The Effects of Eye Exercises on Eye-Hand Coordination, Cognitive Functions and Balance Ability of the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
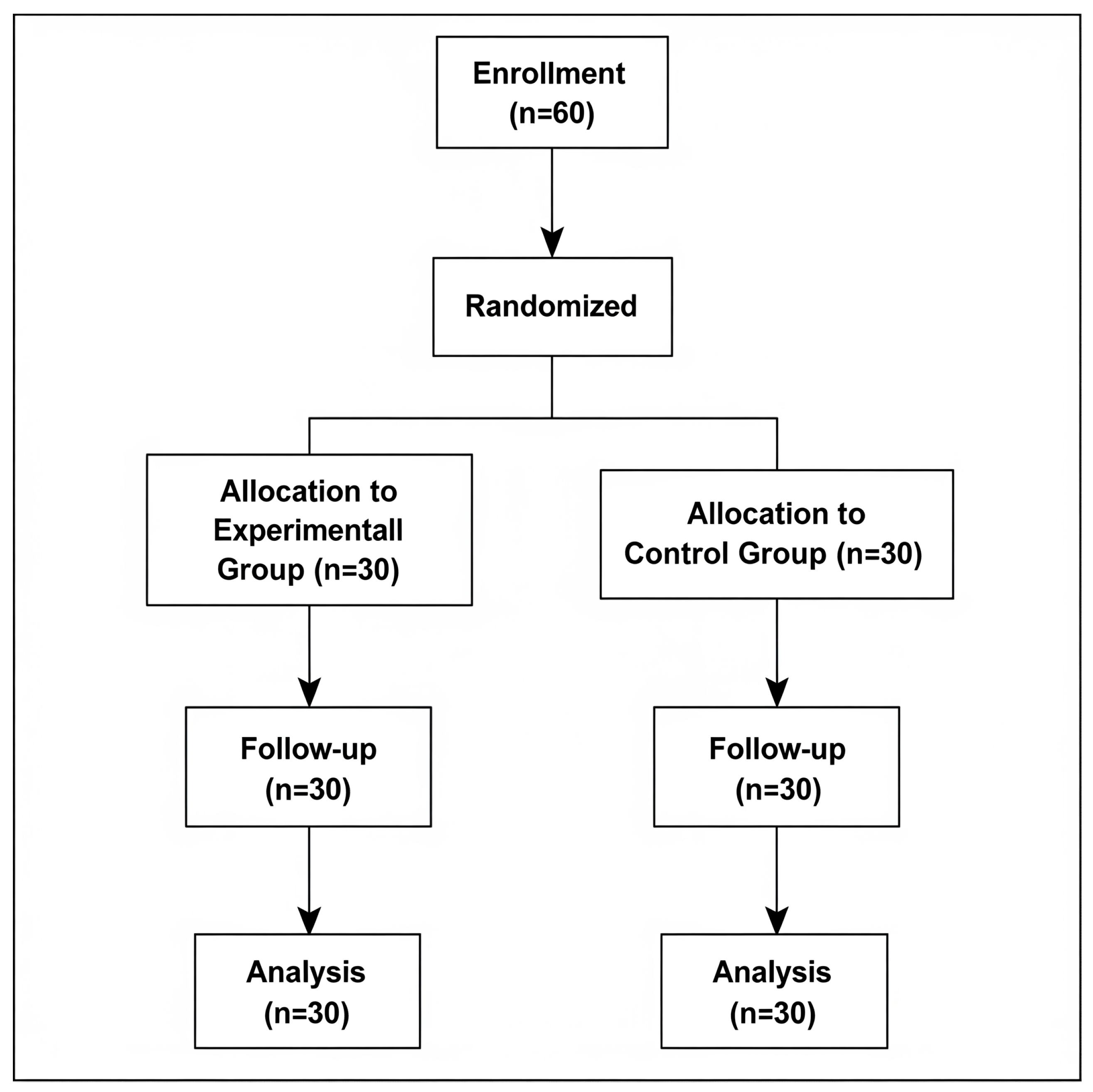
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. GSE Intervention
2.3. Outcome Measures
- (1)
- All assessments were conducted one week before and one week after the four-week training period by a single outcome assessor who was blinded to the participants’ group allocation. O’Connor Finger Dexterity Apparatus Test:
- (2)
- Picture Completion Test (Healy Pictorial Completion Test I (Healy, 1914))
- (3)
- Timed Up and Go (TUG) Test
2.4. Test Procedures and Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GSE | Gaze Stability Exercise |
| TUG | Time up and go test |
| TMSE | Thai Mental State Examination |
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Clinical Consortium on Healthy Ageing: Topic Focus: Frailty and Intrinsic Capacity: Report of Consortium Meeting, 1–2 December 2016 in Geneva, Switzerland (No. WHO/FWC/ALC/17.2); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Beard, J.R.; Officer, A.; de Carvalho, I.A.; Sadana, R.; Pot, A.M.; Michel, J.P.; Lloyd-Sherlock, P.; Epping-Jordan, J.E.; Peeters, G.M.E.E.G.; Mahanani, W.R.; et al. The World report on ageing and health: A policy framework for healthy ageing. Lancet 2016, 387, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anton, S.D.; Woods, A.J.; Ashizawa, T.; Barb, D.; Buford, T.W.; Carter, C.S.; Clark, D.J.; Cohen, R.A.; Corbett, D.B.; Cruz-Almeida, Y.; et al. Successful aging: Advancing the science of physical independence in older adults. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 24 Pt B, 304–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Giovannini, S.; Brau, F.; Galluzzo, V.; Santagada, D.A.; Loreti, C.; Biscotti, L.; Laudisio, A.; Zuccalà, G.; Bernabei, R. Falls among Older Adults: Screening, Identification, Rehabilitation, and Management. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iamtrakul, P.; Chayphong, S.; Jomnonkwao, S.; Ratanavaraha, V. The Association of Falls Risk in Older Adults and Their Living Environment: A Case Study of Rural Area, Thailand. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Ou, X.; Li, J. The risk of falls among the aging population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 902599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moreland, J.D.; Richardson, J.A.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Clase, C.M. Muscle weakness and falls in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Jin, K. Age-Related Dysfunction in Balance: A Comprehensive Review of Causes, Consequences, and Interventions. Aging Dis. 2024, 16, 714–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, Z.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hong, Z.; Ding, D. Sensory impairments and cognitive decline in older adults: A review from a population-based perspective. Aging Health Res. 2021, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segev-Jacubovski, O.; Herman, T.; Yogev-Seligmann, G.; Mirelman, A.; Giladi, N.; Hausdorff, J.M. The interplay between gait, falls and cognition: Can cognitive therapy reduce fall risk? Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 1057–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lord, S.R.; Fitzpatrick, R.C. Choice stepping reaction time: A composite measure of falls risk in older people. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M627–M632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Halewyck, F.; Lavrysen, A.; Levin, O.; Boisgontier, M.P.; Elliott, D.; Helsen, W.F. Both age and physical activity level impact on eye-hand coordination. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2014, 36, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papalia, G.F.; Papalia, R.; Diaz Balzani, L.A.; Torre, G.; Zampogna, B.; Vasta, S.; Fossati, C.; Alifano, A.M.; Denaro, V. The Effects of Physical Exercise on Balance and Prevention of Falls in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.-J.; Meng, Q.; Su, C.-H. Mechanism-Driven Strategies for Reducing Fall Risk in the Elderly: A Multidisciplinary Review of Exercise Interventions. Healthcare 2024, 12, 2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrington, C.; Fairhall, N.; Kwok, W.; Wallbank, G.; Tiedemann, A.; Michaleff, Z.A.; Ng, C.A.C.M.; Bauman, A. Evidence on physical activity and falls prevention for people aged 65+ years: Systematic review to inform the WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, A.; Patti, A.; Bellafiore, M.; Battaglia, G.; Sahin, F.N.; Paoli, A.; Cataldo, M.C.; Mammina, C.; Palma, A. Group fitness activities for the elderly: An innovative approach to reduce falls and injuries. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2014, 26, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira-Machado, L.; Arida, R.M.; Mari, J.J. Dance for neuroplasticity: A descriptive systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 96, 232–240, ISSN 0149-7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, D.; Jahn, K. Gaze stabilisation exercises in vestibular rehabilitation: Review of the evidence and recent clinical advances. J. Neurol. 2019, 266 (Suppl. S1), 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horning, E.; Gorman, S. Vestibular rehabilitation decreases fall risk and improves gaze stability for an older individual with unilateral vestibular hypofunction. J. Geriatr. Phys. Ther. 2007, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.H. The effects of eyeball exercise on balance ability and falls efficacy of the elderly who have experienced a fall: A single-blind, randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2017, 68, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, M.; Lee, E. Effects of gaze stability exercises on cognitive function, dynamic postural ability, balance confidence, and subjective health status in old people with mild cognitive impairment. J. Exerc. Rehabil. 2019, 15, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gosewade, N.B.; Shende, V.S.; Kashalikar, S.J. Effect of Various Eye Exercise Techniques along with Pranayama on Visual Reaction Time: A Case Control Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 1870–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawstron, J.A.; Burley, C.D.; Elder, M.J. A systematic review of the applicability and efficacy of eye exercises. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus. 2005, 42, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Noto, P.; Uta, S.; DeSouza, J.F. Eye exercises enhance accuracy and letter recognition, but not reaction time, in a modified rapid serial visual presentation task. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nimmi, K.P.; Anjupriya, D.; Ahmad, H.A. Comparison of effects of Otago exercise program vs gaze stability exercise on balance and fear of fall in older adults: A randomized trial. Medicine 2024, 103, e38345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosewade, N.B.; Shende, V.S.; Saraf, C.; Drugkar, A. Effect of pranayama and eye exercises on eye to hand coordination: Study by finger dexterity test. J. Evid. Based Med. Healthc. 2015, 2, 7400–7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, H.; Asai, Y.; Johnson, E.; Lohman, E.; Khoo, K.; Mizutani, Y.; Mizutani, T. Effect of oculo-motor and gaze stability exercises on postural stability and dynamic visual acuity in healthy young adults. Gait Posture 2011, 33, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rand, M.K.; Rentsch, S. Eye-hand coordination during visuomotor adaptation: Effects of hemispace and joint coordination. Exp. Brain Res. 2017, 235, 3645–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, K. Training Effects of Eye Movement on Improving Basic Cognitive Ability of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Patients and Normal Aging (NA) People. Int. J. Sci. 2019, 8, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.; Parkin, A.; Dagnall, N. Effects of Saccadic Bilateral Eye Movements on Episodic and Semantic Autobiographical Memory Fluency. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, A.; Parker, A.; Dagnall, N. Effects of saccadic eye movements on episodic & semantic memory fluency in older and younger participants. Memory 2023, 31, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Experimental Group | Control Group | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) Median (IQR) | 62.00 (3.00) | 63.00 (3.00) | 0.097 a |
| Gender (Male: Female) | 7:23 | 13:17 | 0.01 *c |
| Weight (kg) Mean ± SD | 57.66 ± 9.24 | 58.57 ± 7.95 | 0.684 b |
| Height (cm) Median (IQR) | 155.00 (10.00) | 155.00 (15.00) | 0.858 a |
| BMI (kg/m2) Mean ± SD | 23.32 ± 3.12 | 23.95 ± 3.37 | 0.460 b |
| TMSE (score) Mean ± SD | 23.03 ± 2.85 | 22.53 ± 3.39 | 0.539 b |
| Experimental Group | Within-Group p-Value a | Control Group | Within-Group p-Value a | Adjusted Mean Difference [95% CI] b | ANCOVA p-Value | Effect Size (ηp2) c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before | After | Before | After | ||||||
| O’Connor finger dexterity (pins) | 22.5 (9) | 28(11) | 0.004 ** | 21 (11) | 27.5 (9) | 0.005 ** | −0.992 [−3.978, 1.994] | 0.508 | 0.008 |
| Picture completion (pictures) | 2 (3) | 5(1) | 0.005 ** | 2 (2) | 3 (2) | 0.007 ** | 1.005 [0.11, 0.899] | 0.028 * | 0.084 |
| Time up and go test (second) | 8 (2) | 7(1) | 0.017 * | 8 (2) | 8 (2) | 0.706 | −0.850 [−1.421, −0.280] | 0.004 ** | 0.140 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mueangson, O.; Keawmai, W.; Pabbumnan, R.; Chukaithai, A.; Thongdonmuean, P.; Vongvaivanichakul, P. The Effects of Eye Exercises on Eye-Hand Coordination, Cognitive Functions and Balance Ability of the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101564
Mueangson O, Keawmai W, Pabbumnan R, Chukaithai A, Thongdonmuean P, Vongvaivanichakul P. The Effects of Eye Exercises on Eye-Hand Coordination, Cognitive Functions and Balance Ability of the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(10):1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101564
Chicago/Turabian StyleMueangson, Onchuma, Wanchai Keawmai, Radamanee Pabbumnan, Aisada Chukaithai, Ploynapas Thongdonmuean, and Parinya Vongvaivanichakul. 2025. "The Effects of Eye Exercises on Eye-Hand Coordination, Cognitive Functions and Balance Ability of the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 10: 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101564
APA StyleMueangson, O., Keawmai, W., Pabbumnan, R., Chukaithai, A., Thongdonmuean, P., & Vongvaivanichakul, P. (2025). The Effects of Eye Exercises on Eye-Hand Coordination, Cognitive Functions and Balance Ability of the Elderly: A Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(10), 1564. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101564








