Effects of Outdoor and Household Air Pollution on Hand Grip Strength in a Longitudinal Study of Rural Beijing Adults
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Collection
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Air Pollution Measurements
2.3.1. Measurement of Household (Indoor) PM2.5
2.3.2. Measurement of Outdoor (Community) PM2.5
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Grip Strength Measurements
2.6. Multiple Imputation for Missing Data
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
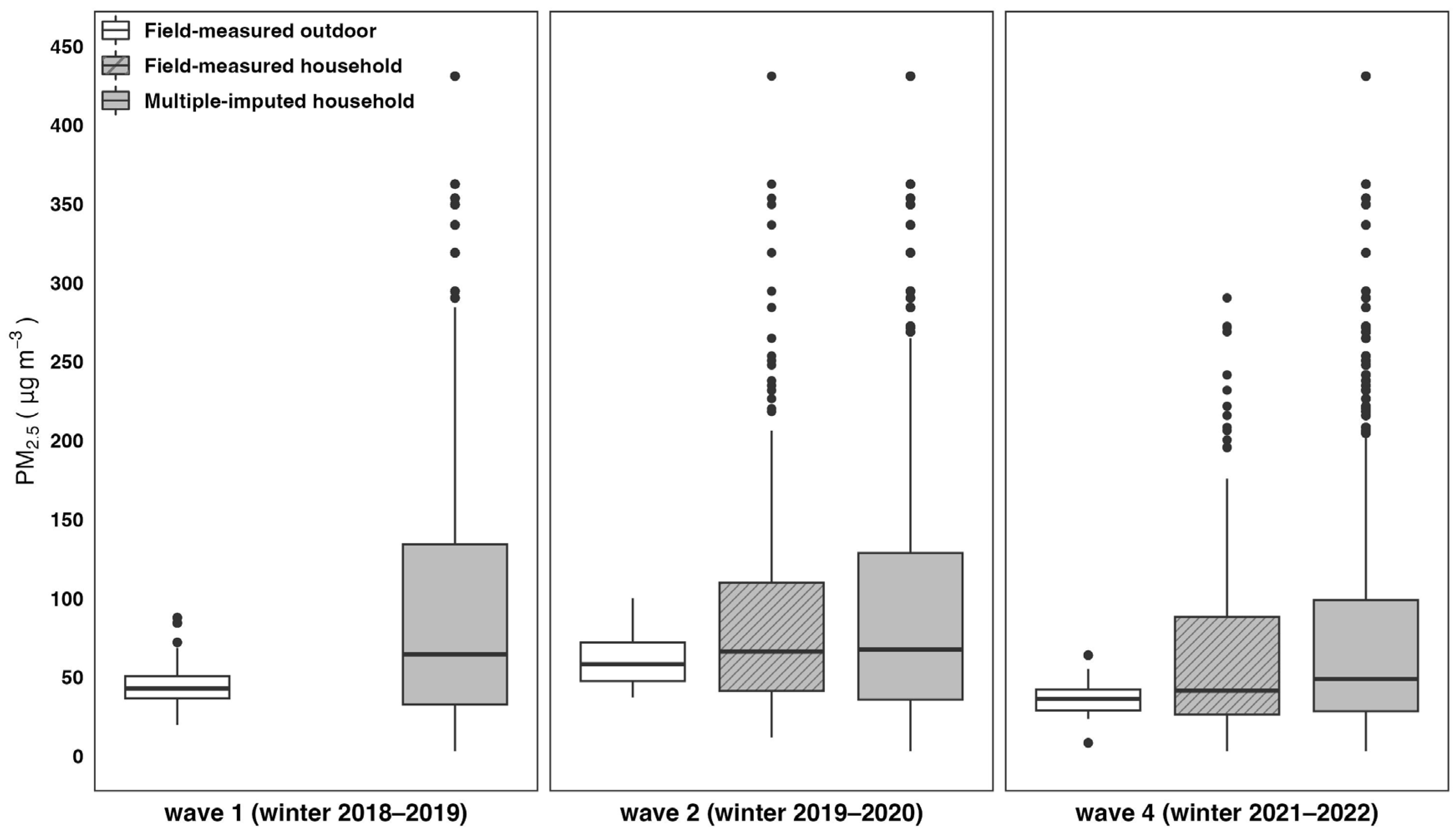
3.2. Exposure to Household and Outdoor PM2.5
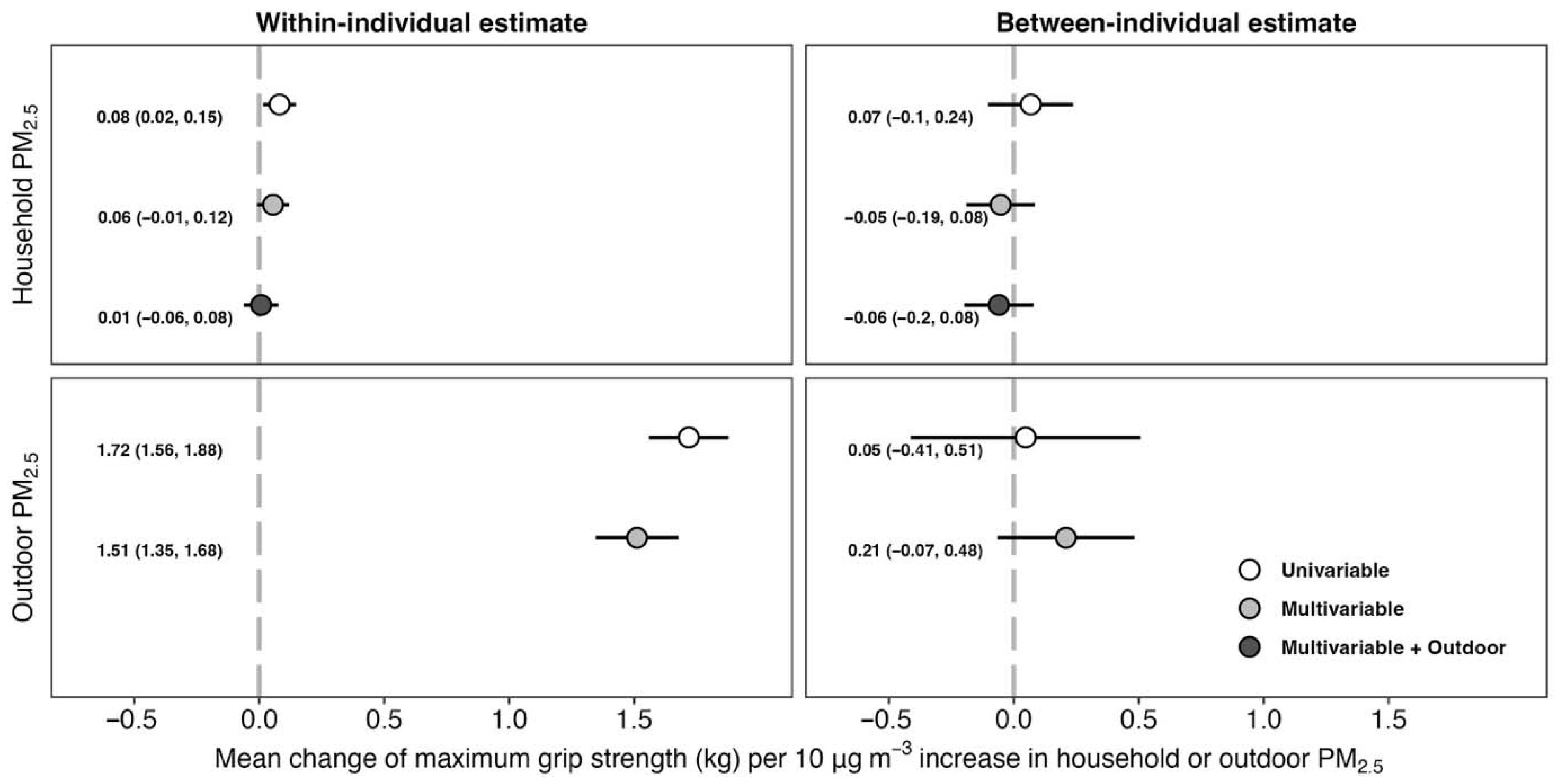
3.3. Effect of Household and Outdoor PM2.5 Exposure on Maximum Grip Strength
4. Discussion
5. Strengths and Limitations
6. Public Health Implications and Future Research
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | confidence interval |
| df | degrees of freedom |
| PM2.5 | fine particulate matter |
| SD | standard deviation |
References
- Health Effects Institute. State of Global Air 2020; Health Effects Institutes: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, S.; Ru, M.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, Q.; Li, B.; Shen, G.; Pan, X.; Meng, W.; Chen, Y.; Shen, H.; et al. Quantifying the Rural Residential Energy Transition in China from 1992 to 2012 through a Representative National Survey. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Carter, E.; Yan, L.; Chan, Q.; Elliott, P.; Ezzati, M.; Kelly, F.; Schauer, J.J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Determinants of Personal Exposure to PM2.5 and Black Carbon in Chinese Adults: A Repeated-Measures Study in Villages Using Solid Fuel Energy. Environ. Int. 2021, 146, 106297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Chen, Y.; Xue, C.; Lin, N.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; et al. Pollutant Emissions from Improved Coal- and Wood-Fuelled Cookstoves in Rural Households. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6590–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer-Nicholls, S.; Carter, E.; Kumar, R.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Frostad, J.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Cohen, A.; Brauer, M.; Baumgartner, J.; et al. The Regional Impacts of Cooking and Heating Emissions on Ambient Air Quality and Disease Burden in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 9416–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantanen, T.; Guralnik, J.M.; Foley, D.; Masaki, K.; Leveille, S.; Curb, J.D.; White, L. Midlife Hand Grip Strength as a Predictor of Old Age Disability. JAMA 1999, 281, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijk, J.M.; Roos, P.R.; Deckx, L.; van den Akker, M.; Buntinx, F. Prognostic Value of Handgrip Strength in People Aged 60 Years and Older: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2016, 16, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Trevisan, C.; Bolzetta, F.; De Rui, M.; Solmi, M.; Sartori, L.; Musacchio, E.; Zambon, S.; Perissinotto, E.; et al. What Physical Performance Measures Predict Incident Cognitive Decline among Intact Older Adults? A 4.4year Follow up Study. Exp. Gerontol. 2016, 81, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, T.; Zhang, D. Association of Grip Strength With Risk of All-Cause Mortality, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Cancer in Community-Dwelling Populations: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 551.e17–551.e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishya, R.; Misra, A.; Vaish, A.; Ursino, N.; D’Ambrosi, R. Hand Grip Strength as a Proposed New Vital Sign of Health: A Narrative Review of Evidences. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Verma, I.M. NF-[Kappa]B Regulation in the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, A.; Lightfoot, A.P. NF-kB and Inflammatory Cytokine Signalling: Role in Skeletal Muscle Atrophy. In Muscle Atrophy; Xiao, J., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 267–279. ISBN 9789811314353. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.; Cheng, Z.; Li, N.; Mao, S.; Ma, R.; He, H.; Niu, Z.; Chen, X.; Xiang, H. The Short- and Long-Term Associations of Particulate Matter with Inflammation and Blood Coagulation Markers: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Guo, X.; Wu, S. Association between Short-Term Exposure to Ambient Particulate Air Pollution and Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 191, 110105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbatecola, A.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Ceda, G.; Russo, C.R.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Barbieri, M.; Valenti, G.; Paolisso, G. Insulin Resistance and Muscle Strength in Older Persons. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2005, 60, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Freire, M.; de Cabo, R.; Studenski, S.A.; Ferrucci, L. The Neuromuscular Junction: Aging at the Crossroad between Nerves and Muscle. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2014, 6, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Livshits, G. Sarcopenic Obesity or Obese Sarcopenia: A Cross Talk between Age-Associated Adipose Tissue and Skeletal Muscle Inflammation as a Main Mechanism of the Pathogenesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 200–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, J.; El Assar, M.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L. Frailty and Sarcopenia as the Basis for the Phenotypic Manifestation of Chronic Diseases in Older Adults. Mol. Asp. Med. 2016, 50, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, A.E.; Hepgul, N.; Kon, S.; Maddocks, M. Sarcopenia and Frailty in Chronic Respiratory Disease. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2017, 14, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, Y. Longitudinal Associations Between Household Solid Fuel Use and Handgrip Strength in Middle-Aged and Older Chinese Individuals: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 881759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ou, Y.; Cai, A.; Huang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Nie, Z. Household Use of Solid Fuel and Sarcopenia among Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Maturitas 2024, 182, 107925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.M.; Jia, K.X.; Liu, J.Y.; Chen, X.; Shen, Y.L.; Cai, J.J.; Guo, Q.W.; Lin, J.; Fang, D.Z. Indoor Air Pollution by Solid Fuel Usages for Cooking Is Longitudinally Associated with Possible Sarcopenia in Middle-Aged Chinese Population. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, A.; Lei, L.; Ma, H.; Yang, Y. Effects of Household Solid Fuel Use on Sarcopenia in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Evidence from a Nationwide Cohort Study. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1337979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Guo, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Kowal, P.; Di, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Xiao, J.; Hoogendijk, E.O.; Dent, E.; Vaughn, M.G.; et al. Association of Indoor and Outdoor Air Pollution with Hand-Grip Strength Among Adults in Six Low- and Middle-Income Countries. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 75, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Sakhvidi, M.J.; Lafontaine, A.; Yang, J.; Lequy, E.; Artaud, F.; Canonico, M.; Ozguler, A.; Vienneau, D.; Zins, M.; Jacquemin, B. Association between Outdoor Air Pollution Exposure and Handgrip Strength: Findings from the French CONSTANCES Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2022, 130, 057701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Su, T.; Chen, T.; Wei, J.; Cribb, M. The Urban–Rural Heterogeneity of Air Pollution in 35 Metropolitan Regions across China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, B. Distinguishing Urban-Rural Difference in Chinese Population Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 334, 120704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, G. Spatial-Temporal Characteristics of PM2.5 in China: A City-Level Perspective Analysis. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Strezov, V.; Jiang, Y.; Kan, T.; Evans, T. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Air Pollution across China from 2015 to 2018. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 112, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, J.; Harper, S.; Barrington-Leigh, C.; Brehmer, C.; Carter, E.M.; Li, X.; Robinson, B.E.; Shen, G.; Sternbach, T.J.; Shu, T.; et al. How Do Household Energy Transitions Work? Health Effects Institutes: Boston, MA, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Bulot, F.M.J.; Russell, H.S.; Rezaei, M.; Johnson, M.S.; Ossont, S.J.J.; Morris, A.K.R.; Basford, P.J.; Easton, N.H.C.; Foster, G.L.; Loxham, M.; et al. Laboratory Comparison of Low-Cost Particulate Matter Sensors to Measure Transient Events of Pollution. Sensors 2020, 20, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Baumgartner, J.; Harper, S.; Zhang, X.; Sternbach, T.; Barrington-Leigh, C.; Brehmer, C.; Robinson, B.; Shen, G.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Field Measurements of Indoor and Community Air Quality in Rural Beijing before, during, and after the COVID-19 Lockdown. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e13095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Baumgartner, J.; Barrington-Leigh, C.; Harper, S.; Robinson, B.; Shen, G.; Sternbach, T.; Tao, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Socioeconomic and Demographic Associations with Wintertime Air Pollution Exposures at Household, Community, and District Scales in Rural Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 8308–8318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-C.; Wu, L.-C.; Chiang, S.-L.; Lu, L.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Ni, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H. Validating the Capability for Measuring Age-Related Changes in Grip-Force Strength Using a Digital Hand-Held Dynamometer in Healthy Young and Elderly Adults. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6936879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.; Barnett, F. Reliability and Validity of an Electronic Dynamometer for Measuring Grip Strength. Int. J. Ther. Rehabil. 2011, 18, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Hand Therapists. Clinical Assessment Recommendations, 3rd ed.; MacDermid, J., Solomon, G., Valdes, K., Eds.; American Society of Hand Therapists: Mount Laurel, NJ, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-692-52515-9. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, D.B.; Schenker, N. Multiple Imputation in Health-Care Databases: An Overview and Some Applications. Stat. Med. 1991, 10, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Buuren, S.; Groothuis-Oudshoorn, K. Mice: Multivariate Imputation by Chained Equations in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 45, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.; Fairbrother, M.; Jones, K. Fixed and Random Effects Models: Making an Informed Choice. Qual. Quant. 2019, 53, 1051–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schempf, A.H.; Kaufman, J.S. Accounting for Context in Studies of Health Inequalities: A Review and Comparison of Analytic Approaches. Ann. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtin, C.; Ter Riet, G.; Puhan, M.A.; Waschki, B.; Garcia-Aymerich, J.; Pinto-Plata, V.; Celli, B.; Watz, H.; Spruit, M.A. Handgrip Weakness and Mortality Risk in COPD: A Multicentre Analysis. Thorax 2016, 71, 86–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celis-Morales, C.A.; Welsh, P.; Lyall, D.M.; Steell, L.; Petermann, F.; Anderson, J.; Iliodromiti, S.; Sillars, A.; Graham, N.; Mackay, D.F.; et al. Associations of Grip Strength with Cardiovascular, Respiratory, and Cancer Outcomes and All Cause Mortality: Prospective Cohort Study of Half a Million UK Biobank Participants. BMJ 2018, 361, k1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M. Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamasaki, H.; Kawashima, Y.; Katsuyama, H.; Sako, A.; Goto, A.; Yanai, H. Association of Handgrip Strength with Hospitalization, Cardiovascular Events, and Mortality in Japanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sferra da Silva, G.; de Almeida Lourenço, M.; de Assis, M.R. Hand Strength in Patients with RA Correlates Strongly with Function but Not with Activity of Disease. Adv. Rheumatol. 2018, 58, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindemann, U.; Oksa, J.; Skelton, D.A.; Beyer, N.; Klenk, J.; Zscheile, J.; Becker, C. Effect of Cold Indoor Environment on Physical Performance of Older Women Living in the Community. Age Ageing 2014, 43, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Schmidt, S.M.; Malmgren Fänge, A.; Hoshi, T.; Ikaga, T. Lower Physical Performance in Colder Seasons and Colder Houses: Evidence from a Field Study on Older People Living in the Community. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posit Team RStudio. Integrated Development Environment for R 2023; R Studio Team: Boston, MA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Stockfelt, L.; Xu, Y.; Gudmundsson, A.; Rissler, J.; Isaxon, C.; Brunskog, J.; Pagels, J.; Nilsson, P.T.; Berglund, M.; Barregard, L.; et al. A Controlled Chamber Study of Effects of Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Particles and Noise on Heart Rate Variability and Endothelial Function. Inhal. Toxicol. 2022, 34, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimbrone, M.A.; García-Cardeña, G. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, J.; Carter, E.; Schauer, J.J.; Ezzati, M.; Daskalopoulou, S.S.; Valois, M.-F.; Shan, M.; Yang, X. Household Air Pollution and Measures of Blood Pressure, Arterial Stiffness and Central Haemodynamics. Heart 2018, 104, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.-Y.; Qian, Z.; Howard, S.W.; Vaughn, M.G.; Fan, S.-J.; Liu, K.-K.; Dong, G.-H. Global Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wang, Z.; Arnold, L.; Song, Y.; Wang, H.-J.; Ma, J. The Association between Blood Pressure and Grip Strength in Adolescents: Does Body Mass Index Matter? Hypertens. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hypertens. 2016, 39, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Y. Handgrip Strength Is Positively Related to Blood Pressure and Hypertension Risk: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taekema, D.G.; Maier, A.B.; Westendorp, R.G.J.; de Craen, A.J.M. Higher Blood Pressure Is Associated With Higher Handgrip Strength in the Oldest Old. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.Z.; Messi, M.L.; Wang, Z.-M.; Abba, M.C.; Pereyra, A.; Birbrair, A.; Zhang, T.; O’Meara, M.; Kwan, P.; Lopez, E.I.S.; et al. The Sympathetic Nervous System Regulates Skeletal Muscle Motor Innervation and Acetylcholine Receptor Stability. Acta Physiol. Oxf. Engl. 2019, 225, e13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, G.D.; Kabéle, M.; Brown, R.; Macefield, V.G.; Sandström, T.; Bosson, J.A. Acute Exposure to Diesel Exhaust Increases Muscle Sympathetic Nerve Activity in Humans. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 10, e018448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R.K.; Birrell, M.A.; Adcock, J.J.; Wortley, M.A.; Dubuis, E.D.; Chen, S.; McGilvery, C.M.; Hu, S.; Shaffer, M.S.P.; Bonvini, S.J.; et al. Mechanistic Link between Diesel Exhaust Particles and Respiratory Reflexes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1074–1084.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor-Clark, T.E. Air Pollution-Induced Autonomic Modulation. Physiology 2020, 35, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucht, S.; Hennig, F.; Moebus, S.; Führer-Sakel, D.; Herder, C.; Jöckel, K.-H.; Hoffmann, B. Air Pollution and Diabetes-Related Biomarkers in Non-Diabetic Adults: A Pathway to Impaired Glucose Metabolism? Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 370–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Dorans, K.S.; Wilker, E.H.; Rice, M.B.; Kloog, I.; Schwartz, J.D.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A.; Gold, D.R.; Meigs, J.B.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution, Adipokines, and Glucose Homeostasis: The Framingham Heart Study. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brook, R.D.; Sun, Z.; Brook, J.R.; Zhao, X.; Ruan, Y.; Yan, J.; Mukherjee, B.; Rao, X.; Duan, F.; Sun, L.; et al. Extreme Air Pollution Conditions Adversely Affect Blood Pressure and Insulin Resistance. Hypertension 2016, 67, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walowski, C.O.; Herpich, C.; Enderle, J.; Braun, W.; Both, M.; Hasler, M.; Müller, M.J.; Norman, K.; Bosy-Westphal, A. Analysis of the Adiponectin Paradox in Healthy Older People. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 14, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinis-Sobrinho, C.; Santos, R.; Moreira, C.; Abreu, S.; Lopes, L.; Oliveira-Santos, J.; Rosário, R.; Póvoas, S.; Mota, J. Association between Serum Adiponectin Levels and Muscular Fitness in Portuguese Adolescents: LabMed Physical Activity Study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 26, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glencross, D.A.; Ho, T.-R.; Camiña, N.; Hawrylowicz, C.M.; Pfeffer, P.E. Air Pollution and Its Effects on the Immune System. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, P.E.; Levesque, C.; Butler, O.; Chénier, M.; Gardner, H.D. Selection of Metric for Indoor-outdoor Source Apportionment of Metals in PM2.5: Mg/Kg versus Ng/M3. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, P.; Park, D.; Lee, Y.-C. Recent Insights into Particulate Matter (PM2.5)-Mediated Toxicity in Humans: An Overview. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejczyk, P.; Chen, L.-C.; Thurston, G. The Role of Fossil Fuel Combustion Metals in PM2.5 Air Pollution Health Associations. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesinger, R.B. The Health Impact of Common Inorganic Components of Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) in Ambient Air: A Critical Review. Inhal. Toxicol. 2007, 19, 811–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.; Lepeule, J. Is Ambient PM2.5 Sulfate Harmful? Schwartz and Lepeule Respond. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, a454–a455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Lee, M.; Carter, E.; Chan, Q.; Elliott, P.; Ezzati, M.; Kelly, F.; Yan, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Chemical Investigation of Household Solid Fuel Use and Outdoor Air Pollution Contributions to Personal PM2.5. Exposures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 15969–15979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, A.M.; Clark, S.; Carter, E.; Shan, M.; Ni, K.; Yang, X.; Baumgartner, J.; Schauer, J.J. Impacts of Stove/Fuel Use and Outdoor Air Pollution on Chemical Composition of Household Particulate Matter. Indoor Air 2020, 30, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.D.; Awe, Y.A.; Ostro, B.D.; Sanchez-Triana, E. Are All Air Pollution Particles Equal: How Constituents and Sources of Fine Air Pollution Particles (PM 2.5) Affect Health; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. (In English) [Google Scholar]
- Wierzbicka, A.; Nilsson, P.T.; Rissler, J.; Sallsten, G.; Xu, Y.; Pagels, J.H.; Albin, M.; Österberg, K.; Strandberg, B.; Eriksson, A.; et al. Detailed Diesel Exhaust Characteristics Including Particle Surface Area and Lung Deposited Dose for Better Understanding of Health Effects in Human Chamber Exposure Studies. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 86, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.L.; Peel, J.L.; Balakrishnan, K.; Breysse, P.N.; Chillrud, S.N.; Naeher, L.P.; Rodes, C.E.; Vette, A.F.; Balbus, J.M. Health and Household Air Pollution from Solid Fuel Use: The Need for Improved Exposure Assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1120–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zheng, H.; Gong, B. Rural Income Growth, Ethnic Differences, and Household Cooking Fuel Choice: Evidence from China. Energy Econ. 2022, 107, 105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Pan, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, F.; Du, J.; Pa, L.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z.; Ren, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Social-Economic Inequalities and Early-Life Exposure to Famine Contribute to Low Grip Strength: The China National Health Survey. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2025, 35, 103842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Household (Indoor) PM2.5 Quartile (μg/m3) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | ≤25th % | 25th to 50th % | 50th to 75th % | >75th % | |
| 3 < Household ≤ 32 | 32 < Household ≤ 61 | 61 < Household ≤ 120 | 120 < Household ≤ 431 | ||
| Age, years | 61.8 (9.0) | 61.8 (9) | 62.1 (8.9) | 61.8 (8.9) | 61.6 (9.1) |
| Sex, % female | 60.6 | 61.5 | 61.7 | 62.6 | 56.6 |
| Marital status | |||||
| Married | 87.1 | 88.4 | 88.1 | 87.0 | 85.3 |
| Divorced or separated | 1.9 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 3.7 |
| Widowed | 10.0 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 10.4 | 9.4 |
| Never married | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Highest education | |||||
| No school | 11.8 | 12.6 | 12.3 | 11.2 | 10.9 |
| Primary school | 75.7 | 73.3 | 73.7 | 76.8 | 78.8 |
| Secondary or high school | 11.2 | 11.6 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 9.7 |
| Higher education | 1.3 | 2.5 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.6 |
| Current occupation | |||||
| Agriculture | 58.8 | 54.7 | 56.3 | 59.8 | 64.5 |
| Other manual labor a | 1.8 | 1.0 | 1.9 | 2.0 | 2.4 |
| Non-manual labor b | 7.5 | 9.9 | 8.7 | 7.1 | 4.2 |
| Unemployed | 26.0 | 27.9 | 26.2 | 25.2 | 24.7 |
| Others | 5.9 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 5.8 | 4.3 |
| Tobacco smoke | |||||
| Current smoker | 25.0 | 14.0 | 17.4 | 25.1 | 43.2 |
| Former smoker | 14.3 | 18.3 | 17.1 | 13.2 | 8.6 |
| Never smoker lived with smoker | 41.8 | 40.1 | 41.3 | 45.5 | 40.2 |
| No exposure to tobacco smoke | 19.0 | 27.6 | 24.2 | 16.2 | 8.0 |
| Frequency of drinking | |||||
| Never | 50.6 | 49.5 | 51.5 | 52.9 | 48.5 |
| Occasional (≤3 times a month) | 21.7 | 22.9 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 22.7 |
| Regular (≤5 times a week) | 7.9 | 9.6 | 9.4 | 7.5 | 5.3 |
| Everyday | 19.8 | 18.1 | 18.6 | 19.0 | 23.5 |
| Frequency of farming | |||||
| Never | 40.5 | 40.4 | 40.4 | 40.7 | 40.6 |
| Occasional (≤2 days a week) | 30.1 | 30.6 | 29.1 | 31.2 | 29.6 |
| Regular (≤5 days a week) | 18.9 | 20.5 | 20.5 | 18.3 | 16.3 |
| Everyday | 10.5 | 8.6 | 10.0 | 9.8 | 13.6 |
| Frequency of exercising | |||||
| Never | 21.9 | 18.2 | 21.3 | 21.6 | 26.3 |
| Occasional (≤2 days a week) | 14.1 | 16.2 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 12.0 |
| Regular (≤5 days a week) | 10.8 | 11.3 | 11.0 | 11.1 | 9.9 |
| Everyday | 53.2 | 54.3 | 52.8 | 54.0 | 51.8 |
| Self-reported health | |||||
| Excellent | 3.4 | 3.4 | 2.8 | 3.3 | 4.2 |
| Good | 43.0 | 46.9 | 43.4 | 41.8 | 39.9 |
| Fair | 17.2 | 15.3 | 16.8 | 18.4 | 18.4 |
| Poor | 36.4 | 34.4 | 37.0 | 36.5 | 37.6 |
| Asset-based wealth index c | |||||
| Bottom quartile (poorest) | 24.5 | 25.1 | 24.6 | 24.1 | 24.4 |
| 2nd quartile | 24.7 | 24.7 | 24.5 | 25.3 | 24.2 |
| 3rd quartile | 25.7 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 25.3 | 27.3 |
| Top quartile (wealthiest) | 25.1 | 25.2 | 25.8 | 25.2 | 24.1 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 26.0 (3.6) | 26 (3.5) | 26 (3.6) | 26 (3.8) | 25.9 (3.6) |
| Waist circumference, cm | 88.5 (10.1) | 88.6 (10.0) | 88.5 (10.3) | 88.3 (10.5) | 88.6 (9.8) |
| Outdoor PM2.5, μg/m3 | 45.6 (1.4) | 43.3 (1.4) | 45.7 (1.4) | 46.8 (1.5) | 46.8 (1.4) |
| Maximum grip strength, kg | 31.1 (10.3) | 30.9 (10.5) | 30.8 (10.5) | 30.6 (9.9) | 31.9 (10.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, W.; Li, X.; Brehmer, C.; Sternbach, T.; Zhang, X.; Carter, E.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, G.; Tao, S.; Baumgartner, J.; et al. Effects of Outdoor and Household Air Pollution on Hand Grip Strength in a Longitudinal Study of Rural Beijing Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081283
Yuan W, Li X, Brehmer C, Sternbach T, Zhang X, Carter E, Zhang Y, Shen G, Tao S, Baumgartner J, et al. Effects of Outdoor and Household Air Pollution on Hand Grip Strength in a Longitudinal Study of Rural Beijing Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(8):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081283
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Wenlu, Xiaoying Li, Collin Brehmer, Talia Sternbach, Xiang Zhang, Ellison Carter, Yuanxun Zhang, Guofeng Shen, Shu Tao, Jill Baumgartner, and et al. 2025. "Effects of Outdoor and Household Air Pollution on Hand Grip Strength in a Longitudinal Study of Rural Beijing Adults" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 8: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081283
APA StyleYuan, W., Li, X., Brehmer, C., Sternbach, T., Zhang, X., Carter, E., Zhang, Y., Shen, G., Tao, S., Baumgartner, J., & Harper, S. (2025). Effects of Outdoor and Household Air Pollution on Hand Grip Strength in a Longitudinal Study of Rural Beijing Adults. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(8), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081283






