Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments for Problematic Use of Internet, Video Games, Social Media and Instant Messaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- To identify and analyze the psychological, therapeutic, and preventive interventions implemented with adolescents to address problematic use of video games, online gaming, social media, and instant messaging.
- (2)
- To evaluate the effectiveness of cognitive behavioral interventions in reducing symptoms associated with problematic ICT use.
- (3)
- To compare the magnitude of effects of psychological therapeutic and preventive interventions relative to control groups.
- (4)
- To synthesize available evidence to establish evidence-based recommendations for clinical practice and future research focused on the prevention and treatment of problematic use of video games, social media, and instant messaging among adolescents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection, Quality and Risk of Bias Assessment
2.3. Certainty of Evidence (GRADE Approach)
2.4. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
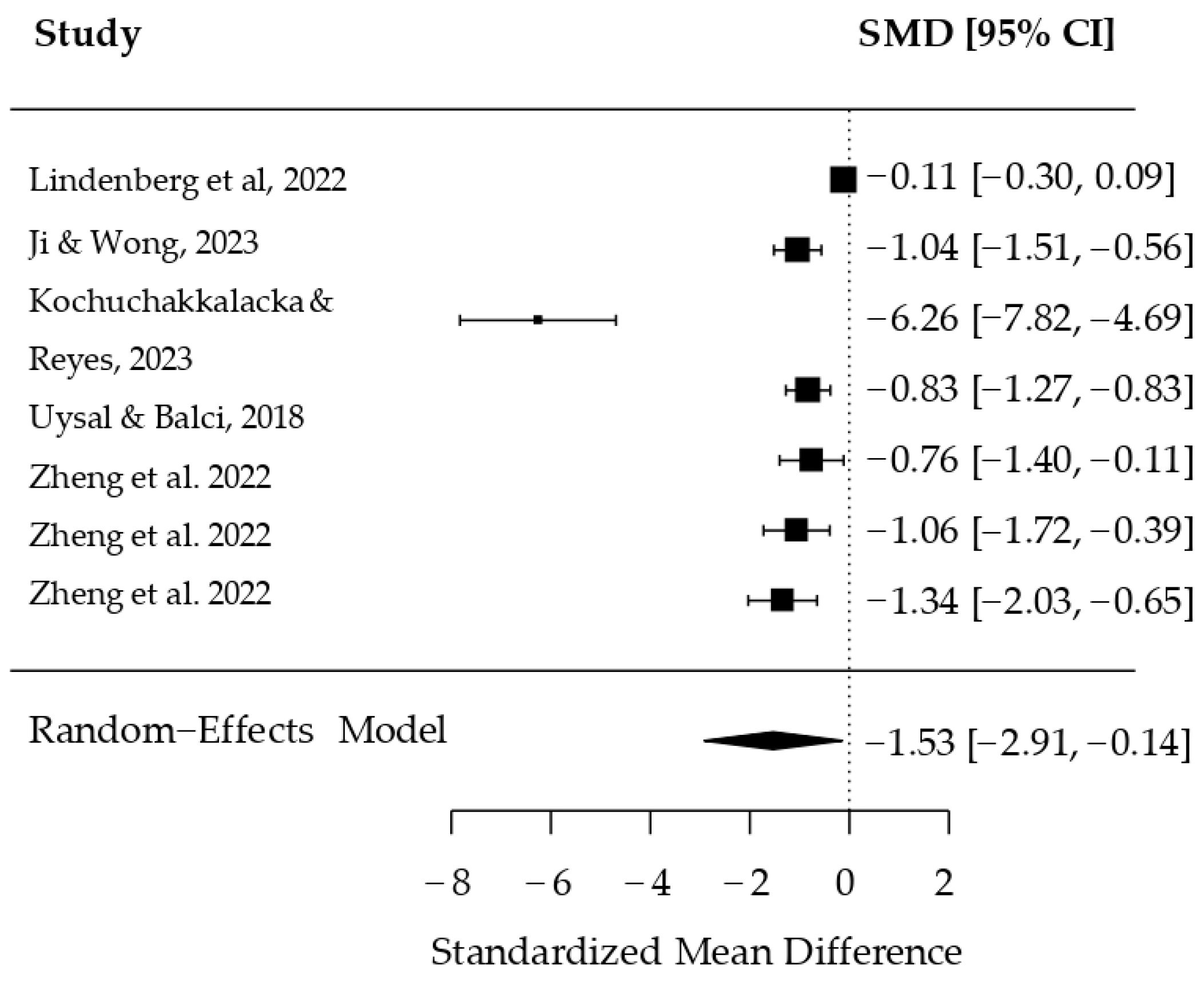
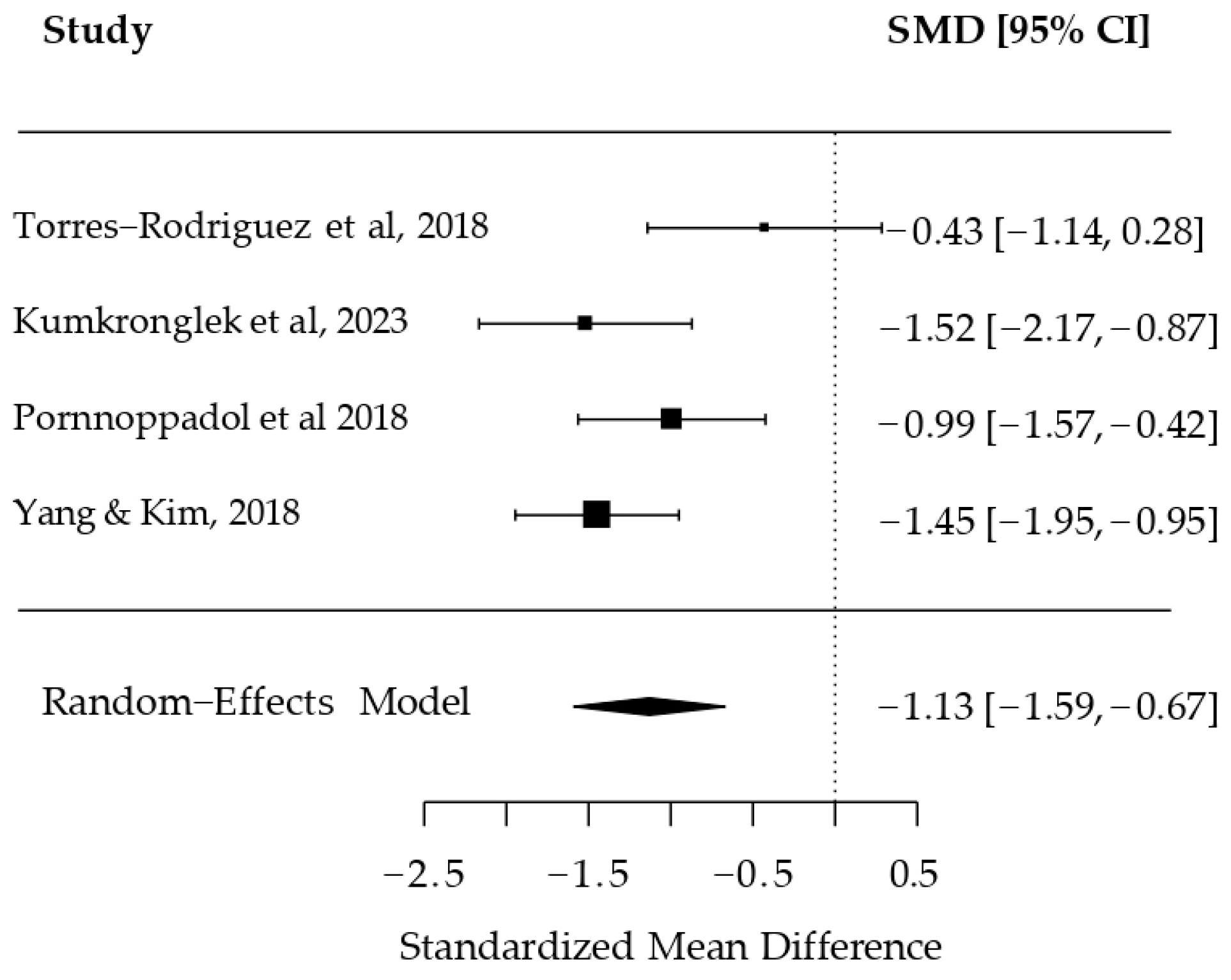
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection in the Review
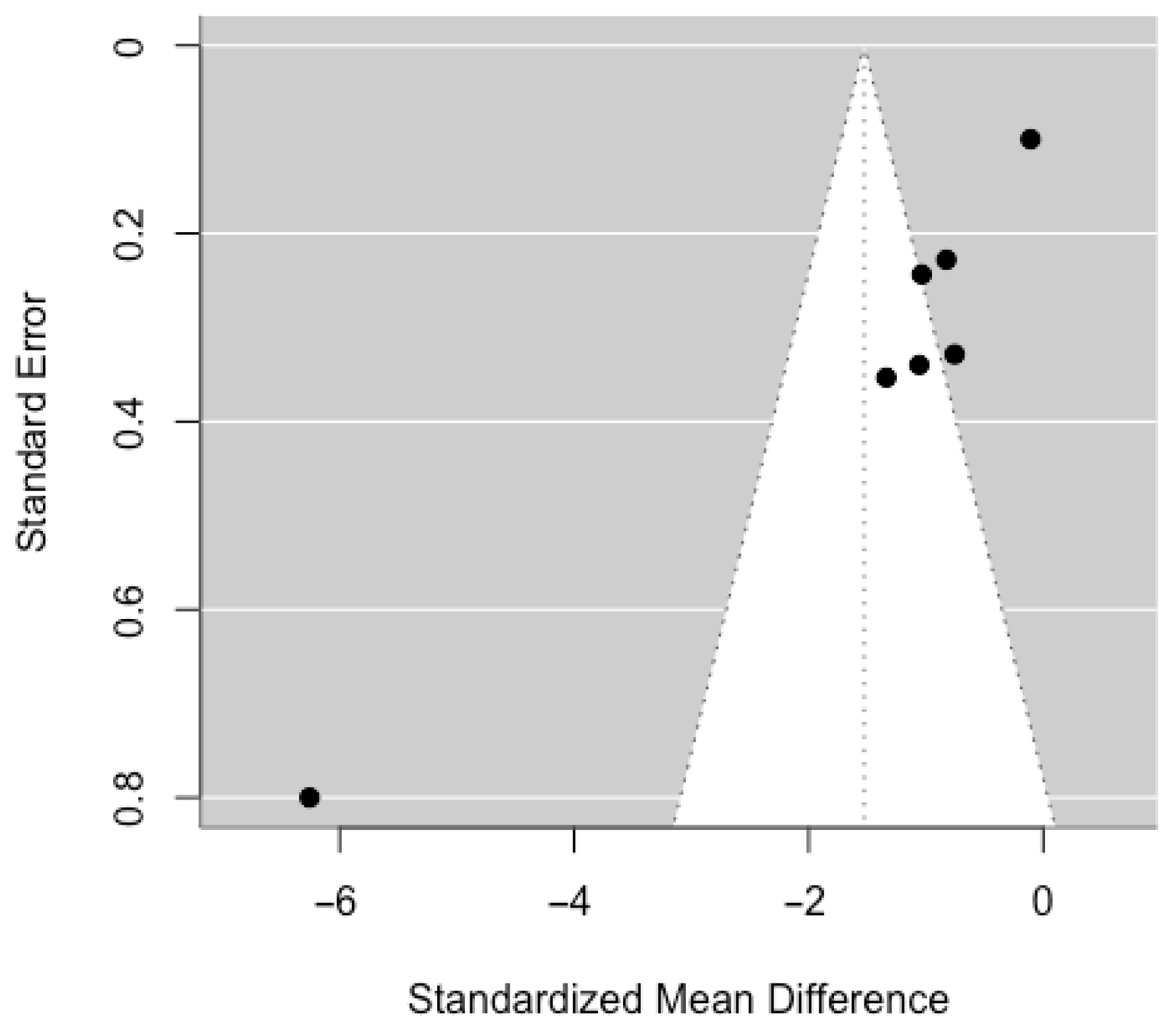
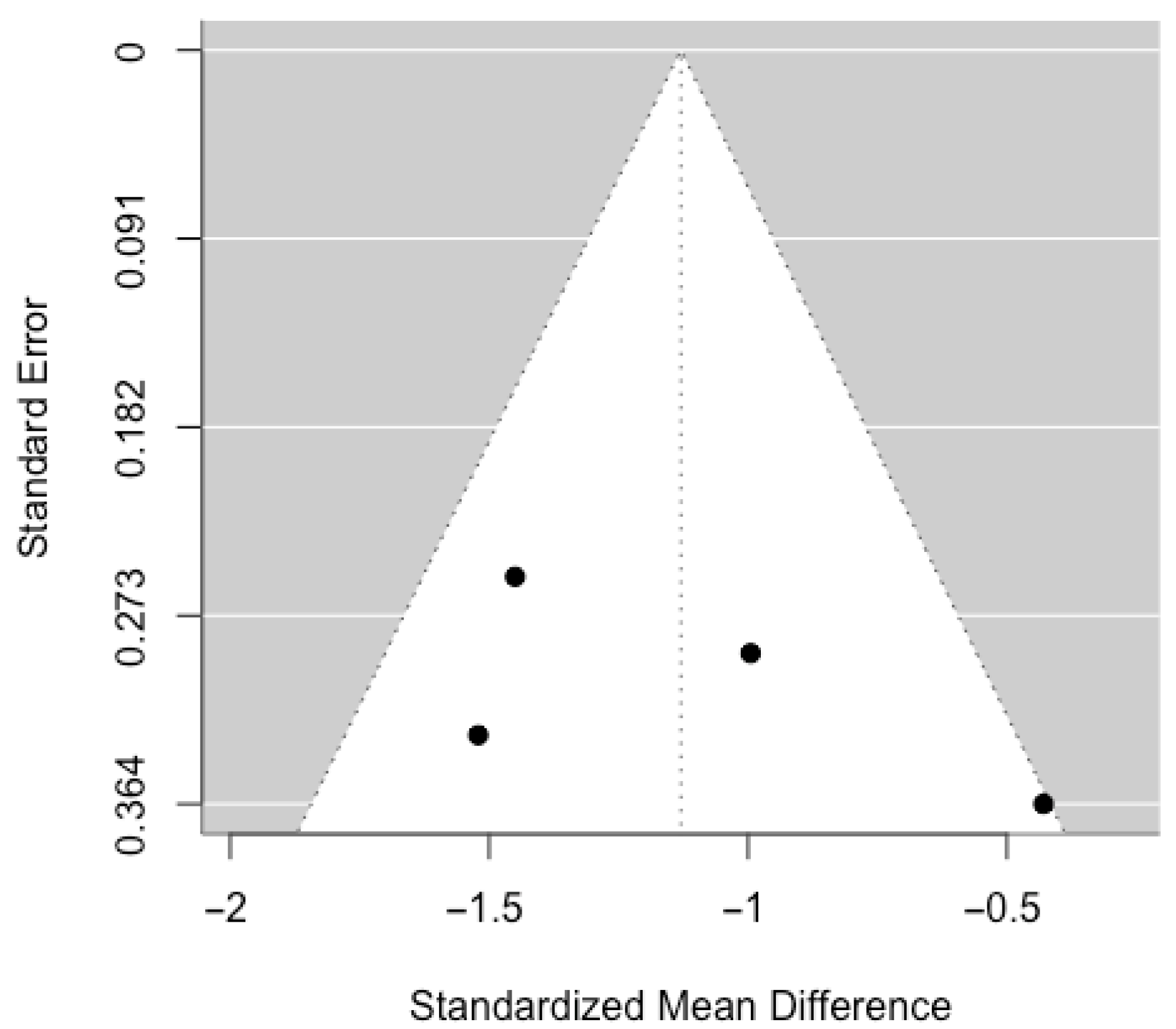
3.2. Risk of Bias of the Studies
3.3. Model of Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICT | Information and Communication Technologies |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| DSM-5 | Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition |
| PIU | Problematic Internet Use |
| BMHD | Bioecological Model of Human Development |
| IAM | Internet Addiction Model |
| I-PACE | An Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution |
| UCJC | Universidad Camilo José Cela |
| IGD | Internet Gaming Disorder Multidisciplinary |
| EG | Experimental Group |
| CG | Control Group |
| CBT | Cognitive Behavioral Therapy |
| SMA | Social Media Addiction |
| DMUD | Digital media-use disorders |
| IUD | Internet Use Disorder |
| GAS | Game Addiction Scale; NODS-CLiP |
| IGD-20 | Test: Internet Gaming Disorder Test |
| YSR/11–18 | Youth Self-Report for Ages 11–18 |
| CBCL/6–18 | Child Behavior Checklist for Ages 6–18 Years |
| MACI | Expressed Concern Scales of the Millon Adolescent Clinical Inventory |
| TMMS-24 | Trait Meta-Mood Scale |
| EHS | Escala de Habilidades Sociales |
| WATOCI | Satisfaction with the treatment. The Working Alliance Theory of Change Inventory |
| CSAS | Computerspielabhäng-igkeitsskala |
| SCL-90-R | Symptom Checklist-Revised |
| STAI | State-Trait Anxiety Index |
| DQVMIA | Diagnostic Questionnaires for Video Games, Mobile Phone or Internet Addiction |
| S-MASS | Social Media Addiction Screening Scale |
| GADIS-A | Gaming Disorder Scale for Adolescents |
| SOMEDIS-A | Social Media Disorder Scale for Adolescents |
| STREDIS-A | Streaming Disorder Scale for Adolescents |
| SDQ | Strength and Difficulties Questionnaire |
| PSQI | Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index |
| ESS-CHAD | Epworth Sleepiness Scale-Children and Adolescents |
| PSS-10 | Perceived Stress Scale |
| FCS | Family Communication Scale |
| MAAS-5 | Mindfulness Attention Awareness Scale |
| CIAS | Chen Internet Addiction Scale |
| SAS | Self-rating Anxiety Scale |
| SDS | Self-rating Depression Scale |
| BISS-11 | Barrat Impulsiveness; |
| fMRI | functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| GD | Game-related outcome |
| C-RIGC | Revised Internet Gaming Cognition Scale |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire |
| GAD | Generalized Anxiety Disorder |
References
- Karaman Aksentijević, N.; Ježić, Z.; Zaninović, P.A. The Effects of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Use on Human Development—A Macroeconomic Approach. Economies 2021, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, B.; Guadix, I.; Rial, A.; Suárez, F. Impacto de la Tecnología en la Adolescencia. Relaciones, Riesgos y Oportunidades. Available online: https://www.infocop.es/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/Estudio-impacto-tecnologia-adolescencia.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Gil del Pino, C.; García-Segura, S.; García-Fernández, C.M. Las Nuevas Tecnologías y el Rendimiento Académico: Estudio de Caso en Educación Primaria. Available online: http://www.scielo.org.co/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2145-94442023000200034 (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Ortiz-Sobrino, M.Á.; Núñez-Gómez, P.; Gálvez-Caja, A. Digital Platforms, Participation, and Learning Environments Within MOOCs. In MOOCs and the Participatory Challenge: From Revolution to Reality; Frau-Meigs, D., Osuna-Acedo, S., Marta-Lazo, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timotheou, S.; Miliou, O.; Dimitriadis, Y.; Sobrino, S.V.; Giannoutsou, N.; Cachia, R.; Monés, A.M.; Ioannou, A. Impacts of digital technologies on education and factors influencing schools’ digital capacity and transformation: A literature review. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2023, 28, 6695–6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Kundu, A.; Bhattacharya, A. Technology adaptation and survival of SMEs: A longitudinal study of developing countries. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2020, 10, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, N.S.; Gómez, A.G.; Flores, R.G. El impacto de la tecnología de la información en la gestión empresarial. Nexus Res. J. 2024, 3, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Global Trends in Government Innovation 2024: Fostering Human-Centred Public Services, OECD Public Governance Reviews; OECD: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashchey, N.; Spornik, A.; Shipulin, V. Personal And Collective Identity: Transformations In The Digital Age. In Man, Society, Communication, Proceedings of the European Proceedings of Social and Behavioural Sciences, Chelyabinsk, Russia, 22–23 April 2021; European Publisher: London, UK. [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo Vicario, M.I.; González-Fierro, M.J.C. Adolescencia. Aspectos físicos, psicológicos y sociales. An. Pediatría Contin. 2014, 12, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, I.J.; Pellitero, S.R.; Paniagua, S.M.P. 1 Definición y Etapas de la Adolescencia. Atención Integral al Adolescente. Unpublished work. Available online: https://www.semfyc.es/storage/publication/Guia_adolescencia_paginasmuestra_2.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Organización Mundial de la Salud. Indicadores De Salud Del Adolescente Propuestos Por La Acción Mundial Para La Medición De La Salud Del Adolescente: Orientación Para El Seguimiento De La Salud Del Adolescente a Nivel Nacional, Regional Y Mundial. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/376933/9789240095472-spa.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Guidelines on the Inclusion and Protection of Adolescent Minors and Young Adults in Health Research: A Position Statement of the Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. J. Adolesc. Heal. 2025, 76, 944–953. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawyer, S.M.; Azzopardi, P.S.; Wickremarathne, D.; Patton, G.C. The age of adolescence. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2018, 2, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Red PROEMO. Necesidades Y Recomendaciones de la Red PROEMO Para la Promoción de la Salud Mental y Emocional en Las Personas Adolescentes y Jóvenes. Informe y Hoja de Ruta 2025. Available online: https://www.consaludmental.org/publicaciones/Red-PROEMO-bienestar-emocional-adolescentes-jovenes.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Ford, C.A.; Boyer, C.B.; Halpern, C.T.; Katzman, D.K.; Ross, D.A.; Berg, T.D.; Santoa, T.D. The Distinguished Dozen: 2024 Journal of Adolescent Health Articles Making Distinguished Contributions to Adolescent and Young Adult Health. J. Adolesc. Health 2025, 76, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, D. El cerebro adolescente: Época de cambio y transformación. Rev. Gen. Derecho Penal 2024, 42, 12. Available online: https://www.ub.edu/neuroedu_temp/wp-content/uploads/articles/EL-CEREBRO-ADOLESCENTE-Revista-general-de-Derecho-Penal-42.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Llanderal, I.T.C.; Hernández, M.A.P. El increíble cerebro adolescente y la educación. Rev. Innov. Práct. 2023, 2, 6–12. Available online: https://www.revistainnovapractica.com/index.php/ojs/article/view/24 (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Prieto, A.; Pimienta, A. Manual de Intervención Individual con Adolescentes y Jóvenes en Prevención de Adicciones Desde la Educación Social; Instituto De Adicciones. Madrid Salud: Madrid, Spain, 2016; Available online: https://madridsalud.es/pdf/adicciones/MANUAL_IVRA-MS.pdf (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. Declaración PRISMA 2020: Una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2021, 74, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Observatorio Nacional de Tecnología y Sociedad. Digital Future Society. Impacto del Aumento del uso de Internet y las Redes Sociales en la Salud Mental de Jóvenes y Adolescentes; Confederación Salud Mental España: Madrid, Spain, 2023; Available online: https://consaludmental.org/centro-documentacion/impacto-internet-redes-sociales-salud-mental-jovenes/ (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- Adolescent—Overview. Available online: https://platform.who.int/data/maternal-newborn-child-adolescent-ageing/adolescent-data (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- de Heer, C.; Finkenauer, C.; Stevens, G. Different trajectories of adolescent mental health problems before and over the course of COVID-19: Evidence of increase, decrease, and stability. PLoS Ment. Health 2025, 2, e0000292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirvent, C.M.; Blanco, P.; Palacios, L.; Villa, M.; Rivas, C. Guía Adicciones Comportamentales; Fundación Instituto Spiral: Oviedo, Spain, 2023. Available online: https://fispiral.com.es/guia-adicciones-comportamentales/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Clasificación Internacional de Enfermedades Para Estadísticas de Mortalidad y Morbilidad (CIE-11). Available online: https://icd.who.int/es/docs/Guia%20de%20Referencia%20(version%2014%20nov%202019).pdf (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5TM, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.: Arlington, VA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socidrogalcohol. Guía Clínica Sobre Adicciones Comportamentales Basada en la Evidencia. Available online: https://socidrogalcohol.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Guia_Adicciones_Comportamentales_completa-1.pdf (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Fernández, O.L.; Romo, L.; Rousseau, A.; Lelonek-Kuleta, B.; Chwaszcz, J.; Männikkö, N.; Gässler, A.-K.; Demetrovics, Z.; Achab, S.; Kuss, D.J.; et al. Problematic Internet use among adults: A longitudinal European study. Adicciones 2025, 37, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineberg, N.A.; Menchón, J.M.; Hall, N.; Dell′Osso, B.; Brand, M.; Potenza, M.N.; Chamberlain, S.R.; Cirnigliaro, G.; Lochner, C.; Billieux, J.; et al. Advances in problematic usage of the internet research—A narrative review by experts from the European network for problematic usage of the internet. Compr. Psychiatry 2022, 118, 152346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.L.; Steen, E.; Stavropoulos, V. Internet use and Problematic Internet Use: A systematic review of longitudinal research trends in adolescence and emergent adulthood. Int. J. Adolesc. Youth 2017, 22, 430–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronfenbrenner, U.; Morris, P.A. The Bioecological Model of Human Development. Available online: https://awspntest.apa.org/record/2006-08774-014 (accessed on 9 May 2025).
- Douglas, A.C.; Mills, J.E.; Niang, M.; Stepchenkova, S.; Byun, S.; Ruffini, C.; Lee, S.K.; Loutfi, J.; Lee, J.-K.; Atallah, M.; et al. Internet addiction: Meta-synthesis of qualitative research for the decade 1996–2006. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2008, 24, 3027–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Young, K.S.; Laier, C.; Wölfling, K.; Potenza, M.N. Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific Internet-use disorders: An Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, T.; Buodo, G.; Demetrovics, Z.; Potenza, M.N. Tracing 20 years of research on problematic use of the internet and social media: Theoretical models, assessment tools, and an agenda for future work. Compr. Psychiatry 2022, 112, 152286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunney, C.; Rooney, B. Using Theoretical Models of Problematic Internet Use to Inform Psychological Formulation: A Systematic Scoping Review. Clin. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 810–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Király, O.; Demetrovics, Z. Problematic Internet Use. In Textbook of Addiction Treatment: International Perspectives; el-Guebaly, N., Carrà, G., Galanter, M., Baldacchino, A.M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.R.; Carbonell, X. Actualización y propuesta de Tratamiento de la Adicción a los Videojuegos en línea: El programa PIPATIC. Rev. Psicoter. 2017, 28, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federación Española de Jugadores de Azar Rehabilitados (FEJAR). Manual y Guía Breve de Intervención en Tratamiento de Trastorno por Juego y Videojuego. Available online: https://saludextremadura.ses.es/stadiccionextremadura/manual-de-intervencion-en-tratamiento-de-trastorno-por-juego-y-videojuego-fejar/ (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Li, W.A.; Mills, D.J.; Stanmyre, J.F.; Nower, L. Facets of mindfulness among video game players: A latent profile analysis. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2023, 37, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, Y.; Patil, R.; Toshniwal, S.; Sinha, N. Internet Addiction Management: A Comprehensive Review of Clinical Interventions and Modalities. Cureus 2024, 16, e55466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gleeson, J.; Fraser, M.I.; Ciarrochi, J.; Hofmann, S.G.; Hayes, S.C.; Sahdra, B. The efficacy of personalized psychological interventions in adolescents: A scoping review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 2024, 15, 1470817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüzer, N.; Gürcan-Yıldırım, D. Behavioral addictions and psychological distress: Insights from psychology students in Eastern Turkey. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Antons, S.; Bőthe, B.; Demetrovics, Z.; Fineberg, N.A.; Jimenez-Murcia, S.; King, D.L.; Mestre-Bach, G.; Moretta, T.; Müller, A.; et al. Current Advances in Behavioral Addictions: From Fundamental Research to Clinical Practice. Am. J. Psychiatry 2025, 182, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. Br. Med. J. 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Morgan, R.L.; Rooney, A.A.; Taylor, K.W.; Thayer, K.A.; Silva, R.A.; Lemeris, C.; Akl, E.A.; Bateson, T.F.; Berkman, N.D.; et al. A tool to assess risk of bias in non-randomized follow-up studies of exposure effects (ROBINS-E). Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. (Eds.) Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.5 (Updated August 2024); Cochrane: Prague, Czech Republic, 2024; Available online: www.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rodríguez, A.; Griffiths, M.D.; Carbonell, X.; Oberst, U. Treatment efficacy of a specialized psychotherapy program for Internet Gaming Disorder. J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindenberg, K.; Kindt, S.; Szász-Janocha, C. Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy–Based Intervention in Preventing Gaming Disorder and Unspecified Internet Use Disorder in Adolescents. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2148995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, G.; Balci, S. Evaluation of a School-Based Program for Internet Addiction of Adolescents in Turkey. J. Addict. Nurs. 2018, 29, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Wong, D.F.K. Effectiveness of an integrated motivational cognitive-behavioral group intervention for adolescents with gaming disorder: A randomized controlled trial. Addict. Abingdon Engl. 2023, 118, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; He, J.; Fan, L.; Qiu, Y. Reduction of symptom after a combined behavioral intervention for reward sensitivity and rash impulsiveness in internet gaming disorder: A comparative study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2022, 153, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumkronglek, J.; Sirisatayawong, P.; Chupradit, S. Effects of a Life Skills Enhancement Program on the Life Skills and Risk Behaviors of Social Media Addiction in Early Adolescence. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2023, 19, e174501792301110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornnoppadol, C.; Ratta-Apha, W.; Chanpen, S.; Wattananond, S.; Dumrongrungruang, N.; Thongchoi, K.; Panchasilawut, S.; Wongyuen, B.; Chotivichit, A.; Laothavorn, J.; et al. A comparative study of psychosocial interventions for internet gaming disorder among adolescents aged 13–17 years. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2020, 18, 932–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochuchakkalackal Kuriala, G.; Reyes, M.E.S. Cross-Cultural Efficacy of the Acceptance and Cognitive Restructuring Intervention Program (ACRIP) on the Internet Gaming Disorder Symptoms of Selected Asian Adolescents. Psychol. Stud. 2023, 68, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Kim, H.S. Effects of a prevention program for internet addiction among middle school students in South Korea. Public Health Nurs. 2018, 35, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.; Levin, M.E.; Garland, E.L.; Romanczuk-Seiferth, N. Mindfulness in Treatment Approaches for Addiction—Underlying Mechanisms and Future Directions. Curr. Addict. Rep. 2021, 8, 282–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, A.K.D.; Griffiths, M.D. Problematic Gaming and Students’ Academic Performance: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2024, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, J.M.; Hur, J.O.; Talebloo, J.; Lee, S.; Choi, W.W.; Kim, S.J.; Lavender, J.M.; Moreno, M.A. Problematic Social Media Use Interventions for Mental Health Outcomes in Adolescents. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2025, 27, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Rich, M. Social Media and Adolescent Mental Health. Curr. Pediatr. Rep. 2023, 11, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Wegmann, E.; Stark, R.; Müller, A.; Wölfling, K.; Robbins, T.W.; Potenza, M.N. The interaction of person-affect-cognition-execution (I-PACE) model for addictive behaviors: Update, generalization to addictive behaviors beyond internet-use disorders, and specification of the process character of addictive behaviors. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019, 104, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.L.; Delfabbro, P.H.; Wu, A.M.; Doh, Y.Y.; Kuss, D.J.; Pallesen, S.; Mentzoni, R.; Carragher, N.; Sakuma, H. Treatment of Internet gaming disorder: An international systematic review and CONSORT evaluation. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 54, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Non-Pharmacological Interventions for Problematic Substance Use: A Rapid Overview of Cochrane Systematic Reviews. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11469-023-01090-2 (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Winkler, A.; Dörsing, B.; Rief, W.; Shen, Y.; Glombiewski, J.A. Treatment of internet addiction: A meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2013, 33, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S. CBT-IA: The First Treatment Model for Internet Addiction. J. Cogn. Psychother. 2011, 25, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Increasing Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Conduct Problems in Children and Adolescents: What Can We Learn from Neuroimaging Studies? Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10567-021-00346-4 (accessed on 24 July 2025).
- Shek, D.T.L.; Zhu, X.; Dou, D. Influence of Family Processes on Internet Addiction Among Late Adolescents in Hong Kong. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Yang, N. Digital resilience and technological stress in adolescents: A mixed-methods study of factors and interventions. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 19067–19113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orben, A.; Dienlin, T.; Przybylski, A.K. Social media’s enduring effect on adolescent life satisfaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 116, 10226–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.; Egger, M.; Moher, D. Addressing Reporting Biases. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions: Cochrane Book Series; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 297–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augner, C.; Vlasak, T.; Aichhorn, W.; Barth, A. Tackling the “digital pandemic”: The effectiveness of psychological intervention strategies in problematic Internet and smartphone use—A meta-analysis. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2022, 56, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinauskas, R.; Malinauskiene, V. A meta-analysis of psychological interventions for Internet/smartphone addiction among adolescents. J. Behav. Addict. 2019, 8, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Roz, A.; Castaño, Y.; Krotter, A.; Salazar-Cedillo, A.; Gervilla, E. Emotional dysregulation in relation to substance use and behavioral addictions: Findings from five separate meta-analyses. Int. J. Clin. Health Psychol. 2024, 24, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañas, E.; Estévez, E. Intervention Programs for the Problematic Use of the Internet and Technological Devices: A Systematic Review. Electronics 2021, 10, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Blasco, R.; Latorre-Martínez, M.; Cortés-Pascual, A. Screen addicts: A meta-analysis of internet addiction in adolescence. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2022, 135, 106373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Wiesner, M.; Bühler, K.-M.; López-Moreno, J.A.; López-Salmerón, M.D. Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments for Problematic Use of Internet, Video Games, Social Media and Instant Messaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101598
Pérez-Wiesner M, Bühler K-M, López-Moreno JA, López-Salmerón MD. Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments for Problematic Use of Internet, Video Games, Social Media and Instant Messaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(10):1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101598
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Wiesner, Mateo, Kora-Mareen Bühler, José Antonio López-Moreno, and Maria Dolores López-Salmerón. 2025. "Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments for Problematic Use of Internet, Video Games, Social Media and Instant Messaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 10: 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101598
APA StylePérez-Wiesner, M., Bühler, K.-M., López-Moreno, J. A., & López-Salmerón, M. D. (2025). Effectiveness of Psychological Treatments for Problematic Use of Internet, Video Games, Social Media and Instant Messaging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(10), 1598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101598