Evolutionary Characteristics and Driving Forces of Green Space in Guangzhou from a Zoning Perspective
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
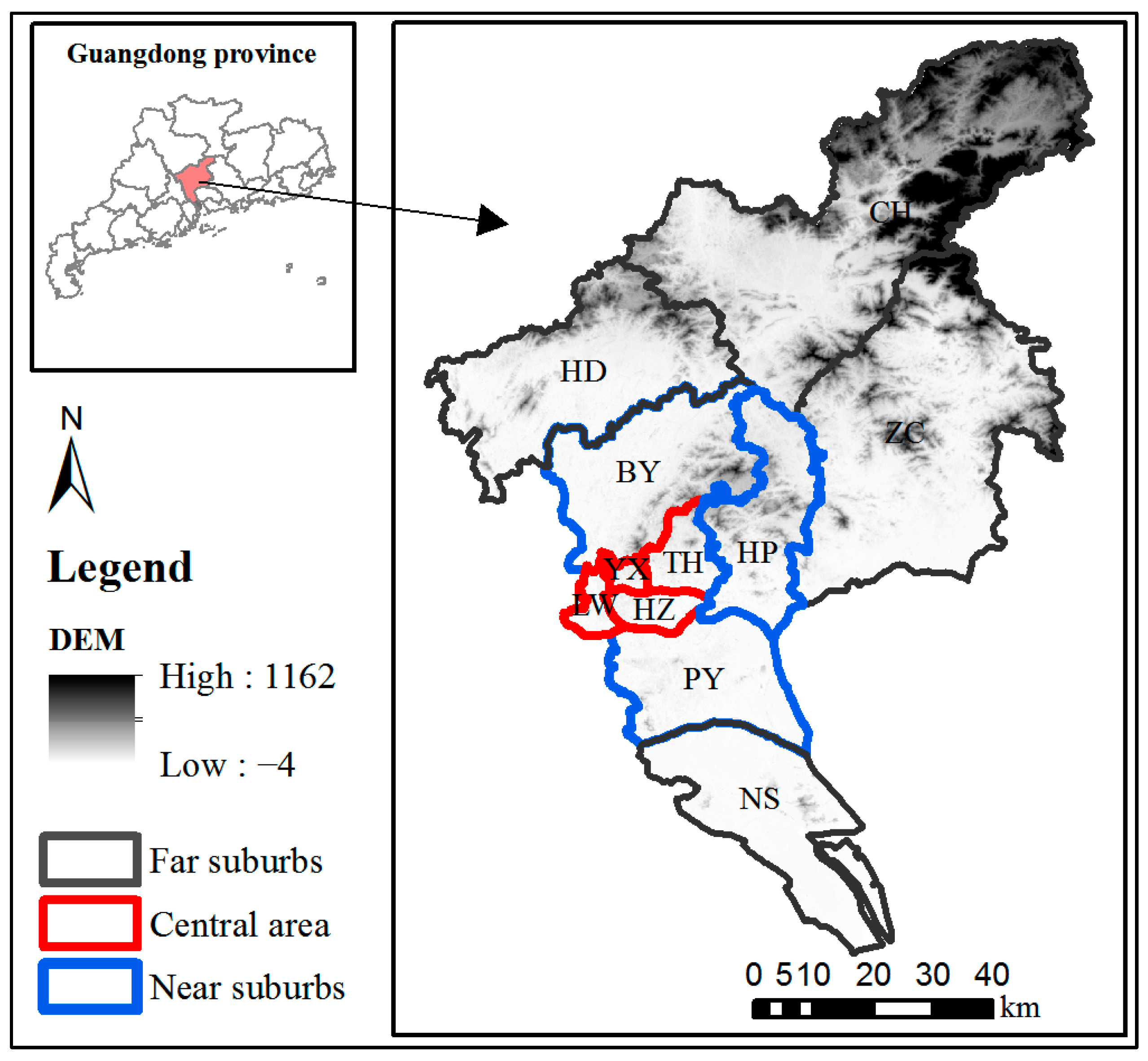
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Dynamic Degree of Green Space Change
2.3.2. Landscape Metrics
2.3.3. Land Use Transfer Matrix
2.3.4. Geodetector
2.3.5. Driving Factor Selection
3. Results
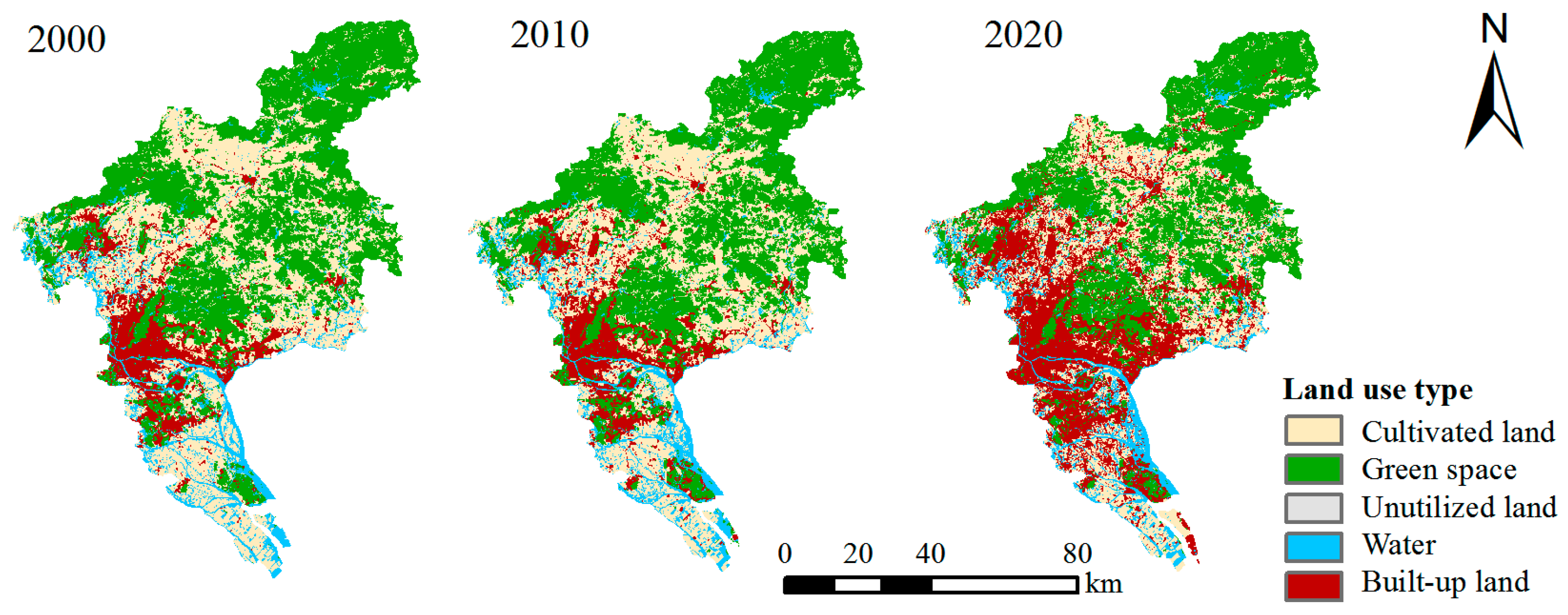
3.1. Spatiotemporal Change in Green Space Pattern
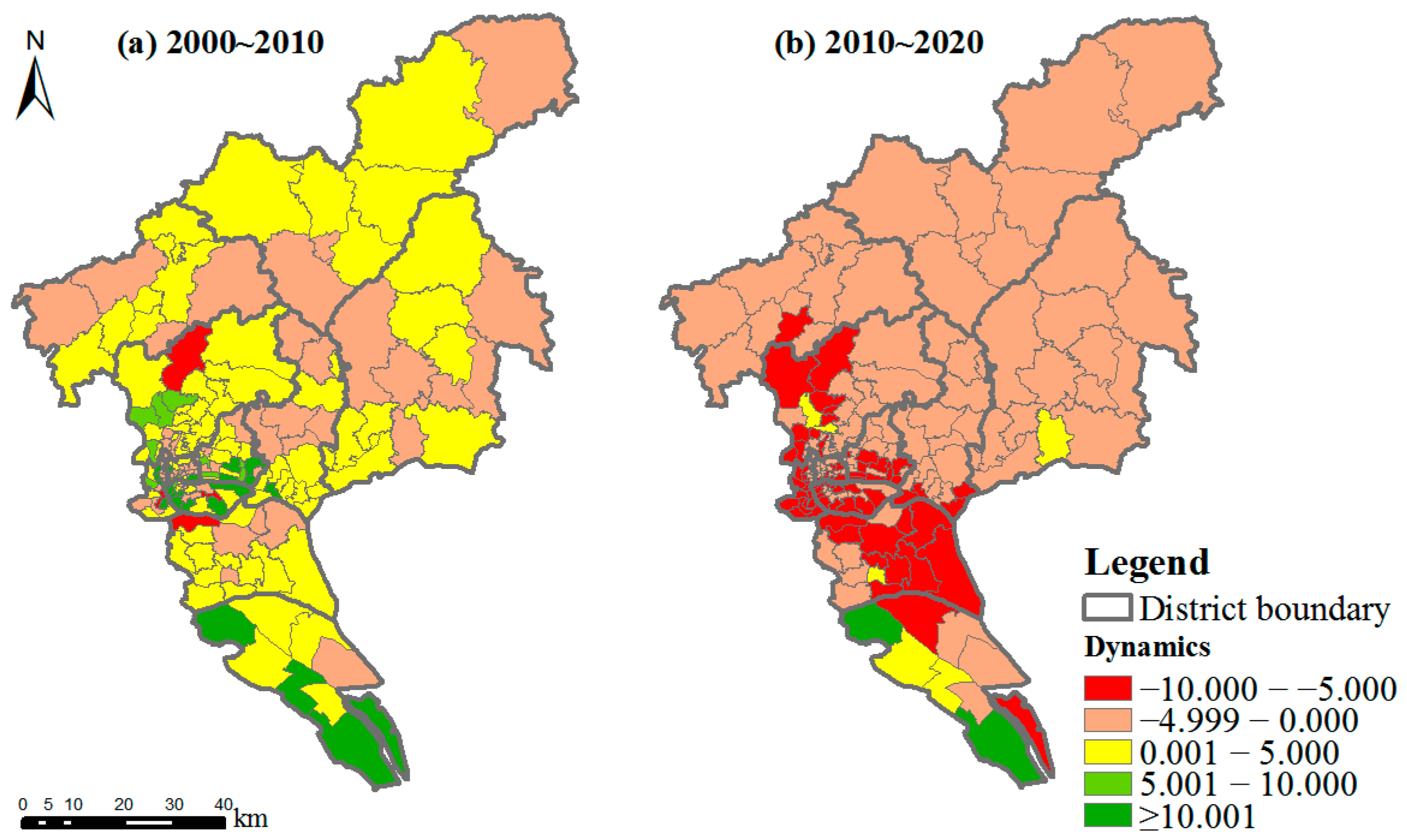
3.1.1. Green Space Dynamics Intensity
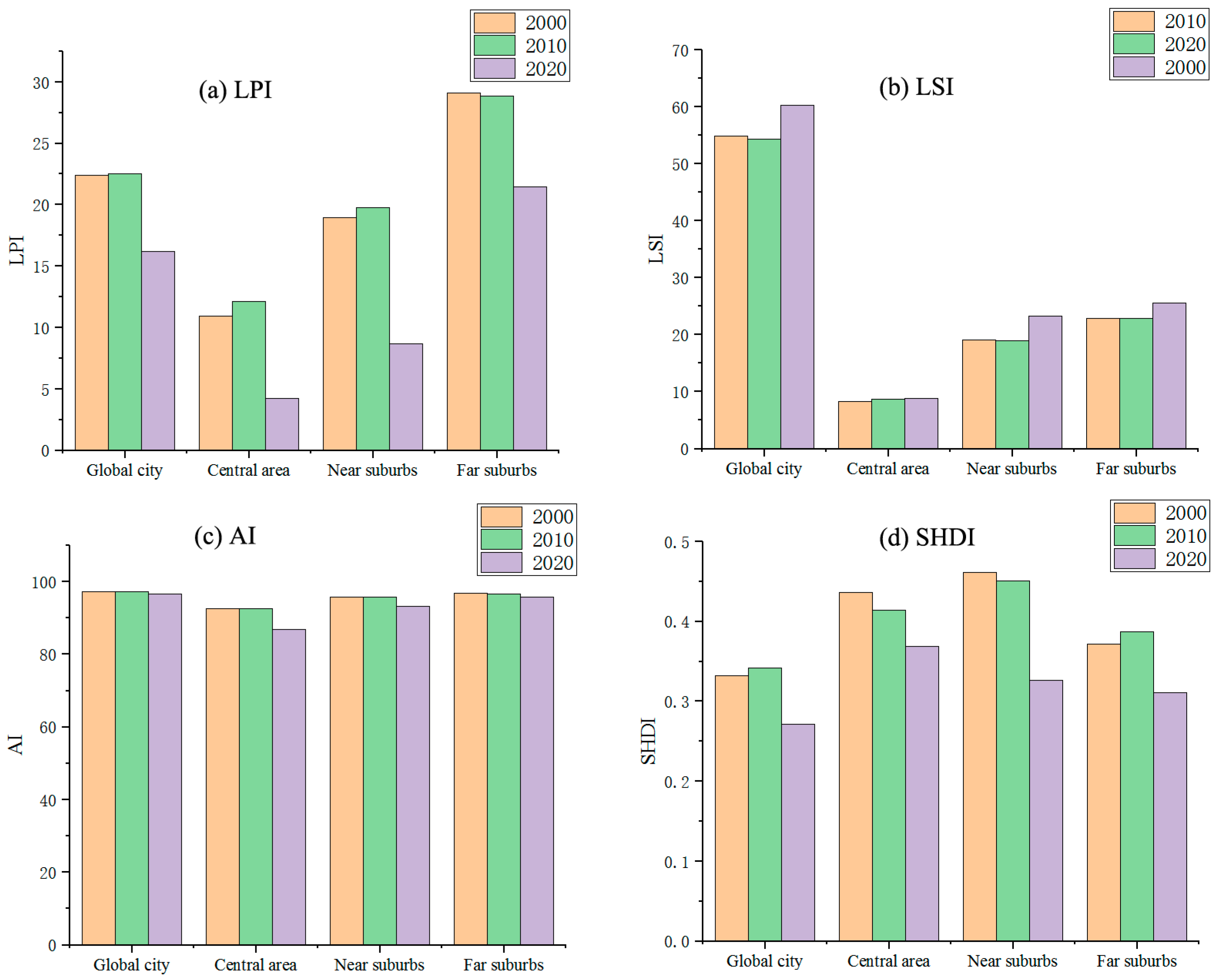
3.1.2. Green Space Landscape Change
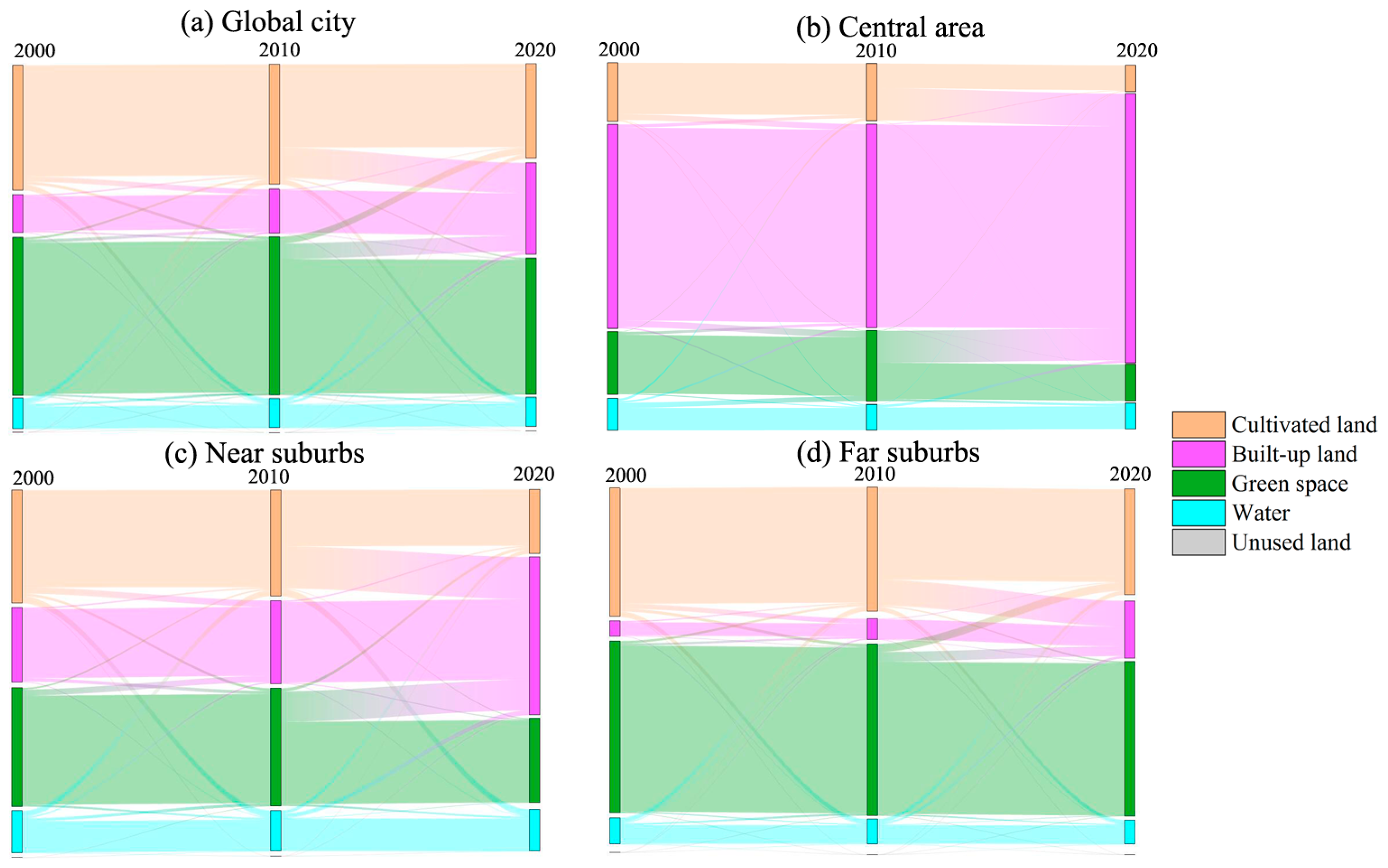
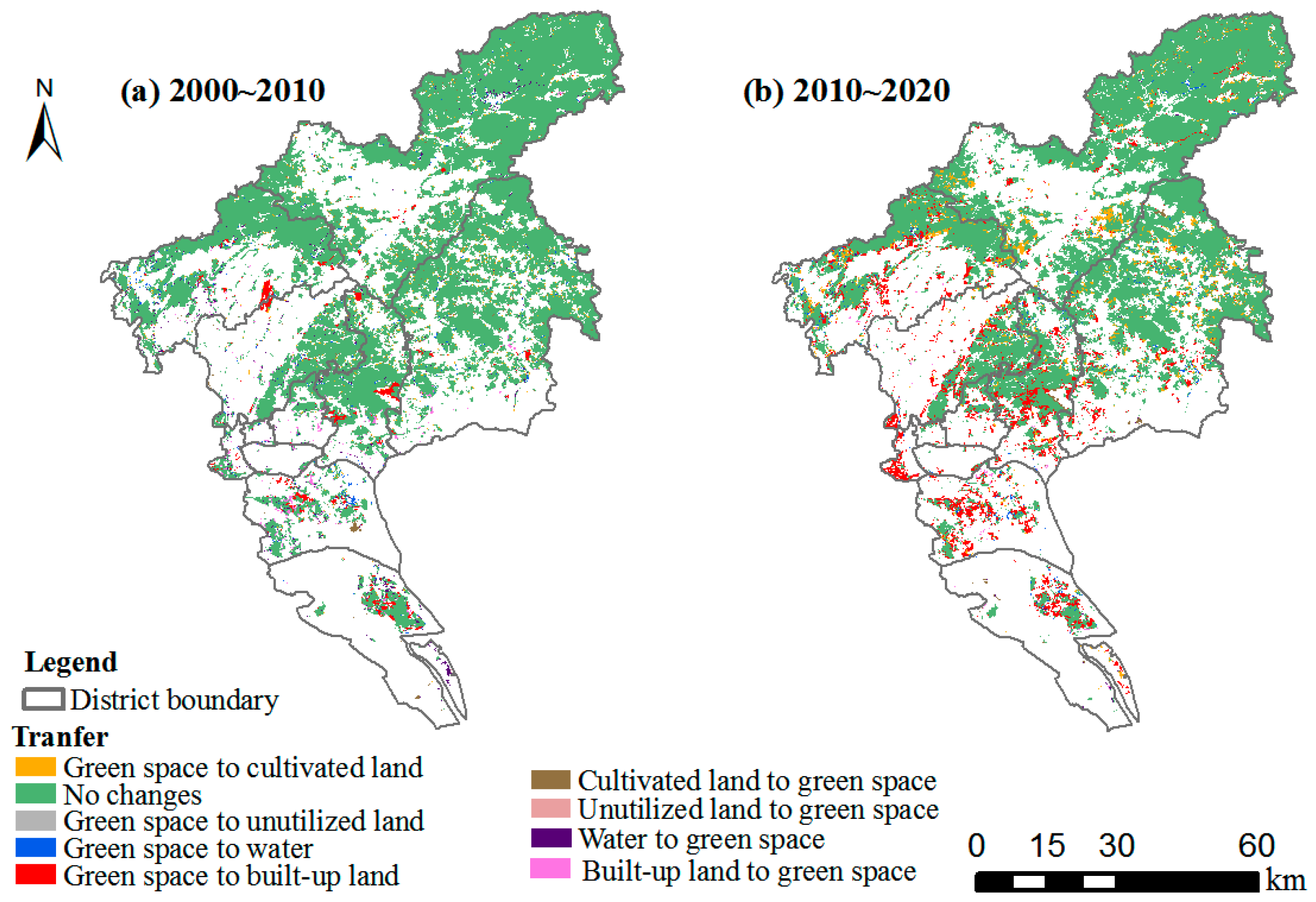
3.2. Green Space Transfer Change
3.3. Driving Factors of Green Space Change
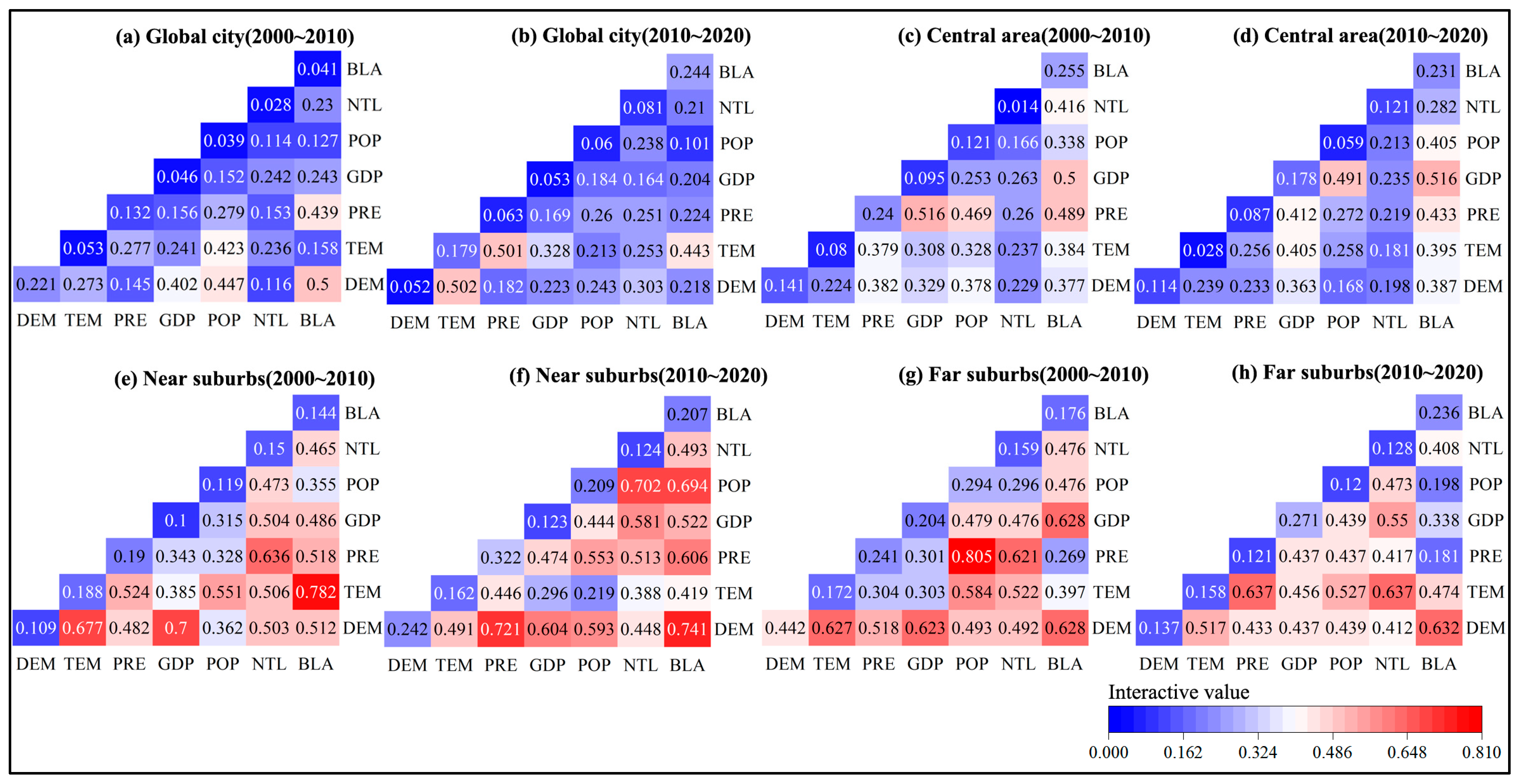
3.3.1. Driving Factor Detection
3.3.2. Interactive Detection
4. Discussion
4.1. Regional Heterogeneity in the Change and Drivers of Green Space
4.2. Application and Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Qiu, S.; Tan, X.; Zhuang, Y. Measuring the Relationship between Morphological Spatial Pattern of Green Space and Urban Heat Island Using Machine Learning Methods. Build. Environ. 2023, 228, 109910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.; Liang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhong, K.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Exploring the Variation Trend of Urban Expansion, Land Surface Temperature, and Ecological Quality and Their Interrelationships in Guangzhou, China, from 1987 to 2019. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Spatial–Temporal Dynamics and Driving Factor Analysis of Urban Ecological Land in Zhuhai City, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, R.M.; Spake, R.; Brown, K.A.; Ogutu, B.O.; Smith, D.; Eigenbrod, F. A Systematic Map of Research Exploring the Effect of Greenspace on Mental Health. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 201, 103823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlden, V.; de Albuquerque, J.P.; Weich, S.; Jarvis, S. A Spatial Analysis of Proximate Greenspace and Mental Wellbeing in London. Appl. Geogr. 2019, 109, 102036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajosaari, A.; Hasanzadeh, K.; Fagerholm, N.; Nummi, P.; Kuusisto-Hjort, P.; Kyttä, M. Predicting Context-Sensitive Urban Green Space Quality to Support Urban Green Infrastructure Planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2024, 242, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasi, R.; Ruggiero, F.; Berardi, U. Influence of Cross-Ventilation Cooling Potential on Thermal Comfort in High-Rise Buildings in a Hot and Humid Climate. Build. Environ. 2023, 248, 111096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, B. Evidence of Green Space Sparing to Ecosystem Service Improvement in Urban Regions: A Case Study of China’s Ecological Red Line Policy. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, R.; Meadows, M.E.; Sengupta, D.; Xu, D. Changing Urban Green Spaces in Shanghai: Trends, Drivers and Policy Implications. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek-Jakubska, J.; Filipiak, M.; Michalski, A.; Napierała-Filipiak, A. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Urban Forests and Planning Evolution in a Highly Dynamical Urban Area: The Case Study of Wrocław, Poland. Forests 2020, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Han, L. Understanding the Dynamic of Greenspace in the Urbanized Area of Beijing Based on High Resolution Satellite Images. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fang, C.; Mu, X.; Li, G.; Xu, G. Urban Green Space Quality in China: Quality Measurement, Spatial Heterogeneity Pattern and Influencing Factor. Urban For. Urban Green. 2021, 66, 127381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-B.; Ma, J.; Meadows, M.E.; Banzhaf, E.; Huang, T.-Y.; Liu, Y.-F.; Zhao, B. Spatio-Temporal Changes in Urban Green Space in 107 Chinese Cities (1990–2019): The Role of Economic Drivers and Policy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, C. Exploring Urban Green Spaces in China: Spatial Patterns, Driving Factors and Policy Implications. Land Use Policy 2019, 89, 104249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Jiao, F.; Yin, J.; Li, T.; Gong, H.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z. Nonlinear Relationship of Vegetation Greening with Nature and Human Factors and Its Forecast—A Case Study of Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Driving Factors of Regional Green Spaces during Rapid Urbanization in Nanjing Metropolitan Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Xu, T.; Dong, J.; Yu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhu, J.; Dong, J.; Xu, Y.; et al. Elevation-Dependent Effects of Climate Change on Vegetation Greenness in the High Mountains of Southwest China during 1982–2013. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 2029–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Jialin, L.; Ruiqing, L.; Zhongyi, W.; Haifeng, W.; Yongqiang, L. Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Greenspace System and Evaluation of Ecosystem Services in the Core Area of the Yangtze River Delta. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 956. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, M.; Ye, J. The Spatio-Temporal Trends of Urban Green Space and Its Interactions with Urban Growth: Evidence from the Yangtze River Delta Region, China. Land Use Policy 2023, 128, 106598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Xia, B. A Significant Increase in the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index during the Rapid Economic Development in the Pearl River Delta of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L. The Temporal Trend of Urban Green Coverage in Major Chinese Cities between 1990 and 2010. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xia, C. Towards a Greening City: How Does Regional Cooperation Promote Urban Green Space in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macau Greater Bay Area? Urban For. Urban Green. 2023, 86, 128033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, M.J.; Christien, L.; García-Escalona, E.; González-García, C. Sensitivity of Green Spaces to the Process of Urban Planning. Three Case Studies of Madrid (Spain). Cities 2020, 100, 102655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. Green Space Equity: Spatial Distribution of Urban Green Spaces and Correlation with Urbanization in Xiamen, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 25, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H. Characterizing the Inequalities in Urban Public Green Space Provision in Shenzhen, China. Habitat Int. 2016, 56, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dai, F.; Diehl, J.A.; Chen, M.; Bai, J. Exploring the Spatial Pattern of Community Urban Green Spaces and COVID-19 Risk in Wuhan Based on a Random Forest Model. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zhu, M.; Shi, Y.; Pei, H.; Nie, W.; Nan, X.; Zhu, X.; Yang, G.; Bao, Z. Equity Analysis of the Green Space Allocation in China’s Eight Urban Agglomerations Based on the Theil Index and GeoDetector. Land 2023, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, R.; Sha, Z. Exploring the Dynamics of Urban Greenness Space and Their Driving Factors Using Geographically Weighted Regression: A Case Study in Wuhan Metropolis, China. Land 2020, 9, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Xi, X.; Yang, W.; Liang, L. Monitoring Land Use/Cover Change Using Remotely Sensed Data in Guangzhou of China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, J.; Huang, H.; Lin, X. Research on the spatial correlation between the high-quality basic education resources and housing prices to pursuing a balanced development: A case study of Guangzhou. World Reg. Stud. 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Q.; Xue, D.; Gong, J. Influencing factors of online shopping frequency of residents and spatial differences of these factors in Guangzhou City. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2020, 40, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, D.; Yan, Z.; Wang, X.; Han, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Urban Green Space in Changchun: Changes, Transformations, Landscape Patterns, and Drivers. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianshe, X.; Bin, Q.; Guoqian, C.; Feifei, S.; Xiaoyun, C.; Cunxiong, Z. Land Use Change and Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value in Maduo County of Source Region of the Yellow River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 510–521. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q. Analyzing the Influence of Landscape Pattern Change on Ecological Water Requirements in an Arid/Semiarid Region of China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 578, 124098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Qin, K.; Yang, X. Effect of Landscape Pattern of Urban Surface Evapotranspiration on Land Surface Temperature. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Liu, M.; Yu, Z. Quantifying Ecological Landscape Quality of Urban Street by Open Street View Images: A Case Study of Xiamen Island, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Guo, W.; Wang, H.; Yu, L.; Cheng, S.; Huang, L.; Jiao, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H. Temporal and Spatial Variations in Landscape Habitat Quality under Multiple Land-Use/Land-Cover Scenarios Based on the PLUS-InVEST Model in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Land 2023, 12, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wei, X. Rural Resilience Evaluation and Influencing Factor Analysis Based on Geographical Detector Method and Multiscale Geographically Weighted Regression. Land 2023, 12, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Dong, G.; Wei, Y. Quantitative Analysis of NDVI Driving Factors Based on the Geographical Detector Model in the Chengdu-Chongqing Region, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor, A.N.M.; Corstanje, R.; Harris, J.A.; Brewer, T. Impact of Rapid Urban Expansion on Green Space Structure. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 81, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Xu, C. An Optimal Parameters-Based Geographical Detector Model Enhances Geographic Characteristics of Explanatory Variables for Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis: Cases with Different Types of Spatial Data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 593–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanifard, H.; Roshandel, T.; Ghodrati, S. Assessment and Ranking of Influencing Factors in the Relationship between Spatial Patterns of Urban Green Spaces and Socioeconomic Indices in Mashhad Urban Districts, Iran. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 1589–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Xie, H.; Jiang, L.; Lei, Z. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Urban Green Space Influenced by Rapid Urbanization and Land Use Policies in Shanghai. Forests 2021, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyra, M.; Kleemann, J.; Calò, N.C.; Schürmann, A.; Fürst, C. Protection of Peri-Urban Open Spaces at the Level of Regional Policy-Making: Examples from Six European Regions. Land Use Policy 2021, 107, 105480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Xie, S.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Yu, C. Urban Green Space Fragmentation and Urbanization: A Spatiotemporal Perspective. Forests 2019, 10, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Bi, L.; Zhu, K. Study on Spatial-Temporal Change of Urban Green Space in Yangtze River Economic Belt and Its Driving Mechanism. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D.R.; Passy, P.; Oh, R.R.Y. Impacts of Population Density and Wealth on the Quantity and Structure of Urban Green Space in Tropical Southeast Asia. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 157, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Determinants of Urban Land Use Efficiency under Green Development Orientation: Insights from 284 Cities and Eight Economic Zones in China, 2005–2019. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 161, 103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Xiao, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Evolution of Landscape Pattern of Green Space in Fujian Province: Influencing Factors and Spatial Differences Based on GWR Model. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2022, 37, 242–250. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Nie, P. Tracking the History of Urban Expansion in Guangzhou (China) during 1665–2017: Evidence from Historical Maps and Remote Sensing Images. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. Construction of Greenspace Landscape Ecological Network Based on Resistance Analysis of GeoDetector in Jinan. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, K. Spatial-Temporal Patterns and Influencing Factors of Ecological Land Degradation-Restoration in Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, C. Law and Mechanism of Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Urban Greenspace in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2023, 45, 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Ma, J.; Liu, H.; Song, L.; Cao, W.; Ren, Y. Spatial Heterogeneity Analysis of Urban Forest Ecosystem Services in Zhengzhou City. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X. Quantifying Influences of Natural and Anthropogenic Factors on Vegetation Changes Based on Geodetector: A Case Study in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.L.; Mitchell, M.G.; Shanahan, D.; Wilson, K.A.; Ives, C.D.; Lovelock, C.E.; Rhodes, J.R. The Role of Socio-Economic Factors in Planning and Managing Urban Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| A1 | A2 | … | Aj | |
| A1 | S11 | S12 | … | S1j |
| A2 | S12 | S22 | … | S2j |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| Ai | Si1 | Si2 | … | Sij |
| Variable | Dimension | Subcategory | Indicator | Abbreviation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent variable | Dynamics intensity of green space change | Y | |||
| Economic development | GDP | GDP | [16,33] | ||
| Independent variable | Social and economic | Urban expansion | Built-up land area | BLA | [33,48] |
| Human activity intensity | Population density | POD | [33,43] | ||
| Nighttime light | NTL | [46,49] | |||
| Nature and environment | Climatic | Average annual temperature | TEM | [50] | |
| Annual precipitation | PRE | ||||
| Topography | DEM | DEM | [50] | ||
| Indicator | UGS Area (km2) | UGS Area Change Intensity (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | |
| Central area | 57.002 | 64.052 | 33.090 | 1.237 | −4.834 |
| Near suburbs | 567.926 | 563.409 | 403.512 | −0.080 | −2.838 |
| Far suburbs | 2616.733 | 2616.862 | 2357.744 | 0.000 | −0.990 |
| Global City | Central Area | Near Suburbs | Far Suburbs | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | 2000–2010 | 2010–2020 | |||||||||
| q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | q | p | |
| TEM | 0.053 * | 0.064 | 0.179 *** | 0.001 | 0.080 | 0.463 | 0.028 | 0.927 | 0.188 | 0.183 | 0.162 | 0.272 | 0.172 | 0.224 | 0.158 | 0.525 |
| PRE | 0.132 *** | 0.006 | 0.063 ** | 0.034 | 0.240 *** | 0.009 | 0.087 | 0.399 | 0.190 | 0.166 | 0.322 ** | 0.016 | 0.241 | 0.277 | 0.121 | 0.690 |
| GDP | 0.046 | 0.284 | 0.053 | 0.190 | 0.095 | 0.351 | 0.178 ** | 0.031 | 0.100 | 0.550 | 0.123 | 0.198 | 0.204 | 0.243 | 0.271 * | 0.098 |
| POP | 0.039 | 0.309 | 0.060 | 0.164 | 0.121 * | 0.065 | 0.059 | 0.367 | 0.119 | 0.438 | 0.209 | 0.124 | 0.294 | 0.184 | 0.120 | 0.430 |
| NTL | 0.028 | 0.350 | 0.081 ** | 0.032 | 0.014 | 0.987 | 0.121 | 0.489 | 0.150 | 0.201 | 0.124 | 0.420 | 0.159 | 0.541 | 0.128 | 0.535 |
| BLA | 0.041 | 0.321 | 0.244 *** | 0.000 | 0.255 *** | 0.001 | 0.231 *** | 0.009 | 0.144 | 0.222 | 0.207 | 0.142 | 0.176 | 0.455 | 0.236 | 0.324 |
| DEM | 0.221 *** | 0.000 | 0.052 | 0.201 | 0.141 | 0.140 | 0.114 | 0.300 | 0.109 | 0.368 | 0.242 ** | 0.019 | 0.442 ** | 0.014 | 0.137 | 0.475 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Lin, C.; Ou, S.; Feng, Q.; Guo, K.; Xie, J.; Wei, X. Evolutionary Characteristics and Driving Forces of Green Space in Guangzhou from a Zoning Perspective. Forests 2024, 15, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010135
Wang H, Lin C, Ou S, Feng Q, Guo K, Xie J, Wei X. Evolutionary Characteristics and Driving Forces of Green Space in Guangzhou from a Zoning Perspective. Forests. 2024; 15(1):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010135
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huimin, Canrui Lin, Sihua Ou, Qianying Feng, Kui Guo, Jiazhou Xie, and Xiaojian Wei. 2024. "Evolutionary Characteristics and Driving Forces of Green Space in Guangzhou from a Zoning Perspective" Forests 15, no. 1: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010135
APA StyleWang, H., Lin, C., Ou, S., Feng, Q., Guo, K., Xie, J., & Wei, X. (2024). Evolutionary Characteristics and Driving Forces of Green Space in Guangzhou from a Zoning Perspective. Forests, 15(1), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f15010135





