Abstract
Pine wilt disease has caused great economic loss and become an ecological threat since it was introduced into East Asia. In China, Pinus massoniana Lamb. is highly susceptible. The pathogenic of this disease is linked to the invasion of P. massoniana by the pine wood nematode (PWN, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus), leading to various physiological activities. However, the migration pathway of PWN and the defense mechanisms of P. massoniana tissue structure following invasion remain unclear. This knowledge is vital for understanding the pathogenesis of pine wood nematode disease. To address this issue, we analyzed the tissue structure damage, horizontal and vertical migration pathways, and histochemical reactions of P. massoniana after PWN inoculation. The results are as follows: susceptible P. massoniana exhibited more tissue structure damage compared to highly resistant P. massoniana. PWN reproduced and migrated by feeding on and damaging cells. In susceptible P. massoniana, PWN propagated and migrated throughout the entire plant. Highly resistant P. massoniana displayed limited horizontal and vertical migration of PWN, making it challenging for PWNs to move from cambium to xylem. After P. massoniana was damaged by PWNs, a protein cross-linking phenomenon appeared rapidly, with highly resistant P. massoniana exhibiting less protein cross-linking than the susceptible variety. Lignin synthesis is a crucial factor in the tissue defense of P. massoniana. Protein crosslinking provides time for lignin synthesis and is an vital component of tissue defense.
1. Introduction
Pine wilt disease, characterized by its rapid onset and high mortality [1], has inflicted significant damage on pine trees since its introduction in China. While some progress has been achieved in chemical and biological control, the disease continues to exhibit a propensity for spreading [2].
Pinus massoniana Lamb. is an evergreen tree belonging to the Pinaceae family, which is known for its quick-growth and drought-tolerant characteristics. It is a pioneer tree species of high-yield timber and tallow forest, which is widely distributed in China’s subtropical regions [3,4,5]. The ninth forest resources inventory reveals that P. massoniana covers 8.04 million hectares. However, P. massoniana is susceptible to pine wilt disease, and dies within a short time after infection. It is an extremely dangerous epidemic, which seriously affects the balance of forest ecology and the sustainable development of forestry industry in China, causing huge economic losses and ecological threats [6].
At present, a number of highly resistant P. massoniana families and clones have been bred in China. After the invasion of PWNs, plant resistance is an important basis for resisting adverse environment [7,8,9]. The structural defense of P. massoniana extends from the outermost bark to the xylem. This defense is facilitated by the thickened cell walls with lignification and embolization, which serve a hydrophobic function and act as a multifunctional barrier against external environmental factors [10]. PWNs are transmitted by Monochamus alternatus, which naturally invade pine trees through wounds in the tender branches when feeding on pine [11,12]. In this process, the tissue structure of pine from periderm to xylem serves as a “threshold” for PWN. The difference in tissue structure defense between highly resistant and susceptible P. massoniana determines the resistance of pine wood nematode to some extent. Rutherford et al. [13] believed that the rapid migration and reproduction of PWN in the host was an important factor promoting the development of the disease; Jin Gang [14] proposed that the incidence of P. thunbergii was directly related to the propagation and diffusion rate of nematodes in the tree; Mamiya [15] suggested that nematodes moved in pine within a short period of invasion, and with the propagation of PWN, pine physiology also changed. The fluorescence wheat germ lectin (F-WGA) with isothiocyanate can be bound to the epidermis of nematode, but not to plant tissue. Precise detection of PWN distribution and quantity is achievable, overcoming the limitations of the Baermann’s funnel. However, the migration pathway of pine wood nematodes in the tree and the resistance defense mechanism of tissue structure of P. massoniana infected with pine wood nematodes remain unclear. In this study, we compared the tissue damage expansion and tissue response of different resistant P. massoniana inoculated with pine wood nematodes. Fluorescent staining clarified the migration pathway and reproduction process of PWNs, thus providing a theoretical basis for determining effective inhibition methods of pine wood nematodes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin and Culture of Pine Wood Nematode
Botrytis cineta was inoculated on a potato glucose agar (PDA) medium and incubated in a mold incubator at 28 °C for 5 days. After the coloration, colonies grew into the upper lid of the petri dish, the highly pathogenic pine wood nematode “Guangde-3B” (mortality rates of susceptible P. massoniana were all 100% after inoculating with it at three sites. In the previous test, they were inoculated into the colonies of B. cineta and incubated at 28 °C for about 10 days, so that the colonies were completely eaten by PWNs. PWNs were isolated by Baermann’s funnel [16]. The nematode culture medium was broken into a funnel with a padded filter, and ultrapure water was added to infiltrate the culture medium. After 6 h, the water stop clamp at the lower end of the funnel was opened to collect and separate part of the collected nematode, and then the water stop clamp was closed, and ultrapure water was added to infiltrate the culture medium. After 12 h, they were collected in a 10.0 mL centrifuge tube, rinsed with sterile water three times, and centrifuged at 300 RPM for 5 min to remove the supernatant. A suspension containing 50 pine wood nematodes per 1 μL was prepared by aggregating and mixing all the obtained centrifuge tubes.
2.2. Origin of Plant Material Nematode Inoculation, and Sampling
The experimental material was a 5-year old P. massoniana forest located in Linhai City, Zhejiang Province, at the forestry technology extension and nursery tourism service station. According to the resistance index of P. massoniana clones to pine wood nematode disease measured by Anhui Academy of Forestry in the early period, the clones of P. massoniana were divided into 1 to 4 grades, with grade 1 representing susceptibility and grade 4 indicating high resistance [17]. The five-year-old clones of P. massoniana Xiuning-5 and Huangshan-1 were from Fuyang, Zhejiang province in China, which Xiuning-5 features highly resistant and Huangshan-1 features susceptible characteristics. At about 30 days after inoculation of PWNs, the highly resistant clones were asymptomatic and susceptible P. massoniana wilted and withered (Figure 1). In the previous test, the morality rates of “Xiuning-5” were all 0% after inoculating with PWN at three sites; the mortality rates of “Huangshan-1” clones were all 100% after inoculation with PWN at three sites.
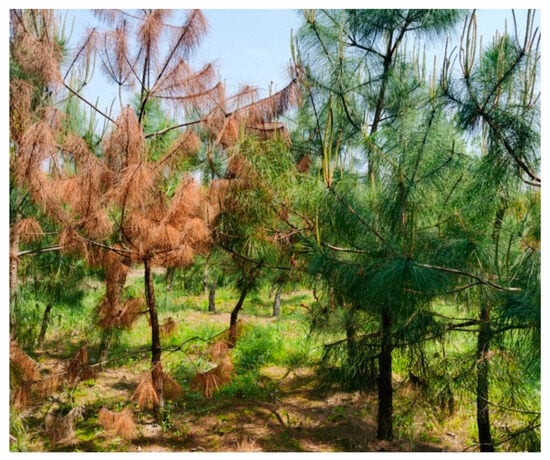

Figure 1.
Resistant and susceptible symptoms of P. massoniana. Note: Left: Susceptible P. massoniana. Light: resistant P. massoniana.
On 28 July 2021, 10 highly resistant P. massoniana and 10 susceptible P. massoniana were selected on a sunny day with a temperature above 30 °C. Inoculation was performed using the peeling method, involving a 5 cm incision at the base of the annual shoot tooth marks in the wound to simulate the gnawing marks of the pine beetle were created by a file [18], and then 200 μL nematode suspension was evenly injected into the wound. After inoculation, the bark was covered over the wound and wrapped with cling film to ensure the survival of nematodes and to not be affected by the external environment.
The sampling location of P. massoniana included the site of inoculation, a site 1~3 cm above the inoculation point, the shoots that are 15~17 cm above the inoculation point, and the top of the shoots that are 30~35 cm above the inoculation point (Figure 2). The paraffin section prepared from the stem segment with highly resistant and susceptible P. massoniana before and after inoculation with pine wood nematodes at 1 d, 7 d, 15 d and 30 d. Three strains of the same clone were selected at each time point as biological replicates. These stem segments were collected and immediately put into the configured FAA fixing solution (70% tert-butanol: formaldehyde: propionic acid: glycerol = 17:1:1:1, v/v/v/v) for paraffin sections.
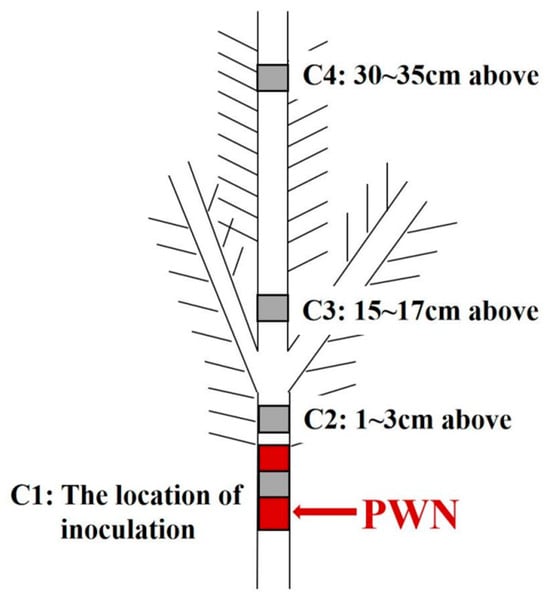
Figure 2.
Inoculation and sampling site of P. massoniana. Note: The red part indicates the inoculating position. The gray part indicates the sampling position.
2.3. Paraffin Section Preparation and Staining
The fixed material was cut into slices with a thickness of 15 μm according to the paraffin section step [19]. Following the treatment, a Leica DM 4000 B microscope was used to observe and take photos. In order to observe the quantity and migration of pine wood nematodes, the paraffin sections after baking and dewaxing were cleaned three times with 0.01 M phosphate solution containing 0.05% Tween-20, soaked in 10 mM phosphate buffer containing 0.01% F-WGA for 1 h, and then cleaned three times with 0.01 M phosphate solution containing 0.05% Tween-20 [20]. A solution was prepared by adding 5.0 g of toluidine to 100.0 mL 30% ethanol. The solution was heated to 65 °C, stirred for 30 min, and then applied to dye the paraffin sections [21] for the purpose of observing the tissue and structural damage in P. massoniana; 100.0 mg Coomasil blue G-250 was dissolved in 50.0 mL 90% ethanol, then 85% phosphoric acid was added to 100.0 mL, and finally the paraffin sections were stained with distilled water to 1000.0 mL to observe the cross-linking of proteins in the tissue structure [22]; A solution was prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of phloroglucinol in 100.0 mL of 95% ethanol. The solution was used to stain for 2 min, after which 25% HCl was added for an additional 2 min to develop color and observe the accumulation of lignin in the tissue structure [23].
2.4. Tissue Damage Evaluation
The damaged cortical and xylem axial resin canals in the paraffin sections were observed and recorded microscopically. The resin canal area was measured using ImageJ. Tissue damage was assessed by calculating the ratio of the area of the axial resin canal in the damaged and undamaged cortex and xylem.
3. Results
3.1. The Tissue Structure Is Damaged and Dilated
The tissue structure of susceptible P. massoniana was damaged after inoculation with PWN, and the damage degree of susceptible P. massoniana was higher than that of highly resistant P. massoniana after inoculation with PWNs. The cortical cells and xylem cells of susceptible P. massoniana were damaged at 1 day after inoculation. The damage rate of P. massoniana with high resistance accounted for 1.15% (Table 1), and only the cells around the resin canal were damaged. At the same time, a few PWNs were observed in the canal (Figure 3A). After 7 and 15 days of inoculation with PWN, most epithelial cells in the cortex cells, xylem cells and resin canal in segments of susceptible P. massoniana 1~3 cm below the inoculation point were damaged by PWNs (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Highly resistant P. massoniana showed damage in the cells around the resin canal and cortical cells at 7 days after inoculation. After 30 days of inoculation with PWN, the phloem cortex cells in segments of susceptible P. massoniana 30~35 cam below the inoculation point were damaged and a large number of cavities were generated (Figure 4 and Figure 5A). In the contract, highly resistant P. massoniana exhibited a tissue structure damage ratio of 1.26%, with no expansion of the damaged area (Table 1).

Table 1.
Tissue structure damage of P. massoniana inoculated with PWN with different resistance.
As for the degree of tissue structure damage, Table 1 showed that there was a significant difference in the tissue structure damage ratio between highly resistant and susceptible P. massoniana (p < 0.05) at 7, 15 and 30 days after inoculation with PWN, and the damage ratio of susceptible P. massoniana was higher than that of highly resistant P. massoniana.
3.2. Distribution of Pine Wood Nematode
3.2.1. Horizontal Migration of Nematodes
In susceptible P. massoniana, 1 day after inoculated with PWN, PWNs were predominantly located in the cortical resin canal, and no PWN was found in other parts (Figure 3A). Notably, the tissue structure was damaged by PWNs (Figure 5B); 7 days after inoculation, the number of PWNs increased and PWNs distributed in the cortical resin canal, cortical cells, cambium, xylem cortical resin canal and xylem cells in large numbers (Figure 3 and Figure 5C). After 15 days of inoculation, PWNs were distributed in all parts in susceptible P. massoniana, and began to appear in the pith (Figure 3D and Figure 5D). After 30 days of inoculation with PWNs, the gap between cambium and xylem became larger, and there were a large number of PWN in cortical resin canal, cortical tissue, cambium, xylem cortical resin canal and pith.
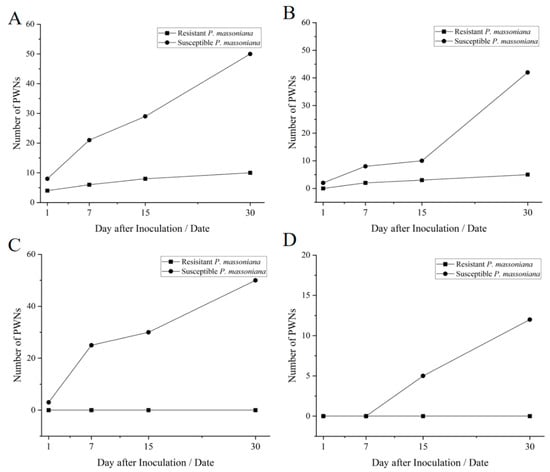
Figure 3.
Number of pine wood nematodes with different tissue structure and different inoculation time of resistant and susceptible P. massoniana. Note: (A) The number of PWNs in cortical resin canal of P. massoniana after inoculation; (B) The number of PWNs in cambium of P. massoniana after inoculation; (C) The number of PWNs in xylem cortical resin canal of P. massoniana after inoculation; (D) The number of PWNs in the pith of P. massoniana after inoculation.
In highly resistant P. massoniana, 1 day after inoculation with PWN, a small number of PWNs were migrating in the cortical resin canal, but no PWN appeared in other parts (Figure 3A). Notably, the tissue structure was not damaged by PWNs (Figure 6); after 7 days of inoculation, the number of PWNs did not increase, and PWNs were distributed in cortical cells and cortical resin canal (Figure 3C); after 15 days of inoculation, PWNs were able to migrate to cambium (Figure 3B); after 30 days of inoculation, the number of PWNs in all parts of P. massoniana with high resistance did not increase, and distribution positions did not spread (Figure 3 and Figure 6).
3.2.2. Vertical Migration of Nematodes
In susceptible P. massoniana, 1 day after inoculation with PWN, PWNs congregated near the inoculation site (Figure 4A); after 7 days of inoculation, PWNs began to migrate and spread but were still limited to the inoculated branch (Figure 4B); after 15 days of inoculation, a few needle leaves turned yellow and withered, and the number of PWNs increased significantly: a few PWNs were able to migrate upward and downward for a short distance (Figure 4C); after 30 days of inoculation, the number of PWNs increased significantly, and a large number of PWNs were detected in all parts of the plant (Figure 4D).
In highly resistant P. massoniana, 1 day after inoculation with PWN, PWNs gathered near the inoculation site (Figure 4A); after 7 days of inoculation, PWNs began to spread but were confined to the vicinity of the inoculation site (Figure 4B); after 15 days of inoculation, there was no change in the number and distribution of PWNs (Figure 4C); after 30 days of inoculation, the number of PWNs remained unchanged, and they were confined to the area around the inoculation site (Figure 4D).
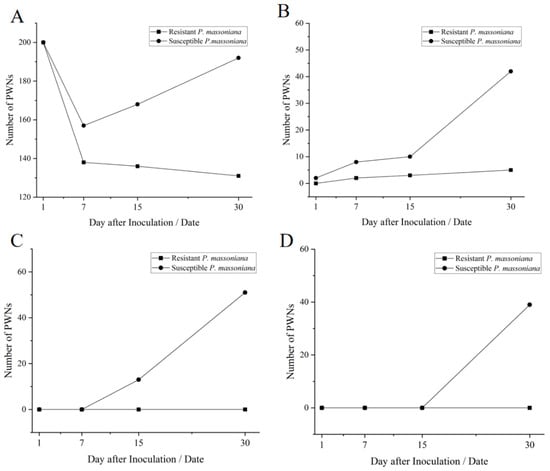
Figure 4.
Number of pine wood nematodes with different sampling position and different inoculation time of resistant and susceptible P. massoniana. Note: (A) The number of PWNs in C1 site of P. massoniana after inoculation; (B) The number of PWNs in C2 site of P. massoniana after inoculation; (C) The number of PWNs in C3 site of P. massoniana after inoculation; (D) The number of PWNs in the C4 site of P. massoniana after inoculation.
3.3. Histochemical Reaction
The invasion of PWNs rapidly stimulated protein synthesis and the protein cross-linking phenomenon. After 1 day of inoculation, the protein cross-linking phenomenon was observed in cells around the damaged cambium and the intact cortical resin canal of susceptible P. massoniana. In contrast, highly resistant P. massoniana showed no protein cross-linking phenomenon except in the intact cortical resin tract (Table 2). After 7 days of inoculation, the protein cross-linking phenomenon was observed in cortical cells, damaged cambium and the pith of susceptible P. massoniana (Figure 5E). In highly resistant P. massoniana, only cortical resin canal and damaged cortical cells showed an obvious protein cross-linking phenomenon (Figure 6D). Significantly, the level of protein cross-linking phenomenon in susceptible P. massoniana was higher than that in highly resistant P. massoniana (p < 0.05).

Table 2.
SDS staining of tissue structure in P. massoniana with different resistance after inoculation with pine wood nematodes.
After inoculation of PWN, the accumulation of lignin occurred more slowly compared to the protein defense response. After 1 day of inoculation, there was no lignification observed in susceptible or highly resistant P. massoniana (Table 3). After 15 days of inoculation, there showed lignification in the cortical cells, the cell walls around the cortical cells, and the cells of the space between cambium and xylem of highly resistant P. massoniana (Figure 6E). In contrast, susceptible P. massoniana showed no lignification except in cortex cells (Figure 5F). Notably, highly resistant P. massoniana displayed significantly higher levels of lignification compared to the susceptible variety (p < 0.05).

Table 3.
HCl-phloroglucinol staining of tissue structure in P. massoniana with different resistance after inoculation with pine wood nematodes.
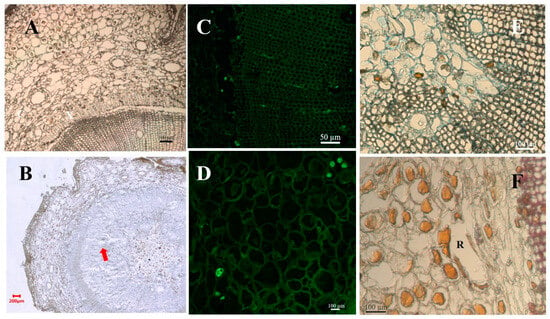
Figure 5.
Tissue structure profile of susceptible P. massoniana after inoculation with pine wood nematodes. Note: Cross-sections of resistant P. massoniana stems inoculated with pine wood nematodes. (A) A partially non-stained section at 7 days after inoculation. (B) A partially non-stained section at 1 day after inoculation. The arrow pointed at the damage of the tissue structure. (C) Epifluorescent image of partially fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (F-WGA)-stained section at 7 days after inoculation. Round green fluorescence indicated the presence of nematodes. (D) Epifluorescent image of partially fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (F-WGA)-stained section at 30 days after inoculation. (E) SDS Coomassie blue stained section 7 days after inoculation. Blue color indicates accumulation of protein cross-linking. (F) Phloroglucinol-HCl stained section 15 days after inoculation. Red color indicates lignin accumulation. C indicated cambium. X indicated xylem. R indicated resin canal.
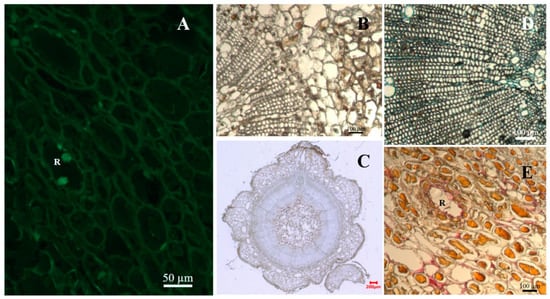
Figure 6.
Tissue structure profile of P. massoniana with high resistance after inoculation with pine wood nematodes. Note: Cross-sections of resistant P. massoniana stems inoculated with pine wood nematodes. (A) Epifluorescent image of fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated wheat germ agglutinin (F-WGA)-stained section at 30 days after inoculation. Round green fluorescence indicated the presence of nematodes. (B) A partially non-stained section at 1 day after inoculation. (C) A non-stained section at 7 days after inoculation. (D) SDS Coomassie blue stained section 7 days after inoculation. Blue color indicates accumulation of protein cross-linking. (E) Phloroglucinol-HCl stained section 15 days after inoculation. Red color indicates lignin accumulation. R indicated resin canal.
4. Discussion
In general, the damage expansion of the cortex, cambium and xylem parenchyma, including the axial resin canal, in resistant P. massoniana was slower than that in susceptible P. massoniana at the same time. At the later stage of infection, some PWNs were concentrated in the resin canal of resistant P. massoniana, while being distributed in the tissues of susceptible P. massoniana. This suggests that PWN primarily migrated and propagated in the resin canal. In line with previous studies, the migration rate of PWN in resistant species was slower than that in susceptible species after inoculation of PWN, and the degree of cell damage in resistant species was less than that in susceptible species within the same time [24,25,26,27]. The concentrated distribution of PWN in the space between the cambium and xylem of resistant P. massoniana indicated that PWN could not easily migrate horizontally from the cambium to xylem and pith. At 30 days after inoculation, PWN distribution was found in all tissues of susceptible P. massoniana, with the quantity significantly higher than in highly resistant P. massoniana. This difference may be attributed to the challenge of horizontal PWN migration in highly resistant P. massoniana. In addition, PWN diffusion sites in highly resistant P. massoniana were confined to inoculated branches, indicating an obstruction of vertical PWN migration. Son et al. [28] proposed that PWN invaded P. thunbergii and secreted a large amount of resin, thus interrupting the cortical resin tract and thus limiting the vertical migration of PWN.
Protein crosslinking refers to the process of forming covalent bonds between multiple skin chains within proteins or between protein molecules, which can significantly improve the functional properties of proteins. PWNs invaded P. massoniana, and protein cross-linking reaction occurred in the attacked cell wall within a short time [29]. In this study, at 7 days after inoculation, protein cross-linking of susceptible P. massoniana was significantly higher than that of highly resistant P. massoniana (Figure 4E and Figure 5D) (p < 0.05). The protein crosslinking degree of highly resistant P. massoniana at 30 days after inoculation was similar to that of susceptible P. massoniana at 1 day after inoculation. These observations suggest that the expression of proteins related to cell wall strength is beneficial to limit migration and prevent cell destruction to a certain extent.
Lignin synthesis occurs continuously as phloem cells discolor and necrotize. Lignin synthesis and lignification a more time-consuming and require a more potent defense compared to protein-based defenses [30]. The pine resistance mechanism delays the rate of cell destruction, giving the tree enough time to accumulate lignin in its surrounding tissues. Phloem cells near the cambium of highly resistant P. massoniana exhibited extensive lignification at 15 days after inoculation, and PWNs were absent in the tissue structure of highly resistant P. massoniana 30 days after inoculation. Combined with the tissue damage of highly resistant P. massoniana inoculated with PWN, it can be inferred that highly resistant P. massoniana restricted PWN feeding behavior and inhibited its reproduction by generating lignin to strengthen the cell wall.
Kusumoto et al. [31] found that cell wall lignification effectively inhibited PWN migration and reproduction in resistant P. thunbergii. This study showed that highly resistant P. massoniana obstructed PWNs migration by impeding their progress through the cortex, cambium and xylem, which not only depended on protein defense, but also lignin defense. Xylem damage expansion eventually leads to tracheid embolism and the death of the tree [32]. If PWNs breach cambium defenses and regenerate, they can spread throughout the tree, potentially attacking living tissue on a large scale before lignin defenses come into play. Therefore, obstructing PWN migration from the cambium is crucial for inhibiting PWN reproduction. Consequently, rapid prevention of tissue destruction after PWNs invasion is the pivotal factor in P. massoniana resistance against pine wilt disease.
5. Conclusions
By analyzing the damage of P. massoniana tissue structure, the horizontal and vertical migration of PWNs after inoculation, and the histochemical reaction of P. massoniana allowed us to speculate on the migration and feeding routes of pine wood nematodes after inoculation and defense mechanisms of P. massoniana tissue structure. The results showed that PWNs could not easily migrate horizontally from the cambium to xylem and pith. The PWNs diffusion site in highly resistant P. massoniana was confined to the inoculation site, which indicated that PWNs vertical migration was impeded. After the invasion of PWNs, protein cross-linking occurred rapidly and did not increase significantly over time. Moreover, the resistance mechanism of P. massoniana slows down the rate of cell destruction, providing sufficient time for the tree to accumulate lignin in the surrounding tissues. After the phloem cells became discolored and necrotic, lignin began to be synthesized. It can be inferred that highly resistant P. massoniana limits PWNs’ feeding behavior by generating lignin to strengthen the cell wall, thus inhibiting their growth and reproduction. Therefore, preventing PWNs migration from cambium is particularly important for inhibiting PWNs reproduction. Our results provide an important scientific basis for the early control of pine wilt disease of P. massoniana in China.
Author Contributions
Q.L. and Z.Z. conceived of and designed the project. W.L., Y.Z. and L.D. collected the material. W.L., Y.Z. and Y.X. analysed the data and drew the diagram. W.L. and Q.L. wrote the manuscript. K.G., Z.Z. and Q.L. supervised the test. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Zhejiang Science and Technology Program (2020C02007), the Forestry Science and Technology Innovation Special Project of Jiangxi Forestry Bureau (2021. No. 13), and the Zhejiang Science and Technology Major Program on Agricultural New Variety Breeding (2021C02070-5-2).
Data Availability Statement
The data that has been used is confidential.
Acknowledgments
We greatly thank Anhui Academy of Forestry for providing Botrytis cineta materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
- Jiang, M.; Huang, B.; Yu, X.; Zheng, W.T.; Jin, Y.L.; Liao, M.N.; Ni, J. Distribution, Damage and control of pine wilt disease. Zhejiang Sci. Technol. 2018, 38, 83–91. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, F.F.; Lin, R.Z.; Wang, H.M. Occurrence status of main forestry invasive species in China and their research trends. Plant Prot. 2022, 48, 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- An, N.; Li, H.G.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, X.G.; Mo, R.Y.; Zou, H.L.; Wang, W.Z.; Meng, F.L. Relationship between the resin yield and needle morphology characteristics of Pinus massoniana. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2020, 35, 108–111. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.J.; Wu, W.B.; Lian, X.L. Analysis on the cultivation technology of Pinus massoniana seedling. Farm Staff. 2019, 7, 102. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, K.S.; Wang, Z.R.; Chen, T.H.; Wang, M.X. Cyclophysis and effect of rejuvenation with continued cuttage in Pinus massoniana cutting propagation. J. Zhejiang For. Coll. 1999, 16, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.C.; Liu, Q.H.; Zhou, Z.C.; Xu, L.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Hao, Y.P. Changes of chemical signals in needles of Pinus massoniana with different resistance after inoculation of pine wood nematodep. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2018, 54, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.X.; Zhang, M.H. The recent advances on the function and application of flavonoids. Acta Zoonutrimenta Sin. 2003, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B. Functional Characterization of Key Genes for Terpene Biosynthesis Involves in Defense to Pine Wood Nematode in Pinus massoniana. Ph.D. Thesis, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing, China, 2020; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Sambaraju, K.R.; Carrol, A.L.; Aukema, B.H. Multiyear weather anomalies associated with range shifts by the mountain pine beetle preceding large epidemics. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 438, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Kang, Y. Defensive strategy of Pinus armandii and prevention and control of codling of Pinus armandii. Gansu For. 2015, 3, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.H.; Ma, T.; Lu, X.L.; Shen, J.; Sun, Z.H.; Wen, X.J.; Deng, P.X. Research progress in adult behavior and chemical ecology of Monochamus alternatus. For. Res. 2017, 30, 854–865. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, Y.X.; Yang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Tang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.L. Distribution and function of the ovarian nematode Contortylenchus genitalicola (Tylenchida: Allantonematidae) on Monochamus alternatus (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) in China. For. Res. 2018, 31, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Rutherford, T.A.; Mamiya, Y.; Webster, J.M. Nematode-induced pine wilt disease: Factors influencing its occurrence and distribution. For. Sci. 1990, 36, 145–155. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G. Research of Programmed Cell Death in interaction between Pinus thunbergii and Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2007; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Mamiya, Y. Pine lethal waiting disease caused by the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus lignicolus. In Proceedings of the 2nd World Technical Consultation on Forest Disease and Insects, New Delhi, India, 7–12 April 1975; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Chen, F.; Luo, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.; Xie, B.Y. First isolation of pine wood nematode from Pinus tabuliformis forests in China. Forest Pathol. 2013, 43, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Q.H.; Zhou, Z.C.; Xu, L.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Luo, N. Identification of candidate constitutive expressed resistant genes of pine wilt disease in Pinus massoniana based on high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. For. Res. 2019, 32, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Q.H.; Zhou, Z.C.; Luo, N.; Xie, Y.N.; Chen, X.Z. Cloning of β-pinene synthase gene in Pinus massoniana and its response to pine wood nematode infection. For. Res. 2020, 33, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Gou, X.H.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Zhang, F.; Cao, Z.Y.; Zhou, F.F. Improved method of obtaining micro-core paraffin sections in dendroecological research. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2013, 37, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Son, J.; Matsushita, N.; Hogetsu, T. Fluorescein-labeled wheat germ agglutinin stains the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. For. Res. 2008, 13, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.X.; Li, X.Z.; Liu, P.; Yin, J.J.; Wu, X. Study on histological section preparation and microstructure of Lotus Rhizome. Shandong Agric. Sci. 2015, 47, 29–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, J. Determination of soluble protein in alfalfa by Coomath bright blue G-250 staining. Agric. Eng. Technol. 2016, 36, 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, C.T.; Qi, Y.Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, S.R. Analysis on the accumulation of lingnin in the stem of Soybean. Agric. Boreali-Simica 2022, 37, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.; Ye, J.R. Research on the relationship between the pathogenicity and the distribution velocity of the nematode in seedling of Pinus thunbergii. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2007, 31, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.Y.; Ge, M.H.; Zhang, P. Studies on resistance mechanisms of Masson Pine orovenance resisitance to pine wood nematode (PWN). J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2000, 24, 85–88. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.X.; Wu, X.Q.; Yu, L.Z. The relationship between difference of superoxide anion and lesion in the interaction of different varieties of pines and Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nanjing For. Univ. 2011, 35, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.S.; Liu, J.; Ye, J.R. Resistance and histopathological observation of wilt-resistant Pinus thunbergii families from Japan to Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Acta Phytopathol. Sin. 2008, 38, 44–50. [Google Scholar]
- Son, J.A.; Komatsu, M.; Matsushita, N.; Hogetsu, T. Migration of pine wood nematodes in the tissues of Pinus thunbergii. J. For. Res. 2010, 15, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.F.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.Y. Mechanisms and applications of enzyme-catalyzed protein cross-linking. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 2499–2512. [Google Scholar]
- Kusumoto, D. Concentrations of lignin and wall-bound ferulic acid after wounding in the phloem of Chamaecyparis obtusa. Trees 2005, 19, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, D.; Yonemichi, T.; Inoue, H.; Hirao, T.; Watanabe, A.; Yamada, T. Comparison of histological responses and tissue damage expansion between resistant and susceptible Pinus thunbergii infected with pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. For. Res. 2014, 19, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, T.; Kiyohara, T. Water relations, xylem embolism and histological features of Pinus thunbergii inoculated with virulent or avirulent pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Exp. Bot. 1995, 46, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).