The Unseen Aftermath: Associations Between the COVID-19 Pandemic and Shifts in Mortality Trends in Japan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Statistical Analysis
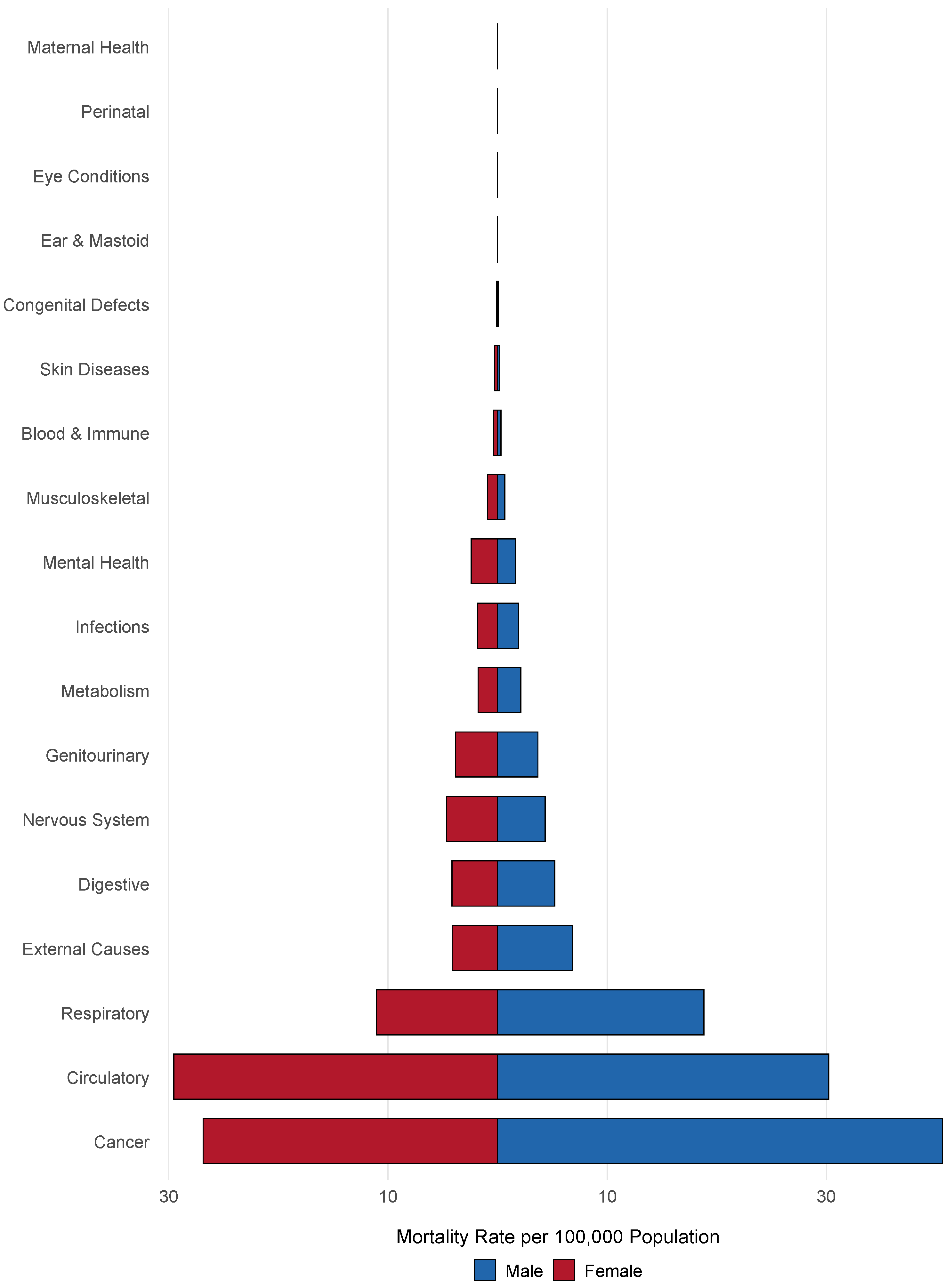
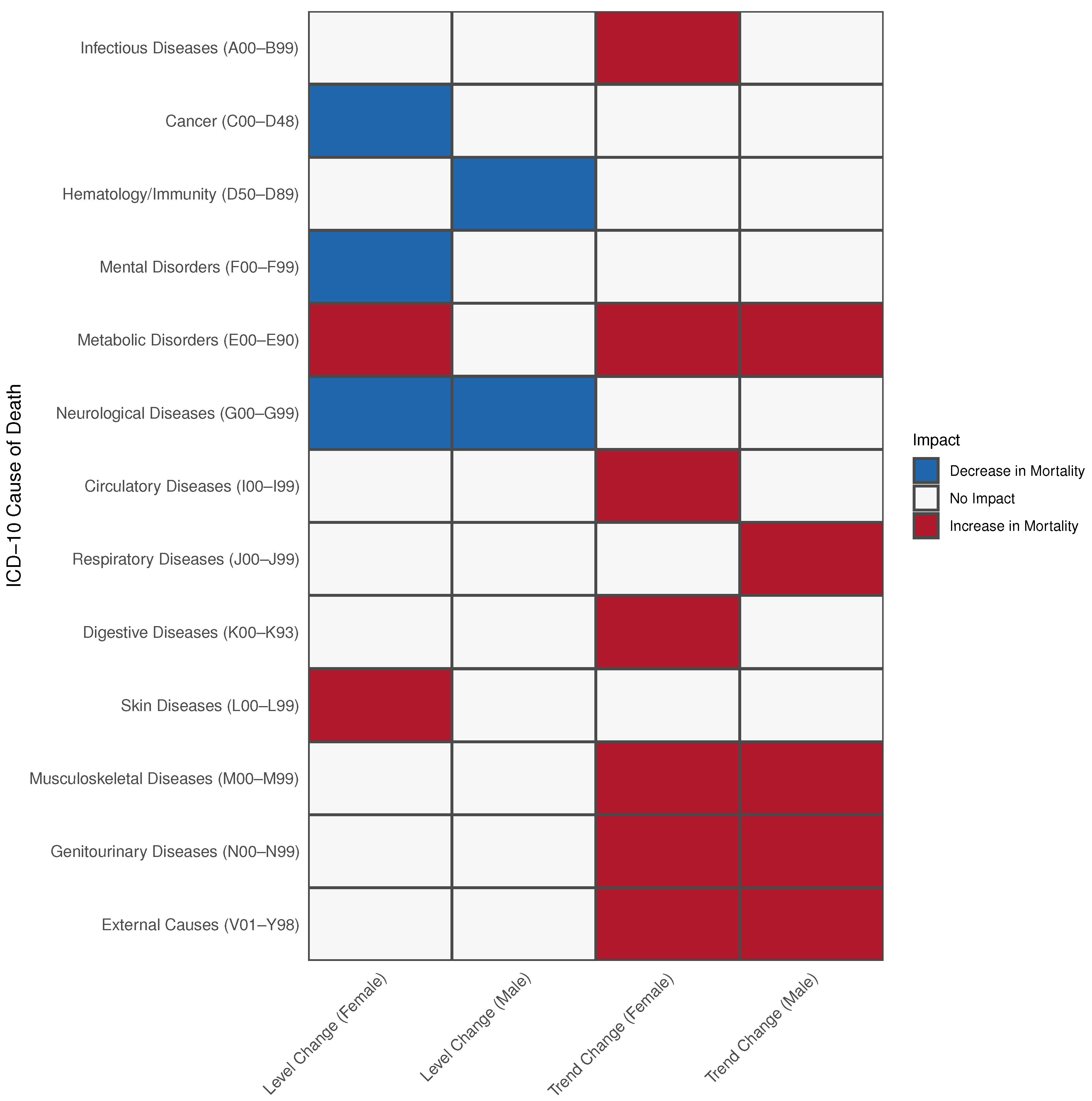
3. Results
3.1. Mortality Modelling
3.2. Diseases of the Endocrine System (E00–E89)
3.3. Diseases of the Circulatory System (I00–I99)
3.4. Diseases of the Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue (L00–L99)
3.5. Diseases of the Genitourinary System (N00–N99)
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease of 2019 |
| ICD-10 | International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision |
| MHLW | Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare |
| NCDs | Non-Communicable Diseases |
| PHCs | Public Health Centers |
| IRR | Incidence Rate Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
References
- Onyeaka, H.; Anumudu, C.K.; Al-Sharify, Z.T.; Egele-Godswill, E.; Mbaegbu, P. COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of the Global Lockdown and Its Far-Reaching Effects. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 00368504211019854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsenault, C.; Gage, A.; Kim, M.K.; Kapoor, N.R.; Akweongo, P.; Amponsah, F.; Aryal, A.; Asai, D.; Awoonor-Williams, J.K.; Ayele, W.; et al. COVID-19 and Resilience of Healthcare Systems in Ten Countries. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Hospital and Outpatient Clinician Workforce: Challenges and Policy Responses. Available online: https://aspe.hhs.gov/reports/covid-19-health-care-workforce (accessed on 23 November 2023).
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Postacute Sequelae of COVID-19 at 2 Years. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2347–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunniff, L.; Alyanak, E.; Fix, A.; Novak, M.; Peterson, M.; Mevis, K.; Eiden, A.L.; Bhatti, A. The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Vaccination Uptake in the United States and Strategies to Recover and Improve Vaccination Rates: A Review. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2023, 19, 2246502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, N.; Saunders, H.; Rudowitz, R. The Implications of COVID-19 for Mental Health and Substance Use. Kais. Fam. Found. 2023, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kadomatsu, N. Legal Countermeasures against COVID-19 in Japan: Effectiveness and Limits of Non-Coercive Measures. China-EU Law J. 2022, 8, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan’s COVID-19 Measures: Controlling the Spread Without Lockdowns. Available online: https://www.nippon.com/en/in-depth/d00592/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Japan: COVID-19 Vaccination Rate 2023. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1239927/japan-covid-19-vaccination-rate/ (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Hamaguchi, R.; Negishi, K.; Higuchi, M.; Funato, M.; Kim, J.-H.; Bitton, A. A Regionalized Public Health Model To Combat COVID-19: Lessons from Japan. Health Aff. Forefr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Bureau Population Estimates. Available online: https://www.e-stat.go.jp/en/statistics/00200524 (accessed on 27 November 2023).
- Fragala, M.S.; Shiffman, D.; Birse, C.E. Population Health Screenings for the Prevention of Chronic Disease Progression. Am. J. Manag. Care 2019, 25, 548–553. [Google Scholar]
- Splinter, M.J.; Velek, P.; Ikram, M.K.; Kieboom, B.C.T.; Peeters, R.P.; Bindels, P.J.E.; Ikram, M.A.; Wolters, F.J.; Leening, M.J.G.; de Schepper, E.I.T.; et al. Prevalence and Determinants of Healthcare Avoidance during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Population-Based Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fueled by COVID-19 Fears, Approximately Half of Hispanics and Black Americans Would Fear Going to the Hospital If Experiencing Symptoms of a Heart Attack or Stroke. Available online: http://newsroom.heart.org/news/fueled-by-covid-19-fears-approximately-half-of-hispanics-and-black-americans-would-fear-going-to-the-hospital-if-experiencing-symptoms-of-a-heart-attack-or-stroke (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Crane, M.A.; Lam, A.; Ekanayake, E.; Alshawkani, Y.Y.; Christmas, C.; Gemmill, A.; Romley, J.A. Mortality Due to Hyperglycemic Crises in the US, 1999–2022. JAMA 2024, 331, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, N.; Hinohara, Y.; Tomita, K.; Hamajima, N. Structure and Roles of Public Health Centers (Hokenjo) in Japan. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2011, 73, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zintel, S.; Flock, C.; Arbogast, A.L.; Forster, A.; von Wagner, C.; Sieverding, M. Gender Differences in the Intention to Get Vaccinated against COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Public Health 2023, 31, 1303–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Bowe, B.; Xie, Y. Long COVID after Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yoshida, Y.; Ma, K.S.-K.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F.; Lee, C.-C. Gender Differences in Health Protective Behaviours and Its Implications for COVID-19 Pandemic in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesca, L.; Conversano, E.; Vianello, F.A.; Martelli, L.; Gualeni, C.; Bassani, F.; Brugnara, M.; Rubin, G.; Parolin, M.; Anselmi, M.; et al. How Covid-19 Changed the Epidemiology of Febrile Urinary Tract Infections in Children in the Emergency Department during the First Outbreak. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Xu, E.; Al-Aly, Z. Kidney Outcomes in Long COVID. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2851–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, P.; Kupferwasser, D.; Flores, E.A.; Tran, D.P.; Ortega, A.; Miller, L.G. Skin and Soft Tissue Infection Incidence before and during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Epidemiol. Infect. 2023, 151, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Managing the Surge: Delayed Chronic Wound Care During COVID-19. Available online: https://www.ajmc.com/view/managing-the-surge-delayed-chronic-wound-care-during-covid-19 (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Markovskaya, Y.; Gavioli, E.M.; Cusumano, J.A.; Glatt, A.E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Secondary Bacterial Infections and the Impact on Antimicrobial Resistance during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Antimicrob. Steward. Healthc. Epidemiol. 2022, 2, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pira, A.; Sinagra, J.L.M.; Moro, F.; Mariotti, F.; Di Zenzo, G. Autoimmune Bullous Diseases during COVID-19 Pandemic: 2022 Update on Rituximab and Vaccine. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1112823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Gasparini, G.; Cozzani, E.; D’Agostino, F.; Parodi, A. Absolving COVID-19 Vaccination of Autoimmune Bullous Disease Onset. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 834316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan COVID-Coronavirus Statistics-Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/country/japan/ (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Ayoubkhani, D.; Khunti, K.; Nafilyan, V.; Maddox, T.M.; Humberstone, B.; Diamond, I.; Banerjee, A. Post-Covid Syndrome in Individuals Admitted to Hospital with Covid-19: Retrospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2021, 372, n693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Chapter | Block | Title | Included | Abbreviated Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | A00–B99 | Certain infectious and parasitic diseases | Yes | Infectious Diseases |
| II | C00–D48 | Neoplasms | Yes | Cancer |
| III | D50–D89 | Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism | Yes | Hematology/Immunity |
| IV | E00–E90 | Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases | Yes | Metabolic Disorders |
| V | F00–F99 | Mental and behavioural disorders | Yes | Mental Disorders |
| VI | G00–G99 | Diseases of the nervous system | Yes | Neurological Diseases |
| VII | H00–H59 | Diseases of the eye and adnexa | No | — |
| VIII | H60–H95 | Diseases of the ear and mastoid process | No | — |
| IX | I00–I99 | Diseases of the circulatory system | Yes | Circulatory Diseases |
| X | J00–J99 | Diseases of the respiratory system | Yes | Respiratory Diseases |
| XI | K00–K93 | Diseases of the digestive system | Yes | Digestive Diseases |
| XII | L00–L99 | Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue | Yes | Skin Diseases |
| XIII | M00–M99 | Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue | Yes | Musculoskeletal Diseases |
| XIV | N00–N99 | Diseases of the genitourinary system | Yes | Genitourinary Diseases |
| XV | O00–O99 | Pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium | Yes | Maternal Health |
| XVI | P00–P96 | Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period | No | — |
| XVII | Q00–Q99 | Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities | Yes | Congenital Defects |
| XVIII | R00–R99 | Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified | No | Clinical Findings |
| XIX | S00–T98 | Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes | Yes | External Causes |
| XX | V01–Y98 | External causes of morbidity and mortality | Yes | External Causes |
| XXI | Z00–Z99 | Factors influencing health status and contact with health services | No | — |
| XXII | U00–U99 | Codes for special purposes | No | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jamil, H.; Nomura, S.; Gilmour, S. The Unseen Aftermath: Associations Between the COVID-19 Pandemic and Shifts in Mortality Trends in Japan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2025, 22, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22010074
Jamil H, Nomura S, Gilmour S. The Unseen Aftermath: Associations Between the COVID-19 Pandemic and Shifts in Mortality Trends in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2025; 22(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22010074
Chicago/Turabian StyleJamil, Hasan, Shuhei Nomura, and Stuart Gilmour. 2025. "The Unseen Aftermath: Associations Between the COVID-19 Pandemic and Shifts in Mortality Trends in Japan" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 22, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22010074
APA StyleJamil, H., Nomura, S., & Gilmour, S. (2025). The Unseen Aftermath: Associations Between the COVID-19 Pandemic and Shifts in Mortality Trends in Japan. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 22(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph22010074







