Effect of Coupling Treatment on Interfacial Bonding Properties of Wood Veneer/Wood Flour–Polyvinyl Chloride Composites with Sandwich Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the WPVCs
2.3. Preparation of the WWPVCs Using Various Coupling Agents
2.4. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
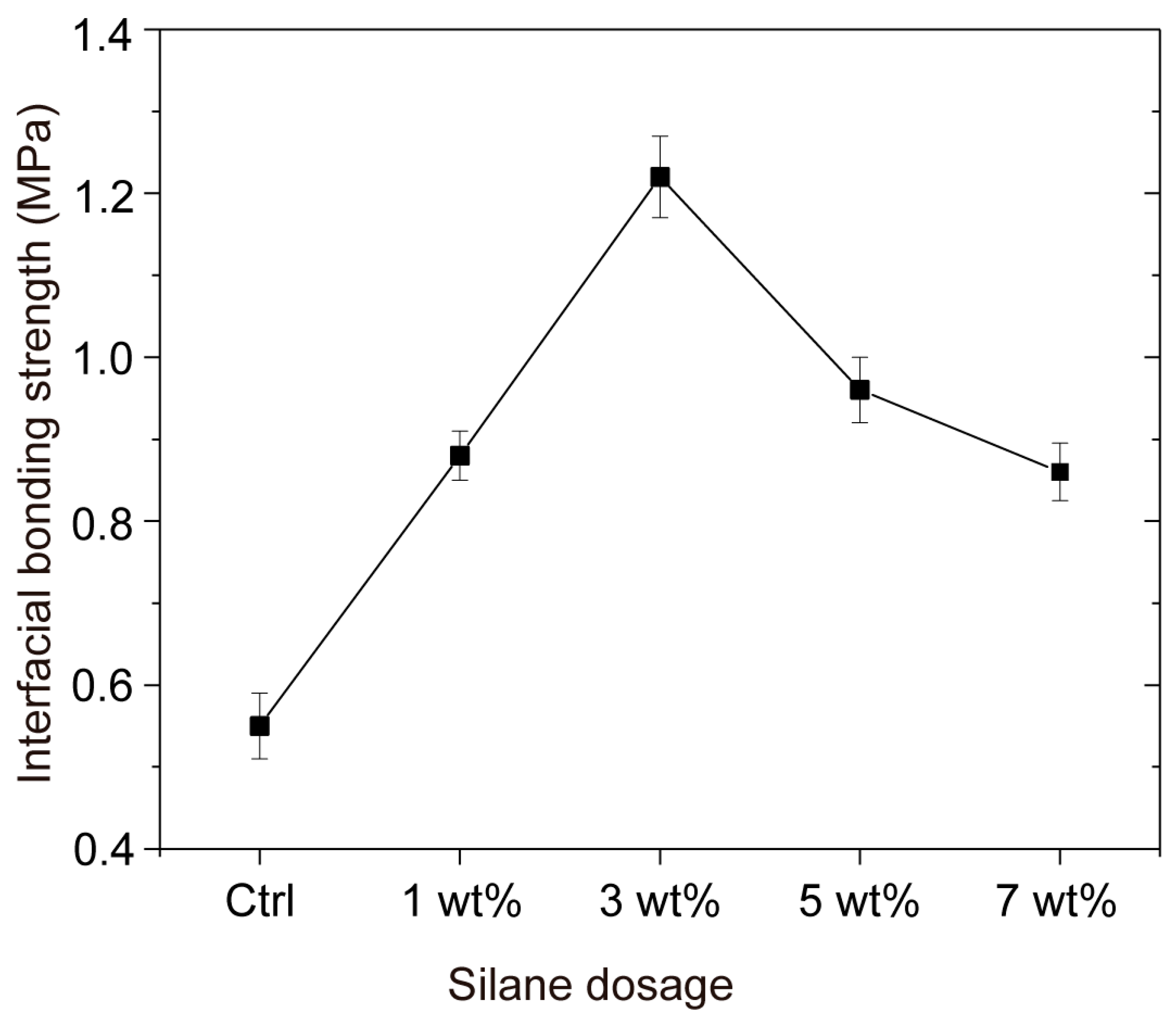
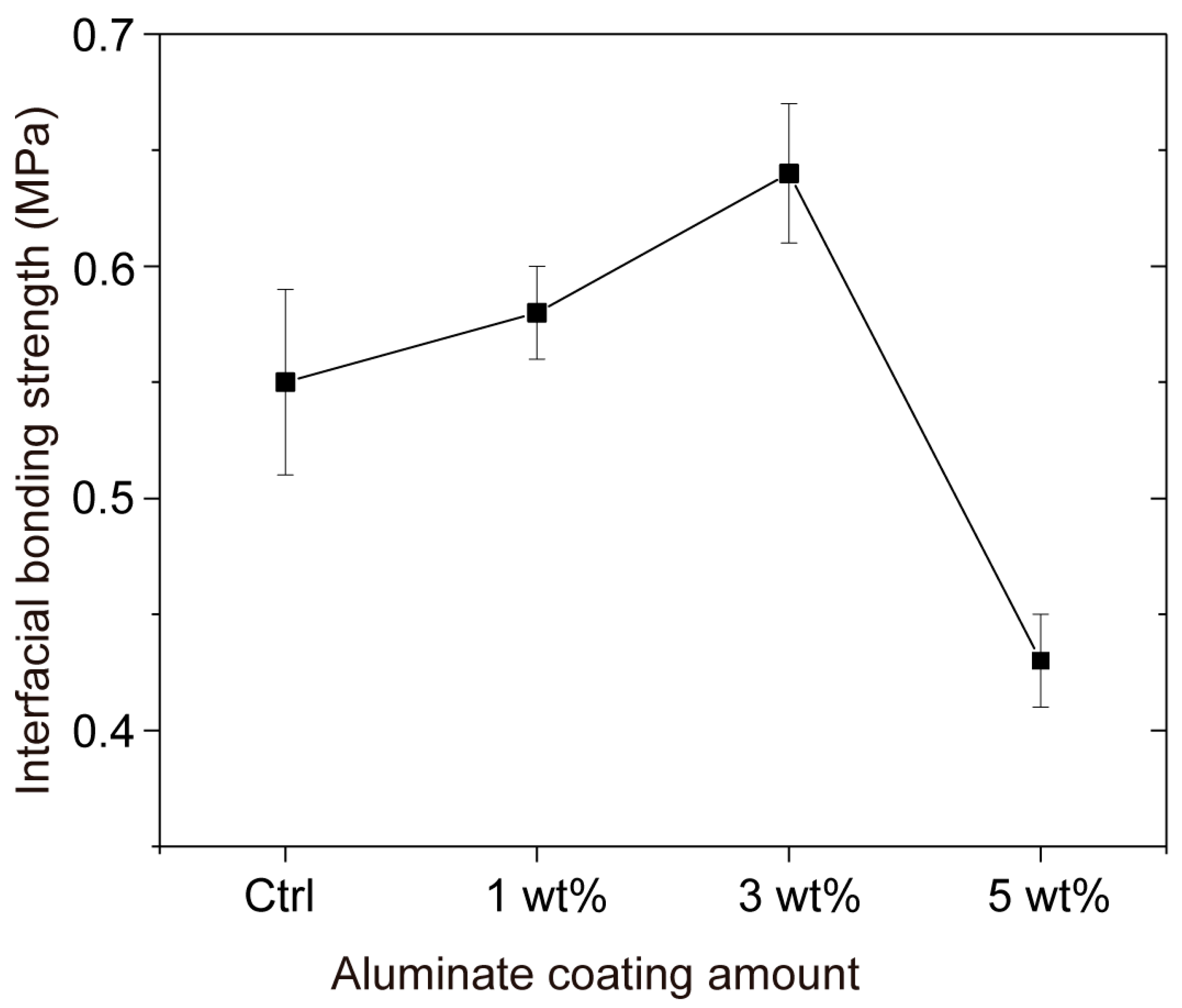
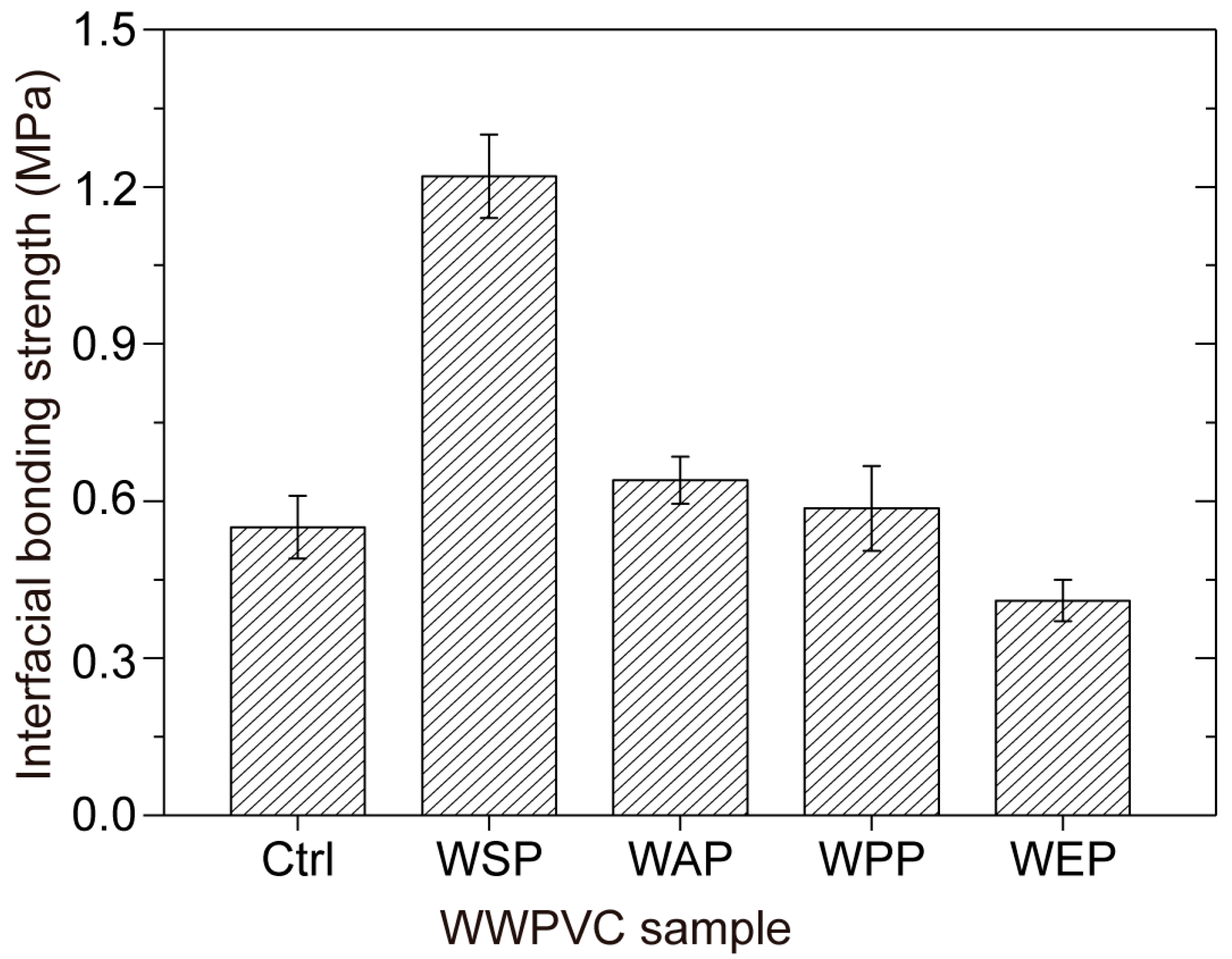
3.1. Interfacial Bonding Strength
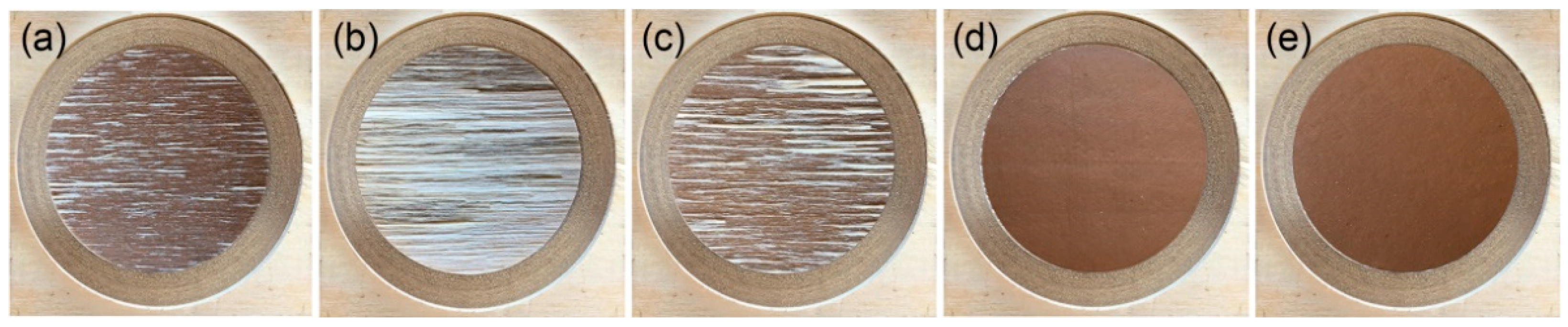
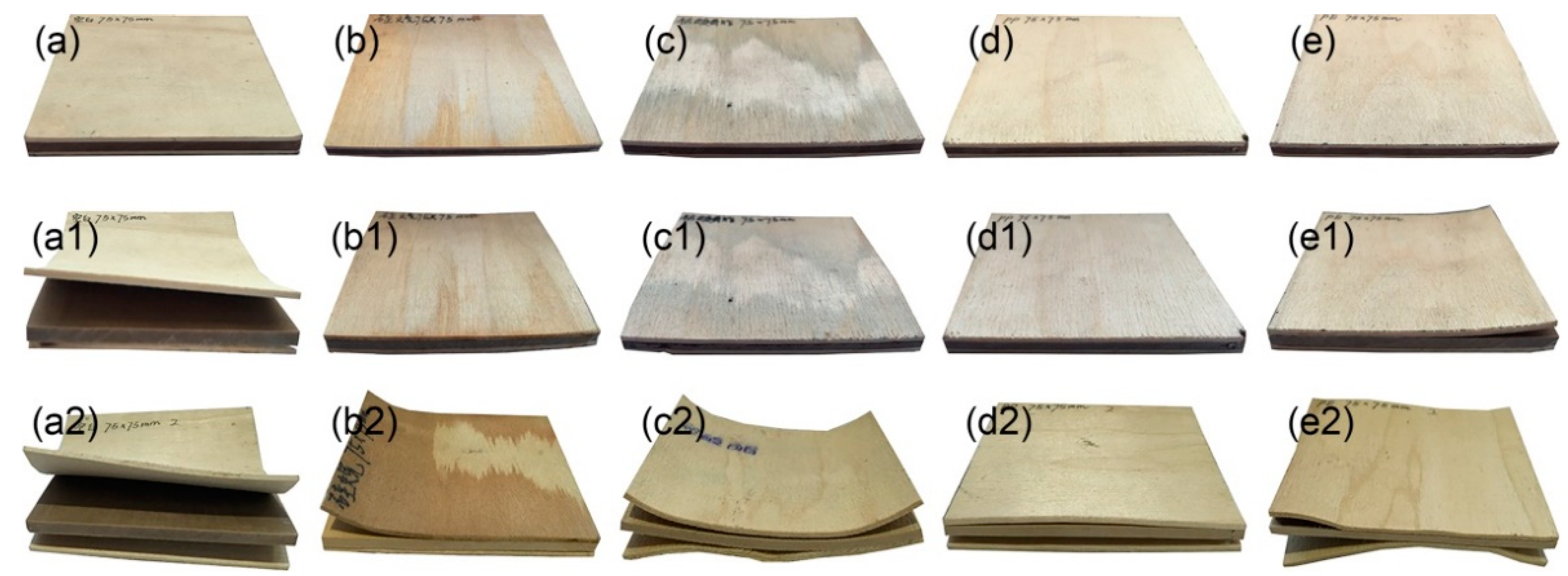
3.2. Wood Failure Ratio
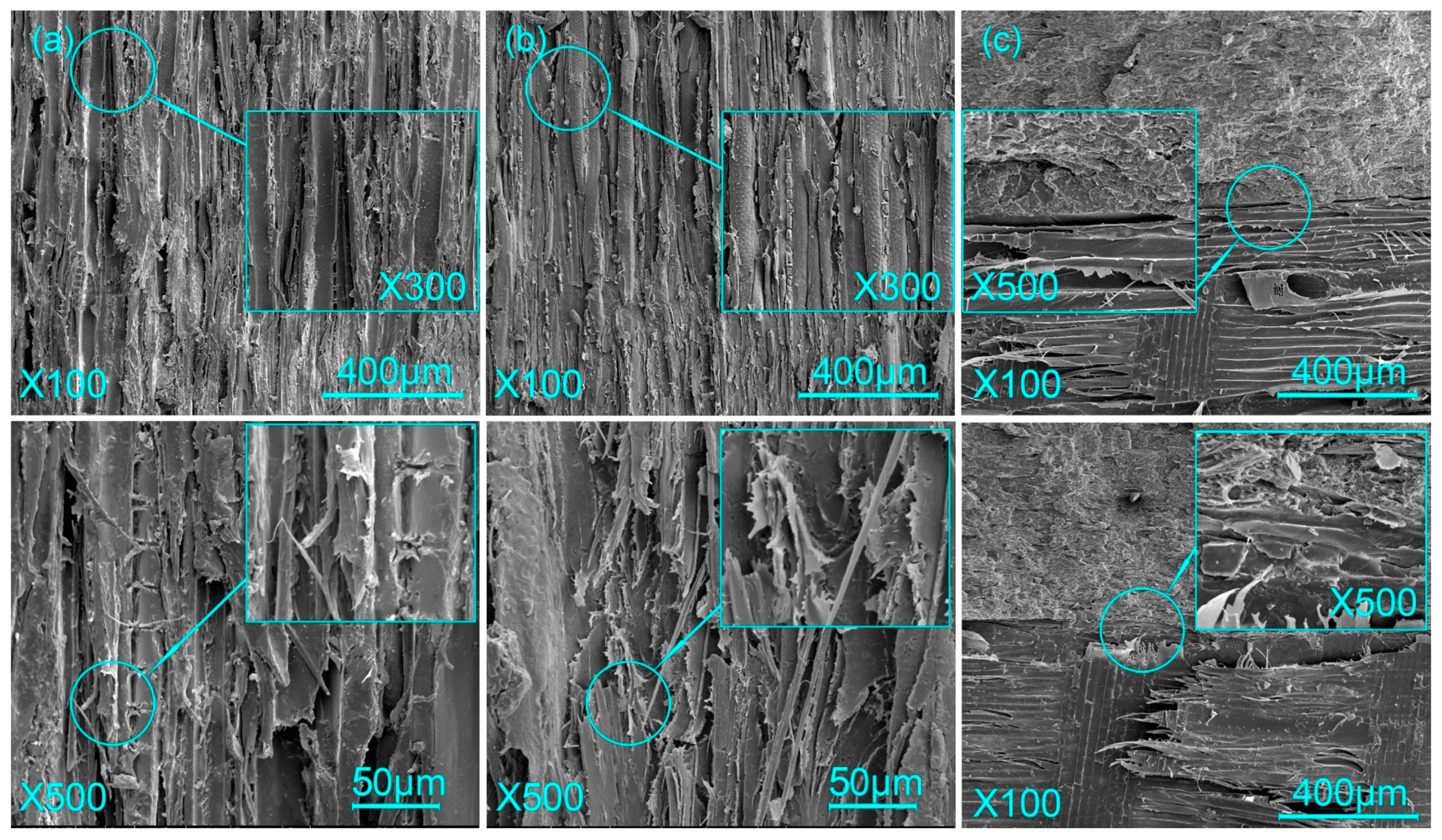
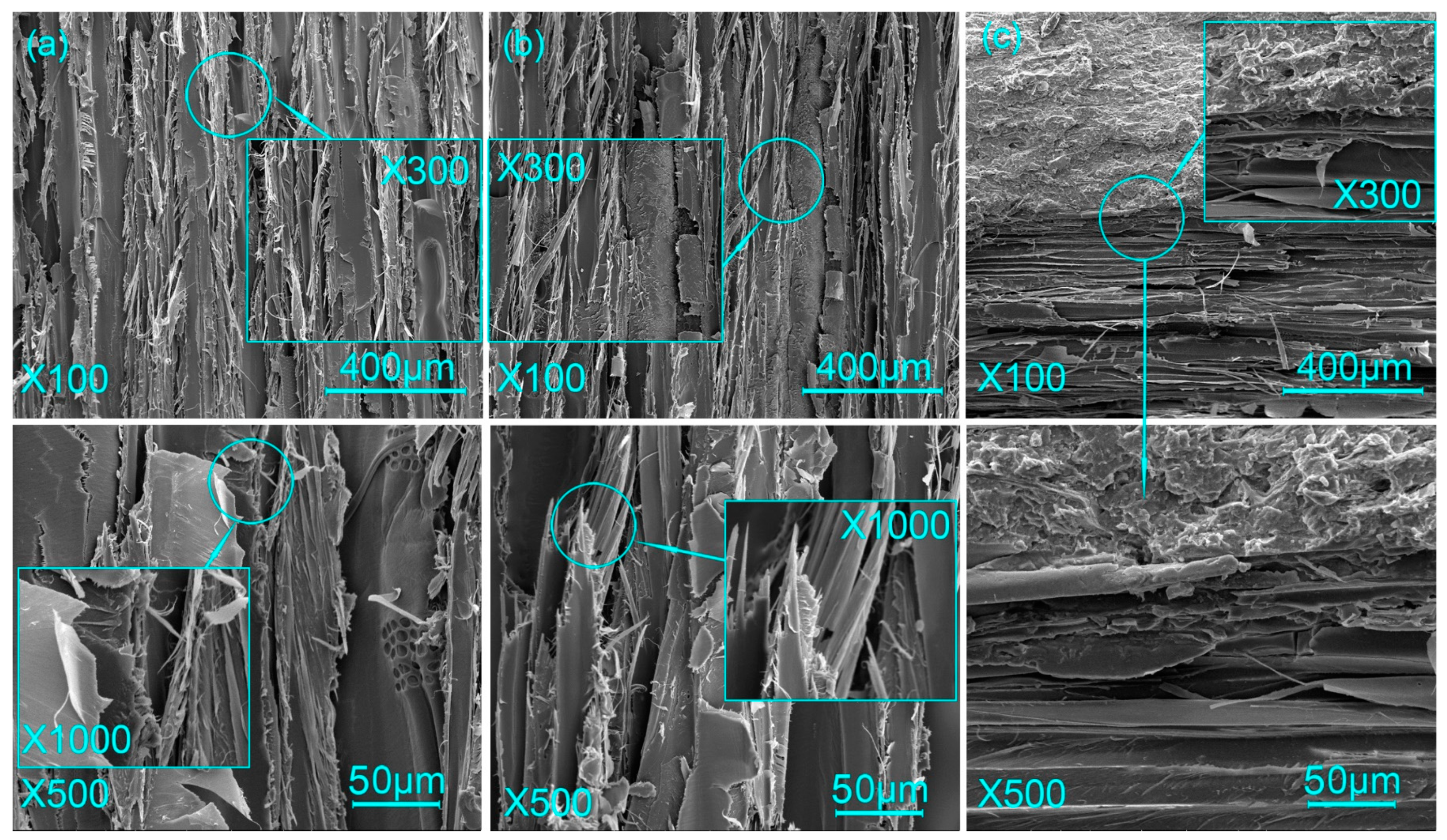
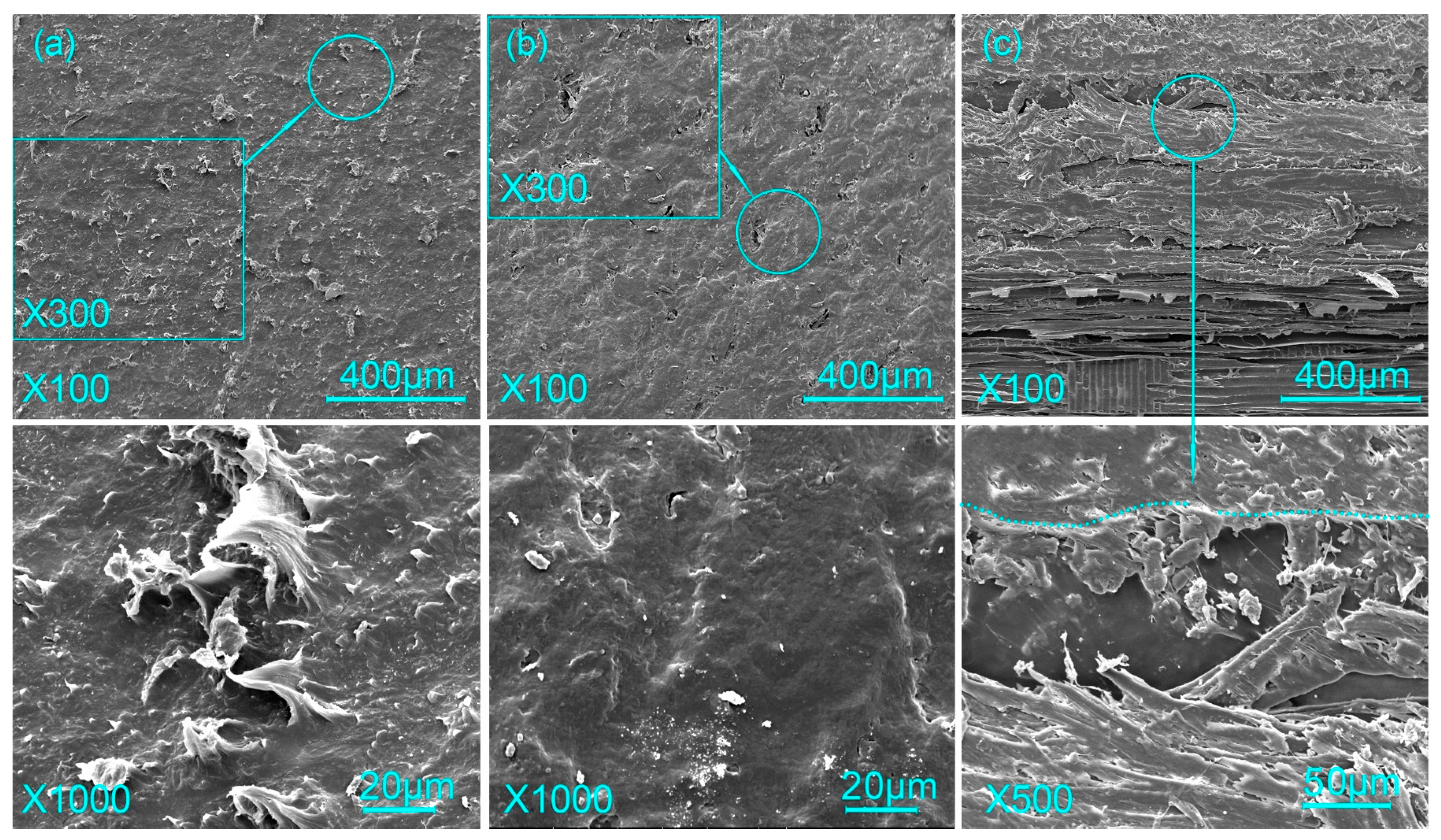
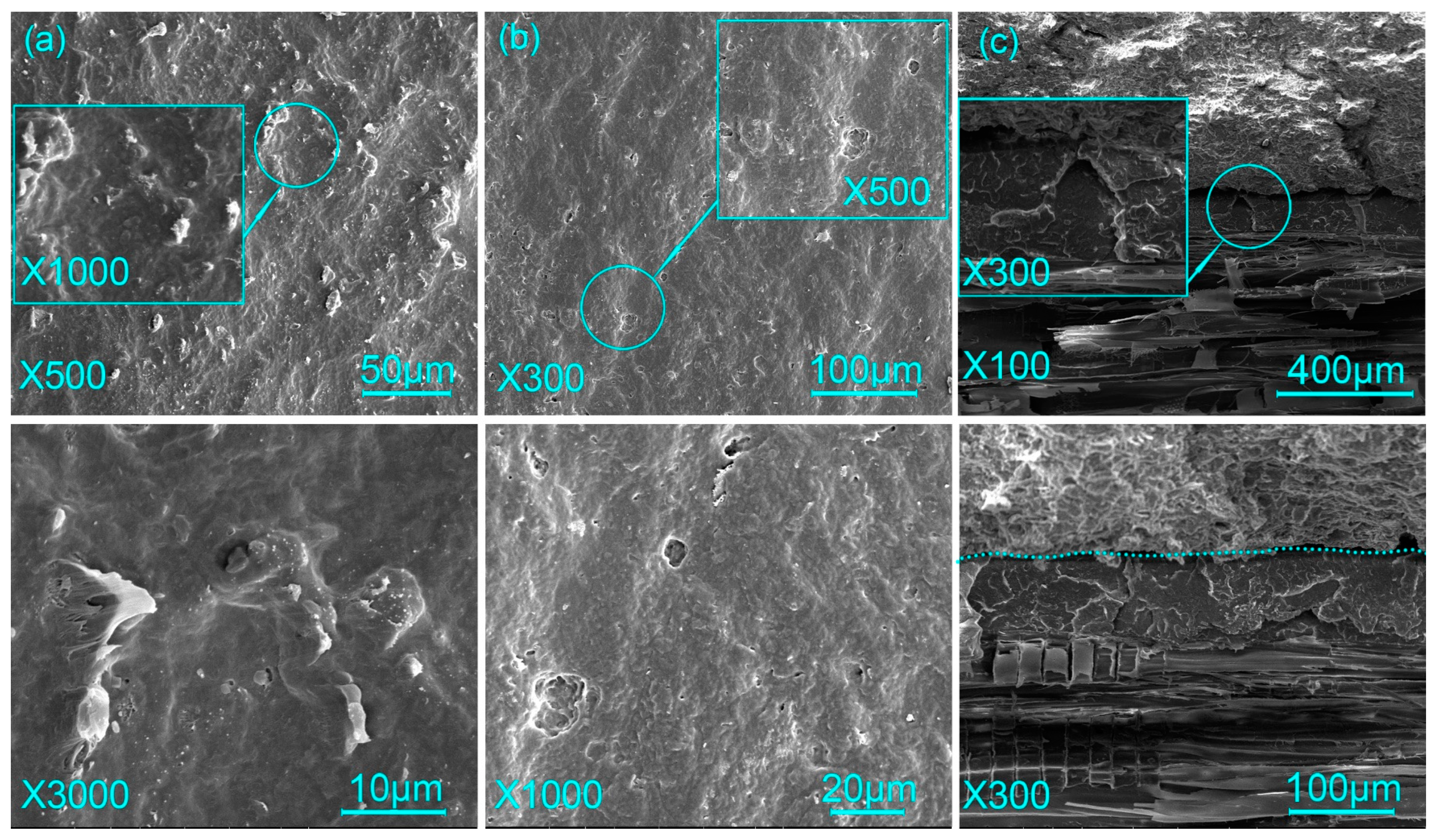
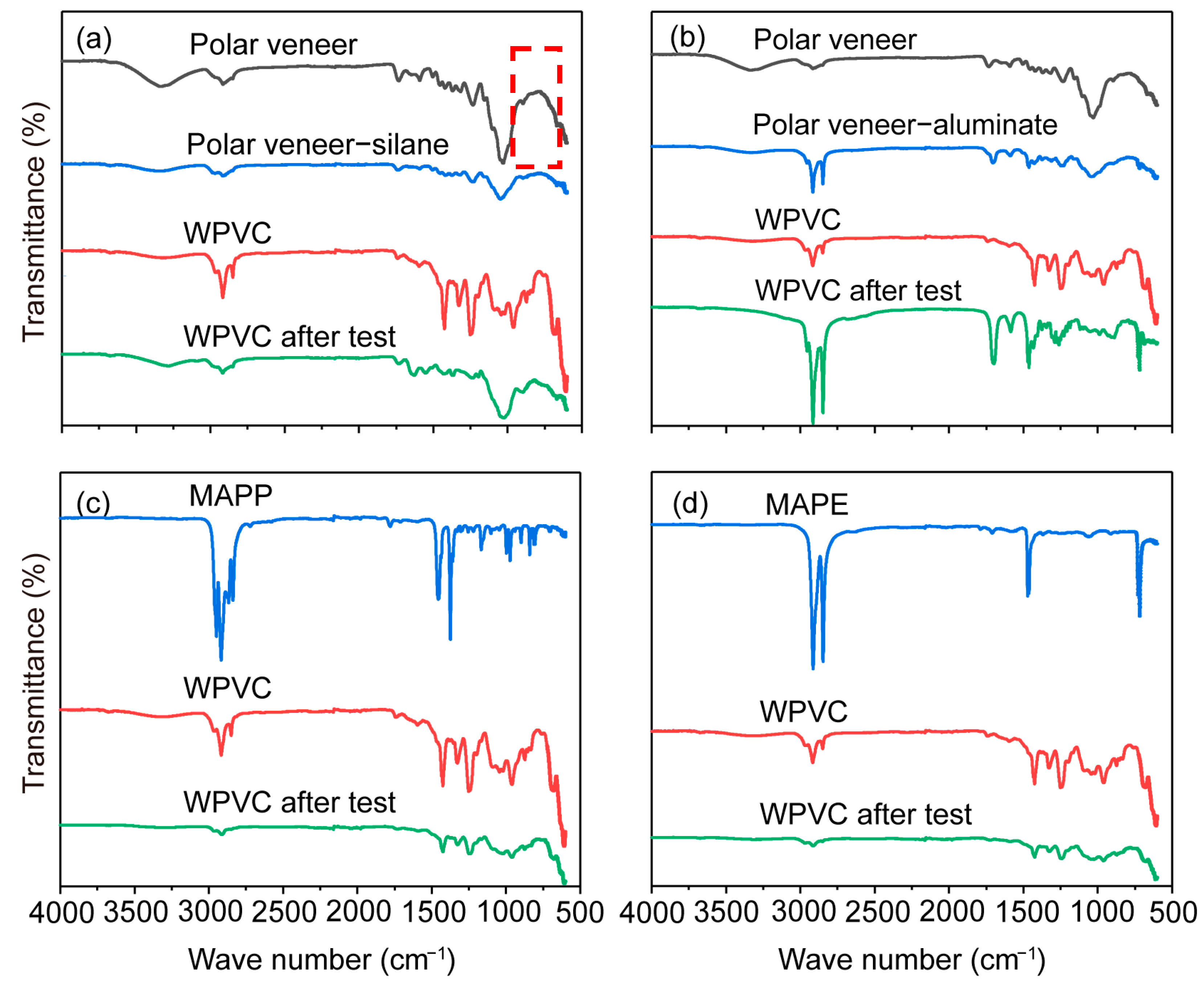
3.3. Micromorphology
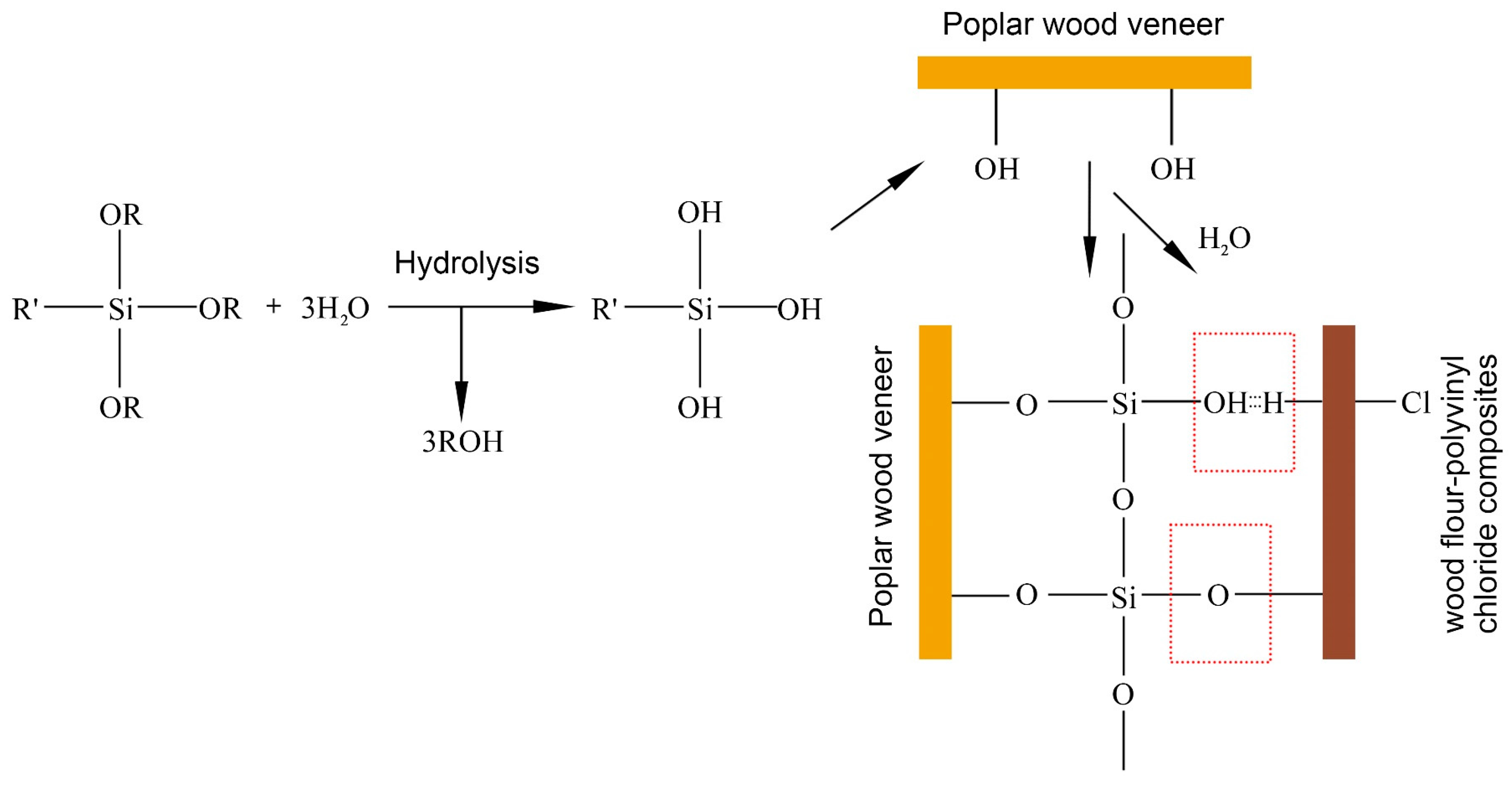
3.4. Analysis of the Surface Chemical Elements
3.5. Dipping–Peeling Strength
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Khan, M.U.; Lin, X.; Cai, H.; Lei, H. Temperature varied biochar as a reinforcing filler for high–density polyethylene composites. Compos. Part B–Eng. 2019, 175, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffo, M.; de la Mata, M.; Molina, S. A sugar–beet waste based thermoplastic agro–composite as substitute for raw materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 257, 120382. [Google Scholar]
- Arribasplata–Seguin, A.; Quispe–Dominguez, R.; Tupia–Anticona, W.; Acosta–Sullcahuaman, J. Rotational molding parameters of wood–plastic composite materials made of recycled high density polyethylene and wood particles. Compos. Part B–Eng. 2021, 217, 108876. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Li, W.; Hao, X.; Zong, G.; Yi, X.; Xu, J.; Ou, R.; Wang, Q. Recycling end–of–life WPC products into ultra–high–filled, high–performance wood fiber/polyethylene composites: A sustainable strategy for clean and cyclic processing in the WPC industry. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourmaud, A.; Le Duigou, A.; Gourier, C.; Baley, C. Influence of processing temperature on mechanical performance of unidirectional polyamide 11–flax fibre composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 84, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, G.; Hao, X.; Hao, J.; Tang, W.; Fang, Y.; Ou, R.; Wang, Q. High–strength, lightweight, co–extruded wood flour–polyvinyl chloride/lumber composites: Effects of wood content in shell layer on mechanical properties, creep resistance, and dimensional stability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 244, 118860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H. Decorated wood fiber/high density polyethylene composites with thermoplastic film as adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2019, 95, 102391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirp, A.; Plinke, B.; Napolow, D. Effectiveness of organic and inorganic pigments for mass colouration of thermo–mechanical pulp used in wood–plastic composites. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2015, 73, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Guo, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, W. Effects of two staining methods on color stability of wood flour/polypropylene composites during accelerated UV weathering. Polym. Compos. 2017, 38, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Shen, T.; Sun, Y.; Dun, M.; Shan, W.; Wang, W. Improve the bonding between wood veneer and wood fiber/high–density polyethylene composite board for decoration. Polym. Compos. 2022, 43, 2163–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Arya, S.; Kumar, R.; Chauhan, S.; Kelkar, B.U. Development of natural fiber reinforced thermoplastic bonded hybrid wood veneer composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 368, 130459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Panigrahi, S.; Tabil, L.; Crerar, W. Pre–treatment of Flax Fibers for use in Rotationally Molded Biocomposites. J. Reinf. Plast. Comp. 2007, 26, 447–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhilash, S.S.; Singaravelu, D.L. Effect of Fiber Content on Mechanical and Morphological Properties of Bamboo Fiber–Reinforced Linear Low–Density Polyethylene Processed by Rotational Molding. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, B.; Tang, W.; Liu, T.; Hao, X.; Wang, Q.; Ou, R. Comparative study of high–density polyethylene–based biocomposites reinforced with various agricultural residue fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, H.Y.; Ho, M.P.; Lau, K.T.; Cardona, F.; Hui, D. Natural fibre–reinforced composites for bioengineering and environmental engineering applications. Compos. Part B–Eng. 2009, 40, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, M.; Fu, H.; Hao, J.; Shan, W.; Wang, W. Tailoring flexible interphases in bamboo fiber–reinforced linear low–density polyethylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 150, 106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalaiah, M.A.; Setty, R.N.V.; Johns, J. Effect of Compatibilizer on the Properties of Areca–Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 15261–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, V.; Mollica, F. In–line rheometry of polypropylene based Wood Polymer Composites. Polym. Test. 2015, 47, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Hao, X.; Ou, R.; Liu, T.; Guo, C.; Wang, Q.; Yi, X.; Sun, L. Rheological Properties of Wood–Plastic Composites by 3D Numerical Simulations: Different Components. Forests 2021, 12, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Yi, X.; Zong, G.; Song, Y.; Wang, W.; Cheng, H.; Wang, G. Fabrication of long bamboo fiber–reinforced thermoplastic composite by extrusion and improvement of its properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 173, 114120. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hao, X.; Tang, W.; Zhou, H.; Chen, L.; Guo, C.; Wang, Q.; Ou, R. Mechanical properties, morphology, and creep resistance of ultra–highly filled bamboo fiber/polypropylene composites: Effects of filler content and melt flow index of polypropylene. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 310, 125289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Dun, M.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Ou, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, Q. Creep response of wood flour–high–density polyethylene/laminated veneer lumber coextruded composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H. Modifying wood veneer with silane coupling agent for decorating wood fiber/high–density polyethylene composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaraki, P.; Krause, A. Correlation between physical bonding and mechanical properties of wood plastic composites: Part 1: Interaction of chemical and mechanical treatments on physical properties. J. Adhes. Sci.Technol. 2020, 34, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H.Z.; Nourbakhsh, A.; Ashori, A. Effects of nanoclay and coupling agent on the physico–mechanical, morphological, and thermal properties of wood flour/polypropylene composites. Polym. Eng. SCI 2011, 51, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, W.; Song, Y. Interface Bonding Properties and Mechanism of Poplar Board–Veneered Wood Fiber/Polypropylene Composites with Chlorinated Polypropylene Films as an Intermediate Layer. Langmuir 2019, 35, 13934–13941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lin, L.; Pang, J.; Chen, F.; Li, Q. Effects of Impulse–cyclone Drying and Silane Modification on the Properties of Wood Fiber/HDPE Composite Material. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 207, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhai, S.; Wang, K.; Xie, T. Modification of bonding properties and microstructure of resin–cement interface by coupling agents. Compos. Interface 2017, 25, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, T.; Huang, L.; Li, G. Effect of chemical modification on the properties of wood/polypropylene composites. J. For. Res. 2005, 16, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.M.; Wang, W.H.; Wang, Q.W.; Yan, N. Decorating wood flour/HDPE composites with wood veneers. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, N.; Li, F.; Liu, K.; Shao, Y.; Guo, K. Effects of coupling agents on the properties of cotton stalk–polypropylene film boards. Bioresources 2020, 15, 8617–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, K.; Suzuki, S.; Kojima, Y.; Kobori, H.; Ito, H.; Ogoe, S.; Okamoto, M. The Effects of Different Types of Maleic Anhydride–Modified Polypropylene on the Physical and Mechanical Properties of Polypropylene–based Wood/Plastic Composites. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2018, 38, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.; Wei, W.; Zhang, S. Effect of silane coupling agent on mechanical properties of eucalyptus veneer/polyvinyl chloride (PVC) composites. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2016, 38, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Chang, L.; Guo, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. Influence of silane surface modification of veneer on interfacial adhesion of wood–plastic plywood. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Horie, K.; Asakura, T. Hydrolysis and condensation mechanisms of a silane coupling agent studied by 13C and 29Si NMR. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 34, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PVC (wt%) | Wood Flour (wt%) | Calcium Zinc Stabilizer (wt%) | ACR (wt%) | PE Wax (wt%) | Stearic Acid (wt%) | Calcium Stearate (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 40 | 6 | 4 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Grade | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peeling length | L = 0 | 0 < L ≤ 25 mm | L > 25 mm |
| Characteristic | No peeling | Slight peeling | Severe peeling |
| Description | Qualified | Qualified | Unqualified |
| Silane Dosage | 0 wt% | 1 wt% | 3 wt% | 5 wt% | 7 wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interfacial bonding strength (MPa) | 0.55 | 0.88 | 1.22 | 0.96 | 0.86 |
| Aluminate Coating Amount | 0 wt% | 1 wt% | 3 wt% | 5 wt% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interfacial bonding strength (MPa) | 0.55 | 0.58 | 0.64 | 0.43 |
| Category | Ctrl | WSP | WAP | WPP | WEP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade II peeling length (mm) | Complete peeling | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 × 75 |
| Grade I peeling length (mm) | Complete peeling | 18 × 75 | Complete peeling | 23 × 75 | Complete peeling |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zong, G.; Gong, J.; Shi, Z.; Hao, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, F. Effect of Coupling Treatment on Interfacial Bonding Properties of Wood Veneer/Wood Flour–Polyvinyl Chloride Composites with Sandwich Structure. Forests 2023, 14, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14112147
Zong G, Gong J, Shi Z, Hao J, Yang X, Wang F. Effect of Coupling Treatment on Interfacial Bonding Properties of Wood Veneer/Wood Flour–Polyvinyl Chloride Composites with Sandwich Structure. Forests. 2023; 14(11):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14112147
Chicago/Turabian StyleZong, Guanggong, Jiayun Gong, Ziyi Shi, Jianxiu Hao, Xiaomeng Yang, and Fangfang Wang. 2023. "Effect of Coupling Treatment on Interfacial Bonding Properties of Wood Veneer/Wood Flour–Polyvinyl Chloride Composites with Sandwich Structure" Forests 14, no. 11: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14112147
APA StyleZong, G., Gong, J., Shi, Z., Hao, J., Yang, X., & Wang, F. (2023). Effect of Coupling Treatment on Interfacial Bonding Properties of Wood Veneer/Wood Flour–Polyvinyl Chloride Composites with Sandwich Structure. Forests, 14(11), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/f14112147






