Early-Life Exposure to Organic Chemical Pollutants as Assessed in Primary Teeth and Cardiometabolic Risk in Mexican American Children: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Phenotypic Data
2.3. Tooth Preparation
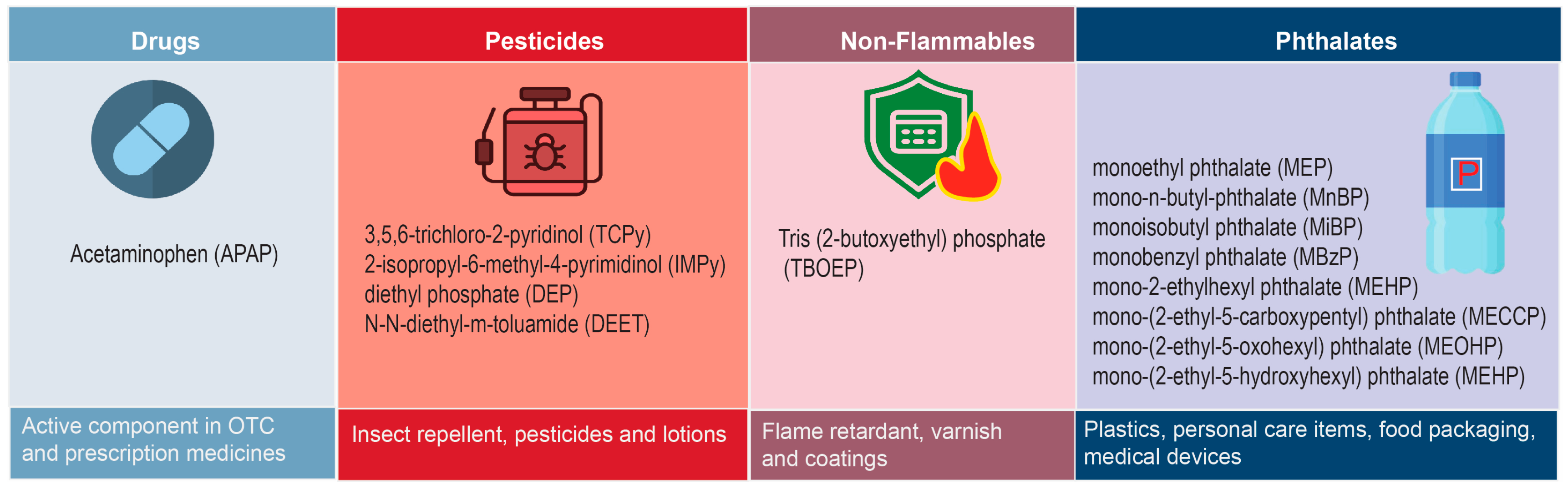
2.4. Extraction and Analysis by Liquid Chromatograpgy-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| APAP | Acetaminophen |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AST/ALT ratio | Aspartate aminotransferase/Alanine aminotransferase ratio |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BPA | Bisphenol A |
| CMTs | Cardiometabolic traits |
| CVD | Cardiovascular diseases |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| DDE | Dichlorodiphenyldichloroethylene |
| DEET | N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide |
| DEP | Diethyl phosphate |
| DL | Detection limit |
| DXA | Dual X-ray Absorptiometry |
| EDC | Endocrine disrupting chemicals |
| FG | Fasting glucose |
| FI | Fasting insulin |
| FM | Fat mass |
| HDL-C | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| HCB | Hexachlorobenzene |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model of assessment-insulin resistance |
| HPLC/MS/MS | High-performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry |
| IMPy | 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinol |
| MAs | Mexican Americans |
| MBzP | Monobenzyl phthalate |
| MECPP | Mono-(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate |
| MEHHP | Mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate |
| MEHP | Mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate |
| MEOHP | Mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate |
| MEP | Monoethyl phthalate |
| MiBP | Monoisobutyl phthalate |
| MnBP | Mono-n-butyl phthalate |
| MS | Metabolic syndrome |
| NR | Not reported |
| OCs | Organic chemicals |
| OTC | Over the counter |
| PCBs | Polychlorinated biphenyls |
| PFAS | Perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances |
| POPs | Persistent organic pollutants |
| SAFARI | San Antonio Family Assessment of Metabolic Risk Indicators in Youth |
| SAFDGS | San Antonio Family Diabetes/Gallbladder Study |
| SAFHS | San Antonio Family Heart Study |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| SPSS | Statistical Package for the Social Sciences |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| TBOEP | Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate |
| TCPy | 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| VAGES | Veterans Administration Genetic Epidemiology Study |
| WC | Waist circumference |
References
- Arisaka, O.; Ichikawa, G.; Koyama, S.; Sairenchi, T. Childhood obesity: Rapid weight gain in early childhood and subsequent cardiometabolic risk. Clin. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2020, 29, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deboer, M.D. Ethnicity, obesity and the metabolic syndrome: Implications on assessing risk and targeting intervention. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Pinot de Moira, A.; Power, C. Predicting cardiovascular disease risk factors in midadulthood from childhood body mass index: Utility of different cutoffs for childhood body mass index. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Fernandez, C.; Bazzano, L.; He, J.; Xue, F.; Chen, W. Long-term Impact of Temporal Sequence from Childhood Obesity to Hyperinsulinemia on Adult Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes: The Bogalusa Heart Study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horesh, A.; Tsur, A.M.; Bardugo, A.; Twig, G. Adolescent and Childhood Obesity and Excess Morbidity and Mortality in Young Adulthood—A Systematic Review. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2021, 10, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, A.C.; Perrin, E.M.; Moss, L.A.; Skelton, J.A. Cardiometabolic Risks and Severity of Obesity in Children and Young Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128.9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyberg, S.T.; Batty, G.D.; Pentti, J.; Virtanen, M.; Alfredsson, L.; Fransson, E.I.; Goldberg, M.; Heikkila, K.; Jokela, M.; Knutsson, A.; et al. Obesity and loss of disease-free years owing to major non-communicable diseases: A multicohort study. Lancet Public Health 2018, 3, e490–e497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.M.; Ekstrom, C.T.; Sorensen, T.I.A. Emergence of the obesity epidemic preceding the presumed obesogenic transformation of the society. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Diabetes, E. Childhood obesity: A growing pandemic. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jebeile, H.; Kelly, A.S.; O’Malley, G.; Baur, L.A. Obesity in children and adolescents: Epidemiology, causes, assessment, and management. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierman, B.; Afful, J.; Carroll, M.D.; Chen, T.C.; Davy, O.; Fink, S.; Fryar, C.D.; Gu, Q.; Hales, C.M.; Hughes, J.P.; et al. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2017–March 2020 Prepandemic Data Files-Development of Files and Prevalence Estimates for Selected Health Outcomes. Natl. Health Stat. Rep. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, N.B.; Baur, L.A.; Felix, J.F.; Hill, A.J.; Marcus, C.; Reinehr, T.; Summerbell, C.; Wabitsch, M. Child and adolescent obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga-Lopez, A.; Pu, Y.; Gingrich, J.; Padmanabhan, V. Obesogenic Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Identifying Knowledge Gaps. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, C. Childhood obesity: Are genetic differences involved? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1494S–1501S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The genetics of obesity: From discovery to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.K. Biological, environmental, and social influences on childhood obesity. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesi, A.; Grant, S.F. The Genetics of Pediatric Obesity. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faienza, M.F.; Wang, D.Q.; Fruhbeck, G.; Garruti, G.; Portincasa, P. The dangerous link between childhood and adulthood predictors of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2016, 11, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G. Rare and common variants: Twenty arguments. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, P.; Barouki, R.; Bellinger, D.C.; Casteleyn, L.; Chadwick, L.H.; Cordier, S.; Etzel, R.A.; Gray, K.A.; Ha, E.H.; Junien, C.; et al. Life-Long Implications of Developmental Exposure to Environmental Stressors: New Perspectives. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3408–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S.; Cox, N.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Hindorff, L.A.; Hunter, D.J.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ramos, E.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Chakravarti, A.; et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009, 461, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, D.L. Childhood Obesity: Influential Factors and Interventions. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2018, 42, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.M.; Beserra, B.T.S.; Silva, N.G.; Lima, C.L.; Rocha, P.R.S.; Coelho, M.S.; Neves, F.A.R.; Amato, A.A. Exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals and anthropometric measures of obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e033509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, K.; Lumeng, C.N. The initiation of metabolic inflammation in childhood obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasande, L.; Cronk, C.; Durkin, M.; Weiss, M.; Schoeller, D.A.; Gall, E.A.; Hewitt, J.B.; Carrel, A.L.; Landrigan, P.J.; Gillman, M.W. Environment and obesity in the National Children’s Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Hong, A.; Yu, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zou, B.; Ji, S.; Zhang, L.; Zou, K.; et al. Traffic-related environmental factors and childhood obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22 (Suppl. 1), e12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillman, M.W.; Ludwig, D.S. How early should obesity prevention start? N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2173–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivert, M.F.; Perng, W.; Watkins, S.M.; Newgard, C.S.; Kenny, L.C.; Kristal, B.S.; Patti, M.E.; Isganaitis, E.; DeMeo, D.L.; Oken, E.; et al. Metabolomics in the developmental origins of obesity and its cardiometabolic consequences. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2015, 6, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Aris, I.M.; Lin, P.D.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Perng, W.; Woo Baidal, J.A.; Wen, D.; Oken, E. Longitudinal associations of modifiable risk factors in the first 1000 days with weight status and metabolic risk in early adolescence. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, L.L.; Ventura, A.K. Preventing childhood obesity: What works? Int. J. Obes. 2009, 33 (Suppl 1), S74–S81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, M.A.; Gluckman, P.D. Early developmental conditioning of later health and disease: Physiology or pathophysiology? Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1027–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A. Developmental and epigenetic pathways to obesity: An evolutionary-developmental perspective. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32 (Suppl 7), S62–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gluckman, P.D.; Hanson, M.A.; Buklijas, T.; Low, F.M.; Beedle, A.S. Epigenetic mechanisms that underpin metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaseth, J.; Javorac, D.; Djordjevic, A.B.; Bulat, Z.; Skalny, A.V.; Zaitseva, I.P.; Aschner, M.; Tinkov, A.A. The Role of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Obesity: A Review of Laboratory and Epidemiological Studies. Toxics 2022, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Qian, H.; Yang, J.; Hu, Y. The exposure to volatile organic chemicals associates positively with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross-sectional study from the NHANES program. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1098683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, J.J.; Alvarez, J.A.; Atlas, E.; Cave, M.C.; Chatzi, V.L.; Collier, D.; Corkey, B.; Fischer, D.; Goran, M.I.; Howard, S.; et al. Obesogens and Obesity: State-of-the-Science and Future Directions Summary from a Healthy Environment and Endocrine Disruptors Strategies Workshop. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 118, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals-Casas, C.; Desvergne, B. Endocrine disruptors: From endocrine to metabolic disruption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011, 73, 135–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals-Casas, C.; Feige, J.N.; Desvergne, B. Interference of pollutants with PPARs: Endocrine disruption meets metabolism. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32 (Suppl 6), S53–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtcamp, W. Obesogens: An environmental link to obesity. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, a62–a68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Merrill, M.; Birnbaum, L.S. Childhood obesity and environmental chemicals. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 2011, 78, 22–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guil-Oumrait, N.; Stratakis, N.; Maitre, L.; Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Urquiza, J.; Fabbri, L.; Basagana, X.; Heude, B.; Haug, L.S.; Sakhi, A.K.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Chemical Mixtures and Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2412040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, R.; Stewart, A.W.; Braithwaite, I.; Beasley, R.; Hancox, R.J.; Mitchell, E.A.; ISAAC Phase Three Study Group. Association between paracetamol use in infancy or childhood with body mass index. Obesity 2015, 23, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, Z.; Nohr, E.A.; Morgen, C.S.; Ernst, A.; Li, J.; Sorensen, T.I.A.; Olsen, J. Prenatal Exposure to Acetaminophen and Overweight in Childhood. Obesity 2019, 27, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrow, P.; Maguire, R.; Murphy, S.K.; Belcher, S.M.; Hoyo, C. Elevated metabolites of acetaminophen in cord blood of children with obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longnecker, M.P.; Michalek, J.E. Serum dioxin level in relation to diabetes mellitus among Air Force veterans with background levels of exposure. Epidemiology 2000, 11, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, I.K.; Porta, M.; Steffes, M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Relationship between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome among non-diabetic adults: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, I.K.; Jin, S.H.; Steffes, M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Association between serum concentrations of persistent organic pollutants and insulin resistance among nondiabetic adults: Results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2002. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.J.; Bhattacharya, J.; Butte, A.J. An Environment-Wide Association Study (EWAS) on type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Peterson, K.E. Maternal Exposure to Synthetic Chemicals and Obesity in the Offspring: Recent Findings. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2015, 2, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafeiadi, M.; Georgiou, V.; Chalkiadaki, G.; Rantakokko, P.; Kiviranta, H.; Karachaliou, M.; Fthenou, E.; Venihaki, M.; Sarri, K.; Vassilaki, M.; et al. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Persistent Organic Pollutants with Obesity and Cardiometabolic Traits in Early Childhood: The Rhea Mother-Child Cohort (Crete, Greece). Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vafeiadi, M.; Myridakis, A.; Roumeliotaki, T.; Margetaki, K.; Chalkiadaki, G.; Dermitzaki, E.; Venihaki, M.; Sarri, K.; Vassilaki, M.; Leventakou, V.; et al. Association of Early Life Exposure to Phthalates with Obesity and Cardiometabolic Traits in Childhood: Sex Specific Associations. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtveld, K.; Thomas, K.; Tulve, N.S. Chemical and non-chemical stressors affecting childhood obesity: A systematic scoping review. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Roig, M.D.; Pascal, R.; Cahuana, M.J.; Garcia-Algar, O.; Sebastiani, G.; Andreu-Fernandez, V.; Martinez, L.; Rodriguez, G.; Iglesia, I.; Ortiz-Arrabal, O.; et al. Environmental Exposure during Pregnancy: Influence on Prenatal Development and Early Life: A Comprehensive Review. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2021, 48, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heindel, J.J.; Howard, S.; Agay-Shay, K.; Arrebola, J.P.; Audouze, K.; Babin, P.J.; Barouki, R.; Bansal, A.; Blanc, E.; Cave, M.C.; et al. Obesity II: Establishing causal links between chemical exposures and obesity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 199, 115015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andra, S.S.; Austin, C.; Arora, M. Tooth matrix analysis for biomonitoring of organic chemical exposure: Current status, challenges, and opportunities. Environ. Res. 2015, 142, 387–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Austin, C. Teeth as a biomarker of past chemical exposure. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2013, 25, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charisiadis, P.; Andrianou, X.D.; van der Meer, T.P.; den Dunnen, W.F.A.; Swaab, D.F.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.R.; Makris, K.C.; van Vliet-Ostaptchouk, J.V. Possible Obesogenic Effects of Bisphenols Accumulation in the Human Brain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Lee, H.K.; Kong, A.P.S.; Lim, L.L.; Cai, Z.; Chung, A.C.K. Early-life exposure to endocrine disrupting chemicals associates with childhood obesity. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 23, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; Cena, H.; Loperfido, F.; Rossi, V.; Grazi, R.; Quatrale, A.; De Giuseppe, R.; Manuelli, M.; Zuccotti, G. Evaluating Phthalates and Bisphenol in Foods: Risks for Precocious Puberty and Early-Onset Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaskulak, M.; Zimowska, M.; Rolbiecka, M.; Zorena, K. Understanding the role of endocrine disrupting chemicals as environmental obesogens in the obesity epidemic: A comprehensive overview of epidemiological studies between 2014 and 2024. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 299, 118401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camann, D.E.; Schultz, S.T.; Yau, A.Y.; Heilbrun, L.P.; Zuniga, M.M.; Palmer, R.F.; Miller, C.S. Acetaminophen, pesticide, and diethylhexyl phthalate metabolites, anandamide, and fatty acids in deciduous molars: Potential biomarkers of perinatal exposure. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.F.; Heilbrun, L.; Camann, D.; Yau, A.; Schultz, S.; Elisco, V.; Tapia, B.; Garza, N.; Miller, C. Organic Compounds Detected in Deciduous Teeth: A Replication Study from Children with Autism in Two Samples. J. Environ. Public Health 2015, 2015, 862414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, S.P.; Puppala, S.; Arya, R.; Chittoor, G.; Farook, V.S.; Schneider, J.; Resendez, R.G.; Upadhayay, R.P.; Vandeberg, J.; Hunt, K.J.; et al. Genetic epidemiology of cardiometabolic risk factors and their clustering patterns in Mexican American children and adolescents: The SAFARI Study. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1059–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.D.; Kammerer, C.M.; Blangero, J.; Mahaney, M.C.; Rainwater, D.L.; Dyke, B.; Hixson, J.E.; Henkel, R.D.; Sharp, R.M.; Comuzzie, A.G.; et al. Genetic and environmental contributions to cardiovascular risk factors in Mexican Americans. The San Antonio Family Heart Study. Circulation 1996, 94, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppala, S.; Dodd, G.D.; Fowler, S.; Arya, R.; Schneider, J.; Farook, V.S.; Granato, R.; Dyer, T.D.; Almasy, L.; Jenkinson, C.P.; et al. A genomewide search finds major susceptibility loci for gallbladder disease on chromosome 1 in Mexican Americans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, D.K.; Schneider, J.; Hu, S.L.; Dyer, T.D.; Puppala, S.; Farook, V.S.; Arya, R.; Lehman, D.M.; Blangero, J.; DeFronzo, R.A.; et al. Genome-wide linkage scan for genes influencing plasma triglyceride levels in the Veterans Administration Genetic Epidemiology Study. Diabetes 2009, 58, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sly, P.; Blake, T.; Islam, Z. Impact of prenatal and early life environmental exposures on normal human development. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 40, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.; Bauer, J.A.; Austin, C.; Downs, T.J.; Tripodis, Y.; Heiger-Bernays, W.; White, R.F.; Arora, M.; Claus Henn, B. Multiple metals in children’s deciduous teeth: Results from a community-initiated pilot study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2022, 32, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahata, M.C.; Powell, D.A.; Durrell, D.E.; Miller, M.A. Acetaminophen accumulation in pediatric patients after repeated therapeutic doses. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1984, 27, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgman, M.J.; Garrard, A.R. A review of acetaminophen poisoning. Crit. Care Clin. 2012, 28, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Huo, Y.; Yin, S.; Hu, H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, L.J.; Tong, M.J.; Busuttil, R.W.; Hiatt, J.R. Acetaminophen hepatotoxicity and acute liver failure. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ni, J.; Chen, L. Advances in the study of acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1239395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlak, J.; Chatterji, B.; Londhe, K.B.; Watkins, P.B. Serum acute phase reactants hallmark healthy individuals at risk for acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Shah, Y.M.; Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Serum metabolomics reveals irreversible inhibition of fatty acid beta-oxidation through the suppression of PPARalpha activation as a contributing mechanism of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadas, S.; Aslan, M.; Gonullu, H.; Kati, C.; Duran, L.; Olmez, S.; Kucukoglu, M.E.; Demir, H. Acetaminophen intoxication is associated with decreased serum paraoxonase and arylesterase activities and increased lipid hydroperoxide levels. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manka, P.; Olliges, V.; Bechmann, L.P.; Schlattjan, M.; Jochum, C.; Treckmann, J.W.; Saner, F.H.; Gerken, G.; Syn, W.K.; Canbay, A. Low levels of blood lipids are associated with etiology and lethal outcome in acute liver failure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, Z.; Ritz, B.; Virk, J.; Olsen, J. Maternal use of acetaminophen during pregnancy and risk of autism spectrum disorders in childhood: A Danish national birth cohort study. Autism Res. 2016, 9, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, Z.; Ritz, B.; Rebordosa, C.; Lee, P.C.; Olsen, J. Acetaminophen use during pregnancy, behavioral problems, and hyperkinetic disorders. JAMA Pediatr. 2014, 168, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sordillo, J.E.; Scirica, C.V.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Gillman, M.W.; Bunyavanich, S.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Weiss, S.T.; Gold, D.R.; Litonjua, A.A. Prenatal and infant exposure to acetaminophen and ibuprofen and the risk for wheeze and asthma in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeli, S. Central and peripheral cannabinoid receptors as therapeutic targets in the control of food intake and body weight. In Appetite Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 357–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, P.; Thomsen, C.; Casas, M.; de Bont, J.; Haug, L.S.; Maitre, L.; Papadopoulou, E.; Sakhi, A.K.; Slama, R.; Saulnier, P.J.; et al. Socioeconomic position and exposure to multiple environmental chemical contaminants in six European mother-child cohorts. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milosevic, N.; Milic, N.; Zivanovic Bosic, D.; Bajkin, I.; Percic, I.; Abenavoli, L.; Medic Stojanoska, M. Potential influence of the phthalates on normal liver function and cardiometabolic risk in males. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 190, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, P.M.; Zethelius, B.; Lind, L. Circulating levels of phthalate metabolites are associated with prevalent diabetes in the elderly. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perng, W.; Watkins, D.J.; Cantoral, A.; Mercado-Garcia, A.; Meeker, J.D.; Tellez-Rojo, M.M.; Peterson, K.E. Exposure to phthalates is associated with lipid profile in peripubertal Mexican youth. Environ. Res. 2017, 154, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.M.; Ebrahimpour, K.; Parastar, S.; Shoshtari-Yeganeh, B.; Hashemi, M.; Mansourian, M.; Poursafa, P.; Fallah, Z.; Rafiei, N.; Kelishadi, R. Association of urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites with cardiometabolic risk factors and obesity in children and adolescents. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasande, L.; Spanier, A.J.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Attina, T.M.; Blustein, J. Urinary phthalates and increased insulin resistance in adolescents. Pediatrics 2013, 132, e646–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariana, M.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Soares, A.M.; Cairrao, E. Phthalates’ exposure leads to an increasing concern on cardiovascular health. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.Q.; Karvonen-Gutierrez, C.A.; Herman, W.H.; Mukherjee, B.; Park, S.K. Phthalate exposure is associated with more rapid body fat gain in midlife women: The Study of Women’s Health Across the Nation (SWAN) Multi-Pollutant Study. Environ. Res. 2023, 216, 114685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.; Zhao, C.Y.; Na, X.L.; Zhang, Y.B. Association between phthalate exposure and obesity risk: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 102, 104240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, M.C.; Murray, H.E.; Scinicariello, F. Age and sex differences in childhood and adulthood obesity association with phthalates: Analyses of NHANES 2007-2010. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2014, 217, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, K.G.; Berger, K.; Rauch, S.; Kogut, K.; Claus Henn, B.; Calafat, A.M.; Huen, K.; Eskenazi, B.; Holland, N. Association of prenatal urinary phthalate metabolite concentrations and childhood BMI and obesity. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.J.; Ferguson, P.L.; Bloom, M.S.; Neelon, B.; Pearce, J.; Commodore, S.; Newman, R.B.; Roberts, J.R.; Bain, L.; Baldwin, W.; et al. Phthalate and phthalate replacement concentrations in relationship to adiposity in a multi-racial cohort of children. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupsco, A.; Wu, H.; Calafat, A.M.; Kioumourtzoglou, M.A.; Cantoral, A.; Tamayo-Ortiz, M.; Pantic, I.; Pizano-Zarate, M.L.; Oken, E.; Braun, J.M.; et al. Prenatal maternal phthalate exposures and trajectories of childhood adiposity from four to twelve years. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahlhut, R.W.; van Wijngaarden, E.; Dye, T.D.; Cook, S.; Swan, S.H. Concentrations of urinary phthalate metabolites are associated with increased waist circumference and insulin resistance in adult U.S. males. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzel, T.M.; Kuiper, J.R.; Wang, X.; Mueller, N.T.; Calafat, A.M.; Cecil, K.M.; Chen, A.; Lanphear, B.P.; Yolton, K.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; et al. Associations of early life phthalate exposures with adolescent lipid levels and insulin resistance: The HOME Study. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2023, 248, 114102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Lee, H.A.; Park, B.; Park, B.; Hong, Y.S.; Ha, E.H.; Park, H. Associations of phthalate exposure with lipid levels and insulin sensitivity index in children: A prospective cohort study. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.C.V.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Sol, C.M.; El Marroun, H.; Martinez-Moral, M.P.; Kannan, K.; Trasande, L.; Santos, S. Phthalate and Bisphenol Urinary Concentrations, Body Fat Measures, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Dutch School-Age Children. Obesity 2021, 29, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.; Lee, J.; Cho, G.; Choi, S.; Choi, G.; Kim, S.Y.; Eun, S.H.; Suh, E.; Kim, S.K.; et al. Association of diethylhexyl phthalate with obesity-related markers and body mass change from birth to 3 months of age. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2016, 70, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasande, L.; Attina, T.M. Association of exposure to di-2-ethylhexylphthalate replacements with increased blood pressure in children and adolescents. Hypertension 2015, 66, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Chen, D.Y.; Yin, J.W.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, J.Q.; Lu, S.Y.; Li, H.H.; Wen, Y.; Wu, Y. Phthalate exposure linked to high blood pressure in Chinese children. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Lou, C.; Jing, X.; Ding, S.; Hong, H.; Ding, G.; Shen, L. Phthalate exposure and blood pressure in U.S. children aged 8–17 years (NHANES 2013–2018). Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvergne, B.; Feige, J.N.; Casals-Casas, C. PPAR-mediated activity of phthalates: A link to the obesity epidemic? Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, C.H.; Waxman, D.J. Activation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma by environmental phthalate monoesters. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 74, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxvig, C.; Dreisig, K.; Boberg, J.; Nellemann, C.; Schelde, A.B.; Pedersen, D.; Boergesen, M.; Mandrup, S.; Vinggaard, A.M. Differential effects of environmental chemicals and food contaminants on adipogenesis, biomarker release and PPARgamma activation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 361, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepsen, K.F.; Abildtrup, A.; Larsen, S.T. Monophthalates promote IL-6 and IL-8 production in the human epithelial cell line A549. Toxicol. In Vitro 2004, 18, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasande, L.; Sathyanarayana, S.; Trachtman, H. Dietary phthalates and low-grade albuminuria in US children and adolescents. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouki, R.; Gluckman, P.D.; Grandjean, P.; Hanson, M.; Heindel, J.J. Developmental origins of non-communicable disease: Implications for research and public health. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sol, C.M.; Delgado, G.; Kannan, K.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Trasande, L.; Santos, S. Fetal exposure to phthalates and body mass index from infancy to adolescence. The Generation R study. Environ. Res. 2025, 274, 121253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable * | N | Mean ± SD or % |
|---|---|---|
| Girls | 25 | 56 |
| Age (years) | 25 | 10.48 ± 3.61 |
| Body mass index [BMI] (kg/m2) | 25 | 22.36 ± 6.62 |
| Waist circumference [WC] (mm) | 24 | 750.69 ± 190.44 |
| Systolic blood Pressure [SBP] (mmHg) | 25 | 103.04 ± 6.07 |
| Diastolic blood pressure [BP] (mmHg) | 25 | 62.56 ± 4.85 |
| HDL cholesterol [HDL-C] (mg/dL) | 24 | 45.63 ± 5.91 |
| Triglycerides [TG] (mg/dL) | 23 | 69.91 ± 20.07 |
| Fasting glucose [FG] (mg/dL) | 25 | 88.69 ± 7.29 |
| Fasting insulin [FI] (µIU/mL) | 24 | 13.57 ± 6.98 |
| Fat mass [FM] (kg) | 25 | 11.02 ± 15.36 |
| HOMA-IR | 24 | 1.96 ± 0.95 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase [AST] (unit/L) | 24 | 24.00 ± 6.40 |
| Alanine aminotransferase [ALT] (unit/L) | 24 | 16.99 ± 8.18 |
| AST/ALT ratio | 24 | 2.17 ± 2.21 |
| Analyte | DL @ | Detections | Concentration (ng/g) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ng/g | No. @ | % | Median | 75th %ile @ | Max. @ | |
| Acetaminophen (APAP) | 1 | 9 | 36 | 1.7 | 9.6 | |
| 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol (TCPy) | 1 | 6 | 24 | 0.8 | 62.2 | |
| 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinol (IMPy) # | 1 | 2 # | 8 | 5 | ||
| Diethyl phosphate (DEP) | 5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) *# | 17 | 24 # | 100 | 45 | 289 | 946 |
| Tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate (TBOEP) *# | 3 | 2 # | 12 | 71.5 | ||
| Monoethyl phthalate (MEP) *# | 1200 | 4 # | 100 & | 4000 | ||
| Mono-n-butyl phthalate (MnBP) * | 26 | 25 | 100 | 715 | 1670 | 19,700 |
| Monoisobutyl phthalate (MiBP) * | 13 | 25 | 100 | 186 | 622 | 5680 |
| Monobenzyl phthalate (MBzP) | 5 | 1 | 4 | 26 | ||
| Mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate (MEHP) *# | 12 | 21 # | 100 | 158 | 799 | 2610 |
| Mono-(2-ethyl-5-carboxypentyl) phthalate (MECPP) | 5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Mono-(2-ethyl-5-oxohexyl) phthalate (MEOHP) | 5 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Mono-(2-ethyl-5-hydroxyhexyl) phthalate (MEHHP) | 5 | 1 | 4 | 30.5 | ||
| Variable # | FM | HDL-C | TG | SBP | DBP | FI | HOMA-IR | AST | ALT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APAP | 0.278 | −0.518 | 0.399 | 0.342 | 0.197 | 0.279 | 0.301 | 0.376 | 0.471 |
| (0.179) | (0.009) | (0.059) | (0.940) | (0.345) | (0.187) | (0.154) | (0.07) | (0.02) | |
| DEET & | 0.149 | −0.059 | 0.010 | 0.114 | −0.127 | 0.181 | 0.215 | −0.152 | 0.035 |
| (0.476) | (0.786) | (0.964) | (0.586) | (0.546) | (0.396) | (0.312) | (0.479) | (0.872) | |
| MnBP | −0.212 | 0.025 | 0.072 | −0.428 | −0.537 | −0.161 | −0.183 | −0.002 | −0.199 |
| (0.308) | (0.908) | (0.745) | (0.033) | (0.006) | (0.453) | (0.393) | (0.993) | (0.350) | |
| MiBP | 0.496 | −0.092 | −0.285 | 0.030 | −0.037 | 0.594 | 0.56 | −0.012 | 0.227 |
| (0.012) | (0.669) | (0.188) | (0.887) | (0.862) | 0.002 | 0.004 | (0.957) | (0.287) | |
| MEHP | 0.174 | 0.115 | −0.485 | −0.120 | −0.212 | 0.209 | 0.195 | −0.194 | 0.075 |
| (0.405) | (0.593) | (0.019) | (0.569) | (0.310) | (0.326) | (0.361) | 0.363 | (0.726) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farook, V.S.; Akhtar, F.; Arya, R.; Yau, A.; Mummidi, S.; Lopez-Alvarenga, J.C.; Diaz-Badillo, A.; Resendez, R.; Fowler, S.P.; Kulkarni, H.; et al. Early-Life Exposure to Organic Chemical Pollutants as Assessed in Primary Teeth and Cardiometabolic Risk in Mexican American Children: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101494
Farook VS, Akhtar F, Arya R, Yau A, Mummidi S, Lopez-Alvarenga JC, Diaz-Badillo A, Resendez R, Fowler SP, Kulkarni H, et al. Early-Life Exposure to Organic Chemical Pollutants as Assessed in Primary Teeth and Cardiometabolic Risk in Mexican American Children: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(10):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101494
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarook, Vidya S., Feroz Akhtar, Rector Arya, Alice Yau, Srinivas Mummidi, Juan C. Lopez-Alvarenga, Alvaro Diaz-Badillo, Roy Resendez, Sharon P. Fowler, Hemant Kulkarni, and et al. 2025. "Early-Life Exposure to Organic Chemical Pollutants as Assessed in Primary Teeth and Cardiometabolic Risk in Mexican American Children: A Pilot Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 10: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101494
APA StyleFarook, V. S., Akhtar, F., Arya, R., Yau, A., Mummidi, S., Lopez-Alvarenga, J. C., Diaz-Badillo, A., Resendez, R., Fowler, S. P., Kulkarni, H., Golla, V., Choudhury, M., Lynch, J. L., Lehman, D. M., Hale, D. E., DeFronzo, R. A., Blangero, J., Camann, D. E., Duggirala, R., & Challa, S. N. (2025). Early-Life Exposure to Organic Chemical Pollutants as Assessed in Primary Teeth and Cardiometabolic Risk in Mexican American Children: A Pilot Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(10), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22101494









