Abstract
Several studies have highlighted the benefit of implementing agroforestry for rural communities. From the perspective of socio-economic, agroforestry can potentially improve smallholders’ income, increase food security, promote gender equality and stimulate cultural activities in rural areas. Furthermore, agroforestry can enhance ecosystem service through improved soil structure, increased carbon sequestration and higher water retention. Despite having many advantages, the adoption of agroforestry among rural communities, particularly among smallholder farmers in developing countries remains limited. The absence of agroforestry in public policy causes little recognition of this system to tackle the climate crisis as well as to improve rural livelihood. This may be due to, among others, a less comprehensive evidence on impacts that simultaneously touch upon social, economic as well as environmental aspects of agroforestry on the community. This review gives a special emphasis on the current evidence depicting the characteristics of agroforestry adoption, its benefits and potential drawbacks, as well as challenges for the adoption in some developing countries. The outcomes might help related stakeholders to make appropriate decisions to improve rural livelihood.
1. Introduction
Climate change poses negative impacts on agriculture and natural ecosystems around the world. Increased temperature has changed precipitation frequency which led to prolonged drought and heavy rainfall across geographical locations [1,2]. Such extreme climate variability can potentially reduce crop yields and therefore threaten food security [3,4]. To feed the growing population however, crop production must continue amidst the changing climate, although it is often at the expense of land expansion. Consequently, conversion of primary and secondary forests into arable areas is inevitable causing further land degradation and contributing to the release of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in the atmosphere [5]. Furthermore, forests are home for a tremendous terrestrial biodiversity and hold a significant value to support the livelihood of the surrounding community [6]. Deforestation, therefore, not only exacerbates biodiversity loss but also threatens the livelihood of people whose lives are dependent on the locally-harvested forest products. Hence, sustainable forest management and/or reforestation of currently degraded lands is of importance to protect such a valuable ecosystem thus it can continuously provide its service for the people and planet.
Agroforestry can be used as an alternative way to tackle ecological crisis, while at the same time, sustaining crop production [7,8,9,10,11]. This system integrates tree growing and crop cultivation and/or animal production on the same land management, based on spatial arrangement or temporal sequence [12,13]. With such tree integration, agroforestry can preserve natural ecosystems through sustainable land management (including reforestation) and optimal resource utilization. Moreover, agroforestry can potentially mitigate climate change, as several practices within the system are found to improve carbon sequestration and therefore reducing GHG emissions [10,14]. Moreover, the system can promote biodiversity through the incorporation of different species of plants/crops which may provide homes for various wildlife [15,16,17]. Apart from its positive impact on the environment, several studies have also highlighted the socio-economic benefits of agroforestry for rural communities [18]. The implementation of a diverse agroecosystem including trees (timbers, fruits) and livestock might provide alternative incomes for the community promoting economic resilience [19]. Furthermore, the system might improve household food security through diversified food sources [20,21]. Thus, agroforestry might also become a solution for the existing socio-economic issues.
Despite the reported benefits, the rate of agroforestry adoption in developing countries remains relatively low [10,22,23]. Challenges hampering the establishment include knowledge barriers among the farmers on agroforestry practices, lack of policy support and limited access to funding [24]. The absence of agroforestry in public policy causes little recognition of such tree-based systems to tackle the climate crisis as well as to improve rural livelihood [25,26]. This may be due to, among others, a less comprehensive evidence that simultaneously touches upon socio-economic as well as environmental aspects of agroforestry on rural communities [27]. In addition, studies often focus on one aspect at a farm level, hence the outcome is difficult to generalize as it might be context-specific and limited to local conditions. Consequently, limited funding is available and no regulation is sufficiently provided by the governments or private sectors which further impede the establishment of agroforestry in rural areas. By studying some examples of agroforestry research around the world, this review gives a special emphasis on the evidence depicting the characteristics of agroforestry adoption in some developing countries, its benefits and potential drawbacks on rural communities particularly smallholder farmers. Finally, we discuss possible challenges in order to understand aspects hindering the adoption and strategies to overcome such barriers.
2. Characteristics of Agroforestry Adoption in Developing Countries
Agriculture plays a crucial role in developing countries as it becomes the main source of people’s livelihood, particularly those who live in rural areas [28]. Traditional agroforestry has long been practiced by rural communities to improve their livelihood. Communities who live near forest areas, for instance, often utilize forest products such as selling timbers or consuming fruits or edible plants which naturally grow in the area [15]. Moreover, subsistence farmers in rural areas often cultivate crops along with growing some perennial trees or raise livestock in order to make a living [20,29].
In general, several agroforestry practices exist around the world such as silvoarable systems (combination of trees/shrubs with crops), silvopastoral (a combination between trees and livestock), agro-silvopastoral (a combination of shrubs/trees with both crop and livestock), multipurpose trees, riparian buffer and improved fallow [12] (see Table 1). Although with some adjustments on the components, some of these practices exist in several developing countries. For instance, in Sub-Sahara Africa, the diversity of agroforestry can be found in different places including the multi-story homegardens on Mt. Kilimanjaro in Tanzania, silvoarable (cacao system) in Côte d’Ivoire and rational woodlots in Kenya [10]. Similarly, in Latin America, the practices show strong regional variation. This includes silvopastoral combining eucalyptus, pine and native grass species for cattle production in Chilean and Argentinian rangelands [18], silvoarable with intercropping coffee and native tree species in Brazilizan Cerrado [30] and agro-silvopastoral combining livestock production (cattle, goat/sheep) with crops and/or native tree plantation in the Andean region of Venezuela, Colombia, Peru and Ecuador [31]. Meanwhile, in South East Asia, agroforestry system can range from homegardens, the agro-silvopastoral (cattle, oil palm and timbers), silvoarable (coffee or cacao with timbers) and silvopastoral (combination between livestock and timber) [20,32,33].

Table 1.
Several practices of agroforestry that are commonly adopted in several developing countries and their brief description according to Mosquera-Losada et al. [12].
The presence of an agroforestry system in a particular area, however, depends on several factors including resource availability, economic feasibility, topographical, socio-cultural and environmental conditions [8,34,35]. McGinty et al. [22], for instance, used multiple regression and logistic model analysis to investigate socio-economic factors contributing to farmers’ intention to adopt agroforestry in the Atlantic rainforest, Brazil. They found that farmers’ adoption was influenced by attitudes about conservation, perceived behavioral control and labor availability. In another study, Nguyen at al. [32], showed that the presence of coffee agroforestry system in Northwest Vietnam was influenced by market access, ecological suitability and plot location.
Some approaches are available to define an individual characteristic of agroforestry practices suitable for the community [36,37]. However, the inclusivity of several characteristics is vital to reveal all major distinctive features to select practices suitable for the adoption [10]. The availability of natural resources and geographical location, for instance, might affect a farmer’s choice to adopt a particular practice/system [22,24,35,38]. For instance, people who live in the surrounding forests and own livestock might prefer to adopt silvopastoral or agro-silvopastoral practices as the resources (cattle, goats etc.) are available and they can possibly access the feed from naturally-grown shrubs or grasses in the forests while generating another income from growing timber or crops [24,38]. Moreover, some forms of agroforestry require low input and less maintenance yet still generate a higher recycling rate, making them more profitable and therefore preferable by low income farmers [39]. Several agroforestry systems, however, are applicable for different agro-ecological zones, although with a component variability, yet they have the same functions, particularly for livelihoods and landscapes. Therefore, no universal standard can be applied to define the best agroforestry system for the adoption [36].
Agroforestry encompasses many different practices and techniques depending on resource availability and environmental condition. Better assessment into their independent performance with respect to different environmental, socio-cultural and political situations is of paramount importance to determine factors underlying agroforestry adoption and establishment. Perhaps, the trade-off upon a farmer’s choice on different land management (including non-agroforestry approaches) might be worth investigating to determine the rationale underlying the selection process. These aforementioned factors might vary across spatial and temporal scales, generating a niche for further research, particularly on the development of tools for agroforestry intervention.
3. Digging Deeper into the Impacts of Agroforestry for Rural Communities
3.1. Socio-Economic Impacts of Agroforestry
The distinction of agroforestry as compared to other land use systems lies in the inclusion of woody plants within the system. On the economic perspective, the adoption of such tree-based farming can improve economic resilience through product diversification [8]. The utilization of multipurpose trees, in particular, might improve the profitability of agroforestry as they can serve for various functions such as alternative incomes, sources for fodder or foods (i.e., wild edible fruits) during deficit periods among the rural communities [40]. Furthermore, some woods with higher economic value can provide additional incomes for the community apart from the earnings generated from annual crops. Research on teak-agroforestry (Tectona grandis) systems in Indonesia, for instance, can generate up to 12% of total household income despite its lower recycling time (due to slow growing period) [41]. Furthermore, a study on damar (Agathis dammara) agroforestry in Pesisir, West Sumatra, showed that the damar production yielded up to 50% of the total household income [42]. Additionally, the adoption of a coffee agroforestry in Wey-Besay Watershed, Lampung, contributed to more than 50% household income compared to only 12% from the conventional agriculture system (non-agroforestry system) [43]. Consideration, however, needs to be taken when comparing the economic benefits from different practices as the outcomes might be influenced by various aspects such as type of trees included, environmental conditions (pest availability, weather conditions, etc.) and commodity price volatility.
Increased benefit-to-cost ratio can also be achieved through agroforestry. Some practices include cultivation of woody plants requiring low inputs (chemical fertilizers, pesticides, etc.), thus it can minimize the production costs and improve income gained by the farmers [9,19]. However, such an outcome might highly depend on the farmers’ knowledge of the practice, particularly on how to make optimal plant/tree selection for their system. Some trees can grow better when they were cultivated along with their complementary crops. On the contrary, the wrong selection of tree or crop components can cause nutrient competition [44], which consequently reduce yield and therefore the profit gained by the farmers.
The implementation of agroforestry can also open up new job opportunities in rural areas for off-farm activities such as crop drying, wood cuttings, furniture making etc. [23]. Increased job opportunities might also benefit women as they can be directly involved in the production activities, which can improve gender equality in rural areas [21]. Furthermore, job absorption in the rural areas might prevent rural exodus [45,46] and therefore, can contribute to improved rural economy. Nevertheless, caution needs to be taken when creating industrial sites around the conservation area or near the primary forest as the risk of human encroachment to such protected areas might occur and can potentially damage the ecosystem [46].
Apart from generating income, agroforestry can also play a role in improving food security among the community near the forests. In this case, Ickowitz et al. [47] employed spatial data to elucidate micronutrient uptake among children between one to five years old in Indonesia. They found a correlation between agroforestry and increased consumption of legumes at the national level. Meanwhile, at regional level, their findings displayed a correlation between the presence of agroforestry and increased consumption of vitamin A-rich fruits and leafy vegetables. Furthermore, agroforestry systems were also associated with higher meat consumption particularly from those people adopting silvopastoral practice [47]. Increased volume of food productivity and diversity was also shown among the low-income farmers who had engaged in agroforestry training, indicating higher food availability following the implementation of agroforestry [48]. Evidence on the positive correlation between agroforestry adoption and food security among communities were also depicted by other studies, such as in several countries in Sub-Sahara Africa, South Asia and in Latin America [10,21,49].
Agroforestry might also stimulate socio-cultural activity among the adopters. For instance, farming communities can meet with each other and discuss the cultivation method, choice of tree species or crop varieties, fertilizer management and so on. A study conducted by Mungmachon [50] found that gathering was part of the culture among small forest communities in Thailand. They often discussed the problems they were facing and found solutions together. They began by collectively studying their problems, rediscovering traditional wisdom and existing knowledge, and then integrating new knowledge. By doing this, the community becomes more engaged and knowledgeable through peer-to-peer discussion and community participation. The summary of socio-economic impacts of agroforestry and their respective studies (references) on rural communities can be seen in Table 2.
3.2. Environmental Impacts of Agroforestry
Agroforestry poses several ecological-based practices that can potentially improve the ecosystem service for the rural community. These practices include crop diversification (crop-tree integration), crop rotation, soil conservation (cover crop integration), improved fallows and boundary planting. For instance, increased soil fertility and physical structure (soil conservation) can be achieved by utilizing pruning materials (from the trees or crop residues) as soil amendments [51]. This practice, however, can yield a different outcome depending on the quality of pruning materials available in the system. Plant residues have different C/N ratio which can affect their decomposability in soils. Consequently, the amount of nutrients released in the soil might vary between type of residues resulting in distinct soil chemical content [52], and therefore its impacts on crop growth. Different decomposition rate due to variation in C/N ratio can also influence soil carbon content (either increase or decrease), which may compromise the carbon sequestration capability of a particular agroforestry system as a whole [33,53].
The cultivation of different tree species in agroforestry system also improves biodiversity providing a habitat for the wildlife [16]. In addition, trees can also prevent soil erosion and landslides (in the higher slopes) due to the strong rooting system around the soil matrix [7,54]. The presence of trees in agroforestry systems can also change microclimatic conditions through shading which might reduce the sun radiation buffering the temperature around the farm [55]. Highly intensified solar radiation can hamper crop physiology and growth, hence incorporating trees through agroforestry can improve crop growth and subsequently, its yield [55,56]. Caution needs to be taken however, when selecting tree coverage, as overshading can significantly reduce the light penetration which can potentially reduce the growth of co-cultivated crops and increase disease emergence [57].
Another ecological benefit of agroforestry for the community is improved water conservation. Such ecosystem service might result from optimal water uptake by the integrated tree-crop system. A research that was done on an agroforestry system (maize-tree) in Kenya shows that during the dry season, only about 25% of the rain water was transpired from plant biomass, indicating the efficiency of the system in utilizing off-season rainfall (which accounts for 15–20% of the total annual rainfall). Meanwhile, the rest of the water remains in the soil layers even after the harvest period [58]. Improved organic carbon in agroforestry soils (as a result of organic amendment addition) can increase water retention and therefore prevent excessive evaporation or water runoff [59]. However, again, the choice of the tree species matters as water uptake might vary between plant species. Water uptake by plant roots is generated by the water potential difference between the soil and the atmosphere when leaf stomata are open and this depends on the root exploration capacity of a particular plant species [60].
In addition, a conducted trial showed that higher vegetation density (due to more biomass from trees/shrubs) positively correlates with the precipitation rates with reduced vegetation decreasing the rainfall. Such decline in precipitation might be attributed to the reduced evapotranspiration and increased light reflection to the atmosphere under less vegetation density [61]. Furthermore, analysis of the water cycle highlights the importance of managing tree cover to improve the quantity of rainfall [62,63]. Agroforestry, therefore, can be one of the strategies to alleviate drought in some arid areas and increase community resilience in the changing climate. Although promising, these studies were only performed at farm level and rely on data correlation or modeling. Hence, more studies need to be done to validate such findings covering different geographical locations. A brief summary of environmental impacts of agroforestry on rural communities and their respective studies (references) can be seen in Table 2.

Table 2.
Summary of previous studies depicting socio-economic and environmental impacts of agroforestry for rural communities.
Table 2.
Summary of previous studies depicting socio-economic and environmental impacts of agroforestry for rural communities.
| Aspect | Impact Description | Type of Impact | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic |
| Positive | [64,65] |
| Positive | [23] | |
| Positive | [9,19] | |
| Negative | [66] | |
| Negative | [46] | |
| Social |
| Positive | [21] |
| Positive | [21,67] | |
| Positive | [46] | |
| Positive | [45] | |
| Positive | [68] | |
| Negative | [46] | |
| Environment |
| Positive | [7,54] |
| Positive | [54] | |
| Positive | [7,51] | |
| Positive | [69] | |
| Positive | [17] | |
| Positive | [11,69] | |
| Negative | [46] | |
| Negative | [70] | |
| Negative | [66,71] |
4. Setting Up a Baseline: Revisiting the Research Gap on Agroforestry Impact Assessment
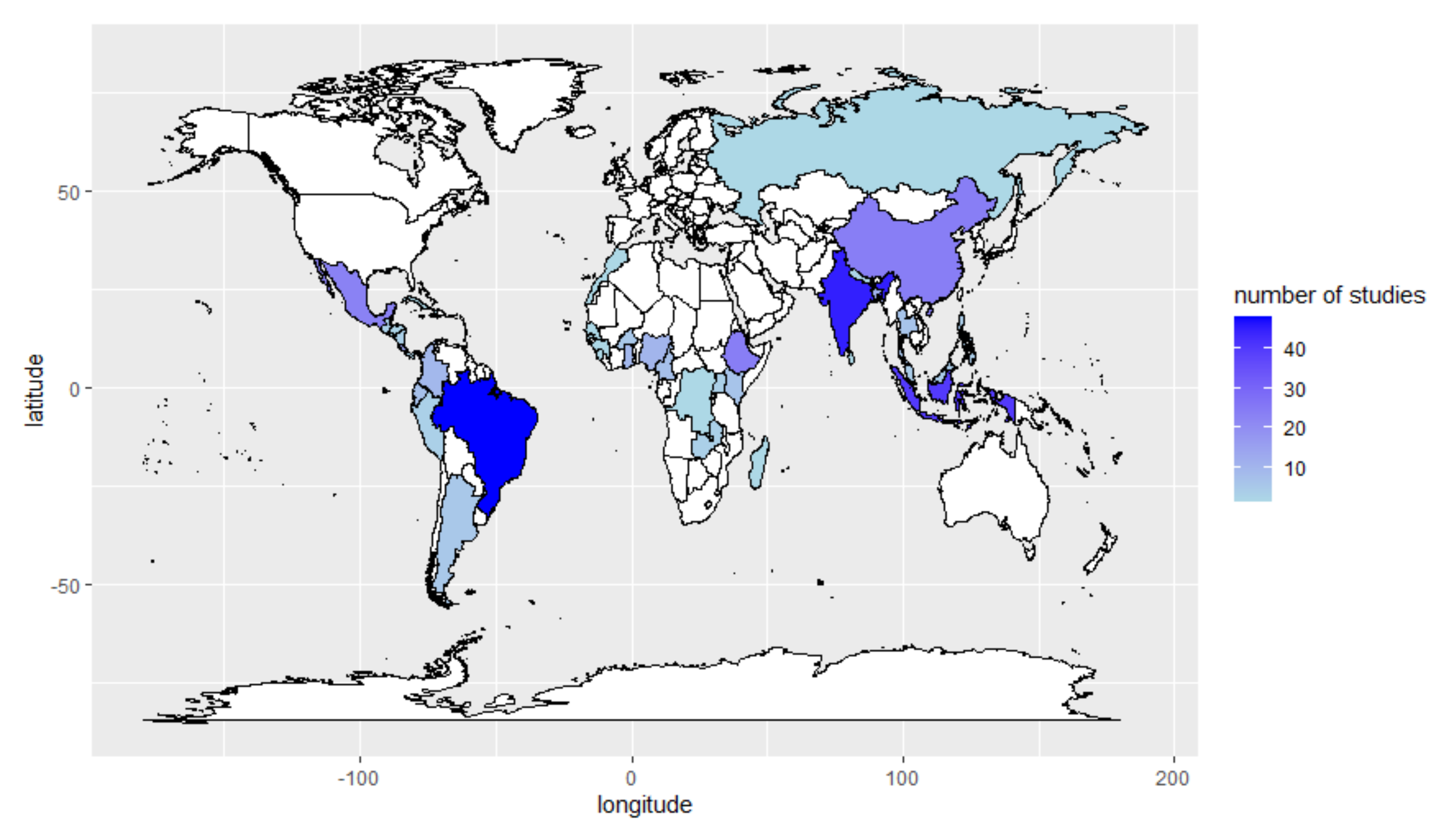
Numerous research regarding agroforestry have been reported around the world, particularly in several developing countries (see Figure 1). However, studies focusing on long-term agroforestry impact assessment remain very limited. A systematic literature study conducted by Miller et al. [72] indicated a lack of rigorous evidence on the long-term impact of agroforestry globally. Research duration is among the major constraints posing a challenge to agroforestry impact assessments. Compared to annual crops for instance, trees require a longer period to grow, therefore, it can take decades to see the resulting impact of a particular agroforestry system. On the other hand, project funding might fall within a shorter time period which possibly stops the research before the actual impact is seen in the field. To overcome this problem, a research study can use a predictive model to estimate the impact of several agroforestry systems with respect to other alternative land use including a mainstream conventional system (monoculture). Model parameters such as above-ground biomass, tree growth rates, number of vegetation, carbon storage capacity as well as changes in input and output prices can be used to estimate the impact of agroforestry systems on both society and environment [73,74].
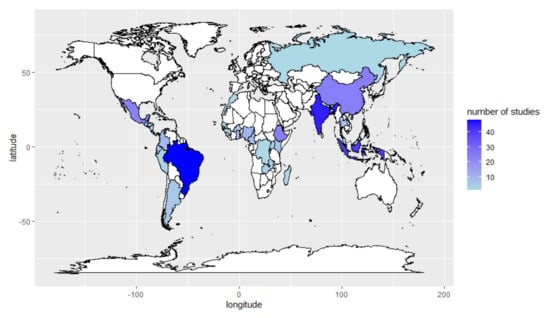
Figure 1.
Mapping of agroforestry research in developing countries adapted from Miller et al. [72].
Another gap in agroforestry research is lack of collaborative action between studies, particularly those addressing socio-economic and ecological impact simultaneously. The majority of agroforestry studies, however, perform impact assessments on the basis of individual aspect, be it social, economic or environmental parameters separately. For instance, studies on economic and environmental aspects of agroforestry are relatively well-documented. However, each study is conducted individually along with its unique assessment technique resulting in different units and evaluation matrices. While it is already a great step to disentangle the impact of agroforestry, a consensus will be difficult to generate from such an individual research focus. As mentioned before, the agroforestry system involves different practices with flexibility in design and components. Such variability makes the agroforestry system difficult to compare with alternative land uses. Ultimately, the general aim of agroforestry intervention is to create a sustainable farming system which gives a positive impact to both people and planet. Thus, it is impossible to separate the close relationship between human well-being and environmental conditions.
Several approaches have been conducted to evaluate socio-economic and environmental impacts of agroforestry on rural communities simultaneously. For instance, Public Goods Tool (PG tool) was employed as a multi-criteria analysis tool to investigate the sustainability aspect of agroforestry [75,76] in rural areas of Northern, Southern and Eastern Europe [77]. Similarly, the Response-Inducing Sustainability Evaluation (RISE) methodology was used to analyze socio-economic and ecological impacts of agroforestry [78,79,80] on the indigenous community of Ecuadorian Kichwas focusing on a traditional agroforestry system (chakra) [81]. PG tool and RISE employ data collection via questionnaire and/or interview from respondents to assess the agroforestry’s impact quantitatively and qualitatively. Each question is created based on specific criteria. For instance, PG Tool using SAFA (Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture System) indicators [77], which consists of the domains of good governance, environmental integrity, economic resilience and social well-being [82]. Meanwhile, RISE methodology uses three types of questions namely open, drop-down list and Boolean developed by the Swiss College of Agriculture (SHL). Such methodology uses 10 different criteria to assess the sustainability index of an agriculture system such as: land use, livestock production, use of materials and environmental protection, water use, energy and climate, biodiversity, working conditions, quality of life, economic viability and administration [81]. The collected data from PG Tool and RISE methodology are then used to score the sustainability index before transforming it into a specific diagram (i.e., radar chart). Such a diagram can therefore be used to better visualize trade-off of agroforestry systems in comparison to other alternative land uses. As a result, it allows researchers and decision makers to gain a better understanding on the impact of agroforestry on both people and the planet.
5. Challenge and Future Outlook
Apart from numerous studies depicting the benefits of agroforestry, the speedy transition of such tree-based farming has not taken place in many developing countries. One of the reasons could be that agroforestry is seen as an approach which goes against the main narrative namely “a monoculture system with high output” [46]. Agroforestry employs a more highly complex system consisting of different components (tree species, crops and/or livestock), while synergy between each component is vital to generate optimal outcomes, both economically and environmentally. Consequently, the impact (either positive or negative) will depend on communities’ knowledge on good agricultural practices (GAP). For instance, the yields or harvestable parts of crops or trees can decrease due to nutrient or light competition among the species introduced in the agroforestry system [66]. Furthermore, some crop or tree species are nutrient- and water-demanding which can potentially cause soil mining and water resource depletion [66,71]. Therefore, agronomy is one of the prerequisite knowledges needed by rural communities in order to achieve successful agroforestry adoption. An extension of workers (from NGO, government bodies and research institutes) are therefore important in order to perform knowledge transfer to the communities.
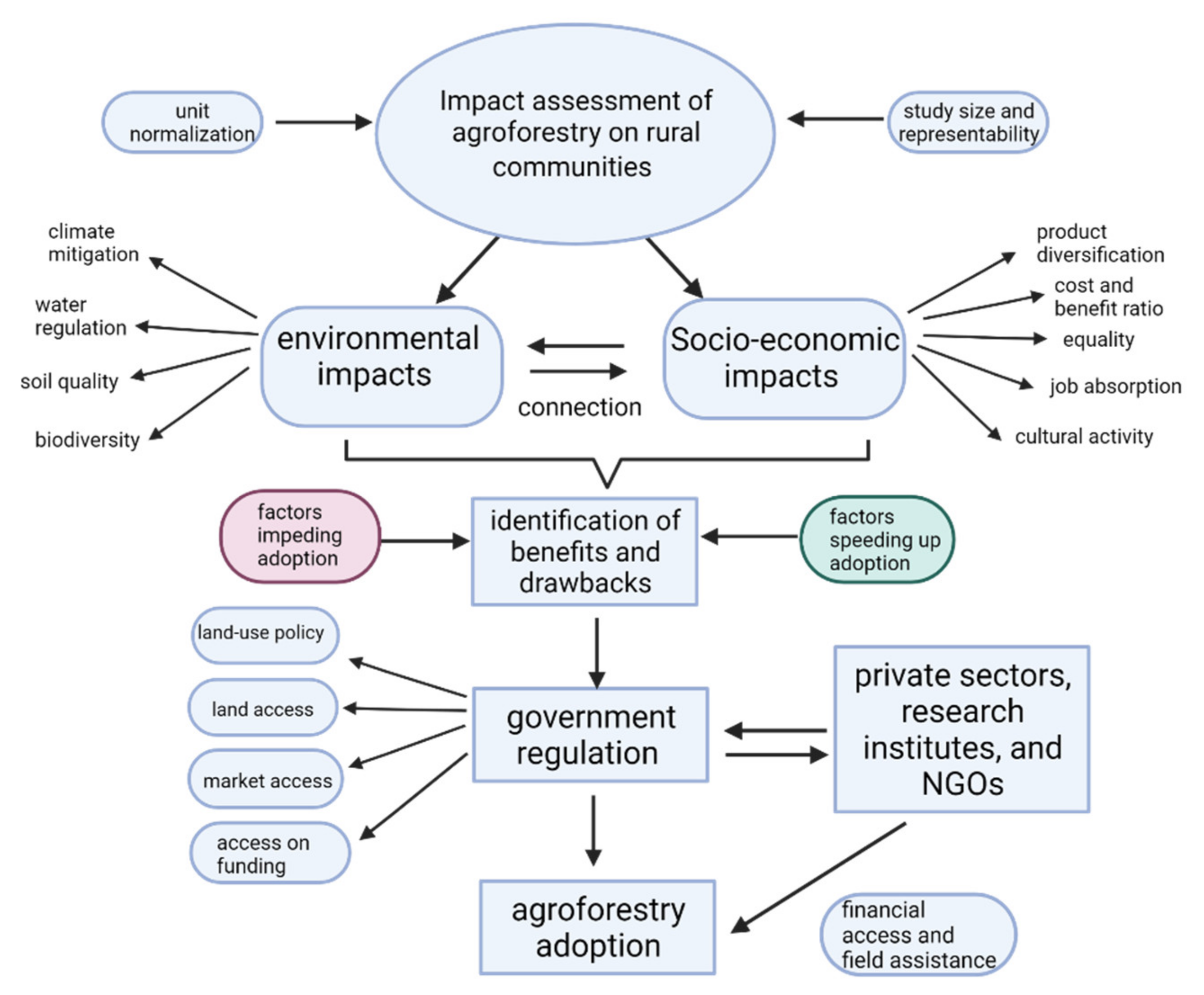
Another challenge hampering the adoption arises from the policy sector where agroforestry is rarely involved in the national agenda supporting a sustainable agriculture transition. This challenge perhaps spurs from the less defined of an agroforestry term as compared to, for instance, other more familiar practices such as organic farming. The presence of different tree-based systems, although falling under the same umbrella of agroforestry, might generate different outcomes depending on the type of components. Furthermore, even though researches had been done over decades to investigate the impact of agroforestry, the majority of them focus on the farm level involving only one parameter of impact (either social, economic or environment), whereas comprehensive studies on broader levels such as national or even continental scope are mostly absent [46]. Consequently, it is difficult to generate a clear consensus on the impact of agroforestry, one of the reasons is that agroforestry owns less trust from policy makers. With this challenge at hand, future research can be more directed to investigate more comprehensive impacts of agroforestry involving its social, economic and environmental aspects (Figure 2).
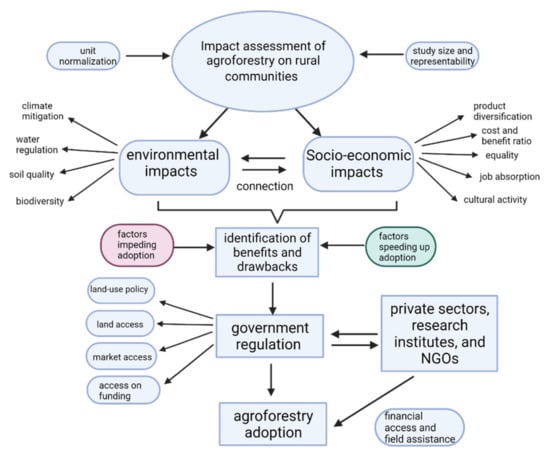
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of agroforestry impact assessment on rural communities. The assessment should cover socio-economic and environmental aspects of agroforestry as depicted on the top of the diagram. To make an equal comparison between the assessments, the studies’ outcome can be adjusted according to output unit and study size (covering different geographical locations). Based on such assessments, the benefits and drawbacks can be identified and combined with the existing studies explaining factors affecting the agroforestry adoption among rural communities. The results can then be used as recommendations for government (in collaboration with private sectors or NGOs) to create policy to speed up the adoption while optimizing benefits of agroforestry upon implementation. NGOs and research institutes can provide, for instance, capital and technical assistance to improve communities’ knowledge on some agroforestry practices.
Several attempts are available to mainstream the agroforestry concept through the collaboration with private sectors focusing on the development of huge plantations. Although the strategy is seen as a good initiative to speed up the adoption rate, the concern is raised particularly on the practice of “industrial” agroforestry [83]. Such practice may potentially go from more diversified components into a limited intercropping system with one species of tree as the dominant product. Furthermore, by using a legitimated term of agroforestry, such ‘’commercial’’ agroforestry, instead of protecting, may transform pristine forests into the plantation of mixed commodities (i.e., spices, palm oil, banana, etc.), causing further biodiversity loss. In this case, regulation must present with clear boundaries, particularly on the definition of an agroforestry term to prevent ‘’a new form’’ of deforestation. Instead, agroforestry can be implemented in degraded areas outside the primary forests, to revitalize soil quality and improve biodiversity. Many rural communities, particularly smallholder farmers, do not own sufficient resources such as lands (mostly owned by industries or governments), germplasms and seedlings to implement an agroforestry system [40]. Therefore, government or NGOs can reclaim such degraded areas to those who are interested in adopting agroforestry systems. Additionally, government can give provisional supports such as market accesses, post-harvest tools, or price stability to the communities in order to improve their economic resilience (Figure 2).
Some studies have shown that the involvement of the community in collaboration with private or governmental agencies [84,85] is also important to achieve agroforestry goals. This is particularly true to lower the risks of overharvesting activities on common-pool resources [86], for instance, by creating institutions that help organize and manage all activities related to farming activities. Some studies showed strong evidence that local communities can establish institutions to manage local resources [87,88]. Moreover, more researchers are interested in how institutions help manage ecological systems [89,90]. Thus, some recommendations are beneficial for the current government and private agencies to formulate their strategy, programs and regulation on how to help the local community manage their natural resources with the help of institutions. i.e., Forest Stewardship Council. A study case in Burkina Faso, Mali, Niger and Senegal [91] which assessed the effect of local institutions on adopting agroforestry innovations can be one of the examples. The effects that were being analyzed focus on FMNR (farmer managed natural regeneration), income, agricultural production, caloric intake and diet. The results showed that well-structured informal and formal institutions provide better collaboration attitude, good management and natural resource protection, as well as better livelihoods.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M., M.S.R. and I.H.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.R. and I.H.; writing—review and editing, I.M., M.S.R. and I.H.; funding acquisition, I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Malang.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dai, A.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. Climate Change and Drought: A Precipitation and Evaporation Perspective. Curr. Clim. Change Rep. 2018, 4, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabari, H. Climate change impact on flood and extreme precipitation increases with water availability. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukal, M.S.; Irmak, S. Climate-driven crop yield and yield variability and climate change impacts on the U.S. great plains agricultural production. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Vanga, S.K.; Saxena, R.; Orsat, V.; Raghavan, V. Effect of Climate Change on the Yield of Cereal Crops: A Review. Climate 2018, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, B. Changes in soil greenhouse gas fluxes by land use change from primary forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 2656–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persha, L.; Fischer, H.; Chhatre, A.; Agrawal, A.; Benson, C. Biodiversity conservation and livelihoods in human-dominated landscapes: Forest commons in South Asia. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 2918–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dollinger, J.; Jose, S. Agroforestry for soil health. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, D.; Wondie, M.; Mekuria, W.; Darr, D. Agroforestry of Smallholder Farmers in Ethiopia: Practices and Benefits. Small-Scale For. 2019, 18, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, G.D.C.; Schlindwein, M.M.; Padovan, M.P.; Vogel, E.; Ruviaro, C.F. Environmental performance of agroforestry systems in the Cerrado biome, Brazil. World Dev. 2019, 122, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbow, C.; Van Noordwijk, M.; Luedeling, E.; Neufeldt, H.; Minang, P.A.; Kowero, G. Agroforestry solutions to address food security and climate change challenges in Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 6, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez, V.E.; Tanzi, S.C. Livelihood and Environmental Trade-Offs of Climate Mitigation in Smallholder Coffee Agroforestry Systems; Routledge: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mosquera-Losada, M.R.; McAdam, J.H.; Romero-Franco, R.; Santiago-Freijanes, J.J.; Rigueiro-Rodróguez, A. Rigueiro Rodróguez Definitions and Components of Agroforestry Practices in Europe; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; ISBN 9781402082719. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, A.; Venturi, M.; Bertani, R.; Agnoletti, M. A Review of the Role of Forests and Agroforestry Systems in the FAO Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) Programme. Forests 2020, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Huang, Y.; Ren, W.; Coyne, M.; Jacinthe, P.-A.; Tao, B.; Hui, D.; Yang, J.; Matocha, C. Responses of soil carbon sequestration to climate-smart agriculture practices: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 2591–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaba, K.F.; Chirwa, P.; Syampungani, S.; Ajayi, C.O. Contribution of Agroforestry to Biodiversity and Livelihoods Improvement in Rural Communities of Southern African Regions. In Environmental Science and Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assogbadjo, A.E.; Kakaï, R.G.; Vodouhê, F.G.; Djagoun, C.A.M.S.; Codjia, J.T.C.; Sinsin, B. Biodiversity and socioeconomic factors supporting farmers’ choice of wild edible trees in the agroforestry systems of Benin (West Africa). For. Policy Econ. 2012, 14, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, P.Z.F.; Crouzeilles, R.; Sansevero, J.B.B. Can agroforestry systems enhance biodiversity and ecosystem service provision in agricultural landscapes? A meta-analysis for the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browder, J.O.; Wynne, R.H.; Pedlowski, M.A. Agroforestry diffusion and secondary forest regeneration in the Brazilian Amazon: Further findings from the Rondônia Agroforestry Pilot Project (1992–2002). Agrofor. Syst. 2005, 65, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, A.G.; Eusebio, G.D.S.; Fasiaben, M.D.C.R.; Moraes, A.S.; Assad, E.D.; Pugliero, V.S. The economic impacts of the diffusion of agroforestry in Brazil. Land Use Policy 2021, 108, 105489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, C.; Toth, G.G.; Hagan, R.P.O.; McKeown, P.C.; Rahman, S.A.; Widyaningsih, Y.; Sunderland, T.C.H.; Spillane, C. Agroforestry contributions to smallholder farmer food security in Indonesia. Agrofor. Syst. 2021, 95, 1109–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiptot, E.; Franzel, S.; Degrande, A. Gender, agroforestry and food security in Africa. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 6, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinty, M.M.; Swisher, M.E.; Alavalapati, J. Agroforestry adoption and maintenance: Self-efficacy, attitudes and socio-economic factors. Agrofor. Syst. 2008, 73, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandar, J.; Iskandar, B.S.; Partasasmita, R. Responses to environmental and socio-economic changes in the Karangwangi traditional agroforestry system, South Cianjur, West Java. Biodiversitas 2016, 17, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, A.D.; Mekonnen, A.; Randall, B.; Deribe, R. Household Level Determinants of Agroforestry Practices Adoption in Rural Ethiopia. For. Trees Livelihoods 2019, 28, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishaw, B.; Neufeldt, H.; Mowo, J.; Abdelkadir, A.; Muriuki, J.; Dalle, G.; Assefa, T.; Guillozet, K.; Kassa, H.; Dawson, I.K.; et al. Farmers’ Strategies for Adapting to and Mitigating Climate Variability and Change through Agroforestry in Ethiopia and Kenya; Forestry Communications Group: Corvallis, OR, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Beddington, J.R.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Clark, M.E.; Fernández Bremauntz, A.; Guillou, M.D.; Howlett, D.J.B.; Jahn, M.M.; Lin, E.; Mamo, T.; Negra, C.; et al. Agriculture: What next for Agriculture after Durban? Science 2012, 335, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiptot, E.; Hebinck, P.; Franzel, S.; Richards, P. Adopters, testers or pseudo-adopters? Dynamics of the use of improved tree fallows by farmers in western Kenya. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Hazell, P.; Thurlow, J. The Role of Agriculture in African Development. World Dev. 2010, 38, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, R.; Peri, P.L.; Bahamonde, H.A.; Gargaglione, V.; Ormaechea, S.; Herrera, A.H.; Jardón, L.S.; Lorenzo, C.; Pastur, G.J.M. Assessing Knowledge Production for Agrosilvopastoral Systems in South America. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 71, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Neto, N.E.; Nascimento, D.R.; Carvalho, F.A. Biodiversity inventory of trees in a neotropical secondary forest after abandonment of shaded coffee plantation. iForest—Biogeosci. For. 2017, 10, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avellaneda-Torres, L.M.; Sicard, T.E.L.; Rojas, E.T. Impact of potato cultivation and cattle farming on physicochemical parameters and enzymatic activities of Neotropical high Andean Páramo ecosystem soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.P.; Vaast, P.; Pagella, T.; Sinclair, F. Local Knowledge about Ecosystem Services Provided by Trees in Coffee Agroforestry Practices in Northwest Vietnam. Land 2020, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besar, N.A.; Suardi, H.; Phua, M.-H.; James, D.; Bin Mokhtar, M.; Ahmed, M.F. Carbon Stock and Sequestration Potential of an Agroforestry System in Sabah, Malaysia. Forests 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiyu, A.; Teketay, D.; Gratzer, G.; Shete, M. Tree Planting by Smallholder Farmers in the Upper Catchment of Lake Tana Watershed, Northwest Ethiopia. Small-Scale For. 2016, 15, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Rojas, R.; Russy, S.; Roco, L.; Fleming-Muñoz, D.; Engler, A. Factors Affecting the Adoption of Agroforestry Practices: Insights from Silvopastoral Systems of Colombia. Forests 2020, 11, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torquebiau, E.F. Agronomy / Agronomie A Renewed Perspective on Agroforestry Concepts and Classification. C R Acad Sci III 2000, 11, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, F.L. A general classification of agroforestry practice. Agrofor. Syst. 1999, 46, 161–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkamleu, G.B.; Manyong, V.M. Factors affecting the adoption of agroforestry practices by farmers in Cameroon. Small-Scale For. Econ. Manag. Policy 2005, 4, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezeer, R.E.; Santos, M.J.; Boot, R.G.A.; Junginger, M.; Verweij, P.A. Effects of shade and input management on economic performance of small-scale Peruvian coffee systems. Agric. Syst. 2018, 162, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebru, B.M.; Wang, S.W.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, W.-K. Socio-Ecological Niche and Factors Affecting Agroforestry Practice Adoption in Different Agroecologies of Southern Tigray, Ethiopia. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshetko, J.M.; Rohadi, D.; Perdana, A.; Sabastian, G.; Nuryartono, N.; Pramono, A.A.; Widyani, N.; Manalu, P.; Fauzi, M.A.; Sumardamto, P.; et al. Teak agroforestry systems for livelihood enhancement, industrial timber production, and environmental rehabilitation. For. Trees Livelihoods 2013, 22, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, E.; Nawir, A.A. Turning straw into gold: Specialization among damar agroforest farmers in pesisir, sumatra. For. Trees Livelihoods 2005, 15, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyanto, S.; Khususiyah, N.; Leimona, B. Poverty and Environmental Services: Case Study in Way Besai Watershed, Lampung Province, Indonesia. Ecol. Soc. 2007, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, P.E.; Simpson, J.A.; Thevathasan, N.V.; Gordon, A.M. Effects of tree competition on corn and soybean photosynthesis, growth, and yield in a temperate tree-based agroforestry intercropping system in southern Ontario, Canada. Ecol. Eng. 2007, 29, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Alcântara Laudares, S.S.; Coimbra Borges, L.A.; de Ávila, P.A.; de Oliveira, A.L.; da Silva, K.G.; de Alcântara Laudares, D.C. Sistemas Agroflorestais Como Alternativa Sustentável Para Regularização Ambiental de Ocupações Rurais Consolidadas. Cerne 2017, 23, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ollinaho, O.I.; Kröger, M. Agroforestry transitions: The good, the bad and the ugly. J. Rural Stud. 2021, 82, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ickowitz, A.; Rowland, D.; Powell, B.; Salim, M.A.; Sunderland, T. Forests, Trees, and Micronutrient-Rich Food Consumption in Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratiwi, A.; Suzuki, A. Reducing Agricultural Income Vulnerabilities through Agroforestry Training: Evidence from a Randomised Field Experiment in Indonesia. Bull. Indones. Econ. Stud. 2019, 55, 83–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Bohra, B.; Pragya, N.; Ciannella, R.; Dobie, P.; Lehmann, S. Bioenergy from agroforestry can lead to improved food security, climate change, soil quality, and rural development. Food Energy Secur. 2016, 5, 165–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roikhwanphut Mungmachon, M. Knowledge and Local Wisdom: Community Treasure. Int. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2012, 2, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Shrestha, B.M.; Chang, S.X.; Bork, E.W.; Carlyle, C.N. Enrichment Planting and Soil Amendments Enhance Carbon Sequestration and Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Agroforestry Systems: A Review. Forests 2018, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Siddique, M.R.H.; Rahman, M.S.; Hossain, M.Z.; Hasan, M.M. Nutrient dynamics associated with leaf litter decomposition of three agroforestry tree species (Azadirachta indica, Dalbergia sissoo, and Melia azedarach) of Bangladesh. J. For. Res. 2011, 22, 577–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hendrix, P.F.; Dame, L.E.; Burke, R.A.; Wu, J.; Neher, D.A.; Li, J.; Shao, Y.; Fu, S. Earthworms facilitate carbon sequestration through unequal amplification of carbon stabilization compared with mineralization. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, H.N.; Goede, R.G.M.; Brussaard, L.; Cardoso, I.M.; Duarte, E.M.G.; Fernandes, R.B.A.; Gomes, L.C.; Pulleman, M.M. Protective shade, tree diversity and soil properties in coffee agroforestry systems in the Atlantic Rainforest biome. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.E.; Ong, C.K.; Black, C.R. Understorey microclimate and crop performance in a Grevillea robusta-based agroforestry system in semi-arid Kenya. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1140–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, B.O.; Sgarbossa, J.; Schwerz, F.; Elli, E.F.; Eloy, E.; Behling, A. Dynamics of solar radiation and soybean yield in agroforestry systems. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2018, 90, 3799–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand-Bessart, C.; Tixier, P.; Quinteros, A.; Andreotti, F.; Rapidel, B.; Tauvel, C.; Allinne, C. Analysis of interactions amongst shade trees, coffee foliar diseases and coffee yield in multistrata agroforestry systems. Crop. Prot. 2020, 133, 105137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lott, J.E.; Khan, A.A.H.; Black, C.R.; Ong, C.K. Water use in a Grevillea robusta–maize overstorey agroforestry system in semi-arid Kenya. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 180, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawls, W.J.; Pachepsky, Y.A.; Ritchie, J.C.; Sobecki, T.M.; Bloodworth, H. Effect of soil organic carbon on soil water retention. Geoderma 2003, 116, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayala, J.; Prieto, I. Water acquisition, sharing and redistribution by roots: Applications to agroforestry systems. Plant Soil 2020, 453, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.; Tucker, C.J.; Sy, H. Tree density and species decline in the African Sahel attributable to climate. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 78, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ent, R.J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Schaefli, B.; Steele-Dunne, S.C. Origin and fate of atmospheric moisture over continents. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.; Futter, M.N.; Bishop, K. On the Forest Cover-Water Yield Debate: From Demand- to Supply-Side Thinking. Glob. Change Biol. 2012, 18, 806–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, L.; Siswanto, D.; Rahardi, B.; Zayadi, H. Fostering Coffee Agroforestry for Agrotourism Development in Degraded Land in a Buffer Zone of a National Park: A Case Study from Poncokusumo, Malang, Indonesia. EurAsian J. Biosci. 2019, 13, 1613–1620. [Google Scholar]
- Cerda, R.; Avelino, J.; Harvey, C.A.; Gary, C.; Tixier, P.; Allinne, C. Coffee agroforestry systems capable of reducing disease-induced yield and economic losses while providing multiple ecosystem services. Crop. Prot. 2020, 134, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, F.; Chen, C.; Liu, W.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. Recognizing the role of plant species composition in the modification of soil nutrients and water in rubber agroforestry systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhlis, I. Food Security for Communities Around the Forest in Alleviating Poverty. KnE Soc. Sci. 2019, 3, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyono, E.D.; Fairuzzana, S.; Willianto, D.; Pradesti, E.; McNamara, N.P.; Rowe, R.L.; Van Noordwijk, M. Agroforestry Innovation through Planned Farmer Behavior: Trimming in Pine–Coffee Systems. Land 2020, 9, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quandt, A.; Neufeldt, H.; McCabe, J.T. The role of agroforestry in building livelihood resilience to floods and drought in semiarid Kenya. Ecol. Soc. 2017, 22, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loss, S.R.; Noden, B.H.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Woody plant encroachment and the ecology of vector-borne diseases. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 59, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, M. Contentious Agency and Natural Resource Politics; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.C.; Ordoñez, P.J.; Brown, S.E.; Forrest, S.; Nava, N.J.; Hughes, K.; Baylis, K. The impacts of agroforestry on agricultural productivity, ecosystem services, and human well-being in low-and middle-income countries: An evidence and gap map. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2020, 16, e1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jalón, S.G.; Graves, A.; Palma, J.H.N.; Williams, A.; Upson, M.; Burgess, P.J. Modelling and valuing the environmental impacts of arable, forestry and agroforestry systems: A case study. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, P.; Rezaei, E.E.; Breuer, L.; Ewert, F.; Große-Stoltenberg, A.; Kleinebecker, T.; Seserman, D.M.; Nendel, C. Modelling Agroforestry’s Contributions to People—A Review of Available Models. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtfouse, E.; Navarrete, M.; Debaeke, P.; Souchère, V.; Alberola, C. Sustainable Agriculture; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; ISBN 9789048126651. [Google Scholar]
- Paraskevopoulou, C.; Theodoridis, A.; Johnson, M.; Ragkos, A.; Arguile, L.; Smith, L.; Vlachos, D.; Arsenos, G. Sustainability Assessment of Goat and Sheep Farms: A Comparison between European Countries. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.G.; Westaway, S.; Mullender, S.; Ghaley, B.B.; Xu, Y.; Lehmann, L.M.; Pisanelli, A.; Russo, G.; Borek, R.; Wawer, R.; et al. Assessing the multidimensional elements of sustainability in European agroforestry systems. Agric. Syst. 2022, 197, 103357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häni, F.; Stämpfli, A.; Tello, J.R.; Braga, F. Farm Sustainability Assessment using the IDEA Method. From the concept of farm sustainability to case studies on French farms. In Proceedings of the INFASA Symposium, Bern, Switzerland, 16–17 March 2006; Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-02278989 (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Porsche, H.; Fischer, M.; Braga, F.; Häni, F. Introduction of the Sustainability Assessment Tool RISE into Canadian Agriculture. J. Univ. Guelph. 2004, 11, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
- Grenz, J.; Thalmann, C.; Stämpfli, A.; Studer, C.; Häni, F. Rise, a Method for Assessing the Sustainability of Agricultural Production at Farm Level. Available online: https://www.hafl.bfh.ch/fileadmin/docs/Forschung_Dienstleistungen/Agrarwissenschaften/Nachhaltigkeitsbeurteilung/RISE/Publikationen/E_RDN_1_2009.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Heredia-R, M.; Torres, B.; Cayambe, J.; Ramos, N.; Luna, M.; Diaz-Ambrona, C.G.H. Sustainability Assessment of Smallholder Agroforestry Indigenous Farming in the Amazon: A Case Study of Ecuadorian Kichwas. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Safa Sustainability Assessment of Food and Agriculture Systems Guidelines. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3957e.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2022).
- Dhiman, R. Status and Impact of Commercial Agroforestry in India; Indian Society of Agroforestry: Jhansi, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nagendra, H. Drivers of Reforestation in Human-Dominated Forests. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15218–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinzen-Dick, R. Beyond panaceas in water institutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15200–15205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Western, D.; Wright, R.M.; Strum, S.C. Natural Connections Perspectives in Community-Based Conservation; Shirley, C., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; ISBN 1-55963-802-8. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, D.; Klepeis, P. Deforestation, Forest Transitions, and Institutions for Sustainability in Southeastern Mexico, 1900–2000. Environ. Hist. 2005, 11, 194–223. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, E. The Economic Analysis of Institutions Ions and the Environment; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, M. Toward a Comparative Institutional Analysis; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001; ISBN 0-262-26721-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ostrom, E. Governing the Commons: The Evolution of Institutions for Collective Action; Canto Classics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015; ISBN 1-316-45536-X. [Google Scholar]
- Binam, J.N.; Place, F.; Djalal, A.A.; Kalinganire, A. Effects of local institutions on the adoption of agroforestry innovations: Evidence of farmer managed natural regeneration and its implications for rural livelihoods in the Sahel. Agric. Food Econ. 2017, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).