Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments: A Case Study of Eutrophic Bukwałd Lake Located in an Agricultural Catchment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gownarisab, N.J.; Rountosab, K.J.; Kaufmancd, L.; Koldinge, J.; Lwizaa, K.M.M.; Pikitchab, E.K. Water level fluctuations and the ecosystem functioning of lakes. J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincon-Leitea, B.; Casenave, C. Modelling eutrophication in lake ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2985–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Brucet, S.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Papastergiadou, E.; Stefanidis, K.; Nõges, T.; Nõges, P.; Attayde, J.L.; Zohary, T.; Coppens, J.; et al. Ecological impacts of global warming and water abstraction on lakes and reservoirs due to changes in water level and related changes in salinity. Hydrobiologia 2015, 750, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekhovskikh, V.; Volkova, Z.; Katunin, D.; Kazmiruk, V.; Kazmiruk, T.; Ostrovskaya, E. Heavy metal in bottom sediment in the upper and lower Volga. Water Resour. 2002, 5, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kükrer, S. Pollution, source, and ecological risk assessment of trace elements in surface sediments of Lake Aktaş, NE Turkey. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assessment 2017, 23, 1629–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, M.I.; Song, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.; Mehmood, M.S.; Sajid, M.; Khan, A.J. Contamination level, ecological risk, and source identification of heavy metals in the hyporheic zone of the Weihe River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Jasiewicz, C.; Tarnawski, M. Effect of bottom sediment supplement to light soil on the content and uptake of macroelements by maize. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2012, 19, 863–872. [Google Scholar]
- Tomczyk, P.; Gałka, B.; Wiatkowski, M.; Wdowczyk, A.; Gruss, Ł. Toxicity studies on sediments near hydropower plants on the Ślęza and Bystrzyca rivers, Poland, to establish their potential for use for soil enrichment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 756–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymes, I.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Szymczyk, S.; Sidoruk, M.; Potasznik, A. Distribution and potential risk assessment of heavy metals and arsenic in sediments of a dam reservoir: A case study of the Łoje retention reservoir, NE Poland. J. Elementol. 2017, 22, 843–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briffa, J.; Sinagra, E.; Blundell, R. Heavy metal pollution in the environment and their toxicological effects on humans. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlović, P.; Marković, M.; Kostić, O.; Sakan, S.; Dordević, D.; Perović, V.; Pavlović, D.; Pavlović, M.; Čakmak, D.; Jarić, S.; et al. Evaluation of potentially toxic element contamination in the riparian zone of the River Sava. Catena 2019, 174, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.; Pandita, S.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Cerda, A. A review of ecological risk assessment and associated health risks with heavy metals in sediment from India. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Luo, G.; Gao, J.; Yuan, S.; Du, J.; Wang, Z. Quantitative evaluation of potential ecological risk of heavy metals in sewage sludge from three wastewater treatment plants in the main urban area of Wuxi, China. Chem. Ecol. 2015, 31, 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Kalamdhad, A.S. Effects of Heavy Metals on Soil, Plants, Human Health and Aquatic Life. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Malvandi, H. Preliminary evaluation of heavy metal contamination in the Zarrin-Gol River sediments. Iran. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ding, L.; Gu, X.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Shi, Y.; Huang, T.; Cheng, S. Levels and ecological risk assessment of metals in soils from a typical e-waste recycling region in southeast China. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1947–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Do, D.D.; Nguyen, T.X.; Nguyen, V.N.; Duong, T.P.N.; Nguyen, M.H.; Truong, H.T.T.; Dong, H.P.; Le, A.H.; Bach., Q. Seasonal, spatial variation, and pollution sources of heavy metals in the sediment of the Saigon River, Vietnam. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaskuła, J.; Sojka, M.; Fiedler, M.; Wróżyński, R. Analysis of Spatial Variability of River Bottom Sediment Pollution with Heavy Metals and Assessment of Potential Ecological Hazard for the Warta River, Poland. Minerals 2021, 11, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cymes, I.; Draganska, E.; Szymczyk, S. The influence of weather conditions on mid-field ponds situated in a reclaimed area in Sepopolska Plain. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2010, 39, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragańska, E.; Szwejkowski, Z.; Cymes, I.; Panfil, M. Characteristics of the forest growing season in Poland on the basis of selected scenario of climate changes. Sylwan 2017, 161, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Pribyl, D.W. A critical review of the conventional SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 2010, 156, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. Ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control, a sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, G. Index of geo-accumulation in sediments of the Rhine River. Geo. J. 1969, 2, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Bojakowska, I.; Sokołowska, G. Geochemiczne klasy czystości osadów wodnych. Prz. Geol. 1998, 46, 49–54. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Bhuiyon, M.A.H.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomlinson, D.L.; Wilson, J.G.; Harris, C.R.; Jeffrey, D.W. Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol. Meeresun. 1980, 33, 566–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Likuku, A.S.; Mmolawa, K.B.; Gaboutloeloe, G.K. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment and degree of contamination around the copper-nickel mine in the Selebi Phikwe region, Eastern Botswana. Environ. Ecol. Res. 2013, 1, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrovsky, I.; Tęgowski, J. Hydroacoustic analysis of spatial and temporal variability of bottom sediment characteristics in Lake Kinneret in relation to water level fluctuation. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2010, 30, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middelburg, J.J.; Levin, L.A. Coastal hypoxia and sediment biogeochemistry. Biogeosciences 2009, 6, 1273–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, S.A.; Moussa, E.M.M.; El-Sabagh, M.E.I. Valuation of heavy metal content in Qaroun Lake, El-Fayoum, Egypt. Part I: Bottom sediments. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2015, 8, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobus, S.Z.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Sidoruk, M.; Skwierawski, A.; Obolewski, K.; Timofte, C.M.; Sowiński, P. Effect of hydrological connectivity on physicochemical properties of bottom sediments of floodplain lakes—A case study of the Łyna river, Northern Poland. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2016, 15, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skwierawski, A. Carbon Sequestration Potential in the Restoration of Highly Eutrophic Shallow Lakes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saroja, K.B.; Pradipta, R.M.; Bita, M.; Prasanta, R.; Srikanta, S. Spatial distribution and potential biological risk of some metals in relation to granulometric content in core sediments from Chilika Lake, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 572–587. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Y.; Duo, W.; Zehui, L.; Zijie, Y.; Lili, N.; Huan, Z.; Jie, C.H.; Aifeng, Z. Holocene-Anthropocene transition in northwestern Yunnan revealed by records of soil erosion and trace metal pollution from the sediments of Lake Jian, southwestern China. J. Paleolimnol. 2022, 68, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Baran, A.; Mierzwa-Hersztek, M.; Gondek, K.; Tarnawski, M.; Szara, M.; Gorczyca, O.; Koniarz, T. The influence of the quantity and quality of sediment organic matter on the potential mobility and toxicity of trace elements in bottom sediment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 2893–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostka, A.; Leśniak, A. Spatial and geochemical aspects of heavy metal distribution in lacustrine sediments, using the example of Lake Wigry (Poland). Chemosphere 2000, 240, 124879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrizo, D.; Sánchez-García, L.; Javier, M.R.; García-Rodríguez, F. Discriminating sources and preservation of organic matter in Surface sediments from five Antarctic lakes in the Fildes Peninsula (King George Island) by lipid biomarkers and compound-specific isotopic analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świercz, A.; Tomczyk-Wydrych, I.; Bąk, Ł. Quality of Bottom Sediments of Sołtmany Lake (Masurian Lake District, Poland) in the Light of Geochemical and Ecotoxicological Criteria—Case Study. Water 2022, 14, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, P.; Ledo, L.; Soares, S.; Barbosa, I.R.; Alvarenga, P. Spatial and temporal variability of the water and sediments quality in the Alqueva reservoir (Guadiana Basin; southern Portugal). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 471, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, E.A.; Callejon Mochon, M.; Jimenez Sanchez, J.C.; Ternero Rodriguez, M. Heavy metal extractable forms in sludge from wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere 2002, 47, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorbiłowicz, E.; Skorbiłowicz, M.; Misztal, W. Distribution of Nickel, Copper and Cobalt in the Grain Fractions of Bottom Sediments of the Sokołda River and its Tributaries (Poland). J. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 21, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.A.; Ferrari, R.G.; Kato, L.S.; Hauser-Davis, R.A.; Conte-Junior, C.A.A. Systematic Review on Metal Dynamics and Marine Toxicity Risk Assessment Using Crustaceans as Bioindicators. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 881–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frémion, F.; Bordas, F.; Mourier, B.; Lenain, J.F.; Kestens, T.; Courtin-Nomade, A. Influence of dams on sediment continuity: A study case of a natural metallic contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sojka, M.; Jaskuła, J.; Siepak, M. Heavy Metals in Bottom Sediments of Reservoirs in the Lowland Area of Western Poland: Concentrations, Distribution, Sources and Ecological Risk. Water 2019, 11, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, H.I.; Aly, W. Effect of site on sedimentological characteristics and metal pollution in two semi-enclosed embayments of great freshwater reservoir: Lake Nasser, Egypt. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2018, 141, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, X.C.; Ma, H.T.; Qian, J.; Zhai, J.B. Distribution of extractable fractions of heavy metals in sludge during the wastewater treatment process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnitskiy, S. Nickel: The last of the essential micronutrients. Agron. Colomb. 2011, 29, 49–56. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Wu, S. Heavy metals in food crops, soil, and water in the Lihe River watershed of the Taihu Region and their potential health risks when ingested. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juśkiewicz, W.; Gierszewski, P. Toxic metal pollution of aquatic ecosystems of European Union nature protection areas in a region of intensive agriculture (Lake Gopło, Poland). Aquat. Sci. 2022, 84, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratte, S.; Bao, K.; Shen, J.; De Vleeschouwer, F.; Roux, D. Centennial records of cadmium and lead in NE China lake sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 548–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshan, P.; Mahesh, M.K.; Ramachandra, T.V. Dynamics of Metal Pollution in Sediment and Macrophytes of Varthur Lake, Bangalore. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzetala, M.A. Assessment of Toxic Metal Contamination of Bottom Sediments in Water Bodies in Urban Areas. Soil. Sediment Contam. 2014, 24, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulbat, E.; Sokołowska, A. Methods of Assessment of Metal Contamination in Bottom Sediments (Case Study: Straszyn Lake, Poland). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 77, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahra, A.; Hashmi, M.Z.; Malik, R.N.; Ahmed, Z. Enrichment and geo-accumulation of heavy metals and risk assessment of sediments of the Kurang Nallah-Feeding tributary of the Rawal Lake Reservoir, Pakistan. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 470–471, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreibrodt, S.; Wiethold, J. Lake Belau and its catchment (northern Germany): A key archive of environmental history in northern central Europe since the onset of agriculture. Holocene 2015, 25, 296–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malsiu, A.; Shehu, I.; Stafilov, T.; Faiku, F. Assessment of Heavy Metal Concentrations with Fractionation Method in Sediments and Waters of the Badovci Lake (Kosovo). J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 2020, 3098594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tylmann, W.; Gołębiewski, R.; Woźniak, P.P.; Czarnecka, K. Heavy metals in sediments as evidence for recent pollution and quasi-estuarine processes: An example from Lake Druzno, Poland. Environ. Geol. 2007, 53, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorbiłowicz, E.; Rogowska, W.; Skorbiłowicz, M.; Ofman, P. Spatial Variability of Metals in Coastal Sediments of Ełckie Lake (Poland). Minerals 2022, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuriata-Potaszni, A.; Szymczyk, S.; Skwierawski, A.; Glińska-Lewczuk, K.; Cymes, I. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Surface Layer of Bottom Sediments in a Flow-Through Lake: A Case Study of Lake Symsar in Northern Poland. Water 2016, 8, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
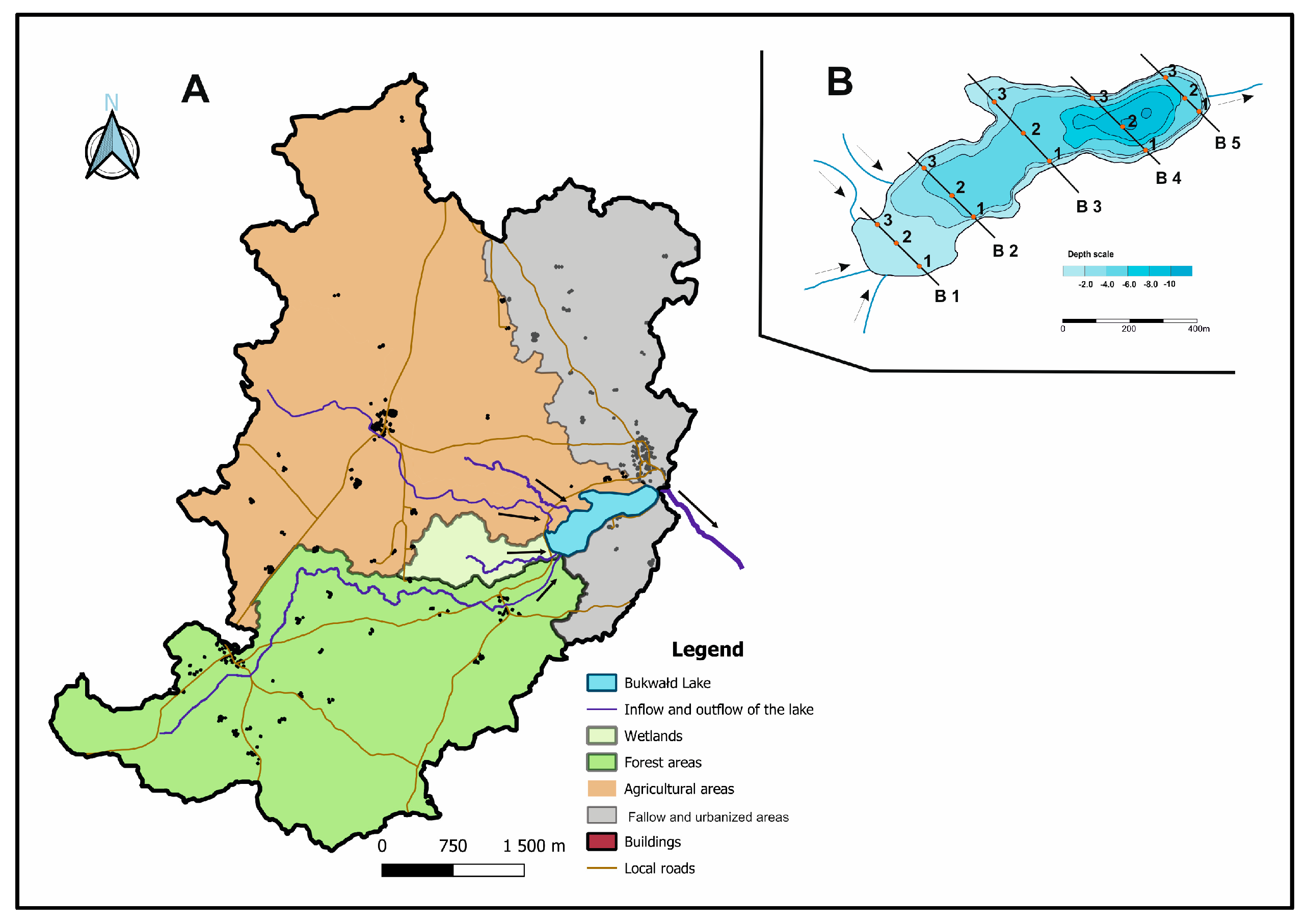
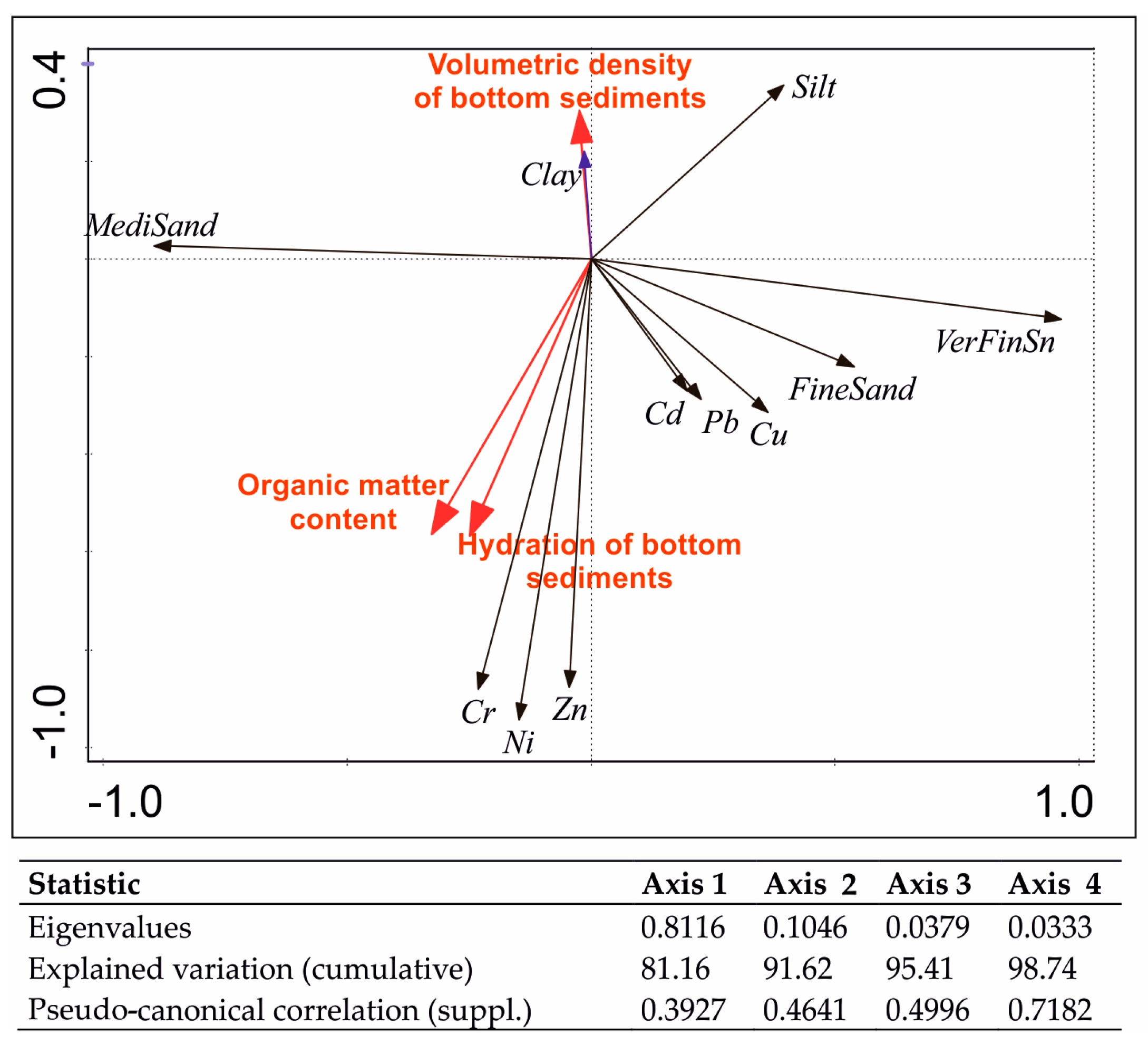
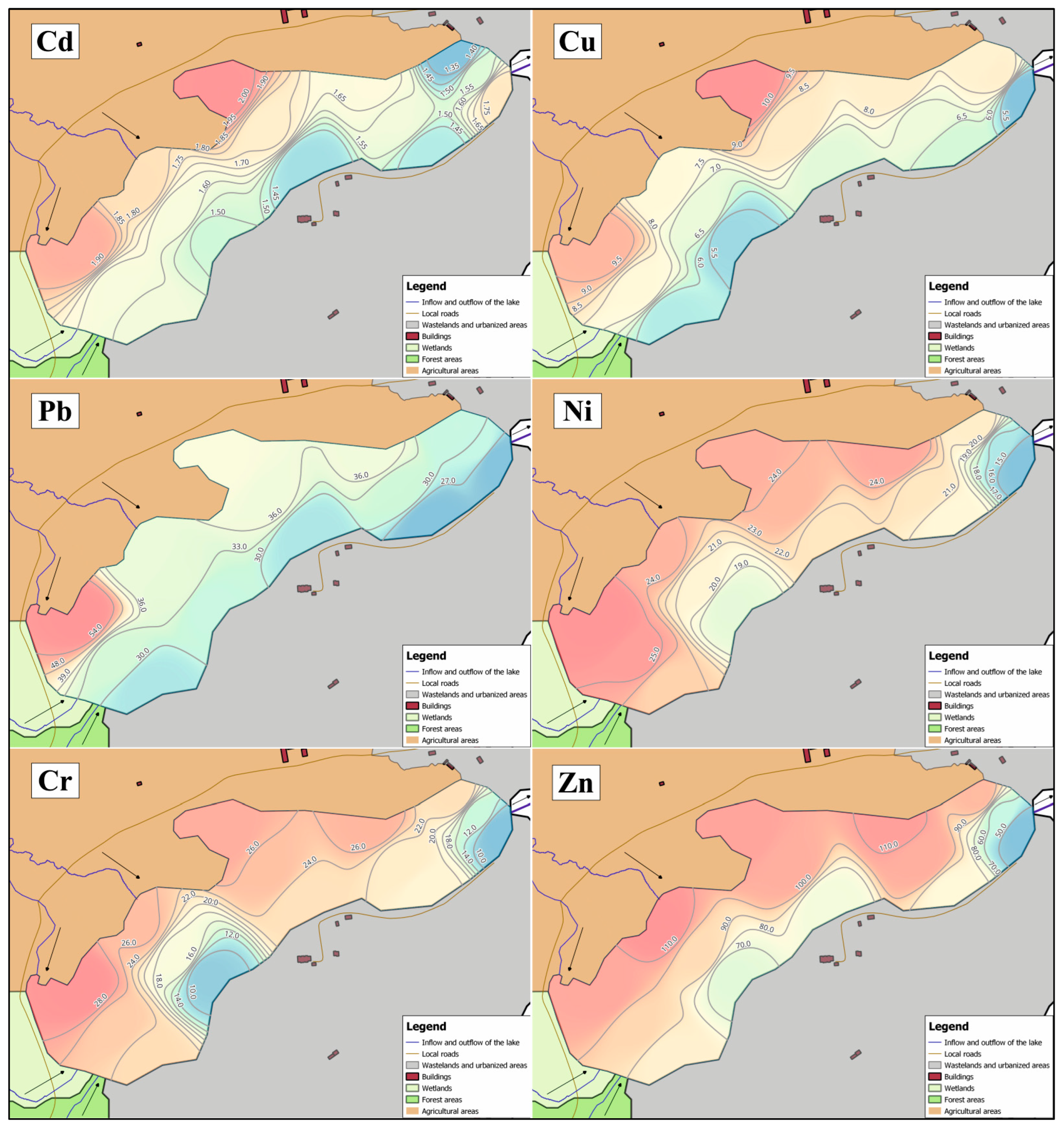
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Area [ha] | 36.2 |
| Maximum depth [m] | 12.4 |
| Average depth [m] | 5.4 |
| Relative depth | 0.021 |
| Depth indicator | 0.44 |
| Maximum length [m] | 1140.0 |
| Maximum width [m] | 325.0 |
| Shoreline length [m] | 4020 |
| Development of the coastline | 1.88 |
| Potential Ecological Risk Index Er | Ecological Risk Level of Single-Factor Pollution | Potential Toxicity Index (RI) | General Level of Potential Ecological Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Er < 40 40 ≤ Er < 80 80 ≤ Er < 160 160 ≤ Er < 320 Er ≥ 320 | Low risk Moderate risk Considerable risk High risk Very high risk | RI < 150 150 ≤ RI < 300 300 ≤ RI < 600 RI ≥ 600 | Low risk Moderate risk Considerable risk Very high risk |
| Geochemical Index (Igeo) | Contamination Factor (CF) | Pollutant Load Index (PLI) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geochemical Index Range | Level of Factor Pollution | Contamination Factor Range | Level of Factor Pollution | Pollutant Load Index Range | Level of Factor Pollution |
| Igeo < 0, class 0 | uncontaminated sediments | CF < 1, class I | low contamination | PLI < 0.5 | no drastic rectification measures are needed |
| 0 < Igeo < 1, class I | uncontaminated to moderately contaminated sediments | 1 ≤ CF ≤ 3, class I | moderate contamination | ||
| 0.5 ≤ PLI ≤ 1 | more detailed study is needed to monitor the site | ||||
| 1 < Igeo < 2, class II | moderately contaminated sediments | 3 < CF < 6, class III | considerable contamination | ||
| 2 < Igeo < 3, class III | moderately to highly contaminated sediments | CF ≥ 6, class IV | very high contamination | PLI ≥ 1 | immediate intervention to ameliorate pollution |
| 3 < Igeo < 4, class IV | highly contaminated sediments | ||||
| 4 < Igeo < 5, class V | highly to extremely contaminated sediments | ||||
| Igeo > 5, class VI | extremely contaminated sediments | ||||
| Sample No. | Percentage of Granulometric Fractions | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <2 µm Clay | 2–50 µm Silt | 50–100 µm Very Fine Sand | 100–250 µm Fine Sand | 250–500 µm Medium Sand | |
| B1-1 | 0.2 | 3.6 | 6.5 | 58.7 | 31.1 |
| B1-2 | 0.1 | 2.7 | 10.6 | 62.5 | 24.1 |
| B1-3 | 0.1 | 3.7 | 7.2 | 62.3 | 26.8 |
| B2-1 | 0.2 | 3.7 | 9.0 | 58.1 | 29.0 |
| B2-2 | 0.1 | 2.4 | 6.5 | 57.3 | 33.8 |
| B2-3 | 0.3 | 3.6 | 14.5 | 47.3 | 34.4 |
| B3-1 | 0.3 | 7.3 | 3.7 | 30.4 | 58.3 |
| B3-2 | 0.2 | 3.3 | 4.9 | 29.3 | 62.4 |
| B3-3 | 0.1 | 5.7 | 18.5 | 44.3 | 31.4 |
| B4-1 | 0.2 | 5.2 | 8.0 | 45.2 | 41.4 |
| B4-2 | 0.1 | 2.6 | 10.2 | 44.5 | 42.6 |
| B4-3 | 0.3 | 8.2 | 13.7 | 46.7 | 31.1 |
| B5-1 | 0.2 | 5.2 | 2.8 | 31.4 | 60.3 |
| B5-2 | 0.3 | 9.72 | 28.2 | 43.3 | 18.5 |
| B5-3 | 0.1 | 6.9 | 15.4 | 60.4 | 17.2 |
| Sample No. | Bulk Density [g·cm−3] | Sediment Hydration [%] | Mineral Content [%] | Organic Matter Content [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B1-1 | 1.24 | 81.09 | 86.0 | 14.0 |
| B1-2 | 1.18 | 82.64 | 84.3 | 15.7 |
| B1-3 | 1.17 | 79.69 | 86.2 | 13.8 |
| B2-1 | 1.11 | 86.28 | 81.7 | 18.3 |
| B2-2 | 1.07 | 86.82 | 81.0 | 19.0 |
| B2-3 | 1.16 | 68.54 | 89.7 | 10.3 |
| B3-1 | 1.13 | 84.37 | 83.2 | 16.8 |
| B3-2 | 1.17 | 86.05 | 82.6 | 17.4 |
| B3-3 | 1.19 | 80.97 | 86.5 | 13.5 |
| B4-1 | 1.21 | 76.86 | 88.4 | 11.6 |
| B4-2 | 1.08 | 86.24 | 80.1 * | 19.9 * |
| B4-3 | 1.39 | 66.25 | 91.6 * | 8.4 * |
| B5-1 | 1.28 | 72.33 | 91.0 * | 9.0 * |
| B5-2 | 1.14 | 80.64 | 86.0 | 14.0 |
| B5-3 | 1.25 | 67.98 | 91.9 * | 8.1 * |
| Heavy Metal | Min | Max | Me | CV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1.64 ± 0.20 | 1.33 | 2.02 | 1.63 | 12 |
| Cu | 7.42 ± 1.49 | 5.00 | 10.25 | 7.85 | 20 |
| Pb | 33.03 ± 7.69 | 24.00 | 56.00 | 31.50 | 23 |
| Ni | 21.71 ± 3.36 | 14.45 | 25.45 | 21.80 | 16 |
| Cr | 21.36 ± 6.60 | 8.20 | 29.35 | 23.35 | 31 |
| Zn | 91.09 ± 21.39 | 45.91 | 112.92 | 96.99 | 24 |
| Heavy Metal | Min | Max | Me | CV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 7.17 | 7.40 | 7.24 | - |
| N | 3.22 ± 2.83 | 0.30 | 9.30 | 1.73 | 0.88 |
| P | 0.71 ± 0.16 | 0.49 | 1.11 | 0.69 | 0.22 |
| C | 18.39 ± 2.03 | 15.37 | 22.75 | 17.91 | 0.11 |
| Heavy Metal | Value of Potential Ecological Risk Index (Er) | Ecological Risk Level of Single-Factor Pollution |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 98.41 | Considerable risk |
| Pb | 16.58 | Low risk |
| Zn | 1.90 | Low risk |
| Cr | 8.54 | Low risk |
| Ni | 21.71 | Low risk |
| Cu | 6.19 | Low risk |
| Heavy Metal | Value of the Geochemical Index (Igeo) | Igeo Class |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1.13 | class II |
| Pb | 1.14 | class II |
| Zn | 0.34 | class I |
| Cr | 1.51 | class II |
| Ni | 1.53 | class II |
| Cu | −0.28 | class 0 |
| Heavy Metal | Value of the Contamination Factor (CF) | Purity Classes |
|---|---|---|
| Cd | 1.64 | class II |
| Pb | 3.32 | class III |
| Zn | 1.90 | class II |
| Cr | 4.27 | class III |
| Ni | 4.34 | class III |
| Cu | 1.24 | class II |
| The Method of Using the Catchment Area of Lakes | Index | Cd | Pb | Zn | Cr | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urbanized catchment area | Igeo | 2.53–2.72 (2.55) | 1.41–3.62 (2.45) | 3.83–7.14 (4.10) | −1.3–2.71 (1.01) | 0.11–2.76 (0.97) | 1.10–2.5 1(1.27) |
| CF | 1.54–4.62 (2.12) | 0.32–3.93 (1.27) | 16.14–28.61 (17.20) | 1.21–2.15 (1.42) | 1.22–3.34 (1.56) | 9.22–17.43 (10.29) | |
| PLI | 0.69–8.95 (1.5) | ||||||
| Agricultural catchment area | Igeo | 0.10–0.42 (0.11) | 0.11–2.34 (0.60) | 0.01–2.39 (0.58) | 0.02–0.32 (0.17) | 0.05–2.46 (0.42) | 0.11–1.66 (0.54) |
| CF | 0.20–4.01 (1.92) | 0.26–3.56 (3.29) | 0.40–2.90 (1.84) | 0.10–3.20 (1.22) | 0.30–16.10 (4.53) | 0.80–2.79 (1.28) | |
| PLI | 0.40–4.90 (1.35) | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sidoruk, M. Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments: A Case Study of Eutrophic Bukwałd Lake Located in an Agricultural Catchment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032387
Sidoruk M. Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments: A Case Study of Eutrophic Bukwałd Lake Located in an Agricultural Catchment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032387
Chicago/Turabian StyleSidoruk, Marcin. 2023. "Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments: A Case Study of Eutrophic Bukwałd Lake Located in an Agricultural Catchment" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032387
APA StyleSidoruk, M. (2023). Pollution and Potential Ecological Risk Evaluation of Heavy Metals in the Bottom Sediments: A Case Study of Eutrophic Bukwałd Lake Located in an Agricultural Catchment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 2387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20032387






