The Role of Cognition and Social Factors in Competition: How Do People with Intellectual Disabilities Respond to Opponents?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
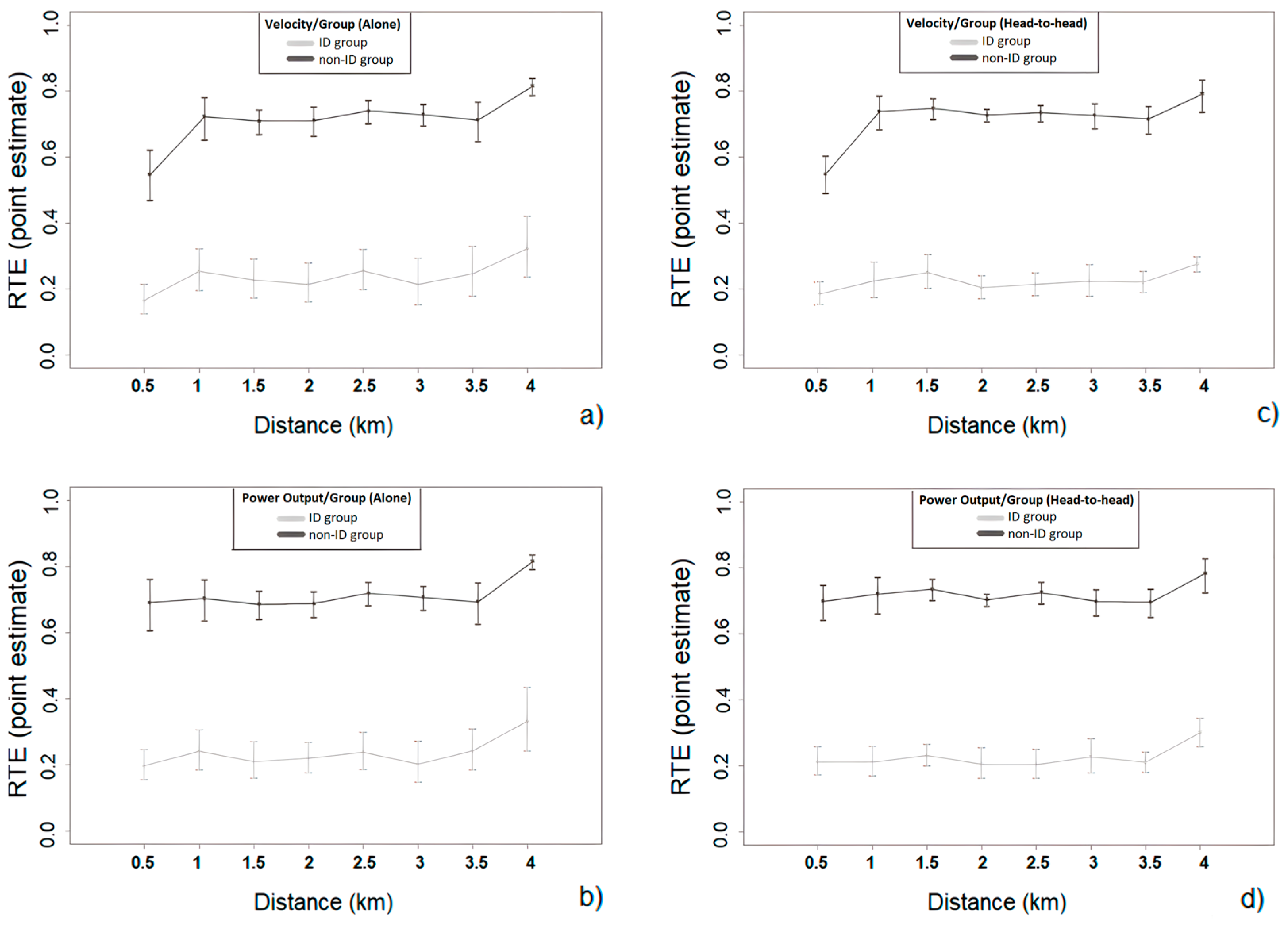
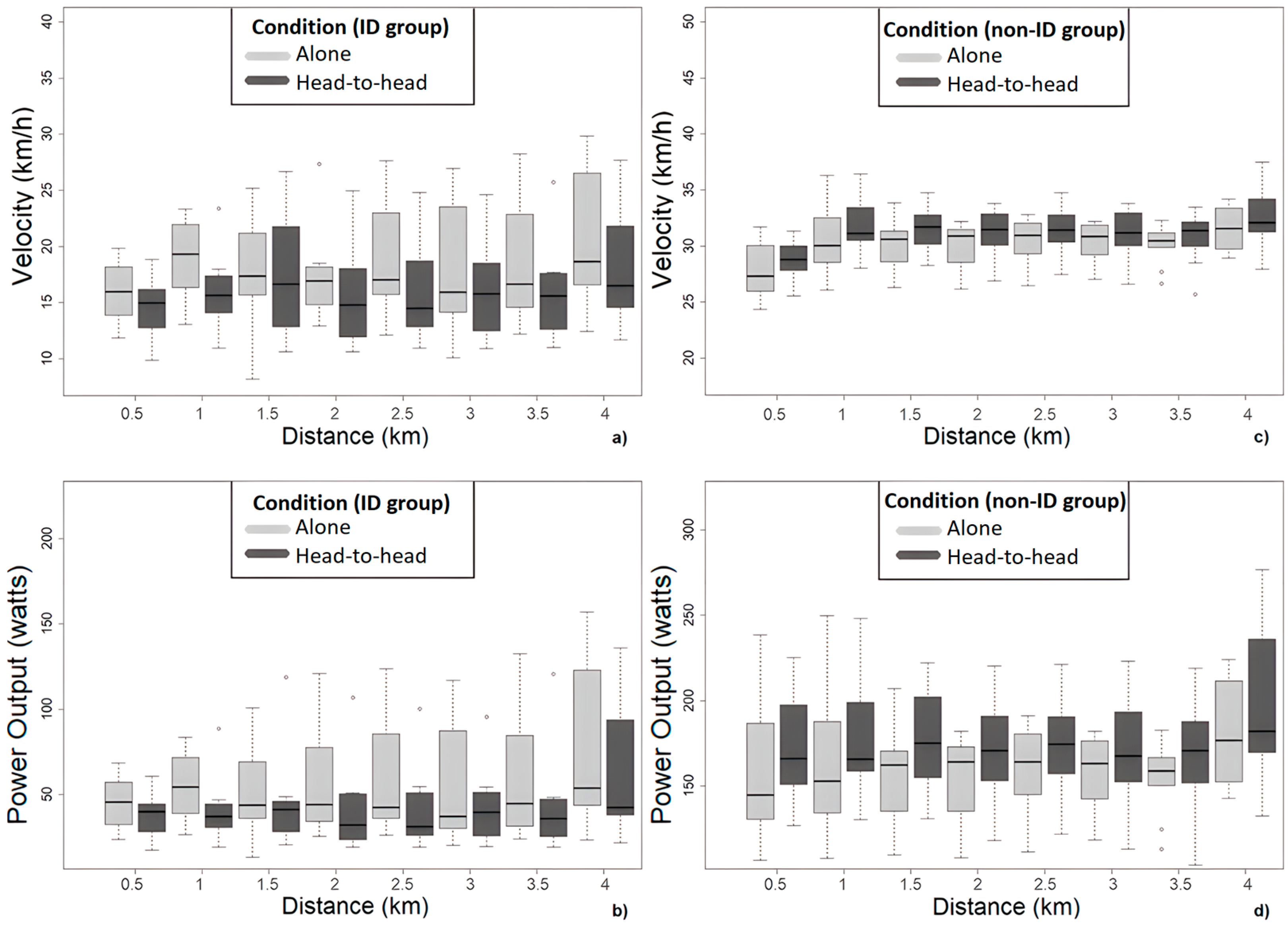
3.1. Pacing and Performance Differences between Groups (ID and Non-ID Group in Each Condition; Aim 1)
3.2. Pacing and Performance Differences between Conditions (‘Alone’ and ‘Head-to-Head’; Aim 2)
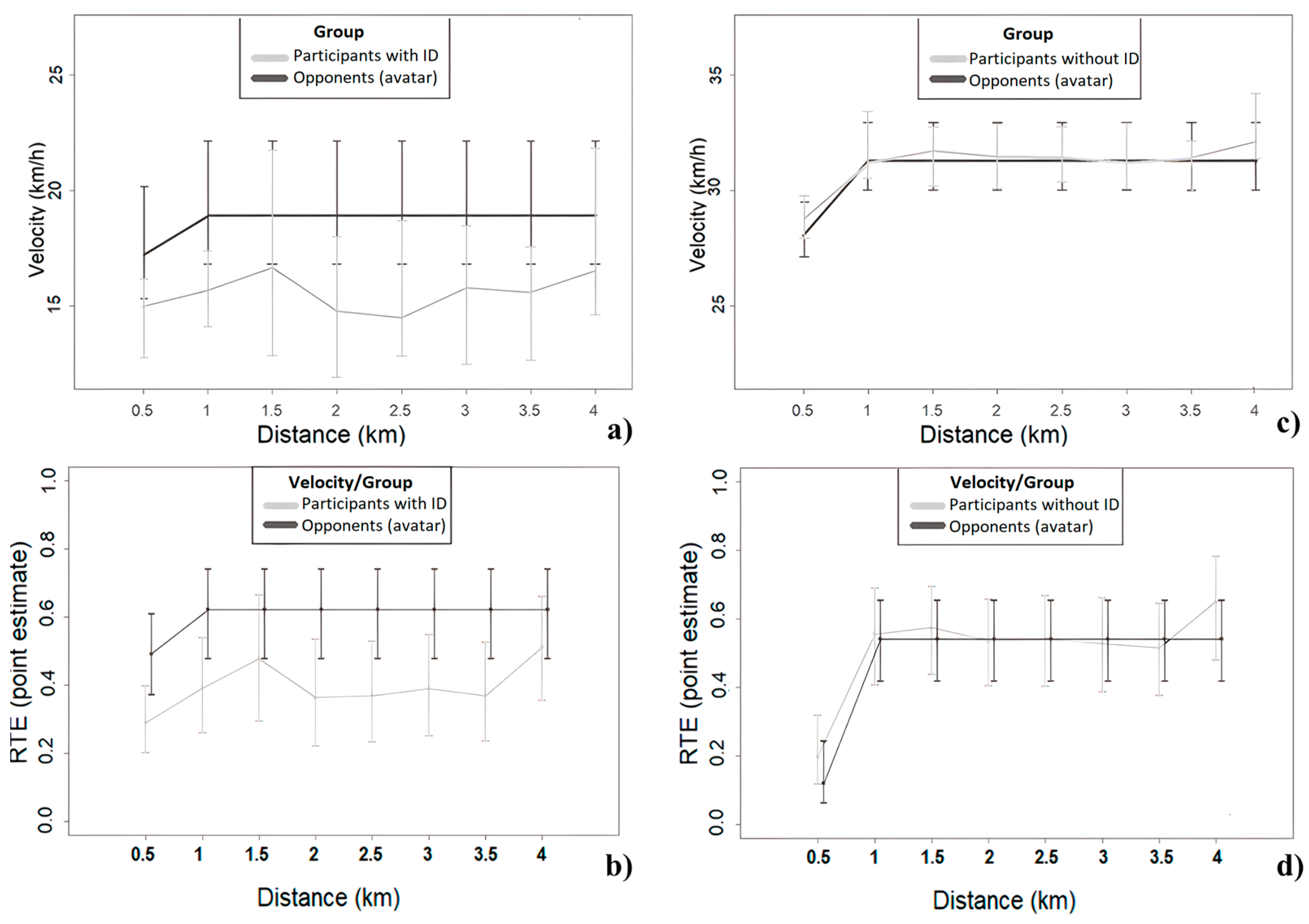
3.3. Pacing and Performance Differences between Participants with and without ID and Their Virtual Opponents (‘Head-to-Head’ Condition)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakalidis, K.E.; Fadeeva, A.; Hettinga, F.J.; Ling, F. The role of the social environment in sports participation of athletes with Intellectual Impairment through the coaches’ eyes: A qualitative inquiry. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misener, L.; Darcy, S. Managing disability sport: From athletes with disabilities to inclusive organisational perspectives. Sport Manage. Rev. 2014, 17, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalidis, K.E.; Burns, J.; Van Biesen, D.; Dreegia, W.; Hettinga, F.J. The impact of cognitive functions and intellectual impairment on pacing and performance in sports. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2021, 52, 101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilinger, E.L.; Stiehl, K.A.M.; Bagnall, H.; Scior, K. Intellectual disability literacy and its connection to stigma: A multinational comparison study in three European countries. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, N.; Stonebridge, J. Coaching athletes with intellectual disabilities. Same thing but different? In Sport Coaching with Diverse Populations: Theory and Practice, 1st ed.; Wallis, J., Lambert, J., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Van Biesen, D.; Hettinga, F.J.; McCulloch, K.; Vanlandewijck, Y. Pacing Profiles in Competitive Track Races: Regulation of Exercise Intensity Is Related to Cognitive Ability. Front. Physiol. 2016, 20, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society, B.P. Learning Disability: Definitions and Contexts; British Psychological Society: Leicester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- AAIDD. Intellectual Disability, Definition, Classification and Systems of Support, 11th ed.; AAIDD: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Tilinger, P. Comparison of athletics records of intellectually disabled persons with records of intact athletes. Kinanthropologica 2013, 49, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biesen, D.; Hettinga, F.J.; McCulloch, K.; Vanlandewijck, Y.C. Pacing Ability in Elite Runners with Intellectual Impairment. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2017, 49, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, B.L.; Pepping, G.J.; Hettinga, F.J. Pacing and decision making in sport and exercise: The roles of perception and action in the regulation of exercise intensity. Sport. Med. 2014, 44, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elferink-Gemser, M.T.; Hettinga, F.J. Pacing and Self-regulation: Important Skills for Talent Development in Endurance Sports. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.; De Koning, J.J.; Hettinga, F.; Lampen, J.; La Clair, K.L.; Dodge, C.; Bobbert, M.; Porcari, J.P. Pattern of energy expenditure during simulated competition. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2003, 35, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.; De Koning, J.J.; Hettinga, F.J.; Lampen, J.; Dodge, C.; Bobbert, M.; Porcari, J.P. Effect of competitive distance on energy expenditure during simulated competition. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2004, 25, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menting, S.G.; Edwards, A.M.; Hettinga, F.J.; Elferink-Gemser, M.T. Pacing behaviour development and acquisition: A systematic review. Sport. Med. Open 2022, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyland-Monks, R.; Cronin, L.; McNaughton, L.; Marchant, D. The role of executive function in the self-regulation of endurance performance: A critical review. Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 240, 353–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, M.J.; Schoenmakers, P.P.; Walker, A.J.; Hettinga, F.J. The behavior of an opponent alters pacing decisions in 4-km cycling time trials. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 158, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hettinga, F.J.; Konings, M.J.; Pepping, G.J. The Science of Racing against Opponents: Affordance Competition and the Regulation of Exercise Intensity in Head-to-Head Competition. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konings, M.J.; Hettinga, F.J. Objectifying Tactics: Athlete and Race Variability in Elite Short-Track Speed Skating. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, M.J.; Parkinson, J.; Zijdewind, I.; Hettinga, F.J. Racing an Opponent: Alteration of Pacing, Performance, and Muscle-Force Decline but Not Rating of Perceived Exertion. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, E.L.; Jones, H.S.; Andy Sparks, S.; Marchant, D.C.; Midgley, A.W.; Mc Naughton, L.R. Competitor presence reduces internal attentional focus and improves 16.1km cycling time trial performance. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2015, 18, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, M.J.; Hettinga, F.J. Pacing Decision Making in Sport and the Effects of Interpersonal Competition: A Critical Review. Sport. Med. 2018, 48, 1829–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.J.; Hettinga, F.J.; Beedie, C. You don’t need to administer a placebo to elicit a placebo effect: Social factors trigger neurobiological pathways to enhance sports performance. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2020, 20, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakalidis, K.E.; Menting, S.; Elferink-Gemser, M.; Hettinga, F.J. The role of social environment on pacing and sports performance: A narrative review from a self-regulatory perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micklewright, D.; Kegerreis, S.; Raglin, J.; Hettinga, F. Will the Conscious-Subconscious Pacing Quagmire Help Elucidate the Mechanisms of Self-Paced Exercise? New Opportunities in Dual Process Theory and Process Tracing Methods. Sport. Med. 2017, 47, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khudair, M.; Van Biesen, D.; Pérez-Tejero, J.; Hettinga, F.J. The pacing behaviour of basketball players with Intellectual Impairment: Does the dynamic environment influence how they pace? J. Sport. Sci. 2021, 52, 101840. [Google Scholar]
- Hutzler, Y.; Oz, M.; Barak, S. Goal perspectives and sport participation motivation of Special Olympians and typically developing athletes. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 2149–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, J.L.; Chi, L.; Newton, M.L.; Walling, M.D. Task and ego orientation and intrinsic motivation in sport. Int. J. Sport Psychol. 1995, 26, 40–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kitchin, P.J.; Peile, C.; Lowther, J. Mobilizing capacity to achieve the mainstreaming of disability sport. Manag. Sport Leis. 2019, 24, 424–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biesen, D.; Burns, J.; Mactavish, J.; Van de Vliet, P.; Vanlandewijck, Y. Conceptual model of sport-specific classification for para-athletes with intellectual impairment. J. Sport. Sci. 2021, 39, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biesen, D.; Mactavish, J.; McCulloch, K.; Lenaerts, L.; Vanlandewijck, Y.C. Cognitive profile of young well-trained athletes with intellectual disabilities. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2016, 53–54, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konings, M.J.; Foulsham, T.; Micklewright, D.; Hettinga, F.J. Athlete-Opponent Interdependency Alters Pacing and Information-Seeking Behavior. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2020, 52, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjostrom, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dairo, Y.; Collett, J.; Dawes, H.; Clark, C. Measuring sedentary behaviour across the spectrum of adults with intellectual disabilities: A comparison between accelerometer and international physical activity questionnaire. Physiotherapy 2021, 113, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.; Reading, J.; Shephard, R.J. Revision of the Physical-Activity Readiness Questionnaire (PAR-Q). Can. J. Sport Sci. 1992, 17, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Cardinal, B.J.; Esters, J.; Cardinal, M.K. Evaluation of the revised physical activity readiness questionnaire in older adults. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 1996, 28, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D.E.R.; Jamnik, V.K.; SSD, S.S.D.B.; Gledhill, N. The Physical Activity Readiness Questionnaire for Everyone (PAR-Q+) and Electronic Physical Activity Readiness Medical Examination. Health Fit. J. Can. 2011, 4, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Menting, S.G.P.; Elferink-Gemser, M.T.; Edwards, A.M.; Hettinga, F.J. Effects of Experience and Opponents on Pacing Behavior and 2-km Cycling Performance of Novice Youths. Res. Q Exerc Sport 2019, 90, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.J.; Goss, F.L.; Bell, J.A.; Dixon, C.B.; Gallagher, K.I.; Lagally, K.M.; Timmer, J.M.; Abt, K.L.; Gallagher, J.D.; Thompkins, T. Self-regulated cycling using the Children’s OMNI Scale of Perceived Exertion. Med. Sci. Sport. Exerc. 2002, 34, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, K.; Gel, Y.R.; Brunner, E.; Konietschke, F. nparLD: An R Software Package for the Nonparametric Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Factorial Experiments. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 50, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, E.; Domhof, S.; Langer, F. Nonparametric Analysis of Longitudinal Data in Factorial Experiments; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, E.; Puri, M.L. Nonparametric Methods in Factorial Designs. Stat. Pap. 2001, 42, 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konietschke, F.; Placzek, M.; Schaarschmidt, F.; Hothorn, L.A. nparcomp: An R Software Package for Nonparametric Multiple Comparisons and Simultaneous Confidence Intervals. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 64, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrus, N.; Hall, L. Intellectual Disability and Language Disorder. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 26, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevan, F. Challenging behaviour and communication difficulties. Br. J. Learn. Disabil. 2003, 31, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.C.; Appleton, P.R.; Duda, J.L.; Bortoli, L.; Robazza, C. Social Environmental Antecedents of Athletes’ Emotions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, C.Q.; Vera, V.D.; López, C.; Jaramillo, J. Impact of sport on social cognition: An analysis based on structural equational models. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2020, 20, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Pinilla, J.; Pérez-Tejero, J.; Sampedro, J.; Román, I.; Lorenzo, A.; Lorenzo, J.; Vanlandewijck, Y.; Van Biesen, D. Influence of intellectual impairment (II) on basketball players’ capacity to solve a game situation: Towards evidence-based classification systems in II-basketball. Psychol. Soc. Educ. 2016, 8, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardel, M.H.; Fontayne, P.; Colombel, F.; Schiphof-Godart, L. Effects of match result and social comparison on sport state self-esteem fluctuations. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 2010, 11, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, G.; Jahoda, A.; Gumley, A.; Knott, F. Young people with intellectual disabilities attending mainstream and segregated schooling: Perceived stigma, social comparison and future aspirations. J. Intellect. Disabil. Res. 2006, 50, 432–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, L.; McKenzie, K.; Lindsay, B. Stigma, social comparison and self-esteem in adults with an intellectual disability. J. Appl. Res. Intellect. Disabil. 2012, 25, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J. The participation of people with intellectual disability in Parasports. J. Paralympic Res. Group 2020, 13, 41–59. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C.; Howe, P. The (In)validity of Supercrip Representation of Paralympian Athletes. J. Sport Soc. 2012, 36, 174–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biesen, D.; Mactavish, J.; Patty, N.; Vanlandewijck, Y. Technical proficiency among table tennis players with and without intellectual disabilities. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2012, 31, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtinen, U.; Rintala, P.; Malin, A. Physical performance of individuals with intellectual disability: A 30 year follow up. Adapt. Phys. Activ. Q 2007, 24, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeli, E.; Imam, B.; Merrick, J. The relationship of pre-sarcopenia (low muscle mass) and sarcopenia (loss of muscle strength) with functional decline in individuals with intellectual disability (ID). Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2012, 55, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borji, R.; Zghal, F.; Zarrouk, N.; Sahli, S.; Rebai, H. Individuals with intellectual disability have lower voluntary muscle activation level. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 3574–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimmer, J.H. Fitness and Rehabilitation Programs for Special Populations; WCB Brown & Benchmark Publishers: Madison, WI, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Bongard, V.; McDermott, A.Y.; Dallal, G.E.; Schaefer, E.J. Effects of age and gender on physical performance. Age 2007, 29, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abonie, U.S.; Edwards, A.M.; Hettinga, F.J. Optimising activity pacing to promote a physically active lifestyle in medical settings: A narrative review informed by clinical and sports pacing research. J. Sport. Sci. 2020, 38, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abonie, U.S.; Hettinga, F.J. Effect of a Tailored Activity Pacing Intervention on Fatigue and Physical Activity Behaviours in Adults with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abonie, U.S.; Saxton, J.; Baker, K.; Hettinga, F.J. Objectively-assessed physical activity and self-reported activity pacing in adults with multiple sclerosis: A pilot study. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Source | Mdn | IQR | Min | Max | np-CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power output | ||||||
| ID group (alone) | 45.05 | 42.01 | 28.71 | 107.93 | 14.51 | |
| Non-ID group (alone) | 161.49 | 40.46 | 117.42 | 197.31 | 12.93 | |
| ID group (head-to-head) | 36.13 | 23.63 | 19.76 | 102.83 | 21.60 | |
| Non-ID group (head-to-head) | 176.77 | 43.71 | 122.17 | 214.26 | 12.42 | |
| Velocity | ||||||
| ID group (alone) | 16.77 | 6.29 | 13.74 | 25.56 | 9.54 | |
| Non-ID group (alone) | 30.33 | 2.72 | 26.70 | 32.58 | 4.63 | |
| ID group (head-to-head) | 15.13 | 5.37 | 11.07 | 24.58 | 16.33 | |
| Non-ID group (head-to-head) | 31.45 | 2.66 | 27.04 | 33.67 | 4.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakalidis, K.E.; Menting, S.G.P.; Hettinga, F.J. The Role of Cognition and Social Factors in Competition: How Do People with Intellectual Disabilities Respond to Opponents? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032670
Sakalidis KE, Menting SGP, Hettinga FJ. The Role of Cognition and Social Factors in Competition: How Do People with Intellectual Disabilities Respond to Opponents? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032670
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakalidis, Kandianos Emmanouil, Stein Gerrit Paul Menting, and Florentina Johanna Hettinga. 2023. "The Role of Cognition and Social Factors in Competition: How Do People with Intellectual Disabilities Respond to Opponents?" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032670
APA StyleSakalidis, K. E., Menting, S. G. P., & Hettinga, F. J. (2023). The Role of Cognition and Social Factors in Competition: How Do People with Intellectual Disabilities Respond to Opponents? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2670. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032670







