Initial Floristic Response to High Severity Wildfire in an Old-Growth Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens (D. Don) Endl.) Forest
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Sampling Design and Measurements
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
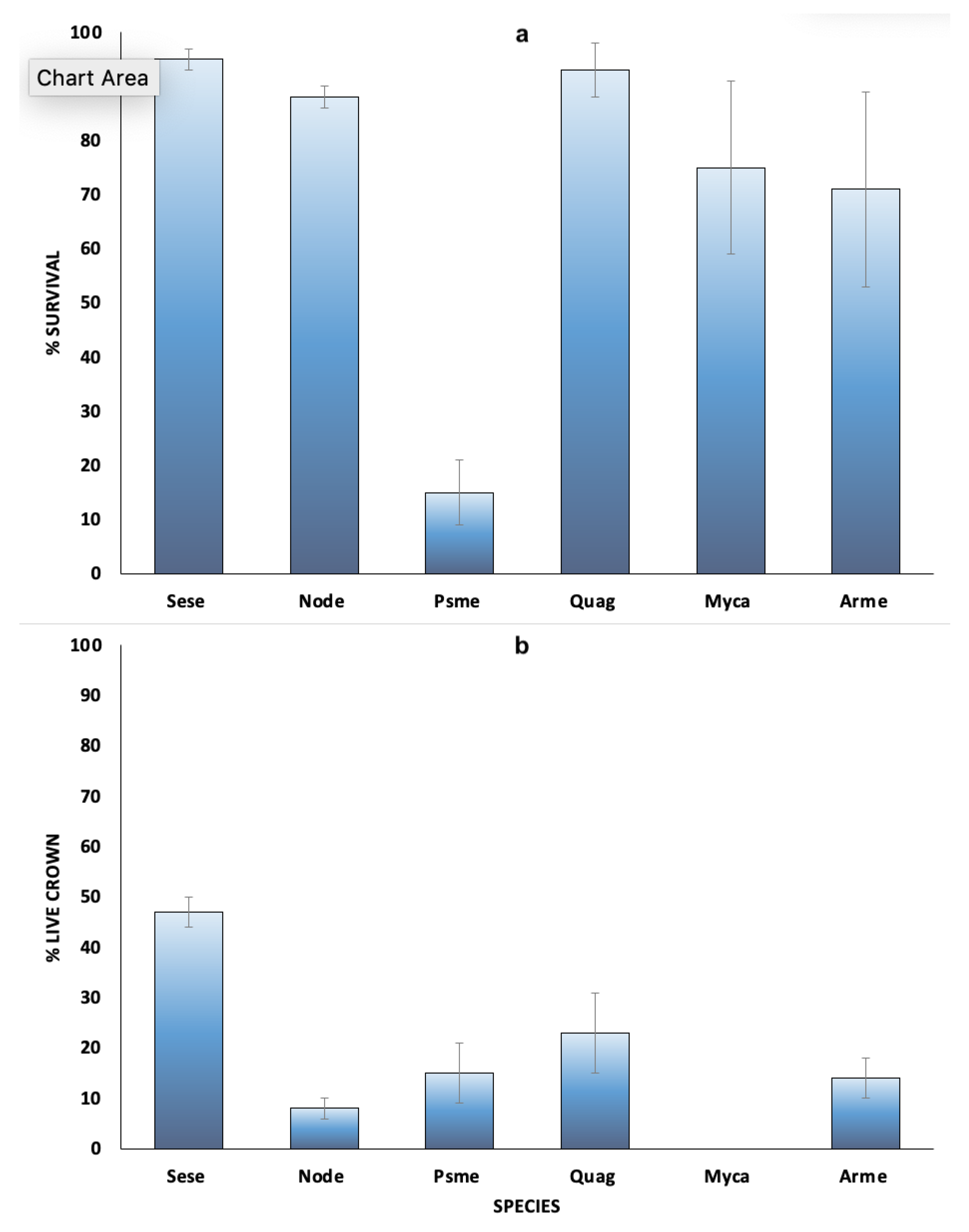
3.1. Post Fire Survival
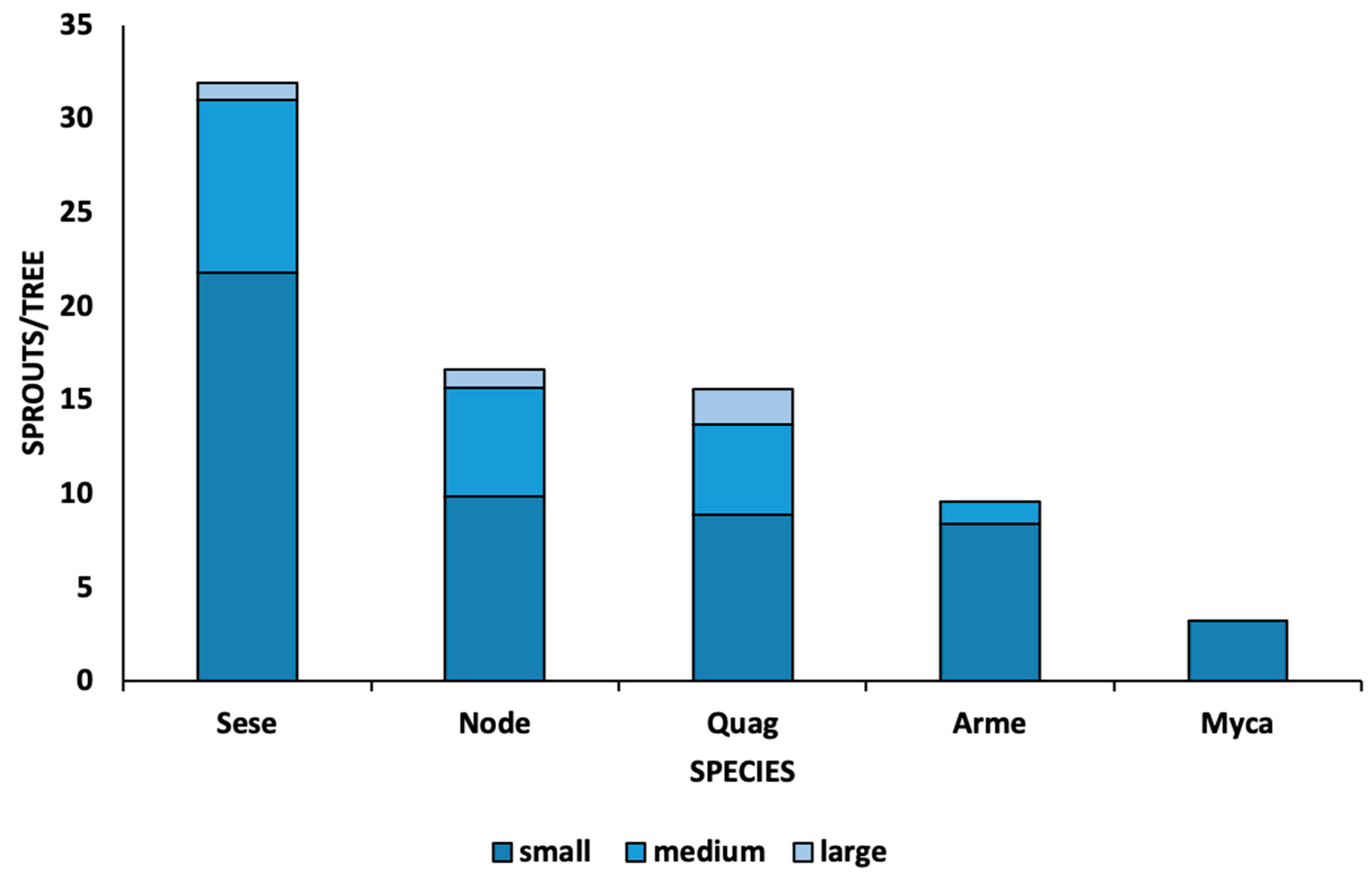
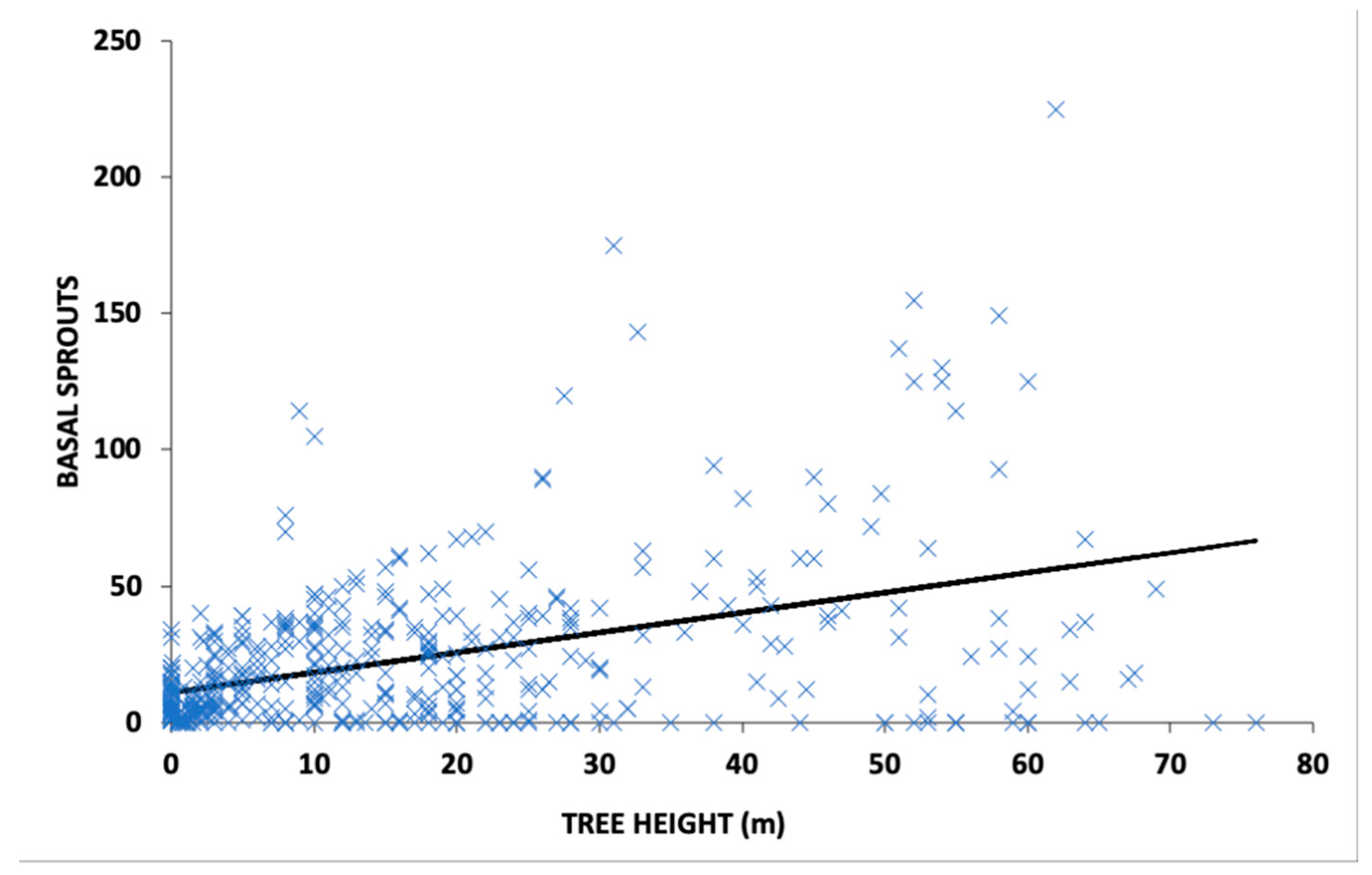
3.2. Post Fire Recovery of Trees
3.3. Reestablishment of Understory Species
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keeley, J.E. Fire in Mediterranean climate ecosystems—A comparative overview. J. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 58, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J. Global change and forest disturbances in the Mediterranean basin: Breakthroughs, knowledge gaps, and recommendations. Forests 2021, 12, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, J.E. Fire intensity, fire severity and burn severity: A brief review and suggested usage. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2009, 18, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedia, J.; Herrera, S.; Camia, A.; Moreno, J.M.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Forest fire danger projections in the Mediterranean using ENSEMBLES regional climate change scenarios. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stephens, S.L.; Agee, J.K.; Fule, P.Z.; North, M.P.; Romme, W.H.; Swetnam, T.W.; Turner, M.G. Managing forests and fire in changing climates. Science 2013, 342, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, S.L.; Collins, B.M.; Fettig, C.J.; Finney, M.A.; Hoffman, C.M.; Knapp, E.E.; North, M.P.; Safford, H.; Wayman, R.B. Drought, tree mortality, and wildfire in forests adapted to frequent fire. BioScience 2018, 68, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steel, Z.L.; Safford, H.D.; Viers, J.H. The fire frequency-severity relationship and the legacy of fire suppression in California forests. Ecosphere 2015, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, J.A.; Dawson, T.E. Climatic context and ecological implications of summer fog decline in the coast redwood region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4533–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.L.; Sillett, S.C.; Van Pelt, R. Tree-ring indicators of fire in two old-growth coast redwood forests. Fire Ecol. 2018, 14, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, P.M.; Baxter, W.T. Fire history in coast redwood forests of the Mendocino Coast, California. Northwest Sci. 2003, 77, 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee, J.M.; Langenheim, J.H. Historic fire regimes and their relation to vegetation patterns in the Monterey Bay area of California. Am. Midl. Nat. 1990, 124, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Russell, W. Approximation of fire-return intervals with point samples in the southern range of the coast redwood forest, California, USA. Fire Ecol. 2015, 11, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorimer, C.G.; Porter, D.J.; Madej, M.A.; Stuart, J.D.; Veirs, S.D.; Norman, S.P.; O’Hara, K.L.; Libby, W.J. Presettlement and modern disturbance regimes in coast redwood forests: Implications for the conservation of old-growth stands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 258, 1038–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, S.L.; Fry, D.L. Fire history in coast redwood stands in the northeastern Santa Cruz Mountains, California. Fire Ecol. 2005, 1, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendan, R.M.; Neilson, R.P.; Drapek, R.; Lenihan, J.M.; Wells, J.R.; Bachelet, D.; Law, B.E. Impacts of climate change on fire regimes and carbon stocks of the U.S. Pacific Northwest. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116, G3. [Google Scholar]
- Dennison, P.E.; Brewer, S.C.; Arnold, J.D.; Moritz, M.A. Large wildfire trends in the western United States, 1984–2011. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2928–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrill, J.; O’Hara, K.L.; Kichas, N.E. Bark thickness in coast redwood (Sequoia Sempervirens (D. Don) Endl.) varies according to tree- and crown size, stand structure, atitude and genotype. Forests 2020, 11, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri-Aerts, R.; Russell, W. Survival and recovery following wildfire in the southern range of the coast redwood forest. Fire Ecol. 2014, 10, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.T.; Odion, D.C.; DellaSala, D.A.; Baker, W.L. Overestimation of fire risk in the Northern Spotted Owl Recovery Plan. Conserv. Biol. 2009, 23, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganio, L.M.; Progar, R.A. Mortality predictions of fire-injured large Douglas-fir and ponderosa pine in Oregon and Washington, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 390, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tappeiner, J.C., II; McDonald, P.M. Development of tanoak understories in conifer stands. Can. J. For. Res. 1984, 14, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, J.B.; Martin, R.E. Sprouting shrub response to different seasons and fuel consumption levels of prescribed fire in Sierra Nevada mixed conifer ecosystems. For. Sci. 1990, 36, 748–764. [Google Scholar]
- Ramage, B.S.; O’Hara, K.L.; Caldwell, B.T. The role of fire in the competitive dynamics of coast redwood forests. Ecosphere 2010, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneal, C.B.; Stuart, J.D.; Steinberg, S.J.; Fox, L. Geographic analysis of natural fire rotation in the California redwood forest during the suppression era. Fire Ecol. 2006, 2, 73–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, B.D.; Dietterick, B.C.; White, R.A.; Mastin, T.B. Classification of plot-level fire-caused tree mortality in a redwood forest using digital orthophotography and LiDAR. Remote. Sens. 2014, 6, 1954–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torn, M.S.; Fried, J.S. Predicting the impacts of global warming on wildland fire. Clim. Chang. 1992, 21, 257–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limm, E.B.; Dawson, T.E. Polystichum munitum (Dryopteridaceae) varies geographically in its capacity to absorb fog water by foliar uptake within the redwood forest ecosystem. Am. J. Bot. 2010, 97, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriondo, M.; Good, P.; Durao, R.; Bindi, M.; Giannakopoulos, C.; Corte-Real, J. Potential impact of climate change on fire risk in the Mediterranean area. Clim. Res. 2006, 31, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenihan, J.M.; Bachelet, D.; Neilson, R.P.; Drapek, R. Response of vegetation distribution, ecosystem productivity, and fire to climate change scenarios for California. Clim. Chang. 2008, 87, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, B.D.; Romme, W.H.; Evangelista, P.H. Early postfire response of a northern range margin coast redwood forest community. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 462, 117966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, G.E. Syncarpia and Tristaniopsis (Myrtaceae) possess specialized fire-resistant epicormic structures. Aust. J. Bot. 2008, 56, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, G.E. Epicormic strand structure in Angophora, Eucalyptus and Lophostemon (Myrtaceae)-implications for fire resistance and recovery. New Phytol. 2002, 153, 111–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pelt, R.; Sillett, S.C. Crown development of coastal Pseudotsuga menziesii, including a conceptual model for tall conifers. Ecol. Monogr. 2008, 78, 283–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, K.L.; Valappil, N.I. Epicormic sprouting of pruned western larch. Can. J. For. Res. 2000, 30, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowman, D.; Russell, W. Fuel load, stand structure, and understory species composition following prescribed fire in an old-growth coast redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) forest. Fire Ecol. 2021, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, W. Herbaceous understory indicators of post-harvest recovery in coast redwood (Sequoia sempervirens) forests. Open J. For. 2020, 10, 204–216. [Google Scholar]


| Species | Mean% Cover (±SE) |
|---|---|
| All species combined | 3.97 (±1.6) |
| Vaccinium ovatum Pursh. | 2.79 (±1.4) |
| Equisetum arvense L. | 0.67 (±0.67) |
| Polystichum munitum (Kaulf.) C. Presl. | 0.31 (±0.30) |
| Viola sempervirens Greene | 0.31 (±0.30) |
| Stachys bullata Benth. | 0.30 (±0.30) |
| Oxalis oregana Nutt. | 0.20 (±0.17) |
| Galium spp. | 0.17 (±0.17) |
| Cardamine californica (Nutt.) Greene | 0.04 (±0.33) |
| Trillium ovatum Pursh | 0.02 (±0.01) |
| Pteridium aquilinum (L.) Kuhn | 0.01 (±0.01) |
| Lysimachia latifolia (Hook.) Cholewa | 0.01 (±0.01) |
| Toxicoscordion fremontii (Torr.) Rydb. | 0.01 (±0.01) |
| Rubus ursinus Cham. & Schltdl. | 0.01 (±0.01) |
| Adenocaulon bicolor Hook. | 0.01 (±0.01) |
| Viola cuneate S. Watson | 0.01 (±0.01) |
| Prosartes hookeri Torr. | 0.01 (±0.01) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahdizadeh, M.; Russell, W. Initial Floristic Response to High Severity Wildfire in an Old-Growth Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens (D. Don) Endl.) Forest. Forests 2021, 12, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12081135
Mahdizadeh M, Russell W. Initial Floristic Response to High Severity Wildfire in an Old-Growth Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens (D. Don) Endl.) Forest. Forests. 2021; 12(8):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12081135
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahdizadeh, Mojgan, and Will Russell. 2021. "Initial Floristic Response to High Severity Wildfire in an Old-Growth Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens (D. Don) Endl.) Forest" Forests 12, no. 8: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12081135
APA StyleMahdizadeh, M., & Russell, W. (2021). Initial Floristic Response to High Severity Wildfire in an Old-Growth Coast Redwood (Sequoia sempervirens (D. Don) Endl.) Forest. Forests, 12(8), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12081135






