Organic Materials and AMF Addition Promote Growth of Taxodium ‘zhongshanshan’ by Improving Soil Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Plot Setting
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Sample Collection
2.5. The Determination of Samples
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Result
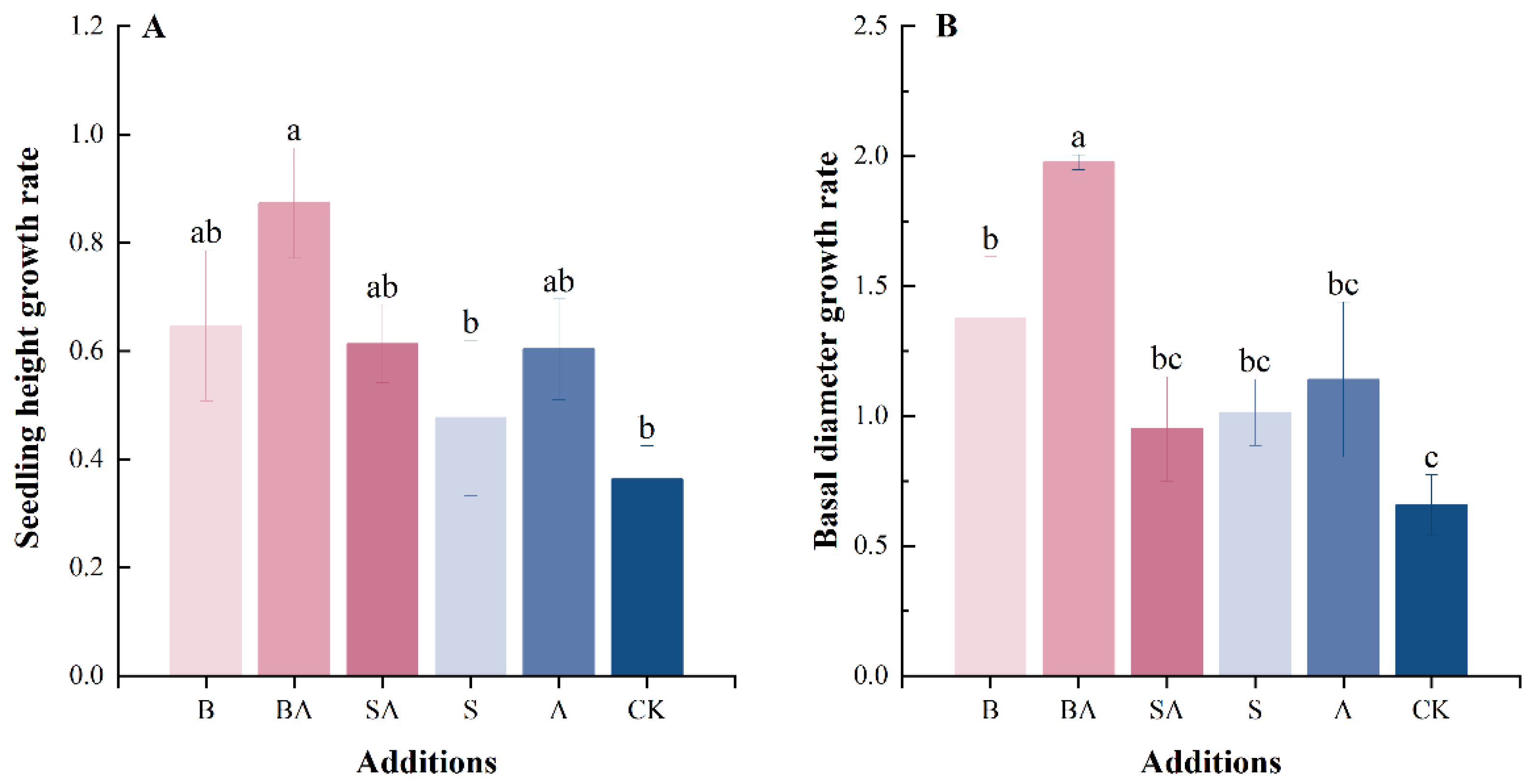
3.1. Plant Growth Rate
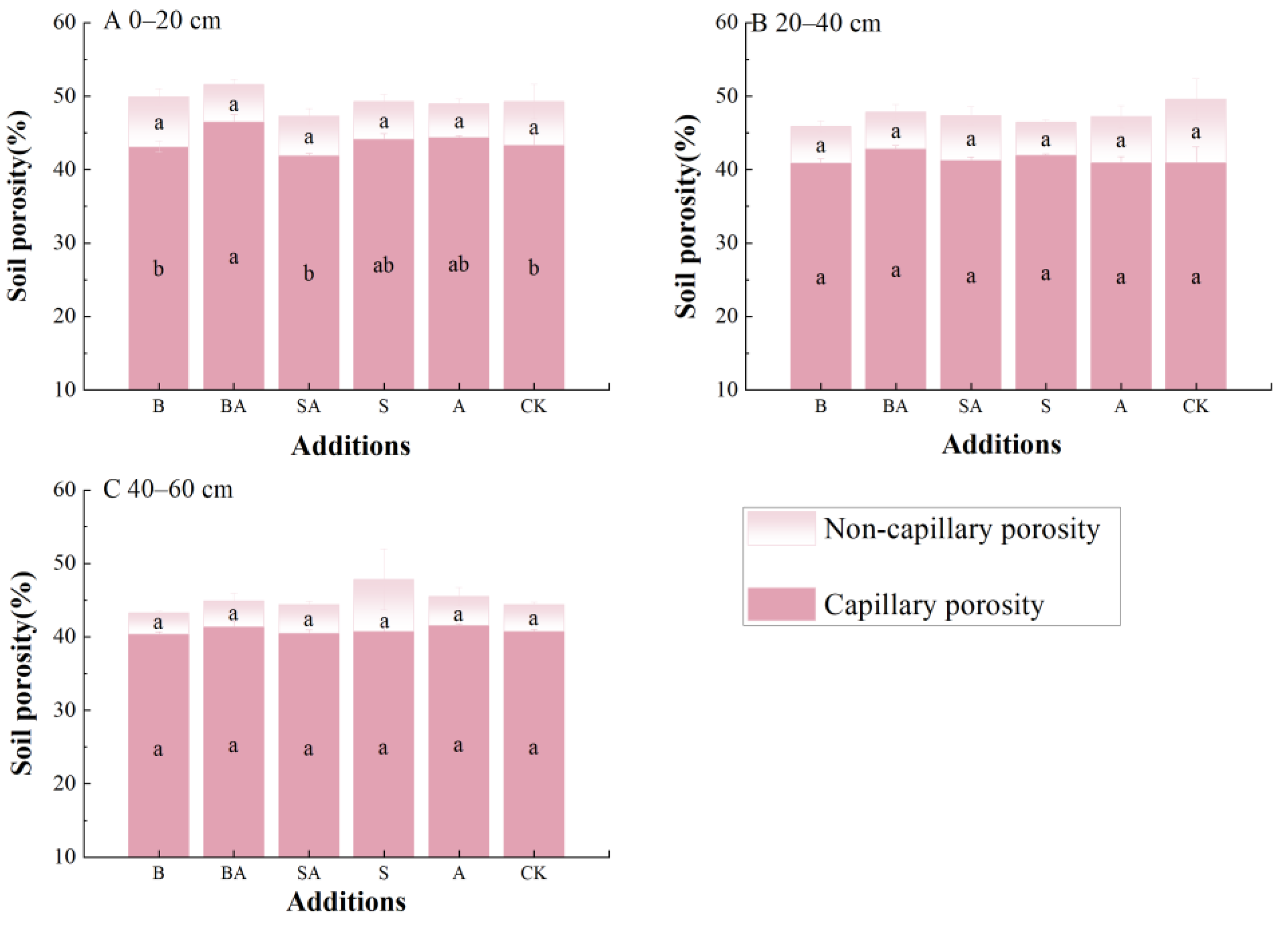
3.2. Soil Porosity
3.3. Soil Aggregate Stability
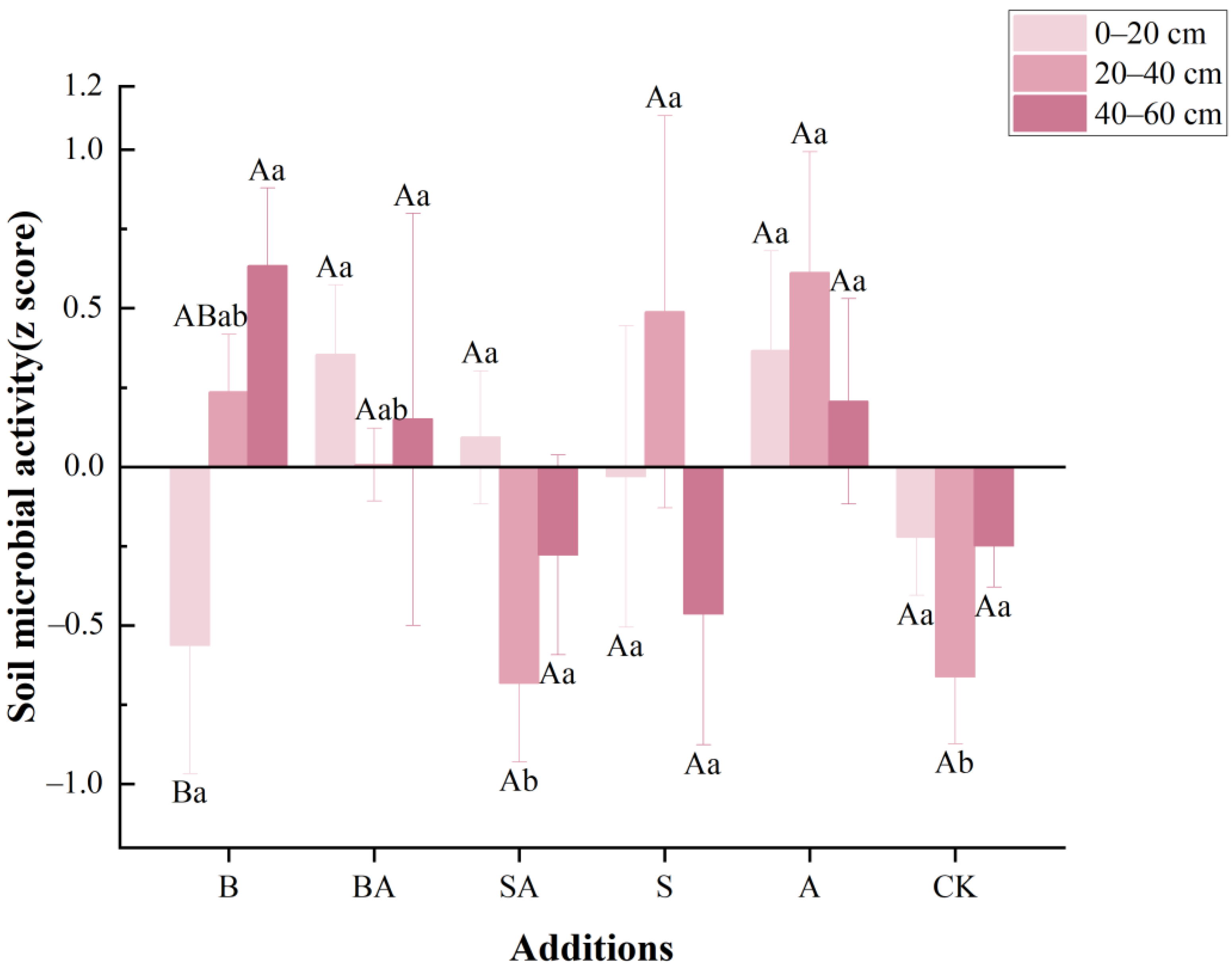
3.4. Soil Microbial Activity
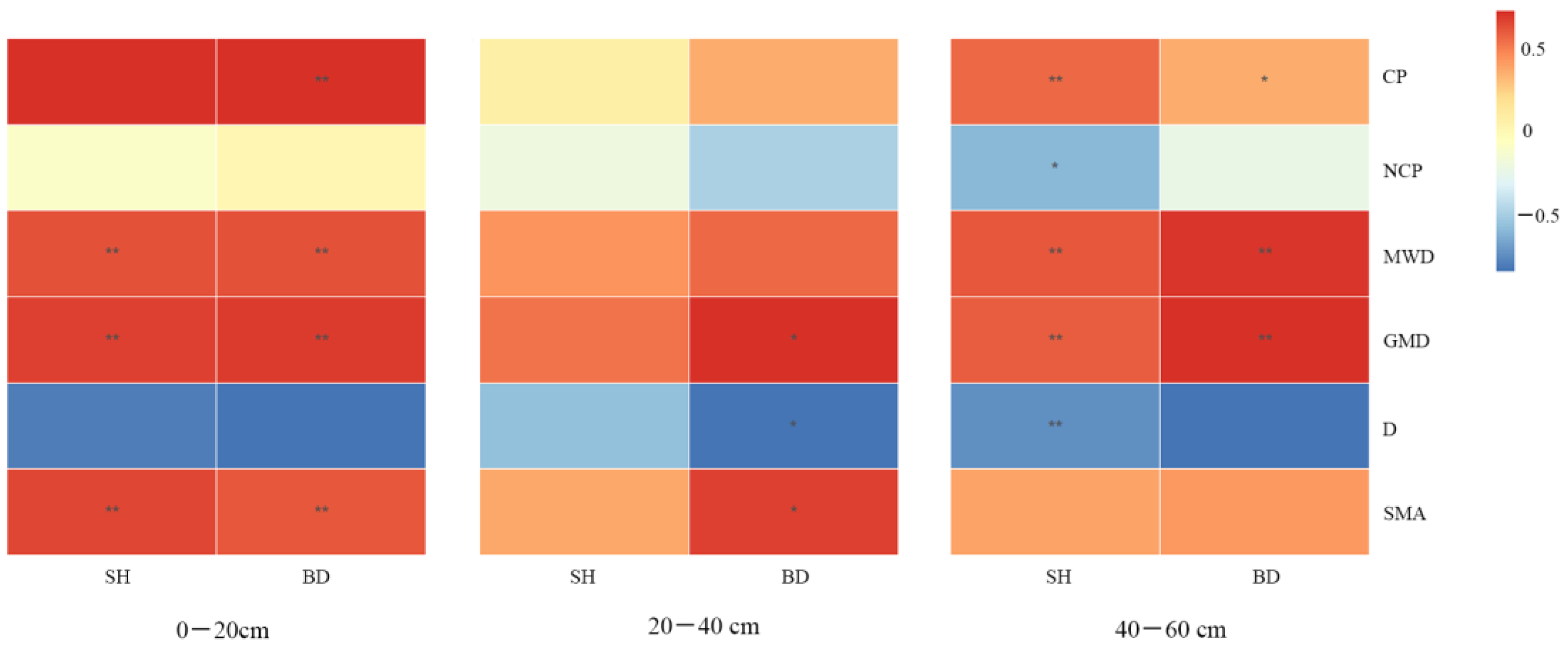
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Organic Materials and AMF Addition on Plant Growth
4.2. Effects of Organic Materials and AMF Additions on Soil Structure
4.3. Effects of Organic Materials and AMF Addition on Soil Microbial Activities
4.4. Combined Effect of Organic Materials and AMF on Soil Condition and Plant Growth
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations/Nomenclature
References
- Shao, T.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Long, X.; Shao, H.; Liu, Z.; Rengel, Z. Balance between salt stress and endogenous hormones influence dry matter accumulation in jerusalem artichoke. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, N. Study on the harm of saline alkali land and its improvement technology in China. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 692, 042053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y.; Cui, G.; Liang, Z. Analysis of spatial-temporal variation of the saline-sodic soil in the west of jilin province from 1989 to 2019 and influencing factors. Catena 2022, 217, 106492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, E.B.; Bever, J.D.; Wilson, G.W.T. Role of plant relatedness in plant–soil feedback dynamics of sympatric asclepias species. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 13, e9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, B.; Chen, M. Recent progress on the salt tolerance mechanisms and application of tamarisk. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, B. The effect of salt stress on the chlorophyll level of the main sand-binding plants in the shelterbelt along the tarim desert highway. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, A.; Sinha, R.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A.; Singh, A.K. Shaping the root system architecture in plants for adaptation to drought stress. Physiol. Plant. 2022, 174, e13651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri-Polizeli, K.M.V.; Marcolino, F.C.; Tormena, C.A.; Keller, T.; Moraes, A. Soil structural quality and relationships with root properties in single and integrated farming systems. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Rengasamy, P.; Smernik, R.; Mosley, L.M. Does the high potassium content in recycled winery wastewater used for irrigation pose risks to soil structural stability? Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xing, X.; Bai, J.; Li, D. Soil aggregate structure, stability, and stoichiometric characteristics in a smelter-impacted soil under phytoremediation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalassery, S.; Sjögersten, S.; Sparkes, D.L.; Sturrock, C.J.; Mooney, S.J. The effect of soil aggregate size on pore structure and its consequence on emission of greenhouse gases. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 132, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauke, S.L.; Landl, M.; Koch, M.; Hofmann, D.; Nagel, K.A.; Siebers, N.; Schnepf, A.; Amelung, W. Macropore effects on phosphorus acquisition by wheat roots—A rhizotron study. Plant Soil 2017, 416, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alò, F.; Odriozola, I.; Baldrian, P.; Zucconi, L.; Ripa, C.; Cannone, N.; Malfasi, F.; Brancaleoni, L.; Onofri, S. Microbial activity in alpine soils under climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 783, 147012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hou, K.; Qian, H.; Gao, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, W.; Ren, W. Characterization of soil salinization and its driving factors in a typical irrigation area of northwest china. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Heng, T.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Feng, Y. Study on the farmland improvement effect of drainage measures under film mulch with drip irrigation in saline–alkali land in arid areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Feng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Geng, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, C. Theoretical and technological problems in the development of planting paddy in saline-alkali land of songnen plain. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2012, 34, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Bing, X.; Jiao, L.; Xiao, H.; Li, B.; Sun, H. Amelioration effects of coastal saline-alkali soil by ball-milled red phosphorus-loaded biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, J.; Wei, J.; Gong, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y. Biochar increases plant growth and alters microbial communities via regulating the moisture and temperature of green roof substrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Hina, K.; Hussain, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhu, J. Revitalizing coastal saline-alkali soil with biochar application for improved crop growth. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, A.; Bhattacharyya, R. Wheat residue mulch and anti-transpirants improve productivity and quality of rainfed soybean in semi-arid north-indian plains. Field Crops Res. 2017, 210, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gong, S.; Xu, D.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, B. Straw mulching improves soil water content, increases flag leaf photosynthetic parameters and maintaines the yield of winter wheat with different irrigation amounts. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 249, 106809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Nie, S.; Li, W.; Fan, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Pan, K. Wheat straw increases the defense response and resistance of watermelon monoculture to fusarium wilt. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Ouyang, Z. Effects of straw application on coastal saline topsoil salinity and wheat yield trend. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 169, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Kwong, R.W.M.; Tang, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, H. Straw return enhances the risks of metals in soil? Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, R.; Joseph, S.; Shi, W.; Li, L.; Taherymoosavi, S.; Pan, G. Biochar dom for plant promotion but not residual biochar for metal immobilization depended on pyrolysis temperature. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifton, M.A.; Lim, P.; Smith, S.M.; Thomas, S.C. Interactive effects of biochar and n-fixing companion plants on growth and physiology of acer saccharinum. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 74, 127652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, G.; Makó, A.; Takács, T.; Skic, K.; Füzy, A.; Horel, Á. Biochar alters soil physical characteristics, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi colonization, and glomalin production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, X.; da Silva, E.B.; de Oliveira, L.M.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.Q. Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: Biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 2017, 178, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Meng, J.; Lan, Y.; Shi, G.; Yang, X.; Cao, D.; Chen, W.; Han, X. Long-term effects of biochar amendment on soil aggregate stability and biological binding agents in brown earth. Catena 2021, 205, 105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marro, N.; Grilli, G.; Soteras, F.; Caccia, M.; Longo, S.; Cofre, N.; Borda, V.; Burni, M.; Janouskova, M.; Urcelay, C. The effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal species and taxonomic groups on stressed and unstressed plants: A global meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xie, X.; Chang, H.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Sun, K.; He, W.; et al. Mycorrhizal symbiosis modulates the rhizosphere microbiota to promote rhizobia–legume symbiosis. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi-Chu, L.; Yong, J.; Ma-bo, L.; Wen-xu, Z.; Nan, X.; Hui-Hui, Z. Improving plant growth and alleviating photosynthetic inhibition from salt stress using amf in alfalfa seedlings. J. Plant Interact. 2019, 14, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sawah, A.M.; Abdel-Fattah, G.G.; Holford, P.; Korany, S.M.; Alsherif, E.A.; AbdElgawad, H.; Ulhassan, Z.; Jośko, I.; Ali, B.; Sheteiwy, M.S. Funneliformis constrictum modulates polyamine metabolism to enhance tolerance of zea mays L. To salinity. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajtor, M.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Prospects for arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (amf) to assist in phytoremediation of soil hydrocarbon contaminants. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlüter, S.; Sammartino, S.; Koestel, J. Exploring the relationship between soil structure and soil functions via pore-scale imaging. Geoderma 2020, 370, 114370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Timms, W.; Mahmud, M.A.P. Optimising water holding capacity and hydrophobicity of biochar for soil amendment—A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; Li, H.; Lin, T.; Gao, J.; Fu, Q. Relationship between salinity, electrical conductivity and water content in a typical coastal mudflat grassland in northern jiangsu province. Water Sav. Irrig. 2015, 240, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgisson, W.; Cobb, A.; Tschierschke, A.; Dyer, F. The role of environmental water and reedbed condition on the response of Phragmites australis reedbeds to flooding. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y. Hyperspectral identification of chlorophyll fluorescence parameters of Suaeda salsa in coastal wetlands. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Heo, Y.M.; Yun, J.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.-J.; Kang, H. Changes in archaeal community and activity by the invasion of spartina anglica along soil depth profiles of a coastal wetland. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, C.; Guo, Z.; Dai, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. A multiscale approach to identifying spatiotemporal pattern of habitat selection for red-crowned cranes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, E.T. Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Kong, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Banerjee, S.; Ishii, S.J.; Sadowsky, M.; Gao, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Halophytes increase rhizosphere microbial diversity, network complexity and function in inland saline ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhangi-Abriz, S.; Torabian, S. Effect of biochar on growth and ion contents of bean plant under saline condition. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11556–11564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, Z.; Huang, J.; Hussain, S.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X.; Jin, Q. Biochar alleviated the salt stress of induced saline paddy soil and improved the biochemical characteristics of rice seedlings differing in salt tolerance. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Sarmah, A.K.; Bordoloi, S.; Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Sooriyakumar, P.; Khan, B.A.; Ahmad, M.; Solaiman, Z.; et al. Soil acidification and the liming potential of biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 317, 120632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Joseph, S.; Tsechansky, L.; Schreiter, I.J.; Schüth, C.; Taherysoosavi, S.; Mitchell, D.R.G.; Graber, E.R. Mechanistic evaluation of biochar potential for plant growth promotion and alleviation of chromium-induced phytotoxicity in ficus elastica. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindo, K.; Goron, T.L.; Kurebito, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Masunaga, T.; Mori, K.; Miyakawa, K.; Nagao, S.; Tokunari, T. Sustainable plant growth promotion and chemical composition of pyroligneous acid when applied with biochar as a soil amendment. Molecules 2022, 27, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Bu, X.; Li, J.; Ji, Z.; Wang, C.; Xiao, X.; Li, F.; Wu, Z.-H.; Wu, G.; Jia, P.; et al. Application of biochar and compost improved soil properties and enhanced plant growth in a pb–zn mine tailings soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 32337–32347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.C.; Frye, S.; Gale, N.; Garmon, M.; Launchbury, R.; Machado, N.; Melamed, S.; Murray, J.; Petroff, A.; Winsborough, C. Biochar mitigates negative effects of salt additions on two herbaceous plant species. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 129, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Berruti, F.; Greenhalf, C.; Tian, X.; Henry, H.A.L. Increased retention of soil nitrogen over winter by biochar application: Implications of biochar pyrolysis temperature for plant nitrogen availability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 236, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, G. Mechanisms of straw biochar’s improvement of phosphorus bioavailability in soda saline-alkali soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 47867–47872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Tomar, R.S.; Jajoo, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (amf) protects photosynthetic apparatus of wheat under drought stress. Photosynth. Res. 2019, 139, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Sharma, M.P.; Jajoo, A. Improved photosynthetic efficacy of maize (zea mays) plants with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (amf) under high temperature stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 180, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; He, Y.; Xu, X.; Umer, M.; Liu, X.; Xia, T.; Guo, Y.; Wu, B.; Xu, H.; Zang, L.; et al. Effects of amf on plant nutrition and growth depend on substrate gravel content and patchiness in the karst species bidens pilosa L. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndiate, N.I.; Saeed, Q.; Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Nkoh, J.N.; Mustafa, A. Co-application of biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improves salinity tolerance, growth and lipid metabolism of maize (zea mays L.) in an alkaline soil. Plants 2021, 10, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujre, N.; Soni, A.; Rangan, L.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Mitra, S. Sustainable improvement of soil health utilizing biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuther, F.; Schlüter, S. Impact of freeze–thaw cycles on soil structure and soil hydraulic properties. Soil 2021, 7, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, B.S.; Hallett, P.D.; Kuan, H.L.; Gregory, A.S.; Watts, C.W.; Whitmore, A.P. Functional resilience of soil microbial communities depends on both soil structure and microbial community composition. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 44, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecon, R.; Or, D. Biophysical processes supporting the diversity of microbial life in soil. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 599–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mentges, M.I.; Reichert, J.M.; Rodrigues, M.F.; Awe, G.O.; Mentges, L.R. Capacity and intensity soil aeration properties affected by granulometry, moisture, and structure in no-tillage soils. Geoderma 2016, 263, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Niu, L.; Hu, K.; Hao, J.; Li, F.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X. Influence of tillage, straw-returning and mineral fertilization on the stability and associated organic content of soil aggregates in the north china plain. Agronomy 2020, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavel, C. Mean weight-diameter of soil aggregates as a statistical index of aggregation1. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1950, 14, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Neyshabouri, M.-R.; Rouhipour, H.; Asadi, H. Fractal dimension of soil aggregates as an index of soil erodibility. J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Lu, S. Pyrolysis temperature affects pore characteristics of rice straw and canola stalk biochars and biochar-amended soils. Geoderma 2021, 397, 115097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbi, S.M.F.; Minasny, B.; McBratney, A.B.; Young, I.M. Microbial processing of organic matter drives stability and pore geometry of soil aggregates. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, X.; Lin, J.; Guo, G.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, G. The mineralization and sequestration of soil organic carbon in relation to gully erosion. CATENA 2022, 214, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Sun, K.; Yang, Y.; Xia, X.; Li, F.; Yang, Z.; Xing, B. Biochar’s stability and effect on the content, composition and turnover of soil organic carbon. Geoderma 2020, 364, 114184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Zeng, G.; Lin, J. Effect of forest management operations on aggregate-associated soc dynamics using a 137cs tracing method. Forests 2021, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornoza, R.; Acosta, J.A.; Faz, A.; Bååth, E. Microbial growth and community structure in acid mine soils after addition of different amendments for soil reclamation. Geoderma 2016, 272, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ur, R.M.; Ramzani, P.M.A.; Zubair, M.; Rasool, B.; Khan, M.K.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, S.A.; Turan, V.; Iqbal, M. Associative effects of lignin-derived biochar and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi applied to soil polluted from pb-acid batteries effluents on barley grain safety. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.J.; Lee, D.J.; Wee, C.D.; Kim, H.L.; Cheong, Y.H.; Cho, J.S.; Sohn, B.K. Effects of amf inoculation on growth of panax ginseng c.A. Meyer seedlings and on soil structures in mycorrhizosphere. Sci. Hortic. 2009, 122, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chi, S.; Lin, C.; Cai, C.; Yang, L.; Peng, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, J. Combination of biochar and amf promotes phosphorus utilization by stimulating rhizosphere microbial co-occurrence networks and lipid metabolites of phragmites. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Li, G.; Sun, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Sun, J. Can arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and biochar enhance plant resistance to low-temperature stress? Agron. J. 2021, 113, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, L.; Beiyuan, J.; Cui, Y.; Peng, Q.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X. Improvement of alfalfa resistance against cd stress through rhizobia and arbuscular mycorrhiza fungi co-inoculation in cd-contaminated soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Xie, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Hao, Z.; Chen, B. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can compensate for the loss of indigenous microbial communities to support the growth of liquorice (glycyrrhiza uralensis fisch.). Plants 2020, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, B.; Diao, F.; Zhang, J.; Bao, Z.; Guo, W. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi alter microbiome structure of rhizosphere soil to enhance maize tolerance to la. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 111996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F. Occurrence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in mining-impacted sites and their contribution to ecological restoration: Mechanisms and applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 1901–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakouridis, A.; Hagen, J.A.; Kan, M.P.; Mambelli, S.; Feldman, L.J.; Herman, D.J.; Weber, P.K.; Pett-Ridge, J.; Firestone, M.K. Routes to roots: Direct evidence of water transport by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to host plants. New Phytol. 2022, 236, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mediated enhanced biomass, root morphological traits and nutrient uptake under drought stress: A meta-analysis. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hodge, A.; Feng, G. Carbon and phosphorus exchange may enable cooperation between an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and a phosphate-solubilizing bacterium. New Phytol. 2016, 210, 1022–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, X.; Chen, X.; Fang, J.; Ji, C.; Shen, H.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, B. Soil microbial carbon and nutrient constraints are driven more by climate and soil physicochemical properties than by nutrient addition in forest ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadem, A.; Raiesi, F. Influence of biochar on potential enzyme activities in two calcareous soils of contrasting texture. Geoderma 2017, 308, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Qin, S.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Liao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J. Organic Materials and AMF Addition Promote Growth of Taxodium ‘zhongshanshan’ by Improving Soil Structure. Forests 2023, 14, 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040731
Zeng J, Ma S, Liu J, Qin S, Liu X, Li T, Liao Y, Shi Y, Zhang J. Organic Materials and AMF Addition Promote Growth of Taxodium ‘zhongshanshan’ by Improving Soil Structure. Forests. 2023; 14(4):731. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040731
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jingyi, Shilin Ma, Jing Liu, Shenghua Qin, Xin Liu, Tao Li, Yi Liao, Yuxuan Shi, and Jinchi Zhang. 2023. "Organic Materials and AMF Addition Promote Growth of Taxodium ‘zhongshanshan’ by Improving Soil Structure" Forests 14, no. 4: 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040731
APA StyleZeng, J., Ma, S., Liu, J., Qin, S., Liu, X., Li, T., Liao, Y., Shi, Y., & Zhang, J. (2023). Organic Materials and AMF Addition Promote Growth of Taxodium ‘zhongshanshan’ by Improving Soil Structure. Forests, 14(4), 731. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040731




