Cation Composition Influences the Toxicity of Salinity to Freshwater Biota
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tested Chemicals
2.2. Maintenance of Laboratorial Cultures of the Test Species
2.3. Lethal and Sublethal Assays
2.3.1. Growth Assay with R. subcapitata
2.3.2. The 48-h Mortality Assay with D. magna
2.3.3. The 24-h Feeding Inhibition Assays with D. magna
2.3.4. Somatic Growth Rate Assay with D. magna
2.3.5. The 24-h Mortality and 48-h Reproduction Assays with B. calyciflorus
2.3.6. The 96-h Mortality and Malformation Assay with H. viridissima
2.3.7. The 96-h Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity Assay (FET) with Danio rerio
3. Data Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Lethal Assays
4.2. Sublethal Assays
4.3. Comparing with Data for NaCl
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leitao, J.; Ribeiro, R.; Soares, A.M.; Lopes, I. Tolerance to Copper and to Salinity in Daphnia longispina: Implications within a Climate Change Scenario. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coldsnow, K.D.; Mattes, B.M.; Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. Rapid evolution of tolerance to road salt in zooplankton. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venâncio, C.; Anselmo, E.; Soares, A.; Lopes, I. Does increased salinity influence the competitive outcome of two producer species? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 5888–5897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.-J.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M. Lost in translation: The German literature on freshwater salinization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, J.K.; Funk, D.H. Temperature affects acute mayfly responses to elevated salinity: Implications for toxicity of road de-icing salts. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2018, 374, 20180081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, D.R.; Gulley, D.D.; Hockett, J.R.; Garrison, T.D.; Evans, J.M. Statistical models to predict the toxicity of major ions to Ceriodaphnia dubia, Daphnia magna and Pimephales promelas (fathead minnows). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1997, 16, 2009–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, T.; Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Canhoto, C.; Branco, P. Does short-term salinization of freshwater alter the behaviour of the Iberian barbel (Luciobarbus bocagei, Steindachner 1864)? Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venâncio, C.; Ribeiro, R.; Lopes, I. Active emigration from climate change-caused seawater intrusion into freshwater habitats. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.F.; Tavşanoğlu, N.; Vidal, N.; Yu, J.; Mello, F.T.-D.; Çakiroglu, A.I.; He, H.; Liu, Z.; Jeppesen, E. Salinity shapes zooplankton communities and functional diversity and has complex effects on size structure in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2018, 813, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Cánovas, C.; Sánchez-Fernández, D.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Millán, A.; Velasco, J.; Acosta, R.; Fortuno, P.; Otero, N.; Soler, A.; Bonada, N. Do all roads lead to Rome? Exploring community trajectories in response to anthropogenic salinization and dilution of rivers. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Kunz, J.L.; Dorman, R.A.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Steevens, J.A.; Hammer, E.J.; Bauer, C.R. Evaluation of chronic toxicity of sodium chloride or potassium chloride to a unionid mussel (Lampsilis siliquoidea) in water exposures using standard and refined toxicity testing methods. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 3050–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Ivey, C.D.; Dorman, R.A.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Steevens, J.; Hammer, E.J.; Bauer, C.R.; Mount, D.R. Acute toxicity of sodium chloride and potassium chloride to a unionid mussel (Lampsilis siliquoidea) in water exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 3041–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofoegbu, P.U.; Campos, D.; Soares, A.M.V.M.; Pestana, J.L.T. Combined effects of NaCl and fluoxetine on the freshwater planarian, Schmidtea mediterranea (Platyhelminthes: Dugesiidae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 11326–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venâncio, C.; Castro, B.B.; Ribeiro, R.; Antunes, S.; Abrantes, N.; Soares, A.; Lopes, I. Sensitivity of freshwater species under single and multigenerational exposure to seawater intrusion. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venâncio, C.; Castro, B.; Ribeiro, R.; Antunes, S.; Lopes, I. Sensitivity to salinization and acclimation potential of amphibian (Pelophylax perezi) and fish (Lepomis gibbosus) models. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 172, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelting, D.L.; Laxson, C.L. Review of Effects and Costs of Road De-Icing with Recommendations for Winter Road Management in the Adirondack Park; Adirondack Watershed Institute: Paul Smiths, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ružinskas, A.; Bulevičius, M.; Sivilevičius, H. Laboratory investigation and efficiency of deicing materials used in road maintenance. Transport 2016, 31, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarek, S.; Górecka, A.; Salabert, B.; Wojtal-Frankiewicz, A. Acute toxicity of seven de-icing salts on four zooplankton species–is there an “eco-friendly” alternative? Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2022, 22, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valleau, R.E.; Celis-Salgado, M.P.; Arnott, S.E.; Paterson, A.M.; Smol, J.P. Assessing the Effect of Salinization (NaCl) on the Survival and Reproduction of Two Ubiquitous Cladocera Species (Bosmina longirostris and Chydorus brevilabris). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldsnow, K.D.; Relyea, R.A. Toxicity of various road-deicing salts to Asian clams (Corbicula fluminea). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1839–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hintz, W.D.; Relyea, R.A. Impacts of road deicing salts on the early-life growth and development of a stream salmonid: Salt type matters. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Frick, C. The Effects of Road Salts on Aquatic Ecosystems; Environment Canada: Gatineau, QC, Canada, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Venâncio, C.; Ribeiro, R.; Lopes, I. Seawater intrusion: An appraisal of taxa at most risk and safe salinity levels. Biol. Rev. 2021, 97, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Kefford, B.J.; Piscart, C.; Prat, N.; Schäfer, R.B.; Schulz, C.-J. Salinisation of rivers: An urgent ecological issue. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 173, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPPC. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/site/assets/uploads/sites/3/2019/11/09_SROCC_Ch05_FINAL-1.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Van Dam, R.A.; Hogan, A.C.; McCullough, C.D.; Houston, M.A.; Humphrey, C.L.; Harford, A.J. Aquatic toxicity of magnesium sulfate, and the influence of calcium, in very low ionic concentration water. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fuentetaja, A.; Goodberry, F. Daphnia’s challenge: Survival and reproduction when calcium and food are limiting. J. Plankton Res. 2016, 38, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shetty, P.; Gitau, M.M.; Maróti, G. Salinity Stress Responses and Adaptation Mechanisms in Eukaryotic Green Microalgae. Cells 2019, 8, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffith, M.B. Toxicological perspective on the osmoregulation and ionoregulation physiology of major ions by freshwater animals: Teleost fish, crustacea, aquatic insects, and Mollusca. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 36, 576–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, J.L.; Conley, J.M.; Buchwalter, D.B.; Norberg-King, T.J.; Kemble, N.E.; Wang, N.; Ingersoll, C.G. Use of reconstituted waters to evaluate effects of elevated major ions associated with mountaintop coal mining on freshwater invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 2826–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, S.J.; Azizishirazi, A.; Pyle, G.G. Challenges and future prospects for developing Ca and Mg water quality guidelines: A meta-analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2018, 374, 20180364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soucek, D.J.; Mount, D.R.; Dickinson, A.; Hockett, J.R. Influence of dilution water ionic composition on acute major ion toxicity to the mayfly Neocloeon triangulifer. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 201: Freshwater Alga and Cyanobacteria, Growth Inhibition Test; Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Lemna sp. Growth Inhibition Test. Test Guideline 221. Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- OECD. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. Test Guideline 236. Fish Embryo Acute Toxicity (FET) Test; Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–62. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, B.; Gagné; F; Blaise, C. Hydra, a model system for environmental studies. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2012, 56, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, H.W. Handbook of Phycological Methods; Stein, J.R., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1973; pp. 16–17. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM—American Society of Testing and Materials. Standard Guide for Conducting Acute Toxicity Tests on Test Materials with Fishes, Microinvertebrates, and Amphibians. Annual Book of ASTM Standards. 1105; American Society of Testing and Materials: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 729–796. [Google Scholar]
- Trottier, S.; Blaise, C.; Kusui, T.; Johnson, E.M. Acute toxicity assessment of aqueous samples using a microplate-based Hydra attenuata assay. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. Int. J. 1997, 12, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira-Santos, M.; Soares, A.M.; Ribeiro, R. An in situ bioassay for freshwater environments with the microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- OCDE. Daphnia sp., Acute Immobilisation Test. Test Guideline 202. Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals; OECD: Paris, France, 2004; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, Y.; Calow, P.; Baird, D.J. A mechanistic model of contaminant-induced feeding inhibition in Daphnia magna. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 1995, 14, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, C.W. Crowding-Induced changes in growth, reproduction and morphology of Daphnia. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 43, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilby, O.K. The Hydra regeneration assay. In Proceedings of Workshop Organised by Association Francaise de Teratologie; Association Francaise de Teratologie: Royaumont, France, 1988; pp. 108–124. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma, M. Probit analysis of preference data. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1998, 33, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azimonti. Comparison of NOEC Values to EC10/EC20 Values, Including Confidence Intervals, in Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecotoxicological Risk Assessment; EFSA Supporting Publication: Parma, Italy, 2016; 274p. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, A.M.; Castro, B.B.; Pardal, M.A.; Gonçalves, F. Salinity effects on survival and life history of two freshwater cladocerans (Daphnia magna and Daphnia longispina). Ann. Limnol. Int. J. Limnol. 2007, 43, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisinger, K.E.; Christensen, G.M. Effects of various metals on survival, growth, reproduction, and metabolism of Daphnia magna. J. Fish. Board Can. 1972, 29, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, J.R.F.; Bergh, K.D.; Bailey, H.C. Chronic toxicity of chloride to freshwater species: Effects of hardness and implications for water quality guidelines. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, C.D.; Besser, J.M.; Ingersoll, C.G.; Wang, N.; Rogers, D.C.; Raimondo, S.; Bauer, C.R.; Hammer, E.J. Acute sensitivity of the vernal pool fairy shrimp, Branchinecta lynchi (Anostraca; Branchinectidae), and surrogate species to 10 chemicals. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 36, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, E.A.; Wong, W.H.; Harman, W.N. Toxicity of potassium chloride compared to sodium chloride for zebra mussel decontamination. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2018, 30, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, J.V.; Bazante-Yamaguishi, R.; Madeira, F.F.; Concilio, P.L.; Caruso, N.P.P.; Barbieri, E. Potassium chloride and sodium chloride as reference toxicants to assess quality of toxicity tests carried out with the microcrustacean cladocera Ceriodaphnia dubia. Bol. do Inst. de Pesca 2018, 44, e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsarskaia, O.; Roosen-Runge, F.; Schreiber, F. Multivalent ions and biomolecules: Attempting a comprehensive perspective. ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsubara, S.; Kawada, T.; Satake, H. Invertebrate Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Receptor Signaling and Its Relevant Biological Actions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alstad, N.E.W.; Skardal, L.; Hessen, D.O. The effect of calcium concentration on the calcification of Daphnia magna. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauer-Jákli, M.; Tränkner, M. Critical Leaf Magnesium Thresholds and the Impact of Magnesium on Plant Growth and Photo-Oxidative Defense: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis From 70 Years of Research. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundararajan, P.; Manivannan, A.; Ko, C.H.; Park, J.E.; Jeong, B.R. Evaluation of relative toxicity caused by deicing agents on photosynthesis, redox homeostasis, and the osmoregulatory system in creeper-type plants. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2019, 60, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuler, M.S.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hintz, W.D.; Dyack, B.; Birk, S.; Relyea, R.A. Regulations are needed to protect freshwater ecosystems from salinization. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2018, 374, 20180019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soucek, D.J.; Linton, T.K.; Tarr, C.D.; Dickinson, A.; Wickramanayake, N.; Delos, C.G.; Cruz, L.A. Influence of water hardness and sulfate on the acute toxicity of chloride to sensitive freshwater invertebrates. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mount, D.R.; Erickson, R.J.; Highland, T.L.; Hockett, J.R.; Hoff, D.J.; Jenson, C.T.; Norberg-King, T.J.; Peterson, K.N.; Polaske, Z.M.; Wisniewski, S. The acute toxicity of major ion salts to Ceriodaphnia dubia: I. Influence of background water chemistry. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 3039–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiry, R.; Stelzer, J.A.A.; Maltchik, L.; Arenzon, A. Sensitivity of Danio rerio (Teleostei, Cyprinidae) during two stages of development based on acute toxicity tests. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 93, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, J.A. Toxicity of major cations and anions (Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl−, and SO) to a macrophyte and an alga. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1370–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
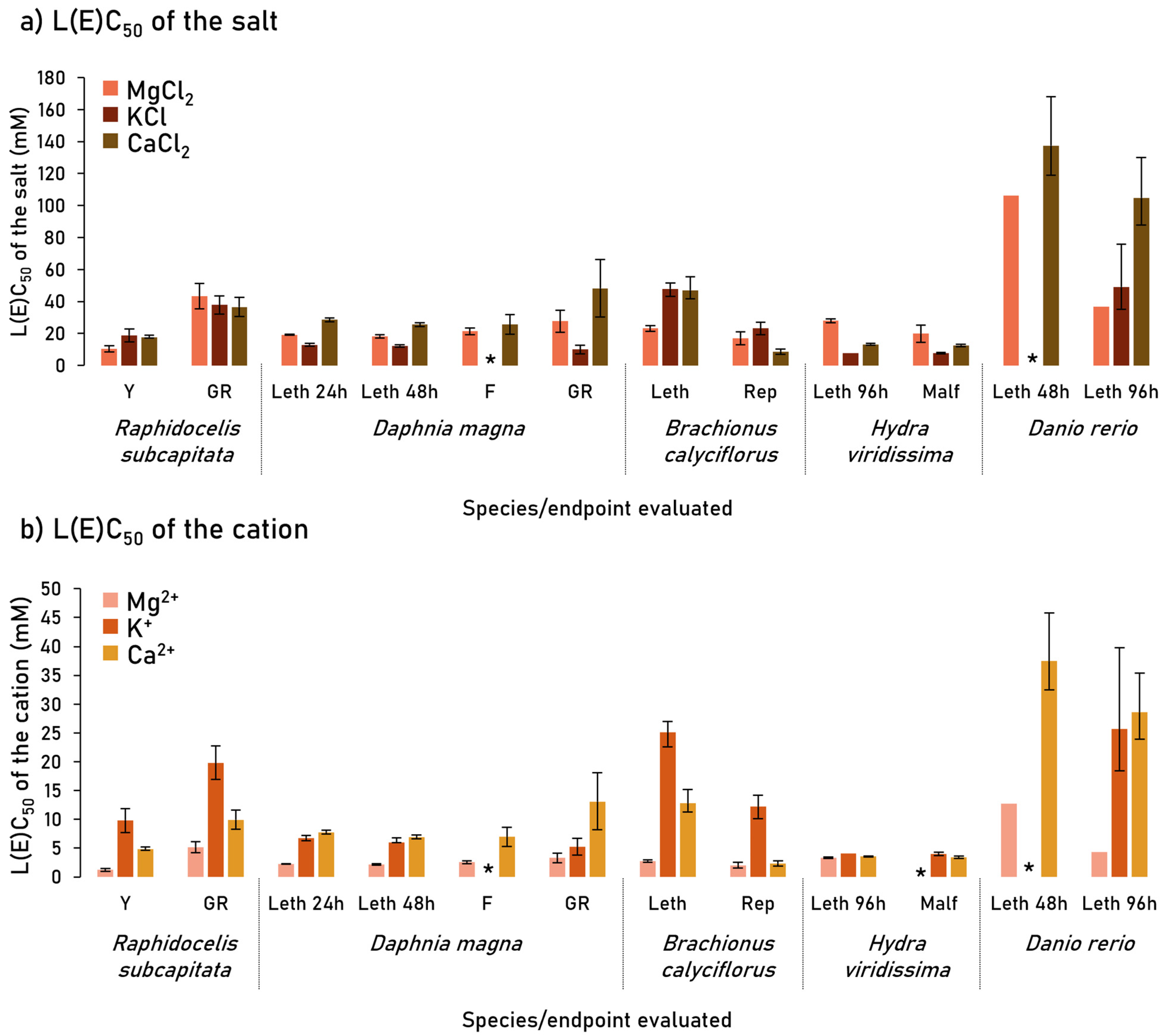
| Species | Endpoint | L(E)Cx,h (CL 95%) | MgCl2·6H2O mM | Mg2+ mM | KCl mM | K+ mM | CaCl2·2H2O mM | Ca2+ mM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raphidocelis subcapitata | Yield | EC50,72h | 10.3 (8.36–12.3) | 1.24 A (1.00–1.47) | 18.8 (14.8–22.8) | 9.85 B (7.74–11.9) | 17.7 (17.0–19.0) | 4.82 C (4.64–5.19) |
| EC20,72h | x> | x> | 6.71 (4.02–8.05) | 3.52 A (2.11–4.22) | 12.9 (11.6–14.3) | 3.52 A (3.15–3.89) | ||
| Growth rate | EC50,72h | 43.2 (35.5–51.2) | 5.17 A (4.25–6.12) | 37.8 (32.2–43.5) | 19.8 B (16.9–22.8) | 36.5 (30.5–42.5) | 9.94 C (8.33–11.6) | |
| EC20,72h | 13.4 (8.76–18.0) | 1.60 A (1.05–2.15) | 15.2 (11.0–19.5) | 7.95 B (5.77–10.2) | 20.0 (14.2–25.7) | 5.45 B (3.88–7.01) | ||
| Daphnia magna | Mortality | LC50,24h | 19.2 (18.9–19.5) | 2.29 A (2.26–2.33) | 12.9 (11.9–13.7) | 6.75 B (6.26–7.17) | 28.5 (27.3–29.7) | 7.77 B (7.44–8.10) |
| LC20,24h | 18.7 (18.4–19.0) | 2.24 A (2.21–2.28) | 11.0 (9.79–11.7) | 5.77 B (5.13–6.12) | 26.7 (24.9–27.7) | 7.27 B (6.79–7.57) | ||
| Mortality | LC50,48h | 18.2 (17.1–19.2) | 2.17 A (2.05–2.30) | 12.2 (11.4–13.0) | 6.40 B (5.98–6.82) | 25.5 (24.4–26.7) | 6.95 B (6.64–7.29) | |
| LC20,48h | 16.0 (14.7–16.9) | 1.91 A (1.75–2.02) | 10.6 (9.39–11.3) | 5.56 B (4.92–5.91) | 23.6 (21.8–24.7) | 6.43 B (5.95–6.73) | ||
| Feeding | EC50,24h | 21.4 (19.2–23.5) | 2.55 A (2.30–2.81) | x> | x> | 25.6 (19.5–31.8) | 6.99 B (5.30–8.66) | |
| EC20,24h | 20.0 (17.2–22.8) | 2.39 A (2.06–2.72) | x> | x> | 16.6 (9.05–26.3) | 4.52 A (2.47–7.16) | ||
| Growth | EC50,72h | 27.6 (20.8–34.5) | 3.30 A (2.48–4.12) | 9.93 (7.24–12.7) | 5.21 AB (3.80–6.68) | 48.2 (30.2–66.3) | 13.1 B (8.23–18.1) | |
| EC20,72h | 13.0 (10.9–15.2) | 1.56 A (1.30–1.81) | 3.76 (1.61–5.90) | 1.97 AB (0.84–3.09) | 14.4 (9.73–19.2) | 3.93 B (2.65–5.23) | ||
| Brachionus calyciflorus | Mortality | LC50,24h | 23.2 (21.4–25.0) | 2.77 A (2.55–2.98) | 47.9 (43.1–51.5) | 25.1 B (22.6–27.0) | 47.0 (41.6–55.6) | 12.8 C (11.3–15.2) |
| LC20,24h | 17.8 (15.5–19.6) | 2.13 A (1.86–2.34) | 38.6 (31.5–42.9) | 20.3 B (16.5–22.5) | 28.4 (22.3–32.6) | 7.73 C (6.08–8.90) | ||
| Reproduction | EC50,48h | 17.0 (12.9–21.1) | 2.03 A (1.54–2.52) | 23.2 (19.2–27.1) | 12.2 B (10.1–14.2) | 8.64 (7.01–10.3) | 2.36 A (1.91–2.80) | |
| EC20,48h | 11.1 (6.10–16.2) | 1.33 A (0.73–1.94) | 11.9 (6.44–17.4) | 6.26 B (3.38–9.15) | 8.30 (5.85–10.8) | 2.26 A (1.59–2.93) | ||
| Hydra viridissima | Mortality | LC50,48h | x> | x> | 8.32 (7.38–9.39) | 4.36 A (3.87–4.92) | 18.5 (18.0–19.0) | 5.04 A (4.91–5.17) |
| LC20,48h | 27.2 (26.0–28.3) | 3.25 A (3.11–3.39) | 7.78 (5.23–8.32) | 4.08 A (2.74–4.36) | 18.1 (17.6–18.6) | 4.93 B (4.80–5.06) | ||
| Mortality | LC50,96h | 28.0 (26.8–29.2) | 3.35 A (3.21–3.49) | 7.78 (-) | 4.08 A (-) | 13.1 (12.7–13.3) | 3.58 A (3.47–3.62) | |
| LC20,96h | 27.2 (-) | 3.25 A (-) | 6.71 (-) | 3.52 A (-) | 12.9 (12.5–13.3) | 3.50 A (3.39–3.62) | ||
| Malformation | EC50,48h | x> | x> | 7.91 (7.78–8.18) | 4.15 A (4.08–4.29) | 17.0 (16.1–17.8) | 4.64 A (4.38–4.86) | |
| EC20,48h | 6.25 (-) | 0.75 A (-) | 7.51 (7.11–7.78) | 3.94 B (3.73–4.08) | 15.6 (14.3–17.1) | 4.26 B (3.89–4.65) | ||
| Malformation | EC50,96h | 19.8 (14.5–25.1) | 2.37 A (1.74–3.00) | 7.65 (7.11–8.18) | 4.01 B (3.73–4.29) | 12.5 (11.8–13.2) | 3.39 B (3.21–3.60) | |
| EC20,96h | 7.97 (3.10–12.8) | 0.95 A (0.37–1.53) | 6.98 (5.63–8.32) | 3.66 B (2.95–4.36) | 11.0 (9.80–12.0) | 2.99 B (2.67–3.28) | ||
| Danio rerio | Mortality | LC50,48h | 106.2 (-) | 12.7 A (-) | x> | x> | 137.4 (119.0–168.0) | 37.5 B (32.5–45.8) |
| LC20,48h | 67.4 (-) | 8.06 A (-) | x> | x> | 71.4 (54.5–82.3) | 19.5 B (14.9–22.4) | ||
| Mortality | LC50,96h | 36.7 (-) | 4.35 A (-) | 49.1 (35.0–75.9) | 25.7 B (18.4–39.8) | 104.8 (87.8–129.9) | 28.6 B (23.9–35.4) | |
| LC20,96h | 31.4 (24.2–35.2) | 3.76 A (2.89–4.21) | 18.4 (8.58–23.7) | 9.64 B (4.50–12.5) | 48.6 (36.5–57.8) | 13.2 AB (9.96–15.7) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venâncio, C.; Caon, K.; Lopes, I. Cation Composition Influences the Toxicity of Salinity to Freshwater Biota. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031741
Venâncio C, Caon K, Lopes I. Cation Composition Influences the Toxicity of Salinity to Freshwater Biota. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(3):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031741
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenâncio, Cátia, Karen Caon, and Isabel Lopes. 2023. "Cation Composition Influences the Toxicity of Salinity to Freshwater Biota" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 3: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031741
APA StyleVenâncio, C., Caon, K., & Lopes, I. (2023). Cation Composition Influences the Toxicity of Salinity to Freshwater Biota. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(3), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031741







