Municipal Wastewater Effluents as a Source of Listerial Pathogens in the Aquatic Milieu of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa: A Concern of Public Health Importance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
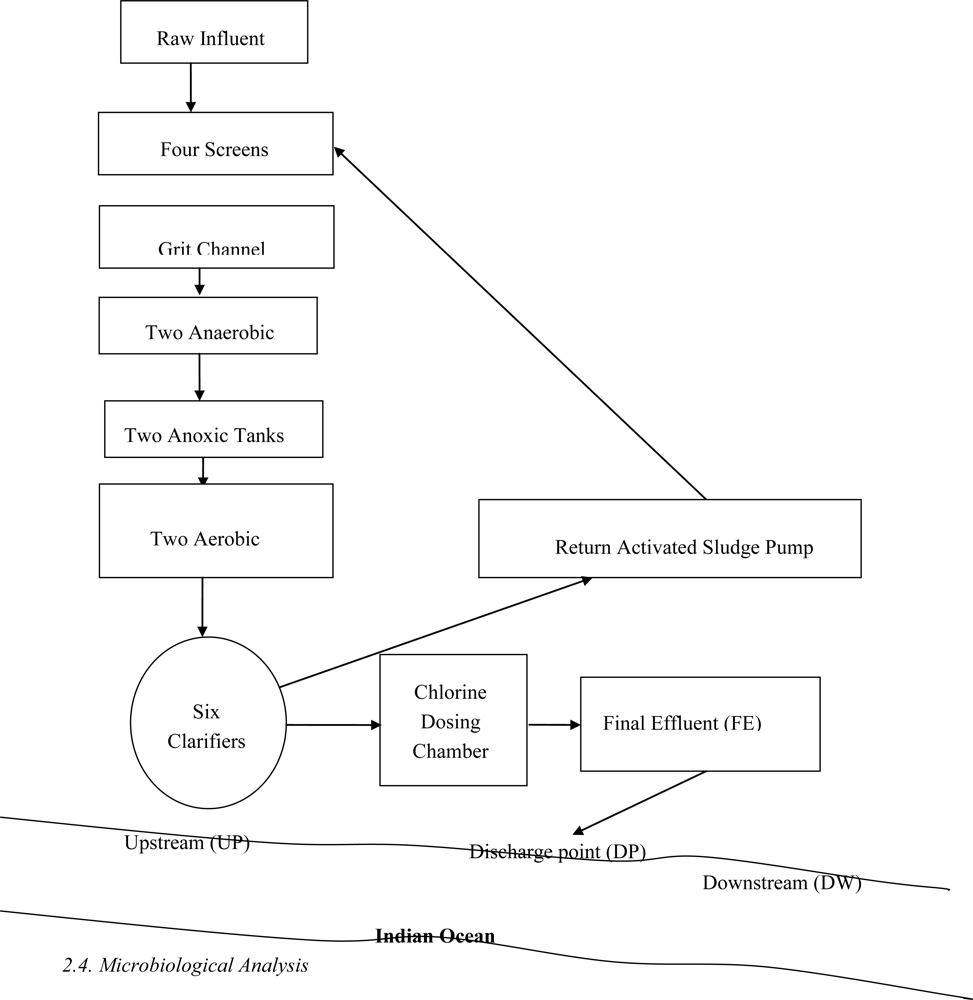
2.1. Description of Sampling Site
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Processing
2.4. Microbiological Analysis
2.5. Physicochemical Analyses
2.6. Antimicrobial Agents
2.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
2.8. Bacterial DNA Extraction and Amplification of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
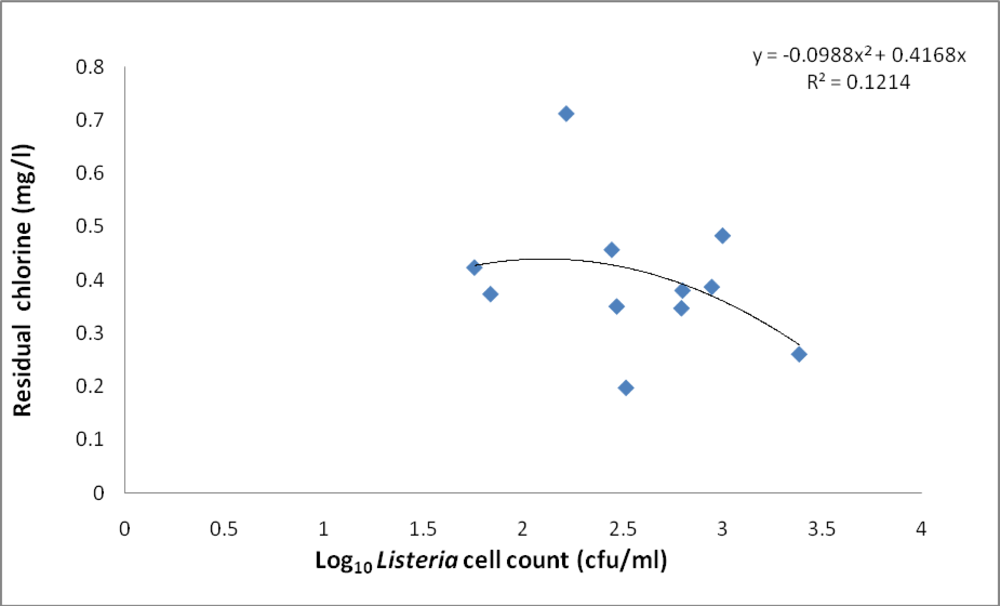
3.1. Abundance of Listeria
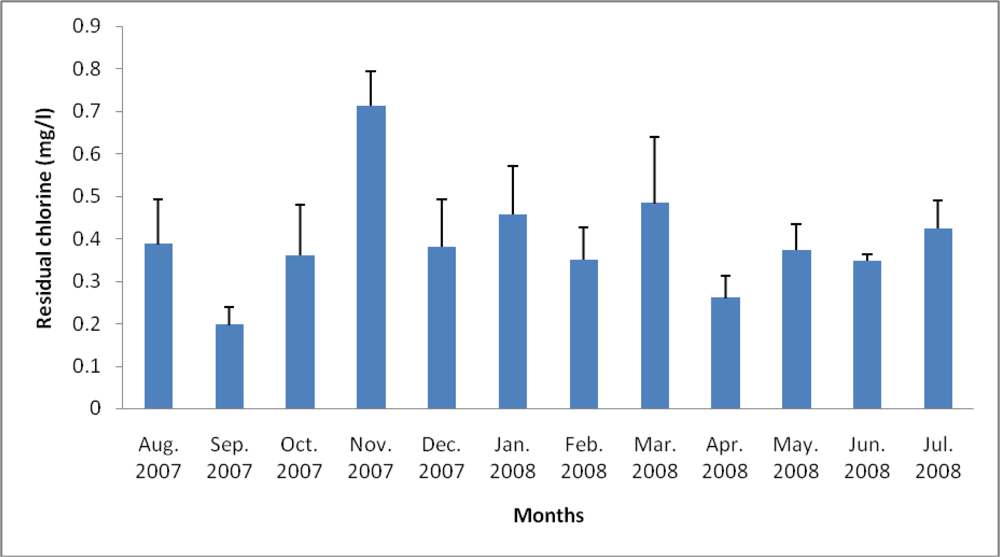
3.2. Physicochemical Analyses
3.4. Antibiogram and Resistance Gene Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Roberts, AJ; Wiedmann, M. Pathogen, host and environmental factors contributing to the pathogenesis of listeriosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2003, 60, 904–918. [Google Scholar]
- Brugere-Picoux, O. Ovine listeriosis. Small Ruminant Res 2008, 76, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, AJ; Fielding, AK; McLauchlin, J. Listeria ivanovii infection in a patient with AIDS. J. Infect 1994, 28, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Cocolin, L; Rantsiou, K; Iacumin, L; Cantoni, C; Comi, G. Direct identification in food samples of Listeria spp. and Listeria monocytogenes by molecular methods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2002, 68, 6273–6282. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, JK; Morgan, JH; McLauchlin, J; Grant, KA; Shallcross, JA. Listeria ivanovii isolated from a case of ovine meningoencephalitis. Vet. Microbiol 1994, 59, 193–202. [Google Scholar]
- Rocourt, J; Jacquet, Ch; Reilly, A. Epidemiology of human listeriosis and seafoods. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2000, 62, 197–209. [Google Scholar]
- Siegman-Igra, Y; Levin, R; Weinberger, M; Golan, Y; Schwartz, D; Samra, Z; Konigsberger, H; Yinnon, A; Rahav, G; Keller, N; Basharat, N; Karpuch, J; Finkelstein, R; Alkan, M; Landau, Z; Novikov, J; Hassin, D; Rudnicki, C; Kitzes, R; Ovadia, S; Shimoni, Z; Lang, R; Shohat, T. Listeria monocytogenes infection in Israel and review of cases worldwide. Emerging Infect. Dis 2002, 8, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ghazali, MR; Al-Azawi, KS. Detection and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes in a sewage treatment plant in Iraq. J. Appl. Bacteriol 1986, 60, 251–254. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ghazali, MR; Al-Azawi, KS. Effects of sewage treatment on the removal of Listeria monocytogenes. J. Appl. Bacteriol 1988, 65, 203–208. [Google Scholar]
- Czeszejko, K; Boguslawska-Was, E; Dabrowski, W; Kaban, S; Umanski, R. Prevalence of Listeria monocytogenes in municipal and industrial sewage. Electron J Pol Agric Univ Environ Dev. 2003, 6.
- Paillard, D; Dubois, V; Thiebaut, R; Nathier, F; Hoogland, E; Caumette, P; Quentin, C. Occurrence of Listeria spp. in effluents of French urban wastewater treatment plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2005, 71, 7562–7566. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, J; Sleath, KP. Isolation and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes from sewage, sewage sludge, and river water. J. Appl. Bacteriol 1981, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Odjadjare, EEO; Okoh, AI. Prevalence and distribution of Listeria pathogens in the final effluents of a rural wastewater treatment facility in the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol 2010, 26, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Mackintosh, G; Colvin, C. Failure of rural schemes in South Africa to provide potable water. Environ. Geol 2003, 44, 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Okoh, AI; Odjadjare, EE; Igbinosa, EO; Osode, AN. Wastewater treatment plants as a source of pathogens in receiving watersheds. Afr. J. Biotechnol 2007, 6, 2932–2944. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, SN. Microbial water quality in the 21st century. SA Water bull 2001, 27, 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- Djordjevic, D; Wiedmann, M; McLandsborough, LA. Microtitre assay for assessment of Listeria monocytogenes biofilm formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2002, 68, 2950–2958. [Google Scholar]
- Lunden, JM; Miettinen, MK; Autio, TJ; Korkeala, H. Persistent Listeria monocytogenes strains show enhanced adherence to food contact surface after short contact times. J. Food Prot 2000, 63, 1204–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Mafu, A; Roy, D; Goulet, J; Magny, P. Attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel, glass, polypropylene and rubber surfaces after short contact times. J. Food Prot 1990, 53, 742–746. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, JA; Jackson, CR. Comparative antimicrobial susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes, L. innocua, and L. welshimeri. Microb. Drug Res 2009, 15, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, V; Nam, HM; Nguyen, LT; Tamilselvam, B; Murinda, SE; Oliver, SP. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance genes in Listeria monocytogenes isolated from dairy farms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis 2005, 2, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Obi, CL; Onabolu, B; Momba, MNB; Igumbor, JO; Ramalivahna, J; Bossong, PO; van Rensburg, EJ; Lukoto, M; Green, E; Mulaudzi, TB. The interesting cross-paths of HIV/AIDS and water in Southern Africa with special reference to South Africa. Water SA 2006, 32, 323–343. [Google Scholar]
- .
- Maugeri, TL; Carbon, M; Fera, MT; Irrera, GP; Gugliandolo, C. Distribution of potentially pathogenic bacteria as free-living and plankton associated in a marine coastal zone. J. Appl. Microbiol 2004, 97, 354–361. [Google Scholar]
- Hitchins, AD. Detection and enumeration of Listeria monocytogenes in foods. Bacteriological Analytical Manual; US Food and Drug Administration: Madison, WI, USA, 2001.
- DWAF. Analytical Methods Manual, TR 151; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry: Pretoria, South Africa, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Fifteenth Informational Supplement; , M100-S15, vol. Volume 25, 1, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2005; p. 163. [Google Scholar]
- Conter, M; Paludi, D; Zanardi, E; Ghidini, S; Vergara, A; Ianieri, A. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance of foodborne Listeria monocytogenes. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2009, 128, 497–500. [Google Scholar]
- Naravaneni, R; Jamil, K. Rapid detection of food-borne pathogens by using molecular techniques. J. Med. Microbiol 2005, 54, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- DWAF. South African Water Quality Guidelines: Domestic Use, 2nd ed; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry: Pretoria, South Africa, 1996; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Rolling Revision of the WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, Draft for Review and Comments Nitrates and Nitrites in Drinking-Water; World Health Organization; (WHO/SDE/WSH/04.08/56), 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fatoki, SO; Gogwana, P; Ogunfowokan, AO. Pollution assessment in the Keiskamma River and in the impoundment downstream. Water SA 2003, 29, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- SA Government Gazette. Requirements for the Purification of Wastewater or Effluent, ; Gazette No. 9225, Regulation 991, 1984.
- DWAF. South African Water Quality Guidelines: Aquatic Ecosystems, 1st ed; Department of Water Affairs and Forestry: Pretoria, South Africa, 1996; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran, K; Takai, T; Navarro, IM; Nakano, H; Hashimoto, H; Siebeling, RJ. Ecology of Vibrio cholerae non-01 and Salmonella spp. and role of zooplankton in their seasonal distribution in Fukuyama coastal waters, Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1989, 55, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Murrell, MC; Hollibaugh, JT; Silver, MW; Wong, PS. Bacterioplankton dynamics in Northern San Francisco Bay: role of particle association and seasonal freshwater flow. Limnol. Oceanogr 1999, 44, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, JL; Fries, JS; Noble, RT. Vibrio and phytoplankton dynamics during the summer of 2004 in a eutrophying estuary. Ecol. Appl 2007, 17, S102–S109. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra, RG. The occurrence of Listeria monocytogenes in surface waters of canals and lakes, in ditches of one big polder and in the effluents and canals of a sewage treatment plant. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Mikrobiol. Hyg. B 1982, 176, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Frances, N; Hornby, H; Hunter, PR. The isolation of Listeria species from freshwater sites in Cheshire and North Wales. Epidemiol. Infect 1991, 107, 235–238. [Google Scholar]
- Lyautey, E; Lapen, DR; Wilkes, G; McCleary, K; Pagotto, F; Tyler, K; Hartmann, A; Piveteau, P; Rieu, A; Robertson, WJ; Medeiros, DT; Edge, TA; Gannon, V; Topp, E. Distribution and characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolates from surface waters of the South Nation River Watershed, Ontario, Canada. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2007, 73, 5401–5410. [Google Scholar]
- Obi, CL; Igumbor, JO; Momba, MNB; Samie, A. Interplay of factors involving chlorine dose, turbidity, flow capacity and pH on microbial quality of drinking water in small treatment plants. Water SA 2008, 34, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- LeChevallier, MW; Cawthan, CD; Lee, RG. Factors promoting survival of bacteria in chlorinated water supplies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1988, 54, 649–654. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, JM; Gerna-Smidt, P; Bruun, B. Antibiotic susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes in Denmark 1958–2001. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand 2005, 113, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Safdar, A; Armstrong, D. Antimicrobial activities against 84 Listeria monocytogenes isolates from patients with systemic listeriosis at a comprehensive cancer center (1955–1997). J. Clin. Microbiol 2003, 41, 483–485. [Google Scholar]
- Abuin, CMF; Fernandez, EJQ; Sampayo, CF; Otero, JTR; Rodriguez, LD; Cepeda, S. Susceptibilities of Listeria species isolated from food to nine antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1994, 38, 1655–1657. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y; Yeh, E; Hall, G; Cripe, J; Bhagwat, AA; Meng, J. Characterization of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from retail foods. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2007, 113, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Aureli, P; Ferrrini, AM; Mannoni, V; Hodzic, S; Wedell-Weergaard, C; Oliva, B. Susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from food in Italy to antibiotics. Int. J. Food Microbiol 2003, 83, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Giger, W; Alder, AC; Golet, EM; Kohler, HE; McArdell, CS; Molnar, E; Siegrist, H; Suter, MJ-F. Occurrence and fate of antibiotics as trace contaminants in wastewaters, sewage sludges, and surface waters. Chimia 2003, 57, 485–491. [Google Scholar]
- Kummerer, K. Significance of antibiotics in the environment. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2003, 52, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann, H; Schwartz, T; Bischoff, P; Kirchen, S; Obst, U. Detection of clinically relevant antibiotic-resistance genes in municipal wastewater using real-time PCR (TaqMan). J. Microbol. Methods 2004, 56, 277–286. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, S; Ozdemir, F. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Listeria spp. in homemade white cheese. Food Control 2008, 19, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Donlan, RM; Costerton, JW. Biofilms: survival mechanism of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, CM; Facinelli, B; Giovanetti, E; Varaldo, PE. Transferable erythromycin in Listeria spp. isolated from food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1996, 62, 269–270. [Google Scholar]
| Gene | Primer | Nucleotide sequence | Amplicon size | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| penA | PenA-F | ATCGAACAGGCGACGATGTC | 500 | [21] |
| PenA-R | GATTAAGACGGTGTTTTACGG | |||
| ampC | AmpC-F | TTCTATCAAMACTGGCARCC | 550 | ” |
| AmpC-R | CCYTTTTATGTACCCAYGA | |||
| ermB | ErmB-F | GAAAAGGTACTCAACCAAATA | 639 | ” |
| ErmB-R | AGTAACGGTACTTAAATTGTTTAC | |||
| ereA | EreA-F | AACACCCTGAACCCAAGGGACG | 420 | ” |
| EreA-R | CTTCACATCCGGATTCGCTCGA | |||
| ereB | EreB-F | AGAAATGGAGGTTCATACTTACCA | 546 | ” |
| EreB-R | CATATAATCATCACCAATGGCA | |||
| su1I | Su1I-F | GTGACGGTGTTCGGCATTCT | 779 | ” |
| Su1I-R | TCCGAGAAGGTGATTGCGCT | |||
| su1II | Su1II-F | CGGCATCGTCAACATAACCT | 721 | ” |
| Su1II-R | TGTGCGGATGAAGTCAGCTC |
| Net Sampling pore Sites sizes | Listeria density (cfu/mL) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||||||||
| Aug. 2007 | Sep. 2007 | Oct. 2007 | Nov. 2007 | Dec. 2007 | Jan. 2008 | Feb. 2008 | Mar. 2008 | Apr. 2008 | May 2008 | Jun. 2008 | Jul. 2008 | ||
| FE | 180 μm | 1.5×100 | 3.5×100 | ND | 4.0×100 | 8.6×101 | 2.5× 101 | 7.6×100 | 3.5×101 | 1.1×101 | 2.7×101 | 4.3×101 | 1.8×01 |
| 60 μm | 2.9×100 | 2.4×100 | ND | 0.0 | 1.0×101 | 1.6 ×101 | 3.0×100 | 1.4×101 | 8.1×100 | 1.0×101 | 3.8×101 | 1.2×101 | |
| 20 μm | 6.3×102 | 7.1×100 | ND | 0.0 | 3.0×102 | 1.2×101 | 9.3×100 | 3.9×100 | 9.4×100 | 1.2×101 | 9.3×101 | 1.1×100 | |
| Free | 2.6×102 | 3.0 ×102 | ND | 1.6×102 | 2.4× 102 | 2.3× 102 | 2.8×102 | 9.5×102 | 2.4×103 | 2.0×101 | 4.5×102 | 2.5×101 | |
| Total | 8.8×102 | 3.3×102 | ND | 1.7×102 | 6.3×102 | 2.8×102 | 2.95×102 | 1.0×103 | 2.4×103 | 6.9×101 | 6.2×102 | 5.7×101 | |
| DP | 180 μm | 3.9×100 | 2.1×100 | ND | 3.0×100 | 1.95×103 | 9.9×100 | 1.5×100 | 2.1×101 | 0.0 | 1.0×101 | 1.8×102 | 0.0 |
| 60 μm | 3.5×100 | 0.0 | ND | 0.0 | 1.9×101 | 2.2×101 | 3.8×100 | 3.5×100 | 7.6×100 | 7.0×100 | 1.8×102 | 0.0 | |
| 20 μm | 2.8×100 | 1.1×100 | ND | 0.0 | 1.2×105 | 6.3×100 | 6.1×100 | 4.7×101 | 6.7×101 | 1.6×101 | 6.9×101 | 0.0 | |
| Free | 5.7×102 | 2.1×102 | ND | 1.5×101 | 4.0×102 | 8.0×101 | 2.1×102 | 3.4×102 | 3.5×101 | 1.5×102 | 8.5×101 | 5.0×100 | |
| Total | 5.8×102 | 2.1×102 | ND | 1.98×101 | 1.2×105 | 1.2×102 | 2.2×102 | 4.1×102 | 1.1×102 | 1.8×102 | 5.1×102 | 5.0×100 | |
| DW | 180 μm | 0.0 | 1.1×100 | ND | 2.9×100 | 0.0 | 2.1×101 | 1.1×100 | 2.9×100 | 0.0 | 4.3×100 | 2.6×101 | 0.0 |
| 60 μm | 0.0 | 0.0 | ND | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5×101 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.9×100 | 3.0×101 | 0.0 | |
| 20 μm | 0.0 | 0.0 | ND | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.2×101 | 1.6×100 | 9.6×100 | 0.0 | 1.96×101 | 1.8×101 | 0.0 | |
| Free | 3.5×101 | 3.5×101 | ND | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0×101 | 1.6×102 | 2.4×103 | 0.0 | 1.5×101 | 5.0×100 | |
| Total | 3.5×101 | 3.6×101 | ND | 2.9×100 | 0.0 | 4.8×101 | 7.8×100 | 1.7×102 | 2.4×103 | 3.1×101 | 8.9×101 | 5.0×100 | |
| UP | 180 μm | 0.0 | 0.0 | ND | 3.5×100 | 0.0 | 2.5×101 | 1.0×100 | 4.4×100 | 0.0 | 4.3×100 | 9.9×100 | 0.0 |
| 60 μm | 0.0 | 0.0 | ND | 0.0 | 0.0 | 8.9×100 | 2.0×100 | 1.1×100 | 0.0 | 2.7×101 | 2.4×101 | 0.0 | |
| 20 μm | 0.0 | 0.0 | ND | 3.6×103 | 0.0 | 7.6×100 | 1.5×100 | 2.4×100 | 0.0 | 1.7×101 | 3.1×101 | 0.0 | |
| Free | 1.5×101 | 5.0×100 | ND | 1.2×102 | 0.0 | 3.5×101 | 1.0×101 | 1.3×102 | 9.0×101 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 5.0×100 | |
| Total | 1.5×101 | 5.0×100 | ND | 1.2×102 | 0.0 | 7.6×101 | 1.5×101 | 1.4×102 | 9.0×101 | 4.8×101 | 6.5×101 | 5.0×100 | |
| Parameter | Raw wastewater | Treated effluent | Recommended target limits | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | Mean±SD | Range | Mean±SD | ||
| pH | 4.97–7.75 | 7.1 ± 0.44 | 6.7–7.7 | 7.1 ± 0.28 | 6–9a |
| Temperature (° C) | 18–26 | 23 ± 2.3 | 18–26 | 22 ± 2.45 | ≤ 25 a |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 86–1,000 | 573 ± 369 | 2.16–16 | 6.09 ± 3.64 | 0–1 a; ≤ 5b |
| TDS (mg/l) | 311–907 | 452 ± 153 | 289–743 | 398 ± 110 | 0–450 a |
| DO (mg/l) | 0.14–7.32 | 1.76 ± 1.78 | 2.38–6.78 | 4.46 ± 0.94 | ≥ 5c |
| COD (mg/l) | 40–2,404 | 489 ± 701 | 4–960 | 143 ± 271 | 30d |
| NO3 (mg/l) | 0.026–5.1 | 3.17 ± 1.32 | 0.25–6.95 | 4.56 ± 2.53 | 6a; 1–5d |
| NO2 (mg/l) | 0.07–3.5 | 0.53 ± 0.93 | 0.07–6.95 | 0.88 ± 1.84 | 0–6a; <0.5e |
| PO4 (mg/l) | 1.33–5.91 | 3.78 ± 1.26 | 0.05–0.73 | 0.34 ± 0.16 | 0.005e |
| Antibiotics | Number of isolates (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible | Intermediate | Resistant | |
| Amikacin (30 μg) | 23(100) | 0(0) | 0(0) |
| Gentamycin(10 μg) | 19(83) | 0(0) | 4(17) |
| Streptomycin(25 μg) | (15)65 | 0(0) | 8(35) |
| Chloramphenicol(30 μg) | 20(87) | 0(0) | 3(13) |
| Tetracyclin(30 μg) | 19(83) | 0(0) | 4(17) |
| Ciprofloxacin(5 μg) | 21(91) | 1(4.5) | 1(4.5) |
| Gatifloxacin(5 μg) | 19(83) | 2(8.5) | 2(8.5) |
| Moxifloxacin(5 μg) | 17(74) | 3(13) | 3(13) |
| Imipenem(10 μg) | 19(83) | 0(0) | 4(17) |
| Meropenem(10 μg) | 23(100) | 0(0) | 0(0) |
| Ertapenem(10 μg) | 23(100) | 0(0) | 0(0) |
| Ampicillin(30 μg) | 3(13) | 0(0) | 20(87) |
| Penicillin G(10 μg) | 1(4.5) | 1(4.5) | 21(91) |
| Linezolid(30 μg) | 18(78) | 0(0) | 5(22) |
| Aztreonam(30 μg) | 21(91) | 0(0) | 2(9) |
| Erythromycin(15 μg) | 4(17) | 0(0) | 19(83) |
| Cephalothin(30 μg) | 17(74) | 1(4) | 5(22) |
| Ceftriaxone(30 μg) | 21(91) | 1(4.5) | 1(4.5) |
| Sulphamethoxazole (25 μg) | 8(35) | 0(0) | 15(65) |
| Trimethoprim(5 μg) | 17(74) | 0(0) | 6(26) |
| Antibiotics | Number of isolates involved | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| E, SMX, LZD, PG, AP | 7a | 31 |
| E, LZD, PG, AP | 2b | 8.7 |
| KF, E, SMX, LZD, PG, AP | 2b | 8.7 |
| E, TM, LZD, MFX, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| E, LZD, MFX, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| C, KF, E, S, T, SMX, LZD, GAT, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| E, S, T, SMX, LZD, MFX, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| KF, E, S, SMX, TM, LZD, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| CRO, KF, E, S, SMX, LZD, PG, AP, | 1b | 4.3 |
| E, S, SMX, LZD, PG | 1b | 4.3 |
| C, E, GM, S, SMX, TM, IMI, PG | 1b | 4.3 |
| GM, TM, IMI, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| ATM, C, GM, S, T, TM, CIP, IMI, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| GM, S, T, TM, LZD, IMI, PG, AP | 1b | 4.3 |
| Total | 22 | 95.7 |
| Antibiotic resistance gene markers | Proportion of Listeria pathogens carrying the resistance genes |
|---|---|
| penA | 0(0) |
| ampC | 0(0) |
| ermB | 0(0) |
| ereA | 0(0) |
| ereB | 0(0) |
| su1I | 0(0) |
| su1II | 5(22%) |
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Odjadjare, E.E.O.; Obi, L.C.; Okoh, A.I. Municipal Wastewater Effluents as a Source of Listerial Pathogens in the Aquatic Milieu of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa: A Concern of Public Health Importance. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 2376-2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7052376
Odjadjare EEO, Obi LC, Okoh AI. Municipal Wastewater Effluents as a Source of Listerial Pathogens in the Aquatic Milieu of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa: A Concern of Public Health Importance. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2010; 7(5):2376-2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7052376
Chicago/Turabian StyleOdjadjare, Emmanuel E.O., Larry C. Obi, and Anthony I. Okoh. 2010. "Municipal Wastewater Effluents as a Source of Listerial Pathogens in the Aquatic Milieu of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa: A Concern of Public Health Importance" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 7, no. 5: 2376-2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7052376
APA StyleOdjadjare, E. E. O., Obi, L. C., & Okoh, A. I. (2010). Municipal Wastewater Effluents as a Source of Listerial Pathogens in the Aquatic Milieu of the Eastern Cape Province of South Africa: A Concern of Public Health Importance. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 7(5), 2376-2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph7052376





