Effect of Forest Management Operations on Aggregate-Associated SOC Dynamics Using a 137Cs Tracing Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
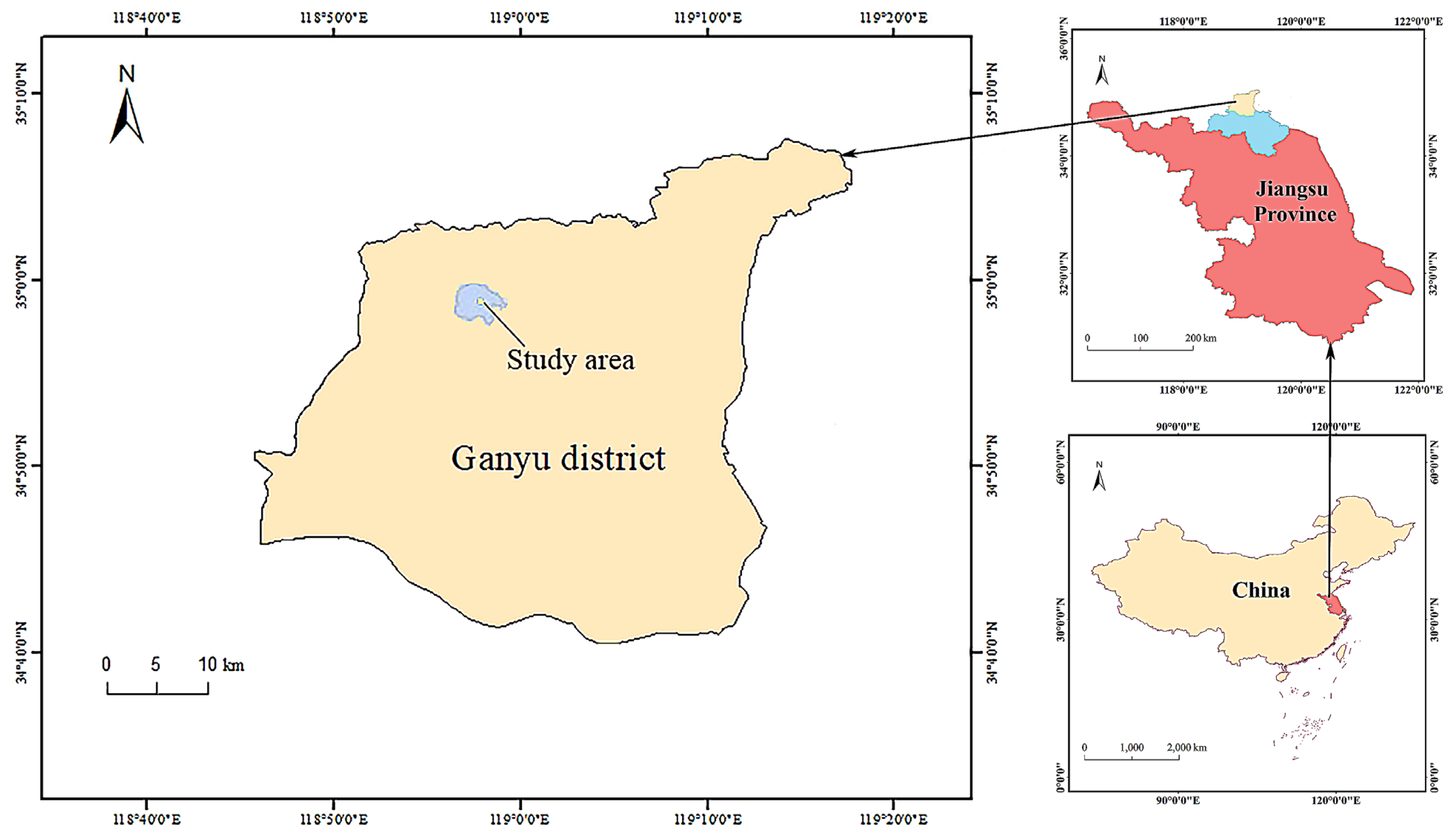
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.4. Soil Aggregate Fractionation
2.5. Calculations
2.6. SOC Storage Estimation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties after Forest Conversion
3.2. Soil Aggregate Fractions and Stability
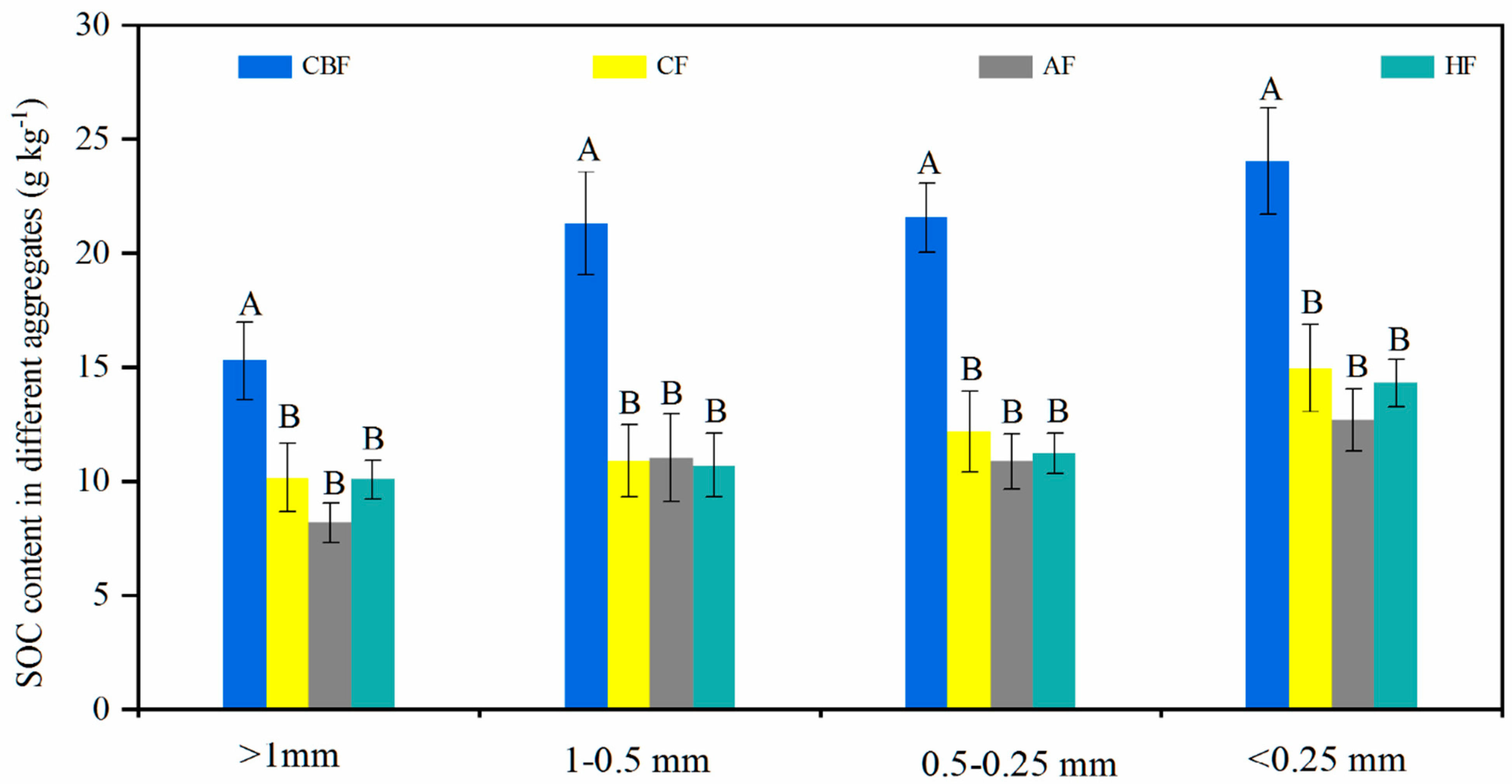
3.3. Aggregate-Associated SOC Contents
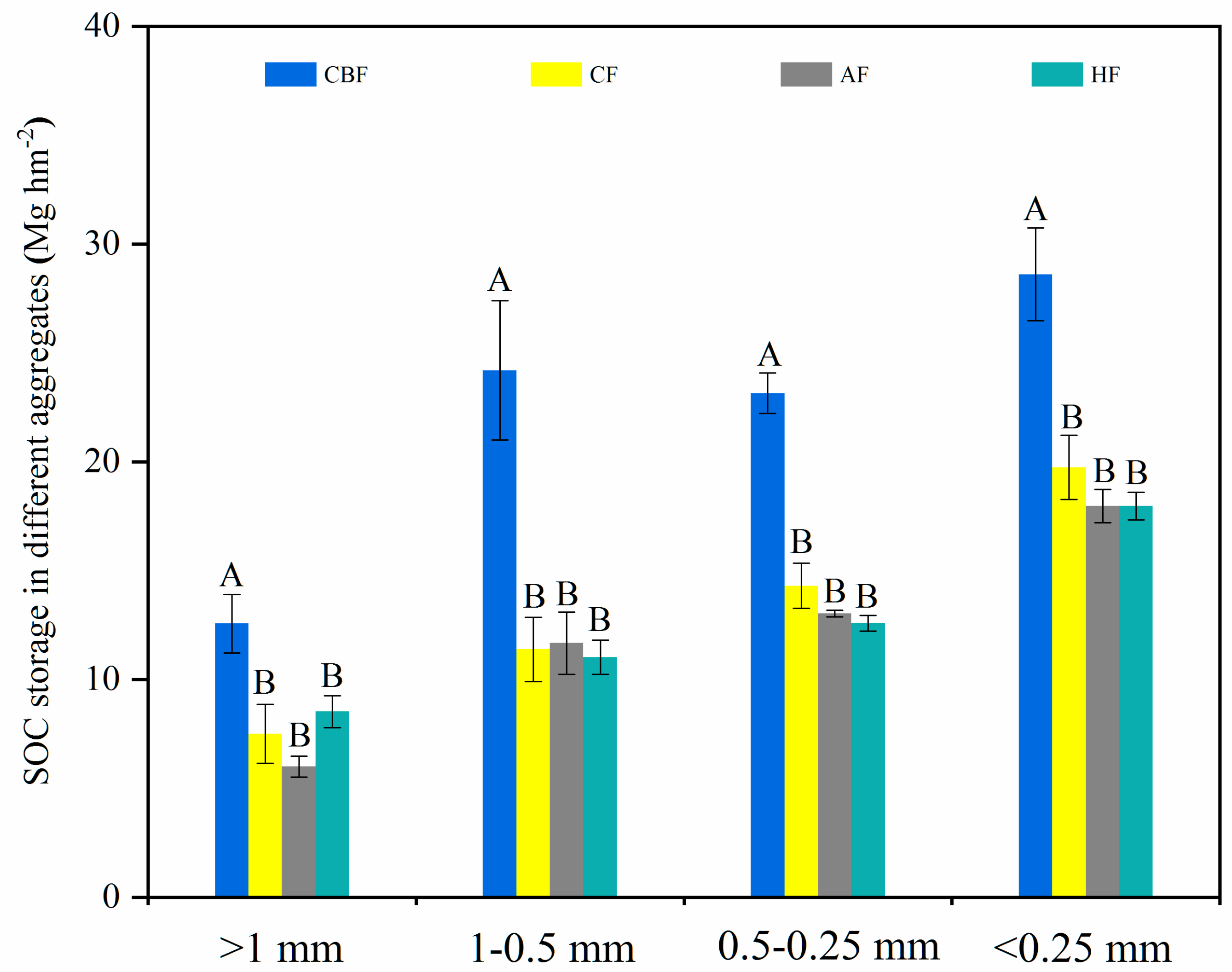
3.4. SOC Sequestration of Soil Aggregates
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Forest Conversion on the Distribution and Stability of Soil Aggregates
4.2. Effect of Forest Conversion on Aggregate-Associated SOC Storage
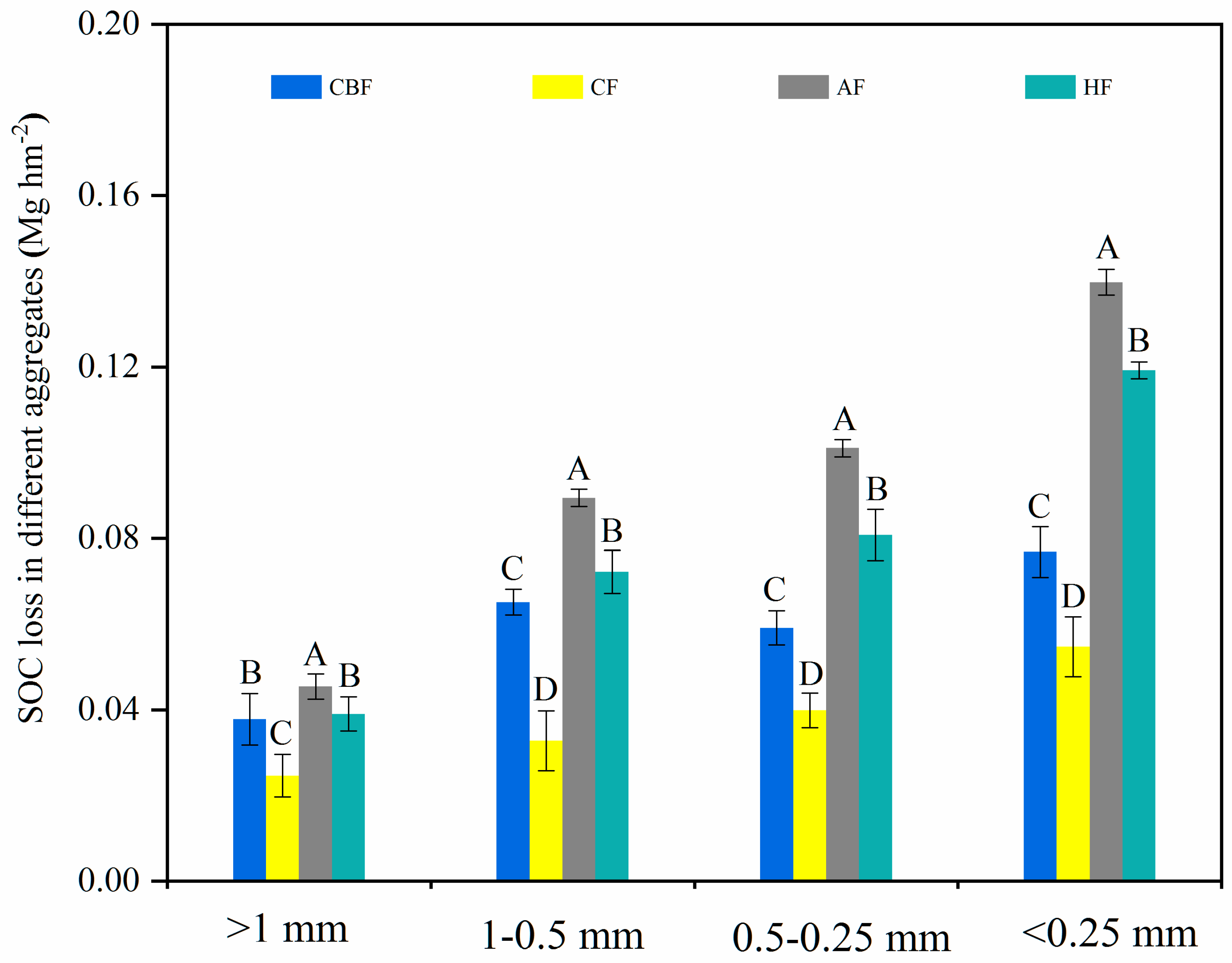
4.3. Estimation of SOC Loss Using 137CS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deng, L.; Kim, D.-G.; Li, M.; Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, M.; Shangguan, Z.; Peng, C. Land-use changes driven by ‘Grain for Green’ program reduced carbon loss induced by soil erosion on the Loess Plateau of China. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2019, 177, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yu, P.; Li, G.; Zhou, D.; Chen, X. Overlooking soil erosion induces underestimation of the soil C loss in degraded land. Quat. Int. 2014, 349, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ran, L.; Fang, N.; Shi, Z. Aggregate stability and associated organic carbon and nitrogen as affected by soil erosion and vegetation rehabilitation on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2018, 167, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiuSui, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, D.; Yan, C.; Sun, T.; Jia, H.; Zhao, X. Soil aggregate and intra-aggregate carbon fractions associated with vegetation succession in an alpine wetland of Northwest China. Catena 2019, 181, 104107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Callewaert, P.; Lenders, S.; De Gryze, S.; Morris, S.J.; Gregorich, E.G.; Paul, E.A.; Paustian, K. Measuring and Understanding Carbon Storage in Afforested Soils by Physical Fractionation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Meena, V.; Alam, N.; Dogra, P.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Sharma, N.; Mishra, P. Impact of conservation practices on soil aggregation and the carbon management index after seven years of maize–wheat cropping system in the Indian Himalayas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 216, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jin, J.; Yu, P.; Fu, W.; Morrison, L.; Lin, H.; Meng, M.; Zhou, X.; Lv, Y.; Wu, J. Converting evergreen broad-leaved forests into tea and Moso bamboo plantations affects labile carbon pools and the chemical composition of soil organic carbon. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 711, 135225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Lin, H.; Fu, W.; Penttinen, P.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Zhao, K.; Wu, J. Soil organic carbon content and microbial functional diversity were lower in monospecific chinese hickory stands than in natural chinese hickory–broad-leaved mixed forests. Forests 2019, 10, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.; et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the World’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chang, S.; Jiang, P.; Zhou, G.; Shen, Z.; Wu, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, M. Converting native shrub forests to Chinese chestnut plantations and subsequent intensive management affected soil C and N pools. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 312, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Li, Z. Soil aggregate-associated organic carbon dynamics subjected to different types of land use: Evidence from 13C natural abundance. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 122, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, G.-H.; Geng, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. Land use impacts on soil detachment capacity by overland flow in the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2015, 124, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Influences of intensive tillage on water-stable aggregate distribution on a steep hillslope. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 151, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidhuner, A.; Hanauer, A.; Krausz, R.; Crittenden, S.J.; Gage, K.; Sadeghpour, A. Tillage impacts on soil aggregation and aggregate-associated carbon and nitrogen after 49 years. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, C.C.; Gebresamuel, G.; Zenebe, A.; Haile, M.; Eze, P.N. Accumulation of organic carbon in various soil aggregate sizes under different land use systems in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 297, 106924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fu, S.; Liu, W.; Ren, C.; Yang, G.; Ren, G. Effects of land use change on organic carbon dynamics associated with soil aggregate fractions on the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Kukal, S.S.; Sharma, S. Landuse impacts on SOC fractions and aggregate stability in typic ustochrepts of Northwest India. Plant Soil 2011, 339, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, Q. Soil aggregate breakdown in response to wetting rate during the inter-rill and rill stages of erosion in a contour ridge system. Catena 2017, 157, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil erosion and carbon dynamics. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 81, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dong, Y.; Cheng, F.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Variation of soil organic carbon and land use in a dry valley in Sichuan province, Southwestern China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermang, J.; Demeyer, V.; Cornelis, W.; Gabriels, D. Aggregate stability and erosion response to antecedent water content of a loess soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2009, 73, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Zeng, Z.; Du, H.; Zou, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, F. Large-scale patterns in forest growth rates are mainly driven by climatic variables and stand characteristics. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 435, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesterdal, L.; Ritter, E.; Gundersen, P. Change in soil organic carbon following afforestation of former arable land. For. Ecol. Manag. 2002, 169, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Deng, J.; Wang, B. Afforestation affects soil seed banks by altering soil properties and understory plants on the eastern Loess Plateau, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 126, 107670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, J.; Chen, C.; Xu, Z.; Ghadiri, H. Soluble organic nitrogen pools in adjacent native and plantation forests of subtropical Australia. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 2723–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eclesia, R.P.; Jobbagy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Biganzoli, F.; Piñeiro, G. Shifts in soil organic carbon for plantation and pasture establishment in native forests and grasslands of South America. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2012, 18, 3237–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-L.; Pang, X.-M. Effect of land-use conversion on C and N distribution in aggregate fractions of soils in the southern Loess Plateau, China. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiho, R.; Sanchez, F.; Tiarks, A.; Dougherty, P.M.; Trettin, C.C. Impacts of intensive forestry on early rotation trends in site carbon pools in the southeastern US. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 174, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.; Lin, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Impacts of forest conversion on soil bacterial community composition and diversity in subtropical forests. Catena 2019, 175, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-S.; Jiang, P.-K.; Chang, S.; Xu, Q.-F.; Lin, Y. Dissolved soil organic carbon and nitrogen were affected by conversion of native forests to plantations in subtropical China. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 90, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Meng, M.; Guo, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, K.; Ding, L.; Shao, Y.; Fu, W. Forest-type shift and subsequent intensive management affected soil organic carbon and microbial community in southeastern China. Eur. J. For. Res. 2017, 136, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Chen, H.; Meng, M.; Biswas, S.; Ye, L.; Zhang, J. Effects of land use change on the composition of soil microbial communities in a managed subtropical forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 373, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z. Effects of soil aggregate stability on soil N following land use changes under erodible environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Zhu, A.-N.; Zhang, J.-B.; Yang, W.-L.; Xin, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-F. Changes in soil organic carbon and aggregate stability after conversion to conservation tillage for seven years in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Y. Aggregate stability and size distribution of red soils under different land uses integrally regulated by soil organic matter, and iron and aluminum oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 167, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Fan, X.; Ren, C.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Doughty, R. Changes of the organic carbon content and stability of soil aggregates affected by soil bacterial community after afforestation. Catena 2018, 171, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lin, J.; Dai, Q.; Xu, Y.; Li, H. Evaluation of Forest Conversion Effects on Soil Erosion, Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen Based on Cs-137 Tracer Technique. Forests 2019, 10, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, A.A.; Harte, J.; Harden, J.W.; Torn, M. The significance of the erosion-induced terrestrial carbon sink. Bioscience 2007, 57, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Liu, L.; Xiao, H.; Liu, C.; Zeng, G. Thermal stability of organic carbon in soil aggregates as affected by soil erosion and deposition. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; He, Q.; Blake, W. Use of 7Be and 137Cs measurements to document short- and medium-term rates of water-induced soil erosion on agricultural land. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-H.; Yan, B.-X.; Zhu, H. Estimating soil erosion in Northeast China using 137Cs and 210Pbex. Pedosphere 2011, 21, 706–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koarashi, J.; Nishimura, S.; Atarashi-Andoh, M.; Matsunaga, T.; Sato, T.; Nagao, S. Radiocesium distribution in aggregate-size fractions of cropland and forest soils affected by the Fukushima nuclear accident. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrb, I. World Reference Base for Soil Resources, 2nd ed.; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Fierro, V.; Fernández-Huerta, N.; Izquierdo, M.T.; Celzard, A. Hydrogen uptake of high surface area-activated carbons doped with nitrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 10453–10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeney, D.R. Chemical and microbiological properties. In Methods of Soil Analysis; American Society of Agronomy Inc & Soil Science Society of America Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.L.; Willett, V.B. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISSAS. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1978; pp. 515–517. [Google Scholar]
- Bavel, C. Mean weight-diameter of soil aggregates as a statistical index of aggregation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1950, 14, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, W.R. Representation of soil aggregate-size distribution by a logarithmic-normal distribution. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1956, 20, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, G. Soil particle size distribution characteristics of different land-use types in the Funiu mountainous region. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 184, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellert, B.H.; Bettany, J.R. Calculation of organic matter and nutrients stored in soils under contrasting management regimes. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1995, 75, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Xie, J.; Ukonmaanaho, L.; Jiang, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, W.; Yang, Y. Land use change exerts a strong impact on deep soil C stabilization in subtropical forests. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 17, 2305–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix-Solera, J.; Cerdà, A.; Arcenegui, V.; Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.M. Fire effects on soil aggregation: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2011, 109, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil macroaggregate turnover and microaggregate formation: A mechanism for C sequestration under no-tillage agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, T.; Rashid, M.I.; Maire, V.; Barot, S.; Perveen, N.; Alvarez, G.; Fontaine, S. Root penetration in deep soil layers stimulates mineralization of millennia-old organic carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearden, B.N.; Petersen, L. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on soil structure and aggregate stability of a vertisol. Plant Soil 2000, 218, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes Sá, J.C.; Gonçalves, D.R.P.; Ferreira, L.A.; Mishra, U.; Inagaki, T.M.; Furlan, F.J.F.; de Oliveira Ferreira, A. Soil carbon fractions and biological activity based indices can be used to study the impact of land management and ecological successions. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Haack, S.E.; Lin, W.; Li, B.; Wu, L.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Z. Soil microbial community structure and metabolic activity of pinus elliottii plantations across different stand ages in a Subtropical Area. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, Q. Evolution of the soil bacterial community structure during the development of pinus massoniana plantations in subtropical china. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2019, 22, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Puget, P.; Chenu, C.; Balesdent, J. Dynamics of soil organic matter associated with particle-size fractions of water-stable aggregates. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 51, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, E.T. Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merilä, P.; Malmivaara-Lämsä, M.; Spetz, P.; Stark, S.; Vierikko, K.; Derome, J.; Fritze, H. Soil organic matter quality as a link between microbial community structure and vegetation composition along a successional gradient in a boreal forest. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fu, B.; Lü, Y.; Chen, L. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil organic carbon sequestration at multiple scales in semi-arid Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2011, 85, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhu, H.; Fu, W.; Shao, M. Responses of soil aggregate stability, erodibility and nutrient enrichment to simulated extreme heavy rainfall. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 709, 136150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wright, A.L.; Wang, X.; Liang, F. Tillage-induced changes in fungal and bacterial biomass associated with soil aggregates: A long-term field study in a subtropical rice soil in China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2011, 48, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdall, J.M.; Oades, J.M. Organic matter and water-stable aggregates in soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Mentler, A.; Mayer, H.; Blum, W.E. Soil aggregation, aggregate stability, organic carbon and nitrogen in different soil aggregate fractions under forest and shrub vegetation on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2010, 81, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Kuhn, N.J. Erosion-induced exposure of SOC to mineralization in aggregated sediment. Catena 2016, 137, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.; Paustian, K.; Doran, J.W. Aggregation and soil organic matter accumulation in cultivated and native grassland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-S.; Yang, Z.-J.; Gao, R.; Xie, J.-S.; Guo, J.-F.; Huang, Z.-Q.; Yang, Y.-S. Carbon storage in a chronosequence of Chinese fir plantations in southern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 300, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Song, X.-L.; Lu, X.-G.; Xue, Z. Ecological stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in estuarine wetland soils: Influences of vegetation coverage, plant communities, geomorphology, and seawalls. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Flessa, H.; Veldkamp, E.; López-Ulloa, M. Stabilization of recent soil carbon in the humid tropics following land use changes: Evidence from aggregate fractionation and stable isotope analyses. Biogeochemistry 2008, 87, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bateman, I.J.; Mace, G.; Fezzi, C.; Atkinson, G.; Turner, K. Economic analysis for ecosystem service assessments. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2010, 48, 177–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ma, P.; Zhai, B.; Zhou, J. Soil moisture decline and residual nitrate accumulation after converting cropland to apple orchard in a semiarid region: Evidence from the Loess Plateau. Catena 2019, 181, 104080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, G.; Yin, Y.; Gao, R.; Lin, C. Effects of forest conversion on soil labile organic carbon fractions and aggregate stability in subtropical China. Plant Soil 2009, 323, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Raga, M.; Palencia, C.; Keesstra, S.; Jordán, A.; Fraile, R.; Angulo-Martinez, M.; Cerdà, A. Splash erosion: A review with unanswered questions. Earth Sci. Rev. 2017, 171, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Accelerated soil erosion as a source of atmospheric CO2. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 188, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, A.A.; Barnes, R.T.; Six, J.; Marín-Spiotta, E. Role of soil erosion in biogeochemical cycling of essential elements: Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2018, 46, 521–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Forest | Human | Age [38] | LAI [38] | Litter Thickness [38] | Slope [38] | Aspect [38] | 137Cs Content [38] | Percentage137Cs Loss [38] | Soil Erosion Modulus | Soil Loss Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types | interference | (year) | (mm) | (°) | (Bq m−2) | (%) | (t km−2 a−1) | (mm) | ||
| CBF | None | 25 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 13 | SE | 546.92 | 68.4 | 1113.73 | 0.79 |
| CF | Weak | 13 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 11 | SE | 495.89 | 71.4 | 1275.35 | 0.87 |
| AF | Strong | 10 | 2.2 | 0 | 13 | SE | 60.6 | 96.5 | 3328.2 | 2.31 |
| HF | Strong | 11 | 2.1 | 0 | 15 | SE | 123.89 | 92.9 | 2606.7 | 1.84 |
| Parameters | CBF | CF | AF | HF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BD (g/cm3) [38] | 1.44 ± 0.12A | 1.43 ± 0.05A | 1.47 ± 0.18A | 1.42 ± 0.12A |
| pH [38] | 5.67 ± 0.27AB | 5.95 ± 0.34A | 5.48 ± 0.26B | 5.67 ± 0.27A |
| Sand (%) [38] | 36.59 ± 7.53AB | 31.57 ± 7.83BC | 41.07 ± 8.65A | 30.84 ± 5.05C |
| Silt (%) [38] | 60.21 ± 6.96AB | 64.66 ± 6.66A | 56.63 ± 4.36B | 65.00 ± 5.63A |
| Clay (%) [38] | 3.20 ± 0.41AB | 3.77 ± 0.18AB | 2.29 ± 0.23B | 4.16 ± 0.36A |
| SSA (m2 g−1) | 2.14 ± 0.17A | 2.26 ± 0.23A | 3.07 ± 0.43A | 2.57 ± 0.82A |
| TN (g kg−1) | 2.57 ± 0.32A | 1.35 ± 0.11B | 1.21 ± 0.03B | 1.52 ± 0.10B |
| C/N | 9.10 ± 0.26A | 7.03 ± 0.67BC | 6.66 ± 0.16C | 7.73 ± 0.26BC |
| C/H | 4.06 ± 0.20A | 2.03 ± 0.30B | 2.17 ± 0.12B | 2.56 ± 0.13B |
| SOC (g kg−1) | 30.86 ± 4.87A | 18.87 ± 1.50B | 11.55 ± 2.18B | 13.83 ± 1.78B |
| DOC (g kg−1) | 0.27 ± 0.02A | 0.26 ± 0.02A | 0.27 ± 0.06A | 0.23 ± 0.06A |
| Parameters | CBF | CF | AF | HF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >1 mm (%) | 21.56 ± 2.08A | 19.6 ± 1.21B | 16.35 ± 1.81C | 14.81 ± 1.56C |
| 1–0.5 mm (%) | 26.64 ± 2.65A | 24.31 ± 1.64A | 23.86 ± 1.17A | 25.81 ± 1.44A |
| 0.5–0.25 mm (%) | 23.91 ± 2.02B | 26.52 ± 1.45A | 27.38 ± 0.90A | 27.52 ± 1.47A |
| <0.25 mm (%) | 27.89 ± 2.73C | 29.58 ± 1.79B | 32.41 ± 2.13A | 31.86 ± 2.49A |
| MWD (mm) | 0.82 ± 0.08A | 0.80 ± 0.02A | 0.66 ± 0.04B | 0.67 ± 0.02B |
| GMD (mm) | 0.51 ± 0.03A | 0.47 ± 0.01B | 0.42 ± 0.02C | 0.43 ± 0.02C |
| FD | 2.14 ± 0.06C | 2.19 ± 0.07B | 2.24 ± 0.07A | 2.23 ± 0.07A |
| K | 0.06 ± 0.01C | 0.07 ± 0.02B | 0.08 ± 0.01A | 0.08 ± 0.02A |
| Parameters | >1 mm | 1–0.5 mm | 0.5–0.25 mm | <0.25 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 137Cs | 0.48 * | 0.67 ** | 0.68 ** | 0.77 ** |
| >1 mm | 0.76 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.54 ** | |
| 1–0.5 mm | 0.84 ** | 0.69 ** | ||
| 0.5–0.25 mm | 0.81 ** | |||
| <0.25 mm | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Zeng, G.; Lin, J. Effect of Forest Management Operations on Aggregate-Associated SOC Dynamics Using a 137Cs Tracing Method. Forests 2021, 12, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070859
Guo G, Li X, Zhu X, Xu Y, Dai Q, Zeng G, Lin J. Effect of Forest Management Operations on Aggregate-Associated SOC Dynamics Using a 137Cs Tracing Method. Forests. 2021; 12(7):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070859
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Geng, Xiao Li, Xi Zhu, Yanyin Xu, Qiao Dai, Guangruo Zeng, and Jie Lin. 2021. "Effect of Forest Management Operations on Aggregate-Associated SOC Dynamics Using a 137Cs Tracing Method" Forests 12, no. 7: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070859
APA StyleGuo, G., Li, X., Zhu, X., Xu, Y., Dai, Q., Zeng, G., & Lin, J. (2021). Effect of Forest Management Operations on Aggregate-Associated SOC Dynamics Using a 137Cs Tracing Method. Forests, 12(7), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12070859






