Road Dust Lead (Pb) in Two Neighborhoods of Urban Atlanta, (GA, USA)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Concentrations
| # analyses | Minimum | 25th percentile | Median | 75th percentile | Maximum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Downtown | 26 | |||||
| Cu | 20 | 53 | 70 | 137 | 226 | |
| Cr | 80 | 119 | 161 | 193 | 310 | |
| Ni | 6 | 11 | 16 | 20 | 68 | |
| Zn | 63 | 128 | 204 | 344 | 789 | |
| Pb | 25 | 52 | 63 | 98 | 278 | |
| NPU-V | 48 | |||||
| Cu | 22 | 49 | 68 | 113 | 1,445 | |
| Cr | 76 | 109 | 129 | 171 | 385 | |
| Ni | 7 | 14 | 18 | 22 | 74 | |
| Zn | 68 | 143 | 220 | 308 | 1,115 | |
| Pb | 17 | 65 | 93 | 142 | 972 |
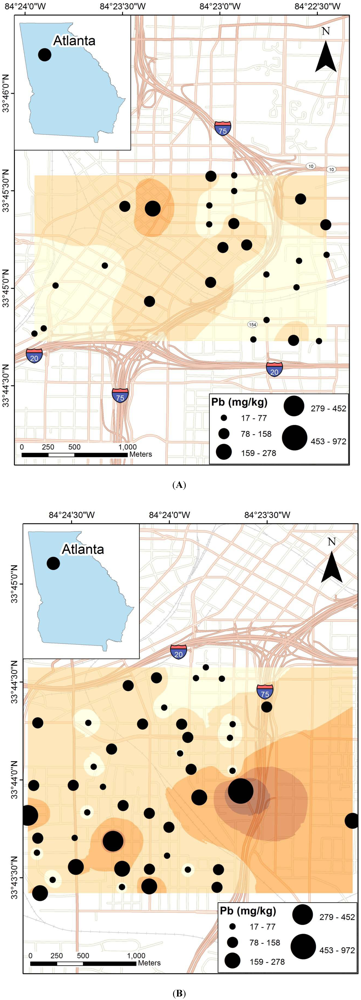
3.2. Intercorrelation
| Ba | Co | Cr | Cu | Fe | Mn | Mo | Ni | P | Pb | S | V | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | –0.01 | –0.15 | 0.48 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.21 | –0.04 | 0.01 | 0.34 | –0.10 | 0.29 | |
| Co | 0.27 | 0.36 | 0.70 | 0.59 | 0.28 | 0.73 | 0.45 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 0.55 | 0.40 | ||
| Cr | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.65 | 0.44 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.37 | |||
| Cu | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 0.56 | 0.24 | 0.65 | ||||
| Fe | 0.88 | 0.42 | 0.88 | 0.69 | 0.05 | 0.69 | 0.85 | 0.54 | |||||
| Mn | 0.35 | 0.82 | 0.71 | 0.10 | 0.71 | 0.74 | 0.55 | ||||||
| Mo | 0.60 | 0.39 | 0.21 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.73 | |||||||
| Ni | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.61 | ||||||||
| P | 0.19 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.72 | |||||||||
| Pb | –0.12 | –0.05 | 0.42 | ||||||||||
| S | 0.62 | 0.63 | |||||||||||
| V | 0.36 | ||||||||||||
| Zn |
4. Discussion
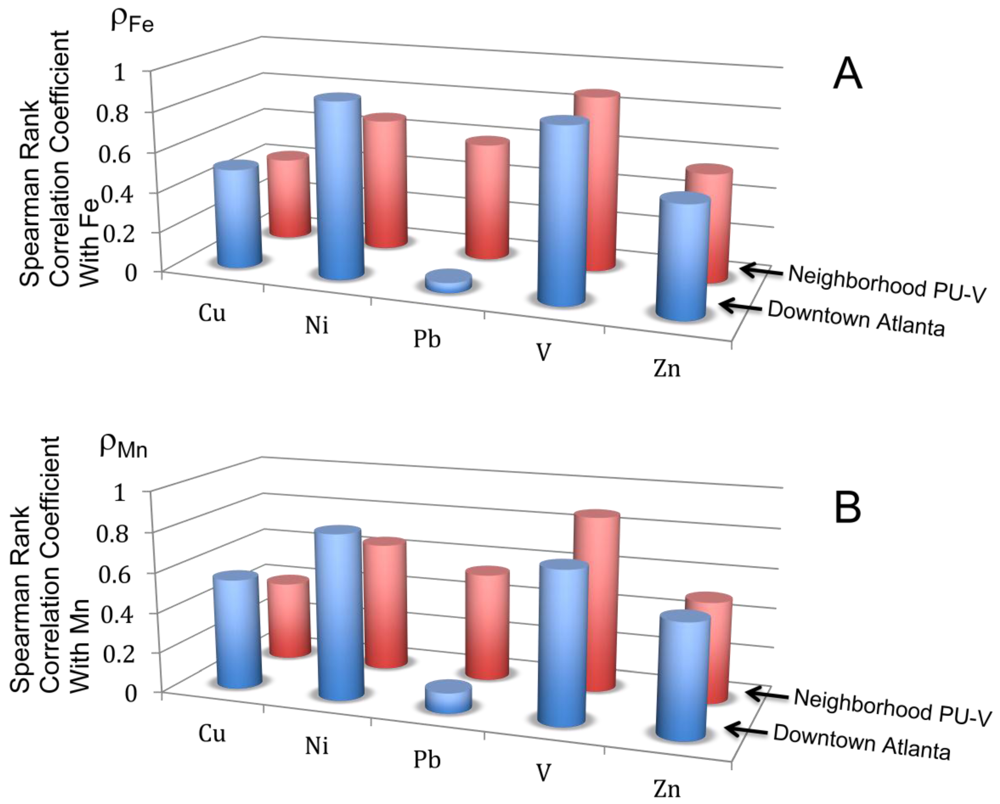
4.1. Statistical Analysis
4.2. Geospatial Distribution
| Ba | Co | Cr | Cu | Fe | Mn | Mo | Ni | P | Pb | S | V | Zn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 0.23 | –0.13 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.22 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.24 | 0.14 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.35 | |
| Co | 0.19 | 0.29 | 0.75 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.45 | 0.27 | 0.81 | 0.50 | ||
| Cr | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 0.47 | 0.05 | 0.39 | 0.21 | 0.24 | 0.36 | |||
| Cu | 0.42 | 0.40 | 0.57 | 0.60 | 0.24 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.62 | ||||
| Fe | 0.85 | 0.16 | 0.67 | 0.62 | 0.59 | 0.24 | 0.87 | 0.54 | |||||
| Mn | 0.18 | 0.65 | 0.71 | 0.54 | 0.44 | 0.87 | 0.50 | ||||||
| Mo | 0.56 | 0.07 | 0.45 | 0.39 | –0.06 | 0.58 | |||||||
| Ni | 0.51 | 0.68 | 0.44 | 0.52 | 0.82 | ||||||||
| P | 0.54 | 0.59 | 0.70 | 0.59 | |||||||||
| Pb | 0.35 | 0.39 | 0.79 | ||||||||||
| S | 0.30 | 0.55 | |||||||||||
| V | 0.35 | ||||||||||||
| Zn |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Jones, R.L.; Homa, D.M.; Meyer, P.A.; Brody, D.J.; Caldwell, K.L.; Pirkle, J.L.; Brown, M.J. Trends in blood lead levels and blood testing among US children aged 1 to 5 years, 1988-2004. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CDC National Surveillance Data (1997–2009), National Center for Environmental Health. 2012. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/nceh/lead/data/national.htm (accessed on 24 April 2012).
- Advisory Committee on Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (ACCLPP). Low Level Lead Exposure Harms Children: A Renewed Call for Primary Prevention; Report to the CDCP. 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Needleman, H.L.; Schell, A.; Bellinger, D.; Leviton, A.; Allred, E.N. The long-term effects of exposure to low doses of lead in childhood. An 11-year follow up report. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binns, H.J.; Campbell, C.; Brown, M.J. Interpreting and managing blood lead levels of less than 10 microg/dL in children and reducing childhood exposure to lead: Recommendations of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee on Childhood Lead Poisoning Prevention. Pediatrics 2007, 120, e1285–e1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, D.C. Lead neurotoxicity and socioeconomic status: Conceptual and analytical issues. Neurotoxicology 2008, 29, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gump, B.B.; Stewart, P.; Reihman, J.; Lonky, E.; Darvill, T.; Parsons, P.J.; Granger, D.A. Low-level prenatal and postnatal blood lead (Pb) exposure and adrenocortical responses to acute stress in children. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 249–255. [Google Scholar]
- Nigg, J.T.; Knottnerus, G.M.; Martel, M.M.; Nikoas, M.; Cavanagh, V.; Karmaus, W.; Rappley, M.D. Low blood lead levels associated with clinically diagnosed attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and mediated by weak cognitive control. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Academy of Pediatrics. Lead exposure in children: Prevention, detection, and management: Statement of policy reaffirmation. Pediatrics 2009, 123, 1421–1422. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Gaitens, J.M.; Jacobs, D.E.; Strauss, W.; Nagaraja, J.; Pivetz, T.; Wilson, J.W.; Ashley, P.J. Exposure of U.S. children to residential dust lead, 1999-2004: II. The contribution of lead-contaminated dust to children’s blood lead levels. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 468–474. [Google Scholar]
- Mielke, H.W.; Laidlaw, M.A.; Gonzales, C.R. Estimation of Leaded (Pb) gasoline’s continuing material and health impacts on 90 urbanized areas. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.A. Inorganic Colored Pigments. In Paint and Coating Testing Manual, 14th; Koleske, J.V., Ed.; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 1–950. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, G.; Tinklenberg, J. Determination of Ti, Zn, and Pb in lead-based house paints by EDXRF. J. Anal. Atom. Spectr. 2003, 18, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaulya, S.K. Air quality status of an open pit mining area in India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 105, 369–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippelli, G.M.; Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Latimer, J.C.; Raftis, R. Urban lead poisoning and medical geology: An unfinished story. Geolog. Soc. Am. Today 2005, 15, 4–11. [Google Scholar]
- Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Zahran, S.; Mielke, H.W.; Taylor, M.P.; Filippelli, G.M. Re-suspension of lead contaminated urban soil as a dominant source of atmospheric lead in Birmingham, Chicago, Detroit and Pittsburgh, USA. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 49, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.W.; Gonzales, C.; Hooper, M.J.; Bayat, A.C.; Fornerette, A.M.; McBride, T.J.; Longoria, T.; Mielke, H.W. Soil lead (Pb) in residential transects through Lubbock, Texas: A preliminary assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicchella, D.; de Vivo, B.; Lima, A.; Albanese, S.; McGill, R.A.R.; Parrish, R.R. Heavy metal pollution and Pb isotopes in urban soils of Napoli, Italy. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2008, 8, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diawara, M.M.; Litt, J.S.; Unis, D.; Alfonso, N.; Martinez, L.; Crock, J.G. Arsenic, cadmium, lead, and mercury in surface soils in Pueblo, Colorado: Implications for population health risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2006, 28, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlap, C.E.; Alpers, C.N.; Bouse, R.; Taylor, H.E.; Unhruh, D.M.; Flegal, A.R. The persistence of lead from past gasoline emissions and mining drainage in a large riparian system: Evidence from lead isotopes in the Sacramento River, California, USA. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2008, 72, 5935–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laidlaw, M.A.S.; Filippelli, G.M. Resuspension of urban soils as a persistent source of lead poisoning in children: A review and new directions. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 2021–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, I. Metal Contamination of Soils in Urban Areas. In Soils in the Urban Environment; Bullock, P., Gregory, P.J., Eds.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 1991; pp. 47–75. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Poon, C.-S.; Liu, P.S. Heavy metal contamination urban soils and street dusts in Hong Kong. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 1361–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, N.; Ozcan, H.K.; Demir, G.; Nemlioglu, S.; Bayat, C. Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Instanbul E-5 highway. Environ. Int. 2004, 29, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalenuik, A.; Deocampo, D.M. Pb in urban road dust of Atlanta, Georgia: Distribution and Geostatistical analyses. Geolog. Soc. Am. Abs. Prog. 2011, 43, 582. [Google Scholar]
- Solt, M.; Deocampo, D. Multivariate analysis of lead in urban soil in Sacramento, CA. Geol. Soc. Am. Abs. Prog. 2010, 42, 615. [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie, E.R.; Money, J.E.; Green, P.G.; Young, T.M. Metals associated with stormwater-relevant brake and tire samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5855–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wong, M.H.; Leharne, S.; Fisher, B. Fractionation and biotoxicity of heavy metals in urban dusts collected in Hong Kong and London. Env. Geochem. Health 1998, 20, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, G.; Burghardt, W. Concentrations and chemical speciations of Cu, Zn, Pb and Cr of urban soils in Nanjing, China. Geoderma 2003, 115, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, R.A. Lead loading of urban streets by motor vehicle wheel weights. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivoruchko, K. Spatial Statisical Data Analysis for GIS Users; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Deocampo, D.M.; Reed, P.J.; Kalenuik, A.P. Road Dust Lead (Pb) in Two Neighborhoods of Urban Atlanta, (GA, USA). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2020-2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9062020
Deocampo DM, Reed PJ, Kalenuik AP. Road Dust Lead (Pb) in Two Neighborhoods of Urban Atlanta, (GA, USA). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2012; 9(6):2020-2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9062020
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeocampo, Daniel M., Phillip Jack Reed, and Alexander P. Kalenuik. 2012. "Road Dust Lead (Pb) in Two Neighborhoods of Urban Atlanta, (GA, USA)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 9, no. 6: 2020-2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9062020
APA StyleDeocampo, D. M., Reed, P. J., & Kalenuik, A. P. (2012). Road Dust Lead (Pb) in Two Neighborhoods of Urban Atlanta, (GA, USA). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 9(6), 2020-2030. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph9062020




