Białowieża Forest—A Relic of the High Naturalness of European Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Geographical and Geological Setting
3.1. Climate
3.2. Biogeography
4. Naturalness and Biodiversity
4.1. Habitats
4.2. Species
4.3. Ecological Processes
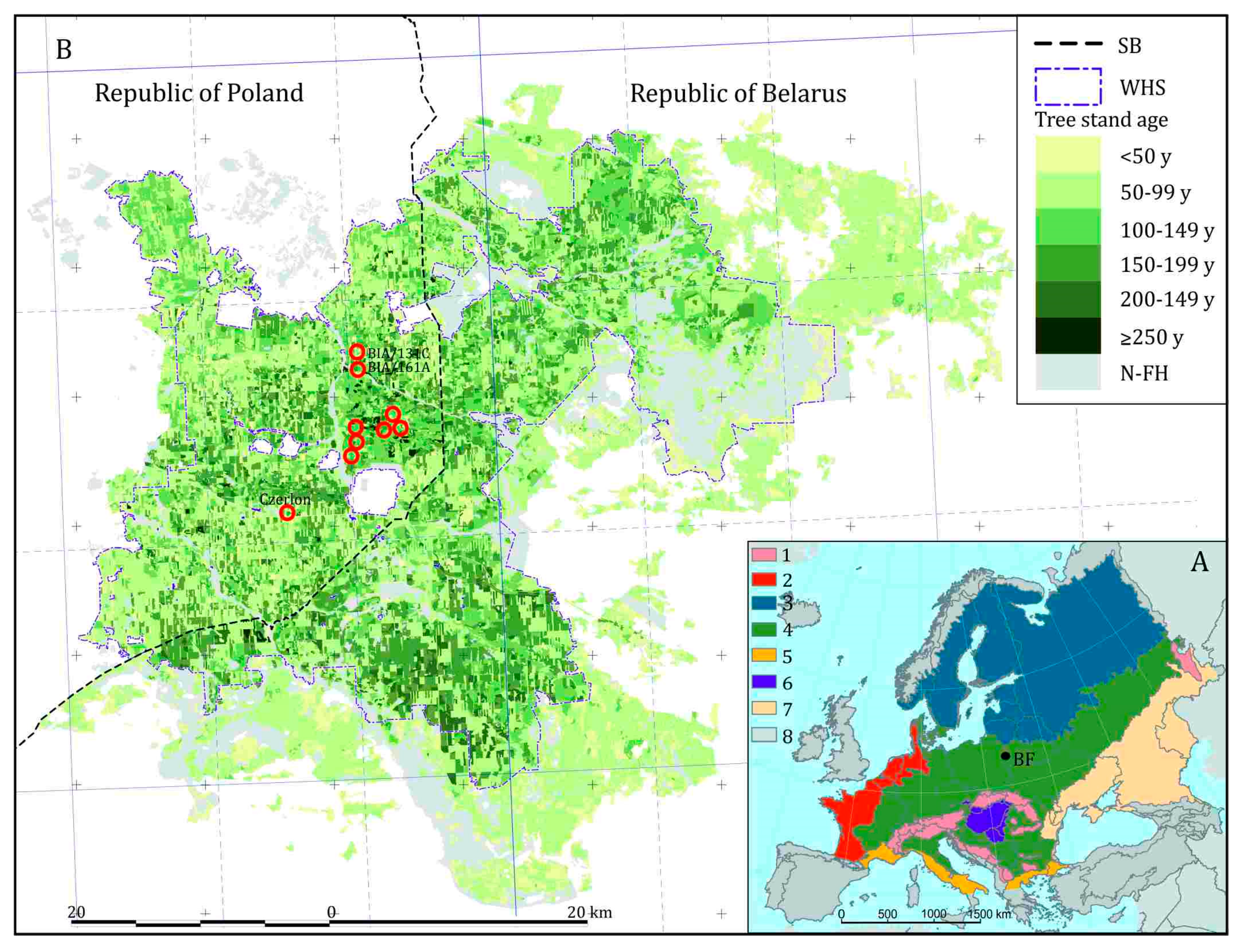
5. Environmental History
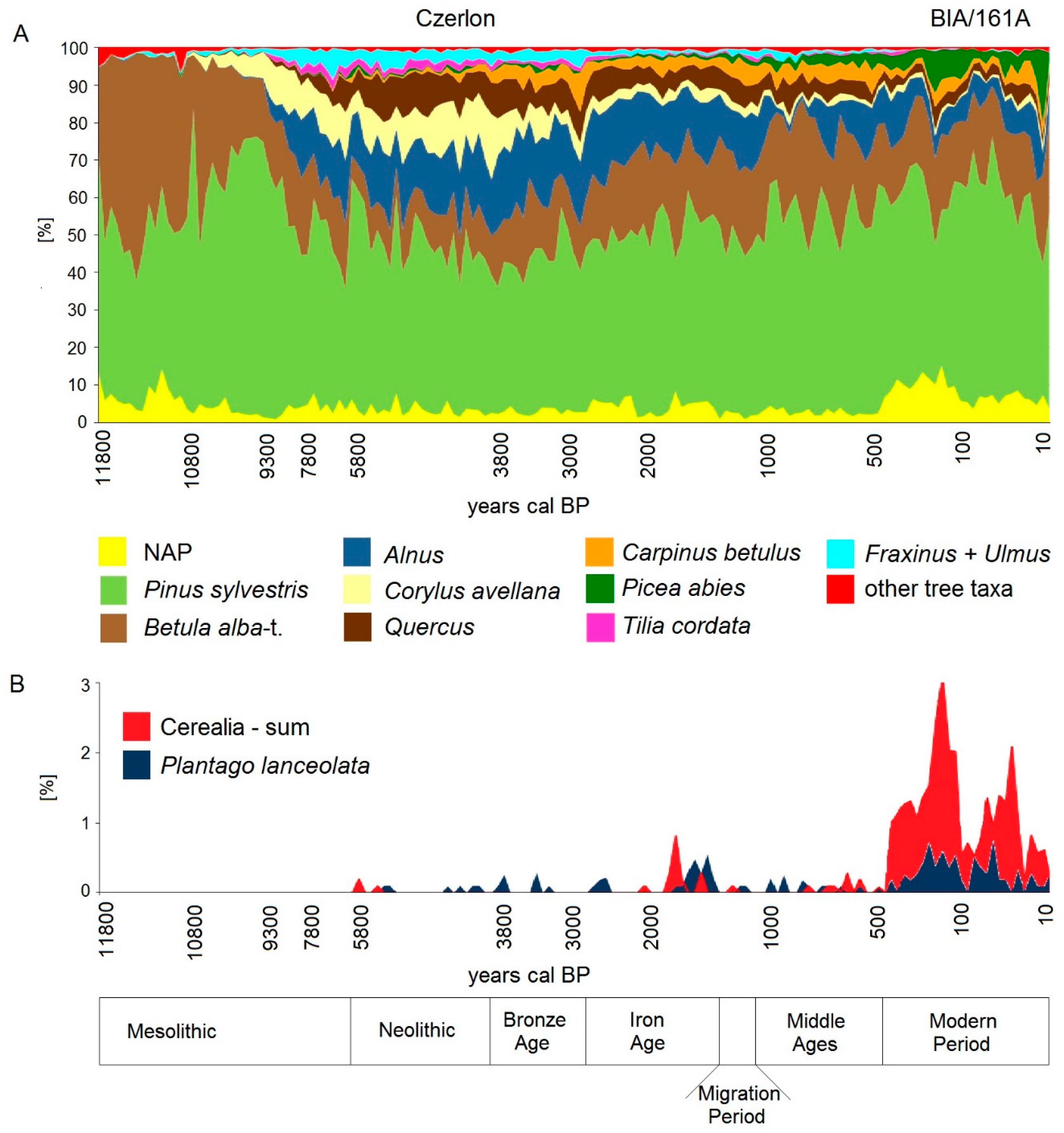
5.1. Holocene Forest History until the Medieval Period
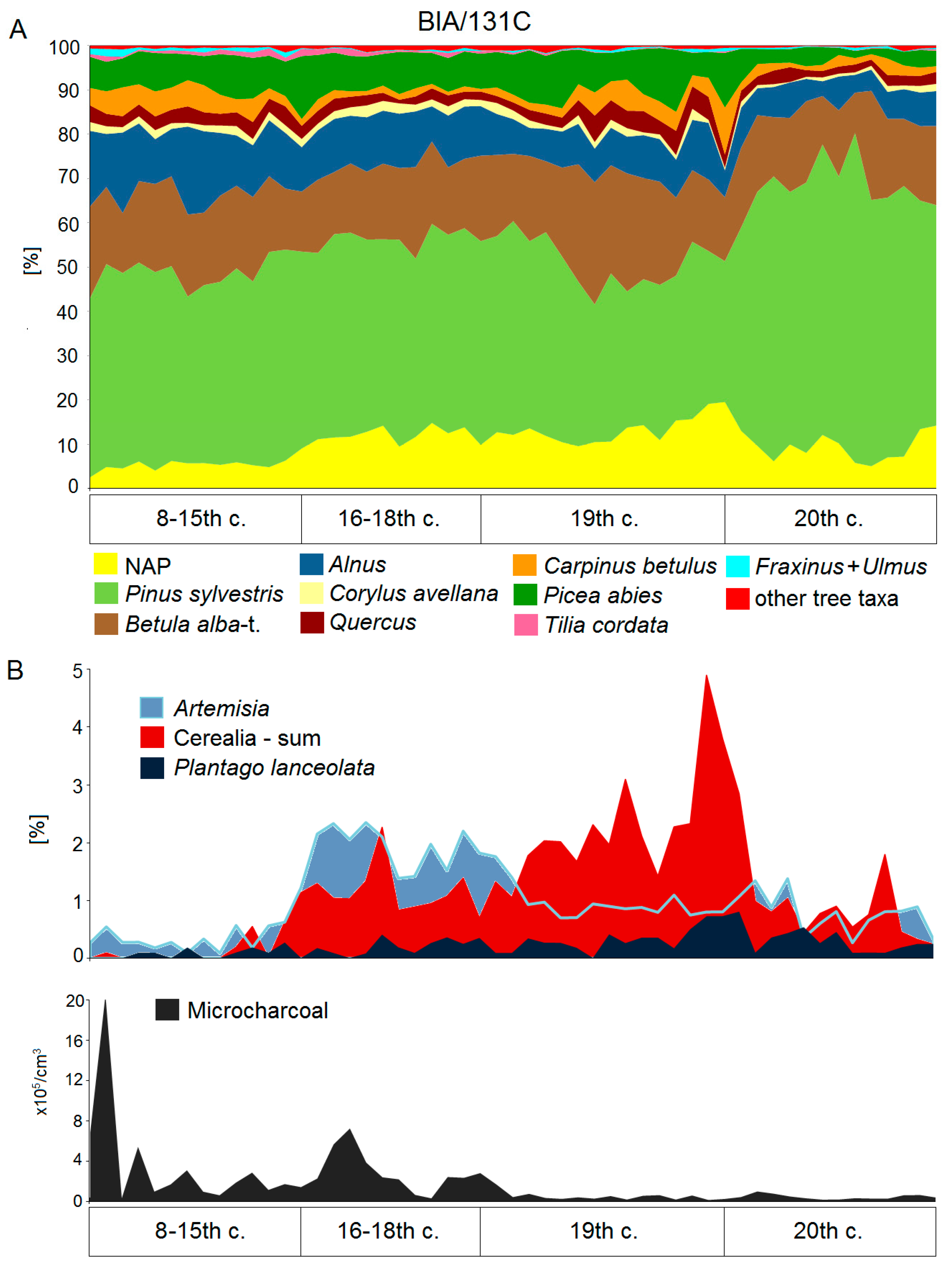
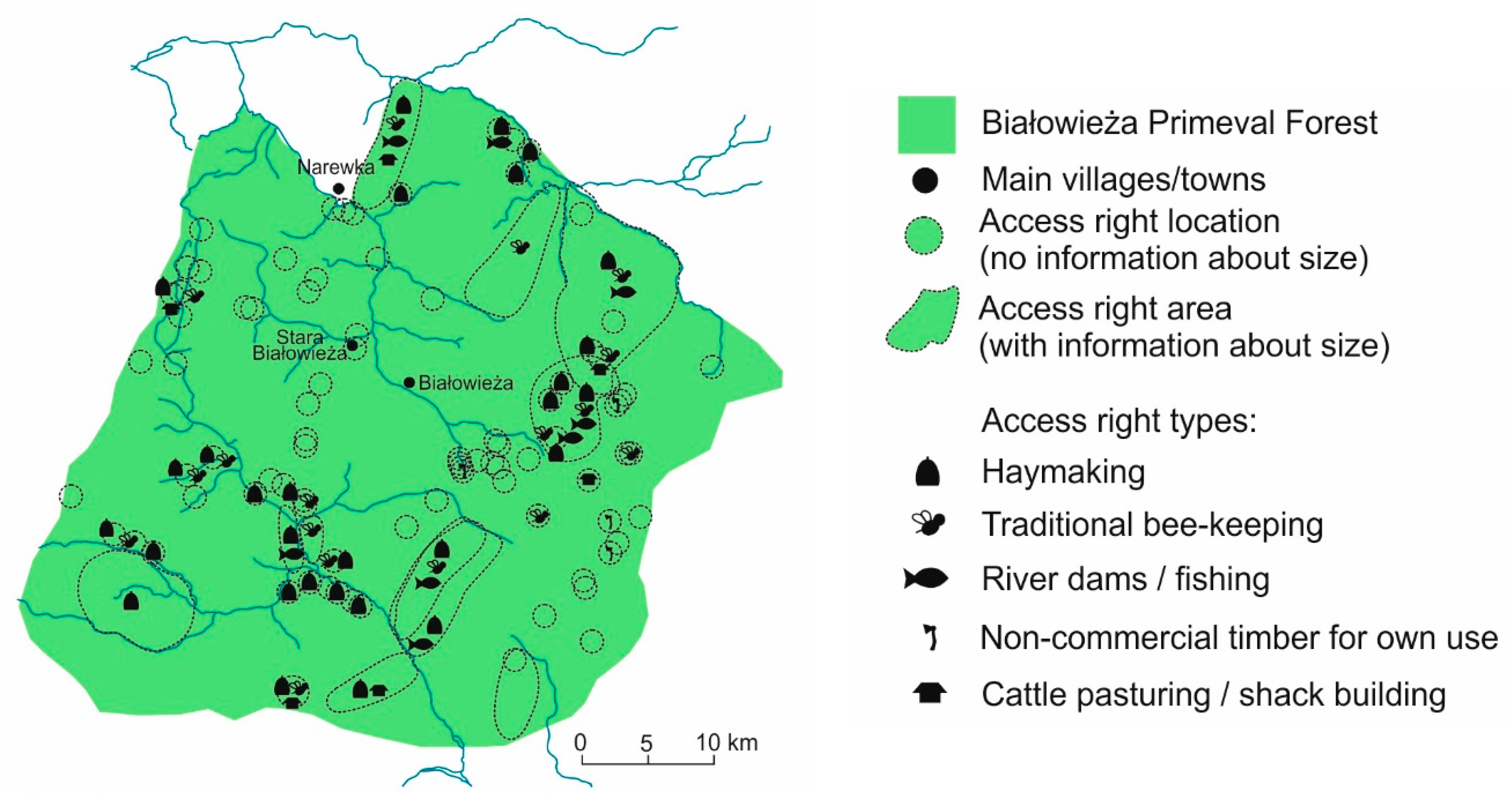
5.2. High Medieval Period and Modern Times
6. The 20th and 21st Centuries: Silviculture versus Conservation
7. Trends and Forecasts
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibisch, P. Food for forest fights. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 32, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Gower, D.B.; Wood, E.F. Accelerating forest loss in Southeast Asian Massif in the 21st century: A case study in Nan Province, Thailand. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 4682–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, M.C.; Potapov, P.V.; Moore, R.; Hancher, M.; Turubanova, S.A.; Tyukavina, A.; Thau, D.; Stehman, S.V.; Goetz, S.J.; Loveland, T.R.; et al. High-resolution global maps of 21st- century forest cover change. Science 2013, 342, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Hidalgo, D.; Oswalt, S.N.; Somanthan, E. Status and trends in global primary forest, protected areas, and areas designated for conservation of biodiversity from the Global Forest Resources Assessment 2015. For. Ecol. Manag. 2015, 352, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbell, F.; Craven, D.; Connolly, J.; Loreau, M.; Schmid, B.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Bezemer, T.M.; Bonin, C.; Bruelheide, H.; de Luca, E.; et al. Biodiversity increases the resistance of ecosystem productivity to climate extremes. Nature 2015, 526, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, T.W.; Glick, H.B.; Covey, K.R.; Bettigole, C.; Maynard, D.S.; Thomas, S.M.; Smith, J.R.; Hintler, G.; Duguid, M.C.; Amatulli, G.; et al. Mapping tree density at a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamfeldt, L.; Snäll, T.; Bagchi, R.; Jonsson, M.; Gustafsson, L.; Kjellander, P.; Ruiz-Jaen, M.C.; Fröberg, M.; Stendahl, J.; Philipson, C.D.; et al. Higher levels of multiple ecosystem services are found in forests with more tree species. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potapov, P.; Hansen, M.C.; Laestadius, L.; Turubanova, S.; Yaroshenko, A.; Thies, C.; Smith, W.; Zhuravleva, I.; Komarova, A.; Minnemeyer, S.; et al. The last frontiers of wilderness: Tracking loss of intact forest landscapes from 2000 to 2013. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1600821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.O.; Kumhardt, K.M.; Zimmermann, N. The prehistoric and preindustrial deforestation of Europe. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2009, 28, 3016–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieler, J.; Uhl, E.; Bieber, P.; Müller, J.; Rötzer, T.; Pretzsch, H. Effect of forest stand management on species composition, structural diversity, and productivity in the temperate zone of Europe. Eur. J. For. Res. 2017, 136, 739–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatini, F.M.; Burrascano, S.; Keeton, W.S.; Levers, C.; Lindner, M.; Pötschner, F.; Verkerk, P.J.; Bauhus, J.; Buchwald, E.; Chaskovsky, O.; et al. Where are Europe’s last primary forests? Divers. Distrib. 2018, 24, 1426–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, E.D.; Bouriaud, O.; Weber, U.; Roscher, C.; Hessenmoeller, D.; Kroiher, F.; Schall, P. Management breaks the natural productivity-biodiversity relationship in forests and grassland: An opinion. For. Ecosyst. 2018, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, T.; Aerts, F.; Berendse, F.; Berg, M.P.; Bruder, A.; Butenschoen, O.; Chauvet, E.; Gessner, M.O.; Jabiol, J.; Makkonen, M.; et al. Consequences of biodiversity loss for litter decomposition across biomes. Nature 2014, 509, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Berens, D.G.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Selva, N.; Brandl, R.; Farwig, N. Correlated loss of ecosystem services in coupled mutualistic networks. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Bohle, V.; Berens, D.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Selva, N.; Farwig, N. Variation in neighbourhood context shapes frugivore-mediated facilitation and competition among co-dispersed plant species. J. Ecol. 2015, 103, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrieu, L.; Cabanettes, A.; Gonin, P.; Lachat, T.; Paillet, Y.; Winter, S.; Bouget, C.; Deconchat, M. Deadwood and tree microhabitat dynamics in unharvested temperate mountain mixed forests: A life-cycle approach to biodiversity monitoring. For. Ecol. Manag. 2014, 334, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuluvainen, T.; Laiho, R. Long-term forest utilization can decrease forest floor microhabitat diversity: Evidence from boreal Fennoscandia. Can. J. For. Res. 2004, 34, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyściak-Kosińska, R.; Arnolbik, V.; Antczak, A. (Eds.) Białowieża Forest. “Belovezhskaya Pushcha/Białowieża Forest” World Heritage Site (33 BIS). Proposed Modification of the Criteria and Boundaries, Change of the Name of the Property. Nomination Dossier to the UNESCO for the Inscription on the World Heritage List. 2012. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/33/documents/ (accessed on 28 April 2019).
- Mikusiński, G.; Bubnicki, J.W.; Churski, M.; Czeszczewik, D.; Walankiewicz, W.; Kuijper, D.P.J. Is the impact of loggings in the last primeval lowland forest in Europe underestimated? The conservation issues of Białowieża Forest. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 227, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokstad, E. Last stands. Foresters and ecologists face off over the future of Europe’s oldest forest. Science 2017, 358, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blicharska, M.; Smithers, R.J. Białowieża Forest: Political stands. Science 2018, 359, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goździewska, K. Puszcza bez Człowieka Zginie. Z Andrzejem Koniecznym, Wiceministrem Środowiska, Rozmawia Karolina Goździewska. Available online: http://www.naszdziennik.pl/polska-kraj/152091,puszcza-bez-czlowieka-zginie.html (accessed on 20 February 2016).
- Goździewska, K. Puszcza Nie Przetrwa bez Człowieka. Rozmowa z prof. Bogdanem Brzezieckim, kierownikiem Katedry Hodowli Lasu Szkoły Głównej Gospodarstwa Wiejskiego w Warszawie. Available online: http://wp.naszdziennik.pl/2016-02-17/234419,puszcza-nieprzetrwa-bez-czlowieka.html (accessed on 20 February 2016).
- Callaway, E.; Castelvecchi, D.; Cyranoski, D.; Gibney, E.; Ledford, H.; Lee, J.J.; Morello, L.; Phillips, N.; Schiermeier, Q.; Tollefson, J.; et al. 2017 in news: The science events that shaped the year. Nature 2017, 552, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, M.J.; Booth, A. A typology of reviews: An analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Inf. Libr. J. 2009, 26, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Web of Science. Available online: www.webofknowledge.com (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Karpiński, J.J.; Okołów, C. Bibliografia Białowieska [Bibliography of Białowieża]; Ministerstwo Leśnictwa i Przemysłu Drzewnego. Zarząd Ochrony Przyrody: Warszawa, Poland, 1969.
- Okołów, C. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 1967–1972 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 1967–1972]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Okołów, C. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 1973–1980 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 1973–1980]; Białowieski Park Narodowy, Muzeum Przyrodniczo-Leśne im prof. Jana Miklaszewskiego: Białowieża, Poland, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Okołów, C. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 1981–1985 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 1981–1985]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Okołów, C. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 1986–1990 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 1986–1990]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Okołów, C. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 1991–1995 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 1991–1995]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Okołów, C. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 1996–2000 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 1996–2000]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bajko, P. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 2001–2005 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 2001–2005]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bajko, P. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 2006–2010 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 2006–2010]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bajko, P. Bibliografia Puszczy Białowieskiej 2011–2015 [Bibliography of Białowieża Forest 2011–2015]; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wojtanowicz, J. Zlodowacenie Warty w Polsce: Pozycja i podział stratygraficzny [Warthian glaciation in Poland: Position and stratigraphic division]. In Zlodowacenie Warty w Polsce; Harasimiuk, M., Terpiłowski, S., Eds.; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej: Lublin, Poland, 2007; pp. 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski, W. Krajobrazy roślinne Puszczy Białowieskiej [Vegetation landscapes of Białowieża Forest]. Phytocoenosis 1994, 6, 35–87. [Google Scholar]
- EEA (European Environmental Agency). Biogeographical Regions in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/data-and-maps/data/biogeographicalregions-europe-3 (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Kottek, M.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boczoń, A. Charakterystyka warunków termiczno-pluwialnych w Puszczy Białowieskiej w latach 1950–2003. [Characteristics of thermal and pluvial conditions in the Bialowieza Primeval Forest between 1950 and 2003]. Leśne Prace Badawcze 2006, 1, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Atmeh, K.; Andruszkiewicz, A.; Zub, K. Climate change is affecting mortality of weasels due to camouflage mismatch. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boczoń, A.; Kowalska, A.; Ksepko, M.; Sokołowski, K. Climate Warming and Drought in the Bialowieza Forest from 1950–2015 and Their Impact on the Dieback of Norway Spruce Stands. Water 2018, 10, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, T.H.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Krawczyk, M.; Tryjanowski, P. Advancing phenology in Europe’s last lowland primeval forest: Non-linear temperature response. Clim. Res. 2009, 39, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EEA (European Environmental Agency). European Forest Types. Categories and Types for Sustainable Forest Management Reporting and Policy, 2nd ed.; European Environment Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, EEA Technical Report 09/2006; Available online: https://www.foresteurope.org/docs/other_meetings/2006/wfc/WFC_4_eea_technical_report_92006.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2019).
- Faliński, J.B. Vegetation Dynamics in Temperate Lowland Primeval Forests: Ecological Studies in Białowieża Forest; Dr. W. Junk Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski, J.M.; Jaroszewicz, B. (Eds.) Catalogue of the Fauna of Białowieża Primeval Forest; Instytut Badawczy Leśnictwa: Warszawa, Poland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zub, K. Mammals. In Białowieża National Park. Know it—Understand it—Protect it; Okołów, C., Karaś, M., Bołbot, A., Eds.; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2009; pp. 127–142. [Google Scholar]
- Adamowski, W. The flora of vascular plants. In Białowieża National Park. Know it—Understand it—Protect it; Okołów, C., Karaś, M., Bołbot, A., Eds.; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2009; pp. 59–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawa, A. The macrofungi. In Białowieża National Park. Know it—Understand it—Protect it; Okołów, C., Karaś, M., Bołbot, A., Eds.; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2009; pp. 88–110. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski, J.M. Kózkowate (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) wschodniej części Polski. Prace Instytutu Badawczego Leśnictwa. Seria A 1995, 811, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski, J.M.; Ługowoj, J. Buprestidae (Coleoptera) of the Białowieża Primeval Forest. Polskie Pismo Entomologiczne 2000, 69, 279–318. [Google Scholar]
- Wesołowski, T.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Kowalczyk, R.; Kujawa, A.; Gutowski, J.M. What and how to protect in the Białowieża Forest—a response to J. Hilszczański and T. Jaworski. Chrońmy Przyrodę Ojczystą 2019, 75, 51–56. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Matuszkiewicz, W.; Faliński, J.B.; Kostrowicki, A.S.; Matuszkiewicz, J.M.; Olaczek, R.; Wojterski, T. Potencjalna Roślinność Naturalna Polski. Mapa Przeglądowa 1:300 000. Arkusze 1–12; IGiPZ PAN: Warszawa, Poland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski, J.M.; Jaroszewicz, B. Białowieża Primeval Forest as a refuge of the European entomofauna. Wiadomości Entomologiczne 2004, 23, 67–87. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiałojć, L.; Wesołowski, T. The avifauna of Białowie·za Forest: A window into the past. Br. Birds 2005, 98, 174–193. [Google Scholar]
- Latałowa, M.; Zimny, M.; Pędziszewska, A.; Kupryjanowicz, M. Postglacjalna historia Puszczy Białowieskiej—roślinność, klimat i działalność człowieka. Parki Narodowe i Rezerwaty Przyrody 2016, 35, 3–49. [Google Scholar]
- Grzywacz, A.; Keczyński, A.; Szczepkowski, A.; Bielak, K.; Drozdowski, S.; Bolibok, L.; Brzeziecki, B. Trees of monumental sizes. In The Forests of Strict Reserve of Białowieża National Park; Keczyński, A., Ed.; Białowieża National Park: Białowieża, Poland, 2017; pp. 214–245. [Google Scholar]
- Angelstam, P.; Dönz-Breuss, M. Measuring forest biodiversity at the stand scale—an evaluation of indicators in European forest history gradients. Ecol. Bull. 2004, 51, 305–332. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20113319 (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Wesołowski, T.; Gutowski, J.M.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Kowalczyk, R.; Niedziałkowski, K.; Rok, J.; Wójcik, J.M. Park Narodowy Puszczy Białowieskiej—Ochrona Przyrody i Rozwój Lokalnych Społeczności. [The National Park of the Białowieża Forest—Nature Conservation and Development of Local Communities]. pp. 1–28. Available online: www.forestbiology.org (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Tomiałojć, L. Classis (gromada): Aves—Ptaki. In Catalogue of the Fauna of Białowieża Primeval Forest; Gutowski, J.M., Jaroszewicz, B., Eds.; Instytut Badawczy Leśnictwa: Warszawa, Poland, 2001; pp. 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Gierczyk, B.; Ślusarczyk, T.; Szczepkowski, A.; Kujawa, A. 23th Exhibition of Fungi of the Białowieża Forest. Materials to the knowledge of mycobiota of the Białowieża Primeval Forest. Przegląd Przyrodniczy 2018, 29, 9–57. [Google Scholar]
- Kujawa, A.; Orczewska, A.; Falkowski, M.; Blicharska, M.; Bohdan, A.; Buchholz, L.; Chylarecki, P.; Gutowski, J.M.; Latałowa, M.; Mysłajek, R.W.; et al. The Białowieża Forest—A UNESCO Natural Heritage Site—protection priorities. Leśn Prace Bad 2016, 77, 302–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermy, M.; Honnay, O.; Firbank, L.; Grashof-Bokdam, C.; Lawesson, J.E. An ecological comparison between ancient and other forest plant species of Europe, and the implications for forest conservation. Biol. Conserv. 1999, 91, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieśliński, S. Lichens. In Białowieża National Park. Know it—Understand it—Protect it; Okołów, C., Karaś, M., Bołbot, A., Eds.; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2009; pp. 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Faliński, J.B. The Białowieża forest, a relict ecosystem in Poland and Belarus. Biodivers. J. Life Earth 2003, 4, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiałojć, L. Characteristics of Old Growth in the Bialowieza Forest, Poland. Nat. Areas J. 1991, 11, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowski, A.W. The Flora of Vascular Plants in the Białowieża Forest; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pucek, Z. Mammalia—Ssaki. In Catalogue of the Fauna of Białowieża Primeval Forest; Gutowski, J.M., Jaroszewicz, B., Eds.; Instytut Badawczy Leśnictwa: Warszawa, Poland, 2001; pp. 326–328. [Google Scholar]
- Jędrzejewska, B.; Jędrzejewski, W. Predation in Vertebrate Communities: The Białowieża Primeval Forest as a Case Study; Ecological Studies (Analysis and Synthesis); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; Volume 135. [Google Scholar]
- Tomiałojć, L.; Wesołowski, T.; Walankiewicz, W. Breeding bird community of a primaeval temperate forest (Białowieża National Park, Poland). Acta Ornithol. 1984, 20, 241–310. [Google Scholar]
- Sokołowski, A.W. Lasy Puszczy Białowieskiej; Centrum Informacyjne Lasów Państwowych: Warszawa, Poland, 2004.
- Brzeziecki, B.; Zajączkowski, J.; Drozdowski, S.; Gawron, L.; Buraczyk, W.; Bielak, K.; Szeligowski, H.; Dzwonkowski, M.; Ostrowski, J.; Widawska, Z.; et al. Operat dynamiki ekosystemów leśnych Białowieskiego Parku Narodowego; Szkoła Główna Gospodarstwa Wiejskiego: Warszawa, Poland, 2010; p. 209. [Google Scholar]
- Preikša, Ž.; Brazaitis, G.; Marozas, V.; Jaroszewicz, B. Dead wood quality influences diversity of rare cryptogams in temperate broadleaved forests of Eastern Europe. iForest Biogeosci. For. 2015, 9, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chećko, E.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Olejniczak, K.; Kwiatkowska-Falińska, A.J. The importance of coarse woody debris for vascular plants in temperate mixed deciduous forests. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesołowski, T.; Tomiałojć, L. Breeding bird dynamics in a primaeval temperate forest: Long-term trends in Bialowieza National Park (Poland). Ecography 1997, 20, 432–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilibert, J.E. Flora Litvanica inchoata (1781–1782); Typis S. R. M.: Grodno, Poland, 1781. [Google Scholar]
- Gorski, S.B. O roślinach Zubrom upodobanych, jakoteż innych w puszczy Białowiezkiey. Dziennik Wileński 1829, 4, 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Okołów, C. Materiały do oceny bioróżnorodności Puszczy Białowieskiej. Nowe dla nauki gatunki organizmów opisane z Puszczy Białowieskiej. Parki Narodowe i Rezerwaty Przyrody 2015, 34, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Muggia, L.; Mancinelli, R.; Tønsberg, T.; Jabłońska, A.; Kukwa, M.; Palice, Z. Molecular analyses uncover the phylogenetic placement of the lichenized hyphomycetous genus Cheiromycina. Mycologia 2017, 109, 588–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malíček, J.; Palice, Z.; Vondrák, J.; Łubek, A.; Kukwa, M. Bacidia albogranulosa (Ramalinaceae, lichenized Ascomycota), a new sorediate lichen from European old-growth forests. MycoKeys 2018, 44, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzow-Krzemińska, B.; Łubek, A.; Kubiak, D.; Ossowska, E.; Kukwa, M. Phylogenetic approaches reveal a new sterile lichen in the genus Loxospora (Sarrameanales, Ascomycota) in Poland. Phytotaxa 2018, 348, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamowski, W.; Dvorak, L.; Ramanjuk, I. Atlas of Alien Woody Species of the Białowieża Primaeval Forest; Białowieska Stacja Geobotaniczna-Wydawn. Uniw. Warszawskiego: Białowieża, Poland, 2002; Phytocoenosis (N.S.), 14. Supplementum Cartographiae Geobotanicae 14, 1–303. [Google Scholar]
- Faliński, J.B.; Mułenko, W. Cryptogamous Plants in the Forest Communities of Białowieża National Park; Białowieska Stacja Geobotaniczna UW: Białowieża, Poland, 1997; Phytocoenosis (N.S.) 1996, 8 Archiwum Geobotanicum 6, 1–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wojewoda, W. Życie i dzieło profesora Stanisława Domańskiego (1916–1993). Wiadomości Botaniczne 1997, 41, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Karasiński, D.; Wołkowycki, M. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of Polypores (Agaricomycetes) of the Białowieża Forest (NE Poland). Pol. Bot. J. 2015, 60, 217–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gutowski, J.M.; Czachorowski, S.; Górski, P.; Wanat, M. Invertebrates. In Białowieża National Park. Know it—Understand it—Protect it; Okołów, C., Karaś, M., Bołbot, A., Eds.; Białowieski Park Narodowy: Białowieża, Poland, 2009; pp. 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Ratcliffe, S.; Wirth, C.; Jucker, T.; van der Plas, F.; Scherer-Lorenzen, M.; Verheyen, K.; Allan, E.; Benavides, R.; Bruelheide, H.; Ohse, B.; et al. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning relations in European forests depend on environmental context. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 1414–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzkin, G.; Wilson, P.; Foster, D.R.; Allen, A. Vegetation patterns in heterogeneous landscapes: The importance of history and environment. J. Veg. Sci. 1999, 10, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, K.; Foster, D.R.; Motzkin, G. Effects of the past and the present on species distribution: Land-use history and demography of wintergreen. J. Ecol. 2003, 88, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro Solar, R.R.; Barlow, J.; Ferreira, J.; Berenguer, E.; Lees, A.C.; Thomson, J.R.; Louzada, J.; Maués, M.; Moura, N.G.; Oliveira, V.H.F.; et al. How pervasive is biotic homogenization in human-modified tropical forest landscapes? Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 1108–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, W.; Dupouey, J.L.; Dambrine, E.; Benoit, M. Influence of past land use on the vegetation and soils of present day forest in the Vosges mountains, France. J. Ecol. 1997, 85, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermy, M.P.; van den Bremt, P.; Tack, G. Effects of site history on woodland vegetation. In European Forest Reserves; Broekmeyer, M.E.A., Vos, W., Koop, H., Eds.; Pudoc Scientific: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1993; pp. 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, J.F.; Lindenmayer, D.; MacMahon, J.; McKee, A.; Magnuson, J.; Perry, D.; Waide, R.B.; Foster, D. Threads of continuity: Ecosystem disturbance, recovery, and theory of biological legacies. Conserv. Biol. Pract. 2000, 1, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnodębski, D.; Olczak, H. Badania archeologiczne na terenie polskiej części Puszczy Białowieskiej—stan obecny, problemy i perspektywy. Biuletyn Konserwatorski Województwa Podlaskiego 2012, 18, 145–168. [Google Scholar]
- Prusinkiewicz, Z.; Michalczuk, C. Gleby Białowieskiego Parku Narodowego; Białowieska Stacja Geobotaniczna UW: Białowieża, Poland, 1998; Phytocoenosis (N.S.), 10 Supplementum Cartographiae Geobotanice 10, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Laurance, W.F. The ecology, distribution, conservation and management of large old trees. Biol. Rev. 2017, 92, 1434–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Laurance, W.F.; Franklin, J.F. Global Decline in Large Old Trees. Science 2012, 338, 1305–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, J.A.; Larson, A.J.; Swanson, M.E.; Freund, J.A. Ecological importance of large−diameter trees in a temperate mixed−conifer forest. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, D.R.; Knight, D.H.; Franklin, J.F. Landscape Patterns and Legacies Resulting from Large, Infrequent Forest Disturbances. Ecosystems 1998, 1, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abs, C.; Fischer, A.; Faliński, J.B. Vegetationsőkologischer Vergleich von Naturwald und Wirtschftswald, dargestellt am Beispiel des Tilio-Carpinetum im Waldgebiet von Bialowieza/Nordost-Polen. Forstwissenschaftliches Centralblatt Vereinigt Mit Tharandter Forstliches Jahrbuch 1999, 118, 181–196. [Google Scholar]
- Pucek, Z.; Jędrzejewski, W.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Pucek, M. Rodent population dynamics in a primeval deciduous forest (Białowieża National Park) in relation to weather, seed crop, and predation. Acta Theriol. 1993, 38, 199–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenseth, N.C.; Viljugrain, H.; Jędrzejewski, W.; Mysterud, A.; Pucek, Z. Population dynamics of Clethrionomys glareolus and Apodemus flavicollis: Seasonal components of density dependence and density independence. Acta Theriol. 2002, 47, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdziewicz, M.; Zwolak, R.; Crone, E.E. How do vertebrates respond to mast seeding? Oikos 2016, 125, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, J.M.; Jaroszewicz, B. Zmiany udziału świerka pospolitego w drzewostanach Puszczy Białowieskiej w kontekście dynamiki liczebności kornika drukarza Ips typographus (L.). [Changes in the abundance of Norway spruce in stands of Białowieża Forest in the context of dynamics of spruce bark beetle Ips typographus (L.) numbers.]. In Stan Ekosystemów Leśnych Puszczy Białowieskiej. Materiały Ogólnopolskiej Konferencji Naukowej Ministerstwa Środowiska i Generalnej Dyrekcji Lasów Państwowych, Warszawa, 28 października 2015; Centrum Informacyjne Lasów Państwowych: Warszawa, Poland, 2016; pp. 87–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wesołowski, T.; Rowiński, P. Tree defoliation by winter moth Operophtera brumata L. during an outbreak affected by structure of forest landscape. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 221, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornulier, T.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Bretagnolle, V.; Brommer, J.E.; Butet, A.; Ecke, F.; Elston, D.A.; Framstad, E.; Henttonen, H.; Hörnfeldt, B.; et al. Europe-wide dampening of population cycles in keystone herbivores. Science 2013, 340, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakoby, O.; Lischke, H.; Wermelinger, B. Climate change alters elevational phenology patterns of the European spruce bark beetle (Ips typographus). Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimmi, U.; Poulter, B.; Wolf, A.; Portner, H.; Weber, P.; Bürgi, M. Soil carbon pools in Swiss forests show legacy effects from historic forest litter raking. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, S.L.; Blondeel, H.; Perring, M.P.; Depauw, L.; Brümelis, G.; Brunet, J.; Decocq, G.; den Ouden, J.; Härdtle, W.; Hédl, R.; et al. Litter quality, land-use history, and nitrogen deposition effects on topsoil conditions across European temperate forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mausolf, K.; Härdtle, W.; Jansen, K.; Delory, B.M.; Hertel, D.; Leuschner, C.; Temperton, V.M.; von Oheimb, G.; Fichtner, A. Legacy effects of land-use modulate tree growth responses to climate extremes. Oecologia 2018, 187, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milecka, K.; Noryśkiewicz, A.M.; Kowalewski, G. History of the Białowieża Primeval Forest, NE Poland. Stud. Quat. 2009, 26, 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Paszewski, A. Dalsze badania nad historią lasów Puszczy Białowieskiej na podstawie analizy pyłkowej torfowisk. Roczniki Nauk Rolniczych i Leśnych 1937, 36, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Paszewski, A.; Poznański, F. Materiały do historji lasów Puszczy Białowieskiej. Roczniki Nauk Rolniczych i Leśnych 1936, 36, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Borowik-Dąbrowska, M.; Dąbrowski, M.J. Naturalne i antropogeniczne zmiany roślinności Białowieskiego Parku Narodowego. Archeologia Polski 1973, 18, 181–200. [Google Scholar]
- Dąbrowski, M.J. Późnoglacjalna i holoceńska historia lasów Puszczy Białowieskiej. Część I. Białowieski Park Narodowy. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 1959, 28, 197–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mitchell, F.J.G.; Cole, E. Reconstruction of long-term successional dynamics of temperate woodland in Białowieża Forest, Poland. J. Ecol. 1998, 86, 1042–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latałowa, M.; Zimny, M.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Samojlik, T. Białowieża Primeval Forest: A 2000-year Interplay of Environmental and Cultural Forces in Europe’s Best Preserved Temperate Woodland. In Europe’s Changing Woods and Forests: From Wildwood to Cultural Landscapes; Kirby, K.J., Watkins, C., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2015; pp. 243–264. [Google Scholar]
- Zieliński, D.; Schwarz, C.J.; Ehrmann, R. Evaluation of the expansion of Mantis religiosa (L.) in Poland based on a questionnaire survey. Anim. Biodiver. Conserv. 2018, 41, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimny, M.; Latałowa, M.; Pędziszewska, A. The Late-Holocene history of forests in the Strict Reserve of Białowieża National Park. In The Forests of the Strict Reserve of Białowieża National Park; Keczyński, A., Ed.; Białowieża National Park: Białowieża, Poland, 2017; pp. 29–59. [Google Scholar]
- Giesecke, T.; Brewer, T.; Finsiger, W.; Leydet, M.; Bradshaw, R.H.W. Patterns and dynamics of European vegetation change over the last 15,000 years. J. Biogeogr. 2017, 44, 1441–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normand, S.; Ricklefs, R.E.; Skov, E.; Bladt, J.; Tackenberg, O.; Svenning, J.C. Postglacial migration supplements climate in determining plant species ranges in Europe. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2011, 278, 3644–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuerkauf, M.; Bos, J.A.A.; Jahns, S.; Janke, W.; Kuparinen, A.; Stebich, M.; Joosten, H. Corylus expansion and persistent openness in the early Holocene vegetation of northern central Europe. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 90, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesecke, T.; Bennett, K.D.; Birks, H.J.B.; Bjune, A.E.; Bozilova, E.; Feurdean, A.; Finsinger, W.; Froyd, C.A.; Pokorný, P.; Rösch, M.; et al. The pace of Holocene vegetation change—testing for synchronous developments. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 2805–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litt, T.; Schölzel, C.; Kűhl, N.; Brauer, A. Vegetation and climate history in the Westeifel Volcanic Field (Germany) during the past 11 000 years based on annually laminated lacustrine maar sediments. Boreas 2009, 38, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralska-Jasiewiczowa, M.; Nalepka, D.; Goslar, T. Some problems of forest transformation at the transition to the oligocratic Homo sapiens phase of the Holocene interglacial in northern lowlands of central Europe. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2003, 12, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Vogt, H. Die Fichte. Band I: Taxonomie—Verbreitung—Morphologie—Waldgesellschaften; Paul Parey: Hamburg, Germany; Berlin, Germany, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Gałka, M.; Tobolski, K.; Zawisza, E.; Goslar, T. Postglacial history of vegetation, human activity and lake-level changes at Jezioro Linówek in northeast Poland, based on multi-proxy data. Veg. Hist. Archaeobot. 2014, 23, 123–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behre, K.E. The interpretation of anthropogenic indicators in pollen diagrams. Pollen et Spores 1981, 23, 225–245. [Google Scholar]
- Wawrusiewicz, A. Okres neolitu i wczesnej epoki brązu na Podlasiu, stan i perspektywy badań. In Na Rubieży Kultur. Badania nad Okresem Neolitu i Wczesną Epoką Brązu; Stankiewicz, U., Wawrusiewicz, A., Eds.; Muzeum Podlaskie w Białymstoku: Białystok, Poland, 2011; pp. 13–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tkachov, O. Preliminary results of archaeological research of the Stone Age and Bronze Age sites within the area of Białowieża Forest. In Na Rubieży Kultur. Badania nad Okresem Neolitu i Wczesną Epoką Brązu; Stankiewicz, U., Wawrusiewicz, A., Eds.; Muzeum Podlaskie w Białymstoku: Białystok, Poland, 2011; pp. 229–236. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskanis, J. Wodzowskie Kurhany Kultury Wielbarskiej na Podlasiu; Muzeum Podlaskie w Białymstoku: Białystok, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jażdżewski, K. O kurhanach nad górną Narwią i o hutnikach sprzed 17 wieków. Z Otchłani Wieków 1939, 14, 2–22. [Google Scholar]
- Olczak, H.; Krasnodębski, K.; Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B. An iron producing settlement of the hatched pottery culture at the Berezowo Clearing in the Białowieża Forest. Wiadomości Archeologiczne 2018, 69, 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T. Bog iron ore extraction sites in the Białowieża Primeval Forest in the 17th-18th centuries. Kwartalnik Historii Kultury Materialnej 2009, 57, 399–411. [Google Scholar]
- Wawrzyniuk, J.; Budziszewski, J.; Jakubczak, M.; Rutyna, M.; Szlązak, R.; Szubski, M.; Urbańczyk, P. Dziedzictwo kulturowe Puszczy Białowieskiej—Wstępne rozpoznanie. Archeologica Hereditas 2017, 8, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Zapłata, R.; Stereńczak, K. Puszcza Białowieska, LIDAR i dziedzictwo kulturowe—Zagadnienia wprowadzające. Raport 2016, 11, 239–255. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T. Anthropogenic changes of the environment of Białowieża Primeval Forest until the end of the 18th century. Ph.D. Thesis, Mammal Research Institute PAS, Białowieża, Poland, 2007; p. 181. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T. Traditional utilisation of Białowieża Primeval Forest (Poland) in the 15th to 18th centuries. Landsc. Archaeol. Ecol. 2010, 8, 150–164. [Google Scholar]
- Hedemann, O. L’histoire de la Foret de Białowieża (Jusqu’a 1798); Instytut Badawczy Lasów Państwowych: Warsaw, Poland, 1939; Rozprawy i Sprawozdania Seria A, Nr 1. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T.; Rotherham, I.; Jędrzejewska, B. Quantifying historic human impacts on forest environments: A case study in Białowieża Forest, Poland. Environ. Hist. 2013, 18, 576–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszkiewicz, P.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Samojlik, T. Puszcza Białowieska w Pracach Przyrodników 1721–1831; Wydawnictwo Naukowe Semper: Warszawa, Poland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Daszkiewicz, P.; Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B. Puszcza Białowieska w Pracach Przyrodników i Podróżników 1831–1863; Wydawnictwo Naukowe Semper: Warszawa, Poland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sahanowicz, H. Historia Białorusi od Czasów Najdawniejszych do Końca XVIII Wieku; Instytut Europy Środkowo-Wschodniej: Lublin, Poland, 2002; pp. 1–411. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T.; Rotherham, I.D.; Jędrzejewska, B. The cultural landscape of royal hunting gardens from the fifteenth to the eighteenth century in Białowieża Primeval Forest. In Cultural Severance and the Environment; Rotherham, I.D., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 191–204. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Krasnodębski, D.; Olczak, H. Dwór łowiecki Wazów w Białowieży w świetle dokumentów źródłowych i badań archeologicznych. Kwartalnik Historii Kultury Materialnej 2014, 62, 73–90. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B. Utilization of Białowieża Forest in the times of Jagiellonian dynasty and its traces in the contemporary forest environment. Sylwan 2004, 148, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.R.; Seager, R.; Kushnir, Y.; Briffa, K.R.; Büntgen, U.; Frank, D.; Krusic, P.; Tegel, W.; Van der Schrier, G.; Andreu-Hayles, L.; et al. Old World megadroughts and pluvials during the Common Era. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Michniewicz, M.; Krasnodębski, D.; Dulinicz, M.; Olczak, H.; Karczewski, A.; Rotherham, I. Tree species used for low-intensity production of charcoal and wood-tar in the 18th-century Białowieża Primeval Forest, Poland. Phytocoenologia 2013, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samojlik, T. The rise and fall of the potash industry in the Białowieża Primeval Forest in the 17th–19th centuries. Rocznik Polskiego Towarzystwa Dendrologicznego 2016, 64, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Niklasson, M.; Zin, E.; Zielonka, T.; Feijen, M.; Korczyk, A.F.; Churski, M.; Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Gutowski, J.M.; Brzeziecki, B. A 350-year tree-ring fire record from Białowieża Primeval Forest, Poland: Implications for Central European lowland fire history. J. Ecol. 2010, 98, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartsov, G. Belovezhskaya Pushcha. Eya istoricheskii ocherk, sovremennoe okhotniche khozaistvo i Vysochaishie okhoty v Puchche; A. Marks: Saint Petersburg, Russia, 1903. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T.; Fedotova, A.; Niechoda, T.; Rotherham, I.D. Culturally modified trees or wasted timber: Different approaches to marked trees in Poland’s Białowieża Forest. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samojlik, T.; Fedotova, A.; Kuijper, D.P.J. Transition from traditional to modern forest management shaped the spatial extent of cattle pasturing in Białowieża Primeval Forest in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Ambio 2016, 45, 904–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczoski, J. Lasy Białowieży; Państwowa Rada Ochrony Przyrody: Poznań, Poland, 1930. [Google Scholar]
- Kocan, T. Szkodliwe wypasy w Puszczy Białowieskiej. Przyroda Polska 1957, 1, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Faliński, J.B. Antropogeniczna Roślinność Puszczy Białowieskiej Jako Wynik Synantropizacji Naturalnego Kompleksu Leśnego [Anthropogenic Vegetation of Białowieża Primeval Forest as a Result of Synanthropization of the Forest]; Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Warszawa, Poland, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Samojlik, T.; Fedotova, A.; Borowik, T.; Kowalczyk, R. Historical data on European bison management in Białowieża Primeval Forest can contribute to a better contemporary conservation of the species. Mammal Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Więcko, E. Puszcza Białowieska [The Białowieża Forest]; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Mikusińska, A.; Zawadzka, B.; Samojlik, T.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Mikusiński, G. Quantifying landscape change during the last two centuries in Białowieża Primeval Forest. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2013, 16, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jędrzejewska, B.; Jędrzejewski, W.; Bunevich, A.N.; Miłkowski, L.; Krasiński, Z.A. Factors shaping population densities and increase rates of ungulates in Białowieża Primeval Forest (Poland and Belarus) in the 19th and 20th century. Acta Theriol. 1997, 42, 399–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijper, D.P.J.; Jędrzejewska, B.; Brzeziecki, B.; Churski, M.; Jędrzejewski, W.; Żybura, H. Fluctuating ungulate density shapes tree recruitment in natural stands of the Białowieża Primeval Forest, Poland. J. Veg. Sci. 2010, 21, 1082–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keczyński, A. Regeneracja grądu Tilio-Carpinetum Tracz. 1962 w następstwie dawnego użytkowania lasu w Białowieskim Parku Narodowym. Sylwan 2007, 151, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bobiec, A.; Jaszcz, E.; Wojtunik, K. Oak (Quercus robur L.) regeneration as a response to natural dynamics of stands in European hemiboreal zone. Eur. J. For. Res. 2011, 130, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pączewski, L. Lasy, Przemysł i Handel Drzewny w Polsce [Forests, Industry and Timber Trade in Poland]; Instytut wydawniczy Bibljoteka Polska: Warszawa, Poland, 1924. [Google Scholar]
- European Court of Justice Judgment of the Court (Grand Chamber) of 17 April 2018. European Commission vs. Republic of Poland. Case C-441/17. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legalcontent/EN/ALL/?uri=CELEX:62017CJ0441 (accessed on 17 April 2019).
- Szafer, W. Pierwsze karty z historii Białowieskiego Parku Narodowego [The first chapters of the history of Białowieża National Park]. Kosmos 1957, 5, 468–475. [Google Scholar]
- Kavalenia, A.A.; Danilovich, V.V.; Dounar, A.B.; Zhylinski, M.G.; Kalechits, A.G.; Litvin, A.M.; Lysenka, P.F.; Liauko, V.M.; Nichyparovich, S.A.; Stashkevich, A.I. (Eds.) Belavezhskaia Pushcha. Vytoki Zapavednastsi. Gistoria i Suchasnasts; Belaruskaia Navuka: Minsk, Belarus, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Barwiński, M. Podlasie jako region pogranicza. Studia z Geografii Politycznej i Historycznej 2014, 3, 281–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczanowski, P.; Kozłowski, J.K. Najdawniejsze Dzieje Ziem Polskich; Forga Oficyna Wydawnicza: Kraków, Poland, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Liszewska, M. Klimat w Polsce w XXI wieku—Prawdopodobne kierunki zmian; perspektywa klimatów lokalnych. In Materiały Pierwszego Panelu Ekspertów w Ramach prac nad Narodowym Programem Leśnym: Klimat—Lasy i Drewno a Zmiany Klimatyczne: Zagrożenia i Szanse; Rykowski, K., Ed.; Instytut Badawczy Leśnictwa: Sękocin Stary, Poland, 2014; pp. 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Szwagrzyk, J. Prawdopodobne zmiany zasięgów występowania gatunków drzewiastych—konsekwencje dla hodowli lasu. In Materiały Pierwszego Panelu Ekspertów w Ramach prac nad Narodowym Programem Leśnym. Klimat. Lasy i Drewno a Zmiany Klimatyczne: Zagrożenia i Szanse; Rykowski, K., Ed.; Instytut Badawczy Leśnictwa: Sękocin Stary, Poland, 2014; pp. 45–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dyderski, M.; Paź, S.; Frelich, L.E.; Jagodziński, A.M. How much does climate change threaten European forest tree species distributions? Glob. Chang. Biol. 2018, 24, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, K.; Degen, B.; Buschbom, J.; Hickler, T.; Thuiller, W.; Sykes, M.T.; de Winter, W.; Van der Werf, B. Modeling exploration of the future of European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) under climate change—range, abundance, genetic diversity and adaptive response. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 2213–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, D.T.; de Rigo, D.; Caudullo, G. Fagus sylvatica in Europe: Distribution, habitat, usage and threats. In European Atlas of Forest Tree Species; San-Miguel-Ayanz, J., de Rigo, D., Caudullo, G., Houston, D.T., Mauri, A., Eds.; Publication Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2016; pp. 94–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ellison, A.M.; Bank, S.M.; Clinton, B.D.; Colburn, E.A.; Elliott, K.; Ford, C.R.; Foster, D.R.; Kloeppel, B.D.; Knoepp, J.D.; Lovett, G.M.; et al. Loss of foundation species: Consequences for the structure and dynamics of forested ecosystems. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2005, 3, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, A.M.; Buckley, H.L.; Case, B.S.; Cardenas, D.; Duque, Á.J.; Lutz, J.A.; Myers, J.A.; Orwig, D.A.; Zimmerman, J.K. Species Diversity Associated with Foundation Species in Temperate and Tropical Forests. Forests 2019, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernadzki, E.; Bolibok, L.; Brzeziecki, B.; Zajączkowski, J.; Żybura, H. Compositional dynamics of natural forests in the Bialowieza National Park, northeastern Poland. J. Veg. Sci. 2009, 9, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrus, C.; Sparks, T.; Tryjanowski, P. First evidence of phenological change in a transcontinental migrant overwintering in the Indian sub-continent: The Red-breasted Flycatcher Ficedula parva. Ornis Fenn. 2005, 82, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Wesołowski, T.; Cholewa, M. Climate variation and bird breeding seasons in a primeval temperate forest. Clim. Res. 2009, 38, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huflejt, T.; Gutowski, J.M. Xylocopa valga (Hymenoptera: Apidae) w Polsce. Leśn Prace Bad 2016, 77, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bernhardt-Römermann, M.; Baeten, L.; Craven, D.; De Frenne, P.; Hédl, R.; Lenoir, J.; Bert, D.; Brunet, J.; Chudomelová, M.; Decocq, G.; et al. Drivers of temporal changes in temperate forest plant diversity vary across spatial scales. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 3726–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łubek, A.; Kukwa, M.; Jaroszewicz, B.; Czortek, P. Changes in the epiphytic lichen biota of Białowieża Primeval Forest are not explained by climate warming. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 643, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, J.; Noss, R.F.; Thorn, S.; Bässler, C.; Leverkus, A.B.; Lindenmayer, D. Increasing disturbance demands new policies to conserve intact forest. Conserv. Lett. 2019, 12, e12449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, H.; Vardon, M.; Stein, J.; Stein, J.; Lindenmayer, D.B. Ecosystem accounts define explicit and spatial trade-offs for managing natural resources. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, C.G.; McFarlane, B.; Muller, M. Human dimensions of forest disturbance by insects: An international synthesis. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 1174–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenmayer, D.B.; Foster, D.R.; Franklin, J.F.; Hunter, M.L.; Noss, R.F.; Schmiegelow, F.A.; Perry, D. Salvage harvesting policies after natural disturbance. Science 2004, 303, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenmayer, D.; Thorn, S.; Banks, S. Please do not disturb ecosystems further. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 1, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Krkošek, M.; Ashe, E.; Branch, T.A.; Clark, S.; Hammond, P.S.; Hoyt, E.; Noren, D.; Rosen, D.A.S.; Winship, A. Competing conservation objectives for predators and prey: Estimating killer whale prey requirements for Chinook salmon. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, D.S.; Mendenhall, C.D.; Callaway, E.; Frishkoff, L.O.; Kareiva, P.M.; Ehrlich, P.R.; Daily, G.C. Confronting and resolving competing values behind conservation objectives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 35, 11132–11137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrs, R.H.; Galtress, K.; Tonga, C.; Cox, E.S.; Blackbird, S.J.; Heyes, T.J.; Pakeman, R.J.; Le Duc, M.G. Competing conservation goals, biodiversity or ecosystem services: Element losses and species recruitment in a managed moorland–bracken model system. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuuluvainen, T. Natural variability of forests as a reference for restoring and managing biological diversity in boreal Fennoscandia. Silva Fenn. 2002, 36, 1–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landres, P.B.; Morgan, P.; Swanson, F.J. Overview of the use of natural variability concepts in managing ecological systems. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Attiwill, P.M. The disturbance dynamics of forest ecosystems: The ecological basis for conservative management. Forest Ecol. Manag. 1994, 63, 247–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbauer, M.J.; Grytnes, J.A.; Jurasinski, G.; Kulonen, A.; Lenoir, J.; Pauli, H.; Rixen, C.; Winkler, M.; Bardy-Durchhalter, M.; Barni, E.; et al. Accelerated increase in plant species richness on mountain summits is linked to warming. Nature 2018, 556, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesołowski, T. Virtual Conservation: How the European Union is Turning a Blind Eye to Its Vanishing Primeval Forests. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jõgiste, K.; Jonsson, B.G.; Kuuluvainen, T.; Gauthier, S.; Moser, W.K. Forest landscape mosaics: Disturbance, restoration, and management at times of global change. Can. J. For. Res. 2015, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halme, P.; Allen, K.A.; Aunins, A.; Bradshaw, R.H.W.; Brumelis, G.; Cada, V.; Clear, J.L.; Eriksson, A.M.; Hannon, G.; Hyvarinen, E.; et al. Challenges of ecological restoration: Lessons from forests in northern Europe. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 167, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangur, A.; Korjus, H.; Jõgiste, K.; Kiviste, A. A conceptual model of forest stand development based on permanent sample-plot data in Estonia. Scand. J. For. Res. 2005, 20, 6, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Taxonomic Group | BF | Poland | Central Sichote Alin | Great Smoky Mts. | Mount Huangshan | Wood Buffalo NP | Yellow-Stone NP | Fenglin Nature Reserve |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1500 km2 | 312,700 km2 | 15,539 km2 | 2090 km2 | 154 km2 | 44,800 km2 | 8983 km2 | 184 km2 | |
| Number of Species | ||||||||
| Animals | 12,000 | 40,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Birds | 250 | 454 | 370 | 240 | 170 | 226 | 311 | 220 |
| Mammals | 59 | 117 | 71 | 66 | 48 | 47 | 67 | 52 |
| Insects | 9600 | 28,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Beetles | 3199 | - | - | 2518 | - | - | - | - |
| Plants | 1280 | 3438 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vascular plants | 1070 | 2491 | 1200 | 1450 | 1650* | - | 1700 | 568 |
| Bryophytes | 263 | 947 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Fungi | 3398 | 11,000 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Macrofungi | 1998 | 3200 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Polypores | 210 | 240 | - | - | - | - | - | 161 |
| Microfungi | 1400 | 6000 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lichenicolous fungi | 50 | 240 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Lichens | 500 | 1655 | 400 | 431 | 1650* | - | 186 | - |
| Tree Species | Western Part | Eastern Part |
|---|---|---|
| Scots pine Pinus sylvestris | 28.3 | 58.0 |
| Norway spruce Picea abies | 26.8 | 10.7 |
| Black alder Alnus glutinosa | 20.0 | 15.3 |
| English oak Quercus robur | 11.0 | 4.7 |
| Silver birch Betula pendula and Downy birch Betula pubescens | 8.3 | 8.3 |
| Hornbeam Carpinus betulus | 2.2 | 1.0 |
| European ash Fraxinus excelsior | 2.2 | 1.1 |
| Aspen Populus tremula | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Other (small-leaved lime Tilia cordata, Norway maple Acer platanoides, Ulmus sp., Salix sp.) | 0.5 | 0.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaroszewicz, B.; Cholewińska, O.; Gutowski, J.M.; Samojlik, T.; Zimny, M.; Latałowa, M. Białowieża Forest—A Relic of the High Naturalness of European Forests. Forests 2019, 10, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100849
Jaroszewicz B, Cholewińska O, Gutowski JM, Samojlik T, Zimny M, Latałowa M. Białowieża Forest—A Relic of the High Naturalness of European Forests. Forests. 2019; 10(10):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100849
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaroszewicz, Bogdan, Olga Cholewińska, Jerzy M. Gutowski, Tomasz Samojlik, Marcelina Zimny, and Małgorzata Latałowa. 2019. "Białowieża Forest—A Relic of the High Naturalness of European Forests" Forests 10, no. 10: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100849
APA StyleJaroszewicz, B., Cholewińska, O., Gutowski, J. M., Samojlik, T., Zimny, M., & Latałowa, M. (2019). Białowieża Forest—A Relic of the High Naturalness of European Forests. Forests, 10(10), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10100849






