A Framework for the Specificity of Addictions
Abstract
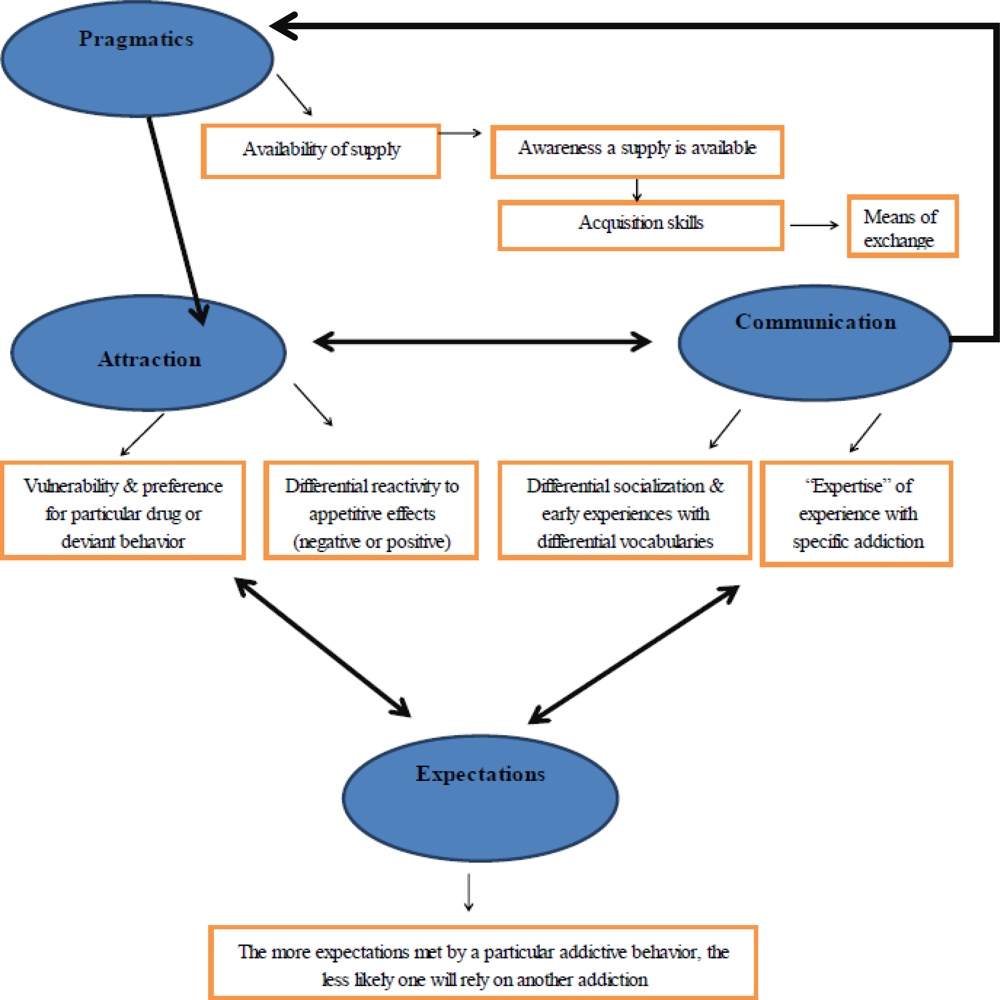
:2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Pragmatics
2.2. Attraction
2.3. Communication
2.4. Expectations
3. Future Research Needs and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References and Notes
- Brewer, JA; Potenza, MN. The neurobiology and genetics of impulse control disorders: Relationships to drug addictions. Biochem. Pharmacol 2008, 75, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, A. Addiction: Definition and implications. Br. J. Addict 1990, 85, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, A. Neurobiology of addiction: An integrative review. Biochem. Pharmacol 2008, 75, 266–322. [Google Scholar]
- Hatterer, LJ. The addictive process. Psychiatr. Q 1982, 54, 149–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, DF. A general theory of addictions: A new theoretical model. J. Gambl. Behav 1986, 2, 15–31. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, I. Behaviour (non-chemical) addictions. Br. J. Addict 1990, 85, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Marlatt, GA; Baer, JS; Donovan, DM; Kivlahan, DR. Addictive behaviors: Etiology and treatment. Annu. Rev. Psychol 1988, 39, 223–252. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, S; Ames, SL. Drug Abuse: Concepts, Prevention and Cessation; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Faber, RJ; Christenson, GA; de Zwaan, M; Mitchell, J. Two forms of compulsive consumption: Comorbidity of compulsive buying and binge eating. J. Consum. Res 1995, 22, 296–304. [Google Scholar]
- Pelchat, ML. Of human bondage: Food craving, obsession, compulsion, and addiction. Physiol. Behav 2002, 76, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, JP; Irons, RR. Assessment and treatment of addictive sexual disorders: Dependency relapse. Subst. Use Misuse 2001, 36, 1795–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer, HJ; LaPlante, DA; LaBrie, RA; Kidman, RC; Donato, AN; Stanton, MV. Toward a syndrome model of addiction: Multiple expressions, common etiology. Harv. Rev. Psychiatry 2004, 12, 367–374. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderwirth, SG; Milkman, H. Behavioral and neurochemical commonalities in addiction. Contemp. Fam. Ther 1991, 13, 421–433. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, S; Lisha, N; Griffiths, M. Prevalence of the addictions: A problem of the majority or the minority. Eval. Health Prof 2011, 34, 3–56. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, TE; Berridge, KC. Mechanisms of action of addictive stimuli. Incentive-sensitization and addiction. Addiction 2001, 96, 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, TE; Berridge, KC. The incentive sensitization theory of addiction: Some current issues. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2008, 363, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar]
- Bechara, A. Decision making, impulse control and loss of willpower to resist drugs: A neurocognitive perspective. Nat. Neurosci 2005, 8, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy, AW; Ames, SL; Knowlton, B. Neurologically plausible distinctions in cognition relevant to drug abuse etiology and prevention. Subst. Use Misuse 2004, 39, 1571–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Tiffany, ST. A cognitive model of drug urges and drug-use behavior: The role of automaatic and non-automatic processes. Psychol. Rev 1990, 97, 147–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wiers, RW; Ames, SL; Hoffmann, W; Krank, M; Stacy, AW. Impulsivity, impulsive and reflective processes and the development of alcohol use and misuse in adolescents and young adults. Front. Psychopathol 2010, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Carnes, PJ; Murray, RE; Charpentier, L. Bargains with chaos: Sex addicts and addiction interaction disorder. Sex. Addict. Compuls 2005, 12, 79–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lesieur, HR; Blume, SB. Pathological gambling, eating disorders and the psychoactive substance use disorders. J. Addict. Behav 1993, 12, 89–102. [Google Scholar]
- Haylett, SA; Stephenson, GM; Lefever, RMH. Covariation in addictive behaviors: A study of addictive orientations using the shorter PROMIS Questionnaire. Addict. Behav 2004, 29, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman, EC. The consciousness of addiction: Toward a general theory of compulsive consumption. J. Consum. Res 1992, 19, 155–179. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, S; Black, DS. Substitute addiction: A concern for researchers and practitioners. J. Drug Educ 2008, 38, 167–180. [Google Scholar]
- Freimuth, M; Waddell, M; Stannard, J; Kelley, S; Kipper, A; Richardson, A; Szuromi, I. Expanding the scope of dual diagnosis and co-addictions: Behavioral addictions. J. Groups Addict. Recover 2008, 3, 137–160. [Google Scholar]
- Iacono, WG; Malone, SM; McGue, M. Behavioral disinhibition and the development of early-onset addiction: Common and specific influences. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol 2008, 4, 325–348. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, SL; McBride, C. Translating genetics, cognitive science and other basic science research findings into applications for prevention of substance use. Eval. Health Prof 2006, 29, 277–301. [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, EJ; Landsman, D. Learning about addiction from the genome. Nature 2001, 409, 834–835. [Google Scholar]
- Ducci, F; Enoch, M-A; Funt, S; Virkkunen, M; Albaugh, B; Goldman, D. Increased anxiety and other similarities in temperament of alcoholics with and without antisocial personality disorder across three diverse populations. Alcohol 2007, 41, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ames, SL; Grenard, J; Thush, C; Sussman, S; Wiers, RW; Stacy, AW. Comparison of indirect assessments of association as predictors of marijuana use among at-risk adolescents. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol 2007, 15, 204–218. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy, AW. Memory association and ambiguous cues in models of alcohol and marijuana use. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol 1995, 3, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy, AW. Memory activation and expectancy as prospective predictors of alcohol and marijuana use. J. Abnorm. Psychol 1997, 106, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, TL. Foundations of Interpersonal Attraction; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, S; Unger, JB. A “drug abuse” theoretical Integration: A transdisciplinary speculation. Subst. Use Misuse 2004, 39, 2055–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Sussman, S; Reynaud, M; Aubin, H-J; Leventhal, AM. Drug addiction, love, and the higher power. Eval. Health Prof 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornish, JW; O’Brien, CP. Crack cocaine abuse: An epidemic with many public health consequences. Annu. Rev. Public Health 1996, 17, 259–273. [Google Scholar]
- Jiggens, J. Australian heroin seizures and the causes of the 2001 heroin shortage. Int. J. Drug Policy 2008, 19, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, E; Stolz, J-A; Li, K; Montaner, JSG; Kerr, T. Changes in Canadian heroin supply coinciding with the Australian heroin shortage. Addiction 2006, 101, 689–695. [Google Scholar]
- Bluthenthal, RN; Cohen, DA; Farley, TA; Scribner, R; Beighley, C; Schonlau, M; Robinson, PL. Alcohol availability and neighborhood characteristics in Los Angeles, California and southern Louisiana. J. Urban Health 2008, 85, 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- LaBrie, RA; Nelson, SE; LaPlante, DA; Peller, AJ; Caro, G; Shaffer, HJ. Missouri casino self-excluders: Distributions across time and space. J. Gambl. Stud 2007, 23, 231–243. [Google Scholar]
- Akers, RL; Krohn, MD; Lanza-Kaduce, L; Radosevich, M. Social learning and deviant behavior: A specific test of a general theory. Am. Sociol. Rev 1979, 44, 636–655. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, LD; O’Malley, PM; Bachman, JG; Schulenberg, JE. Monitoring the Future National Survey Results on Drug Use, 1975–2008; National Institute on Drug Abuse: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2009; Volume I, pp. 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Potenza, MN; Fiellin, DA; Heninger, GR; Rounsaville, BJ; Mazure, CM. Gambling: An addictive behavior with health and primary care implications. J. Gen. Intern. Med 2002, 17, 721–732. [Google Scholar]
- Le Bon, O; Streel, E; Tecco, J; Hanak, C; Hansenne, M; Ansseau, M; Pelc, I; Verbanck, P; Dupont, S. Personality profile and drug of choice: A multivariate analysis using Cloninger's TCI on heroin addicts, alcoholics, and a random population group. Drug Alcohol Depend 2004, 73, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Moffitt, TE; Caspi, A; Dickosn, N; Silva, P; Stanton, W. Childhood-onset versus adolescentonset antisocial conduct problems in males: Natural history from ages 3 to 18 years. Dev. Psychopathol 1996, 8, 399–424. [Google Scholar]
- Freimuth, M. Addicted? Recognizing Destructive Behavior before It's Too Late; Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc.: Lanham, MD, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Di Chiara, G. Nucleus accumbens shell and core dopamine: Differential role in behavior and addiction. Behav. Brain Res 2002, 137, 75–114. [Google Scholar]
- Haertzen, CA; Kocher, TR; Miyasato, K. Reinforcements from the first drug experience can predict later drug habits and/or addiction: Results with coffee, cigarettes, alcohol, barbiturates, minor and major tranquilizers, stimulants, marijuana, hallucinogens, heroin, opiates and cocaine. Drug Alcohol Depend 1983, 11, 147–165. [Google Scholar]
- De Wit, H. Individual differences in acute effects of drugs in humans: Their relevance to risk for abuse. NIDA Res. Monogr 1998, 169, 176–187. [Google Scholar]
- Pepino, MY; Mennella, JA. Factors contributing to individual differences in sucrose preference. Chem. Senses 2005, 30(Suppl 1), i319–i320. [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal, AM; Chasson, GS; Tapia, E; Miller, EK; Pettit, JW. Measuring hedonic capacity in depression: A psychometric analysis of three anhedonia scales. J. Clin. Psychol 2006, 62, 1545–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, LK; Naranjo, CA; Cardenas, L; Herrmann, N; Busto, UE. Probing brain reward system function in major depressive disorder: Altered response to dextroamphetamine. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2002, 59, 409–417. [Google Scholar]
- Tremblay, LK; Naranjo, CA; Graham, SJ; Herrmann, N; Mayberg, HS; Hevenor, S; Busto, UE. Functional neuroanatomical substrates of altered reward processing in major depressive disorder revealed by a dopaminergic probe. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Khantzian, EJ. The self-medication hypothesis of addictive disorders: Focus on heroin and cocaine dependence. Am. J. Psychiatry 1985, 142, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Suh, JJ; Ruffins, S; Robins, CE; Albanese, MJ; Khantzian, EJ. Self-medication hypothesis: Connecting affective experience and drug choice. Psychoanal. Psychol 2008, 25, 518–532. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M. P-impulsive sensation seeking and its behavioral, psychophysiological and biochemical correlates. Neuropsychobiology 1993, 28, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman, M. Behavioral Expressions and Biosocial Bases of Sensation Seeking; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Wiers, RW; Stacy, AW. Handbook of Implicit Cognition and Addiction; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kensinger, EA; Garoff-Eaton, RJ; Schacter, DL. How negative emotion enhances the visual specificity of a memory. J. Cognit. Neurosci 2007, 19, 1872–1887. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, BL; Tiffany, ST. Meta-analysis of cue-reactivity in addiction research. Addiction 1999, 94, 327–340. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, RA; Taylor, JR; Poetnza, MN. Developmental neurocircuitry of motivation in adolescence: A critical period of addiction vulnerability. Am. J. Psychiatry 2003, 160, 1041–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Giedd, JN. The teen brain: Insights from neuroimaging. J. Adolesc. Health 2008, 42, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Giedd, JN; Lalonde, FM; Celano, MJ; White, SL; Wallace, GL; Lee, NR; Lenroot, RK. Anatomical brain magnetic resonance imaging of typically developing children and adolescents. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2009, 48, 465–470. [Google Scholar]
- Leventhal, AM; Waters, AJ; Boyd, S; Moolchan, ET; Heishman, SJ; Lerman, C; Pickworth, WB. Associations between Cloninger's temperament dimensions and acute tobacco withdrawal. Addict. Behav 2007, 32, 2976–2989. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, DG; Brown, SA. Withdrawal and dependency symptoms among adolescent alcohol and drug abusers. Addiction 1995, 90, 627–635. [Google Scholar]
- Elder, G. Life Course and Human Development. In Handbook of Child Psychology; Lerner, RM, Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1998; Volume 1, pp. 939–991. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, J; Schrepferman, L; Oeser, J; Patterson, G; Stoolmiller, M; Johnson, K; Snyder, A. Deviancy training and association with deviant peers in young children: Occurrence and contribution to early-onset conduct problems. Dev. Psychopathol 2005, 17, 397–413. [Google Scholar]
- Bahr, SJ; Hoffmann, JP; Yang, X. Parental and peer influences on the risk of adolescent drug use. J. Primary Prev 2005, 26, 529–551. [Google Scholar]
- Hyde, JP. The language game: “Rat” talk: The special vocabulary of some teenagers. Engl. J 1982, 71, 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: www.ildado.com/casino_glossary.html (accessed on 9 December 2010).
- Nace, EP. Epidemiology of alcoholism and prospects for treatment. Annu. Rev. Med 1984, 35, 293–309. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno, JA. Strategies for challenging police jargon testimony. Crim. Justice 2006, 20, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, V; McIntyre, T; Silmon, H. What's the flavor? Understanding inmate slang usage in correctional education settings. J. Correct. Educ 1997, 48, 192–197. [Google Scholar]
- Dalzell, T; Victor, T. Vice Slang; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rotter, JB. Social Learning and Clinical Psychology; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, MS. Expectancy and risk for alcoholism: The unfortunate exploitation of a fundamental characteristic of neurobehavioral adaptation. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res 2002, 26, 737–746. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, MS; Reich, RR; Darkes, J. Expectancy as a unifying construct in alcohol-related cognition. In Handbook of Implicit Cognition and Addiction; Wiers, R, Stacy, A, Eds.; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 105–121. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, MS; Brown, SA; Christiansen, BA; Smith, GT. Alcoholism and memory: Broadening the scope of alcohol-expectancy research. Psychol. Bull 1991, 110, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, RR; Goldman, MS. Exploring the alcohol expectancy memory network: The utility of free associates. Psychol. Addict. Behav 2005, 19, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, MS; Darkes, J. Alcohol expectancy multiaxial assessment: A memory network-based approach. Psychol. Assess 2004, 16, 4–15. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, DM; Brown, SA; Carr, LG; Wall, TL. ALDH2 status, alcohol expectancies, and alcohol response: Preliminary evidence for a mediation model. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res 2001, 25, 1558–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston, AM; Woolaway-Bickel, K; Schmidt, NB. Social anxiety and alcohol use: Evaluation of the moderating and mediating effects of alcohol expectancies. J. Anxiety Disord 2004, 18, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallo, DA; Smith, AE; Schepis, TS; Desai, R; Potenza, MN; Krishnan-Sarin, S. Smoking expectancies, weight concerns, and dietary behaviors in adolescence. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e66–e72. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, GT. Psychological expectancy as mediator of vulnerability to alcoholism. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 1994, 708, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, DA; Goldman, MS. Using a modified Stroop task to implicitly discern the cognitive organization of alcohol expectancies. J. Abnorm. Psychol 2003, 112, 171–175. [Google Scholar]
- Simons, JS; Dvorak, RD; Lau-Barraco, C. Behavioral inhibition and activation systems: Differences in substance use expectancy organization and activation in memory. Psychol. Addict. Behav 2009, 23, 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Holtgraves, TM. Gambling as self-presentation. J. Gambl. Behav 1988, 4, 78–91. [Google Scholar]
- Herrnstein, RJ; Prelec, D. Melioration: A theory of distributed choice. J. Econ. Perspect 1991, 5, 137–156. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, U; Kirschner, NE; Grusser, SM. Diagnostic instruments for behavioral addiction: An overview. GMS Psycho Soc. Med 2007, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lacy, JH; Evans, CDH. The impulsivist: A multi-impulsive personality disorder. Br. J. Addict 1986, 81, 641–649. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Sussman, S.; Leventhal, A.; Bluthenthal, R.N.; Freimuth, M.; Forster, M.; Ames, S.L. A Framework for the Specificity of Addictions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 3399-3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8083399
Sussman S, Leventhal A, Bluthenthal RN, Freimuth M, Forster M, Ames SL. A Framework for the Specificity of Addictions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2011; 8(8):3399-3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8083399
Chicago/Turabian StyleSussman, Steve, Adam Leventhal, Ricky N. Bluthenthal, Marilyn Freimuth, Myriam Forster, and Susan L. Ames. 2011. "A Framework for the Specificity of Addictions" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 8, no. 8: 3399-3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8083399
APA StyleSussman, S., Leventhal, A., Bluthenthal, R. N., Freimuth, M., Forster, M., & Ames, S. L. (2011). A Framework for the Specificity of Addictions. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 8(8), 3399-3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph8083399





