Response of C:N:P Stoichiometry to Phosphorus Addition and Homeostasis of Plant Tissues in a Subtropical Slash Pine Plantation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
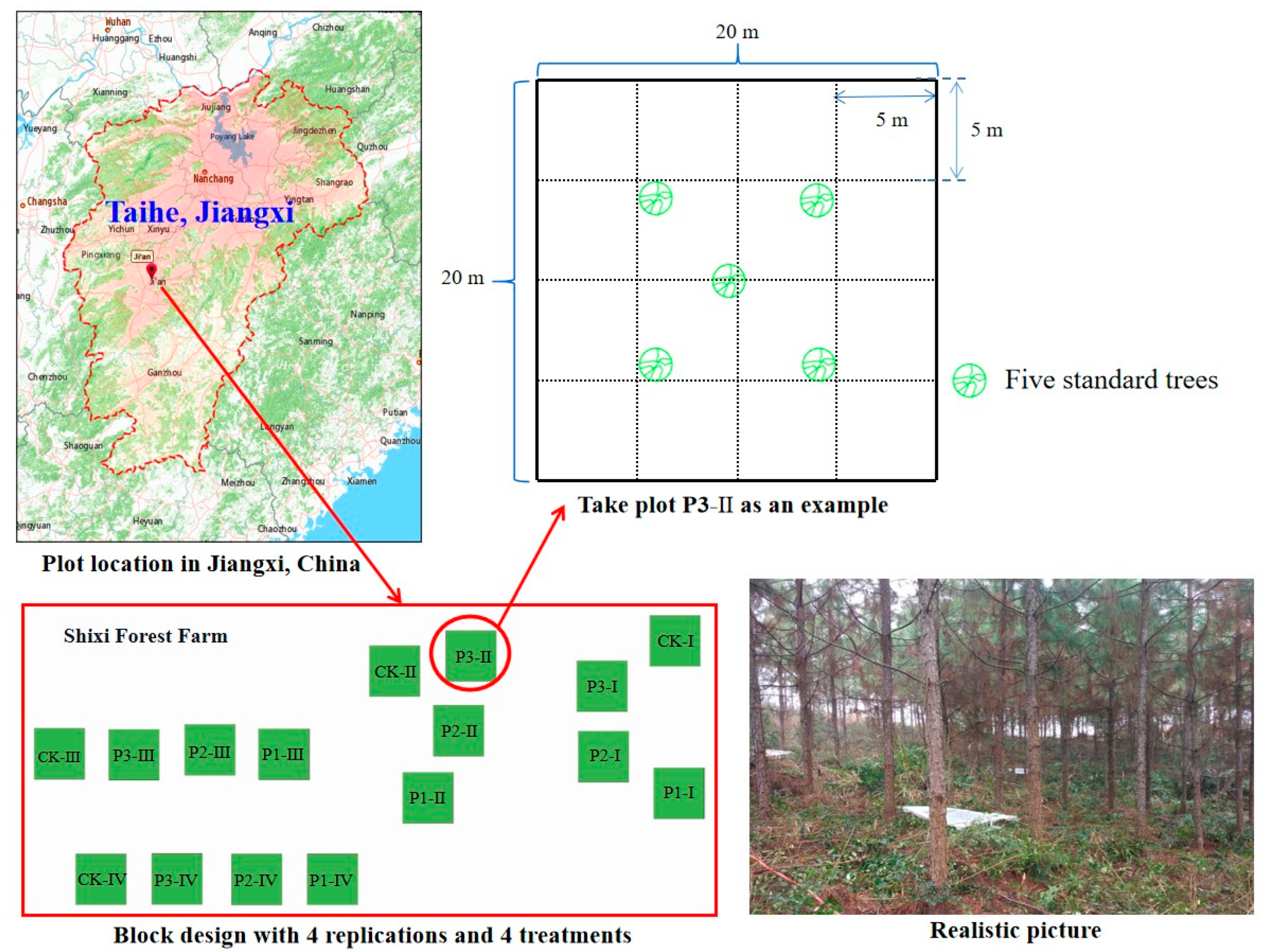
2.1. Study Region
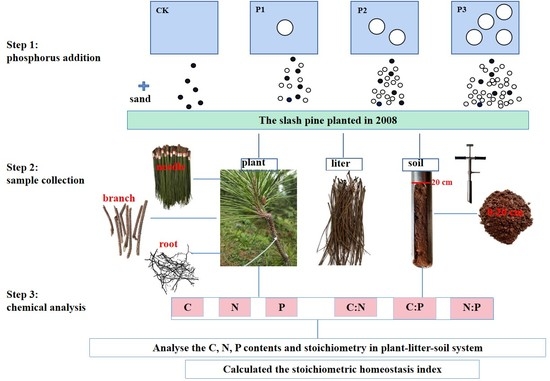
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
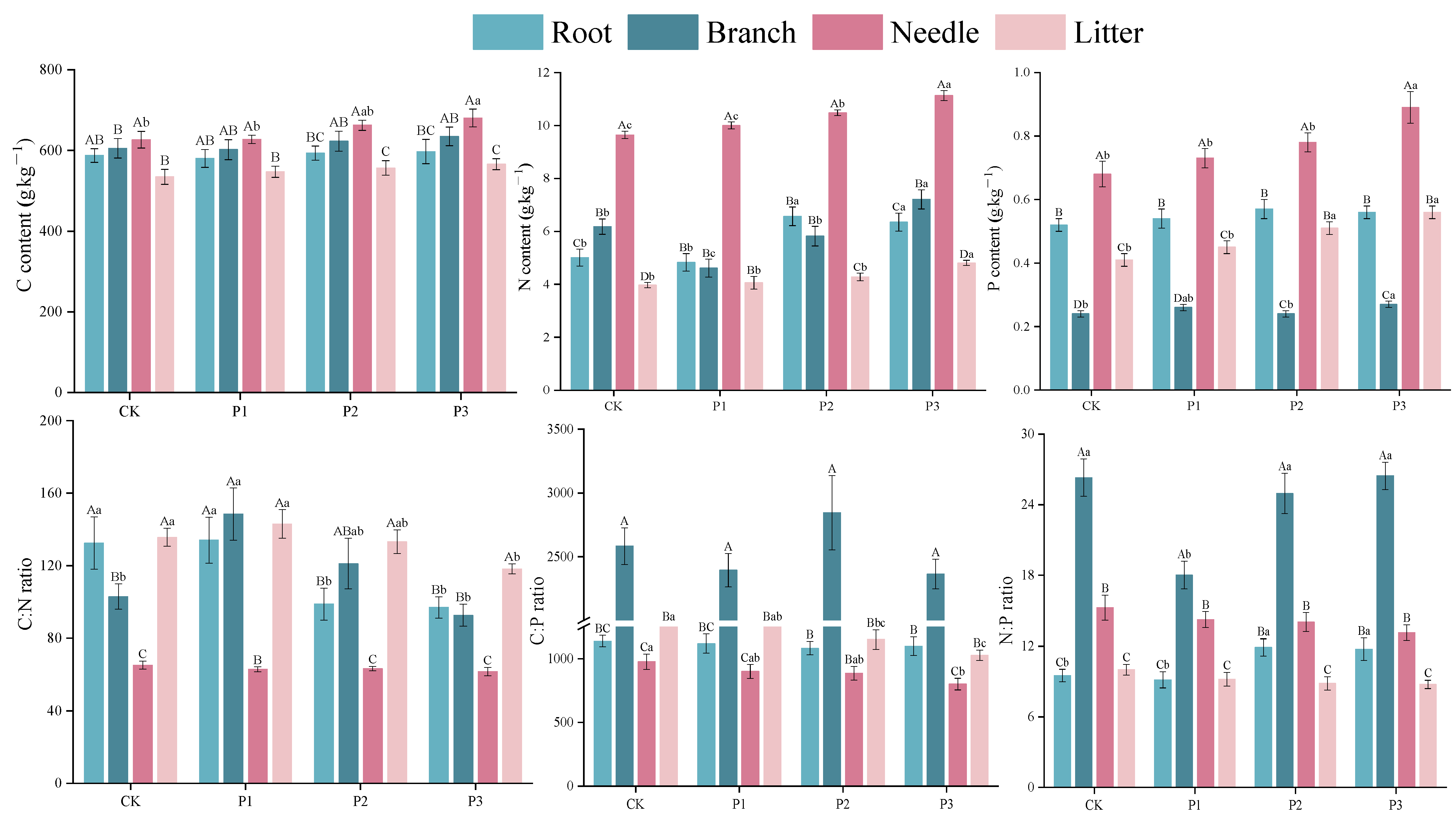
3.1. The Contents of C, N, and P and the C:N:P Stoichiometry in Plant Tissues
3.2. The C, N, and P Contents and the C:N:P Stoichiometry of Soil
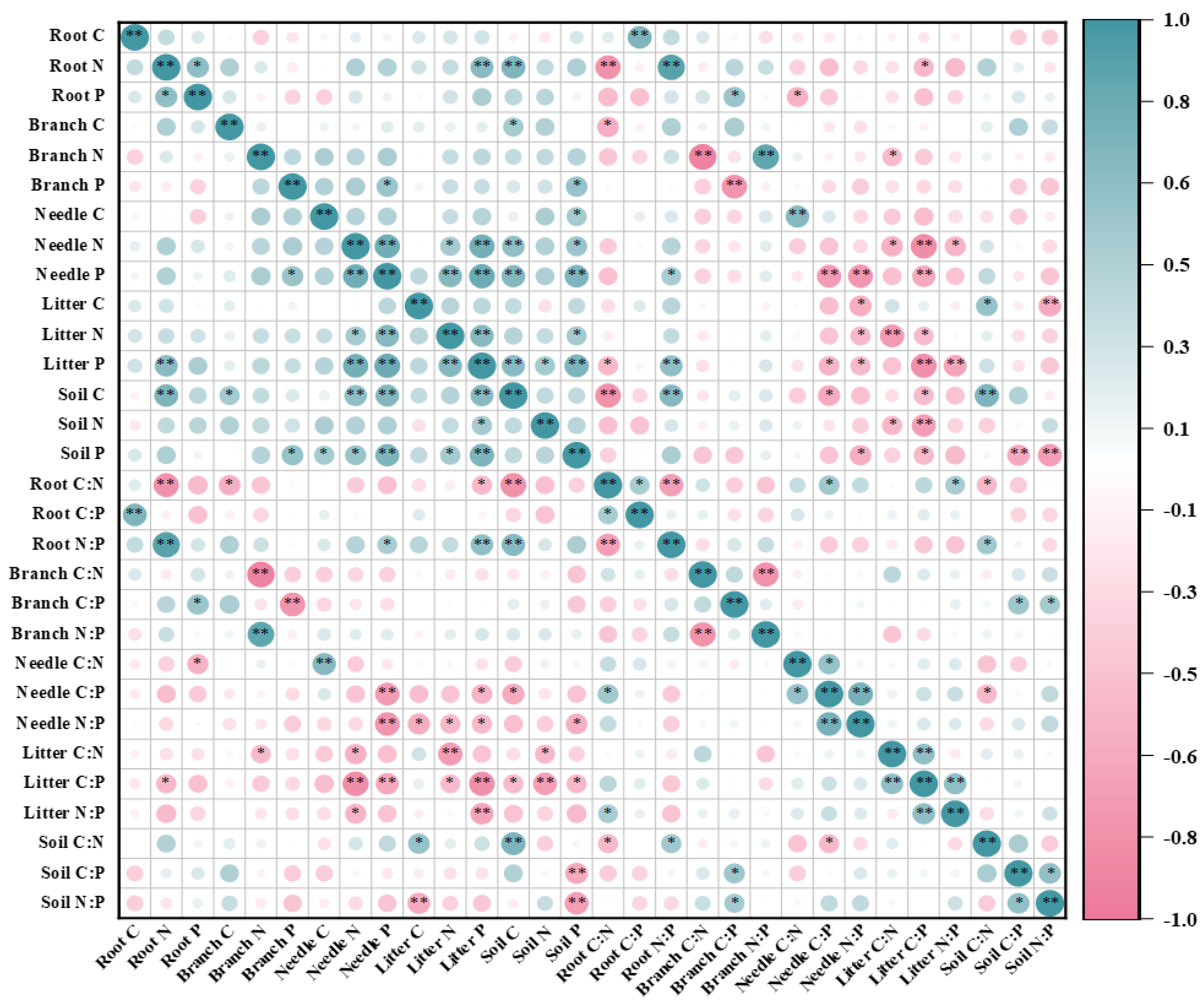
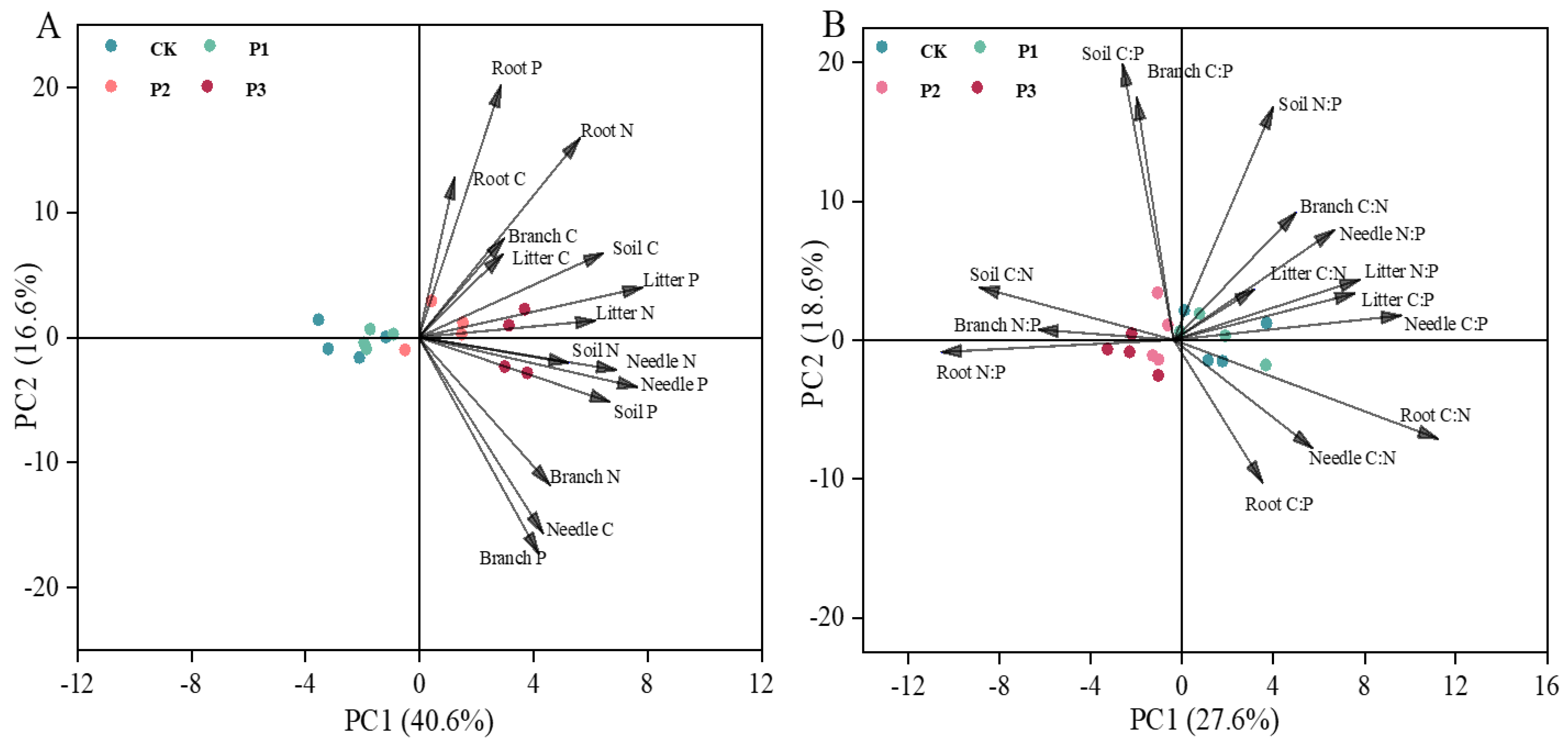
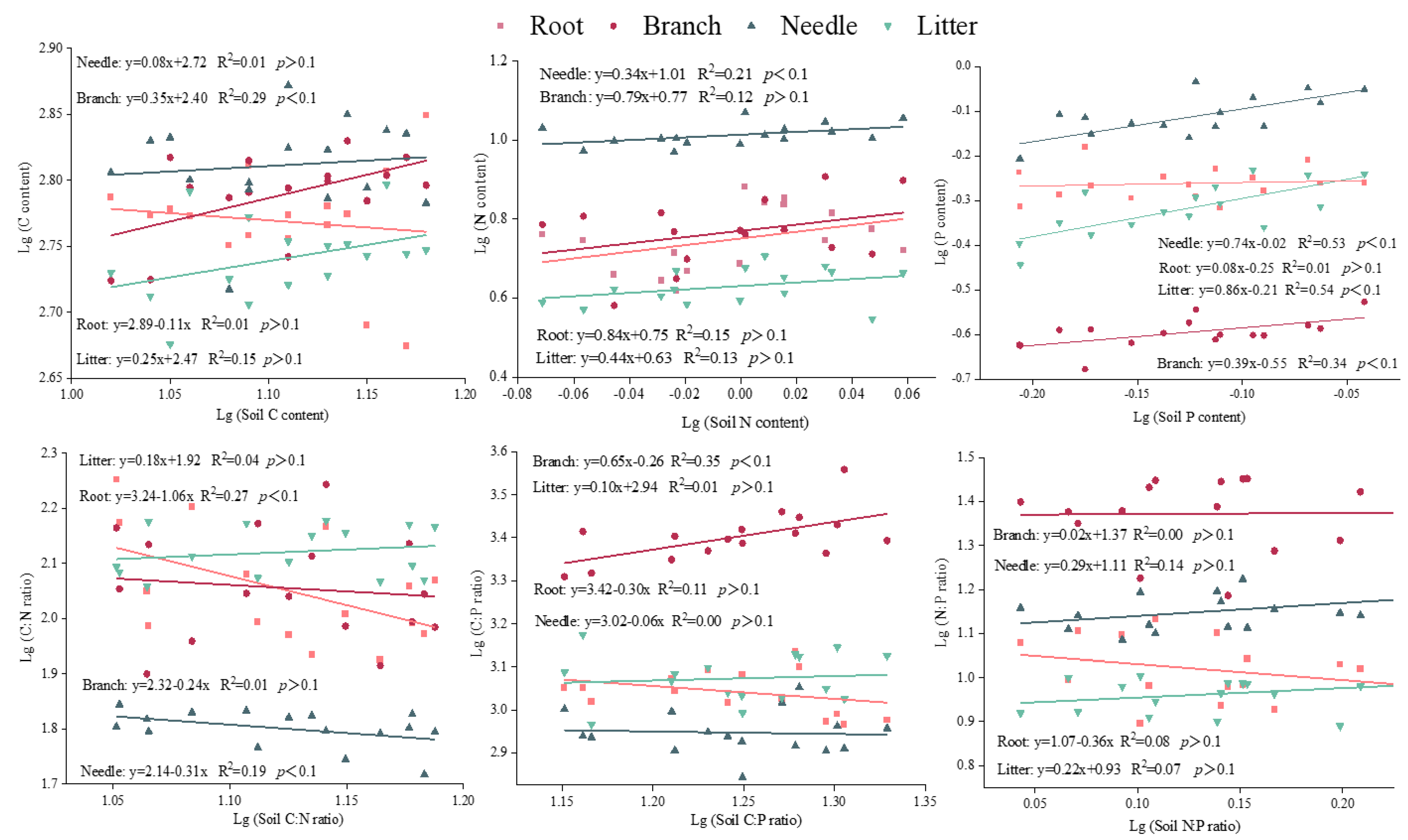
3.3. Relationships of C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometry
3.4. Stoichiometric Homeostasis
4. Discussion
4.1. The C, N, and P Contents and Stoichiometry
4.2. Stoichiometric Homeostasis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Wang, T.; Song, J.C. Effects of different application amont of phosphorus fertilizer on olive growth and rhizosphere soil micro environment. Soil Fert. Sci. Chin. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, E.Q.; Luo, Y.Q.; Kuang, Y.W.; Chen, C.R.; Wen, D.Z. Global meta-analysis shows pervasive phosphorus limitation of above ground plant production in natural terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.L.; Brenes-Arguedas, T.; Condit, R. Pervasive phosphorus limitation of tree species but not communities in tropical forests. Nature 2018, 555, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirriam, A.; Mugwe, J.; Raza, M.A.; Seleiman, M.F.; Maitra, S.; Gitari, H.H. Aggrandizing soybean yield, phosphorus use efficiency and economic returns under phosphatic fertilizer application and inoculation with Bradyrhizobium. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 5086–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.X.; Wang, Q.F.; He, N.P.; Smith, M.D.; Elser, J.J.; Du, J.Q.; Yuan, G.F.; Yu, G.R.; Yu, Q. Imbalanced atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus depositions in China: Implications for nutrient limitation. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Li, P.; Xu, G.C.; Li, Z.B.; Gao, H.D.; Zhao, B.H.; Wang, T.; Wang, F.C.; Cheng, S.D. Effects of soil erosion and land use on spatial distribution of soil total phosphorus in a small watershed on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 184, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S., III. The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1980, 11, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.A.; Ren, X.M.; Bao, F.J. Analysis of soil stoichiometric characteristics and soil physical and chemical properties of different forests in Guandi Mountain. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2020, 48, 956–963. [Google Scholar]
- Elser, J.J.; Hamilton, A. Stoichiometry and the new biology: The future is now. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.H.; Zheng, W.; Zhong, X.P.; Bin, Y. Stoichiometric characteristics of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in Zanthoxylum planispinum var. Dintanensis plantation of different ages. Agron. J. 2020, 113, 685–695. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.G. Research progress on the effect of nitrogen addition on main functional characters of early spring herbaceous plants. Int. J. Ecol. 2021, 10, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, E.N.; Henderson, B.L. C:N:P stoichiometry in Australian soils with respect to vegetation and environmental factors. Plant Soil 2013, 373, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.C.; Xu, M.P.; Deng, J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Feng, Y.Z.; Ren, G.X. Response of forest growth to C:N:P stoichiometry in plants and soils during Robinia pseudoacacia afforestation on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Yan, Z.B.; Fang, J.Y. Review on characteristics and main hypotheses of plant ecological stoichiometry. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2021, 45, 682–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterner, R.; Elser, J. Ecological Stoichiometry: The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 25, p. 1183. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Elser, J.J.; He, N.P.; Wu, H.H.; Chen, Q.S.; Zhang, G.M.; Han, X.G. Stoichiometric homeostasis of vascular plants in the Inner Mongolia grassland. Oecologia 2011, 166, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.N.; Guo, W.H.; Li, Y.G.; Geoff, G.; Wu, T.G. Stoichiometric homeostasis, physiology, and growth responses of three tree species to nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Trees 2018, 32, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Chen, Y.; Yan, Z.; Han, W. Stage-dependent stoichiometric homeostasis and responses of nutrient resorption in Amaranthus mangostanus to nitrogen and phosphorus addition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Shangguan, Z. Stoichiometric homeostasis in response to variable water and nutrient supply in a robinia pseudoacacia plant-soil system. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 15, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Fang, X.M.; Yuan, Y.; Fu, Y.X.; Yi, M.; Yuan, S.G.; Guo, S.M.; Lai, M.; Xie, J.W.; Zhang, L. Phosphorus addition alter the pine resin flow rate by regulating tree growth and non-structural carbohydrates in a subtropical slash pine plantation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 199, 116782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.S.; Niklas, K.J.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.M.; Wan, S.Z.; Wang, H.M. Nitrogen and phosphorus additions alter nutrient dynamics but not resorption efficiencies of Chinese fir leaves and twigs differing in age. Tree Physiol. 2015, 35, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1996, 5, 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory Methods of Soil and Plant Analysis: A Working Manual; Sacred African Publishers: Nairobi, Kenya, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yeomans, J.C.; Bremner, J.M. A rapid and precise method for routine determination of organic carbon in soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1988, 19, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, J.; Fink, P.; Goto, A.; James, M.H.; Jayne, J.; Satoshi, K. To be or not to be what you eat: Regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs. Oikos 2010, 119, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.M. Study on the Stoichiometric Characteristics of Plant Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus of Sandy Mountain Soil in Poyang Lake. Jiangxi Norm. Univ. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H. Stoichiometric characteristics of different aged Pinus sylvestris Var. Mongolica plantations. Liaoning Univ. Eng. Tech. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F.S., III; Schulze, E.; Mooney, H.A. The ecology and economics of storage in plants. Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1990, 21, 423–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, F.I. Drought induces opposite changes in the concentration of non-structural carbohydrates of two evergreen Nothofagus species of differential drought resistance. Ann. For. Sci. 2011, 68, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, M.C.; Sala, A.; Carbone, M.S.; Czimczik, C.I.; Mantooth, J.A.; Richardson, A.D.; Vargas, R. Nonstructural carbon in woody plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 667–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Würth, M.K.; Pelaez-Riedl, S.; Wright, S.J.; Körner, C. Non-structural carbohydrate pools in a tropical forest. Oecologia 2005, 143, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Soong, J.L.; Horton, A.J.; Campbell, E.E.; Haddix, M.L.; Wall, D.H.; Parton, W.J. Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, M.; Huang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y. Response of plant, litter, and soil C:N:P stoichiometry to growth stages in Quercus secondary forests on the Loess Plateau, China. J. For. Res. 2023, 34, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Li, R.L.; Yan, J.H.; Sha, L.Q.; Han, S.J. C:N:P stoichiometric characteristics of four forest types’ dominant tree species in China. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2011, 35, 587–595. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.S.; Wang, L.; Flynn, D.F.B.; Wang, X.P.; Ma, W.H.; Fang, J.Y. Leaf nitrogen: Phosphorus stoichiometry across Chinese grassland biomes. Oecologia 2008, 155, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Wu, H.; He, N.; Lü, X.T.; Wang, Z.P.; Elser, J.J.; Wu, J.G.; Han, X.G. Testing the growth rate hypothesis in vascular plants with above- and below-ground biomass. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.M.F. The vegetation N:P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabine, G. N:P ratios in terrestrial plants: Variation and functional significance. New Phytol. 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.Q.; Chen, G.S.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soil: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.C.; Pan, Y.Z.; Hou, S.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, H.Y. Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on litter decomposition in Hulunber steppe. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2023, 32, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.B.; Wu, J.P.; Liu, W.F.; Yuan, Y.H.; Hu, L.; Cai, Q.K. Linkages of plant and soil C: N: P stoichiometry and their relationships to forest growth in subtropical plantations. Plant Soil 2015, 392, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, B.; An, S.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, H. Response of forest species to C:N:P in the plant-litter-soil system and stoichiometric homeostasis of plant tissues during afforestation on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 183, 104–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Chen, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Yi, M.; Guo, S.M.; Cheng, Z.S.; Li, X.; Zhong, Q.W. Ecological stoichiometry and homeostasis index of needles, branches, roots and soil in Pinus elliottii plantations of different ages. Acta Agric. Nucl. Sin. 2023, 37, 397–404. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Ren, C.J.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Wang, J.; Doughty, R. Changes of soil microbial and enzyme activities are linked to soil C, N and P stoichiometry in afforested ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 427, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Zamin, T.J.; Grogan, P. Stoichiometric homeostasis: A test to predict tundra vascular plant species and community-level response to climate change. Arct. Sci. 2017, 3, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, R.; Chapin, F.S., III. The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: A reevaluation of processes and patterns. Adv. Ecol. Res. 2000, 30, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Blouin, M.; Mathieu, J.; Leadley, P.W. Plant homeostasis, growth and development in natural and artificial soils. Ecol. Complex 2012, 9, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trait | CK | P1 | P2 | P3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C (g kg−1) | 11.50 ± 0.44 c | 12.28 ± 0.56 bc | 13.41 ± 0.51 ab | 14.31 ± 0.56 a |
| N (g kg−1) | 0.94 ± 0.04 | 0.98 ± 0.05 | 1.00 ± 0.04 | 1.06 ±0.04 |
| P (g kg−1) | 0.69 ± 0.03 b | 0.70 ± 0.03 b | 0.77 ± 0.03 ab | 0.83 ± 0.02 a |
| C:N | 12.58 ± 0.73 | 12.94 ±0.74 | 13.84 ± 0.72 | 14.13 ± 1.00 |
| C:P | 17.46 ± 1.20 | 17.98 ±1.06 | 18.04 ± 1.10 | 17.47 ± 0.80 |
| N:P | 1.41 ± 0.09 | 1.43 ± 0.08 | 1.33 ± 0.08 | 1.29 ± 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, T.; Yi, M.; Chen, F.; Lai, M.; Jin, C.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xie, J.; Zhang, L. Response of C:N:P Stoichiometry to Phosphorus Addition and Homeostasis of Plant Tissues in a Subtropical Slash Pine Plantation. Forests 2023, 14, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071355
Jia T, Yi M, Chen F, Lai M, Jin C, Nie Z, Zhou L, Xie J, Zhang L. Response of C:N:P Stoichiometry to Phosphorus Addition and Homeostasis of Plant Tissues in a Subtropical Slash Pine Plantation. Forests. 2023; 14(7):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071355
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Ting, Min Yi, Fusheng Chen, Meng Lai, Cangfu Jin, Zixuan Nie, Linjin Zhou, Jinwen Xie, and Lu Zhang. 2023. "Response of C:N:P Stoichiometry to Phosphorus Addition and Homeostasis of Plant Tissues in a Subtropical Slash Pine Plantation" Forests 14, no. 7: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071355
APA StyleJia, T., Yi, M., Chen, F., Lai, M., Jin, C., Nie, Z., Zhou, L., Xie, J., & Zhang, L. (2023). Response of C:N:P Stoichiometry to Phosphorus Addition and Homeostasis of Plant Tissues in a Subtropical Slash Pine Plantation. Forests, 14(7), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14071355