Identification and Functional Characterization of the Nonexpressor of Pathogenesis-Related Genes 1 (NPR1) Gene in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Treatment
2.2. Identification and Characterization of the NPR1-like Genes from Tea Plants
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of the CsNPR1-like Genes
2.4. Gene Structure, Motif Composition, Gene Duplication, and Synteny Analysis of the CsNPR1-like Genes
2.5. Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements Analysis
2.6. The Structures and Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) Network of NPR1-like Proteins
2.7. Expression Profile Analysis of CsNPR1-like Family Genes
2.8. Cloning and Real-Time Quantitative PCR
2.9. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation Analysis
2.10. Subcellular Localization of CsNPR1a
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of the NPR1-like Genes
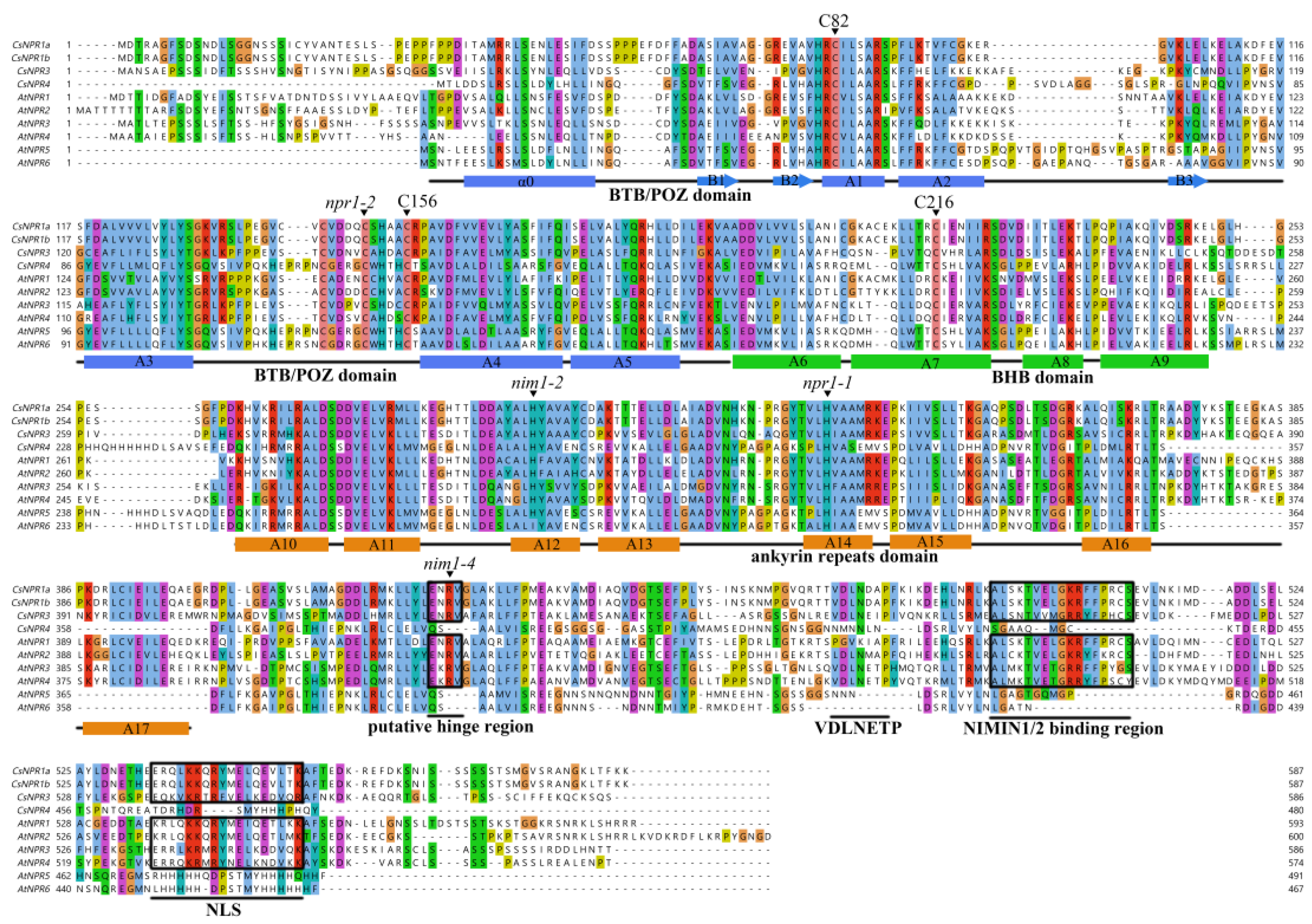
3.2. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of the CsNPR1-like Genes
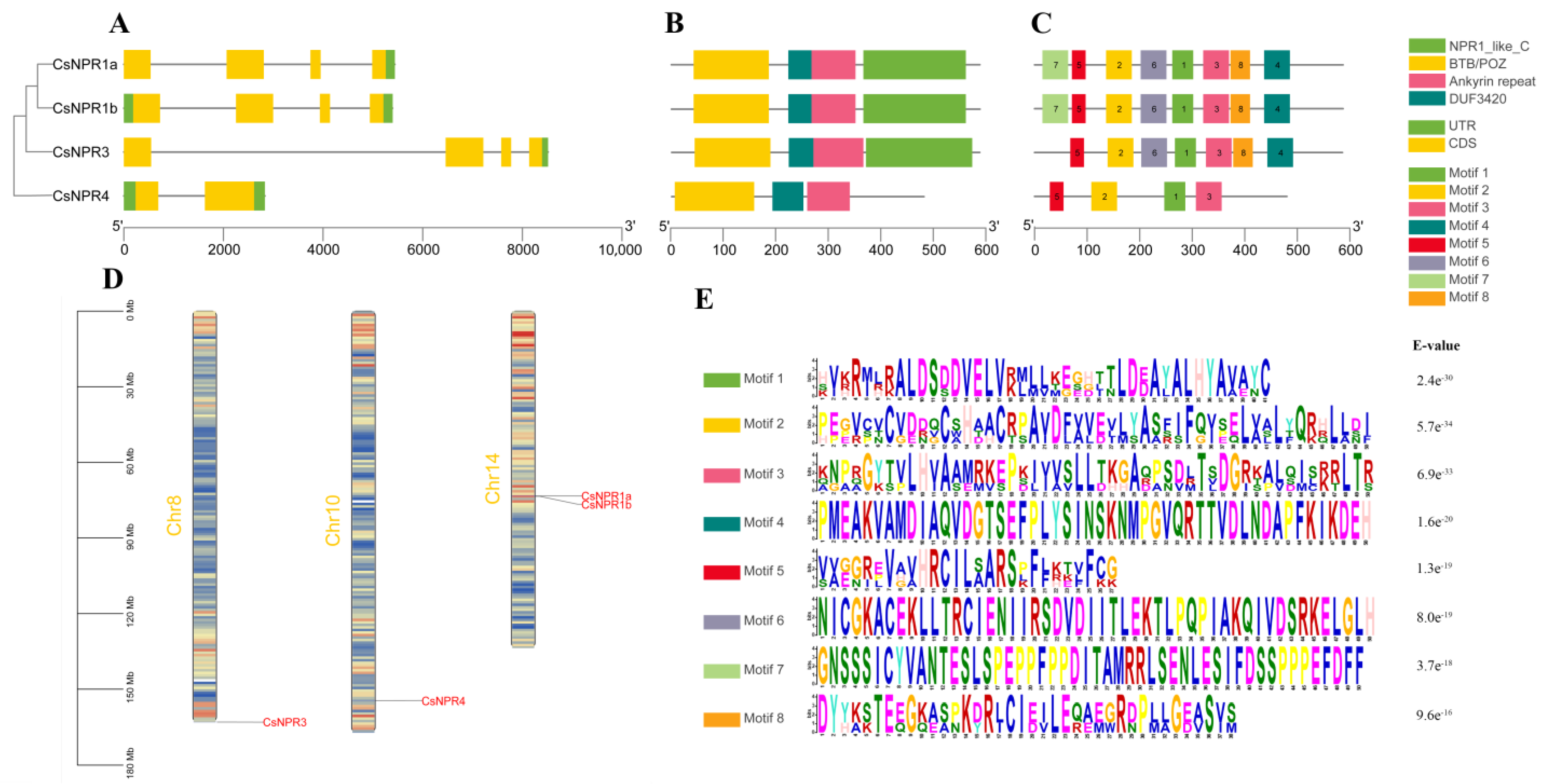
3.3. Chromosomal Distribution, Gene Structure, Gene Duplication, and Synteny Analysis
3.4. Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements Analysis of CsNPR1-like Genes
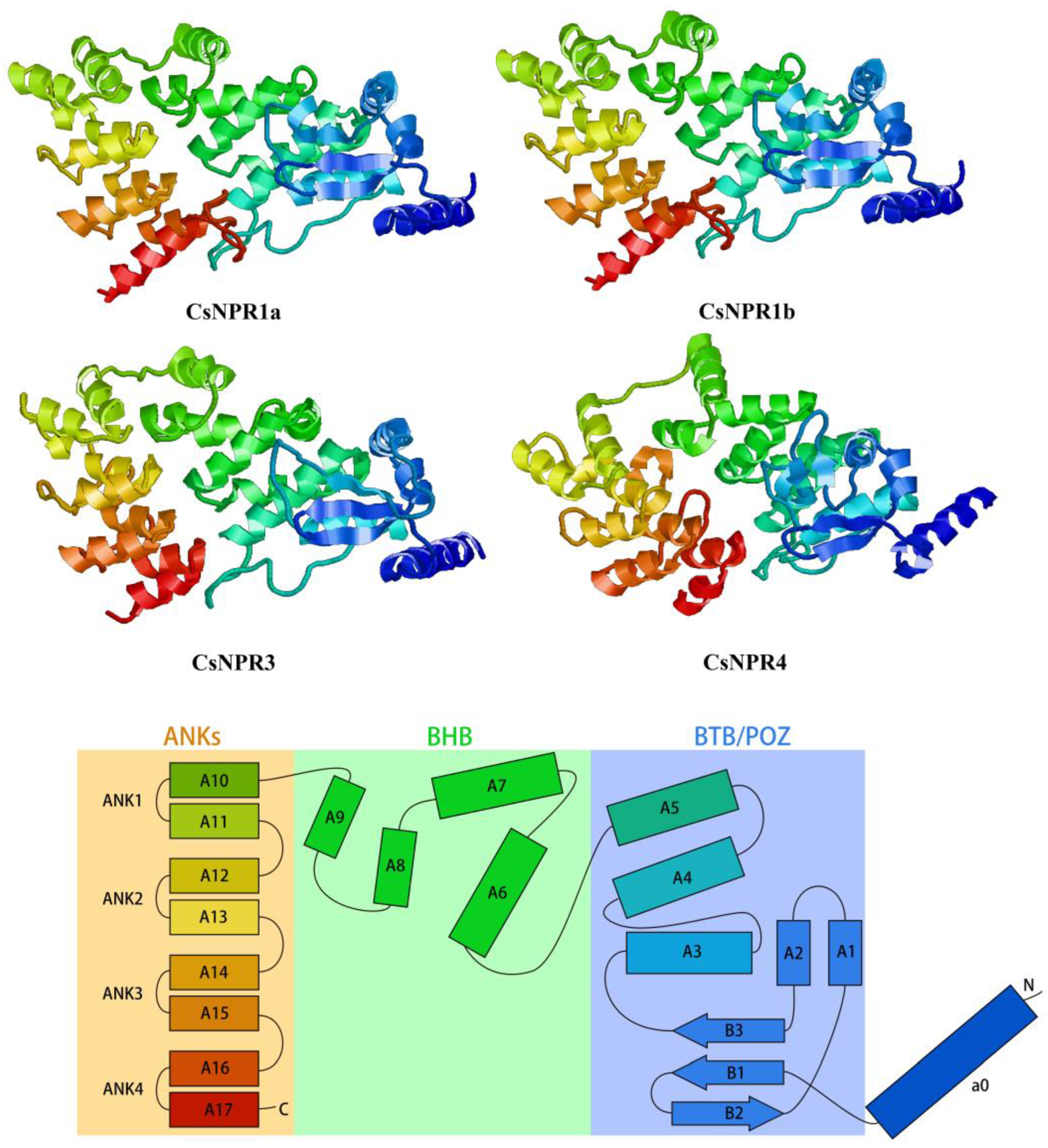
3.5. Secondary and Tertiary Structures of CsNPR1-like Proteins
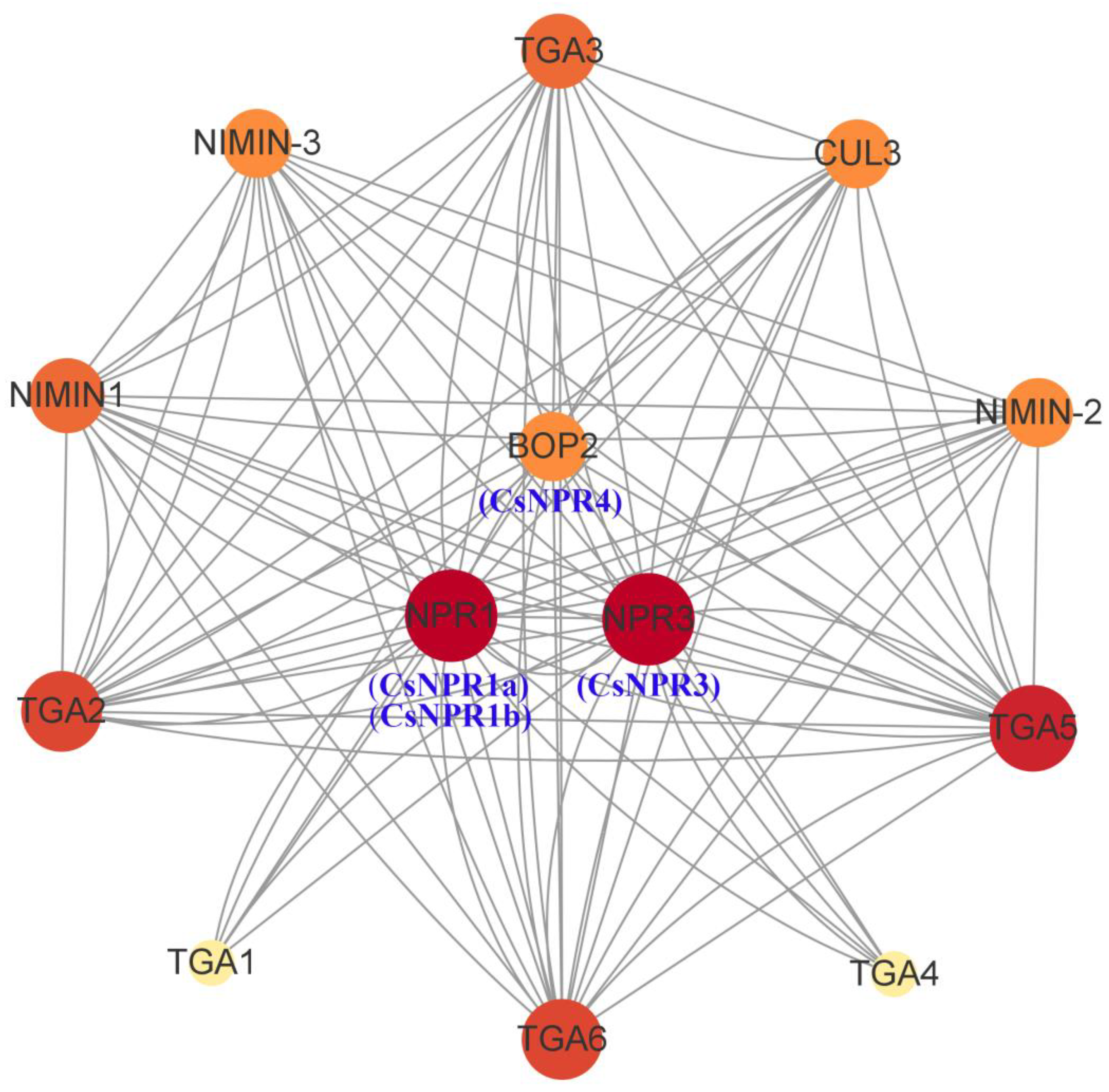
3.6. Network Analysis of Protein-Protein Interactions Involving CsNPR1-like Proteins
3.7. RNA-seq-Based Expression Analysis of CsNPR1-like Genes
3.8. CsNPR1a Interacts with AtTGA2
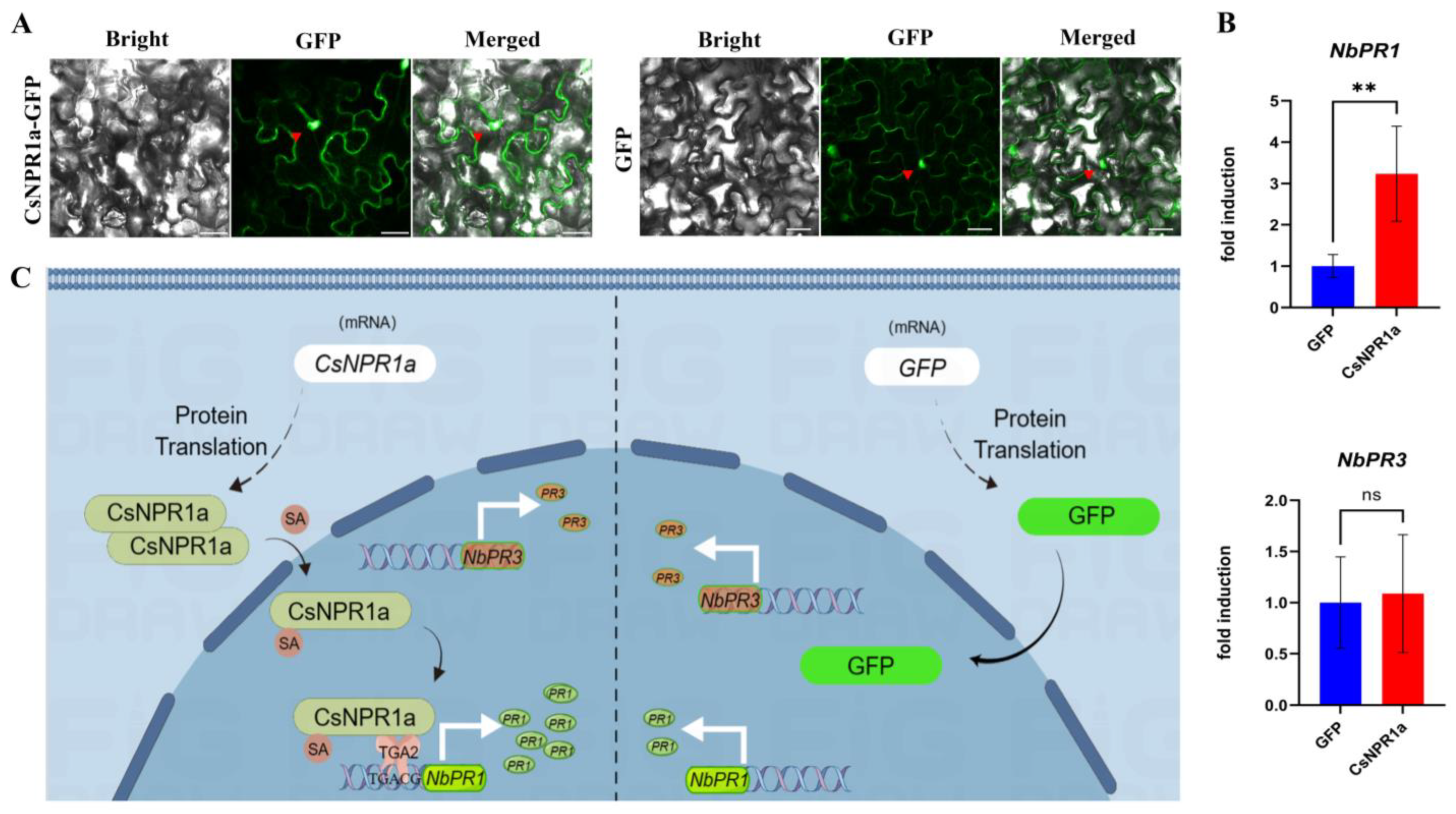
3.9. Subcellular Localization of the CsNPR1a Protein
3.10. Transient Expression of CsNPR1a in N. benthamiana Enhances the Accumulation of NbPR1 Transcripts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, X.-H.; Li, N.; Zhu, H.-T.; Wang, D.; Yang, C.-R.; Zhang, Y.-J. Plant Resources, Chemical Constituents, and Bioactivities of Tea Plants from the Genus Camellia Section Thea. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 5318–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yao, S.; Xia, J.; Li, Y.; Dai, X.; Wang, W.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Effects of Vitro Sucrose on Quality Components of Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis) Based on Transcriptomic and Metabolic Analysis. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, S. Potential Bioactive Components and Health Promotional Benefits of Tea (Camellia sinensis). J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2022, 41, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lin, Q.; Yan, M.; Wang, M.; Wang, P.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Ni, D.; Guo, F. Relationship between Secondary Metabolism and MiRNA for Important Flavor Compounds in Different Tissues of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis) as Revealed by Genome-Wide MiRNA Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 2001–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hasan, M.K.; Zhang, L.; Yan, P.; Fu, J.; Han, W.; Li, X. A Chemical Explanation for Variations in Antioxidant Capacity across Camellia sinensis L. Cultivars. Forests 2023, 14, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Pan, Y.M.; Dai, Y.L.; Gao, Z.M. First Report of Brown Blight Disease Caused by Colletotrichum Gloeosporioides on Camellia sinensis in Anhui Province, China. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Hao, X.-Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, B.; Wang, X.-C.; Yang, Y.-J. Diverse Colletotrichum Species Cause Anthracnose of Tea Plants (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) in China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Holub, E.B.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; Fobert, P.R. An Arabidopsis NPR1-like Gene, NPR4, Is Required for Disease Resistance. Plant J. 2005, 41, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, T.P.; Friedrich, L.; Ryals, J.A. Arabidopsis Signal Transduction Mutant Defective in Chemically and Biologically Induced Disease Resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 6602–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Henanff, G.; Farine, S.; Kieffer-Mazet, F.; Miclot, A.-S.; Heitz, T.; Mestre, P.; Bertsch, C.; Chong, J. Vitis Vinifera VvNPR1.1 Is the Functional Ortholog of AtNPR1 and Its Overexpression in Grapevine Triggers Constitutive Activation of PR Genes and Enhanced Resistance to Powdery Mildew. Planta 2011, 234, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wally, O.; Jayaraj, J.; Punja, Z.K. Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance to Necrotrophic and Biotrophic Pathogens in Transgenic Carrots (Daucus carota L.) Expressing an Arabidopsis NPR1 Gene. Planta 2009, 231, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, T.; Ao, K.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Opposite Roles of Salicylic Acid Receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in Transcriptional Regulation of Plant Immunity. Cell 2018, 173, 1454–1467.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.Q.; Yan, S.; Saleh, A.; Wang, W.; Ruble, J.; Oka, N.; Mohan, R.; Spoel, S.H.; Tada, Y.; Zheng, N.; et al. NPR3 and NPR4 Are Receptors for the Immune Signal Salicylic Acid in Plants. Nature 2012, 486, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelló, M.J.; Medina-Puche, L.; Lamilla, J.; Tornero, P. NPR1 Paralogs of Arabidopsis and Their Role in Salicylic Acid Perception. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0209835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.; van Wees, S.C.; van Pelt, J.A.; Knoester, M.; Laan, R.; Gerrits, H.; Weisbeek, P.J.; van Loon, L.C. A Novel Signaling Pathway Controlling Induced Systemic Resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chu, J.Y.; Boyle, P.; Wang, Y.; Brindle, I.D.; De Luca, V.; Després, C. The Arabidopsis NPR1 Protein Is a Receptor for the Plant Defense Hormone Salicylic Acid. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, C.M.; Jun, J.H.; Nam, H.G.; Fletcher, J.C. BLADE-ON-PETIOLE1 Encodes a BTB/POZ Domain Protein Required for Leaf Morphogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 2004, 45, 1361–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepworth, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; McKim, S.; Li, X.; Haughn, G.W. BLADE-ON-PETIOLE-Dependent Signaling Controls Leaf and Floral Patterning in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 1434–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norberg, M.; Holmlund, M.; Nilsson, O. The BLADE ON PETIOLE Genes Act Redundantly to Control the Growth and Development of Lateral Organs. Development 2005, 132, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.T.; Qu, N.; Zhao, Q.; Bi, D.; Li, X. Negative Regulation of Defense Responses in Arabidopsis by Two NPR1 Paralogs. Plant J. 2006, 48, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Glazebrook, J.; Clarke, J.D.; Volko, S.; Dong, X. The Arabidopsis NPR1 Gene That Controls Systemic Acquired Resistance Encodes a Novel Protein Containing Ankyrin Repeats. Cell 1997, 88, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Li, X.; Dong, X. Generation of Broad-Spectrum Disease Resistance by Overexpression of an Essential Regulatory Gene in Systemic Acquired Resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6531–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canet, J.V.; Dobón, A.; Roig, A.; Tornero, P. Structure-Function Analysis of Npr1 Alleles in Arabidopsis Reveals a Role for Its Paralogs in the Perception of Salicylic Acid. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, R.; Naidoo, S.; van den Berg, N. The NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED GENES 1 (NPR1) and Related Family: Mechanistic Insights in Plant Disease Resistance. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKim, S.M.; Stenvik, G.-E.; Butenko, M.A.; Kristiansen, W.; Cho, S.K.; Hepworth, S.R.; Aalen, R.B.; Haughn, G.W. The BLADE-ON-PETIOLE Genes Are Essential for Abscission Zone Formation in Arabidopsis. Development 2008, 135, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. Fold Prediction and Evolutionary Analysis of the POZ Domain: Structural and Evolutionary Relationship with the Potassium Channel Tetramerization Domain. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochon, A.; Boyle, P.; Wignes, T.; Fobert, P.R.; Després, C. The Coactivator Function of Arabidopsis NPR1 Requires the Core of Its BTB/POZ Domain and the Oxidation of C-Terminal Cysteines. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3670–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoel, S.H.; Mou, Z.; Tada, Y.; Spivey, N.W.; Genschik, P.; Dong, X. Proteasome-Mediated Turnover of the Transcription Coactivator NPR1 Plays Dual Roles in Regulating Plant Immunity. Cell 2009, 137, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X. NPR1, All Things Considered. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardwell, V.J.; Treisman, R. The POZ Domain: A Conserved Protein-Protein Interaction Motif. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1664–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, P.; Le Su, E.; Rochon, A.; Shearer, H.L.; Murmu, J.; Chu, J.Y.; Fobert, P.R.; Després, C. The BTB/POZ Domain of the Arabidopsis Disease Resistance Protein NPR1 Interacts with the Repression Domain of TGA2 to Negate Its Function. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3700–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.; Lamb, C. Systemic Immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006, 9, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Z.; Fan, W.; Dong, X. Inducers of Plant Systemic Acquired Resistance Regulate NPR1 Function through Redox Changes. Cell 2003, 113, 935–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinkema, M.; Fan, W.; Dong, X. Nuclear Localization of NPR1 Is Required for Activation of PR Gene Expression. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, Y.; Spoel, S.H.; Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K.; Mou, Z.; Song, J.; Wang, C.; Zuo, J.; Dong, X. Plant Immunity Requires Conformational Changes [Corrected] of NPR1 via S-Nitrosylation and Thioredoxins. Science 2008, 321, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tessaro, M.J.; Lassner, M.; Li, X. Knockout Analysis of Arabidopsis Transcription Factors TGA2, TGA5, and TGA6 Reveals Their Redundant and Essential Roles in Systemic Acquired Resistance. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2647–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mohan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, H.; Palmer, I.A.; Chang, M.; Qi, G.; Spoel, S.H.; Mengiste, T.; et al. NPR1 Promotes Its Own and Target Gene Expression in Plant Defense by Recruiting CDK8. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, M.; Qi, G.; Zhao, M.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Fu, Z.Q. Two Interacting Transcriptional Coactivators Cooperatively Control Plant Immune Responses. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabl7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrant, W.E.; Dong, X. Systemic Acquired Resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loake, G.; Grant, M. Salicylic Acid in Plant Defence—The Players and Protagonists. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticher, L.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Métraux, J.P. Systemic Acquired Resistance. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1997, 35, 235–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.-X.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Duan, C.-J.; Luo, X.-M.; Le, N.; Wei, H.; Liang, S.; Chu, C.; Pan, Q.; et al. Involvement of OsNPR1/NH1 in Rice Basal Resistance to Blast Fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2011, 131, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, K.A.; Karmakar, S.; Chanda, P.K.; Sarkar, S.N.; Datta, S.K.; Datta, K. Tissue-Specific Expression of Arabidopsis NPR1 Gene in Rice for Sheath Blight Resistance without Compromising Phenotypic Cost. Plant Sci. 2016, 250, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Joshi, S.G.; Bell, A.A.; Rathore, K.S. Enhanced Resistance against Thielaviopsis basicola in Transgenic Cotton Plants Expressing Arabidopsis NPR1 Gene. Transgenic Res. 2013, 22, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Zhou, M.; Ma, H. Resistance against Fusarium Head Blight in Transgenic Wheat Plants Expressing the ScNPR1 Gene. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.-H.; Li, F.-D.; Tong, W.; Li, P.-H.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.-J.; Ge, R.-H.; Li, R.-P.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; et al. Tea Plant Information Archive: A Comprehensive Genomics and Bioinformatics Platform for Tea Plant. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1938–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The Protein Families Database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER Web Server: Interactive Sequence Similarity Searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, X.; Xu, Q.; Yang, L. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the NPR1-Like Gene Family in Bread Wheat and Its Relatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as Designed by Its Users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W216–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.-J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein Localization Predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for Making Accurate Alignments of Many Protein Sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.M.; Procter, J.B.; Martin, D.M.A.; Clamp, M.; Barton, G.J. Jalview Version 2—A Multiple Sequence Alignment Editor and Analysis Workbench. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1189–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (ITOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An Upgraded Gene Feature Visualization Server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for Motif Discovery and Searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A Toolkit for Detection and Evolutionary Analysis of Gene Synteny and Collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a Database of Plant Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements and a Portal to Tools for in Silico Analysis of Promoter Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, M.D.; Grossniklaus, U. A Gateway Cloning Vector Set for High-Throughput Functional Analysis of Genes in Planta. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olate, E.; Jiménez-Gómez, J.M.; Holuigue, L.; Salinas, J. NPR1 Mediates a Novel Regulatory Pathway in Cold Acclimation by Interacting with HSFA1 Factors. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryals, J.; Weymann, K.; Lawton, K.; Friedrich, L.; Ellis, D.; Steiner, H.Y.; Johnson, J.; Delaney, T.P.; Jesse, T.; Vos, P.; et al. The Arabidopsis NIM1 Protein Shows Homology to the Mammalian Transcription Factor Inhibitor I Kappa B. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Cao, Y.; Cheng, X.; Meng, D.; Chen, Y.; Shakoor, A.; Gao, J.; Cai, Y. The Sucrose Synthase Gene Family in Chinese Pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.): Structure, Expression, and Evolution. Molecules 2018, 23, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z. Evidence for an Important Role of WRKY DNA Binding Proteins in the Regulation of NPR1 Gene Expression. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1527–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Cui, D.; Gelvin, S.B. Sequence-Specific Interactions of Wound-Inducible Nuclear Factors with Mannopine Synthase 2′ Promoter Wound-Responsive Elements. Plant Mol. Biol. 1996, 30, 77–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, L. Characterization of Stress-Responsive CIPK Genes in Rice for Stress Tolerance Improvement. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-S.; Mizoi, J.; Yoshida, T.; Fujita, Y.; Nakajima, J.; Ohori, T.; Todaka, D.; Nakashima, K.; Hirayama, T.; Shinozaki, K.; et al. An ABRE Promoter Sequence Is Involved in Osmotic Stress-Responsive Expression of the DREB2A Gene, Which Encodes a Transcription Factor Regulating Drought-Inducible Genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011, 52, 2136–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, P.; Cooper, C.D.O.; Krojer, T.; Murray, J.W.; Pike, A.C.W.; Chaikuad, A.; Keates, T.; Thangaratnarajah, C.; Hojzan, V.; Marsden, B.D.; et al. Structural Basis for Cul3 Protein Assembly with the BTB-Kelch Family of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7803–7814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogios, P.J.; Privé, G.G. The BACK Domain in BTB-Kelch Proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 634–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorina, S.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of the P53 Tumor Suppressor Bound to the Ankyrin and SH3 Domains of 53BP2. Science 1996, 274, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Mahajan, A.; Tsai, M.-D. Ankyrin Repeat: A Unique Motif Mediating Protein-Protein Interactions. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 15168–15178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgwick, S.G.; Smerdon, S.J. The Ankyrin Repeat: A Diversity of Interactions on a Common Structural Framework. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1999, 24, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Zavaliev, R.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Dillard, L.; Powers, J.; Withers, J.; Zhao, J.; Guan, Z.; et al. Structural Basis of NPR1 in Activating Plant Immunity. Nature 2022, 605, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P.; Eggermont, K.; Penninckx, I.A.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Vogelsang, R.; Cammue, B.P.; Broekaert, W.F. Separate Jasmonate-Dependent and Salicylate-Dependent Defense-Response Pathways in Arabidopsis Are Essential for Resistance to Distinct Microbial Pathogens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15107–15111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Identification, Evolution, and Expression Analysis of the NPR1-like Gene Family in Pears. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, R.; Mahomed, W.; Reeksting, B.J.; Engelbrecht, J.; Ibarra-Laclette, E.; van den Berg, N. Phylogenetic and Expression Analysis of the NPR1-like Gene Family from Persea americana (Mill.). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, S.; Qin, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zou, W.; Wang, D.; Feng, A.; Yang, S.; Que, Y.; Su, Y. Characterization and Functional Implications of the Nonexpressor of Pathogenesis-Related Genes 1 (NPR1) in Saccharum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, H.; Cheng, B.; Xiang, Y. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Orthologues of NPR1 Gene from Poplar. J. Phytopathol. 2013, 161, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiao, P.; Zhang, C.; Tong, X.; Wei, Q.; Xu, L. Apple NPR1 Homologs and Their Alternative Splicing Forms May Contribute to SA and Disease Responses. Tree Genet. Genomes 2016, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhong, S.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Lou, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Yang, D.; et al. Functional Analysis of Rice NPR1-like Genes Reveals That OsNPR1/NH1 Is the Rice Orthologue Conferring Disease Resistance with Enhanced Herbivore Susceptibility. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2007, 5, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Maximova, S.; Liu, Y.; Verica, J.; Guiltinan, M.J. The Salicylic Acid Receptor NPR3 Is a Negative Regulator of the Transcriptional Defense Response during Early Flower Development in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton-Rauh, A. Evolutionary Dynamics of Duplicated Genes in Plants. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchy, N.; Lehti-Shiu, M.; Shiu, S.-H. Evolution of Gene Duplication in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.M.; Komatsu, S. Proteomic Analysis of Rice Leaf Sheath during Drought Stress. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, M.; Tian, M.; Klessig, D.F. Salicylic Acid Binds NPR3 and NPR4 to Regulate NPR1-Dependent Defense Responses. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1631–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, F.; Zwicker, S.; Hückelhoven, A.; Meissner, M.; Funk, J.; Pfitzner, A.J.P.; Pfitzner, U.M. NONEXPRESSOR OF PATHOGENESIS-RELATED PROTEINS1 (NPR1) and Some NPR1-Related Proteins Are Sensitive to Salicylic Acid. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Qi, M. In Vivo Analysis of Plant Promoters and Transcription Factors by Agroinfiltration of Tobacco Leaves. Plant J. 2000, 22, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, M.S.; Fitzgerald, H.A.; Yadav, R.C.; Canlas, P.E.; Dong, X.; Ronald, P.C. Evidence for a Disease-Resistance Pathway in Rice Similar to the NPR1-Mediated Signaling Pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2001, 27, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makandar, R.; Essig, J.S.; Schapaugh, M.A.; Trick, H.N.; Shah, J. Genetically Engineered Resistance to Fusarium Head Blight in Wheat by Expression of Arabidopsis NPR1. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.K.; Park, K.S.; Choi, D. Coordinated Expression of Defense-Related Genes by TMV Infection or Salicylic Acid Treatment in Tobacco. Mol. Cells 1998, 8, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Nishiuchi, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Studies on Transcriptional Regulation of Endogenous Genes by ERF2 Transcription Factor in Tobacco Cells. Plant Cell Physiol. 2006, 47, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, D.; Yang, G.; Chen, K.; Yu, P.; Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Li, N.; Huang, L.-J. Identification and Functional Characterization of the Nonexpressor of Pathogenesis-Related Genes 1 (NPR1) Gene in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Forests 2023, 14, 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081578
Jiang D, Yang G, Chen K, Yu P, Chen J, Luo Y, Li N, Huang L-J. Identification and Functional Characterization of the Nonexpressor of Pathogenesis-Related Genes 1 (NPR1) Gene in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Forests. 2023; 14(8):1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081578
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Dong, Guoqun Yang, Kebin Chen, Peiyao Yu, Jiali Chen, Yong Luo, Ning Li, and Li-Jun Huang. 2023. "Identification and Functional Characterization of the Nonexpressor of Pathogenesis-Related Genes 1 (NPR1) Gene in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis)" Forests 14, no. 8: 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081578
APA StyleJiang, D., Yang, G., Chen, K., Yu, P., Chen, J., Luo, Y., Li, N., & Huang, L.-J. (2023). Identification and Functional Characterization of the Nonexpressor of Pathogenesis-Related Genes 1 (NPR1) Gene in the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Forests, 14(8), 1578. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14081578





