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Tian, C. Impacts of Replanting American Ginseng on Fungal Assembly and Abundance in Response to Disease Outbreaks. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2157–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Hättenschwiler, S.; Yang, X. The Plant Microbiome: A Missing Link for Understanding Community Dynamics and Multifunctionality in Forest Ecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 145, 103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Noll, L.; Böckle, T.; Dietrich, M.; Herbold, C.W.; Eichorst, S.A.; Woebken, D.; Richter, A.; et al. Soil Multifunctionality Is Affected by the Soil Environment and by Microbial Community Composition and Diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 136, 107521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Huang, Z. Microbial Diversity Regulates Ecosystem Multifunctionality during Natural Secondary Succession. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 58, 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, H.; Sheng, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Effects of Environmental Factors on Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Diversity in Different Contaminated Districts of Southwest China Mine Tailings. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, S.; Yue, P.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Ma, X.; et al. Contrasting Relationships between Plant-Soil Microbial Diversity Are Driven by Geographic and Experimental Precipitation Changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bing, H.; Zhu, H. Climate Influences the Alpine Soil Bacterial Communities by Regulating the Vegetation and the Soil Properties along an Altitudinal Gradient in SW China. Catena 2020, 195, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Shen, F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Purahong, W.; Yang, L. Contrasting Altitudinal Patterns and Co-Occurrence Networks of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities along Soil Depths in the Cold-Temperate Montane Forests of China. Catena 2022, 209, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xie, C.; Qu, P.; Jiang, K.; Du, H.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Shi, X.; et al. Effects of Different Altitudes on Coffea Arabica Rhizospheric Soil Chemical Properties and Soil Microbiota. Agronomy 2023, 13, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.Y.; Li, M.; Yang, X.J.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.Q. Composition and Altitudinal Response of Soil Fungal Communities around Picea crassifolia in Qinghai. Mycology 2023, 42, 1635–1650. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Gunina, A.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Hemp, A.; Classen, A.T.; Ge, Y. Contrasting Patterns and Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Diversity across a Mountain Gradient. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, Z.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Differential Responses of Soil Microbial Biomass, Diversity, and Compositions to Altitudinal Gradients Depend on Plant and Soil Characteristics. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Guangyu; Deng, Zhiwen; Zhu, Xueping; Wu, Junduo; Dong, Shitao; Xie, Xianjin; Zeng, Ji Genomic characterisation and phylogenetic analysis of Castanopsis hystrix chloroplasts. J. Biol. Eng. 2023, 39, 670–684. (In Chinese) [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Jia, H.; Sun, W.; Ming, A.; Pang, S.; An, N.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Dong, S. Influence of Slope Direction on the Soil Seed Bank and Seedling Regeneration of Castanopsis hystrix Seed Rain. Forests 2021, 12, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Wu, J.; Zhou, B.; Zhu, X.; Zeng, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, H. Effects of Shading on the Growth and Photosynthetic Fluorescence Characteristics of Castanopsis hystrix Seedlings of Top Community-Building Species in Southern Subtropical China. Forests 2023, 14, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Yang, F.; Chen, B.; Liang, J.; Lu, J. Structure of mycorrhizal microbial communities in a mixed Castanopsis hystrix-Pinus massoniana forest in Pingxiang, Guangxi. J. Mycol. 2021, 40, 1343–1356. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liang, T.; Man, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, T. Deciphering Rhizosphere Microbiome Assembly of Castanea Henryi in Plantation and Natural Forest. Microorganisms 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ullah, N.; Tung, S.A.; Ali, B.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, L. Insights into Accumulation of Active Ingredients and Rhizosphere Microorganisms between Salvia miltiorrhiza and S. castanea. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2023, 370, fnad102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Hui, D.; Hou, E.; Xiong, J.; Xing, S.; Deng, Q. Differential Responses and Mechanistic Controls of Soil Phosphorus Transformation in Eucalyptus Plantations with N Fertilization and Introduced N2-fixing Tree Species. New Phytol. 2023, 237, 2039–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, H.; Qin, Z.; Cai, D.; Jia, H.; Li, X.; You, Y. Natural regeneration and environmental interpretations of Castanopsis hystrixs in a southern subtropical Pinus massoniana × Castanopsis hystrix mixed forest. Guangxi Sci. 2019, 26, 207–214. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.H.; Wang, B.G.; He, Z.M. Effects of stand and cultivation pattern on the growth of Castanopsis hystrix. For. Sci. Res. 1999, 519–523. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, S.K.; King, A.J.; Meier, C.L.; Bowman, W.D.; Farrer, E.C.; Suding, K.N.; Nemergut, D.R. Plant–Microbe Interactions at Multiple Scales across a High-Elevation Landscape. Plant Ecol. Divers. 2015, 8, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Lu, J.; Yin, L.; Wang, P.; Cheng, W. Rhizosphere Effects along an Altitudinal Gradient of the Changbai Mountain, China. Forests 2022, 13, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Li, W.; Pang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yin, C. Soil Properties and Root Traits Are Important Factors Driving Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Variations in Alpine Rhododendron Nitidulum Shrub Ecosystems along an Altitudinal Gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Tian, P.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, Z. Rhizosphere Effects on Soil Organic Carbon Processes in Terrestrial Ecosystems: A Meta-Analysis. Geoderma 2022, 412, 115739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, C.; Lu, J.; Yin, L.; Wang, P.; Cheng, W. Strong Linkage of Carbon and Nitrogen Mineralization in Rhizosphere Soils along an Altitudinal Forest Gradient of Changbai Mountain. 2022. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-1588844/v1 (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Cairney, J.W.G. Basidiomycete Mycelia in Forest Soils: Dimensions, Dynamics and Roles in Nutrient Distribution. Mycol. Res. 2005, 109, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundell, T.K.; Mäkelä, M.R.; Hildén, K. Lignin-modifying Enzymes in Filamentous Basidiomycetes—Ecological, Functional and Phylogenetic Review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2010, 50, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beimforde, C.; Feldberg, K.; Nylinder, S.; Rikkinen, J.; Tuovila, H.; Dörfelt, H.; Gube, M.; Jackson, D.J.; Reitner, J.; Seyfullah, L.J.; et al. Estimating the Phanerozoic History of the Ascomycota Lineages: Combining Fossil and Molecular Data. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 78, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Zarre, S.; Tedersoo, L. Regional and Local Patterns of Ectomycorrhizal Fungal Diversity and Community Structure along an Altitudinal Gradient in the Hyrcanian Forests of Northern Iran. New Phytol. 2012, 193, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claridge, A.W.; May, T.W. Mycophagy among Australian Mammals. Aust. J. Ecol. 1994, 19, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenken, L. Die Gattung Russula: Untersuchungen zu ihrer Systematik anhand von Ektomykorrhizen. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität München, München, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, M.; Yuan, Y.; Zuo, J.; Sun, L.; Tao, J. Microbiota Associated with the Rhizosphere of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (Ornamental Cultivar). Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.L.; Bruns, T.D. Community Structure of Ectomycorrhizal Fungi in a Pinus Muricata Forest: Minimal Overlap between the Mature Forest and Resistant Propagule Communities. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Huang, J.; Long, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Diversity and Community Structure of Ectomycorrhizal Fungi Associated with Larix Chinensis across the Alpine Treeline Ecotone of Taibai Mountain. Mycorrhiza 2017, 27, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, P.A.; Wilson, J.; Last, F.T.; Walker, C. The Concept of Succession in Relation to the Spread of Sheathing Mycorrhizal Fungi on Inoculated Tree Seedlings Growing in Unsterile Soils. Plant Soil 1983, 71, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Cao, T.; Nguyễn, T.T.T.; Yuan, H.-S. Six New Species of Tomentella (Thelephorales, Basidiomycota) from Tropical Pine Forests in Central Vietnam. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 864198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redhead, S.A.; Malloch, D.W. The Genus Phaeocollybia (Agaricales) in Eastern Canada and Its Biological Status. Can. J. Bot. 1986, 64, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüelles-Moyao, A.; Garibay-Orijel, R.; Márquez-Valdelamar, L.M.; Arellano-Torres, E. Clavulina-Membranomyces Is the Most Important Lineage within the Highly Diverse Ectomycorrhizal Fungal Community of Abies religiosa. Mycorrhiza 2017, 27, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Tong, Z. Changes in soil nutrients and Acidobacterium community structure in a Cunninghamia lanceolata plantation forest. For. Sci. 2019, 55, 119–127. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Pankratov, T.A.; Ivanova, A.O.; Dedysh, S.N.; Liesack, W. Bacterial Populations and Environmental Factors Controlling Cellulose Degradation in an Acidic Sphagnum Peat. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, D.; Rentz, J.A.; Lilburn, T.G.; Davis, R.E.; Aldrich, H.; Chan, C.; Moyer, C.L. A Novel Lineage of Proteobacteria Involved in Formation of Marine Fe-Oxidizing Microbial Mat Communities. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dworkin, M.; Falkow, S.; Rosenberg, E.; Schleifer, K.-H.; Stackebrandt, E. (Eds.) The Prokaryotes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006; ISBN 978-0-387-25495-1. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Herbert, S.J.; Jin, J. Effectiveness of Elevated CO2 Mediating Bacterial Communities in the Soybean Rhizosphere Depends on Genotypes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 231, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rime, T.; Hartmann, M.; Brunner, I.; Widmer, F.; Zeyer, J.; Frey, B. Vertical Distribution of the Soil Microbiota along a Successional Gradient in a Glacier Forefield. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1091–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, P.; Rodríguez-Echeverría, S.; González, L.; Freitas, H. Effect of Invasive Acacia Dealbata Link on Soil Microorganisms as Determined by PCR-DGGE. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 44, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Xie, X.; Peng, Y.; Chai, J.; Chen, N. Characteristics of Soil Microbial Community Functional and Structure Diversity with Coverage of Solidago Canadensis L. J. Cent. South Univ. 2013, 20, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Lemanceau, P.; Van Der Putten, W.H. Going Back to the Roots: The Microbial Ecology of the Rhizosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, G.T.; Mitkowski, N.A.; Aldrich-Wolfe, L.; Emele, L.R.; Jurkonie, D.D.; Ficke, A.; Maldonado-Ramirez, S.; Lynch, S.T.; Nelson, E.B. Methods for Assessing the Composition and Diversity of Soil Microbial Communities. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2000, 15, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, S.W.; Beiler, K.J.; Bingham, M.A.; Deslippe, J.R.; Philip, L.J.; Teste, F.P. Mycorrhizal Networks: Mechanisms, Ecology and Modelling. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2012, 26, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Põlme, S.; Kõljalg, U.; Yorou, N.S.; Wijesundera, R.; Ruiz, L.V.; Vasco-Palacios, A.M.; Thu, P.Q.; Suija, A.; et al. Global Diversity and Geography of Soil Fungi. Science 2014, 346, 1256688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedersoo, L.; Anslan, S.; Bahram, M.; Drenkhan, R.; Pritsch, K.; Buegger, F.; Padari, A.; Hagh-Doust, N.; Mikryukov, V.; Gohar, D.; et al. Regional-Scale In-Depth Analysis of Soil Fungal Diversity Reveals Strong pH and Plant Species Effects in Northern Europe. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Kang, X. Soil pH and Nutrients Shape the Vertical Distribution of Microbial Communities in an Alpine Wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacke, H.; Thürmer, A.; Wollherr, A.; Will, C.; Hodac, L.; Herold, N.; Schöning, I.; Schrumpf, M.; Daniel, R. Pyrosequencing-Based Assessment of Bacterial Community Structure Along Different Management Types in German Forest and Grassland Soils. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.-H.; Li, M.; Lu, P.; Lv, G.-F.; Niu, Y.-F. Research on the structure of soil bacterial community in the inter-root of Betula platyphylla in Dazhoushan, Hohhot. J. Ecol. 2019, 39, 3586–3596. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Juhnke, M.E.; Mathre, D.E.; Sands, D.C. Identification and Characterization of Rhizosphere-Competent Bacteria of Wheat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, X.; Liang, W.; Chu, H. Soil pH Drives the Spatial Distribution of Bacterial Communities along Elevation on Changbai Mountain. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, W.D.; Folman, L.B.; Summerbell, R.C.; Boddy, L. Living in a Fungal World: Impact of Fungi on Soil Bacterial Niche Development. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 795–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering Fungal: Bacterial Dominance in Soils—Methods, Controls, and Ecosystem Implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanowicz, K.J.; Freedman, Z.B.; Upchurch, R.A.; Argiroff, W.A.; Zak, D.R. Active Microorganisms in Forest Soils Differ from the Total Community yet Are Shaped by the Same Environmental Factors: The Influence of pH and Soil Moisture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2016, 92, fiw149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, G.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Soil pH Determines Fungal Diversity along an Elevation Gradient in Southwestern China. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, G.Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, W.L.; Wang, Y.P.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, H.F. Analysis of the diversity and community composition of soil fungi in Hevea brasiliensis forests based on high-throughput sequencing. South. J. Agric. 2018, 49, 1729–1735. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, H.; Lin, Y.; Tang, X.; Hui, D.; Lambers, H.; Sardans, J.; et al. Soil Phosphorus Availability Affects Diazotroph Communities during Vegetation Succession in Lowland Subtropical Forests. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Ni, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lei, L.; Xu, J.; Xiao, W.; Li, M.-H. Latitudinal Patterns of Soil Extracellular Enzyme Activities and Their Controlling Factors in Pinus massoniana Plantations in Subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 495, 119358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Hu, J.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J. Relationship between Plant Roots, Rhizosphere Microorganisms, and Nitrogen and Its Special Focus on Rice. Agriculture 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, S.; Baoyin, T. Plant and Soil Properties Mediate the Response of Soil Microbial Communities to Moderate Grazing in a Semiarid Grassland of Northern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Koziol, L.; Foster, B.L.; Bever, J.D. Microbial Mediators of Plant Community Response to Long-term N and P Fertilization: Evidence of a Role of Plant Responsiveness to Mycorrhizal Fungi. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2022, 28, 2721–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocking, E.C. Endophytic Colonization of Plant Roots by Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, R.; Benito, B. The Role of Soil Fungi in K+ Plant Nutrition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etesami, H.; Glick, B.R. Exploring the Potential: Can Mycorrhizal Fungi and Hyphosphere Silicate-Solubilizing Bacteria Synergistically Alleviate Cadmium Stress in Plants? Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2023, 6, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Maity, A.; Ray, P.; Biswas, D.R.; Roy, S. Potassium Supply in Agriculture through Biological Potassium Fertilizer: A Promising and Sustainable Option for Developing Countries. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2022, 68, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xin, W.; Lei, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, X.; Sun, Y. Effects of different ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium on the structure of soil bacterial communities in the inter-root of young Camellia oleifera forests. South. For. Sci. 2021, 49, 32–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).