Indoor/Outdoor Particulate Matter and Related Pollutants in a Sensitive Public Building in Madrid (Spain)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Air Quality Monitoring Plan and Measurements
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Meteorological Aspects and Air Pollution
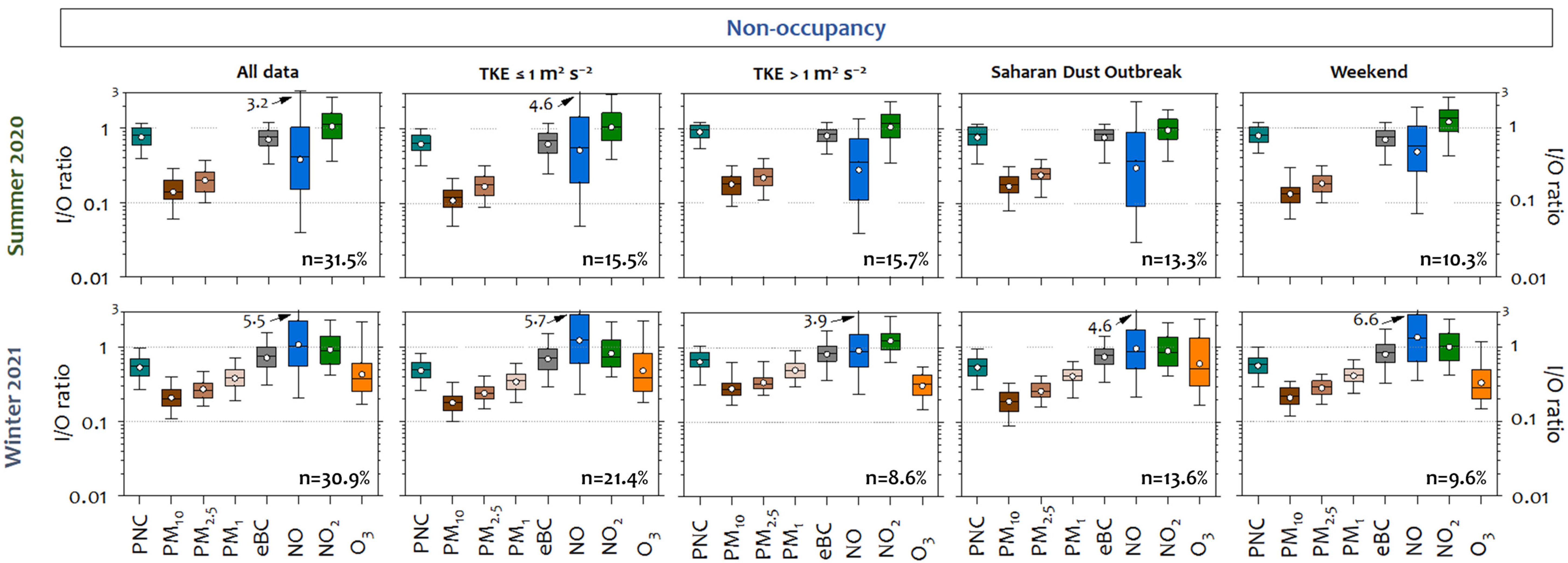
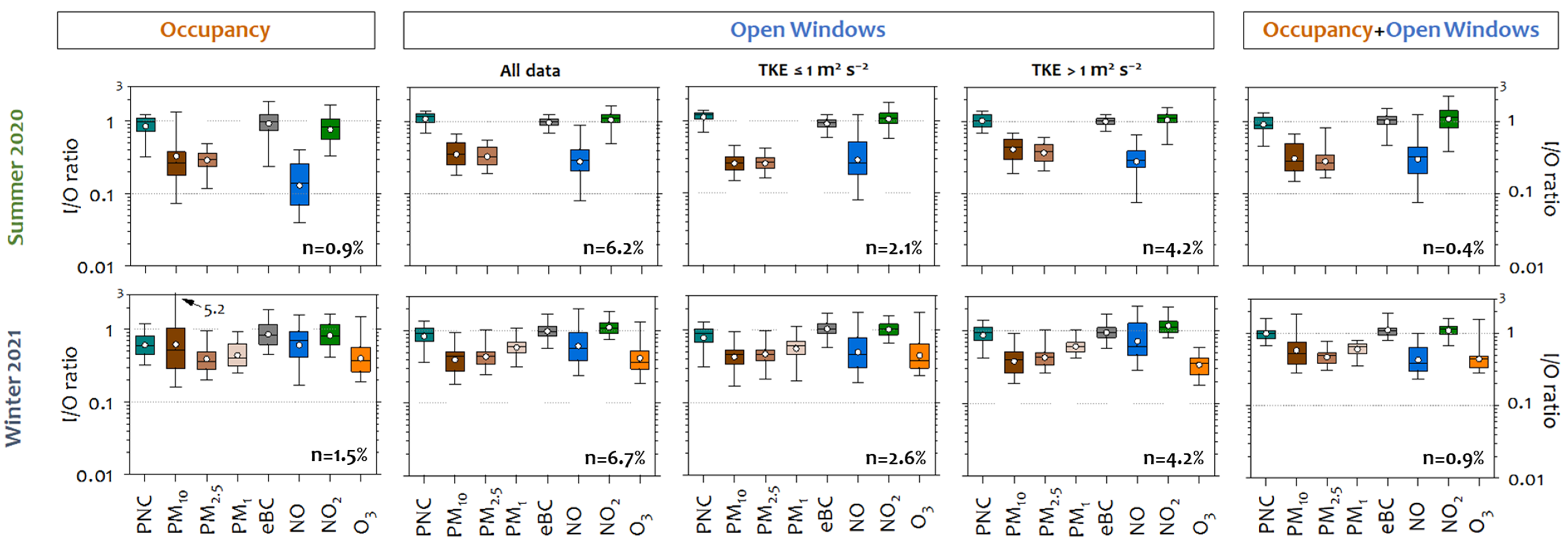
3.2. Indoor-to-Outdoor Ratios Under Different Outdoor (Sources and Meteorology) Conditions
3.3. Indoor Activities and Their Effects on Aerosol Particles and Related Pollutants
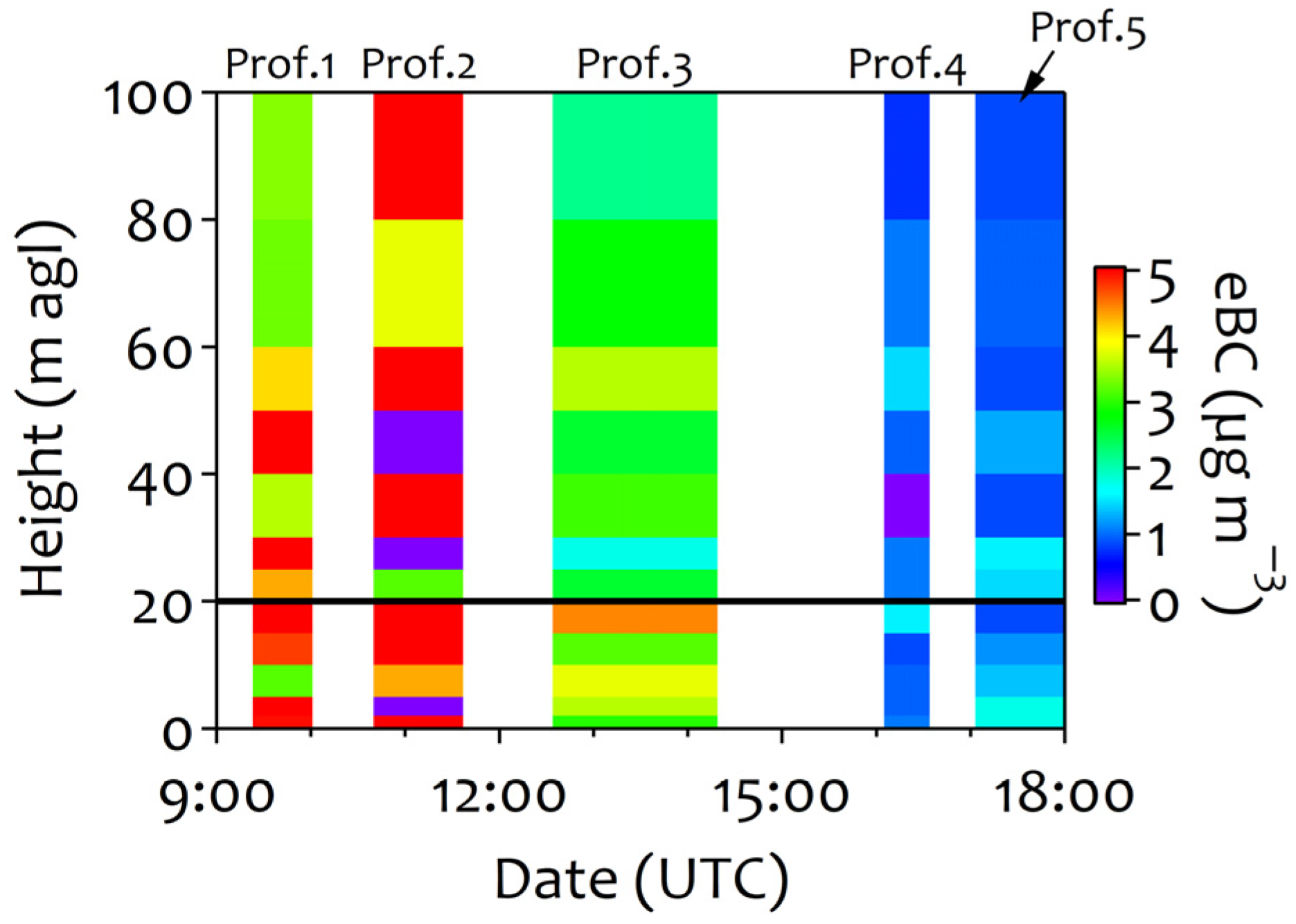
3.4. Vertical Profiles of eBC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EPA. The Inside Story: A Guide to Indoor Air Quality. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/inside-story-guide-indoor-air-quality (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Gaikwad, A.; Shivhare, N. Indoor air pollution-A threat. Int. J. Sci. Res. and Review 2019, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Singh, A.; Arora, T.; Singh, S.; Singh, R. Critical review on emerging health effects associated with the indoor air quality and its sustainable management. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; En, S.C.F.; Elkamel, A.; Ahmadi, L.; Yetilmezsoy, K. A review of standards and guidelines set by international bodies for the parameters of indoor air quality. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraga, D.Ε.; Querol, X.; Duarte, R.M.; Aquilina, N.J.; Canha, N.; Alvarez, E.G.; Jovasevic-Stojanovic, M.; Bekö, G.; Byčenkienė, S.; Kovacevic, R. Source apportionment for indoor air pollution: Current challenges and future directions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 900, 165744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, D.Y. Outdoor-indoor air pollution in urban environment: Challenges and opportunity. Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänninen, O.; Goodman, P. Outdoor air as a source of indoor pollution. Indoor Air Pollut. 2019, 48, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, R.; Eeftens, M.; Phuleria, H.C.; Ineichen, A.; Corradi, E.; Davey, M.; Fierz, M.; Ducret-Stich, R.E.; Aguilera, I.; Schindler, C. Differences in indoor versus outdoor concentrations of ultrafine particles, PM2.5, PMabsorbance and NO2 in Swiss homes. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza_Romero, M.T.; Dudzinska, M.R.; Amouei Torkmahalleh, M.; Barros, N.; Coggins, A.M.; Ruzgar, D.G.; Kildsgaard, I.; Naseri, M.; Rong, L.; Saffell, J. A review of critical residential buildings parameters and activities when investigating indoor air quality and pollutants. Indoor Air 2022, 32, e13144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Directive (EU) 2024/2881; Directive (EU) 2024/2881 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 October 2024 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe (Recast). European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2024.
- Arfin, T.; Pillai, A.M.; Mathew, N.; Tirpude, A.; Bang, R.; Mondal, P. An overview of atmospheric aerosol and their effects on human health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 125347–125369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schraufnagel, D.E. The health effects of ultrafine particles. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-S.; Ryu, M.H.; Carlsten, C. Ultrafine particles: Unique physicochemical properties relevant to health and disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downward, G.S.; van Nunen, E.J.; Kerckhoffs, J.; Vineis, P.; Brunekreef, B.; Boer, J.M.; Messier, K.P.; Roy, A.; Verschuren, W.M.M.; van der Schouw, Y.T. Long-term exposure to ultrafine particles and incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease in a prospective study of a Dutch cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 127007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadzadeh, M.; Khoshakhlagh, A.H.; Grafman, J. Air pollution: A latent key driving force of dementia. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Pee, T.; Vanbrabant, K.; Rasking, L.; Van Eyken, P.; Hogervorst, J.; Caenepeel, P.; Ameloot, M.; Plusquin, M.; Nawrot, T.S. Translocation of black carbon particles to human intestinal tissue. eBioMedicine 2024, 110, 105464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 7708:1995; Air Quality—Particle Size Fraction Definitions for Health-Related Sampling. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/14534.html (accessed on 4 November 2024).
- Directive 2008/50/EC; Directive 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 May 2008 on Ambient Air Quality and Cleaner Air for Europe. European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2008.
- Zanobetti, A.; Franklin, M.; Koutrakis, P.; Schwartz, J. Fine particulate air pollution and its components in association with cause-specific emergency admissions. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marval, J.; Tronville, P. Ultrafine particles: A review about their health effects, presence, generation, and measurement in indoor environments. Build. Environ. 2022, 216, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Rivas, I.; Fussell, J.C.; Kelly, F.J.; Querol, X. Indoor Sources Air Pollutants; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Hu, Z.; Liu, M.; Yang, H.; Kong, Q.; Liu, Y. Review of research on air-conditioning systems and indoor air quality control for human health. Int. J. Refrig. 2009, 32, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Wierzbicka, A.; Löndahl, J.; Lazaridis, M.; Hänninen, O. Indoor aerosol modeling for assessment of exposure and respiratory tract deposited dose. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J. A new air quality monitoring and early warning system: Air quality assessment and air pollutant concentration prediction. Environ. Res. 2017, 158, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Hou, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, S.; Ainiwaer, S.; Shen, G.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, H.; Hu, J.; Wan, Y. Temporal and spatial variation of PM2.5 in indoor air monitored by low-cost sensors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Du, W.; Lei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Tao, S.; Pan, B. Quantifying the dynamic characteristics of indoor air pollution using real-time sensors: Current status and future implication. Environ. Int. 2023, 175, 107934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Marques, G. Indoor Air Quality: An Emerging Problem Domain. In Integrating IoT and AI for Indoor Air Quality Assessment; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Núñez, A.; García, A.M. Effect of the passive natural ventilation on the bioaerosol in a small room. Build. Environ. 2022, 207, 108438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Blanco, E.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Díaz-Ramiro, E.; Fernández, J.; Coz, E.; Yagüe, C.; Román-Cascón, C.; Narros, A.; Borge, R.; Artíñano, B. Real-Time Measurements of Indoor–Outdoor Exchange of Gaseous and Particulate Atmospheric Pollutants in an Urban Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, A.; García, A.M. The aerobiome in a hospital environment: Characterization, seasonal tendencies and the effect of window opening ventilation. Build. Environ. 2023, 230, 110024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmari Tehran, H.; Ghazanfarpour, M.; Akhlaghi, A.; Saeidi, M. Air Pollution in Hospitals: A Critical Public Health Emergency and Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality and Patient Safety. Health Provid. 2025, 5, 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Gola, M.; Settimo, G.; Capolongo, S. Indoor air quality in inpatient environments: A systematic review on factors that influence chemical pollution in inpatient wards. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 8358306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, N.; Tahir, A.; Abbas, M.; Zaman, N.; Qadir, A.; Arshad, M. Temporal trends in indoor bioaerosols: Implications for dental healthcare environments. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2025, 35, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gutiérrez, L.; Rojas, B.B.; Ruiz, M.; Egido, S.H.; Ruiz-Gaitán, A.C.; Laiz, L.; Pemán, J.; Cuétara-García, M.S.; Mellado, E.; Martin-Sanchez, P.M. Fungal burden assessment in hospital zones with different protection degrees. Build. Environ. 2025, 269, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, R.E.; Ballard, E.L.; O’Rourke, P.; Knibbs, L.D.; Morawska, L.; Bell, S.C. Indoor hospital air and the impact of ventilation on bioaerosols: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2019, 103, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Zeeshan, M. Microbiological indoor air quality of hospital buildings with different ventilation systems, cleaning frequencies and occupancy levels. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Ivanov, V.; Falkinham, J.O. Viruses, Bacteria and Fungi in the Built Environment: Designing Healthy Indoor Environments; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Capolongo, S.; Settimo, G.; Gola, M. Indoor Air Quality in Healthcare Facilities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, M.; Chan, A.H. Control and management of hospital indoor air quality. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Gaidajis, G.; Angelakoglou, K. Indoor mass concentrations of particulate matter in hospital environment. Glob. NEST J. 2014, 16, 832–839. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Huang, J.; Xing, J.; Zou, E.Y. (Re) scheduling pollution exposure: The case of surgery schedules. J. Public Econ. 2023, 219, 104825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farraia, M.; Paciência, I.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Moreira, A.; Cavaleiro Rufo, J. Indoor Air Quality in Hospitals: How Is the Situation in Portugal? In Occupational and Environmental Safety and Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Śmiełowska, M.; Marć, M.; Zabiegała, B. Indoor air quality in public utility environments—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 11166–11176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Moreno, F.; Pujadas, M.; Plaza, J.; Rodríguez-Maroto, J.; Martínez-Lozano, P.; Artíñano, B. Influence of seasonal factors on the atmospheric particle number concentration and size distribution in Madrid. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3169–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brines, M.; Dall’Osto, M.; Beddows, D.; Harrison, R.; Gómez-Moreno, F.; Núñez, L.; Artinano, B.; Costabile, F.; Gobbi, G.P.; Salimi, F. Traffic and nucleation events as main sources of ultrafine particles in high-insolation developed world cities. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5929–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, P.; Artíñano, B.; Molero, F.; Viana, M.; Pey, J.; Alastuey, A.; Querol, X. African dust contribution to ambient aerosol levels across central Spain: Characterization of long-range transport episodes of desert dust. Atmos. Res. 2013, 127, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, J.; Sánchez, B.; Román-Cascón, C.; Martilli, A.; Royé, D.; Yagüe, C. Effects of the urban development on the near-surface air temperature and surface energy balance: The case study of Madrid from 1970 to 2020. Urban Clim. 2024, 58, 102198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Cascón, C.; Yagüe, C.; Arrillaga, J.A.; Lothon, M.; Pardyjak, E.R.; Lohou, F.; Inclán, R.M.; Sastre, M.; Maqueda, G.; Derrien, S. Comparing mountain breezes and their impacts on CO2 mixing ratios at three contrasting areas. Atmos. Res. 2019, 221, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Cascón, C.; Yagüe, C.; Ortiz-Corral, P.; Serrano, E.; Sánchez, B.; Sastre, M.; Maqueda, G.; Alonso-Blanco, E.; Artiñano, B.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; et al. Wind and turbulence relationship with NO2 in an urban environment: A fine-scale observational analysis. Urban Clim. 2023, 51, 101663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreiro, M.; Alonso-Blanco, E.; Becerril-Valle, M.; Coz, E.; Díaz, E.; Fernández, A.J.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Molero, F.; Núñez, L.; Palacios, M.; et al. Continuous observations of chemical and physical properties of atmospheric aerosols in southern Europe. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Aerosol Cycle Sources-Aging-Sinks-Impact (ICAC), Lille, France, 21–23 March 2017; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Petzold, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Fiebig, M.; Laj, P.; Li, S.-M.; Baltensperger, U.; Holzer-Popp, T.; Kinne, S.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N. Recommendations for reporting” black carbon” measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8365–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artíñano, B.; Gómez-Moreno, F.; Díaz, E.; Amato, F.; Pandolfi, M.; Alonso-Blanco, E.; Coz, E.; Garcia-Alonso, S.; Becerril-Valle, M.; Querol, X. Outdoor and indoor particle characterization from a large and uncontrolled combustion of a tire landfill. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 593, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Artíñano, B.; Ramiro, E.D.; Barreiro, M.; Núñez, L.; Coz, E.; Dimitroulopoulou, C.; Vardoulakis, S.; Yagüe, C.; Maqueda, G. Urban vegetation and particle air pollution: Experimental campaigns in a traffic hotspot. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Blanco, E.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Díaz-Ramiro, E.; Barreiro, M.; Fernández, J.; Figuero, I.; Rubio-Juan, A.; Santamaría, J.M.; Artíñano, B. Indoor Air Quality at an Urban Primary School in Madrid (Spain): Influence of Surrounding Environment and Occupancy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Alonso, E.; Artíñano, B.; Juncal-Bello, V.; Iglesias-Samitier, S.; Pineiro Iglesias, M.; Mahía, P.L.; Pérez, N.; Pey, J.; Ripoll, A. Intercomparisons of mobility size spectrometers and condensation particle counters in the frame of the Spanish atmospheric observational aerosol network. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.M.; Suh, H.H.; Catalano, P.J.; Koutrakis, P. Using time-and size-resolved particulate data to quantify indoor penetration and deposition behavior. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhao, B. Relationship between indoor and outdoor NO2: A review. Build. Environ. 2020, 180, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EA. Informe de Calidad-Aire en Madrid-2022. 2023. Available online: https://airedemadrid.madrid.es/UnidadesDescentralizadas/Sostenibilidad/CalidadAire/Publicaciones/Memorias_anuales/Ficheros/MEMORIA_2022_02.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2023).
- Miller, S.L.; Facciola, N.A.; Toohey, D.; Zhai, J. Ultrafine and fine particulate matter inside and outside of mechanically ventilated buildings. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halios, C.H.; Helmis, C.G. On the estimation of characteristic indoor air quality parameters using analytical and numerical methods. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 381, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Challoner, A.; Gill, L. Indoor/outdoor air pollution relationships in ten commercial buildings: PM2.5 and NO2. Build. Environ. 2014, 80, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diapouli, E.; Chaloulakou, A.; Spyrellis, N. Indoor and outdoor PM concentrations at a residential environment, in the Athens area. Glob. NEST J. 2008, 10, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Tippayawong, N.; Khuntong, P. Model prediction of indoor particle concentrations in a public school classroom. J. Chin. Inst. Eng. 2007, 30, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xu, H.; Meng, W.; Hou, W.; Zhang, W.; Shen, G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Tao, S. A novel model for regional indoor PM2.5 quantification with both external and internal contributions included. Environ. Int. 2020, 145, 106124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, M.; Zhu, X.; Du, W.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, T.; Pan, X.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, X.; Zeng, E.Y. Exposure and health impact evaluation based on simultaneous measurement of indoor and ambient PM2.5 in Haidian, Beijing. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reche, C.; Rivas, I.; Pandolfi, M.; Viana, M.; Bouso, L.; Àlvarez-Pedrerol, M.; Alastuey, A.; Sunyer, J.; Querol, X. Real-time indoor and outdoor measurements of black carbon at primary schools. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shen, J.; Gao, Z. Ventilation and air quality in student dormitories in China: A case study during summer in Nanjing. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales, C.M.F.; Tamayo, E.G.; Babela, D.L.; Benjamin, M.P. Indoor penetration of ambient particulate pollution in a hospital maternity ward in Manila, Philippines: Perspectives towards holistic city-level air quality management. Environ. Sci. Atmos. 2025, 5, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadyan, M.; Keyvani, S.; Bahrami, A.; Yetilmezsoy, K.; Heibati, B.; Godri Pollitt, K.J. Assessment of indoor air pollution exposure in urban hospital microenvironments. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2019, 12, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukadia, V. Outdoor air pollution: Its ingress and impact on indoor environments. Improving indoor air quality. J. Inst. Environ. Sci. 2021, 30, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kalimeri, K.K.; Bartzis, J.G.; Sakellaris, I.A.; de Oliveira Fernandes, E. Investigation of the PM2.5, NO2 and O3 I/O ratios for office and school microenvironments. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weschler, C.J. Ozone in indoor environments: Concentration and chemistry. Indoor Air 2000, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazaroff, W.W. Ten questions concerning indoor ultrafine particles. Build. Environ. 2023, 243, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, H.; Lv, Y.; Liu, J. Indoor-outdoor relationship of PM2.5 mass concentrations in severe cold regions based on a coupled canopy model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhao, B. Review of relationship between indoor and outdoor particles: I/O ratio, infiltration factor and penetration factor. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.V.; Harrison, R.M. Chemical and physical properties of indoor aerosols. Indoor Air Pollut. 2019, 48, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Taushiba, A.; Dwivedi, S.; Zehra, F.; Shukla, P.N.; Lawrence, A.J. Assessment of indoor air quality and their inter-association in hospitals of northern India—A cross-sectional study. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamseddine, A.Z. Determinants of Indoor Air Quality in Hospitals: Impact of Ventilation Systems with Indoor-Outdoor Correlations and Health Implications. Ph.D. Thesis, American University of Beirut, Beirut, Lebanon, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Tsoulou, I.; Thirumurugesan, S.; Morgan, B.; Gonzalez, S.; Plotnik, D.; Senick, J.; Andrews, C.; Mainelis, G. Effect of heatwaves on PM2.5 levels in apartments of low-income elderly population. A case study using low-cost air quality monitors. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 301, 119697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, R.W.; Devlin, R.B.; Gehr, P.; Giannelli, R.; Hassett-Sipple, B.; Jung, H.; Martini, G.; McDonald, J.; Sacks, J.D.; Walker, K. Ultrafine particle metrics and research considerations: Review of the 2015 UFP workshop. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Menno di Bucchianico, A.; Cusano, M.; Gaddi, R.; Gaeta, A.; Leone, G.; Boccuni, F.; Ferrante, R.; Pelliccioni, A.; Cattani, G. Indoor and Outdoor Particle Number Concentration in the Sapienza University Campus of Rome. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; He, C.; Hitchins, J.; Gilbert, D.; Parappukkaran, S. The relationship between indoor and outdoor airborne particles in the residential environment. Atmos. Environ. 2001, 35, 3463–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Ochoa, M.A.; Bedoya, R.; Gómez, L.M.; Aguiar, D.; Palacio-Tobón, C.A.; Colorado, H.A. A Review on the Characterization and Measurement of the Carbonaceous Fraction of Particulate Matter. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byčenkienė, S.; Gill, T.; Khan, A.; Kalinauskaitė, A.; Ulevicius, V.; Plauškaitė, K. Estimation of Carbonaceous Aerosol Sources under Extremely Cold Weather Conditions in an Urban Environment. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becerril-Valle, M.; Coz, E.; Prévôt, A.S.H.; Močnik, G.; Pandis, S.N.; Sánchez de la Campa, A.M.; Alastuey, A.; Díaz, E.; Pérez, R.M.; Artíñano, B. Characterization of atmospheric black carbon and co-pollutants in urban and rural areas of Spain. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 169, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Chan, K.L.; Wong, K.; Westerdahl, D.; Močnik, G.; Zhou, J.; Cheung, C.S. Black carbon mass size distributions of diesel exhaust and urban aerosols measured using differential mobility analyzer in tandem with Aethalometer. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Osto, M.; Thorpe, A.; Beddows, D.C.S.; Harrison, R.M.; Barlow, J.F.; Dunbar, T.; Williams, P.I.; Coe, H. Remarkable dynamics of nanoparticles in the urban atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6623–6637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauraite, J.; Mainelis, G.; Kecorius, S.; Minderytė, A.; Dudoitis, V.; Garbarienė, I.; Plauškaitė, K.; Ovadnevaite, J.; Byčenkienė, S. Office indoor PM and BC level in Lithuania: The role of a long-range smoke transport Event. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavese, G.; Agresti, F.; Calvello, M.; Esposito, F.; Lettino, A. Outdoor and indoor measurements of number particles size distributions and equivalent black carbon (EBC) at a mechanical manufacturing plant. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. IARC: Diesel engine exhaust carcinogenic. In IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 105. [Google Scholar]
- Janssen, N.A.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; Van Bree, L.; Ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B. Black carbon as an additional indicator of the adverse health effects of airborne particles compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, B. Infiltration of Outdoor Pollutants “Infiltration of Outdoor Pollutants”—Home Energy Magazine, May/June 2015, Brent Stephens, Illinois Institute of Technology (For PDF: Scroll Down to “Other Publications”). 2015. Available online: http://built-envi.com/pubs/ (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Hossain, M.S.; Che, W.; Frey, H.C.; Lau, A.K. Factors affecting variability in infiltration of ambient particle and gaseous pollutants into home at urban environment. Build. Environ. 2021, 206, 108351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, Z.; Doğan, G.; Arslanbaş, D.; Pekey, B.; Pekey, H.; Dumanoğlu, Y.; Bayram, A.; Tuncel, G. Determination of the personal, indoor and outdoor exposure levels of inorganic gaseous pollutants in different microenvironments in an industrial city. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahed, F.; Pardakhti, A.; Motlagh, M.S.; Mohammad Kari, B.; Tavakoli, A. Infiltration of outdoor PM2.5 and influencing factors. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2022, 15, 2215–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Hua, Q.; Zheng, X.; Ji, W.; Zhang, X. Effect of particulate iron on tracking indoor PM2.5 of outdoor origin: A case study in Nanjing, China. Indoor Built Environ. 2021, 30, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyrys, J.; Pitz, M.; Bischof, W.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Heinrich, J. Relationship between indoor and outdoor levels of fine particle mass, particle number concentrations and black smoke under different ventilation conditions. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamp, S.; Burman, E.; Shrubsole, C.; Chatzidiakou, L.; Mumovic, D.; Davies, M. Seasonal variations and the influence of ventilation rates on IAQ: A case study of five low-energy London apartments. Indoor Built Environ. 2022, 31, 607–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, W.-Y.; Noguchi, M.; Yi, E.-E.P.-N.; Thant, Z.; Uchiyama, S.; Win-Shwe, T.-T.; Kunugita, N.; Mar, O. Preliminary assessment of outdoor and indoor air quality in Yangon city, Myanmar. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Young, C.J.; VandenBoer, T.C.; Kahan, T.F. Role of location, season, occupant activity, and chemistry in indoor ozone and nitrogen oxide mixing ratios. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2019, 21, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, L. Infiltration characteristic of outdoor fine particulate matter (PM2.5) for the window gaps. Procedia Eng. 2015, 121, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.T. Indoor–outdoor relationships of particulate matter and nitrogen oxides under different outdoor meteorological conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, P.; Chen, Z.; Cao, S.; Wang, Q.; Xie, G.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lu, B. Influence of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) pollution on indoor environment during winter in Beijing. Build. Environ. 2015, 87, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Burman, E.; Stamp, S.; Shrubsole, C.; Bunn, R.; Oberman, T.; Barrett, E.; Aletta, F.; Kang, J.; Raynham, P. Building performance evaluation of a new hospital building in the UK: Balancing indoor environmental quality and energy performance. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, U. Indoor and outdoor concentrations of ultrafine particles in some Scandinavian rural and urban areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 343, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatoutsidou, S.E.; Ondráček, J.; Tesar, O.; Tørseth, K.; Ždímal, V.; Lazaridis, M. Indoor/outdoor particulate matter number and mass concentration in modern offices. Build. Environ. 2015, 92, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, P.; Iordache, V.; Poupard, O.; Genin, D.; Allard, F. Relationship between outdoor and indoor air quality in eight French schools. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, G. Real-time monitoring of pollutants in occupied indoor environments: A pilot study of a hospital in China. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 59, 105105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, T.L.; Layton, D.W. Deposition, resuspension, and penetration of particles within a residence. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 1487–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serfozo, N.; Chatoutsidou, S.E.; Lazaridis, M. The effect of particle resuspension during walking activity to PM10 mass and number concentrations in an indoor microenvironment. Build. Environ. 2014, 82, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chithra, V.; Nagendra, S.S. Indoor air quality investigations in a naturally ventilated school building located close to an urban roadway in Chennai, India. Build. Environ. 2012, 54, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbayoumi, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Yusof, N.F.F.M.; Al Madhoun, W. Spatial and seasonal variation of particulate matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in Middle Eastern classrooms. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 80, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Mena, K.D.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Chen, P.-S. Cooking/window opening and associated increases of indoor PM2.5 and NO2 concentrations of children’s houses in kaohsiung, Taiwan. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.-C.; Wu, P.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Su, H.-J. Indoor air quality varies with ventilation types and working areas in hospitals. Build. Environ. 2015, 85, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimra, A.; Ali, Z.; Nasir, Z.A.; Tyrrel, S.; Sidra, S. Characterization of indoor air quality in relation to ventilation practices in hospitals of Lahore, Pakistan. Sains Malays. 2021, 50, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seah Cheng Kiat, A. Meteorological Influences on the Vertical Profile of Nitrogen Dioxide in a Residential Building Near an Expresswa. 2017. Available online: https://scholarbank.nus.edu.sg/handle/10635/219934 (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- Rubino, F.M.; Floridia, L.; Tavazzani, M.; Fustinoni, S.; Giampiccolo, R.; Colombi, A. Height profile of some air quality markers in the urban atmosphere surrounding a 100 m tower building. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 3569–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurdakul, S.; Civan, M.; Doğan, G.; Üzmez, Ö.Ö.; Gaga, E.O.; Döğeroğlu, T.; Ayaklı, G.; Tuncel, G. Vertical variation and source evaluation of VOCs and inorganic pollutants in a university building. Environ. Forensics 2018, 19, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-L.; Li, C.-P.; Tang, C.-S.; Lung, S.-C.C.; Chuang, H.-C.; Chou, D.-W.; Chang, L.-T. Risk assessment for people exposed to PM2.5 and constituents at different vertical heights in an urban area of Taiwan. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
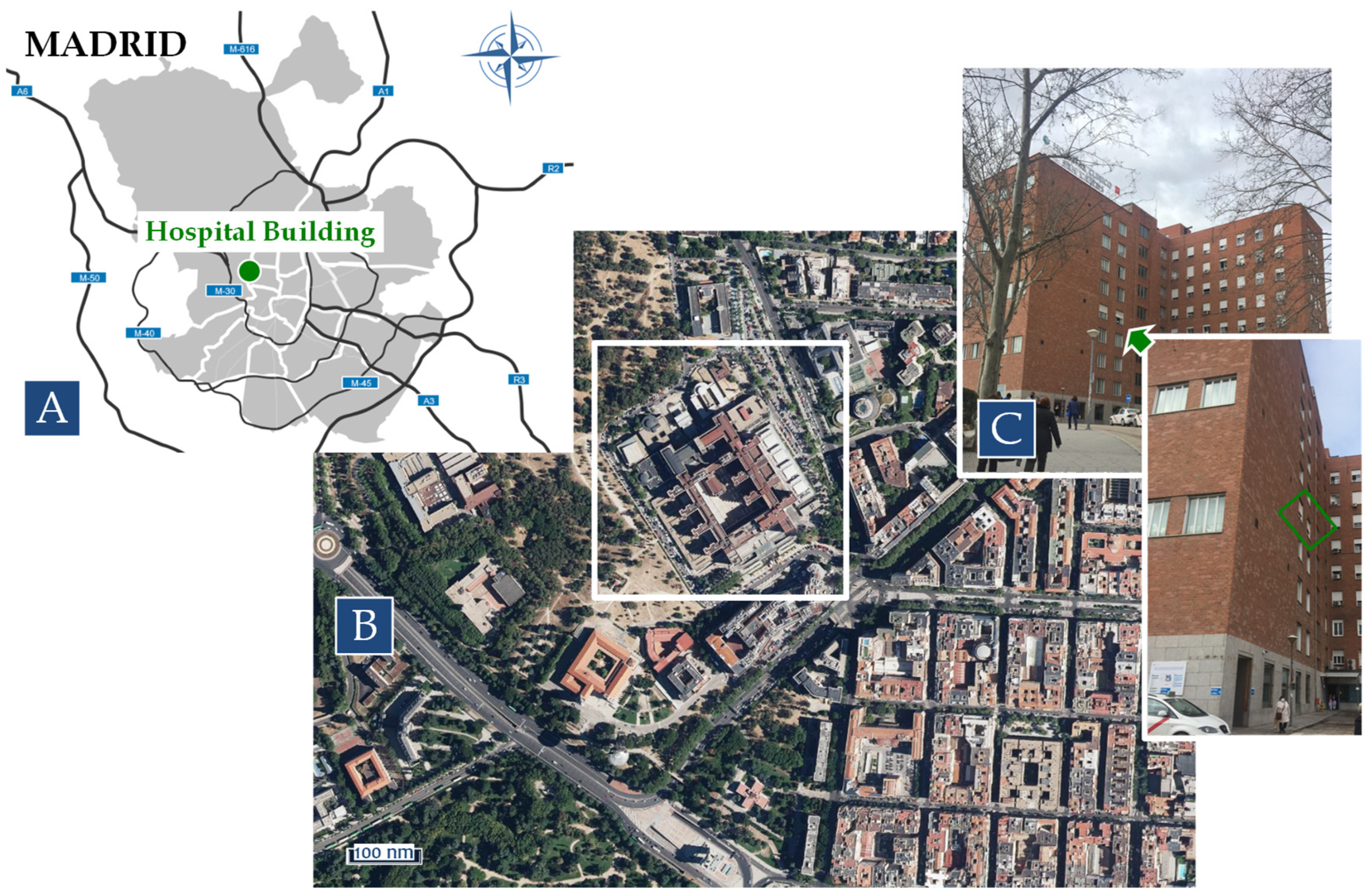
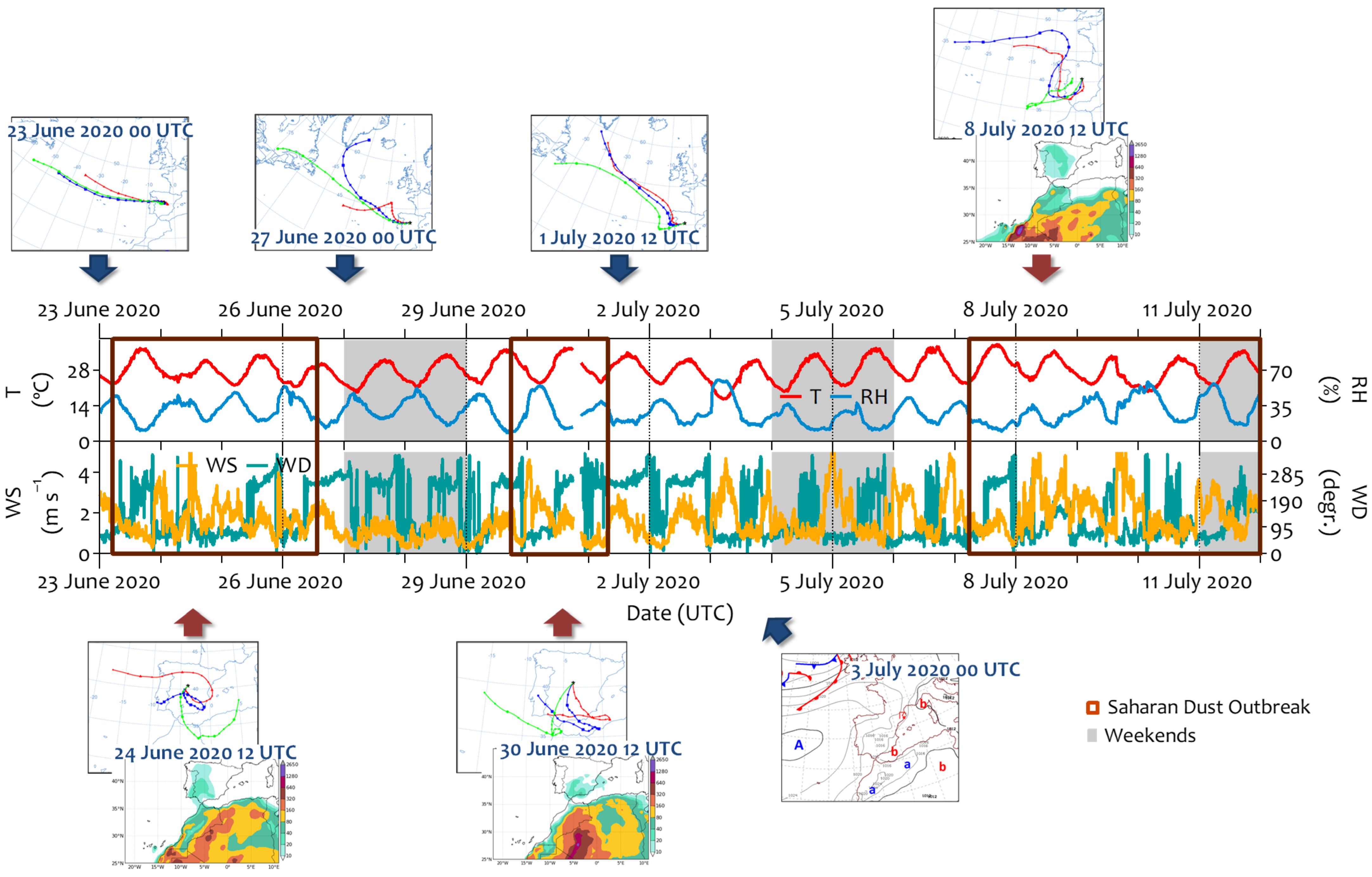
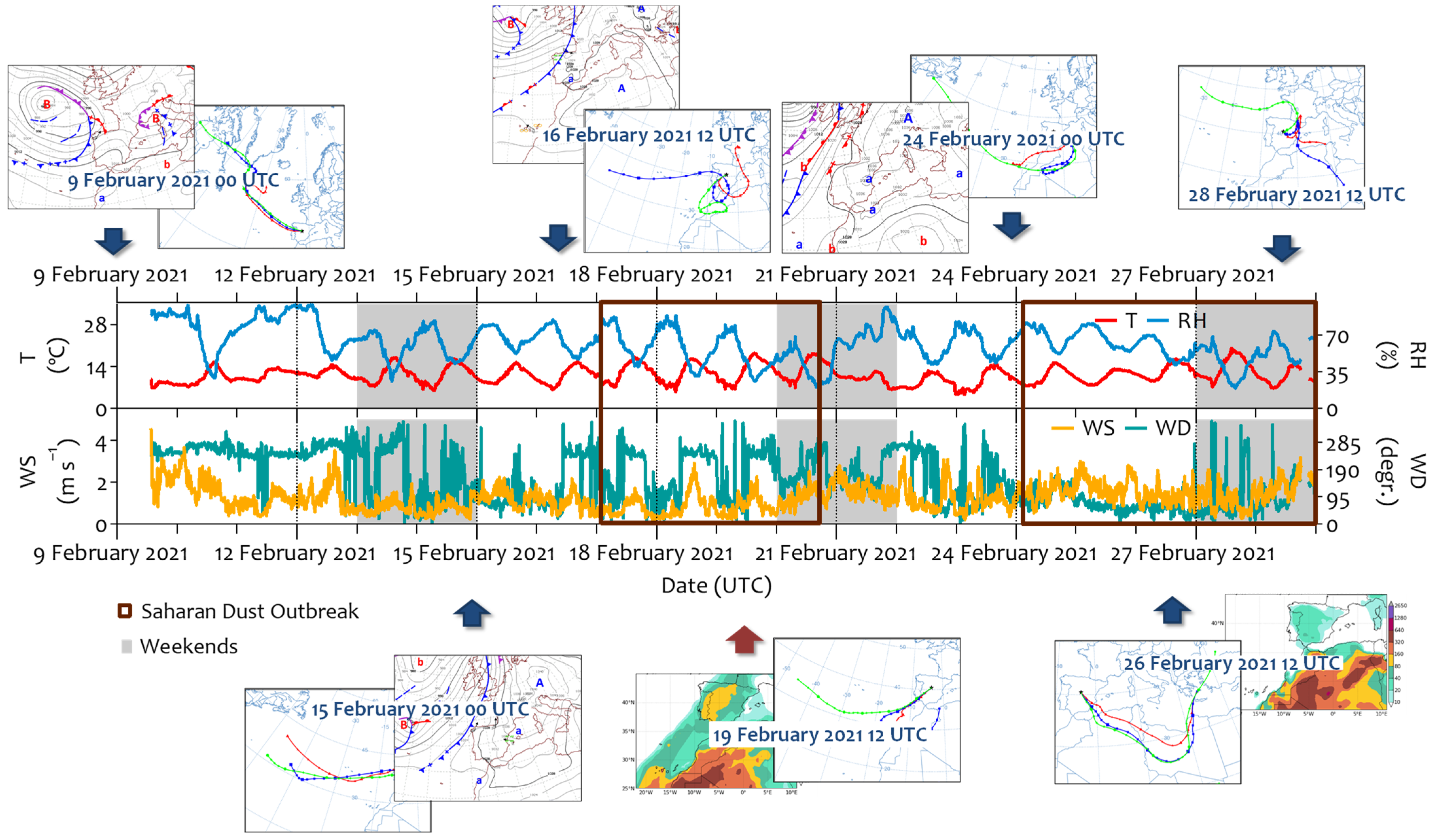
| Sampling Point | Parameters | Instrument (IN/OUT) | Measurement Size Range (µm) | Time Resolution | Data Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer field campaign (23 June to 11 July 2020) | |||||
| Room | PNC | CPC, TSI model 3772 (IN) CPC, Aerosol Dynamics Inc. model MAGIC™ (OUT) | >0.01 0.005 to 2.5 | 1 min 1 s | |
| eBC | 2 MicroAeth® model AE51 (IN + OUT) | Total | 1 min | ||
| PM10, PM2.5, PM1 | Grimm model EDM365 (IN) | Mass concentration of particles < 10, <2.5, and <1 µm respectively | 1 min | ||
| NO, NO2, NOx | NOx analyzer, Thermo Sci. model 42i (IN) NOx analyzer, Thermo Sci. model 42i-TL (OUT) Palmes-type passive diffusion tubes (IN and OUT) | 0–500 ppb | 1 min | ||
| CIEMAT | PM10, PM2.5 | TEOM® 1405-DF (OUT) | Particles < 10 and <2.5 µm, respectively | 5 min | |
| Hospital building roof (~34 m a.g.l.) | T, RH, WS, WD, TKE, u*, SH | Portable meteorological mast | 10 min | ||
| Winter field campaign (9–28 February 2021) | |||||
| Room | PNC | CPC, TSI model 3772 (IN) CPC, Aerosol Dynamics Inc. model MAGIC™ (OUT) | >0.01 0.005 to 2.5 | 1 min 1 s | |
| eBC | MicroAeth® model MA200 (IN) MicroAeth® model AE51 (OUT) (1) | Total | 1 min | ||
| PM10, PM2.5, PM1 | Grimm model EDM365 (IN) Grimm model 11D (OUT) | Particles < 10, <2.5, and <1 µm, respectively | 1 min | ||
| NO, NO2, NOx | NOx analyzer, Thermo Sci. model 42i (IN) NOx analyzer, Thermo Sci. model 42i-TL (OUT) Palmes-type passive diffusion tubes (IN and OUT) | 0–500 ppb | 1 min | ||
| O3 | Ozone Analyzer, Thermo Environmental Instruments model 49 (IN) Ozone Analyzer, Sabio model 6030 (OUT) | 0–500 ppb | 1 min | ||
| Hospital building roof (~34 m a.g.l.) | T, RH, WS, WD, TKE, u*, SH | Portable meteorological mast | 10 min | ||
| TKE (m2 s−2 ) | PNC rat. (95% CI) | PM10 rat. (95% CI) | PM2.5 rat. (95% CI) | PM1 rat. (95% CI) | eBC rat. (95% CI) | NO rat. (95% CI) | NO2 rat. (95% CI) | NO2 Passive Tubes | O3 rat. (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summer campaign 2020 | ||||||||||
| All periods | 1.7 | 0.78 (0.77,0.79) | 0.17 (0.16,0.17) | 0.22 (0.21,0.22) | - | 0.76 (0.75,0.77) | 0.35 (0.34,0.37) | 1.05 (1.03,1.08) | - | - |
| Period 1 (June 23 (00:00 UTC) – July 7 (07:40 UTC)) | 1.5 | 0.64 (0.62,0.66) | 0.14 (0.14,0.15) | 0.21 (0.21,0.22) | - | 0.71 (0.69,0.73) | 0.29 (0.26,0.32) | 0.89 (0.85,0.92) | 0.8 | - |
| Period 2 (July 7 (07:50 UTC) – 11 (23:50 UTC))1 | 2.5 | 0.80 (0.78,0.82) | 0.13 (0.12,0.13) | 0.16 (0.16,0.17) | - | 0.68 (0.66,0.70) | 0.44 (0.41,0.48) | 1.21 (1.17,1.27) | - | - |
| Winter campaign 2021 | ||||||||||
| All periods | 1.0 | 0.58 (0.57,0.59) | 0.25 (0.24,0.25) | 0.30 (0.29,0.30) | 0.42 (0.41,0.42) | 0.78 (0.76,0.79) | 0.95 (0.92,0.98) | 0.95 (0.93,0.97) | - | 0.43 (0.41,0.44) |
| Period 1 (February 9 (00:00 UTC) – 15 (10:40 UTC)) | 1.0 | 0.53 (0.52,0.54) | 0.22 (0.21,0.22) | 0.27 (0.27,0.28) | 0.38 (0.38,0.39) | 0.73 (0.71,0.74) | 1.06 (1.02,1.10) | 0.92 (0.90,0.94) | 1.0 | 0.43 (0.41,0.44) |
| Period 2 (February 15 (10:50 UTC) – 28 (23:50 UTC)) 1 | 1.0 | 0.48 (0.47,0.49) | 0.18 (0.17,1.19) | 0.26 (0.25,0.26) | 0.38 (0.37,0.39) | 0.68 (0.64,0.71) | 0.99 (0.92,1.07) | 0.69 (0.67,0.71) | - | 0.60 (0.56,0.64) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alonso-Blanco, E.; Gómez-Moreno, F.J.; Díaz-Ramiro, E.; Fernández, J.; Coz, E.; Yagüe, C.; Román-Cascón, C.; Gómez-Garre, D.; Narros, A.; Borge, R.; et al. Indoor/Outdoor Particulate Matter and Related Pollutants in a Sensitive Public Building in Madrid (Spain). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081175
Alonso-Blanco E, Gómez-Moreno FJ, Díaz-Ramiro E, Fernández J, Coz E, Yagüe C, Román-Cascón C, Gómez-Garre D, Narros A, Borge R, et al. Indoor/Outdoor Particulate Matter and Related Pollutants in a Sensitive Public Building in Madrid (Spain). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(8):1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081175
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlonso-Blanco, Elisabeth, Francisco Javier Gómez-Moreno, Elías Díaz-Ramiro, Javier Fernández, Esther Coz, Carlos Yagüe, Carlos Román-Cascón, Dulcenombre Gómez-Garre, Adolfo Narros, Rafael Borge, and et al. 2025. "Indoor/Outdoor Particulate Matter and Related Pollutants in a Sensitive Public Building in Madrid (Spain)" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 8: 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081175
APA StyleAlonso-Blanco, E., Gómez-Moreno, F. J., Díaz-Ramiro, E., Fernández, J., Coz, E., Yagüe, C., Román-Cascón, C., Gómez-Garre, D., Narros, A., Borge, R., & Artíñano, B. (2025). Indoor/Outdoor Particulate Matter and Related Pollutants in a Sensitive Public Building in Madrid (Spain). International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(8), 1175. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22081175








