Fight Alone or Together? The Influence of Risk Perception on Helping Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
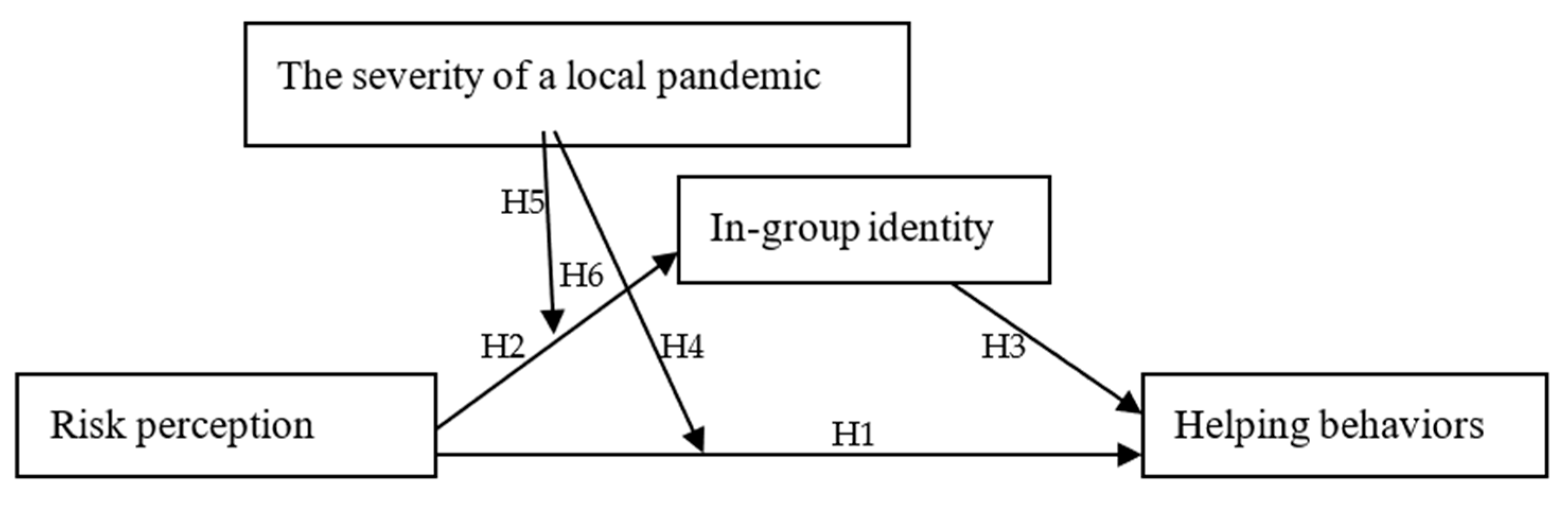
2. Literature Review and Hypotheses Development
2.1. Risk Perception and Helping Behavior
2.2. Mediating Effect of In-Group Identity
2.3. Moderating Effect of the Severity of a Local Pandemic
3. Procedure
3.1. Sample and Procedure
3.2. Study Variables
4. Results
4.1. Reliability and Validity Tests and Correlation Analysis
4.2. Hypothesis Testing
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alen, Nicholas V., LillyBelle K. Deer, Mona Karimi, Elis Feyzieva, Paul D. Hastings, and Camelia E. Hostinar. 2021. Children’s altruism following acute stress: The role of autonomic nervous system activity and social support. Developmental Science 24: e13099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cikara, Mina, and Jay J. Van Bavel. 2014. The neuroscience of intergroup relations: An integrative review. Perspectives on Psychological Science 9: 245–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, Andrew, and Trish Ruebottom. 2011. Stakeholder theory and social identity: Rethinking stakeholder identification. Journal of Business Ethics 102: 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, Amber, Natarshia Corley, and Mark Muraven. 2020. Why am i left out? interpretations of exclusion affect antisocial and prosocial behaviors. The American Journal of Psychology 133: 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farh, Jiing-Lih, Rick D. Hackett, and Jian Liang. 2007. Individual-level cultural values as moderators of perceived organizational support-employee outcome relationships in China: Comparing the effects of power distance and traditionality. Academy of Management Journal 50: 715–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, James H., and Nicholas A. Christakis. 2010. Cooperative behavior cascades in human social networks. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107: 5334–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Qing, Bang Zheng, Maximilian Agostini, Jocelyn J. Bélanger, Ben Gützkow, Jannis Kreienkamp, Anne Margit Reitsema, Jolien A. van Breen, N. Pontus Leander, and PsyCorona Collaboration. 2021. Associations of risk perception of COVID-19 with emotion and mental health during the pandemic. Journal of Affective Disorders 284: 247–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitlin, Steven, Hye Won Kwon, and Rengin Firat. 2021. In- and out-groups across cultures: Identities and perceived group values. Social Science Research 97: 102569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovoor-Misra, Sarah. 2009. Understanding perceived organizational identity during crisis and change. Journal of Organizational Change Management 22: 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Kenneth N., Jessica K. Hlay, Benjamin N. Johnson, and Courtney P. Witmer. 2019. An attachment theoretical perspective on tend-and-befriend stress reactions. Evolutionary Psychological Science 5: 426–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyens, Jacques-Philippe, Paola M. Paladino, Ramon Rodriguez-Torres, Jeroen Vaes, Stephanie Demoulin, Armando Rodriguez-Perez, and Ruth Gaunt. 2016. The emotional side of prejudice: The attribution of secondary emotions to ingroups and outgroups. Personality & Social Psychology Review 4: 186–97. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, Daniel, and David DeSteno. 2016. Suffering and compassion: The links among adverse life experiences, empathy, compassion, and prosocial behavior. Emotion 16: 175–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, Silvia U., Aidan B. Makwana, and Todd A. Hare. 2015. Acute stress impairs self-control in goal-directed choice by altering multiple functional connections within the brain’s decision circuits. Neuron 87: 621–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mai, Yingping, Yenchun Jim Wu, and Yanni Huang. 2021. What type of social support is important for student resilience during COVID-19? a latent profile analysis. Frontiers in Psychology 12: 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margittai, Zsofia, Tina Strombach, M. van Wingerden, M. Joëls, Lars Schwabe, and Tobias Kalenscher. 2015. A friend in need: Time-dependent effects of stress on social discounting in men. Hormones and Behavior 73: 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Lu, Fengjun Liu, Kun Duan, Xi Li, and Tongmao Li. 2021. Impact of intensity of shared human events on citizen behavior in the novel coronavirus pneumonia: Based on the perspective of corporate social responsibility perception. Nankai Business Review 5: 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Xiaoya, Xin Sun, Yi Kuang, and Zuojun Wang. 2021. Co-experiencing the same negative emotional events promotes cooperation. Acta Psychologica Sinica 53: 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayachi, Kazuya, and Taku Ozaki. 2014. A method to improve trust in disaster risk managers: Voluntary action to share a common fate. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 10: 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Li lin, Ru Han, Xiaopeng Ren, Xinwen Bai, Rui Zhang, Huan Liu, Zuojun Wang, Kan Zhang, and Shu Li. 2011. Disadvantage and prosocial behavior: The effects of the Wenchuan earthquake. Evolution and Human Behavior 32: 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savadori, Lucia, and Marco Lauriola. 2021. Risk perception and protective behaviors during the rise of the Covid-19 outbreak in Italy. Frontiers in Psychology 11: 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, Claudia R, Sarah Dryhurst, John Kerr, Alexandra L. J. Freeman, and Sander Van Der Linden. 2021. COVID-19 risk perception: A longitudinal analysis of its predictors and associations with health protective behaviours in the United Kingdom. Journal of Risk Research 24: 294–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staub, Ervin, and Johanna Vollhardt. 2008. Altruism born of suffering: The roots of caring and helping after victimization and other trauma. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry 78: 267–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbeis, Nikolaus, Veronika Engert, Roman Linz, and Tania Singer. 2015. The effects of stress and affiliation on social decision-making: Investigating the tend-and-befriend pattern. Psychoneuroendocrinology 62: 138–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, Shelley E. 2006. Tend and befriend: Biobehavioral bases of affiliation under stress. Current Directions in Psychological Science 15: 273–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, Shelley E., Laura Cousino Klein, Brian P. Lewis, Tara L. Gruenewald, Regan AR Gurung, and John A. Updegraff. 2000. Biobehavioral responses to stress in females: Tend-and-befriend, not fight-or-flight. Psychological Review 107: 411–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, John C. 1981. Toward a cognitive redefinition of the social group. Cahiers De Psychologie Cognitive 1: 93–118. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Xingyong, Leijie Liu, Yiping Zhang, Yaya Peng, and Chenglu Lin. 2020. How prosocial motivation and helping behavior influence contextual performance: The mechanism and context situation of cognitive trust. Nankai Business Review 23: 203–13. [Google Scholar]
- Vesa, Peltokorpi. 2020. Host country national employees’ prosocial behavior toward expatriates in foreign subsidiaries: A common ingroup identity model perspective. International Business Review 29: 1184–99. [Google Scholar]
- Vezzali, Loris, Alessia Cadamuro, Annalisa Versari, Dino Giovannini, and Elena Trifiletti. 2015. Feeling like a group after a natural disaster: Common ingroup identity and relations with outgroup victims among majority and minority young children. British Journal of Social Psychology 54: 519–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Dawans, Bernadette, Urs Fischbacher, Clemens Kirschbaum, Ernst Fehr, and Markus Heinrichs. 2012. The social dimension of stress reactivity: Acute stress increases prosocial behavior in humans. Psychological Science 23: 651–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Yiying, and Yingying Sun. 2021. Discussion on voluntary behavior during the prevention and control of COVID-19 from the perspective of international comparison. Statistics and Management 36: 36–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Jiuchang. 2020. The present and future research on public risk perception evolution and protective action decision amid public health emergencies. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China 34: 776–85. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, Steve, and Yvonne Wong Wee Voon. 1999. The effects of mood on managerial risk perceptions: Exploring affect and the dimensions of risk. Journal of Social Psychology 139: 268–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Xiaofei, Yilu Wang, Siyi Gu, and Wei Li. 2017. Is altruism just other-benefiting? A dual pathway model from an evolutionary perspective. Advances in Psychological Science 25: 1441–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Yali, and Yalin Wang. 2021. The emerging emotions and life changes in the risk situation. Journal of HIT (Social science editon) 23: 50–58. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Dan. 2018. The relationship between traumatic experience and prosocial behavior, and its mechanism. Chinese Social Psychological Review 2: 198–214, 249–250. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Seong Won, Scott M Soltis, Jason R. Ross, and Giuseppe Joe Labianca. 2021. Dormant tie reactivation as an affiliative coping response to stressors during the COVID-19 crisis. Journal of Applied Psychology 106: 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Jiaqi, Sunghoon Kim, Stephen X. Zhang, Maw-Der Foo, Aldo Alvarez-Risco, Shyla Del-Aguila-Arcentales, and Jaime A. Yáñez. 2021. Hospitality workers’ covid-19 risk perception and depression: A contingent model based on transactional theory of stress model. International Journal of Hospitality Management 95: 102935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Yumeng, Karyn L. Wang, and Markus Groth. 2017. Feeling bad and doing good: The effect of customer mistreatment on service employee’s daily display of helping behaviors. Personnel Psychology 70: 769–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Yaping, and Ronggang Zhou. 2021. Promoting social distancing and preventing panic buying during the pandemic of COVID-19: The contributions of people’s psychological and behavioural factors. Journal of Public Health 4: 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Chun dong, Ning Liu, Nan Feng, and Minqiang Li. 2021. Generating mechanism of individual prosocial behavior in the context major public threats: A case of the novel coronavirus pandemic. Journal of Management Sciences in China 24: 63–79. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Tianshuang, Qing Hu, and Lijuan Cui. 2018. Common ingroup identity and intergroup helping: The mediating effect of intergroup threat. Psychological Research 11: 333–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Yue, Yimo Shen, Xia Zhou, and Dong Yang. 2020. A conditional process model of public negative emotions and mental health under the COVID 19: The moderating role of interpersonal alienation. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition) 42: 1–10. [Google Scholar]
| Variables | Mean | SD | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 1.39 | 0.49 | |||||||||
| Age | 2.84 | 0.99 | −0.45 ** | ||||||||
| Education | 2.58 | 1.03 | 0.25 ** | −0.45 ** | |||||||
| Tenure of employment | 4.30 | 1.29 | −0.21 ** | 0.42 ** | −0.20 ** | ||||||
| Marital status | 2.79 | 0.65 | −0.11 ** | 0.41 ** | −0.31 ** | 0.48 ** | |||||
| Experience with the pandemic | 3.95 | 0.24 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.02 | −0.01 | −0.01 | ||||
| Severity of the local pandemic | 2.88 | 0.40 | −0.04 | 0.11 ** | −0.01 | 0.05 | 0.12 ** | 0.03 | |||
| Risk perceptions | 4.13 | 0.89 | −0.02 | −0.05 | −0.01 | 0.03 | 0.02 | −0.03 | −0.03 | ||
| In-group identity | 3.86 | 0.94 | −0.08 * | 0.09 ** | −0.12 ** | 0.10 ** | 0.11 ** | −0.01 | −0.02 | 0.42 ** | |
| Helping behaviors | 4.69 | 0.58 | 0.01 | 0.09 ** | −0.15 ** | 0.09 ** | 0.17 ** | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.20 ** | 0.31 ** |
| Variables | Estimate | S.E. | Est./S.E. | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.092 * | 0.037 | 2.531 | 0.011 |
| Age | 0.031 | 0.043 | 0.708 | 0.479 |
| Education | −0.136 ** | 0.040 | −3.418 | 0.001 |
| Tenure of employment | −0.008 | 0.039 | −0.217 | 0.828 |
| Type of company | −0.101 ** | 0.033 | −3.091 | 0.002 |
| Marital status | 0.112 ** | 0.039 | 2.886 | 0.004 |
| Experience with the pandemic | 0.021 | 0.077 | 0.651 | 0.515 |
| RP → HB | 0.230 ** | 0.036 | 6.467 | 0.001 |
| RP → IGI | 0.558 *** | 0.068 | 8.249 | 0.000 |
| Mediating effect of in-group identity | 0.097 *** | 0.021 | 4.636 | 0.000 |
| Model | Estimate | S.E. | Est./S.E. | p-Value | 95% CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| H4 | High-risk areas | 0.015 | 0.082 | 0.185 | 0.853 | −0.120 | 0.217 |
| Areas with moderate risk | 0.064 | 0.036 | 1.751 | 0.080 | −0.003 | 0.144 | |
| Low-risk areas | 0.135 | 0.032 | 4.164 | 0.000 | 0.080 | 0.204 | |
| Differences between groups | −0.072 | 0.019 | −3.679 | 0.000 | −0.114 | −0.038 | |
| H5 | High-risk areas | 0.790 | 0.151 | 5.245 | 0.000 | 0.430 | 1.048 |
| Areas with moderate risk | 0.413 | 0.047 | 8.845 | 0.003 | 0.318 | 0.501 | |
| Low-risk areas | 0.428 | 0.040 | 10.645 | 0.001 | 0.325 | 0.506 | |
| Differences between groups | −0.805 | 0.153 | −5.255 | 0.002 | −1.070 | −0.441 | |
| H6 | High-risk areas | 0.056 | 0.067 | 0.830 | 0.406 | −0.028 | 0.238 |
| Areas with moderate risk | 0.070 | 0.013 | 5.211 | 0.000 | 0.047 | 0.100 | |
| Low-risk areas | 0.245 | 0.177 | 1.381 | 0.167 | 0.090 | 0.737 | |
| Differences between groups | 0.119 | 0.189 | 0.627 | 0.531 | −0.118 | 0.623 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yin, L.; Wu, Y.-C.J. Fight Alone or Together? The Influence of Risk Perception on Helping Behavior. J. Risk Financial Manag. 2022, 15, 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15020078
Yin L, Wu Y-CJ. Fight Alone or Together? The Influence of Risk Perception on Helping Behavior. Journal of Risk and Financial Management. 2022; 15(2):78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15020078
Chicago/Turabian StyleYin, Liping, and Yen-Chun Jim Wu. 2022. "Fight Alone or Together? The Influence of Risk Perception on Helping Behavior" Journal of Risk and Financial Management 15, no. 2: 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15020078
APA StyleYin, L., & Wu, Y.-C. J. (2022). Fight Alone or Together? The Influence of Risk Perception on Helping Behavior. Journal of Risk and Financial Management, 15(2), 78. https://doi.org/10.3390/jrfm15020078







