Early Warning Systems for Emerging Profiles of Antimicrobial Resistance in Italy: A National Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
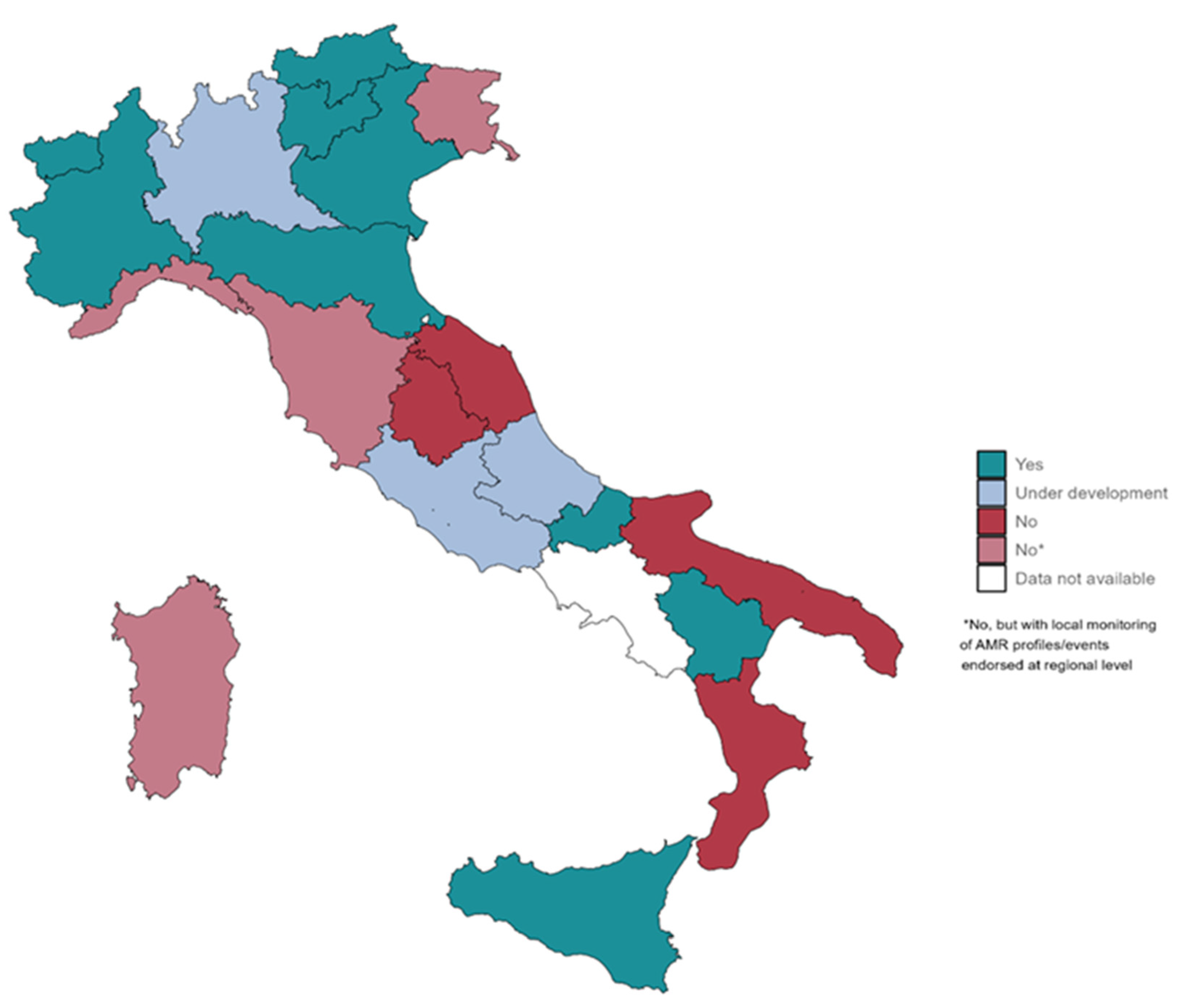
3.1. Mapping Early Warning Systems at Regional Level
3.2. Key Characteristics of Existing Regional Early Warning Systems
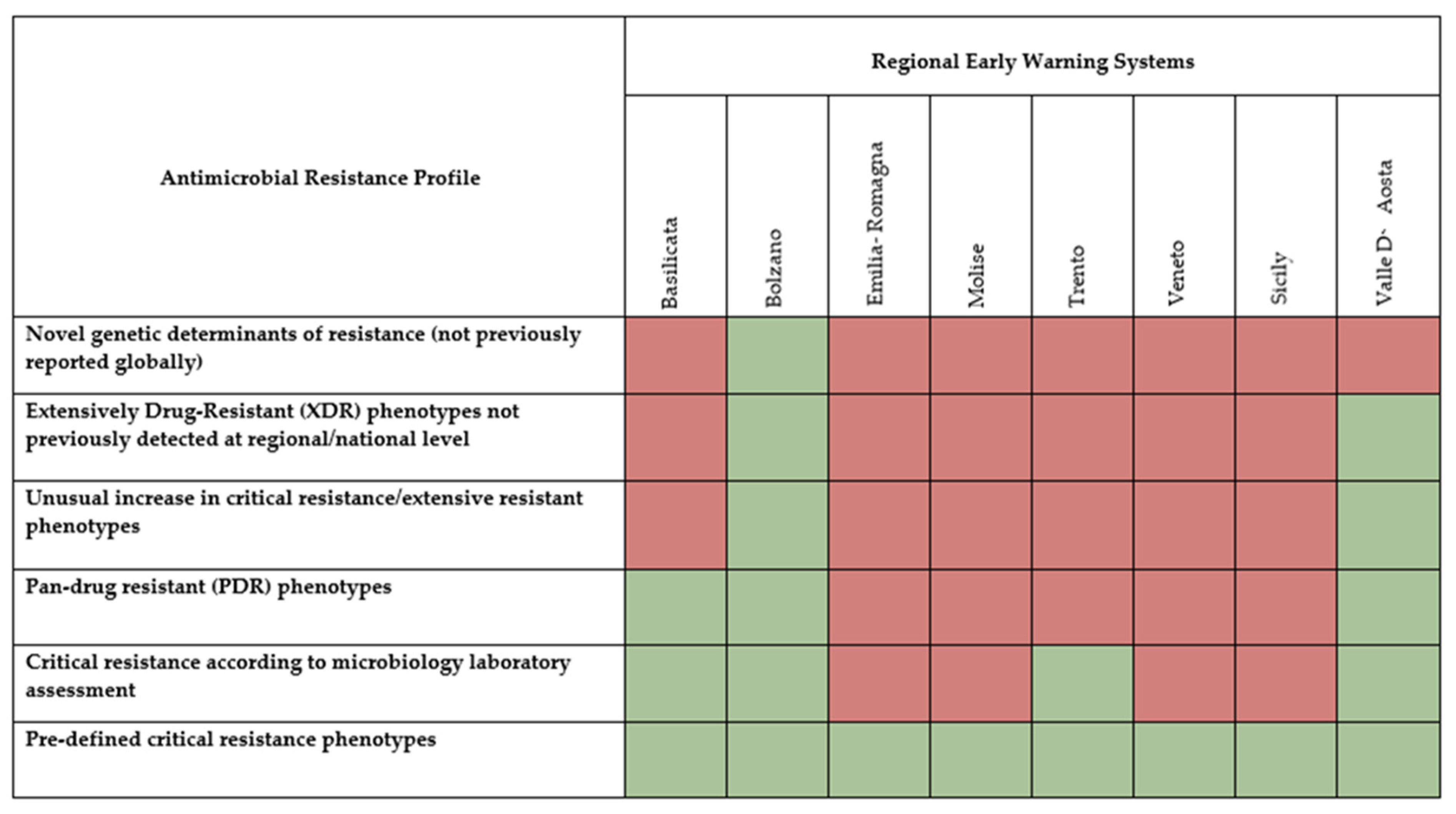
3.2.1. Microorganisms’ Critical Resistance Phenotypes
3.2.2. Specimen Collection and Reporting
3.2.3. Post-Reporting Actions
3.2.4. Availability of Formalized Laboratories Network
3.3. Barriers and Facilitators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable Deaths and Disability-Adjusted Life-Years Caused by Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A Population-Level Modelling Analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and European Centre of Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Antimicrobial Resistance. Tackling the Burden in the European Union; OECD: Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Antimicrobial Resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net)-Annual Epidemiological Report. 2019. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/surveillance-antimicrobial-resistance-europe-2019 (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) Data from the ECDC Surveillance Atlas—Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/antimicrobial-resistance/surveillance-and-disease-data/data-ecdc (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Assessing the Health Burden of Infections with Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in the EU/EEA, 2016–2020; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ministero della Salute. Piano Nazionale Di Contrasto Dell’Antimicrobico-Resistenza (PNCAR) 2017–2020. Rome, Italy. 2017. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_2660_allegato.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- European Commission (EC). A European One Health Action Plan against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR). EC. 2017. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2020-01/amr_2017_action-plan_0.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Bellino, S.; Iacchini, S.; Monaco, M.; Del Grosso, M.; Camilli, R.; Errico, G.; Giufrè, M.; Sisi, S.; D’ancona, F.; Pantosti, A.; et al. AR-ISS: Sorveglianza Nazionale Dell’Antibiotico-Resistenza. Dati 2020; Rapporti ISS Sorveglianza RIS-1/2021; Istituto Superiore di Sanità: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- EpiCentro—Epidemiology for Public Health. Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/en/antimicrobial-resistance/about (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Saltman, R.B.; Bankauskaite, V.; Vrangbaek, K. (Eds.) European Observatory on Health Systems and Policies Decentralization in Health Care: Strategies and Outcomes; McGraw-Hill, Open University Press: England, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ministero della Salute. Piano Nazionale Di Contrasto All’Antimicrobico-Resistenza (PNCAR) 2022–2025. Rome, Italy. 2022. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_3294_allegato.pdf (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Emerging Antimicrobial Resistance Reporting: Guide for Emerging AMR Event Sharing; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Regional Office for Europe Global Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (GLASS): Technical Meeting on the Early Implementation Phase; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global Antimicrobial Resistance and Use Surveillance System (GLASS). Available online: https://www.who.int/initiatives/glass (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- World Health Organization (WHO). Report of the 2nd Meeting of the Global AMR Surveillance System (GLASS) Collaborative Platform; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, C.M.; de Kraker, M.E.A.; Harbarth, S. Surveillance of Resistance to New Antibiotics in an Era of Limited Treatment Options. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Access, Watch, Reserve (AWaRe) Classification of Antibiotics for Evaluation and Monitoring of Use, 2021; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/2021-aware-classification (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- The Medicines Utilisation Monitoring Centre. National Report on Antibiotics Use in Italy. Year 2021; Italian Medicines Agency: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, F. How Health Care Regionalisation in Italy Is Widening the North-South Gap. Health Econ. Policy Law 2014, 9, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Sweden. Swedish Work on Containment of Antibiotic Resistance. In Tools, Methods and Experiences; Public Health Agency of Sweden: Solna, Sweden, 2014; ISBN 978-91-7603-011-0. (accessed on 13 November 2022). [Google Scholar]
- Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. AURA 2021: Fourth Australian Report on Antimicrobial Use and Resistance in Human Health; Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care: Sidney, Australia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tacconelli, E.; Sifakis, F.; Harbarth, S.; Schrijver, R.; van Mourik, M.; Voss, A.; Sharland, M.; Rajendran, N.B.; Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Bielicki, J.; et al. Surveillance for Control of Antimicrobial Resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e99–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, M.L.; Atti, M.C.; D’Amore, C.; Diegoli, G.; Forni, S.; Gagliotti, C.; Gemmi, F.; Iannazzo, S.; Miraglia, V.; Pan, A.; et al. Good Practices for the Surveillance and Control of Antimicrobial Resistance. Epidemiol. Prev. 2019, 43, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charani, E.; Mendelson, M.; Pallett, S.J.C.; Ahmad, R.; Mpundu, M.; Mbamalu, O.; Bonaconsa, C.; Nampoothiri, V.; Singh, S.; Peiffer-Smadja, N.; et al. An Analysis of Existing National Action Plans for Antimicrobial Resistance-Gaps and Opportunities in Strategies Optimising Antibiotic Use in Human Populations. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e466–e474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). European Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Surveillance Network (EURGen-Net). Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/about-us/who-we-work/disease-and-laboratory-networks/EURGen-net (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- EURGen-RefLabCap Project—Technical University of Denmark (DTU)—Statens Serum Institut (SSI). Available online: https://www.eurgen-reflabcap.eu/ (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) Strategy on Antimicrobials 2021–2025. 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/veterinary-regulatory/overview/antimicrobial-resistance/cvmp-strategy-antimicrobials-2021-2025 (accessed on 13 April 2023).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). ECDC Public Health Microbiology Strategy 2018–2022; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antimicrobial Resistance. Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]

| Specimen Collection Setting | Reporting | Reporting Origin | Reporting Target | Timing | Regional IT Platform | Pre-Defined Reporting | Actions | EWS Performance Measurement | Data Quality Monitoring | Formalized RL Network | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basilicata | HB | PB | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | 72 h | No | No | NA | No | No | NA |
| Bolzano A.P. | HB LTCF CB | WB Other methods | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | 24 h | No | Yes | IPC measures | No | No | Yes |
| Emilia-Romagna | HB LTCF CB | WB | Risk manager | Prevention department | 24 h | Yes | Yes | NA | No | No | No |
| Molise | HB | Other methods | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | Results validation | No | No | IPC measures | No | Yes | Yes |
| Piedmont | HB LTCF CB | WB PB Other methods | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | Real-time | No | No | IPC measures | No | Yes | In progress |
| Sicily | HB | WB | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | 48 h | Yes | Yes | IPC measures | No | No | Yes |
| Trento A.P. | HB LTCF | WB PB Other methods | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | Results validation | Yes | Yes | IPC measures | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Valle D’Aosta | HB LTCF CB | WB Other methods | Clinical microbiologist | Health directorate | Real-time | No | No | IPC measures | No | No | No |
| Veneto | HB | Other methods | Risk manager | Clinical risk department | Monthly | No | Yes | NA | No | No | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iera, J.; Seghieri, C.; Tavoschi, L.; Isonne, C.; Baccolini, V.; Petrone, D.; Agodi, A.; Barchitta, M.; Arnoldo, L.; Creti, R.; et al. Early Warning Systems for Emerging Profiles of Antimicrobial Resistance in Italy: A National Survey. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20095623
Iera J, Seghieri C, Tavoschi L, Isonne C, Baccolini V, Petrone D, Agodi A, Barchitta M, Arnoldo L, Creti R, et al. Early Warning Systems for Emerging Profiles of Antimicrobial Resistance in Italy: A National Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(9):5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20095623
Chicago/Turabian StyleIera, Jessica, Chiara Seghieri, Lara Tavoschi, Claudia Isonne, Valentina Baccolini, Daniele Petrone, Antonella Agodi, Martina Barchitta, Luca Arnoldo, Roberta Creti, and et al. 2023. "Early Warning Systems for Emerging Profiles of Antimicrobial Resistance in Italy: A National Survey" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 9: 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20095623
APA StyleIera, J., Seghieri, C., Tavoschi, L., Isonne, C., Baccolini, V., Petrone, D., Agodi, A., Barchitta, M., Arnoldo, L., Creti, R., Forni, S., Raglio, A., Ricchizzi, E., Bandini, L., Grossi, A., & D’Ancona, F. (2023). Early Warning Systems for Emerging Profiles of Antimicrobial Resistance in Italy: A National Survey. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(9), 5623. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20095623







