The Determinants of Forest Products Footprint: A New Fourier Cointegration Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Econometric Methodology
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Size and Power Properties
- -
- we let the persistent measure change in the range {0, 0.9};
- -
- we set , while letting the vary along with ; and,
- -
- we also evaluated two sets of , and as and .
| Model with a Constant | Model with a Constant and a Trend | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T = 100 | T = 300 | T = 100 | T = 300 | ||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.053 | 0.233 | 0.053 | 0.761 | 0.048 | 0.101 | 0.053 | 0.609 |
| 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0.052 | 0.234 | 0.051 | 0.758 | 0.051 | 0.099 | 0.049 | 0.607 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.045 | 0.175 | 0.039 | 0.755 | 0.049 | 0.096 | 0.045 | 0.594 |
| 0.9 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0.046 | 0.173 | 0.038 | 0.753 | 0.050 | 0.095 | 0.043 | 0.598 |
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.066 | 0.214 | 0.053 | 0.816 | 0.048 | 0.097 | 0.053 | 0.646 |
| 0 | 16 | 3 | 0 | 0.066 | 0.217 | 0.051 | 0.815 | 0.051 | 0.098 | 0.049 | 0.646 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0.060 | 0.219 | 0.039 | 0.807 | 0.049 | 0.089 | 0.045 | 0.634 |
| 0.9 | 16 | 3 | 0 | 0.059 | 0.220 | 0.038 | 0.807 | 0.050 | 0.091 | 0.043 | 0.640 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0.053 | 0.677 | 0.053 | 1 | 0.048 | 0.163 | 0.053 | 1 |
| 0 | 16 | 0 | 5 | 0.052 | 0.677 | 0.051 | 1 | 0.051 | 0.164 | 0.049 | 1 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0.045 | 0.638 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.049 | 0.166 | 0.045 | 1 |
| 0.9 | 16 | 0 | 5 | 0.046 | 0.640 | 0.038 | 1 | 0.050 | 0.172 | 0.043 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 0.053 | 0.517 | 0.053 | 1 | 0.048 | 0.117 | 0.053 | 1 |
| 0 | 16 | 3 | 5 | 0.052 | 0.521 | 0.051 | 1 | 0.051 | 0.117 | 0.049 | 1 |
| 0.9 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 0.045 | 0.429 | 0.039 | 1 | 0.049 | 0.105 | 0.045 | 1 |
| 0.9 | 16 | 3 | 5 | 0.046 | 0.430 | 0.038 | 1 | 0.050 | 0.109 | 0.043 | 1 |
Appendix B. Critical Values
| Model with a Constant | Model with a Constant and Trend | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | k | T = 100 | t = 500 | t = 1000 | T = 100 | t = 500 | t = 1000 | ||||||||||||
| 1% | 5% | 10% | 1% | 5% | 10% | 1% | 5% | 10% | 1% | 5% | 10% | 1% | 5% | 10% | 1% | 5% | 10% | ||
| 1 | 1 | −4.906 | −4.302 | −3.988 | −4.756 | −4.198 | −3.898 | −4.738 | −4.175 | −3.886 | −5.354 | −4.731 | −4.423 | −5.128 | −4.576 | −4.293 | −5.074 | −4.555 | −4.274 |
| 2 | −4.665 | −3.995 | −3.648 | −4.517 | −3.912 | −3.589 | −4.503 | −3.898 | −3.579 | −5.243 | −4.582 | −4.250 | −4.995 | −4.433 | −4.136 | −4.973 | −4.410 | −4.119 | |
| 3 | −4.437 | −3.743 | −3.380 | −4.333 | −3.685 | −3.349 | −4.314 | −3.686 | −3.342 | −5.002 | −4.340 | −3.997 | −4.801 | −4.230 | −3.910 | −4.804 | −4.208 | −3.901 | |
| 4 | −4.285 | −3.599 | −3.252 | −4.183 | −3.554 | −3.231 | −4.172 | −3.546 | −3.221 | −4.849 | −4.175 | −3.827 | −4.697 | −4.092 | −3.767 | −4.693 | −4.088 | −3.769 | |
| 5 | −4.190 | −3.520 | −3.187 | −4.091 | −3.478 | −3.165 | −4.081 | −3.477 | −3.165 | −4.774 | −4.086 | −3.739 | −4.634 | −3.997 | −3.683 | −4.593 | −3.994 | −3.677 | |
| 2 | 1 | −5.282 | −4.655 | −4.337 | −5.067 | −4.511 | −4.220 | −5.048 | −4.487 | −4.205 | −5.641 | −5.026 | −4.705 | −5.404 | −4.855 | −4.571 | −5.367 | −4.826 | −4.550 |
| 2 | −5.168 | −4.526 | −4.189 | −4.969 | −4.394 | −4.085 | −4.949 | −4.371 | −4.065 | −5.598 | −4.954 | −4.633 | −5.329 | −4.772 | −4.480 | −5.295 | −4.748 | −4.460 | |
| 3 | −4.958 | −4.283 | −3.938 | −4.804 | −4.183 | −3.870 | −4.778 | −4.172 | −3.852 | −5.450 | −4.781 | −4.436 | −5.199 | 4.620 | −4.313 | −5.167 | −4.597 | −4.292 | |
| 4 | −4.805 | −4.122 | −3.767 | −4.647 | −4.048 | −3.722 | −4.657 | −4.040 | −3.716 | −5.294 | −4.622 | −4.271 | −5.089 | −4.487 | −4.183 | −5.065 | −4.469 | −4.158 | |
| 5 | −4.708 | −4.033 | −3.689 | −4.587 | −3.964 | −3.633 | −4.536 | −3.935 | −3.629 | −5.203 | −4.508 | −4.164 | −5.006 | −4.404 | −4.086 | −4.945 | −4.370 | −4.063 | |
| 3 | 1 | −5.596 | −4.957 | −4.640 | −5.354 | −4.796 | −4.512 | −5.315 | −4.786 | −4.497 | −5.941 | −5.294 | −4.971 | −5.638 | −5.094 | −4.814 | −5.602 | −5.070 | −4.795 |
| 2 | −5.573 | −4.918 | −4.593 | −5.330 | −4.752 | −4.460 | −5.286 | −4.727 | −4.435 | −5.926 | −5.278 | −4.961 | −5.635 | −5.078 | −4.791 | −5.590 | −5.048 | −4.762 | |
| 3 | −5.393 | −4.733 | −4.394 | −5.177 | −4.597 | −4.285 | −5.150 | −4.582 | −4.277 | −5.792 | −5.141 | −4.806 | −5.515 | −4.964 | −4.659 | −5.504 | −4.940 | −4.643 | |
| 4 | −5.271 | −4.605 | −4.252 | −5.071 | −4.468 | −4.148 | −5.035 | −4.134 | −4.455 | −5.698 | −5.023 | −4.681 | −5.441 | −4.843 | −4.534 | −5.404 | −4.835 | −4.529 | |
| 5 | −5.155 | −4.478 | −4.127 | −4.976 | −4.378 | −4.056 | −4.959 | −4.352 | −4.042 | −5.601 | −4.905 | −4.560 | −5.361 | −4.752 | −4.436 | −5.332 | −4.743 | −4.435 | |
References
- FAO. Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020: Main Report; UN Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Global Forest Sector Outlook 2050: Assessing Future Demand and Sources of Timber for a Sustainable Economy—Background Paper for the State of the World’s Forests 2022; FAO Forestry Working Paper, No. 31.; UN Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, E. Brazil: Market Profil; The South Carolina Forestry Commission: Columbia, SC, USA, 2022.
- Ulucak, R.; Lin, D. Persistence of policy shocks to ecological footprint of the USA. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 80, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A.; Bello, M.O. Persistence of policy shocks to an environmental degradation index: The case of ecological footprint in 128 developed and developing countries. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 89, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Gorus, M.S.; Aydin, M. Are shocks to ecological footprint in OECD countries permanent or temporary? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 270–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, A.E.; Alper, F.Ö. Persistence of Policy Shocks to the Ecological Footprint of MINT Countries. Ege Acad. Rev. 2021, 21, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, M.O.; Erdogan, S.; Ch’Ng, K.S. On the convergence of ecological footprint in African countries: New evidences from panel stationarity tests with factors and gradual shifts. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Ulucak, R.; Ozgur, O. Insights for a sustainable environment: Analysing the persistence of policy shocks to ecological footprints of Mediterranean countries. Spat. Econ. Anal. 2022, 17, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Pata, U.K.; Cutcu, I. Testing the persistence of shocks on ecological footprint and sub-accounts: Evidence from the big ten emerging markets. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2022, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucak, R.; Apergis, N. Does convergence really matter for the environment? An application based on club convergence and on the ecological footprint concept for the EU countries. Environ. Sci. Policy 2018, 80, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Bello, M.O. A multi-country convergence analysis of ecological footprint and its components. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Pata, U.K. Convergence of per capita ecological footprint among the ASEAN-5 countries: Evidence from a non-linear panel unit root test. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, C.; Ahmad, M.; Ongan, S.; Ozdemir, D.; Irfan, M.; Alvarado, R. Convergence analysis of the ecological footprint: Theory and empirical evidence from the USMCA countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 32648–32659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillaguango, B.; Alvarado, R.; Dagar, V.; Murshed, M.; Pinzón, Y.; Méndez, P. Convergence of the ecological footprint in Latin America: The role of the productive structure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59771–59783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilanci, V.; Gorus, M.S.; Solarin, S.A. Convergence in per capita carbon footprint and ecological footprint for G7 countries: Evidence from panel Fourier threshold unit root test. Energy Environ. 2022, 33, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Ursavaş, U.; Ursavaş, N. Convergence in ecological footprint across the member states of ECOWAS: Evidence from a novel panel unit root test. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 79241–79252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursavaş, U.; Yilanci, V. Convergence analysis of ecological footprint at different time scales: Evidence from Southern Common Market countries. Energy Environ. 2023, 34, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alper, A.E.; Alper, F.O.; Cil, A.B.; Iscan, E.; Eren, A.A. Stochastic convergence of ecological footprint: New insights from a unit root test based on smooth transitions and nonlinear adjustment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 22100–22114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arogundade, S.; Hassan, A.; Akpa, E.; Mduduzi, B. Closer together or farther apart: Are there club convergence in ecological footprint? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 15293–15310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulali, U.; Weng-Wai, C.; Sheau-Ting, L.; Mohammed, A.H. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) hypothesis by utilizing the ecological footprint as an indicator of environmental degradation. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozturk, I.; Al-Mulali, U.; Saboori, B. Investigating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: The role of tourism and ecological footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulucak, R.; Bilgili, F. A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Ulucak, R.; Dogan, E. Analyzing the environmental Kuznets curve for the EU countries: The role of ecological footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 29387–29396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Destek, M.A.; Sarkodie, S.A. Investigation of environmental Kuznets curve for ecological footprint: The role of energy and financial development. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altıntaş, H.; Kassouri, Y. Is the environmental Kuznets Curve in Europe related to the per-capita ecological footprint or CO2 emissions? Ecol. Indic. 2020, 113, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Ulucak, R.; Kocak, E.; Isik, C. The use of ecological footprint in estimating the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis for BRICST by considering cross-section dependence and heterogeneity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A. Re-visiting the Environmental Kuznets curve for ASEAN: A comparison between ecological footprint and carbon dioxide emissions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 168, 112867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Gokmenoglu, K.K.; Taspinar, N.; Cantos-Cantos, J.M. An approach to the pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses in MINT countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23010–23026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Okumus, I. Does pollution haven hypothesis hold in newly industrialized countries? Evidence from ecological footprint. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 23689–23695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathaniel, S.; Aguegboh, E.; Iheonu, C.; Sharma, G.; Shah, M. Energy consumption, FDI, and urbanization linkage in coastal Mediterranean countries: Re-assessing the pollution haven hypothesis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 35474–35487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, I.S.; Yin, W.; Ali, S.A.; Faheem, M.; Abbas, Q.; Farooq, F.; Ur Rahman, S. Moderating role of institutional quality in validation of pollution haven hypothesis in BRICS: A new evidence by using DCCE approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 9193–9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A.; Gil-Alana, L.A.; Lafuente, C. Persistence and sustainability of fishing grounds footprint: Evidence from 89 countries. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 751, 141594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassouri, Y. Exploring the dynamics of fishing footprints in the Gulf of Guinea and Congo Basin region: Current status and future perspectives. Mar. Policy 2021, 133, 104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A. Towards sustainable development: A multi-country persistence analysis of forest products footprint using a stationarity test with smooth shifts. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 28, 1465–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarin, S.A.; Gil-Alana, L.A.; Lafuente, C. Persistence and non-stationarity in the built-up land footprint across 89 countries. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.S.; Khezri, M.; Khan, Y.A.; Razzaghi, S. Exploring the influence of economic freedom index on fishing grounds footprint in environmental Kuznets curve framework through spatial econometrics technique: Evidence from Asia-Pacific countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 6251–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, U.; Dar, A.B. Is there a Kuznets curve for forest product footprint?—Empirical evidence from India. For. Policy Econ. 2022, 144, 102850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Cutcu, I.; Cayir, B. Is the environmental Kuznets curve related to the fishing footprint? Evidence from China. Fish. Res. 2022, 254, 106392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilanci, V.; Cutcu, I.; Cayir, B.; Saglam, M.S. Pollution haven or pollution halo in the fishing footprint: Evidence from Indonesia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, A.W.; Hansen, B.E. Residual-based tests for cointegration in models with regime shifts. J. Econom. 1996, 70, 99–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, R.; Granger, C. Co-integration and error correction: Representation, estimation, and testing. Econometrica 1987, 55, 251–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatemi-j, A. Tests for cointegration with two unknown regime shifts with an application to financial market integration. Empir. Econ. 2008, 35, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.; Enders, W.; Lee, J. A stationarity test in the presence of an unknown number of smooth breaks. J. Time Ser. Anal. 2006, 27, 381–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallant, R. On the basis in flexible functional form and an essentially unbiased form: The flexible Fourier form. J. Econom. 1981, 15, 211–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perron, P. The great crash, the oil price shock, and the unit root hypothesis. Econometrica 1989, 57, 1361–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, W.; Lee, J. The flexible Fourier form and Dickey–Fuller type unit root tests. Econ. Lett. 2012, 117, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.M.; Robert Taylor, A.M. The Flexible Fourier Form and Local Generalised Least Squares De-trended Unit Root Tests. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 2012, 74, 736–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BP 2022, Statistical Review of World Energy—2022, The Brazilian Energy System in 2021. 2022. Available online: https://www.bp.com/content/dam/bp/business-sites/en/global/corporate/pdfs/energy-economics/statistical-review/bp-stats-review-2022-brazil-insights.pdf (accessed on 15 February 2023).
- Arouri, M.E.H.; Youssef, A.B.; M’henni, H.; Rault, C. Energy consumption, economic growth and CO2 emissions in Middle East and North African countries. Energy Policy 2012, 45, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilham, M.I. Economic development and environmental degradation in ASEAN. Signifikan J. Ilmu Ekon. 2018, 7, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Saud, S.; Saleem, N.; Bari, M.W. Nexus between financial development, energy consumption, income level, and ecological footprint in CEE countries: Do human capital and biocapacity matter? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31856–31872. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.C. The interplay among ecological footprint, real income, energy consumption, and trade openness in 13 Asian countries. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 45148–45160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekoya, O.B.; Oliyide, J.A.; Fasanya, I.O. Renewable and non-renewable energy consumption–Ecological footprint nexus in net-oil exporting and net-oil importing countries: Policy implications for a sustainable environment. Renew. Energy 2022, 189, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, V.G.R.; Tang, C.F. The impacts of transport energy consumption, foreign direct investment and income on CO2 emissions in ASEAN-5 economies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, E.; Turkekul, B. CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: Testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuntuyi, B.V.; Lean, H.H. Economic growth, energy consumption and environmental degradation nexus in heterogeneous countries: Does education matter? Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanger, A.; Usman, M.; Murshed, M.; Mahmood, H.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D. The linkages between natural resources, human capital, globalization, economic growth, financial development, and ecological footprint: The moderating role of technological innovations. Resour. Policy 2022, 76, 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dada, J.T.; Adeiza, A.; Noor, A.I.; Marina, A. Investigating the link between economic growth, financial development, urbanization, natural resources, human capital, trade openness and ecological footprint: Evidence from Nigeria. J. Bioeconomics 2022, 24, 153–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destek, M.A.; Sinha, A. Renewable, non-renewable energy consumption, economic growth, trade openness and ecological footprint: Evidence from organisation for economic Co-operation and development countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sadiq, F.; Ali, W.; Kumail, T. Does tourism development, energy consumption, trade openness and economic growth matters for ecological footprint: Testing the Environmental Kuznets Curve and pollution haven hypothesis for Pakistan. Energy 2022, 245, 123208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.I.; Yaseen, M.R.; Ali, Q. Dynamic relationship between financial development, energy consumption, trade and greenhouse gas: Comparison of upper middle income countries from Asia, Europe, Africa and America. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yasmeen, R.; Hussain, J.; Shah, W.U.H. The repercussions of financial development and corruption on energy efficiency and ecological footprint: Evidence from BRICS and next 11 countries. Energy 2021, 223, 120063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongbuamai, N.; Zafar, M.W.; Zaidi, S.A.H.; Liu, Y. Determinants of the ecological footprint in Thailand: The influences of tourism, trade openness, and population density. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40171–40186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Dolado, J.J.; Hendry, D.F.; Smith, G.W. Exploring equilibrium relationships in econometrics through static models: Some Monte Carlo evidence. Oxf. Bull. Econ. Stat. 1986, 48, 253–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Im, K. More powerful cointegration tests with non-normal errors. Stud. Nonlinear Dyn. Econom. 2015, 19, 397–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Arčabić, V.; Lee, H. Fourier ADL cointegration test to approximate smooth breaks with new evidence from crude oil market. Econ. Model. 2017, 67, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
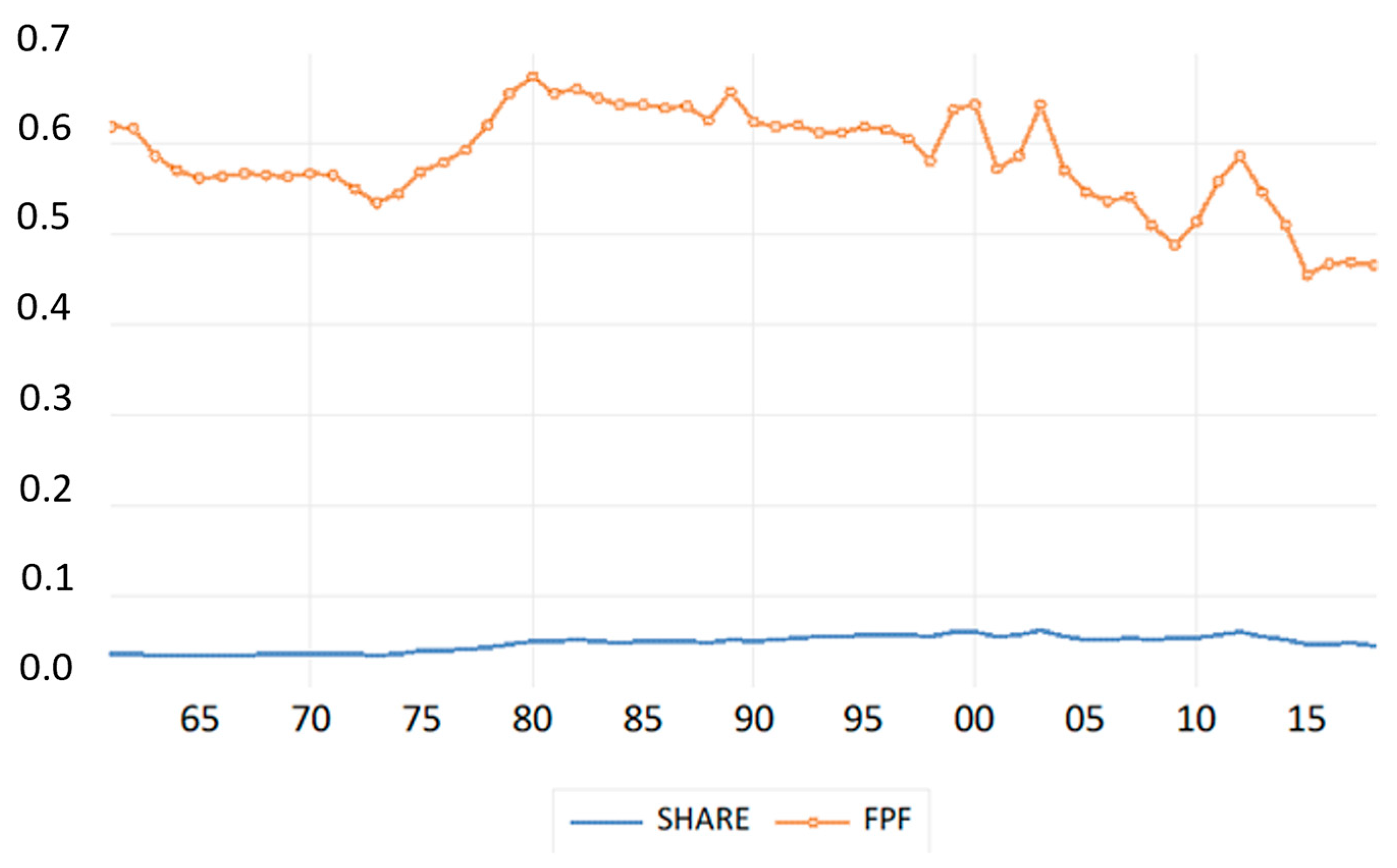
| Mean | Median | Maximum | Minimum | Std. Dev. | Skewness | Kurtosis | Jarque-Bera | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LEC | 3.585 | 3.650 | 4.139 | 2.470 | 0.448 | −1.009 | 3.234 | 9.278 (0.010) ** |
| LFPF | −0.545 | −0.544 | −0.392 | −0.788 | 0.100 | −0.670 | 2.806 | 4.119 (0.127) |
| LGDP | 8.712 | 8.768 | 9.129 | 7.918 | 0.310 | −1.044 | 3.608 | 10.635 (0.005) * |
| LTO | −1.918 | −2.048 | −1.246 | −2.768 | 0.448 | 0.075 | 1.667 | 4.050 (0.132) |
| Series | ADF Unit Root Test | Zivot-Andrews Unit Root Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test Statistics | Test Statistics | Break Date | |
| LEC | −2.231 (0.198) [7] | −4.267 [1] | 1976 |
| LFPF | −0.363 (0.908) [2] | −3.242 [2] | 1978 |
| LGDP | −2.598 (0.1) [5] | −3.974 [2] | 1981 |
| LTO | −1.211 (0.664) [0] | −3.734 [0] | 1992 |
| Variable | Coefficient |
|---|---|
| C | 2.219 (1.501) |
| LEC | 0.835 (4.626) * |
| LGDP | −0.753 (−3.138) * |
| LTO | −0.418 (−7.961) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilanci, V. The Determinants of Forest Products Footprint: A New Fourier Cointegration Approach. Forests 2023, 14, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050875
Yilanci V. The Determinants of Forest Products Footprint: A New Fourier Cointegration Approach. Forests. 2023; 14(5):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050875
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilanci, Veli. 2023. "The Determinants of Forest Products Footprint: A New Fourier Cointegration Approach" Forests 14, no. 5: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050875
APA StyleYilanci, V. (2023). The Determinants of Forest Products Footprint: A New Fourier Cointegration Approach. Forests, 14(5), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14050875








