Abstract
Alcohol dependence is correlated with a wide spectrum of medical, psychological, behavioral, and social problems. Acute alcohol abuse causes damage to and functional impairment of several organs affecting protein, carbohydrate, and fat metabolism. Mitochondria participate with the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetate and the generation of increased amounts of NADH. Prenatal exposure to ethanol during fetal development induces a wide spectrum of adverse effects in offspring, such as neurologic abnormalities and pre- and post-natal growth retardation. Antioxidant effects have been described due to that alcoholic beverages contain different compounds, such as polyphenols as well as resveratrol. This review analyzes diverse topics on the alcohol consumption effects in several human organs and demonstrates the direct participation of mitochondria as potential target of compounds that can be used to prevent therapies for alcohol abusers.
1. Introduction
1.1. Alcoholism
Over the centuries, alcohol has become the most socially-accepted addictive drug worldwide [1]. Excessive alcohol use is the third leading cause of preventable death in the United States [2]. Although normative alcohol use is ubiquitous, alcohol dependence is a serious medical illness [3], experienced by ≈14% of alcohol users [4]. Alcohol dependence constitutes a substantial health and economic burden, costing an estimated $184 billion in expenditures stemming from alcohol-related chronic diseases such as heart disease [5], Alzheimer’ s disease [6], stroke [7], liver disease [8], cancer [9], chronic respiratory disease [10], diabetes mellitus [11] and bone disease [12], which may develop following chronic alcohol ingestion and contribute to the alcoholism-related high morbidity and mortality. Alcohol abuse may also trigger a cascade of acute health problems such as traffic accident-related injuries, social problem including domestic violence, loss of work-place productivity, economic burden on society, crime and public disorder [13].
Alcohol use is characterized by central nervous system (CNS) intoxication symptoms, impaired brain activity, poor motor coordination, and behavioral changes [14], largely as a result of impaired CNS activity due to alcohol’s effect on synthesis [15], release [16] and signaling [17] of neurotransmitters, including serotonin [18], glutamate [19], GABA [20], endocannabinoids [21] and their receptors. Alcohol abuse causes functional impairment of the gastrointestinal tract [22], liver [23], and pancreas [24]. It also affects protein, carbohydrate, and fat metabolism [25], and leads to insufficient immune system responses to infections [26], impairs the ability of the host to counteract hemorrhagic shock [27], augments corticosteroid release [28], and delays wound healing [29], thus contributing to higher morbidity and mortality, and prolonged recovery from trauma [30].
Alcohol intoxication results as a tolerance and physical dependence. Tolerance is defined as a reduced response to a constant amount of ethanol or an increase in the amount necessary to elicit the same effect [31]. Dependence is characterized by a withdrawal syndrome upon cessation of ethanol exposure [31]. Although significant progress had been made in the area of alcohol research during the past several decades, the pathogenesis of alcohol use and abuse is not fully understood. Understanding the mechanism that leads to tolerance and dependence may give valuable insight into alcohol addiction and ultimately result in effective therapeutic intervention to combat this disorder [31].
1.2. Alcohol Metabolism
The effects of alcohol on various tissues depend on its concentration in the blood over time. After oral administration, ethanol is readily absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract; absorption takes place by passive diffusion through the stomach wall (about 20%), being the remaining 80% absorbed through the duodenum and small intestine wall [32]. Elimination of absorbed ethanol occurs primarily through metabolism (95–98%), with small fractions of the administered dose being excreted unchanged in the breath (0.7%), sweat (0.1%), and urine (0.3%) [33].
In adult nonalcoholic individuals, most ethanol metabolism occurs in the liver, mainly via oxidation catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), and catalase [34,35] enzymes (Figure 1). In people who consume alcohol at moderate levels (or only occasionally), the ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is oxidized to acetaldehyde (CH3CHO), in a reversible reaction catalyzed by class I ADH in the cytosol of hepatocytes [36]. Due to high affinity (Km = 0.05–0.1 g/L) and low capacity the enzyme becomes saturated after only few drinks. Subsequently, the acetaldehyde is then oxidized in a nonreversible reaction to acetate by the mitochondrial isoform of ALDH. Since acetaldehyde is highly toxic, it must be eliminated soon after its formation, therefore this enzyme has a very low Km and the elimination of acetaldehyde is very efficient [36]. The activated form of acetate, acetyl CoA, may be further metabolized, leading to ketone bodies, amino acids, fatty acids and steroids [35]; when it is oxidized in the Krebs cycle, CO2 and water are formed as the end-products of ethanol oxidation [5]. Both ADH and ALDH utilize the cofactor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which is reduced to NADH; as a consequence, during ethanol oxidation the ratio NADH/NAD+ is significantly increased, altering the cellular redox state and triggering a number of adverse effects, related to alcohol consumption [32].
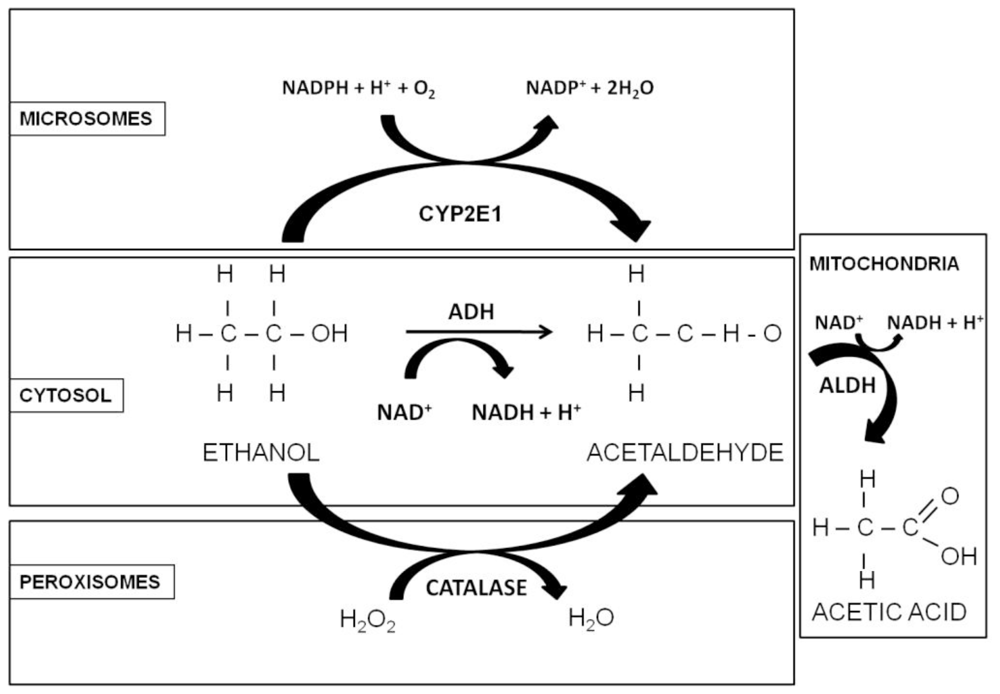
Figure 1.
Oxidative pathways of alcohol metabolism. The enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH), cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1), and catalase all contribute to oxidative metabolism of alcohol. ADH, present in the cytosol, converts ethanol to acetaldehyde. This reaction involves an intermediate carrier of electrons, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), which is reduced by two electrons to form NADH. Catalase, located in peroxisomes, requires hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to oxidize alcohol. CYP2E1, present predominantly in the cell’s microsomes metabolize alcohol to acetaldehyde at elevated ethanol concentrations. Acetaldehyde is metabolized mainly by aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) in the mitochondria to form acetate and NADH (Adapted from [34]).
In people who are chronic alcohol consumers, a second pathway, the microsomal ethanol-oxidizing system (MEOS), which functions in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of hepatocytes, helps rid the body of toxic compounds through cytochrome P450 (CYP2E1), which, like ADH, converts alcohol to acetaldehyde [6,7]. This reaction also requires oxygen and reduced NADPH to form NADP and water. This enzyme is characterized by a low affinity (Km = 0.5–0.8 g/L) with respect to ADH [36]. As a third route of ethanol metabolism, catalase located in the cell bodies called peroxisomes, is capable of oxidizing a small amount (2%) of ethanol in the presence of a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-generating system [35], to form acetaldehyde, without requiring NAD as a cofactor (Figure 1) [37].
Acetaldehyde and acetate, produced from the oxidative metabolism of alcohol, contribute to cell and tissue damage in various ways. Acetaldehyde has the capacity to bind to proteins such as enzymes, microsomal proteins, and microtubules. Formation of protein adducts in hepatocytes impairs protein secretion, which has been proposed to play a role in hepatomegaly [35]. It also forms adducts with the brain signaling chemical dopamine to form salsolinol, which may contribute to alcohol dependence, and with DNA to form carcinogenic DNA adducts such as 1,N2-propanodeoxyguanosine [35]. On the other hand, most of the acetate resulting from alcohol metabolism escapes the liver to the blood and is eventually metabolized to CO2 in heart, skeletal muscle, and brain cells [35]. Acetate increases blood flow into the liver and depresses the central nervous system, as well as affects various metabolic processes [35].
Besides, mitochondria have an important role in the alcohol metabolism, and their function is affected by alcohol consumption. It has been hypothesized that upon chronic alcohol intake the brain starts using acetate rather than glucose as a source of energy [35], and the accumulated acetaldehyde exerts its toxic effects by inhibiting mitochondrial reactions and functions. In addition, there is considerable evidence that chronic alcohol exposure enhances the susceptibility of cells to undergo apoptosis, therefore is important to understand the role of mitochondria during alcohol consumption and metabolism in chronic alcohol consumption.
2. Effects of Alcohol on Mitochondrial Biomolecules
A mitochondrion is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Mitochondria are sometimes described as “cellular power plants” because they generate the majority of the cell’s supply of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used as a source of chemical energy. Its importance lies in that it contains Krebs cycle enzymes, β-oxidation, oxidative phosphorylation, and components of the electron transport chain. The number of mitochondria in a cell varies widely by organism and tissue type. The mitochondria play an important role in the alcohol metabolism via the enzyme ALDH; this enzyme catalyzes the conversion of acetaldehyde into acetate. When this enzyme reaches a saturation point, the acetaldehyde escapes into the blood stream and leads damage to biomolecules such lipids, proteins and nucleic acids which results of the toxic side effects that are associated with alcohol consumption.
There is evidence that ethanol produces alterations in the mitochondrial structure and function of several organs, including liver [38], and heart [39], both in laboratory animals and humans [40]. These changes affect the mitochondrial function decreasing respiratory rates [41] and ATP levels, and might result in increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [42]. Several enzymatic systems, including the cytochrome P450 (CYP2E1), the mitochondrial respiratory chain and the cytosolic enzymes xanthine oxidase and the aldehyde oxidases have been implicated as sources of superoxide anion (O2 •−) and H2O2 in parenchyma cells during ethanol intoxication [43]. Numerous studies shows that mitochondrial levels of ROS may be increased by chronic alcohol consumption as a consequence of increased mitochondrial CYP2E1 levels [44,45] as well as a by-product of the matrix enzyme α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase [42]. The CYP2E1 activity increases in alcohol-treated rodents [46] and humans not only in alcohol abusers, but also in moderate alcohol consumers [47]. It has a high rate of NADPH oxidase activity, which leads to the production of large quantities of O2 •− and H2O2 [48]. In addition, the ethanol metabolism increases the availability of reducing equivalents (i.e., NADH) to the mitochondrion, which results of the redox active semiquinone intermediates within complexes I and III to be a more “reduced” state, thereby facilitating the reduction of O2 to O2 •− [49]. Also, chronic alcohol exposure decrease the activities of all the oxidative phosphorylation complexes, except complex II [50] contributing to decreased functioning of the oxidative phosphorylation system and depressed rates of ATP synthesis [51]. As well, ethanol has been demonstrated to increase the production of ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) and decrease several antioxidant mechanisms in liver [38]. This in turn might result in oxidative modification and inactivation of mitochondrial macromolecules, thereby contributing to mitochondrial dysfunction and a loss in energy conservation [38].
The mitochondrial proteome is exquisitely sensitive to modifications by ROS and RNS and thus offers an opportunity to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying pathobiology from chronic alcohol consumption [52]. The oxidation of mitochondrial proteins is a common feature of both acute and chronic ethanol exposure [53]. Early studies by Coleman and Cunningham established a key link between the chronic alcohol-related defects in complexes I, III, IV, and V, and losses in the 13 mitochondrial encoded polypeptides and redox centers that comprises the oxidative phosphorylation system complexes [54]. Then, proteomic analysis revealed that 40 additional mitochondrial proteins had altered levels in response to chronic alcohol consumption. This includes several key energy metabolism enzymes of β-oxidation, the TCA cycle, and amino acid metabolism [55]. On the other hand, nitric oxide (NO) production is increased in response to chronic alcohol via induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) [56]. NO and its metabolite peroxynitrite (ONOO−) have been implicated as key mediators of mitochondrial dysfunction [57]. This ONOO− can directly or indirectly participate in reactions leading to inactivation of mitochondrial proteins via post-translational modifications [52,58]. Also, the identification of proteins with oxidized and/or modified thiol groups are critical for elucidating the mitochondrial defects that contribute to alcoholic liver disease [52]. A number of reversible and irreversible modifications to cysteine residues are known to occur upon interaction of free sulfhydryl groups (-SH) with ROS, RNS; and reactive lipids [52]. As a consequence of oxidative modification of thiols others have shown an alcohol-dependent loss of function of the mitochondrial low Km ALDH [55]. Additionally, Moon et al. have demonstrated alcohol-dependent inactivation of ALDH and several β-oxidation enzymes via oxidation and nitrosation of thiols [59]. These findings are consistent with the concept that modification of protein thiols may contribute to alcoholic steatosis and mitochondrial dysfunction through inactivation of proteins critical to the energy conservation pathways in liver [52].
On the other hand, lipid peroxidation has been linked to the impairment of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and the appearance of megamitochondria [60]. In patients with alcoholic liver disease (ALD) the serum markers of lipid peroxidation, such as conjugated dienes, malondialdehyde (MDA), 4-hydroxynonenal and F2-isoprostanes are increased [61]. These compounds can form adducts with proteins in the areas of fat liver infiltration, focal necrosis and fibrosis [62]. The levels of hydroxyl radicals, which exert their cytotoxic effects by causing peroxidation of membrane phospholipids, are also increased, increasing membrane permeability plus impairing membrane function [63], leading the collapse of the mitochondrial membrane potential and the onset of mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) [53]. Other studies showed that lipoperoxidation increased the sensitivity of the electron transport chain to inhibition by oxidative stress except at the level of complex II [64]. There is evidence that oxidative stress affects the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
In hepatocytes from male Wistar rats, there is a positive correlation between hepatic ATP content and the number of single-stranded DNA (ss-DNA)-positive cells. A mitochondrial function, at least in part, ATP synthesis was depressed before the damage of mtDNA by chronic ethanol consumption [65]. Mansouri et al. [66] found in the liver tissue and white blood cells from patients with ALD a significantly decreased mtDNA copy number and an increased level of mtDNA deletion, similar to the data obtained by Tsuchishima et al. [67] who also found an acquired mutation of mtDNA, at least in the encoding ATPase region, that may be reversed by stopping drinking. In addition, von Wurmb-Schwark et al. [68] investigated mitochondrial mutagenesis in patients with a chronic and moderate alcoholic disease, and found a relative amount of 4,977 bp deleted in mtDNA in alcoholics compared to controls.
Bailey [38] showed that there is a decrease in several antioxidant mechanisms in liver caused by increased ROS and RNA levels during chronic alcohol exposure. Early studies have shown that a decrease in the liver content or reduced GSH is a common feature in ethanol-fed animals as well as in patients with alcoholism [43]. Chronic alcohol intake lowers the mitochondrial GSH (mtGSH) [69], which makes these organelles more susceptible to oxidative damage, and precedes the development of mitochondrial dysfunctions, such as lipid peroxidation [69], and the impairment of ATP synthesis [70]. Several investigations using the enteral alcohol model [71] have shown a marked decline in enzymatic activity and immunoreactive protein concentrations of liver Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase and GSH peroxidase, suggesting that ethanol might interfere at the post-transcriptional level with the synthesis of antioxidant enzymes or might stimulate their intracellular degradation [43].
The damage accumulated in biomolecules triggered by acetaldehyde exerts its toxic effects by inhibiting the mitochondrial reactions and functions (Figure 2). This compound may injure the electron transport chain (ETC) function, leading to production of ROS, which can oxidize the subunits of ETC complexes, leading injury over electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation [72,73], therefore decreasing the ATP levels. In addition, the ROS may lead oxidative stress over lipids causing lipid peroxidation, which affects the permeability of the outer and/or inner mitochondrial membranes. These allows opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) and lead to mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT), favoring the translocation to the mitochondria of the pro-apoptotic factor Bax that forms a complex with a voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC). Extensive MPT leads to mitochondria swelling as a result of the influx of ions and water, and permits the cytochrome c release [74], leading to caspases activation [75] and DNA fragmentation, which are key events for induction of programmed cell death or apoptosis [74].
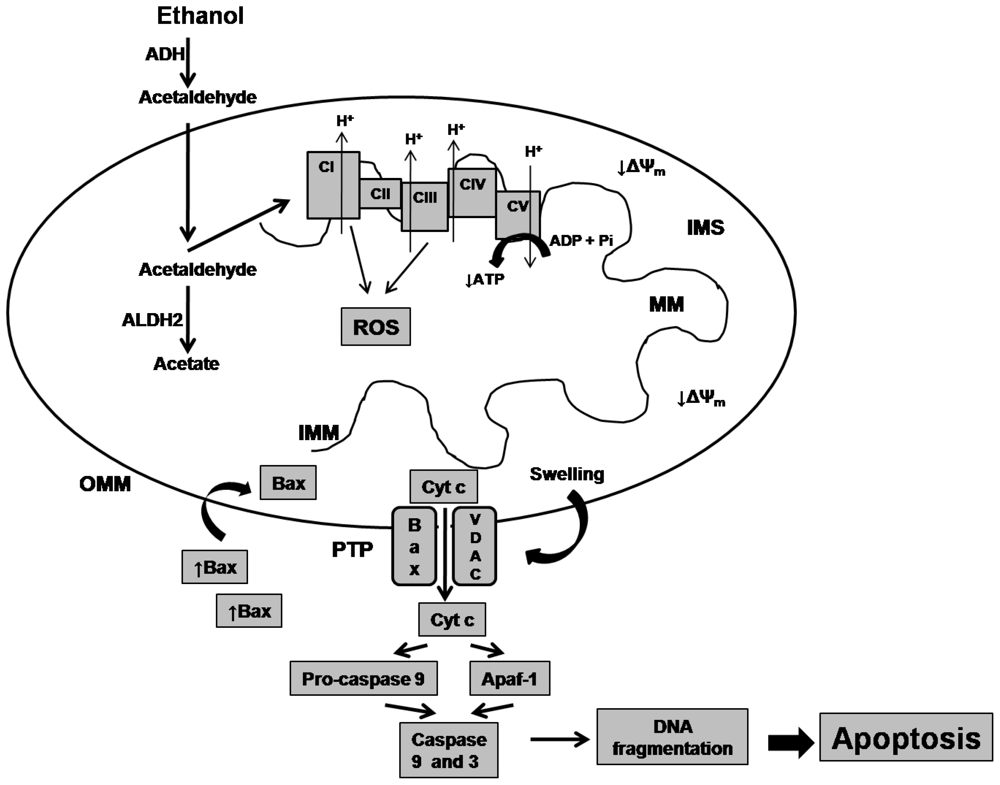
Figure 2.
Ethanol effects on mitochondrial function. Alcohol is metabolized to acetaldehyde by the cytosolic enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH). Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) converts acetaldehyde to acetate. When this enzyme is malfunctioning, acetaldehyde increases and damages the electron transport complexes (CI-CIV) leading over production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), affecting electron transport chain (ETC) and oxidative phosphorylation disturbing ATP synthesis. Also, oxidative stress affects the permeability of the outer/inner mitochondrial membranes (OMM/IMM) promoting opening of the permeability transition pore (PTP) favoring the translocation of the pro-apoptotic factor bax, which forms a complex with voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAV). When the mitochondrial permeability transition is extensive, promotes the mitochondrial swelling and permits the cytochrome c release (Cyt c), caspase activation and DNA fragmentation, leading the programmed cell death or apoptosis. MM, mitochondrial matrix; ΔΨm, mitochondrial membrane potential. IMS, intramitochondrial space; Apaf-1, Apoptotic protease activating factor-1; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ADP, adenosine diphosphate.
3. Alcohol Effects on the Heart
Chronic alcohol abuse has been established as a major cause of cardiomyopathy in humans [76]. The heart becomes enlarged and has flaccid muscle tone, presents scattered areas of muscle degeneration, fibrosis, intracellular edema, lymphocytic infiltration and numerous fat droplets are observed in muscle-cell cytoplasm. These changes may lead the loss of cells by either necrosis or apoptosis as a plausible mechanism for decrease in contractile function [77]. In addition, ethanol causes changes in the spatial reorganization of mitochondria: intermitochondrial contacts disappear, and the mitochondrial population regroups into separate clusters uniformly distributed over the space of a muscle cell. Subsequently, megamitochondria and septate mitochondria appear. These changes may be considered a sign of impairments of myocardial functioning. Data of animal experiments show a decrease in the rates of respiration and oxidative phosphorylation [78]. In baboons the cytochrome c oxidase concentration and activity decreased two-fold, while in rats causes a decrease of oxidative phosphorylation efficiency and weakening of the factor F1 connection with mitochondrial membrane [79].
Alcoholic beverages contain more than 200 compounds with different antioxidant activities to polyphenols, including quercetin, catechin, tannic acids [80], and resveratrol, among others [81]. Resveratrol is a polyphenolic phytoalexin (trans-3,4′,5-trihydroxystilbene) present in purple grape juice, peanuts, and red wine [35,82] and has ability to prevent or slow the progression of a variety of pathologies [83]. It also possesses many health benefits that include cardioprotection [84]. It may reduce the incidence of coronary heart disease by its antioxidant [85] and anti-inflammatory [86] activities, preconditioning against ischemic injury [87], reduced ischemia-reperfusion injury and infarction [88], attenuated hypertrophic response [89], enhanced peri-infarct neovascularization [90], and antiarrhytmic efficacy [91], inhibit cardiac fibroblast proliferation and differentiation in vitro [92].
Resveratrol can retard progression of atherosclerosis. In apolipoprotein E-deficient mice, resveratrol reduces the susceptibility of LDL to oxidation and aggregation [93], while in vascular smooth muscle cells inhibited the platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor (PDGF) that is crucial on the development of atherosclerosis [94]. In addition, it interferes with angiotensin II and epidermal growth factor signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells, which may be a long-term mechanism for inhibition of atherosclerosis [95]. In patients with coronary artery disease resveratrol decreased arterial stiffness [96]. The supplementation of this compound controls the high cholesterol diet-induced myocardial complications such as myocardial and aortic damage in mice [97] and increases infarct size in rats [98], by regulating signal transduction pathways that leads to angiogenesis and cardioprotection in the hypercholesterolemic myocardium [99]. The enhanced neovascularization observed in the infarcted rat myocardium [100] may be due to its ability to modulate certain signal pathways of cell proliferation and survival [83].
4. Alcohol Effects on the Stomach
Alcohol is absorbed rapidly through the bloodstream from the stomach and intestinal tract. High concentrations of ethanol induce vascular endothelium injury of the gastric mucosa, which became edematous, and congestive, present point and scattered bleeding lesions, focal hemorrhage, necrosis, and giant and deep ulcers were visible [101]. Principal cells and parietal cells become swollen and diminished [101]. These cells are rich in mitochondria [102], which provide energy by oxidative phosphorylation, which is critical for maintaining the proper morphology and function of the gastric mucosa. The mitochondrion is an easily injured organelle, and mtDNA is the major target of ethanol-associated intracellular oxidative stress associated [103]. There are evidences that during the expression of mtDNA, the subunits 6 and 8 mRNA of ATPase decreased in ethanol-induced acute injury [101], and the lack of ATP may lead to metabolic acidosis, cellular edema, intracellular calcium overload, and further damage to gastric mucosa cells [104].
Alcohol exposure affects the mitochondrial structure which became swollen and disaggregated, and the cristae were dissolved and disappeared [101], giving rise to megamitochondria [105], which have oxygen consumption, ATP synthesis, and ROS-formation rates lower than those of controls. Therefore, it was proposed that enlargement of the mitochondria is an adaptive process by which cells attempt to decrease the intracellular amount of ROS when they are subjected to oxidative stress [106]. Gastric mucosa is rich in protein sulfhydryl groups, which may be the target of ROS. Oxidized protein sulfhydryl groups lead to protein denaturation or enzyme inactivation and receptor damage or modification of the cell membrane, thus contributing to mucosal injury [107].
5. Alcohol Effects on the Liver
Alcoholic liver disease is damage to the liver due to alcohol abuse and usually occurs after years of excessive drinking. Changes in the liver include steatosis, steatohepatitits to fibrosis and cirrhosis [108,109]. Moreover, chronic alcohol consumption is an established risk factor for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis [110].
In early stages of the ALD, the alcoholic steatosis is the initial pathology characterized by the accumulation of lipids in the liver. The progression to alcoholic steatohepatitis represents the key step in the development of ALD, where hepatic stellate cells are activated and recognized as fibrogenic cells and lead to deposition of collagen [111]. Also, activated Kupffer cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, linking apoptosis in the liver to inflammation [112]. When ALD is established, an accumulation of reducing equivalents in the cytosol and the rates of fatty acids biosynthesis and subsequent esterification into triglycerols are increased [113]. It is also possible to observe massive hepatocyte apoptosis, which induces progressive fibrosis, and could result in liver failure, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma [111].
Liver injury mediated by alcohol involves both liver parenchymal and nonparenchymal cells, including resident and recruited immune cells that contribute to liver damage and inflammation [114]. Biopsies from patients with ALD showed partial villous atrophy, increase in lamina propia infiltrate, and intraepithelial lymphocytes. Ultrastructural evaluation revealed changes such as widened intercellular junction, distorted microvilli, increased rough endoplasmic reticulum, and increased and dilated mitochondria [115]. Chronic alcohol administration favors the formation of megamitochondria, due to increasing mitochondrial membrane permeability and decreasing mitochondrial membrane potential [116] and diminished activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain complexes [117].
Mitochondrial and cellular oxidative stress in chronic alcoholism appears to be the major cause of augmented mitochondrial production of superoxide anion (O2 •−) at complexes I and III, and consequently the production of H2O2 and other ROS, triggered by NADH overproduction. Mitochondrial oxidative stress renders hepatocytes susceptible to ethanol- or acetaldehyde-induced mitochondrial membrane permeability transition (MMPT), apoptosis in chronic alcoholism and biliary cirrhosis [118]. Through phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of Bcl-2 proteins, chronic ethanol may control the sensitivity of mitochondria toward a variety of membrane permeabilization-inducing factors [119].
6. Alcohol Effects on the Nervous System
For a long time the effect of alcohol was thought to be a generalized depression of neural activity causing global impairment of cognitive, psychological, and behavioral domains [120]. Recently, it has been shown that ethanol can alter mentation in a variety of ways affecting many neurotransmitter systems [121]. Early symptoms of acute intoxication are euphoria and disinhibition, which progress to stupor and respiratory depression [122]. Abrupt abstinence after prolonged or binge drinking can result in tremors, hallucinations (visual, auditory, or tactile), seizures, or delirium tremens, with severely constricted attentiveness, fluctuating levels of alertness, agitation, and autonomic instability [123]. It is possible, moreover, that repeated binges and withdrawals cause permanent neuronal damage contributing to more lasting neurological disorders, including dementia [124].
Animal experiments have demonstrated that bouts of binge drinking can produce necrotic neurodegeneration in brain areas most closely associated with the hippocampus [125]. Acute ethanol administration produces dose-dependent impairments in spatial learning, and decreases the spatial specificity of hippocampus place cells [126]. Additionally, adult neurogenesis within the hippocampus’ dentate gyrus is selectively impaired in a rat model of alcoholism. This impaired neurogenesis may be a mechanism that mediates the cognitive deficits observed in alcoholism, thus agree with the hypothesis that alcohol interferes with learning processes and memory recall [127].
To date, the exact mechanism of action of this compound is unknown, but it has been observed that it acts on gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) receptors by enhancing the effects of GABA, producing an anxiolytic effect. It also blocks the binding of glutamate to its receptor, N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA), and reversibly reduces sodium transport in neurotransmission [128] and voltage-dependent calcium channels blocking, thus inhibiting the release of neurotransmitters [129], such as serotonin, acetylcholine, dopamine, noradrenaline, endorphin, encephalin, and neuropeptide Y [128].
Recent investigations have suggested that ethanol influences on special transmitter systems and mechanisms of formation of morphine-analogous condensation products are presented in addiction [130]. During development of alcoholism there is progressive accumulation of acetaldehyde and a parallel increase of dopamine concentration in blood creating conditions for the condensation of acetaldehyde with dopamine [131] producing tetrahydropapaveroline [132], which is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of morphine [133]. Also, biogenic amines may react with acetaldehyde to form isoquinoline or carboline compounds, which may enter neural stores and displace the natural neurotransmitter, thus they can act as false neurotransmitters [132]. These results suggest that these compounds may be responsible for development of alcohol addiction. In addition, as products of alcohol metabolism also generates ROS and nitric oxide (NO) via induction of NADPH/xanthine oxidase and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in human neurons contributing to oxidative and nitrosative stress [134].
Brain mitochondria appear to be the principal targets of the oxidative stress generated by ethanol intoxication and withdrawal. This stress causes extensive degradation and depletion of brain mtDNA in mice [135] and decreases cytochrome c oxidase (COX) activity in a variety of neurodegenerative illnesses, such Parkinson disease and Alzheimer disease (AD). Upon removal of chronic ethanol, excessive glutamate-induced neuronal excitation, increases intracellular concentrations of Ca2+ and ROS, factors that provoke PTP opening, allowing for non-selective passage of solutes and water, leading mitochondrial swelling and possible rupture and decreased efficiency of mitochondrial respiration [136,137]. In AD, epidemiological studies have indicated that alcohol consumption plays a role in the development of the disease, due to enhances beta-amyloid (Abeta)-induced neuronal cell death by increasing ROS and mitochondrial dysfunction [138].
7. Alcohol and Prenatal Effects
Due to its soluble nature, alcohol does not bind to any tissue nor is it bound to plasma proteins, but can cross the blood brain barrier and placenta [139]. Prenatal exposure to ethanol during development induces a wide spectrum of adverse effects in offspring; the most extreme of which is fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS), a condition characterized by microcephaly, neurologic abnormalities, facial dysmorphology, and pre- and post-natal growth retardation [139]. Neuropathologic abnormalities in FAS include neuronal-glial heterotopias, cerebellar dysplasia, and agenesis of the corpus callosum, hydrocephalus, and microcephaly [140]. These lesions are indicative of aberrant migration, decreased proliferation, and the death of neuronal cells. Pregnant women are well advised to abstain from drinking ethanol, due to that serotonin (a trophic factor for brain development) levels are significantly decreased in a ethanol-exposed fetus [141] and reduces the number of developing serotonin (5-HT)-containing neurons by increasing apoptosis. Also, serotonin reduces several prosurvival proteins, such as Bcl-2 [142]. Hence, alcohol may affect the growth of the fetus’s forebrain through its effect on 5-HT signaling [143].
It has been postulated that neuronal alterations found in FAS could be due to some initial damage during development on astrocytes, which are more susceptible to the toxic effect of ethanol during proliferation than during differentiation. The number of mitochondria was lower and they were more elongated [144]. Electron microscopic studies on fetal rat hepatocytes illustrated a slight disruption of mitochondrial structure such as enlargement of mitochondria and dilation of cristae [145]. This disruption was accompanied by mitochondrial swelling, altered mitochondrial membrane potential, decrease in succinate dehydrogenase activity, and decrease in cellular ATP levels [145]. There are evidences that chronic ethanol intake during pregnancy in rats increased fetal liver aldehyde dehydrogenase in the mitochondrial fraction, in which the activity was 10-fold higher than in the placenta mitochondrial fraction [146].
8. Alcoholism Therapeutics at the Mitochondrial Level
It is important to understand the basic mechanisms of alcohol metabolism by the mitochondria, as well as the effects of alcohol on their functioning in order to develop new therapies for the treatment of alcohol addiction. Currently, among techniques used to prevent alcohol addiction-associated cellular injury, it has been employed the compound curcumin, a polyphenolic phytochemical that is extracted from the ryzomes of Curcuma longa, a perennial herb distributed throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world and commonly used in India as a spice and medical agent. Curcumin is known to protect the liver, pancreas, and nervous system from toxic effects caused by alcohol consumption [147]. Numerous studies highlighted that curcumin is a potent scavenger of a variety of ROS, such as superoxide anion, hydroxyl radicals, and nitric oxide [147]. Among of the antioxidant properties of curcumin attributed include inhibition of the oxidative damage of proteins and the peroxidation of membrane lipids in rat liver mitochondria [148], the H-atom abstraction from the phenolic OH groups present in its molecular structure [149], and chelating of metal ions such as iron [150].
The well documented cardioprotective effects of moderate alcohol consumption in animal models and in humans [149] are due to increased blood pressure and also those antioxidants properties, which can prevent oxidative stress. Resveratrol possesses diverse biochemical and physiological actions that include the ability to protect brain, kidney, and heart from ischemic injury [150]. It has estrogenic, antiplatelet, and anti-inflammatory properties [151]. The cardioprotective effects of resveratrol have been attributed to their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [152,153]. This compound inhibits angiotensin II (A-II)-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, because it inhibits production of ROS [154] and reduces 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) levels in hearts from spontaneously hypertensive rats [155] maybe by increasing plasma antioxidant capacity [156] and over expression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase, which improved respiration and normalized mass mitochondria in diabetic mice [99]. In addition, the beneficial role of resveratrol may be due also to increasing mitochondrial number as observed in obese mice [157].
Piceatannol (3,3′,4′,5-tetrahydroxystilbene, astinginin) is a resveratrol derivative with higher antioxidant capacity, found in the seeds of Euphorbia lagascae [157]. Piceatannol possesses an additional hydroxyl group than resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxystilbene) and exerts higher radical scavenging activity which was considered to contribute to the cardioprotective and antiarrhythmic effects in ischaemic-reperfused rat heart [158,159]. Another potential compound in mitochondrial therapeutics is the structural GABA analogue citrocard (phenibut citrate) that prevents the damaging effect of alcohol, which was observed from increased indexes of oxidative phosphorylation in treated animals [78].
Ethanol-related mitochondrial dysfunction has been considered one of the major mechanisms contributing to lipid metabolism changes in the liver leading to steatosis [160]. Treatment of steatosis with IL-6 induces expression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL protein in primary mouse hepatocytes [161], which protects against ethanol-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial injury in the liver [161].
Acetaldehyde is a reactive and toxic metabolite of ethanol that could affect drinking behavior and susceptibility to alcoholism. Acetaldehyde is converted into acetate by cytosolic or mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). Mitochondrial ALDH (ALDH2) might be responsible for 60% of acetaldehyde metabolism. There is evidence that the ALDH2*2 gene encoding the inactive variant of ALDH2 protects nearly all carriers of this gene from alcoholism. Inhibition of ALDH2 has thus become a possible strategy to treat alcoholism [162].
Other agents that have received considerable attention in recent years as a potential therapeutic against alcohol-induced organs injury are betaine and S-adenosyl-l-methionine, which have beneficial effects on mitochondrial functions. Betaine, also known as trimethylglycine, is a methyl donor, which can replace folate or S-ademethionine in the human body [163], where it participates in the methionine recycling, and phosphatidylcholine synthesis [164]. Many studies have indicated that betaine can prevent the alcohol-induced injury and improve the cellular function [165] through the inhibition of inflammatory factor, the decrease of lipid peroxidation, and prevents apoptosis [166]. The other compound, S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM), present in all living cells, is synthesized from methionine and ATP [167] by the enzyme methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT) [168]. Its biochemical functions are: (1) a donor of methyl groups; (2) a sulfur-containing metabolite for the transsulfuration pathway that leads to the synthesis of cysteine and glutathione; and (3) a precursor molecule for the aminopropylation pathway that provokes the synthesis of polyamines [168]. SAM plays an important role in regulating mitochondrial function [169], due to the fact that SAM prevents alcohol-dependent mitochondrial dysfunction via the preservation of mitochondrial respiration, attenuation of mitochondrial O2•− production, and maintenance of the integrity of the mtDNA [170].
9. Concluding Remarks
The metabolism of ethanol is closely linked with stimulation of reactive oxygen species generation and oxidative stress. The ability of alcohol to promote oxidative stress and the role of ROS in alcohol-induced tissue injury clearly are important areas of research in the alcohol field, particularly because such information may be of major therapeutic significance in the development of more effective and selective new medications capable of blocking the actions of ROS and consequently the toxic effects of alcohol. This knowledge will clearly advance the design and testing of novel mitochondria-specific therapeutics on the treatment of diseases in alcoholic patients. The identification of possible biomarkers of susceptibility will represent the main goal in the near future and will contribute to the implementation of adequate prevention strategies, to the development of effective diagnostic test strategies, to detect higher risk drinking behavior and early indicators of tissue damage.
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate the financial support of grants from CIC-UMSNH (2.16, ASM; 2.37, SMA) and CONACYT (144250 to ASM during its sabbatical).
References
- Guo, R; Ren, J. Alcohol and acetaldehyde in public health: From marvel to menace. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1285–1301. [Google Scholar]
- Mokdad, AH; Marks, JS; Stroup, DF; Gerberding, JL. Actual causes of death in the United States. JAMA 2000, 291, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th ed; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 1994.
- Grant, BF; Stinson, FS; Harford, TC. Age at onset of alcohol use and DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence: A 12-year follow-up. J. Substain. Abuse 2001, 13, 493–504. [Google Scholar]
- George, A; Figueredo, VM. Alcohol and arrhythmias: A comprehensive review. J. Cardiov. Med. (Hagerstown) 2010, 11, 221–228. [Google Scholar]
- Marinho, V; Laks, J; Engelhardt, E; Conn, D. Alcohol abuse in an elderly woman taking donepezil for Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol 2006, 26, 683–685. [Google Scholar]
- Ohkubo, T; Metoki, H; Imai, Y. Alcohol intake, circadian blood pressure variation, and stroke. Hypertension 2009, 53, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Cederbaum, AI; Lu, Y; Wu, D. Role of oxidative stress in alcohol-induced liver injury. Arch. Toxicol 2009, 83, 519–548. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, HK; Becker, P. Alcohol metabolism and cancer risk. Alcohol Res. Health 2007, 30, 38–47. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, MJ. Alcohol breath testing in patients with respiratory disease. Thorax 1990, 45, 717–721. [Google Scholar]
- Baliunas, DO; Taylor, BJ; Irving, H; Roerecke, M; Patra, J; Mohapatra, S; Rehm, J. Alcohol as a risk factor for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y; Cui, L; Liao, J; huang, L. Effects of alcohol on bone metabolism and biomechanical property of mice. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi 2009, 26, 780–782. [Google Scholar]
- Rehm, J; Mathers, C; Popova, S; Thavorncharoensap, M; Teerawattananon, Y; Patra, J. Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 2009, 373, 2223–2233. [Google Scholar]
- Gohlke, JM; Griffith, WC; Faustman, EM. Computational models of ethanol-induced neurodevelopmental toxicity across species: Implications for risk assessment. Birth Defects Res. B. Dev. Reprod. Toxicol 2008, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pietrzykowski, AZ; Friesen, RM; Martin, GE; Puig, SI; Nowak, CL; Wynne, PM; Siegelmann, HT; Treistman, SN. Posttranscriptional regulation of BK channel splice variant stability by miR-9 underlies neuroadaptation to alcohol. Neuron 2008, 59, 274–287. [Google Scholar]
- Roberto, M; Treistman, SN; Pietrzykowski, AZ; Weiner, J; Galindo, R; Mameli, M; Valenzuela, F; Zhu, PJ; Lovinger, D; Zhang, TA; Hendricson, AH; Morrisett, R; Siggins, GR. Actions of acute and chronic ethanol on presynaptic terminals. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2006, 30, 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie, MB; Besheer, J; Kelley, SP; Kumar, S; O’Buckley, TK; Morrow, AL; Hodge, CW. Acute ethanol administration rapidly increases phosphorylation of conventional protein kinase C in specific mammalian brain regions in vivo. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2007, 31, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Le Marquand, D; Pihl, RO; Benkelfat, C. Serotonin and alcohol intake, abuse, and dependence: Clinical evidence. Biol. Psychiatry 1994, 36, 326–337. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, RA; Mangrum, CA; Glass, JD. Acute ethanol modulates glutamatergic and serotonergic phase shifts of the mouse circadian clock in vitro. Neuroscience 2008, 152, 837–848. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, M; Hanchar, HJ; Olsen, RW. Low-dose alcohol actions on alpha4beta3delta GABAA receptors are reversed by the behavioral alcohol antagonist Ro15-4513. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8540–8545. [Google Scholar]
- Perra, S; Pillolla, G; Luchicchi, A; Pistis, M. Alcohol inhibits spontaneous activity of basolateral amigdala proyection neurons in the rat: Involvement of the endocannabinoid system. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2008, 32, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, SJ; Lee, IJ; Swaan, PW; Eddington, ND. Evaluation of the effect of ethanol’s toxic metabolite acetaldehyde on the gastrointestinal oligopeptide transporter, PEPT1: In vitro and in vivo studies. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2008, 32, 162–170. [Google Scholar]
- Karinch, AM; Martin, JH; Vary, TC. Acute and chronic ethanol consumption differentially impact pathways limiting hepatic protein synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab 2008, 295, E3–E9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, AL; Vadhavkar, S; Singh, G; Omary, MB. Epidemiology of alcohol-related liver and pancreatic disease in the United States. Arch. Intern. Med 2008, 168, 649–656. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, JW; Lautt, WW. The effect of acute, chronic, and prenatal ethanol exposure on insulin sensitivity. Pharmacol. Ther 2006, 111, 346–373. [Google Scholar]
- Happel, KI; Rudner, X; Quinton, LJ; Movasshaghi, JL; Clark, C; Odden, AR; Zhang, P; Bagby, GJ; Nelson, S; Shellito, JE. Acute alcohol intoxication suppresses the pulmonary ELR-negative CXC chemokine response to lipopolysaccharide. Alcohol 2007, 41, 325–333. [Google Scholar]
- Greiffensstein, P; Mathis, KW; Stouwe, CV; Molina, PE. Alcohol binge before trauma/hemorrhage impairs integrity of host defense mechanisms during recovery. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2007, 31, 704–715. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhry, MA; Li, X; Chaudry, IH. A role for corticosterone in impaired intestinal immunity and barrier function in a rodent model of acute alcohol intoxication and burn injury. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol 2006, 1, 428–434. [Google Scholar]
- Radek, KA; Kovacs, EJ; DiPietro, LA. Matrix proteolytic activity during wound healing: Modulation by acute ethanol exposure. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2007, 31, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Dolganiuc, A; Szabo, G. In vitro and in vivo models of acute alcohol exposure. World J. Gastroenterol 2009, 15, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, DF; Swihart, AR; Ferguson, C; Lariviere, WR; Harrison, NL; Homanics, GE. Alcohol-induced tolerance and physical dependence in mice with ethanol insensitive α1 GABAA receptors. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2009, 33, 289–299. [Google Scholar]
- Norberg, A; Jones, AW; Hahn, RG; Gabrielsson, JL. Role of variability in explaining ethanol pharmacokinetics: Research and forensic applications. Clin. Pharmacokinet 2003, 42, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Holford, NHG. Clinical pharmacokinetics of ethanol. Clin. Pharmacokinet 1987, 13, 273–292. [Google Scholar]
- Zakhari, S. Overview: How is alcohol metabolized by the body? Alcohol Res. Health 2006, 29, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, DP. Genetic polymorphisms of alcohol metabolizing enzymes. Pathol. Biol 2001, 49, 703–709. [Google Scholar]
- Gemma, S; Vichi, S; Testai, E. Individual susceptibility and alcohol effects: Biochemical and genetic aspects. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2006, 42, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, H. Subcellular localization of acetaldehyde oxidation on liver. Ann. NY Acad. Sci 1987, 492, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, H; Harmjanz, D. Effect of ethanol infusion on the ultrastructure of human myocardium. Postgrad. Med. J 1975, 51, 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- Regan, TJ. Alcohol and the cardiovascular system. JAMA 1990, 264, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Pachinger, O; Mao, J; Fauvel, J-M; Bing, RJ. Fleckstein, A, Dhalla, NS, Eds.; Mitochondrial function and excitation-contraction coupling in the development of alcoholic cardiomypathy. In Recent Advances in Studies on Cardiac Structure and Metabolism; University Park Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1975; Volume 5, pp. 423–429. [Google Scholar]
- Albano, E. Sherman, VR, Watson, RR, Eds.; Free radicals and alcohol-induced liver injury. In Ethanol and the Liver; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2002; pp. 153–190. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, MA; Sauvage, I; Grandperret, T; Descatoire, V; Pessayre, D; Fromenty, B. Ethanol increases mitochondrial cytochrome P450 2E1 in mouse liver and rat hepatocytes. FEBS Lett 2005, 579, 6895–6902. [Google Scholar]
- Cederbaum, AI. Microsomal generation of reactive oxygen species and their possible role in alcohol hepatoxicity. Alcohol Alcohol 1991, (Suppl 1), 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Adam-Vizi, V. Production of reactive oxygen species in brain mitochondria: Contribution by electron transport chain and non-electron transport chain sources. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2005, 7, 1140–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Ronis, MJJ; Lindros, KO; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Ioannides, C, Ed.; The CYP2E family. In Cytochromes P450: Metabolic and Toxicological Aspects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 211–239. [Google Scholar]
- Liangpunsakul, S; Kolwankar, D; Pinto, A; Gorski, CJ; Hall, SD; Chalasani, N. Activity of CYP2E1 and CYP3A enzymes in adults with moderate alcohol consumption: A comparison with nonalcoholics. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Albano, E. Alcohol, oxidative stress and free radical damage. Proc. Nutr. Soc 2006, 65, 278–290. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, SM; Pietsch, EC; Cunningham, CC. Ethanol stimulates the production of reactive oxygen species at mitochondrial complexes I and III. Free Radic. Biol. Med 1999, 27, 891–900. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, CC; Coleman, WB; Spach, PI. The effects of chronic ethanol consumption on hepatic mitochondrial energy metabolism. Alcohol Alcohol 1990, 25, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, SM; Cunningham, CC. Effect of dietary fat on chronic ethanol-induced oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 1999, 23, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, SM. A review of the role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in alcohol-induced mitochondrial energy metabolism. Free Radic. Res 2003, 37, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Mantena, SK; King, AL; Andringa, KK; Landar, A; Darley-Usmar, V; Bailey, SM. Novel interactions of mitochondria and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species in alcohol mediated liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol 2007, 13, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, JB; Cahill, A; Pastorino, JG. Alcohol and mitochondria: A dysfunctional relationship. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Coleman, WB; Cunningham, CC. Effect of chronic ethanol consumption on hepatic mitochondrial transcription and translation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1991, 1058, 178–186. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatraman, A; Landar, A; Davis, AJ; Chamlee, L; Sanderson, T; Kim, H; Page, G; Pompilius, M; Ballinger, S; Darley-Usmar, V; Bailey, SM. Modification of the mitochondrial proteome in response to the stress of ethanol-dependent hepatotoxicity. J. Biol. Chem 2004, 279, 22092–22101. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, SM; Robinson, G; Pinner, A; Chamlee, L; Ulasova, E; Pompilius, M; Page, GP; Chhieng, D; Jhala, N; Landar, A; Kharbanda, KK; Ballinger, S; Darley-Usmar, V. S-adenosylmethionine prevents chronic alcohol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in the rat liver. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 2006, 291, G857–G867. [Google Scholar]
- Radi, R; Cassina, A; Hodara, R; Quijano, C; Castro, L. Peroxynitrite reactions and formation in mitocondria. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2002, 33, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, PS; Kraus, DW; Shiva, S; Doeller, JE; Barone, MC; Patel, RP; Lancaster, JR, Jr; Darley-Usmar, V. Control of mitochondrial respiration by NO., effects of low oxygen and respiratory state. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 31603–31609. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, KH; Hood, BL; Kim, BJ; Hardwick, JP; Conrads, TP; Veenstra, TD; Song, BJ. Inactivation of oxidized and S-nitrosylated mitochondrial proteins in alcoholic fatty liver of rats. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi, T; Karbowski, M; Liu, X; Usukura, J; Wozniak, M; Wakabayashi, T. Complete suppression of ethanol-induced formation of megamitochondria by 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6,-tetramethyl-piperidine-1-oxyl (4-OH-TEMPO). Free Radic. Biol. Med 1998, 24, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Meager, EA; Barry, OP; Burke, A; Lucey, MR; Lawson, JA; Rokach, J; FitzGerald, GA. Alcohol-induced generation of lipid peroxidation products in humans. J. Clin. Invest 1999, 104, 805–813. [Google Scholar]
- Niemela, O; Parkkila, S; Yla-Herttuala, S; Halsted, C; Witztum, JL; Lanca, A; Israel, Y. Covalent protein adducts in the liver as a result of ethanol metabolism and lipid peroxidation. Lab. Invest 1994, 70, 537–546. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, TF. Free-radical mechanisms in tissue injury. Biochem. J 1984, 222, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes-Rojo, C; Calderon-Cortes, E; Clemente-Guerrero, M; Estrada-Villagomez, M; Manzo-Avalos, S; Mejia-Zepeda, R; Boldogh, I; Saavedra-Molina, A. Elucidation of the effects of lipoperoxidation on the mitochondrial electron transport chain using yeast mitochondria with manipulated fatty acid content. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr 2009, 41, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Fukumura, A; Tsutsumi, M; Tsuchishima, M; Takase, S. Correlation between adenosine triphosphate content and apoptosis in liver of rats treated with alcohol. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2003, 27, 12S–15S. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, A; Fromenty, B; Berson, A; Robin, MA; Grimbert, S; Beaugrand, M; Erlinger, S; Pessayre, D. Multiple hepatic mitochondrial DNA deletions suggest premature oxidative aging in alcoholic patients. J. Hepatol 1997, 27, 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchishima, M; Tsutsumi, M; Shiroeda, H; Yano, H; Ueshima, Y; Shimanaka, K; Takase, S. Study of mitochondrial DNA deletion in alcoholics. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2000, 24, 12S–15S. [Google Scholar]
- Von Wurmb-Schwark, N; Ringleb, A; Schwark, T; Broese, T; Weirich, S; Schlaefke, D; Wegener, R; Oehmichen, M. The effect of chronic alcohol consumption on mitochondrial DNA mutagenesis in human blood. Mutat. Res 2008, 637, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, T; Kaplowitz, N; Kamimura, T; Tsukamoto, H; Fernandez-Checa, JC. Hepatic mitocondrial GSH depletion and progression of experimental alcoholic liver disease in rats. Hepatology 1992, 16, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Checa, JC; Kaplowitz, N. Hepatic mitochondrial glutathione: Transport and role in disease and toxicity. Toxicol. App. Pharmacol 2005, 204, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Rouach, H; Fattaccioli, V; Gentil, M; French, SW; Morimoto, M; Nordmann, R. Effect of chronic ethanol feeding on lipid peroxidation and protein oxidation in relation to liver pathology. Hepatology 1997, 25, 351–355. [Google Scholar]
- Kowaltowski, AJ; Castillo, RF; Vercesi, AF. Mitochondrial permeability transition and oxidative stress. FEBS Lett 2001, 495, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes-Rojo, C; Clemente-Guerrero, M; Saavedra-Molina, A. Effects of D-amino acids on lipoperoxidation in rat liver and kidney mitochondria. Amino Acids 2006, 32, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, JS; He, L; Lemasters, JJ. Mitochondrial permeability transition: A common pathway to necrosis and apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2003, 304, 463–470. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, WH; Hong, F; Jaruga, B; Zhang, ZS; Fan, SJ; Liang, TJ; Gao, B. Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes primary mouse hepatocytes to ethanol- and TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis by a caspase-3-dependent mechanism. Cell Mol. Immunol 2005, 2, 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Urbano-Marquez, A; Fernandez-Sola, J. Effects of alcohol on skeletal and cardiac muscle. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 689–707. [Google Scholar]
- Capasso, JM; Li, P; Guideri, G; Malhotra, A; Cortese, R; Anversa, P. Myocardial mechanical, biochemical, and structural alterations induced by chronic ethanol ingestion in rats. Circ. Res 1992, 71, 346–356. [Google Scholar]
- Perfilova, VN; Ostrovskii, OV; Verovskii, VE; Popova, TA; Lebedeva, SA; Dib, H. Effect of citrocard on functional activity of cardiomyocyte mitochondria during chronic alcohol intoxication. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med 2007, 143, 341–343. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, RI; Coleman, WB; Eble, KS; Cunningham, CC. Ethanol-elicited alterations in the oligomycin sensitivity and structural stability of the mitochondrial F0.F1 ATPase. J. Biol. Chem 1987, 262, 13285–13289. [Google Scholar]
- Usha, R; Pendurthi, J; Todd, W; Vijya, M. Resveratrol a polyphenolic compound found in wine inhibits tissue factor expression in vascular cells. A possible mechanism for the cardiovascular benefits associated with moderate consumption of wine. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 1999, 19, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Pace-Asciak, CR; Hahn, S; Diamandis, EP; Soleas, G; Goldberg, DM. The red wine phenolics trans-resveratrol and quercetin block human platelet aggregation and eicosanoid synthesis: Implications for protection against coronary heart disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 1995, 235, 207–219. [Google Scholar]
- Bertelli, AAE; Giovannini, L; Giannessi, D; Migliori, M; Bernini, W; Fregoni, M; Bertelli, A. Antiplatelet activity of synthetic and natural resveratrol in red wine. Int. J. Tiss. Reac 1995, 17, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, JA; Sinclair, DA. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol: The in vivo evidence. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov 2006, 5, 493–506. [Google Scholar]
- Howitz, KT; Bitterman, KJ; Cohen, HY; Lamming, DW; Lavu, S; Wood, JG; Zipkin, RE; Chung, P; Kisielewski, A; Zhang, LL; Scherer, B; Sinclair, DA. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extended Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature 2003, 425, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Belguendouz, L; Fremont, L; Gozzelino, MT. Interaction of transresveratrol with plasma lipoproteins. Biochem. Pharmacol 1998, 55, 811–816. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S; Falchi, M; Bertelli, A; Maulik, N; Das, DK. Attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by the anti-inflammatory action of resveratrol. Arzneimittelforschung 2006, 56, 700–706. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S; Alagappan, VK; Bagchi, D; Sharma, HS; Maulik, N; Das, DK. Coordinated induction of iNOS-VEGF-KDR-eNOS after resveratrol consumption: A potential mechanism for resveratrol preconditioning of the heart. Vascul. Pharmacol 2005, 42, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Hattori, R; Otani, H; Maulik, N; Das, DK. Pharmacological preconditioning with resveratrol: Role of nitric oxide. Am. J. Physiol 2002, 282, H1988–H1995. [Google Scholar]
- Li, HL; Wang, AB; Huang, Y; Liu, DP; Wei, C; Williams, GM; Zhang, CN; Liu, G; Liu, YQ; Hao, DL; Hui, RT; Lin, M; Liang, CC. Isorhapontigenin, a new resveratrol analog, attenuates cardiac hypertrophy via blocking signaling transduction pathways. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2005, 38, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Kaga, S; Zhan, L; Matsumoto, M; Maulik, N. Resveratrol enhances neovascularization in the infarcted rat myocardium through the induction of thioredoxin-1, heme oxygenase-1 and vascular endothelial growth factor. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol 2005, 39, 813–822. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y; Liu, Y; Wang, T; Li, H; Wang, Z; Yang, B. Resveratrol, a natural ingredient of grape skin: Antiarrhyhtmic efficacy and ionic mechanisms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2006, 340, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S; Wang, X; Yan, J; Xie, X; Fan, F; Zhou, X; Han, L; Chen, J. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation of cultured rat cardiac fibroblasts: Correlated with NO-cGMP signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2007, 567, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Hayek, T; Fuhrman, B; Vaya, J; Rosenblat, M; Belinky, P; Coleman, R; Elis, A; Aviram, M. Reduced progression of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice following consumption of red wine, or its polyphenols quercetin or catechin, is associated with reduced susceptibility of LDL to oxidation and aggregation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol 1997, 17, 2744–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz, S; Knirel, D; Dietrich, H; Flesch, M; Erdmann, E; Bohm, M. Inhibition of the PDGF receptor by red wine flavonoids provides a molecular explanation for the “French paradox”. FASEB J 2002, 16, 1958–1960. [Google Scholar]
- Halder, UG; Roos, TU; Kontaridis, MI; Neel, BG; Sorescu, D; Griedling, KK; Vollmar, AM; Dirsch, VM. Resveratrol inhibits angiotensin II and epidermal growth factor-mediated Akt activation: Role of Gab1 and Shp2. Mol. Pharmacol 2005, 68, 41–48. [Google Scholar]
- Karatzi, KN; Papamichael, CM; Karatzis, EN; Papaioannou, TG; Aznaouridis, KA; Katsichti, PP; Stamatelopoulos, KS; Zampelas, A; Lekakis, JP; Mavrikakis, ME. Red wine acutely induces favorable effects on wave reflections and central pressures in coronary artery diseases patients. Am. J. Hypertens 2005, 18, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar]
- Baur, JA; Pearson, KJ; Price, NL; Jamieson, HA; Lerin, C; Kalra, A; Prabhu, VV; Allard, JS; Lopez-Lluch, G; Lewis, K; Pistell, PJ; Poosala, S; Becker, KG; Boss, O; Gwinn, D; Wang, M; Ramaswamy, S; Fishbein, KW; Spencer, RG; Lakatta, EG; Le Couteur, D; Shaw, RJ; Navas, P; Puigserver, P; Ingram, DK; de Cabo, R; Sinclair, DA. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 2006, 444, 337–342. [Google Scholar]
- Penumathsa, SV; Thirunavukkarasu, M; Koneru, S; Juhasz, B; Zhan, L; Pant, R; Menon, VP; Otani, H; Maulik, N. Statin and resveratrol in combination induces cardioprotection against myocardial infarction in hypercholesterolemic rat. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol 2007, 42, 508–516. [Google Scholar]
- Penumathsa, SV; Maulik, N. Resveratrol: A promising agent in promoting cardioprotection against coronary heart disease. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol 2009, 87, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, TM; Mullally, JE; Fitzpatrick, FA. Reactive lipid species from cyclooxygenase-2 inactivate tumor suppressor LKB1/STK11: Cyclopentenone prostaglandins and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal covalently modify and inhibits the AMP kinase kinase that modulates cellular energy homeostasis and protein translation. J. Biol. Chem 2006, 281, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, JS; He, SZ; Xu, HZ; Zhan, XJ; Yang, XN; Xiao, HM; Shi, HX. Oxidative stress disturbs energy metabolism of mitochondria in ethanol-induced gastric mucosa injury. World J. Gastroenterol 2008, 14, 5857–5867. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, GY; Zhang, WN; Shen, XJ; Chen, Y; He, XF. Ultrastructure and molecular biological changes of chronic gastritis, gastric cancer and gastric precancerous lesions: A comparative study. World J. Gastroenterol 2003, 9, 851–857. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, JB; Cahill, A; Pastorino, JG. Alcohol and mitochondria: A dysfunctional relationship. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 2049–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, Q; Utevskaya, O; Ramilo, M; Chow, DC; Forte, JG. Nucleotide metabolism by gastric glands and H(+)-k(+)-ATPase-enriched membranes. Am. J. Physiol 1998, 274, G103–G110. [Google Scholar]
- Giannessi, F; Giambelluca, MA; Grasso, L; Scavuzzo, MC; Ruffoli, R. Curcumin protects Leydig cells of mice from damage induced by chronic alcohol administration. Med. Sci. Monit 2008, 14, 237–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi, T. Megamitochondria formation-physiology and pathology. J. Cell Mol. Med 2002, 6, 497–538. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, A; Cederbaum, AI. Alcohol and oxidative liver injury. Hepatology 2006, 43, S63–S74. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, SJ; Harrison, SH. Comparison of the natural history of alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Curr. Gastroenterol. Reports 2010, 7, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, S; Jones, D; Day, CP. Alcoholic liver disease: New insights into mechanisms and preventative strategies. Trends Mol. Med 2001, 7, 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, TR; Mandayam, S; Jamal, MM. Alcohol and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Mendez, A; Lugo-Baruqui, A; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Molecular basis and current treatment for alcoholic liver disease. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1872–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Malhi, H; Gores, GJ. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of liver injury. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1641–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Song, BJ; Moon, KH; Olsson, NU; Salem, N, Jr. Prevention of alcoholic fatty liver and mitochondrial dysfunction in the rat by long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. J. Hepatol 2008, 49, 262–273. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, SL. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, and integrated cellular response to tissue injury. J. Biol. Chem 2000, 275, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar]
- Bronchal, S; Nain, CK; Prasad, KK; Nada, R; Sharma, AK; Sinha, SK; Singh, K. Functional and morphological alterations in small intestine mucosa of chronic alcoholics. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2008, 23, e43–e48. [Google Scholar]
- Kravos, M; Malesic, I. Kinetics and isoforms of serum glutamate dehydrogenase in alcoholics. Alcohol Alcohol 2008, 43, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, DS; Anuradha, CV. Mitochondrial damage, cytotoxicity and apoptosis in iron-potentiated alcoholic liver fibrosis: Amelioration by taurine. Amino Acids 2010, 38, 869–879. [Google Scholar]
- Sastre, J; Serviddio, G; Pereda, J; Minana, JB; Arduini, A; Vendemiale, G; Poli, G; Pallardo, FV; Vina, J. Mitochondrial function in liver disease. Front. Biosci 2007, 12, 1200–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Hajnoczky, G; Buzas, CJ; Pacher, P; Hoek, JB; Rubin, E. Alcohol and mitochondria in cardiac apoptosis: Mechanisms and visualization. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2005, 29, 693–701. [Google Scholar]
- White, AM. What happened? Alcohol, memory blackouts, and the brain. Alcohol Res. Health 2003, 27, 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, KM; Wu, JY. Role of glutamatergic and GABAergic systems in alcoholism. J. Biomed. Sci 2001, 8, 7–19. [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser, J; Sellers, EM; Kalent, HL. Alcohol intoxication and withdrawal. N. Engl. J. Med 1976, 294, 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Kosten, TR; O’Connor, PG. Management of drug and alcohol withdrawal. N. Engl. J. Med 2003, 348, 1786–1795. [Google Scholar]
- Brust, JCM. Ethanol and cognition: Indirect effects, neurotoxicity and neuroprotection: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1540–1557. [Google Scholar]
- Obenier, JA; Bouldin, TW; Crews, FT. Binge ethanol exposure in adult rats causes necrotic cell death. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2002, 26, 547–557. [Google Scholar]
- Silvers, JM; Tokunaga, S; Berry, RB; White, AM; Matthews, DB. Impairment in spatial learning and memory: Ethanol, allopregnanolone, and the hippocampus. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev 2003, 43, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, I. Alcohol and the brain: Neuropsychological correlates. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol 1987, 55, 310–324. [Google Scholar]
- Israel, Y; Kalant, H. Effect of ethanol on the transport of sodium in frog skin. Nature 1963, 200, 476–478. [Google Scholar]
- Blum, K; Noble, EP; Sheridan, PJ; Montgomery, A; Ritchie, T; Jagadeesawaran, P; Nogami, H; Briggs, AH; Cohn, JB. Allelic association of human dopamine D2 and Gaba receptor gene in alcoholism. JAMA 1990, 263, 2055–2060. [Google Scholar]
- Kluge, H; Neumann, J; Seidel, K. Biochemical mechanisms for the effect of alcohol on the brain. Psychiatr. Neurol. Med. Psychol (Leipz) 1979, 31, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kharchenko, NK. Dopamine content in blood and activity of alcohol-transforming enzymes in alcoholism. Ukr. Biokhim. Zh 1997, 69, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, AA. Interaction of biogenic amines with ethanol. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol 1975, 56, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Weiner, H. Relationship between 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde levels and tetrahydropapaveroline formation. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 1978, 2, 127–131. [Google Scholar]
- Haorah, J; Ramírez, SH; Floreani, N; Gorantla, S; Morsey, B; Persidsky, Y. Mechanism of alcohol-induced stress and neuronal injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2008, 45, 1542–1550. [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri, A; Demeilliers, C; Amsellen, S; Pessayre, D; Fromenty, B. Acute ethanol administration oxidatively damages and depletes mitochondrial DNA in mouse liver, brain, heart, and skeletal muscles: Protective effects of antioxidants. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 2001, 298, 737–743. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, ME; Agarwal, R; Simpkins, JW. Ethanol withdrawal posttranslationally decreases the activity of cytochrome c oxidase in an estrogen reversible manner. Neurosci. Lett 2007, 41, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, ME; Simpkins, JW; Wilson, AM; Downey, HF; Mallet, RT. Intermittent hypoxia conditioning prevents behavioral deficit and brain oxidative stress in ethanol-withdrawn rats. J. Appl. Physiol 2008, 105, 510–517. [Google Scholar]
- Lee do, Y; Lee, KS; Lee, HJ; Jung, HY; Lee, JY; Lee, SH; Youn, YC; Seo, KM; Lee, JH; Lee, WB; Kim, SS. Alcohol enhances Abeta42-induced neuronal cell death through mitochondrial dysfunction. FEBS Lett 2008, 582, 4185–4190. [Google Scholar]
- Streissguth, AP; Landersman-Dwyer, S; Martin, JC; Smith, DW. Teratogenic effects of alcohol in humans and laboratory animals. Science 1980, 209, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Clarren, SK; Alvord, EC; Sumi, SM; Streissguth, AP; Smith, DW. Brain malformations related to prenatal exposure to ethanol. J. Pediatr 1978, 92, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Riikonen, RS; Nokelainen, P; Valkonen, K; Kolehmainen, AI; Kumpulainen, KI; Könönen, M; Vanninen, RL; Kuikka, JT. Deep serotonergic and dopaminergic structures in fetal alcoholic syndrome: A study with nor-beta-CIT-single-photon emission computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging volumetry. Biol. Psychiatry 2005, 57, 1565–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Druse, MJ; Tajuddin, NF; Gillespie, RA; Le, P. The effects of ethanol and the serotonin(1A) agonist ipsapirone on the expression of the serotonin(1A) receptor and several antiapoptotic proteins in fetal rhombencephalic neurons. Brain Res 2006, 1092, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sari, Y; Powrozek, T; Zhou, FC. Alcohol deters the outgrowth of serotonergic neurons at midgestation. J. Biomed. Sci 2001, 8, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mayordomo, F; Renau-Piqueras, J; Megias, L; Guerri, C; Iborra, FJ; Azorin, I; Ledig, M. Cytochemical and stereological analysis of rat cortical astrocytes during development in primary culture. Effect of prenatal exposure to ethanol. Int. J. Dev. Biol 1992, 36, 311–321. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, BG; Henderson, GI; Frosto, TA; Schenker, S. Effect of ethanol on rat fetal hepatocytes: Studies on cell replication, lipid peroxidation and glutathione. Hepatology 1993, 18, 648–659. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchis, R; Guerri, C. Alcohol-metabolizing enzymes in placenta and fetal liver: Effect of chronic ethanol intake. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 1986, 10, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, RK; Singh, AK; Gaddipati, J; Srimal, RC. Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short review. Life Sci 2006, 78, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarsini, KI; Maity, DK; Naik, GH; Kumar, MS; Unnikrishnan, MK; Satav, JG; Mohan, H. Role of phenolic O-H and methylene hydrogen on the free radical reactions and antioxidant activity of curcumin. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2003, 35, 475–484. [Google Scholar]
- Churchill, EN; Disatnik, MH; Mochly-Rosen, D. Time-dependent and ethanol-induced cardiac protection from ischemia mediated by mitochondrial translocation of varepsilon PKC and activation of aldehyde dehydrogenase2. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol 2009, 46, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cannon, CP; Braunwald, E; McCabe, CH; Rader, DJ; Rouleau, JL; Belder, R; Joyal, SV; Hill, KA; Skene, AM. Pravastatin or atorvastatin evaluation and infection therapy-thrombolysis in myocardial infarction 22 investigators. N. Engl. J. Med 2004, 350, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, GJ; Ridker, PM. Novel clinical markers of vascular wall inflammation. Circulation Res 2001, 89, 763–771. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, R; Daly, L; Robinson, K; Naughten, E; Cahalane, S; Fowler, B; Graham, I. Hyperhomocysteinemia: An independent risk factor for vascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med 1991, 324, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Brisdelli, F; D’Andrea, G; Bozzi, A. Resveratrol: A natural polyphenol with multiple chemopreventive properties. Curr. Drug Metab 2009, 10, 530–46. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, TH; Liu, JC; Lin, H; Shih, NL; Chen, YL; Huang, MT; Chan, P; Cheng, CF; Chen, JJ. Inhibitory effect of resveratrol on angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol 2004, 369, 239–244. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, AY; Dolinsky, VW; Soltys, CL; Viollet, B; Baksh, S; Light, PE; Dyck, JR. Resveratrol inhibits cardiac hypertrophy via AMP-activated protein kinase and Akt. J. Biol. Chem 2008, 283, 24194–24201. [Google Scholar]
- Serafini, M; Maiani, G; Ferro-Luzzi, A. Alcohol-free red wine enhances plasma antioxidant capacity in humans. J. Nutr 1998, 128, 1003–1007. [Google Scholar]
- Opie, LH; Lecour, S. The red wine hypothesis: From concepts to protective signalling molecules. Eur Heart J 2007, 28, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, LM; Chen, JK; Lee, RS; Liang, HC; Su, MJ. Beneficial effects of astringinin, a resveratrol analogue, on the ischemia and reperfusion damage in rat heart. Free Radic. Biol. Med 2001, 30, 877–883. [Google Scholar]
- Fauconneau, B; Waffo-Teguo, P; Huguet, F; Barrier, L; Decendit, A; Merillon, JM. Comparative study of radical scavenger and antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds from Vitis vinifera cell cultures using in vitro tests. Life Sci 1997, 61, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar]
- El-Assal, O; Hong, F; Kim, W-H; Radaeva, S; Gao, B. IL-6 deficient mice are susceptible to ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis: IL-6 protects against ethanol-induced oxidative stress and mitochondrial permeability transition in the liver. Cell Mol. Immunol 2004, 1, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, F; Kim, WH; Tian, Z; Jaruga, B; Ishac, E; Shen, X; Gao, B. Elevated interleukin-6 during ethanol consumption acts as a potential endogenous protective cytokine against ethanol-induced apoptosis in the liver: Involvement of induction of Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L) proteins. Oncogene 2002, 21, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, ED; Gao, GY; Johnson, LN; Keung, WM. Structure of didzin, a naturally occurring anti-alcohol-addiction agent, in complex with human mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase. J. Med. Chem 2008, 51, 4482–4487. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, YC; Jung, YS; Kim, SK. Effect of betaine supplementation on changes in hepatic metabolism of sulfur-containing amino acids and experimental cholestasis induced by alphanaphthylisothiocyanate. Food Chem. Toxicol 2005, 43, 663–670. [Google Scholar]
- Craig, SA. Betaine in human nutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr 2004, 80, 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P; Gong, ZJ; Wang, LW; Sun, XM; Zhou, XR. Effects of Betaine on hyperhomocysteinemia and lipid peroxidation in rats with ethanol-induced liver injury. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Ganbing Zazhi 2006, 16, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, C; Shinohara, M; Vance, D; Than, TA; Ookhtens, M; Chan, C; Kaplowitz, N. Effect of transgenic extrahepatic expression of betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase on alcohol or homocysteine-induced fatty liver. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res 2008, 32, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar]
- Cantoni, GL. Activation of methionine for transmethylation. J. Biol. Chem 1951, 189, 745–754. [Google Scholar]
- Mato, JM; Alvarez, L; Ortiz, P; Pajares, MA. S-adenosylmethionine synthesis: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Pharmacol. Ther 1997, 73, 265–280. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria, E; Avila, MA; Latasa, MU; Rubio, A; Martin-Duce, A; Lu, SC; Mato, JM; Corrales, FJ. Functional proteomics of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mitochondrial proteins as targets of S-adenosylmethionine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3065–3070. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, SM; Robinson, G; Pinner, A; Chamlee, L; Ulasova, E; Pompilius, M; Page, GP; Chhieng, D; Jhala, N; Landar, A; Kharbanda, KK; Ballinger, S; Darley-Usmar, V. S-adenosylmethionine prevents chronic alcohol-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in the rat liver. Am. J. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 2006, 291, G857–G867. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).