Stand Structure and Abiotic Factors Modulate Karst Forest Biomass in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
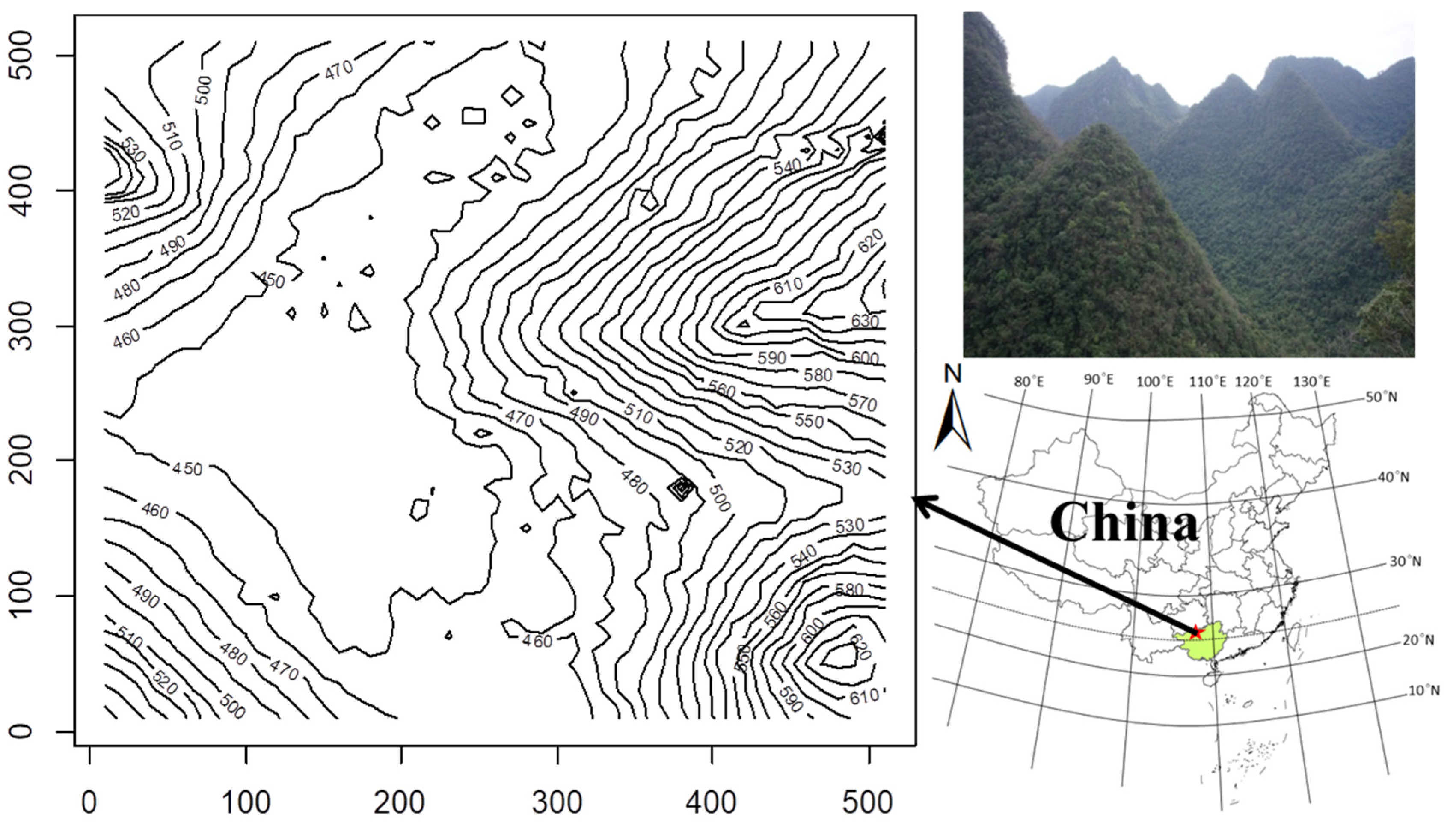
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Predictor Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
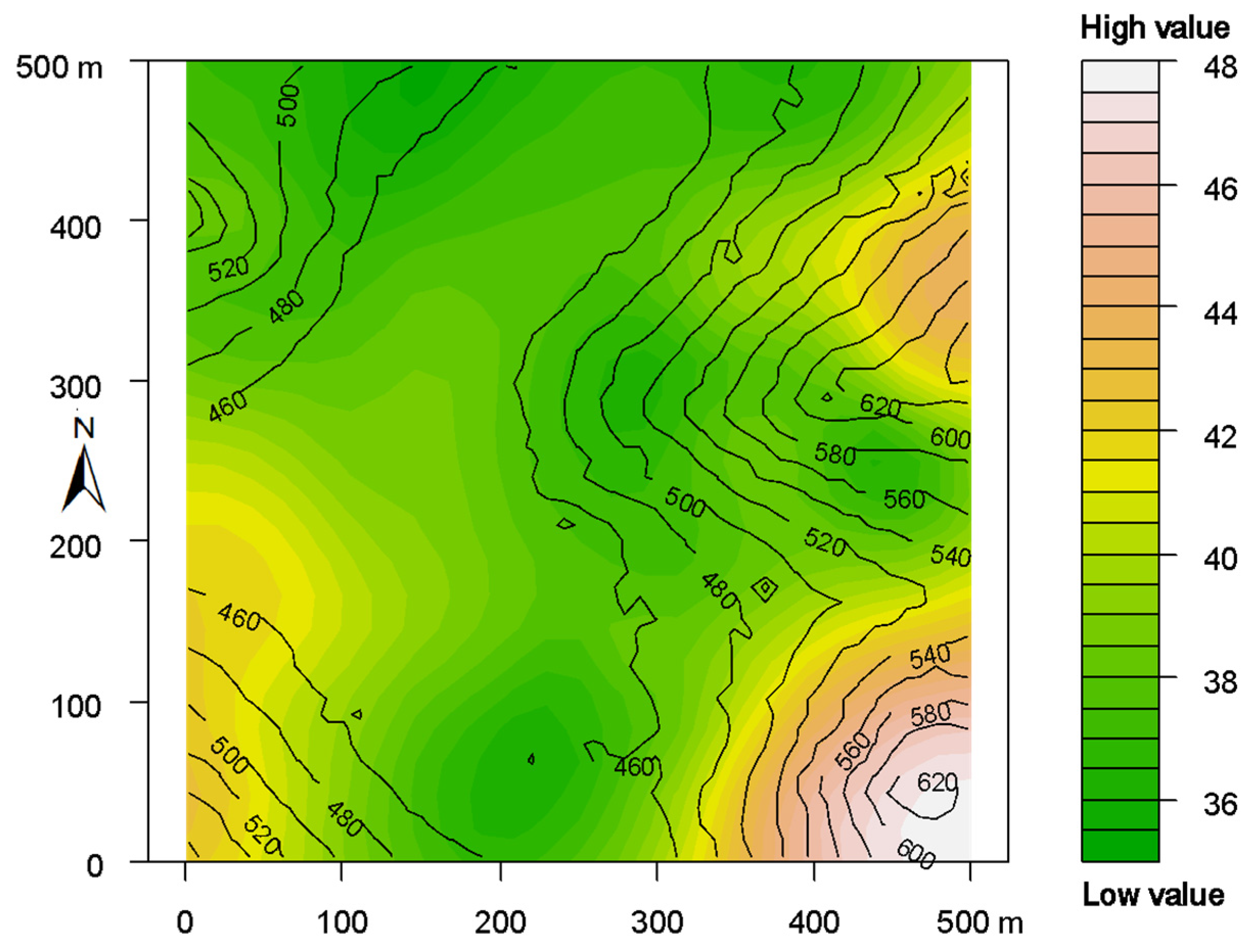
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Jackson, R.B. The structure, distribution, and biomass of the world’s forests. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2013, 44, 593–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, T.Q.; Wang, K.L.; Yang, H.; Yue, Y.M.; Zeng, Z.X.; Peng, W.X.; Zeng, F.P. Influences of stand characteristics and environmental factors on forest biomass and root–shoot allocation in southwest China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 91, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zeng, F.P.; Peng, W.X.; Wang, K.L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Song, T.Q. Carbon Storage in a Eucalyptus Plantation Chronosequence in Southern China. Forests 2015, 6, 1763–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.Z.; Peng, S.S.; Li, X.R.; Guo, Z.D.; Piao, S.L. Changes in forest biomass over China during the 2000s and implications for management. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 357, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.Y.; Ji, B.Y.; Deng, X.; Ying, J.Y.; Zhou, G.M.; Shi, Y.J.; Xu, L.; Tao, J.X.; Zhou, Y.F.; Li, C.; et al. Effects of topographic factors and aboveground vegetation carbon stocks on soil organic carbon in Moso bamboo forests. Plant Soil 2018, 433, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, K.L.; Zeng, Z.X.; Zou, Z.G.; Xu, Y.F.; Zeng, F.P. Multiple Factors Drive Variation of Forest Root Biomass in Southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Hu, F.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, K.L.; Peng, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, Z.X.; Zhang, F.; Song, T.Q. Spatial distribution of tree species in evergreen-deciduous broadleaf karst forests in southwest China. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, L.; Su, L.; Zeng, F.P.; Wang, K.L.; Peng, W.X.; Zhang, H.; Song, T.Q. Seasonal Changes and Vertical Distribution of Fine Root Biomass During Vegetation Restoration in a Karst Area, Southwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.W.; Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.M.; Horion, S.; Wang, K.L.; Keersmaecker, W.D.; Tian, F.; Schurgers, G.; Xiao, X.M.; Luo, Y.Q.; et al. Increased vegetation growth and carbon stock in China karst via ecological engineering. Nat. Sustain. 2018, 1, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, M.; Yue, Y.; Wigneron, J.P.; Tong, X.; Tian, F.; Jepsen, M.R.; Xiao, X.; Verger, A.; Mialon, A.; Al-Yaari, A.; et al. Satellite-Observed Major Greening and Biomass Increase in South China Karst During Recent Decade. Earth’s Future 2018, 6, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Ni, J.; Zhong, Q.L.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Z.H. High Mortality and Low Net Change in Live Woody Biomass of Karst Evergreen and Deciduous Broad-Leaved Mixed Forest in Southwestern China. Forests 2018, 9, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.C.; Liu, Y.G.; Guo, K.; Wang, S.J.; Liu, H.M.; Zhao, H.W.; Qiao, X.G.; Hou, D.J.; Li, S.B. Aboveground carbon stock, allocation and sequestration potential during vegetation recovery in the karst region of southwestern China: A case study at a watershed scale. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 235, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Wu, Y.Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Cheng, A.Y.; Wang, S.J.; Ni, J. Biomass of karst evergreen and deciduous broad-leaved mixed forest in central Guizhou province, southwestern China: A comprehensive inventory of a 2 ha plot. Silva Fenn. 2016, 50, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.Z.; Lee, X.Q.; Theng, B.K.G.; Zhang, L.; Fang, B.; Li, F.S. Biomass accumulation and carbon sequestration in an age-sequence of Zanthoxylum bungeanum plantations under the Grain for Green Program in karst regions, Guizhou province. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 203, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Z.; Franklin, S.B.; Wang, Q.G.; Shi, Z.; Luo, Y.Q.; Lu, Z.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Qiao, X.J.; Jiang, M.X. Topographic and biotic factors determine forest biomass spatial distribution in a subtropical mountain moist forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 357, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cosmo, L.; Gasparini, P.; Tabacchi, G. A national-scale, stand-level model to predict total above-ground tree biomass from growing stock volume. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 361, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, D.F.; Wang, J.; Le, X.; Shen, W.J.; Ren, H. Influences of biotic and abiotic factors on the relationship between tree productivity and biomass in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 264, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sande, M.T.; Peñaeñaaros, M.; Ascarrunz, N.; Arets, E.J.; Licona, J.C.; Toledo, M.; Poorter, L. Abiotic and biotic drivers of biomass change in a Neotropical forest. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, T.; Bongalov, B.; Burslem, D.; Nilus, R.; Dalponte, M.; Lewis, S.L.; Phillips, O.L.; Qie, L.; Coomes, D.A. Topography shapes the structure, composition and function of tropical forest landscapes. Ecol. Lett. 2018, 21, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bao, W.K.; Bongers, F.; Chen, B.; Chen, G.K.; Guo, K.; Jiang, M.X.; Lai, J.S.; Lin, D.M.; Liu, C.J.; et al. Drivers of tree carbon storage in subtropical forests. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 654, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Lin, S.L.; He, J.K.; Kong, F.M.; Yu, J.H.; Jiang, H.S. Climate and soils determine aboveground biomass indirectly via species diversity and stand structural complexity in tropical forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 432, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, X. Species richness promotes canopy packing: A promising step towards a better understanding of the mechanisms driving the diversity effects on forest functioning. Funct. Ecol. 2015, 29, 993–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachi, S.; Loreau, M. Does complementary resource use enhance ecosystem functioning? A model of light competition in plant communities. Ecol. Lett. 2007, 10, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.Y.H. Individual size inequality links forest diversity and above-ground biomass. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punchi-Manage, R.; Getzin, S.; Wiegand, T.; Kanagaraj, R.; Gunatilleke, C.V.S.; Gunatilleke, I.; Wiegand, K.; Huth, A. Effects of topography on structuring local species assemblages in a Sri Lankan mixed dipterocarp forest. J. Ecol. 2013, 101, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.L.; Wang, B.; Mallik, A.U.; Huang, F.Z.; Xiang, W.S.; Ding, T.; Wen, S.J.; Lu, S.H.; Li, D.X.; He, Y.L.; et al. Topographic species–habitat associations of tree species in a heterogeneous tropical karst seasonal rain forest, China. J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 10, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.C.; Du, H.; Song, T.Q.; Peng, W.X.; Zeng, F.P.; Zeng, Z.X.; Zhang, H. Allometric models of major tree species and forest biomass in Guangxi. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 4462–4472. [Google Scholar]
- Borcard, D.; Legendre, P.; Drapeau, P. Partialling out the Spatial Component of Ecological Variation. Ecology 1992, 73, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.G.; Xu, Y.Z.; Lu, Z.J.; Bao, D.C.; Guo, Y.L.; Jun, M.L.; Zhang, K.H.; Liu, H.B.; Meng, H.J.; Qiao, X.J.; et al. Disentangling the effects of topography and space on the distributions of dominant species in a subtropical forest. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2014, 59, 5113–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.G.; Sfair, J.C.; de Paula, A.S.; Barros, M.F.; Rito, K.F.; Tabarelli, M. Multiple drivers of aboveground biomass in a human-modified landscape of the Caatinga dry forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 435, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, J.B.; Anderson, T.M.; Seabloom, E.W.; Borer, E.T.; Adler, P.B.; Harpole, W.S.; Hautier, Y.; Hillebrand, H.; Lind, E.M.; Pärtel, M.; et al. Integrative modelling reveals mechanisms linking productivity and plant species richness. Nature 2016, 529, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, P.J., Jr.; Diggle, P.J.; Ribeiro, M.P.J., Jr.; Suggests, M. The geoR package. R News 2007, 1, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Dray, S.; Legendre, P.; Peres-Neto, P.R. Spatial modelling: A comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbour matrices (PCNM). Ecol. Model. 2006, 196, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M.J.C.E.P. The vegan package. Community Ecol. Package 2007, 10, 631–637. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseel, Y. lavaan: An R Package for Structural Equation Modeling. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 48, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.M.; Lai, J.S.; Mi, X.C.; Ren, H.B.; Ma, K.P. Spatial variation in community structure of a subtropical evergreen broad-leaved forest: Implications for sampling design. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, D.M.; Lai, J.S.; Muller-Landau, H.C.; Mi, X.C.; Ma, K.P. Topographic Variation in Aboveground Biomass in a Subtropical Evergreen Broad-Leaved Forest in China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotis, A.T.; Murphy, S.J.; Ricart, R.D.; Krishnadas, M.; Whitacre, J.; Wenzel, J.W.; Queenborough, S.A.; Comita, L.S. Above-ground biomass is driven by mass-ratio effects and stand structural attributes in a temperate deciduous forest. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, R.W.; Lin, Y.C.; Sun, I.F.; Hsieh, C.F.; Su, S.H.; Chang, L.W.; Song, G.Z.M.; Wang, H.H.; Hwong, J.L.; Lin, K.C.; et al. Topographic and biotic regulation of aboveground carbon storage in subtropical broad-leaved forests of Taiwan. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castilho, C.V.; Magnusson, W.E.; de Araújo, R.N.O.; Luizão, R.C.C.; Luizão, F.J.; Lima, A.P.; Higuchi, N. Variation in aboveground tree live biomass in a central Amazonian Forest: Effects of soil and topography. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 234, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, J.; Riera, B.; Dubois, M.A. Estimation of biomass in a neotropical forest of French Guiana: Spatial and temporal variability. J. Trop. Ecol. 2001, 17, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, J.; Condit, R.; Lao, S.; Caspersen, J.P.; Foster, R.B.; Hubbell, S.P. Spatial and temporal variation of biomass in a tropical forest: Results from a large census plot in Panama. J. Ecol. 2003, 91, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, Y.; Murata, H.; Kikuzawa, K. Effects of topographic heterogeneity on tree species richness and stand dynamics in a subtropical forest in Okinawa Island, southern Japan. J. Ecol. 2004, 92, 230–240. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.X.; Zhang, H.P.; Ou, Z.Y.; Tan, Y.B. Effects of topography on the diversity and distribution pattern of ground plants in karst montane forests in Southwest Guangxi, China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2803–2810. [Google Scholar]




| Factors | R2 | F | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topography | |||
| Elevation | 0.054 | 35.518 | 0.0001 ** |
| VDCN | 0.011 | 7.095 | 0.0088 ** |
| Convexity | 0.010 | 6.712 | 0.0107 * |
| Slope | 0.007 | 4.574 | 0.0338 * |
| Stand Structure | |||
| Density | 0.182 | 138.614 | <0.0001 ** |
| DBH diversity | 0.383 | 547.031 | <0.0001 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Zeng, F.; Song, T.; Wang, K.; Du, H. Stand Structure and Abiotic Factors Modulate Karst Forest Biomass in Southwest China. Forests 2020, 11, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11040443
Liu L, Zeng F, Song T, Wang K, Du H. Stand Structure and Abiotic Factors Modulate Karst Forest Biomass in Southwest China. Forests. 2020; 11(4):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11040443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lu, Fuping Zeng, Tongqing Song, Kelin Wang, and Hu Du. 2020. "Stand Structure and Abiotic Factors Modulate Karst Forest Biomass in Southwest China" Forests 11, no. 4: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11040443
APA StyleLiu, L., Zeng, F., Song, T., Wang, K., & Du, H. (2020). Stand Structure and Abiotic Factors Modulate Karst Forest Biomass in Southwest China. Forests, 11(4), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/f11040443





