Nutrient Resorption and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea Cultivars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Leaf, Litter, and Soil C, N, P, and K Contents and Their Stoichiometry
3.2. Nutrient Use and Resorption Efficiencies of Different Tea Cultivars
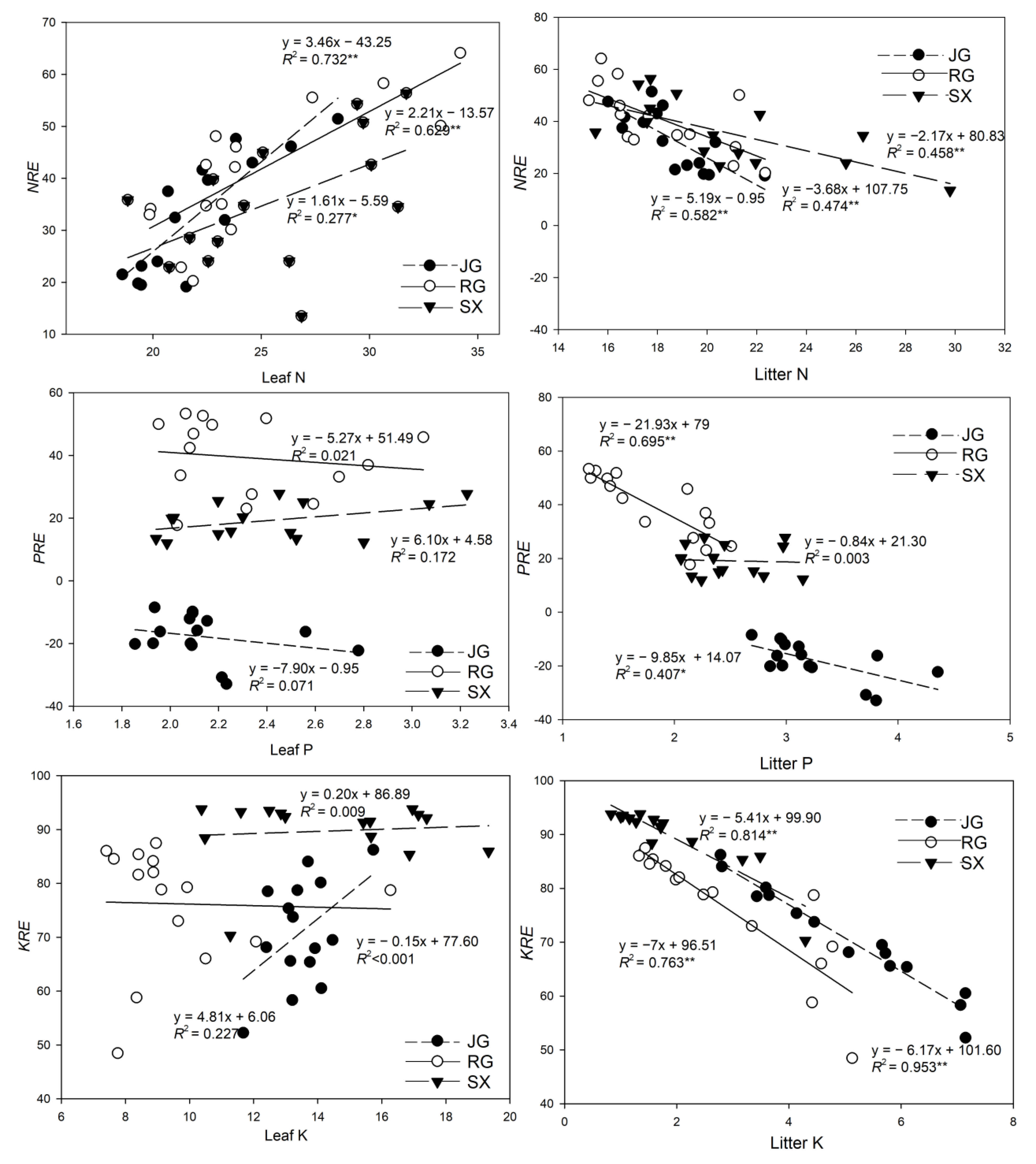
3.3. Relationships between Nutrient Resorption Efficiencies and Leaf and Litter Nutrients
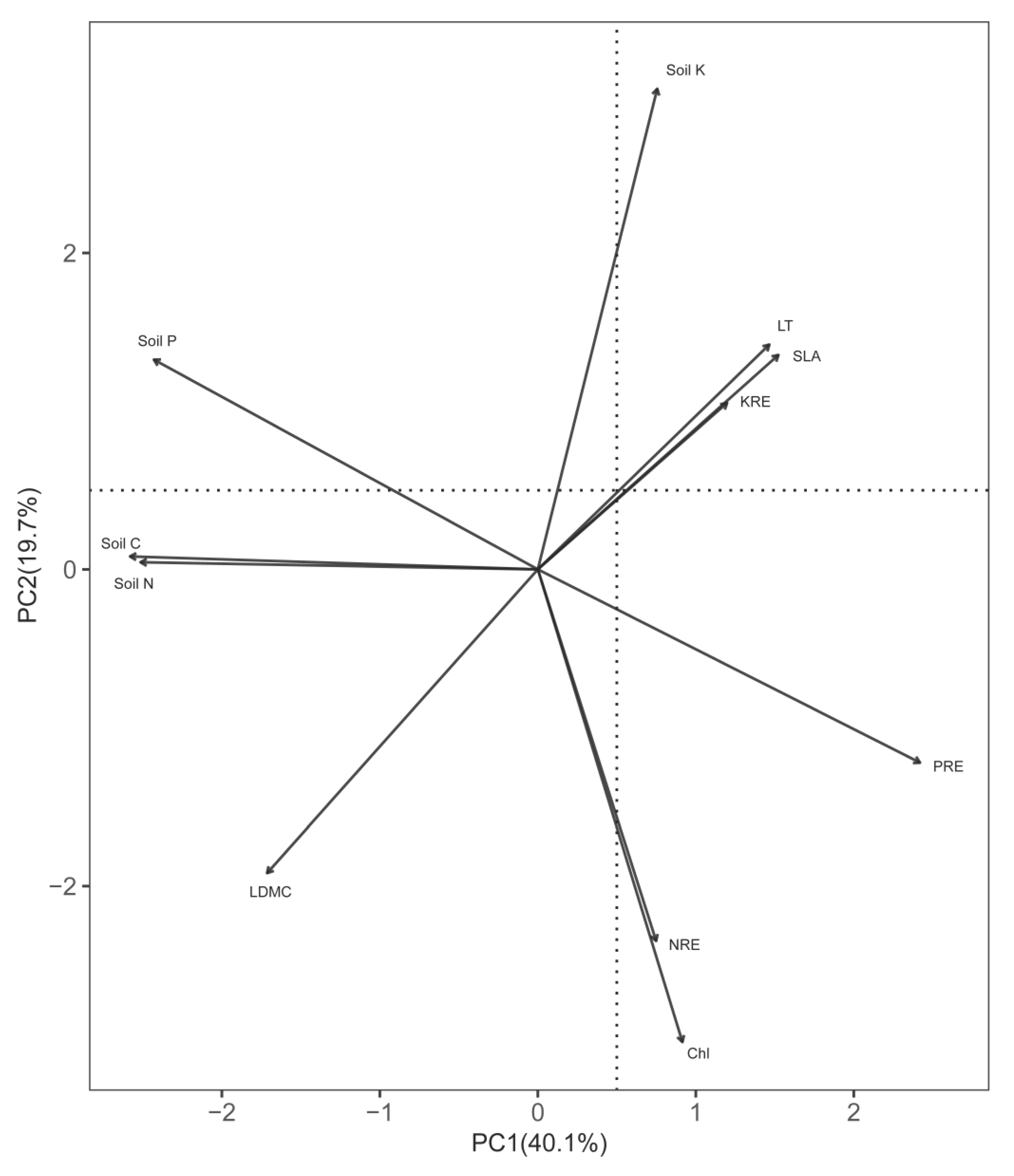
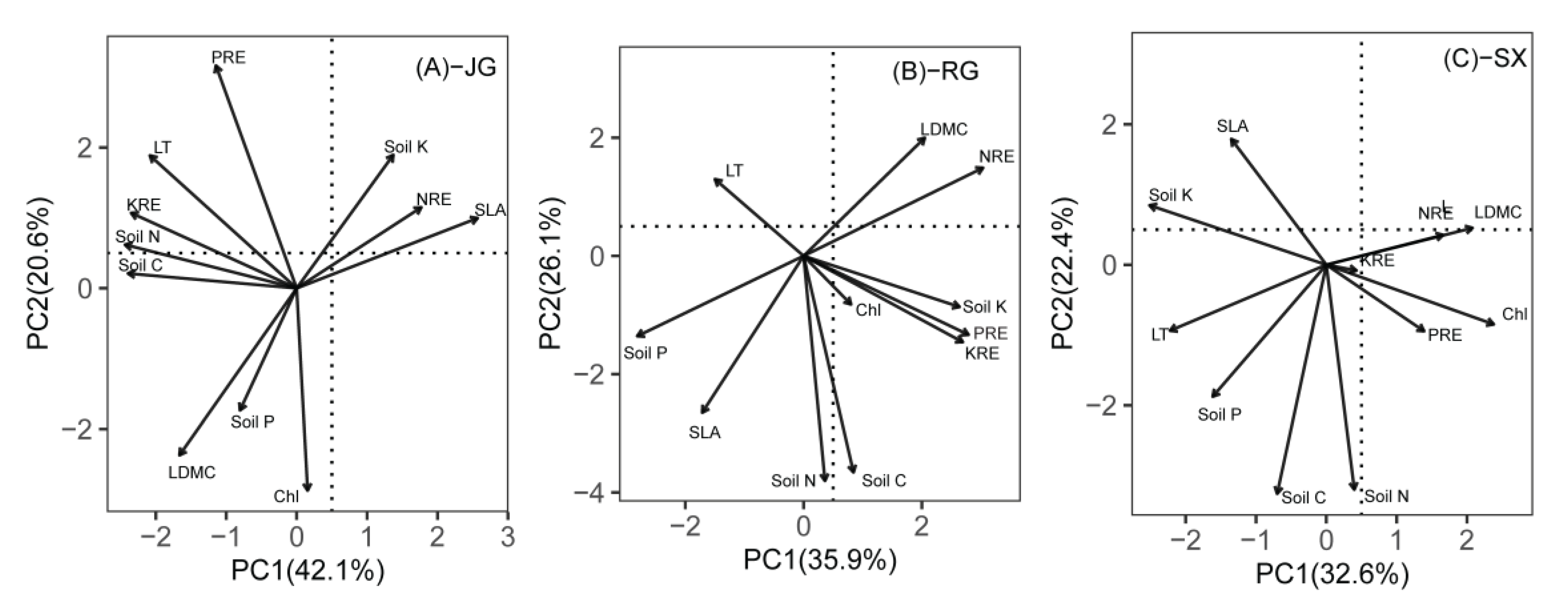
3.4. Relationships of Nutrient Resorption Efficiencies with Leaf Traits and Soil Nutrients
4. Discussion
4.1. Stoichiometry of Wuyi Rock Tea Cultivars
4.2. Nutrient Resorption Efficiencies of Different Tea Cultivars
4.3. Response of Nutrient Homeostasis and Nutrient Utilization Strategies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Reed, S.C.; Lu, X.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Coexistence of multiple leaf nutrient resorption strategies in a single ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 144951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergutz, L.; Manzoni, S.; Porporato, A.; Novais, R.F.; Jackson, R.B. Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol. Monogr. 2012, 82, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, X.; Wang, R.; Li, T.; Cai, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, B.; Lü, X.; Jiang, Y. Nutrient resorption and coupling relationships in two plant species with sulfur addition: A two-year study in a meadow. Plant Soil 2022, 386, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, D. Response of multi-ecological component stoichiometry and tree nutrient resorption to medium-term whole-tree harvesting in secondary forests in the Qinling Mountains, China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 498, 119573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenovsky, R.E.; Pietrasiak, N.; Short, T.H.; Silva, T. Global temporal patterns in plant nutrient resorption plasticity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2019, 28, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerdol, R.; Iacumin, P.; Brancaleoni, L.; Wang, F. Differential effects of soil chemistry on the foliar resorption of nitrogen and phosphorus across altitudinal gradients. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, F.; Lopez, C.M.L.; Bonifacio, E.; Kurokawa, H.; Yamanaka, T.; Celi, L. Seasonal phosphorus and nitrogen cycling in four Japanese cool-temperate forest species. Plant Soil 2022, 472, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.Y.; Chen, H.Y.H. Global-scale patterns of nutrient resorption associated with latitude, temperature and precipitation. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2009, 18, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brant, A.N.; Chen, H.Y.H. Patterns and mechanisms of nutrient resorption in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, B.R.; An, S.S. Ecological stoichiometry in leaves, roots, litters and soil among different plant communities in a desertified region of Northern China. Catena 2018, 166, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Song, H.; Liu, F.; Quan, X.; Wang, C. Timing of leaf fall and changes in litter nutrient concentration compromise estimates of nutrient fluxes and nutrient resorption efficiency. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 513, 12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guan, F.; Fan, S.; Yan, X.; Huang, L. Dynamics of leaf-litter biomass, nutrient resorption efficiency and decomposition in a Moso Bamboo forest after strip clearcutting. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 799424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.C.; Townsend, A.R.; Davidson, E.A.; Cleveland, C.C. Stoichiometric patterns in foliar nutrient resorption across multiple scales. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.Y.H. Foliar nutrient resorption dynamics of trembling aspen and white birch during secondary succession in the boreal forest of central Canada. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 505, 119876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hui, D.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, F.; Long, J.; Mou, Z.; Lu, H.; Ren, H. Leaf nutrient resorption differs among canopy and understory plant species in subtropical Eucalyptus and Acacia plantations. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1662–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, L.; Ge, X.; Cao, Y. Spatial patterns of leaf carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus stoichiometry and nutrient resorption in Chinese fir across subtropical China. Catena 2021, 201, 105221–105229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, J.; Jing, G.; Cheng, J. Forbs dominate plant nutrient resorption of plant community along a 34-year grazing exclusion gradient in a semiarid grassland. Ecol. Engin. 2022, 175, 106497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Sterner, R.W.; Gorokhova, E.A.; Fagan, W.F.; Markow, T.A.; Cotner, J.B.; Harrison, J.F.; Hobbie, S.E.; Odell, G.H.; Weider, L.W. Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2000, 6, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Sheng, M.; Bai, Y.; Jie, Y.; Xiao, H. Response of C, N, and P stoichiometry characteristics of Broussonetia papyrifera to altitude gradients and soil nutrients in the karst rocky ecosystem, SW China. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Hui, D.; Wang, M.; Yang, Q.; Yu, S. Light and competition alter leaf stoichiometry of introduced species and native mangrove species. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Min, Q.; Sardans, J.; Wang, C.; Asensio, D.; Bartrons, M.; Peñuelas, J. Organic cultivation of jasmine and tea increases carbon sequestration by changing plant and soil stoichiometry. Agron. J. 2016, 108, 1636–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, L.; Ye, S.; Wang, S. Soil nutrient contents and stoichiometry within aggregate size classes varied with tea plantation age and soil depth in southern Guangxi in China. Soil 2022, 8, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenovsky, R.E.; Koehler, C.E.; Skelly, K.; Richards, J.H. Potential and realized nutrient resorption in serpentine and non-serpentine chaparral shrubs and trees. Oecologia 2013, 171, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Lin, G.; Liu, B.; Mao, R. Linking leaf nutrient resorption and litter decomposition to plant mycorrhizal associations in boreal peatlands. Plant Soil 2020, 448, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbina, I.; Grau, O.; Sardans, J.; Margalef, O.; Peguero, G.; Asensio, D.; LLusià, J.; Ogaya, R.; Gargallo-Garriga, A.; Van Langenhove, L.; et al. High foliar K and P resorption efficiencies in old-growth tropical forests growing on nutrient-poor soils. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 8969–8982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yao, X.; Zhao, D.; Lu, L. Evaluation of the ecological benefits of tea gardens in Meitan County, China, using the InVEST model. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 7140–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jeong, S.; Park, C.; Mueller, N.D.; Piao, S.; Park, H.; Joo, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Effects of extreme temperature on China’s tea production. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 044040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. China Statistical Yearbook. Tea Plantation Area Statistics Report for the CHN. 2021. Available online: http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/ndsj/2021/indexch.htm (accessed on 1 January 2022).
- Nyamekye, C.; Schönbrodt-Stitt, S.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Zoungrana, B.J.B.; Thiel, M. Usage of MODIS NDVI to evaluate the effect of soil and water conservation measures on vegetation in Burkina Faso. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 32, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Dai, W.; Lu, M.; Xie, D.; Tan, J.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Lv, H.; Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Metabolomic analysis reveals the composition differences in 13 Chinese tea cultivars of different manufacturing suitabilities. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Zhou, X.; Su, X.; Yang, Z. Chinese oolong tea: An aromatic beverage produced under multiple stresses. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 2020, 106, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yu, J.; Jin, S.; Chen, S.; Yue, C.; Wang, W.; Gao, S.; Cao, H.; Zheng, Y.; Gu, M.; et al. Genetic basis of high aroma and stress tolerance in the oolong tea cultivar genome. Hort. Res. 2021, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.; Xu, B.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, W.; Wan, S.; Tan, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Synthetic nitrogen fertilizers alter the soil chemistry, production and quality of tea. A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Yang, F.; Feng, H.; Yu, Z.; Liu, C.; Wei, C.; Liang, T. Organic fertilizer reduced carbon and nitrogen in runoff and buffered soil acidification in tea plantations: Evidence in nutrient contents and isotope fractionations. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamau, D.M.; Spiertz, J.H.J.; Oenema, O. Carbon and nutrient stocks of tea plantations differing in age, genotype and plant population density. Plant Soil 2008, 307, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Wu, A.; Wang, F.; Chen, F. The effects of simulated acid rain on internal nutrient cycling and the ratios of Mg, Al, Ca, N, and P in tea plants of a subtropical plantation. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Harguindeguy, N.; Díaz, S.; Garnier, E.; Lavorel, S.; Poorter, H.; Jaureguiberry, P.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Cornwell, W.K.; Craine, J.M.; Gurvich, D.E.; et al. New handbook for standardised measurement of plant functional traits worldwide. Aust. J. Bot. 2013, 61, 167–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.B. Laboratory Guide for Conducting Soil Tests and Plant Analysis; CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 1–363. [Google Scholar]
- Chapin, I.F.S. The mineral nutrition of wild plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 1980, 11, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L.F. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Koojiman, S.A.L.M. The stoichiometry of animal energetics. J. Theor. Biol. 1995, 177, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, P.B.; Oleksyn, J. Global patterns of plant leaf N and P in relation to temperature and latitude. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11001–11006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, M.V. Soil–plant nutrient balance of tea crops in the northern mountainous region, Vietnam. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 105, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.J.; Fagan, W.F.; Denno, R.F.; Dobberfuhl, D.R.; Folarin, A.; Huberty, A.; Interlandi, S.; Kilham, S.S.; McCauley, E.; Schulz, K.L.; et al. Nutritional constraints in terrestrial and freshwater food webs. Nature 2000, 408, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, J.; Guo, D.; Zhang, Y. Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometry across 753 terrestrial plant species in China. New Phytol. 2005, 168, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.J. Ecological Stoichiometry of Forest Ecosystems Across the North-South Transect of Eastern China; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Koerselman, W.; Meuleman, A.F. The vegetation N: P ratio: A new tool to detect the nature of nutrient limitation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Wang, B.; An, S.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, H. Response of forest species to C:N:P in the plant-litter-soil system and stoichiometric homeostasis of plant tissues during afforestation on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2019, 183, 104186–104194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, S.; Chen, Y.; Chen, G.; Tu, L. Nitrogen addition slows litter decomposition accompanied by accelerated manganese release: A five-year experiment in a subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Xin, Z.; Berg, B.; Burgess, P.J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, C. Global pattern of leaf litter nitrogen and phosphorus in woody plants. Ann. For. Sci. 2010, 67, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tian, D.; Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; et al. Forest soil acidification consistently reduces litter decomposition irrespective of nutrient availability and litter type. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 2753–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P stoichiometry in soil: Is there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2009, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Reed, S.C.; Lü, X.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Global resorption efficiencies of trace elements in leaves of terrestrial plants. Funct. Ecol. 2021, 35, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, I.J.; Reich, P.B.; Westoby, M.; Ackerly, D.D.; Baruch, Z.; Bongers, F.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Chapin, T.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Diemer, M.; et al. The worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Nature 2004, 428, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Lü, X.; Li, M.; Wu, T.; Jin, G. N-limitation increases along a temperate forest succession: Evidences from leaf stoichiometry and nutrient resorption. J. Plant Ecol. 2022, 15, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, F.Y.; Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Tang, S.; Baoyin, T. Enhancement of nutrient resorption efficiency increases plant production and helps maintain soil nutrients under summer grazing in a semi-arid steppe. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 292, 106840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Ji, H.; Peng, C.; Liu, X.; Liu, C. Altitudinal patterns of leaf stoichiometry and nutrient resorption in Quercus variabilis in the Baotianman Mountains, China. Plant Soil 2016, 413, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, K.; Violle, C.; Vile, D.; Vasseur, F.; Villemereuil, P.; Bresson, J.; Gillespie, L.; Fletcher, L.R.; Sack, L.; Kazakou, E. Do leaf nitrogen resorption dynamics align with the slow-fast continuum? A test at the intraspecific level. Funct. Ecol. 2022, 36, 1315–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yan, Z.; Cui, X.; Gong, Y.; Li, K.; Han, W. Scaling the leaf nutrient resorption efficiency: Nitrogen vs. phosphorus in global plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneklaas, E.J.; Lambers, H.; Bragg, J.; Finnegan, P.M.; Lovelock, C.E.; Plaxton, W.C.; Price, C.A.; Scheible, W.R.; Shane, M.W.; White, P.J.; et al. Opportunities for improving phosphorus-use efficiency in crop plants. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Cheng, X.; Kang, F.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Han, H. The patterns of N/P/K stoichiometry in the Quercus wutaishanica community among different life forms and organs and their responses to environmental factors in northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Elser, J.J.; He, N.; Wu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wu, J.; Bai, Y.; Han, X. Linking stoichiometric homoeostasis with ecosystem structure, functioning and stability. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Fang, J.; Reich, P.B.; Ian Woodward, F.; Wang, Z.H. Biogeography and variability of eleven mineral elements in plant leaves across gradients of climate, soil and plant functional type in China. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, S.; Ren, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Yang, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus resorption in relation to nutrition limitation along the chronosequence of black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia L.) plantation. Forests 2019, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| C Content (mg/g) | N Content (mg/g) | P Content (mg/g) | K Content (mg/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuyi Jingui | Leaf | 533.5 ± 3.3 a | 22.1 ± 0.7 a | 2.1 ± 0.1 a | 12.8 ± 0.8 a |
| Litter | 537.0 ± 4.1 a | 18.6 ± 0.4 ab | 3.3 ± 0.1 a | 5.0 ± 0.4 a | |
| Soil | 24.4 ± 1.3 a | 0.9 ± 0.1 a | 0.6 ± 0.1 a | 24.6 ± 1.1 b | |
| Wuyi Rougui | Leaf | 552.1 ± 9.7 a | 24.7 ± 1.2 a | 2.3 ± 0.1 a | 9.5 ± 0.6 b |
| Litter | 511.2 ± 4.5 b | 18.1 ± 0.6 b | 1.8 ± 0.1 c | 2.9 ± 0.4 b | |
| Soil | 12.9 ± 0.7 b | 0.4 ± 0.0 b | 0.1 ± 0.0 c | 16.2 ± 1.8 c | |
| Wuyi Shuixian | Leaf | 542.9 ± 13.2 a | 25.6 ± 1.1 a | 2.4 ± 0.1 a | 14.4 ± 0.7 a |
| Litter | 530.5 ± 4.6 a | 20.8 ± 1.0 a | 2.5 ± 0.1 b | 1.9 ± 0.3 c | |
| Soil | 11.0 ± 0.5 b | 0.3 ± 0.0 b | 0.2 ± 0.0 b | 54.6 ± 5.7 a |
| NUE (%) | PUE (%) | KUE (%) | |
| Wuyi Jingui | 45.9 (1.4) Ac | 471.3 (12.1) Aa | 74.5 (1.4) Bb |
| Wuyi Rougui | 41.6 (1.7) ABc | 438.8 (14.6) Ba | 109.6 (4.9) Ab |
| Wuyi Shuixian | 40.0 (1.7) Bc | 426.2 (16.6) Ba | 72.0 (3.8) Bb |
| NRE (%) | PRE (%) | KRE (%) | |
| Wuyi Jingui | 33.2 (3.0) Ab | −17.9 (1.8) Cc | 72.0 (2.5) Ca |
| Wuyi Rougui | 41.1 (3.3) Ab | 39.3 (3.1) Ab | 76.2 (2.9) Ba |
| Wuyi Shuixian | 35.7 (3.2) Ab | 19.2 (1.5) Bc | 89.7 (1.6) Aa |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, D.; Peng, S.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.; Hui, D. Nutrient Resorption and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea Cultivars. Forests 2023, 14, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040675
Zhu D, Peng S, Liu W, Yu S, Hui D. Nutrient Resorption and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea Cultivars. Forests. 2023; 14(4):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040675
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Dehuang, Suhong Peng, Wenzhen Liu, Shengjie Yu, and Dafeng Hui. 2023. "Nutrient Resorption and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea Cultivars" Forests 14, no. 4: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040675
APA StyleZhu, D., Peng, S., Liu, W., Yu, S., & Hui, D. (2023). Nutrient Resorption and Stoichiometric Characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea Cultivars. Forests, 14(4), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14040675








