Socioeconomic Disparities and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Associated with Environmental Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Florida
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.1.1. Cancer Incidence and Demographic Data
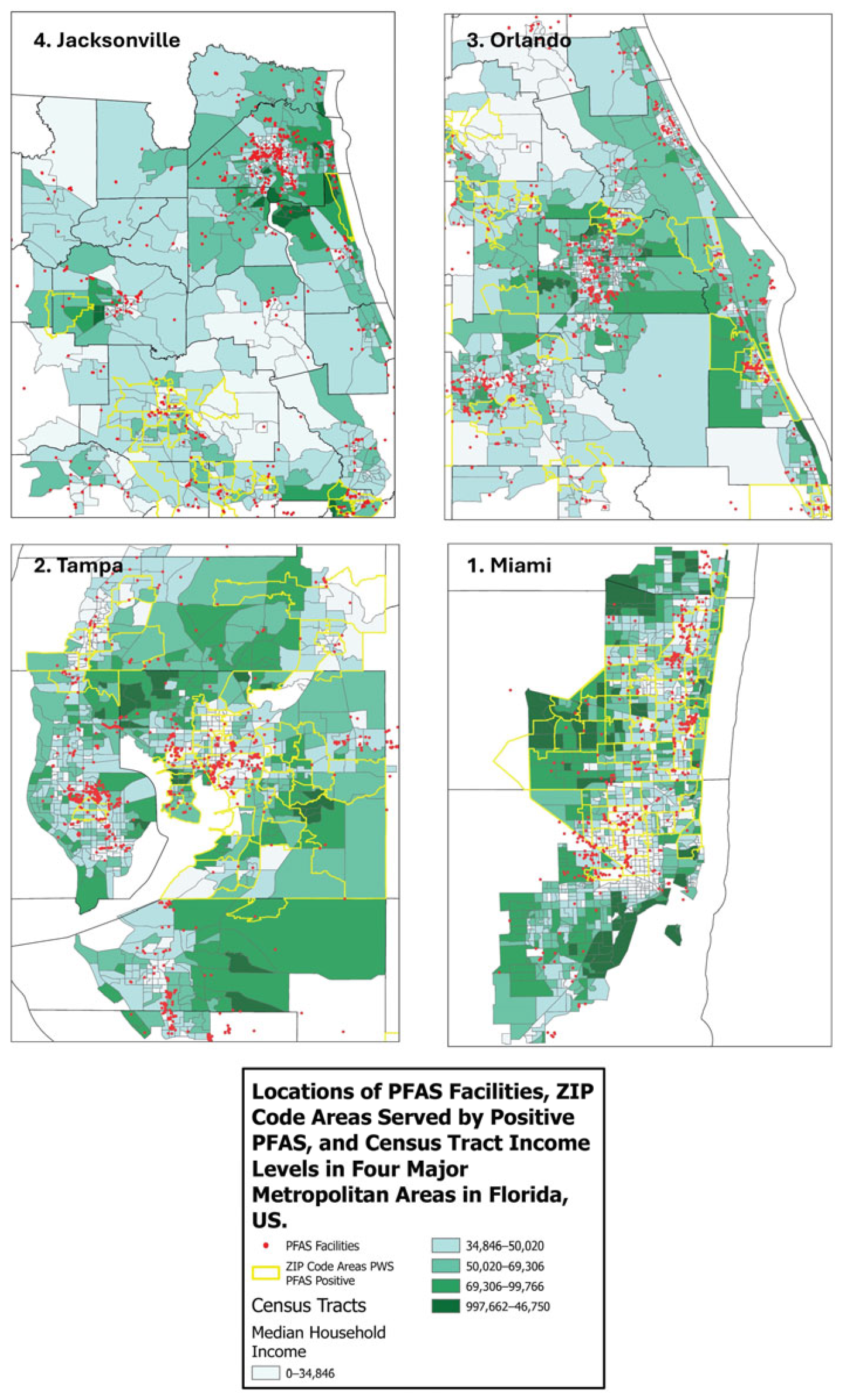
2.1.2. Environmental PFAS Exposure Data
2.2. Data Availability
Measurement of Proximity to PFAS Sites
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| Demographics | NHW | Hispanic | NHB | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 Florida Population | 11,503,781 | 4,599,699 | 2,942,326 | 19,045,806 |
| Number of Patients | 9169 | 3990 | 985 | 14,144 |
| Percent Female | 71.6% | 78.4% | 81.7% | 74.2% |
| Average Age at Diagnosis | 52.46 | 48.86 | 50.56 | 50.63 |
| Number of Mortality | 647 | 147 | 86 | 880 |
| Mortality Odds 1 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
| Socioeconomic Measures | ||||
| Average Median Household Income | 57,569 | 52,139 | 46,010 | 51,906 |
| Average Percentage of Population with a Bachelor’s Degree | 30.94 | 27.43 | 22.11 | 26.83 |
| Average Percentage of Population in Poverty | 13.10 | 17.43 | 20.82 | 17.12 |
| Average Percentage of Population with No Insurance | 14.73 | 22.05 | 20.37 | 19.05 |
| Average Percentage of Population Lacking Physical Activity | 25.97 | 30.72 | 31.54 | 29.41 |
| Average Percentage of Obesity in Population | 28.80 | 29.95 | 33.57 | 30.77 |
| PFAS Contamination | ||||
| Average Number of PFAS Facilities within 5K | 18 | 13 | 13 | 11 |
| Percent Served by PWS with Positive PFAS | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.31 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PFAS | Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances |
| PTC | Papillary Thyroid Cancer |
| EPA | Environmental Protection Agency EPA |
| FCDS | Florida Cancer Data System |
| ACS | American Community Survey |
| NHW | Non-Hispanic White |
| NHB | Non-Hispanic Black |
| CDC | Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| PWS | Public Water System |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
References
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2025. 2025. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2025/2025-cancer-facts-and-figures-acs.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Fwelo, P.; Li, R.; Heredia, N.I.; Nyachoti, D.; Adekunle, T.E.; Adekunle, T.B.; Bangolo, A.; Du, X.L. Disparities in Thyroid Cancer Mortality Across Racial and Ethnic Groups: Assessing the Impact of Socioeconomic, Clinicopathologic, and Treatment Variations. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 32, 1158–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrows, C.E.; Belle, J.M.; Fleishman, A.; Lubitz, C.C.; James, B.C. Financial burden of thyroid cancer in the United States: An estimate of economic and psychological hardship among thyroid cancer survivors. Surgery 2020, 167, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogović Crnčić, T.; Tomaš, M.I.; Girotto, N.; Ivanković, S.G. Risk Factors for Thyroid Cancer: What Do We Know So Far? Acta Clin. Croat. 2020, 59 (Suppl. S1), 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakhtarin, V.V.; Tsyb, A.; Stepanenko, V.; Orlov, M.; Kopecky, K.; Davis, S. Iodine deficiency, radiation dose, and the risk of thyroid cancer among children and adolescents in the Bryansk region of Russia following the Chernobyl power station accident. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2003, 32, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaiem, F.; Rehman, A.; Mazzoni, T. Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ward, M.H.; Kilfoy, B.A.; Weyer, P.J.; Anderson, K.E.; Folsom, A.R.; Cerhan, J.R. Nitrate intake and the risk of thyroid cancer and thyroid disease. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.L. Thyroid cancer genetics: Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, non-medullary familial thyroid cancer, and familial syndromes associated with thyroid cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 18, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gerwen, M.; Colicino, E.; Guan, H.; Dolios, G.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Vermeulen, R.C.H.; Wolff, M.S.; Arora, M.; Genden, E.M.; Petrick, L.M. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exposure and thyroid cancer risk. EBioMedicine 2023, 97, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewapriya, P.; Chadwick, L.; Gorji, S.G.; Schulze, B.; Valsecchi, S.; Samanipour, S.; Thomas, K.V.; Kaserzon, S.L. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in consumer products: Current knowledge and research gaps. J. Hazard. Mater. Lett. 2023, 4, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielsøe, M.; Long, M.; Ghisari, M.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C. Perfluoroalkylated substances (PFAS) affect oxidative stress biomarkers in vitro. Chemosphere 2015, 129, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Louie, A.; Rigutto, G.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ahn, S.; Dahlberg, S.; Sholinbeck, M.; Smith, M.T. A systematic evidence map of chronic inflammation and immunosuppression related to per- and polyfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) exposure. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsen, N.; Ramhøj, L.; Lykkebo, C.A.; Kugathas, I.; Poulsen, R.; Rosenmai, A.K.; Evrard, B.; Darde, T.A.; Axelstad, M.; Bahl, M.I.; et al. PFOS-induced thyroid hormone system disrupted rats display organ-specific changes in their transcriptomes. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 305, 119340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, K.; Li, W.; Chai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chu, B.; Li, N.; Yan, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Y. Varied thyroid disrupting effects of perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) and its novel alternatives hexafluoropropylene-oxide-dimer-acid (GenX) and ammonium 4,8-dioxa-3H-perfluorononanoate (ADONA) in vitro. Environ. Int. 2021, 156, 106745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoker, T.E.; Wang, J.; Murr, A.S.; Bailey, J.R.; Buckalew, A.R. High-Throughput Screening of ToxCast PFAS Chemical Library for Potential Inhibitors of the Human Sodium Iodide Symporter. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2023, 36, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.M.; Calkins, M.M.; Caban-Martinez, A.J.; Stueckle, T.; Grant, C.; Calafat, A.M.; Nematollahi, A.; Jung, A.M.; Graber, J.M.; Jenkins, T.; et al. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, epigenetic age and DNA methylation: A cross-sectional study of firefighters. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 1619–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, J.M.; Troisi, R.; Surcel, H.; Öhman, H.; Kivelä, J.; Kiviranta, H.; Rantakokko, P.; Koponen, J.; Medgyesi, D.N.; Kitahara, C.M.; et al. Prediagnostic serum concentrations of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and risk of papillary thyroid cancer in the Finnish Maternity Cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2024, 154, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, J.; Seery, S.; Ma, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, A.; Guo, H. Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances and the associated thyroid cancer risk: A case-control study in China. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddie, J.M.; Schaider, L.A.; Sunderland, E.M. Sociodemographic Factors Are Associated with the Abundance of PFAS Sources and Detection in U.S. Community Water Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7902–7912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). PFAS Analytic Tools. 2024. Available online: https://echo.epa.gov/trends/pfas-tools (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center. SCAN Data. Scan360. 2025. Available online: https://www.scan360.com (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- National Cancer Institute. 2000, U.S. Standard Population vs. Standard Million. 2025. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/stdpopulations/single_age.html (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- US Census. County Population Totals and Components of Change: 2020–2024. 2025. Available online: https://www.census.gov/data/tables/time-series/demo/popest/2020s-counties-total.html (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Environmental Justice Mapping and Screening Tool. EJScreen Technical Documentation for Version 2.3. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2024-07/ejscreen-tech-doc-version-2-3.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Lee, M.S.; Wild, L.; DiStefano, N.; Forman, G.; Franzmann, E.; Solle, N.; Caban-Martinez, A.; Kobetz, E. An ecological study on environmental exposure to PFAS and thyroid cancer incidence rates by races/ethnicities in Florida. Cancer Res. 2025, 85 (Suppl. S1), 2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkway, T.D.; Mehdi, Q.; Griffin, E.K.; Correia, K.; Camacho, C.G.; Aufmuth, J.; Ilvento, C.; Bowden, J.A. Crowdsourcing citizens for statewide mapping of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in Florida drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fatowe, M.; Lemos, L.; Quinete, N. Spatial distribution of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in waters from Central and South Florida. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 84383–84395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fatowe, M.; Cui, D.; Quinte, N. Assessment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in Biscayne Bay surface waters and tap waters from South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.C.; Andrews, D.Q.; Lindstrom, A.B.; Bruton, T.A.; Schaider, L.A.; Grandjean, P.; Lohmann, R.; Carignan, C.C.; Blum, A.; Balan, S.A.; et al. Detection of Poly- and Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) in U.S. Drinking Water Linked to Industrial Sites, Military Fire Training Areas, and Wastewater Treatment Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, B.E.; Pinney, S.M.; Hines, E.P.; Fenton, S.E.; Ferguson, K.K. Associations between longitudinal serum perfluoroalkyl substance (PFAS) levels and measures of thyroid hormone, kidney function, and body mass index in the Fernald Community Cohort. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242 Pt A, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Winquist, A. PFAS and cancer, a scoping review of the epidemiologic evidence. Environ. Res. 2021, 194, 110690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Gustafson, A.; Luberice, K.; Akmal, S.R.; Li, W.; Hernandez, J.M.; Blakely, A.M.; Snyder, R.A.; Eng, O.S. Underrepresentation of Racial and Ethnic Minorities in Metastatic Colorectal Carcinoma Clinical Trials within the United States. Ann. Surg. 2024; advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency Key EPA Actions to Address, PFAS. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/pfas/key-epa-actions-address-pfas (accessed on 1 October 2024).

| Average Values for NHW | Average Values for Hispanic | Average Values for NHB | Average Values for All Races/Ethnicities | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Proximity to PFAS Facilities 1 | Number of Census Tract | Population | Number of Cases | Age | AAInc 2 | Population | Number of Cases | Age | AAInc | Population | Number of Cases | Age | AAInc | Median Household Income | % in Poverty | % Without Insurance | % with Bachelor’s Degree | % Obesity | % Lack of Physical Activity | Census Tracts Serviced by PWS with Positive PFAS |
| 1 | 1223 | 3424 | 3.1 | 53.0 | 0.98 | 1037 | 1.0 | 48.3 | 0.58 | 434 | 0.2 | 49.2 | 0.35 | 57,043 | 13.5 | 15.1 | 28.4 | 29.4 | 27.1 | 25% |
| 2 | 1223 | 2817 | 2.5 | 53.4 | 0.99 | 1026 | 1.0 | 47.1 | 0.68 | 678 | 0.3 | 50.7 | 0.38 | 53,278 | 15.3 | 16.5 | 29.2 | 29.3 | 27.7 | 30% |
| 3 | 1222 | 2071 | 1.8 | 51.7 | 1.24 | 1257 | 1.2 | 48.6 | 0.75 | 959 | 0.3 | 50.3 | 0.36 | 44,217 | 20.3 | 21.2 | 25.2 | 31.3 | 30.1 | 39% |
| Total | 3668 | 2771 | 2.46 | 52.4 | 1.07 | 1107 | 1.1 | 48.0 | 0.67 | 690 | 0.3 | 50.2 | 0.36 | 51,511 | 16.4 | 17.6 | 27.6 | 30.0 | 28.3 | 31% |
| One-Way ANOVA (p-value) | 0.73 | 0.006 | 0.005 | 0.78 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||
| Average Values for NHW | Average Values for Hispanic | Average Values for NHB | Average Values for All Races/Ethnicities | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PWS PFAS Status 1 | Number of Census Tract | Population | Number of Cases | Age | AAInc 2 | Population | Number of Cases | Age | AAInc | Population | Number of Cases | Age | AAInc | Median Household Income | % in Poverty | % Without Insurance | % with Bachelor’s Degree | % Obesity | % Lack of Physical Activity | Average Proximity to PFAS Sites Within 5 km | ||
| 0 | 2527 | 2924 | 2.5 | 52.3 | 1.03 | 1119 | 1.1 | 48.3 | 0.65 | 647 | 0.3 | 50.1 | 0.35 | 52,343 | 16.0 | 17.1 | 28.3 | 30.1 | 28.1 | 0.003 | ||
| 1 | 1141 | 2431 | 2.3 | 52.8 | 1.16 | 1080 | 1.0 | 47.4 | 0.71 | 787 | 0.3 | 50.4 | 0.39 | 49,670 | 17.1 | 18.6 | 26.2 | 29.7 | 28.8 | 0.005 | ||
| One-Side t-Test Significance (p-value) | 0.07 | 0.12 | 0.20 | <0.001 | 0.003 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.009 | 0.003 | <0.001 | ||||||||||||
| NHW | Hispanic | NHB | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level of Proximity to PFAS Facilities | Number of Cases | Average BMI | Number of Cases | Average BMI | Number of Cases | Average BMI | Number of Cases | Average BMI |
| 1 | 1190 | 30.16 | 423 | 29.69 | 74 | 32.50 | 1807 | 29.91 |
| 2 | 966 | 29.80 | 446 | 29.24 | 98 | 33.25 | 1616 | 29.66 |
| 3 | 708 | 29.73 | 577 | 29.73 | 133 | 33.43 | 1495 | 29.93 |
| Total Cases (with BMI Data) | 2864 | 29.93 | 1446 | 2956 | 305 | 33.15 | 4918 | 29.83 |
| One-Way ANOVA Significance (p-value) | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.74 | 0.50 | ||||
| PWS PFAS Status 1 | ||||||||
| 0 | 2030 | 29.94 | 1003 | 29.35 | 187 | 33.18 | 3441 | 29.74 |
| 1 | 834 | 29.92 | 443 | 30.04 | 118 | 33.09 | 1477 | 30.06 |
| Total Cases (with BMI Data) | 2864 | 29.93 | 1446 | 29.56 | 305 | 33.15 | 4918 | 29.83 |
| One-Way ANOVA Significance (p-value) | 0.48 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 0.11 | ||||
| Available BMI Data | ||||||||
| Number of Cases Missing BMI Data (% Missing) | 6332 (69%) | 2544 (64%) | 680 (69%) | 9226 (65%) | ||||
| Total Papillary Thyroid Cancer Cases | 9196 | 3990 | 985 | 14,144 | ||||
| Independent Variables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dependent Variable | Constant | Proximity Index for PFAS Sites Within 5 km | Percentage of Population with No Insurance | Proximity Index for PFAS Sites Within 20 km | Regression ANOVA |
| NHW Age-Adjusted Incidence | Beta = 0.78 | Beta = 28.24 | Beta = 0.01 | df = 2 | |
| Std. Error = 0.08 | Std. Error = 7.24 | Std. Error = 0 | F = 13.847 | ||
| t = 9.66 | t = 3.9 | t = 2.39 | Sig. < 0.001 | ||
| Sig. < 0.001 | Sig. < 0.001 | Sig. = 0.017 | |||
| Hispanic Age-Adjusted Incidence | Beta = 0.615 | Beta = 12.744 | df = 1 | ||
| Std. Error = 0.029 | Std. Error = 4.363 | F = 8.534 | |||
| t = 21.247 | t = 2.921 | Sig. = 0.004 | |||
| Sig. < 0.001 | Sig. = 0.004 | ||||
| NHB Age-Adjusted Incidence | Beta = 0.307 | Beta = 4.392 | df = 1 | ||
| Std. Error = 0.035 | Std. Error = 2.097 | F = 3.338 | |||
| t = 8.834 | t = 2.095 | Sig. = 0.036 | |||
| Sig. < 0.001 | Sig. = 0.036 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wild, L.E.; DiStefano, N.; Forman, G.; Arocha, B.I.; Lee, M.S.; Borowsky, P.A.; Franzmann, E.; Solle, N.; Caban-Martinez, A.J.; Kobetz, E. Socioeconomic Disparities and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Associated with Environmental Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Florida. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081290
Wild LE, DiStefano N, Forman G, Arocha BI, Lee MS, Borowsky PA, Franzmann E, Solle N, Caban-Martinez AJ, Kobetz E. Socioeconomic Disparities and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Associated with Environmental Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Florida. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(8):1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081290
Chicago/Turabian StyleWild, Laura E., Nicholas DiStefano, Garrett Forman, Bianca I. Arocha, Ming S. Lee, Peter A. Borowsky, Elizabeth Franzmann, Natasha Solle, Alberto J. Caban-Martinez, and Erin Kobetz. 2025. "Socioeconomic Disparities and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Associated with Environmental Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Florida" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 8: 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081290
APA StyleWild, L. E., DiStefano, N., Forman, G., Arocha, B. I., Lee, M. S., Borowsky, P. A., Franzmann, E., Solle, N., Caban-Martinez, A. J., & Kobetz, E. (2025). Socioeconomic Disparities and Risk of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Associated with Environmental Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) in Florida. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(8), 1290. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081290







