Surfing Alone: From Internet Addiction to the Era of Smartphone Dependence
1. Introduction
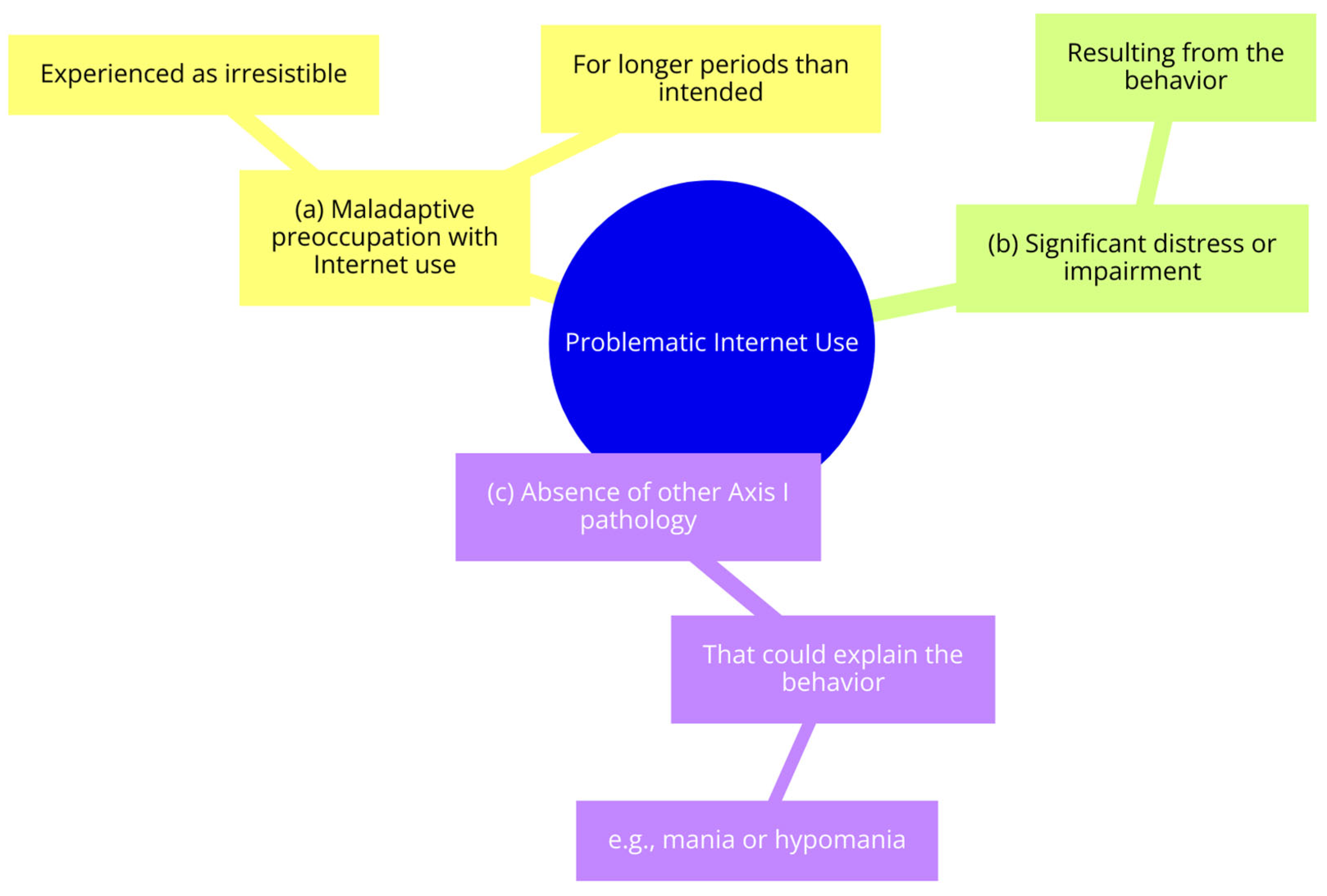
- (a)
- Maladaptive preoccupation with Internet use, experienced as irresistible for longer periods than intended;
- (b)
- Significant distress or impairment resulting from the behavior;
- (c)
- The absence of other Axis I pathology that could explain the behavior, such as mania or hypomania [4].
2. A Multicomponent Model of Problematic Internet Use
3. The Problematic Use of the Internet: A Primary or Secondary Disorder?
4. Dependency, Isolation, and Loneliness: A Clinical Perspective
5. From Internet Addiction to Smartphone Addiction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, K.S. Caught in the Net: How to Recognize the Signs of Internet Addiction and a Winning Strategy for Recovery; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, R. A cognitive-behavioral model of pathological Internet use. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2001, 17, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, N.A.; Goldsmith, T.D.; Keck, P.E.; Khosla, U.M.; McElroy, S.L. Psychiatric features of individuals with problematic internet use. J. Affect. Disord. 2000, 57, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapira, N.A.; Lessig, M.C.; Goldsmith, T.D.; Szabo, S.T.; Lazoritz, M.; Gold, M.S.; Stein, D.J. Problematic internet use: Proposed classification and diagnostic criteria. Depress. Anxiety 2003, 17, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joinson, A.N. Looking at, looking up or keeping up with people? Motives and use of Facebook. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Florence, Italy, 5–10 April 2008; pp. 1027–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Formica, I.; Rizzo, A.; Conti, F. Facebook o Faceboom? Una Ricerca Esplorativa. Psychomedia. 2011. Available online: http://www.psychomedia.it/pm/telecomm/massmedia/formica-rizzo-conti.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Cantelmi, T.; Talli, M. Anatomia di un problema. Una review sui fenomeni psicopatologici Internet correlati. Psicotech 2007, 2, 7–31. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, P.L. Reality in Cyberspace: Analysands’ Use of the Internet and Ordinary Everyday Psychosis. Psychoanal. Rev. 2007, 94, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, V.A.; Dean, D.J.; Pelletier, A. Internet addiction, reality substitution and longitudinal changes in psychotic-like experiences in young adults. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2013, 7, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Della Villa, L.; Crisi, A. Can the Problematic Internet Use evolve in a pre-psychotic state? A single case study with the Wartegg. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 51, 532–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, A.; Wretschko, G.; Fridjhon, P. Online flow experiences, problematic Internet use and Internet procrastination. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2008, 24, 2236–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, G.; Catalano, M.C.; Embi, C.S.; Frankel, R.L. Delusions about the Internet. South. Med. J. Birm. Alabama 1999, 92, 609–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crisi, A. The Wartegg Drawing Completion Test: A new methodology. In Drawings in Assessment and Psychotherapy; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 168–183. [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths, M. Does Internet and Computer “Addiction” Exist? Some Case Study Evidence. CyberPsychology Behav. 2000, 3, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, H.J.; Hall, M.N.; Bilt, J.V. “Computer addiction”: A critical consideration. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2000, 70, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellowlees, P.M.; Marks, S. Problematic Internet use or Internet addiction? Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pies, R. Should DSM-V Designate “Internet Addiction” a Mental Disorder? Psychiatry 2009, 6, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caplan, S.; Williams, D.; Yee, N. Problematic Internet use and psychosocial well-being among MMO players. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2009, 25, 1312–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.D.; Hunt, N. Dependence on Computer Games by Adolescents. Psychol. Rep. 1998, 82, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, C.N.; Lavin, M.J. Internet Dependence in the Collegiate Population: The Role of Shyness. CyberPsychology Behav. 2004, 7, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, S.-K.; Wang, C.-C.; Fang, W. Physical Interpersonal Relationships and Social Anxiety among Online Game Players. CyberPsychology Behav. 2005, 8, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Eijnden, R.J.J.M.; Meerkerk, G.-J.; Vermulst, A.A.; Spijkerman, R.; Engels, R.C.M.E. Online communication, compulsive internet use, and psychosocial well-being among adolescents: A longitudinal study. Dev. Psychol. 2008, 44, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, D.; Peplau, L.A. Toward a social psychology of loneliness. Pers. Relatsh. 1981, 3, 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Qualter, P.; Vanhalst, J.; Harris, R.; Van Roekel, E.; Lodder, G.; Bangee, M.; Maes, M.; Verhagen, M. Loneliness across the life span. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2015, 10, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barari, S.; Caria, S.; Davola, A.; Falco, P.; Fetzer, T.; Fiorin, S.; Hensel, L.; Ivchenko, A.; Jachimowicz, J.; King, G.; et al. Evaluating COVID-19 public health messaging in Italy: Self-reported compliance and growing mental health concerns. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Parmigiani, B.; Amerio, A.; Aguglia, A.; Sher, L.; Amore, M. The psychological impact of COVID-19 on the mental health in the general population. QJM Int. J. Med. 2020, 113, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, W. Parental technoference and smartphone addiction in Chinese adolescents: The mediating role of social sensitivity and loneliness. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020, 118, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, J.; Band, R.; Kinsella, K.; Cheetham-Blake, T.; James, E.; Ewings, S.; Rogers, A. Optimising and profiling pre-implementation contexts to create and implement a public health network intervention for tackling loneliness. Implement. Sci. 2020, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgilés, M.; Espada, J.P.; Delvecchio, E.; Francisco, R.; Mazzeschi, C.; Pedro, M.; Morales, A. Anxiety and depressive symptoms in children and adolescents during covid-19 pandemic: A transcultural approach. Psicothema 2021, 33, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blakemore, S.-J.; Mills, K.L. Is Adolescence a Sensitive Period for Sociocultural Processing? Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2014, 65, 187–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, W.A.; Laursen, B. Parent-adolescent relationships and influences. Handb. Adolesc. Psychol. 2004, 2, 331–362. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, K.; Hards, E.; Moltrecht, B.; Reynolds, S.; Shum, A.; McElroy, E.; Loades, M. Loneliness, social relationships, and mental health in adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 289, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauman, Z. Liquid Modernity; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Chiang, C.-L.; Lin, P.-H.; Chang, L.-R.; Ko, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lin, S.-H. Proposed Diagnostic Criteria for Smartphone Addiction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Manap, A.; Rizzo, A.; Yıldırmaz, A.; Dilekçi, Ü.; Yıldırım, M. The Mediating Role of Procrastination in the Relationship between Fear of Missing Out and Internet Addiction in University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; La Rosa, V.L.; Commodari, E.; Alparone, D.; Crescenzo, P.; Yıldırım, M.; Chirico, F. Wanna Bet? Investigating the Factors Related to Adolescent and Young Adult Gambling. Eur. J. Investig. Heal. Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Princiotta, E.; Iuele, G. Exploring the Link between Smartphone Use, Recorded Violence, and Social Sharing in 80 Case Studies in Italy. Psych 2023, 5, 1241–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağış, Z.G.; Öztekin, G.G.; Aziz, I.A.; Chirico, F.; Rizzo, A.; Yıldırım, M. Meaning in Life and Loneliness as Mediators between COVID-19 Anxiety and Life Satisfaction in the Post-Pandemic among the General Population in Turkey: A Serial Mediation Model. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ. 2023, 13, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar]
- Khabbache, H.; Cherqui, A.; Ouazizi, K.; Ait, D.; Bahramizadeh, M.Y.; Bragazzi, N.L.; Nucera, G.; Szarpak, L.; Rizzo, A.; Chirico, F. The contribution of subjective wellbeing to the improvement of the academic performance of university students through time management as a mediator factor: A structural equation modeling. J. Health Soc. Sci. 2023, 8, 308–322. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, A.; Chaoyun, L. How young adults imagine their future? The role of temperamental traits. Eur. J. Futur. Res. 2017, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnay, J.; Billieux, J.; Blairy, S.; Larøi, F. Which psychological factors influence Internet addiction? Evidence through an integrative model. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 43, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, C.-H.; Yen, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, K.; Yen, C.-F. Tridimensional Personality of Adolescents with Internet Addiction and Substance Use Experience. Can. J. Psychiatry 2006, 51, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-K.; Davis, K.E. Toward a comprehensive theory of problematic Internet use: Evaluating the role of self-esteem, anxiety, flow, and the self-rated importance of Internet activities. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2009, 25, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Yuen, K.S.L.; Li, W.O. A basic need theory approach to problematic Internet use and the mediating effect of psychological distress. Front. Psychol. 2015, 5, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, A.; Munnukka, J.; Scimone, S.; Benedetto, L.; Ingrassia, M. Influencer Credibility: A Model of Personality Traits in Predicting Followers’ Behavior. Qeios 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraut, R.; Patterson, M.; Lundmark, V.; Kiesler, S.; Mukophadhyay, T.; Scherlis, W. Internet paradox: A social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological well-being? Am. Psychol. 1998, 53, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzo, A.; Alparone, D. Surfing Alone: From Internet Addiction to the Era of Smartphone Dependence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040436
Rizzo A, Alparone D. Surfing Alone: From Internet Addiction to the Era of Smartphone Dependence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2024; 21(4):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040436
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzo, Amelia, and Dario Alparone. 2024. "Surfing Alone: From Internet Addiction to the Era of Smartphone Dependence" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 21, no. 4: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040436
APA StyleRizzo, A., & Alparone, D. (2024). Surfing Alone: From Internet Addiction to the Era of Smartphone Dependence. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 21(4), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21040436





