The More the Worse: the Grade of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Associates with the Severity of Tinnitus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Participants
2.2. Audiometry
2.3. Psychometry (Tinnitus Questionnaire)
2.4. Statistics
3. Results
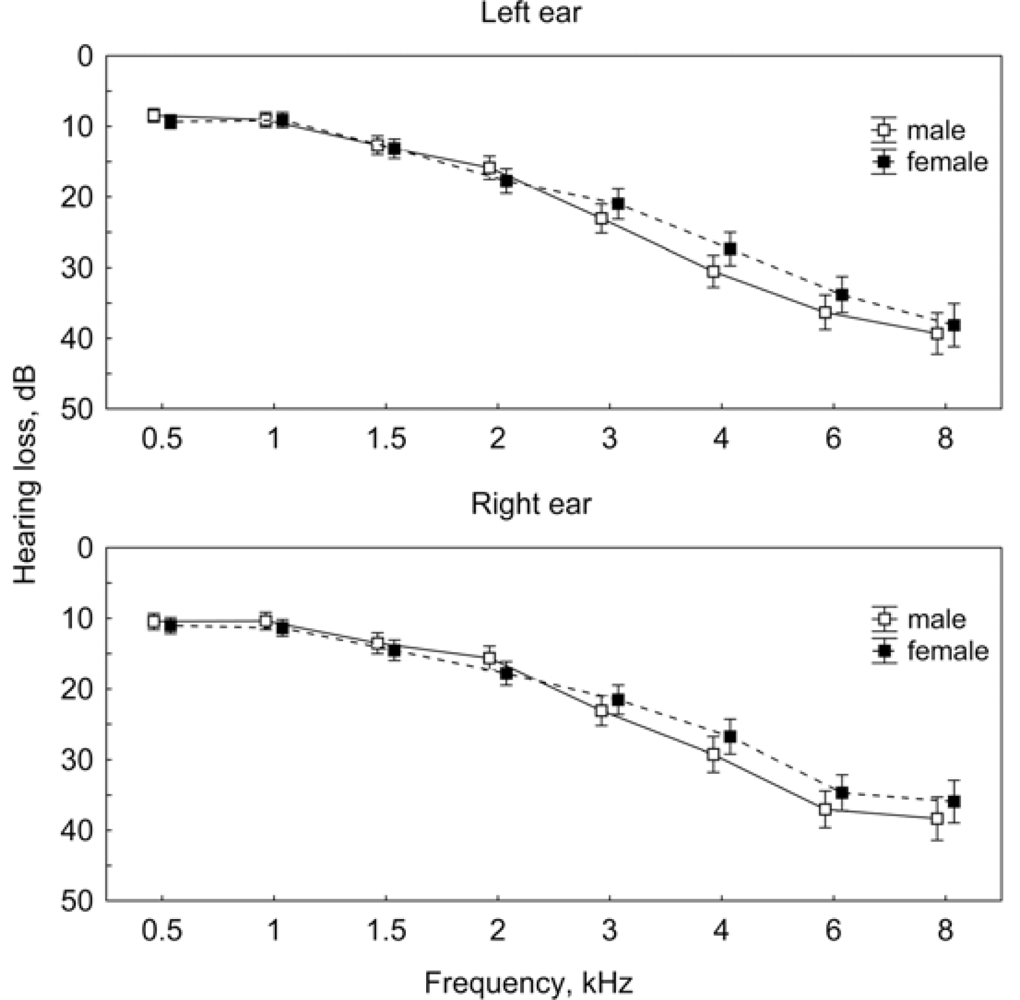
3.1. Predominant Number of Patients with Chronic Tinnitus Has a Hearing Loss
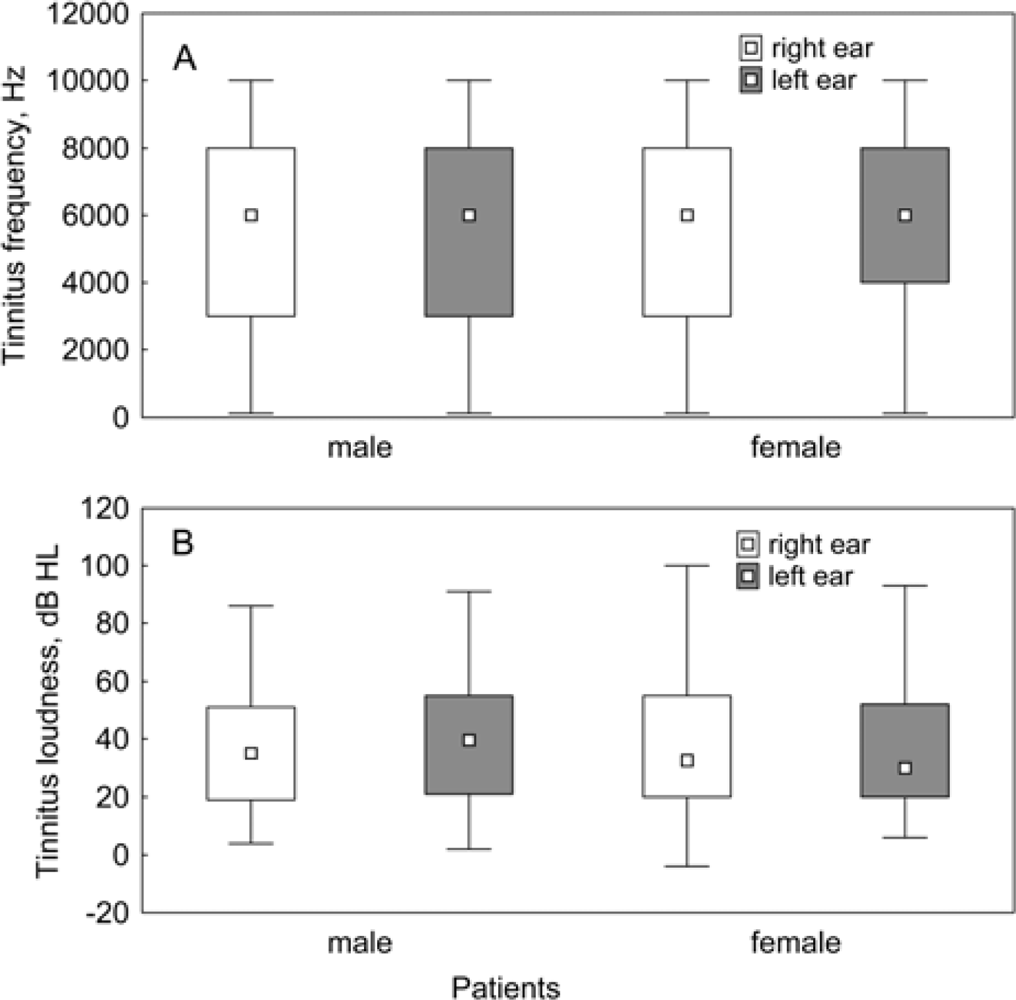
3.2. Tinnitus Characteristics in Patients with Hearing Loss
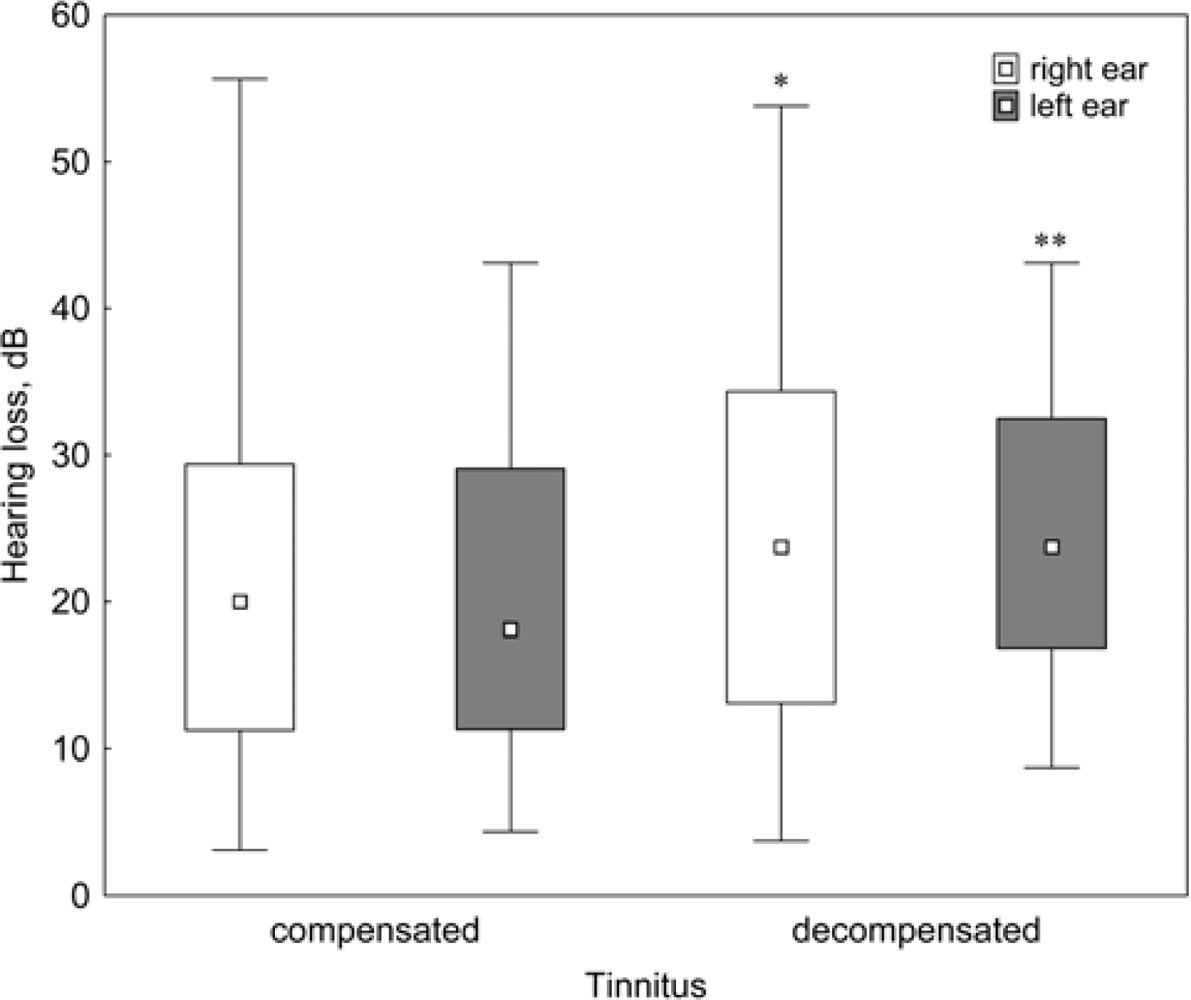
3.3 The Degree of Hearing Loss Correlates with the Loudness of Tinnitus
3.4 The Degree of Hearing Loss Correlates with Some of the Psychometric Parameters Measured by TQ
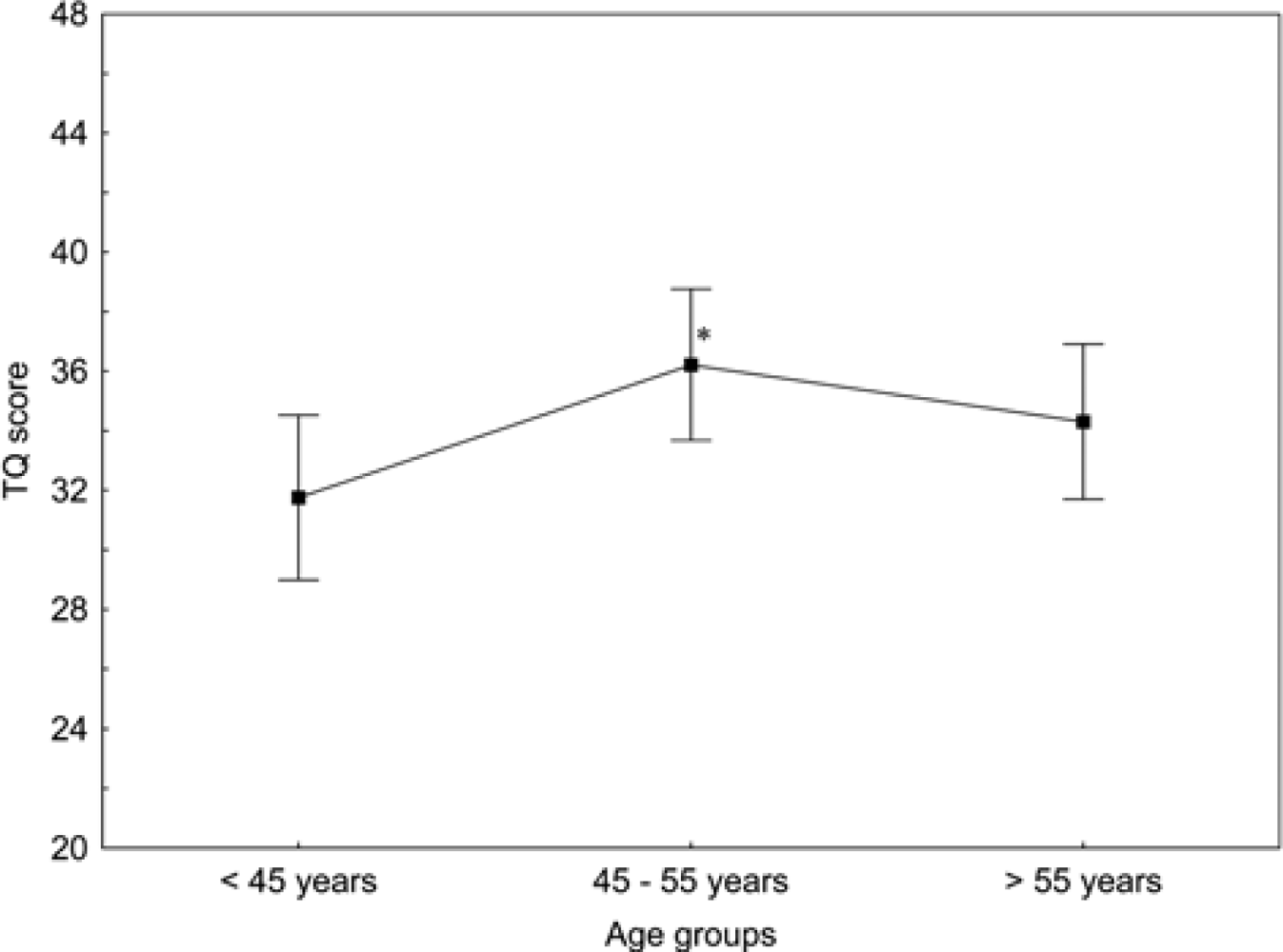
3.5. Influence of Age on the Psychometric Scores
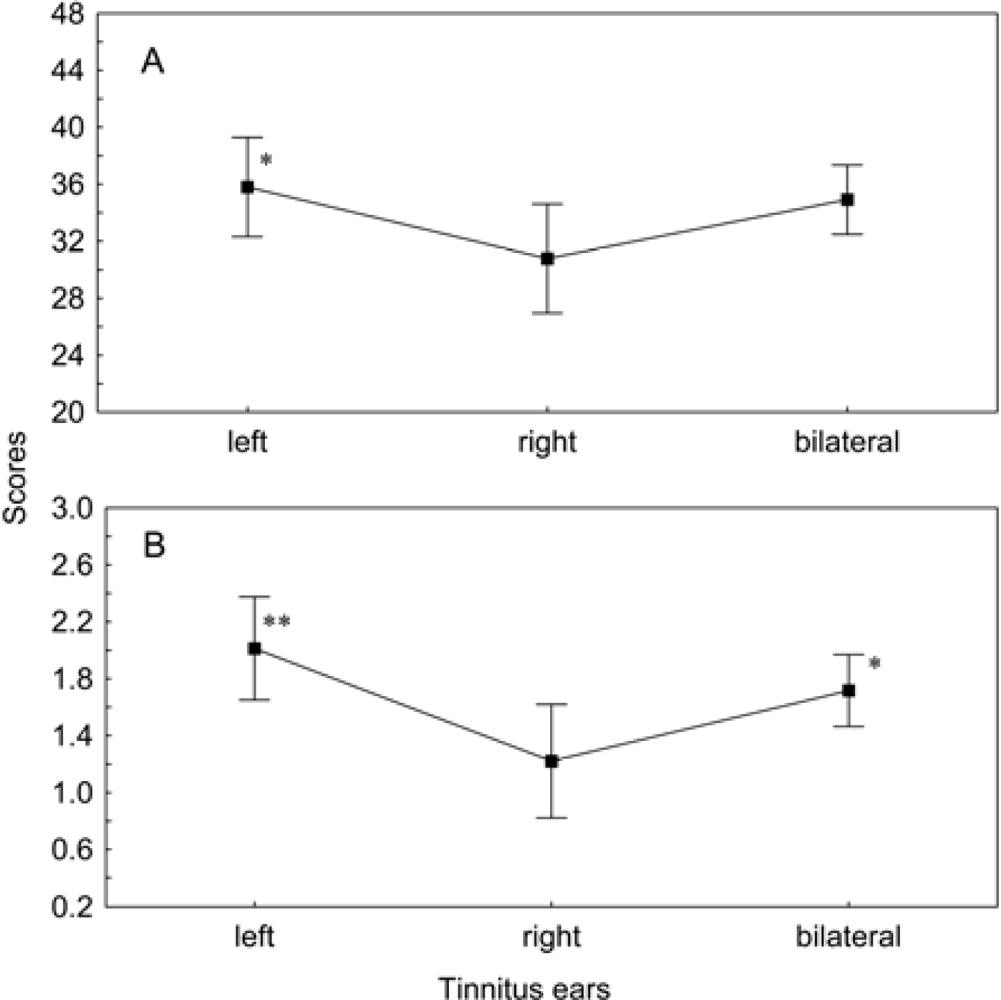
3.6. Influence of Tinnitus Lateralization on the Psychometric Scores
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Jastreboff, PJ. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): mechanisms of generation and perception. Neurosci. Res 1990, 8, 221–254. [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek, B; Fischer, F; Haupt, H; Georgiewa, P; Reisshauer, A; Klapp, BF. A modified version of tinnitus retraining therapy: observing long-term outcome and predictors. Audiol. Neurootol 2006, 11, 276–286. [Google Scholar]
- Tyler, RS; Baker, LJ. Difficulties experienced by tinnitus sufferers. J. Speech Hear. Disord 1983, 48, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hiller, W; Goebel, G. A psychometric study of complaints in chronic tinnitus. J. Psychosom. Res 1992, 36, 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Goldman, DR; Holme, R. Hearing loss and tinnitus--the hidden healthcare time bomb. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 253–255. [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood, AH; Salvi, RJ; Burkard, RF. Tinnitus. N. Engl. J. Med 2002, 347, 904–910. [Google Scholar]
- Abbate, C; Concetto, G; Fortunato, M; Brecciaroli, R; Tringali, MA; Beninato, G; D’Arrigo, G; Domenico, G. Influence of environmental factors on the evolution of industrial noise-induced hearing loss. Environ. Monit. Assess 2005, 107, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, MG; Hong, SM; Shim, HJ; Kim, YD; Cha, CI; Yeo, SG. Hearing threshold of Korean adolescents associated with the use of personal music players. Yonsei Med. J 2009, 50, 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Martines, F; Bentivegna, D; Martines, E; Sciacca, V; Martinciglio, G. Assessing audiological, pathophysiological and psychological variables in tinnitus patients with or without hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 2010. doi: 10.1007/s00405-010-1302-3.. [Google Scholar]
- Savastano, M. Tinnitus with or without hearing loss: are its characteristics different? Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol 2008, 265, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar]
- Attias, J; Reshef, I; Shemesh, Z; Salomon, G. Support for the central theory of tinnitus generation: a military epidemiological study. Int. J. Audiol 2002, 41, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, G; Hiller, W. The tinnitus questionnaire. A standard instrument for grading the degree of tinnitus. Results of a multicenter study with the tinnitus questionnaire. HNO 1994, 42, 166–172. [Google Scholar]
- Nageris, BI; Raveh, E; Zilberberg, M; Attias, J. Asymmetry in noise-induced hearing loss: relevance of acoustic reflex and left or right handedness. Otol. Neurotol 2007, 28, 434–437. [Google Scholar]
- Seydel, C; Haupt, H; Szczepek, AJ; Klapp, BF; Mazurek, B. Long-term improvement in tinnitus after modified tinnitus retraining therapy enhanced by a variety of psychological approaches. Audiol. Neurootol 2010, 15, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hiller, W; Goebel, G. Factors influencing tinnitus loudness and annoyance. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg 2006, 132, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar]
| Subscale | Female | Male |
|---|---|---|
| Emotional distress | 9.49 ± 5.51 | 9.26 ± 5.34 |
| Cognitive distress | 6.04 ± 3.93 | 5.93 ± 3.85 |
| Intrusiveness | 9.68 ± 3.62 | 9.24 ± 3.61 |
| Auditory perceptual difficulties | 4.78 ± 3.60 | 4.23 ± 3.44 |
| Sleep disturbances | 3.35 ± 2.67 | 2.92 ± 2.50 |
| Somatic complaints | 1.98 ± 1.72 | 1.54 ± 1.68* |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazurek, B.; Olze, H.; Haupt, H.; Szczepek, A.J. The More the Worse: the Grade of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Associates with the Severity of Tinnitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 3071-3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7083071
Mazurek B, Olze H, Haupt H, Szczepek AJ. The More the Worse: the Grade of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Associates with the Severity of Tinnitus. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2010; 7(8):3071-3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7083071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazurek, Birgit, Heidi Olze, Heidemarie Haupt, and Agnieszka J. Szczepek. 2010. "The More the Worse: the Grade of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Associates with the Severity of Tinnitus" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 7, no. 8: 3071-3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7083071
APA StyleMazurek, B., Olze, H., Haupt, H., & Szczepek, A. J. (2010). The More the Worse: the Grade of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss Associates with the Severity of Tinnitus. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(8), 3071-3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7083071







