The Influence of Whey Protein on Muscle Strength, Glycemic Control and Functional Tasks in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Resistance Exercise Program: Randomized and Triple Blind Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
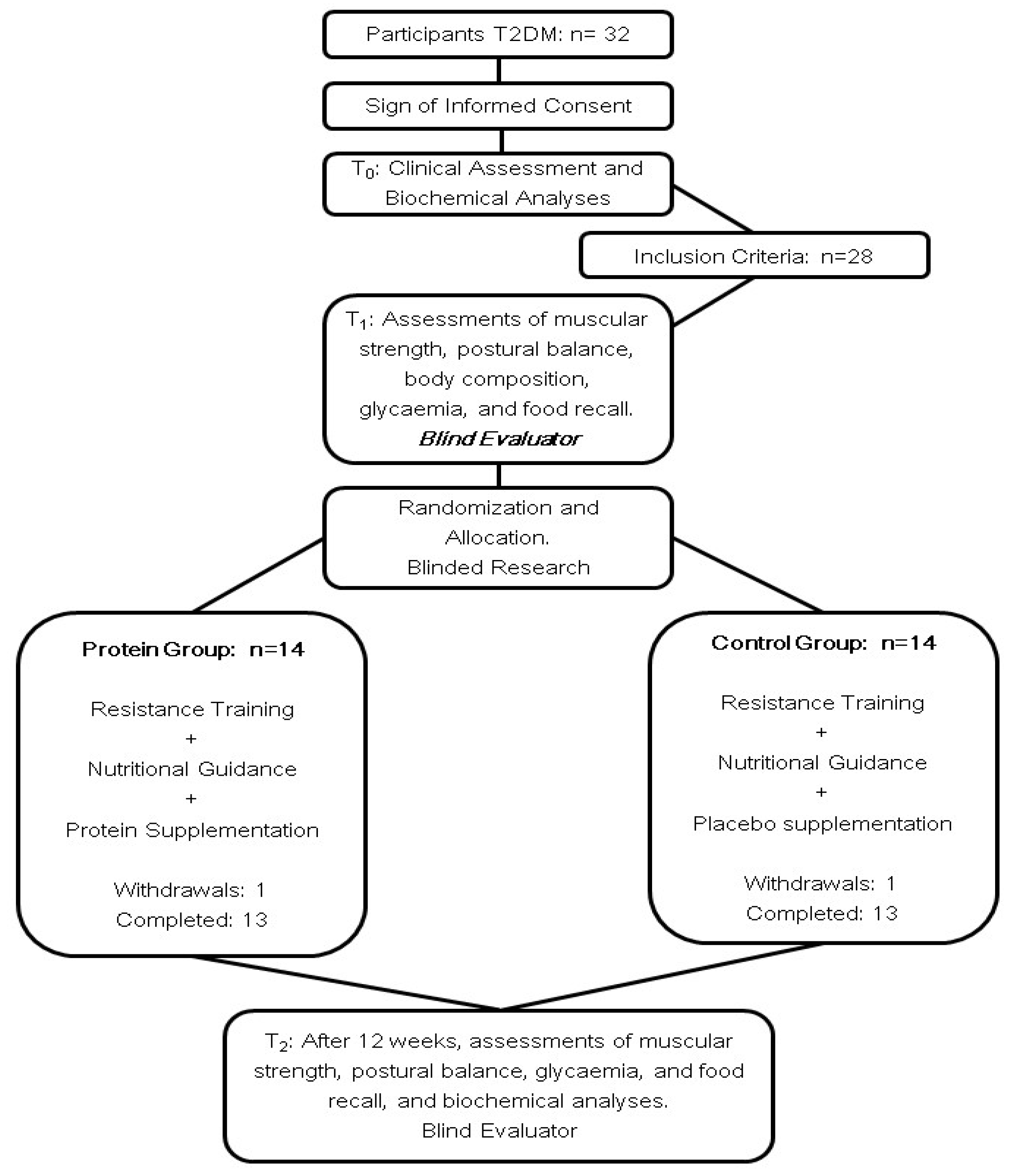
2. Materials and Methods
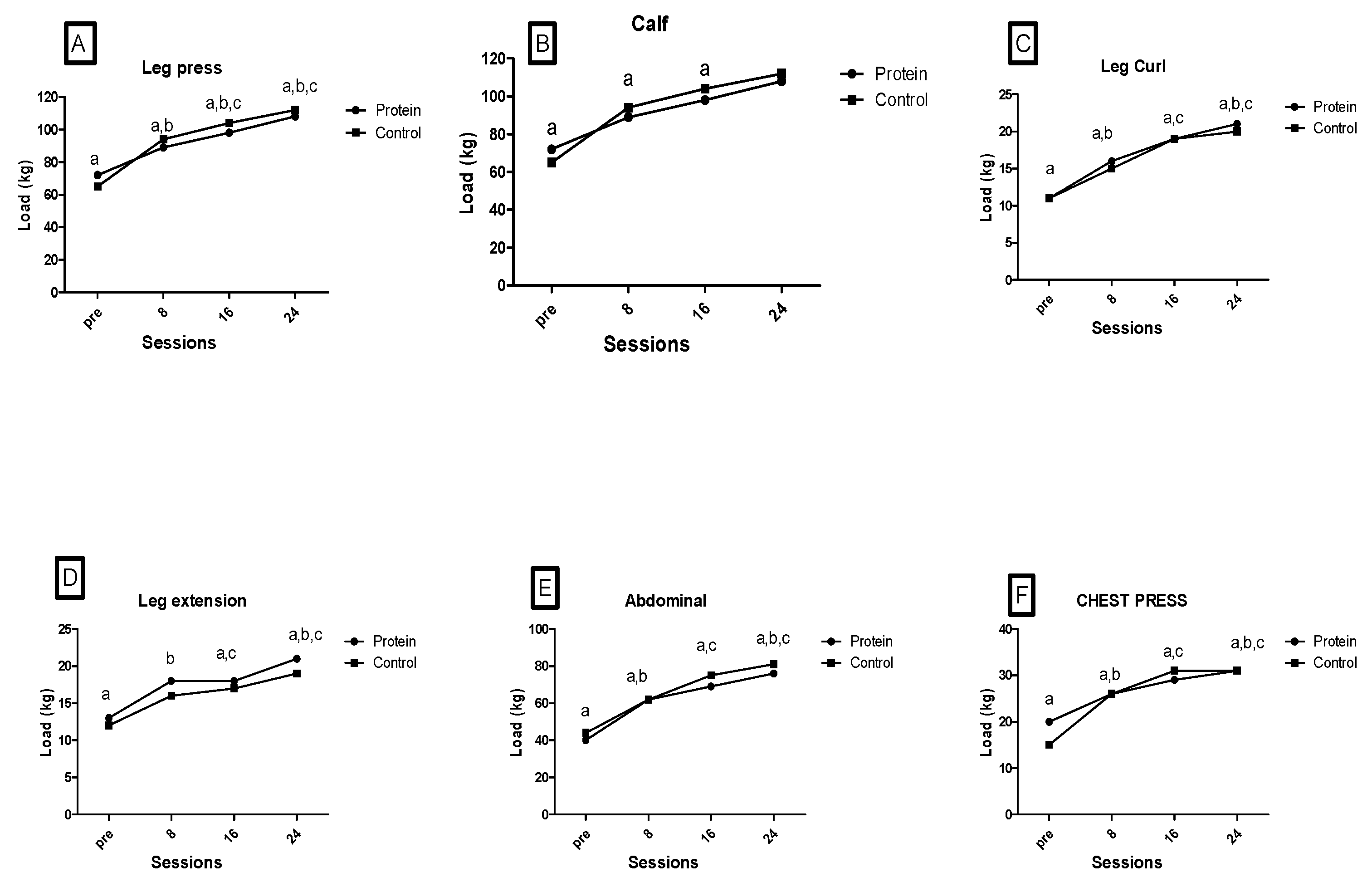
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewgood, J.; Oliveira, B.; Korzepa, M.; Forbes, S.C.; Little, J.P.; Breen, L.; Bailie, R.; Candow, D.G. Efficacy of dietary and supplementation interventions for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.D.; Langenberg, C.; Rapsomaniki, E.; Denaxas, S.; Pujades-Rodriguez, M.; Gale, C.P.; Deanfield, J.; Smeeth, L.; Timmis, A.; Hemingway, H. Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: A cohort study in 1·9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015, 3, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beulens, J.W.J.; Pinho, M.G.M.; Abreu, T.C.; den Braver, N.R.; Lam, T.M.; Huss, A.; Vlaanderen, J.; Sonnenschein, T.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Yuan, Z.; et al. Environmental risk factors of type 2 diabetes—An exposome approach. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argano, C.; Natoli, G.; Mularo, S.; Nobili, A.; Lo Monaco, M.; Mannucci, P.M.; Perticone, F.; Pietrangelo, A.; Corrao, S. Impact of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Comorbidities on Elderly Patients Hospitalized in Internal Medicine Wards: Data from the RePoSi Registry. Healthcare 2022, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudry, K.M.; Devries, M.C. Nutritional Strategies to Combat Type 2 Diabetes in Aging Adults: The Importance of Protein. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, I.; Oberoi, A.; Giezenaar, C.; Soenen, S. Rational use of protein supplements in the elderly—Relevance of gastrointestinal mechanisms. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibañez, J.; Izquierdo, M.; Argüelles, I.; Forga, L.; Larrión, J.L.; García-Unciti, M.; Idoate, F.; Gorostiaga, E.M. Twice-weekly progressive resistance training decreases abdominal fat and improves insulin sensitivity in older men with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadore, E.L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sinclair, A.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of different exercise interventions on risk of falls, gait ability, and balance in physically frail older adults: A systematic review. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, C.; Sagalova, V.; Heesemann, E.; Manne-Goehler, J.; Atun, R.; Bärnighausen, T.; Davies, J.; Vollmer, S. Global economic burden of diabetes in adults: Projections from 2015 to 2030. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, R.M.; Miller, E.G.; Dunstan, D.W.; Kerr, D.A.; Solah, V.; Menzies, D.; Nowson, C.A. The effects of progressive resistance training combined with a whey-protein drink and vitamin D supplementation on glycaemic control, body composition and cardiometabolic risk factors in older adults with type 2 diabetes: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2014, 15, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesta, D.H.; Goncalves, R.L.S.; Madiraju, A.K.; Strasser, B.; Sparks, L.M. Resistance training to improve type 2 diabetes: Working toward a prescription for the future. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaim, C.; Kob, M.; Di Pierro, A.M.; Herrmann, M.; Lucchin, L. Effects of a whey protein supplementation on oxidative stress, body composition and glucose metabolism among overweight people affected by diabetes mellitus or impaired fasting glucose: A pilot study. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 50, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartorius, T.; Weidner, A.; Dharsono, T.; Boulier, A.; Wilhelm, M.; Schön, C. Correction: Postprandial effects of a proprietary milk protein hydrolysate containing bioactive peptides in prediabetic subjects. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.L.; Broughton, K.S. Insulinotropic Effects of Whey: Mechanisms of Action, Recent Clinical Trials, and Clinical Applications. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 69, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannon, B.A.; Fairfield, W.D.; Adams, B.; Kyle, T.; Crow, M.; Thomas, D.M. Use and abuse of dietary supplements in persons with diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakigi, R.; Yoshihara, T.; Ozaki, H.; Ogura, Y.; Ichinoseki-Sekine, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Naito, H. Whey protein intake after resistance exercise activates mTOR signaling in a dose-dependent manner in human skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S.Y.M.; Kanaley, J.A.; Guelfi, K.J.; Marston, K.J.; Fairchild, T.J. The Effect of Exercise Timing on Glycemic Control: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.C.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Luna, N.M.S.; Peterson, M.D.; Bocalini, D.S.; Serra, M.M.; Brech, G.C.; Greve, J.M.D.; Garcez-Leme, L.E. Association between handgrip strength, balance, and knee flexion/extension strength in older adults. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ernandes, R.C.; Brech, G.C.; Luna, N.M.S.; Nunes, M.F.; Greve, J.M.D.A.; Leme, L.E.G.; Alonso, A.C. Relationship of force platform with the clinical balance evaluation systems test in older adults. Acta Ortop. Bras. 2020, 28, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consort—Welcome to the CONSORT Website. Available online: http://www.consort-statement.org/ (accessed on 6 February 2023).
- Bauer, J.; Biolo, G.; Cederholm, T.; Cesari, M.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Morley, J.E.; Phillips, S.; Sieber, C.; Stehle, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations for optimal dietary protein intake in older people: A position paper from the prot-age study group. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promislow, J.H.E.; Goodman-Gruen, D.; Slymen, D.J.; Barrett-Connor, E. Protein consumption and bone mineral density in the elderly: The Rancho Bernardo study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapuri, P.B.; Gallagher, J.C.; Haynatzka, V. Protein intake: Effects on bone mineral density and the rate of bone loss in elderly women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houston, D.K.; Nicklas, B.J.; Ding, J.; Harris, T.B.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Newman, A.B.; Jung, S.L.; Sahyoun, N.R.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B. Dietary protein intake is associated with lean mass change in older, community-dwelling adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition (Health ABC) study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgic, J.; Lazinica, B.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Pedisic, Z. Test–Retest Reliability of the One-Repetition Maximum (1RM) Strength Assessment: A Systematic Review. Sport. Med. Open 2020, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gearhart, R., Jr.; Lagally, K.; Riechman, S.; Andrews, R.; Robertson, R. Stregnth training using the OMNI resistance exercise scale in older mena and women. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2009, 23, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Hector, A.J.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Josse, A.R.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance exercise enhances myofibrillar protein synthesis with graded intakes of whey protein in older men. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ellis, V.; Dhaliwal, S. Effects of whey protein isolate on body composition, lipids, insulin and glucose in overweight and obese individuals. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, E.G.; Nowson, C.A.; Dunstan, D.W.; Kerr, D.A.; Menzies, D.; Daly, R.M. Effects of whey protein plus vitamin D supplementation combined with progressive resistance training on glycaemic control, body composition, muscle function and cardiometabolic risk factors in middle-aged and older overweight/obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaffney, K.; Lucero, A.; Macartney-Coxson, D.; Clapham, J.; Whitfield, P.; Palmer, B.R.; Wakefield, S.; Faulkner, J.; Stoner, L.; Rowlands, D.S. Effects of whey protein on skeletal muscle microvascular and mitochondrial plasticity following 10 weeks of exercise training in men with type 2 diabetes. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini; Chauhan, P.S.; Kumari, S.; Kumar, J.P.; Chawla, R.; Dash, D.; Singh, M.; Singh, R. Intranasal curcumin and its evaluation in murine model of asthma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernandes, R.C.; Brech, G.C.; Luna, N.M.S.; Bega, A.; Guimarães, D.S.; Bocalini, D.S.; Scherrer, G.; Greve, J.M.D.A.; Leme, L.E.G.; Alonso, A.C. Impact of Diabetic Neuropathy on Quality of Life and Postural Balance in Brazilian Older Adults. Acta Ortop. Bras. 2020, 28, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavros, Y.; Kay, S.; Anderberg, K.A.; Baker, M.K.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Meiklejohn, J.; Climstein, M.; O’Sullivan, A.; de Vos, N.; et al. Changes in insulin resistance and HbA1c are related to exercise-mediated changes in body composition in older adults with type 2 diabetes: Interim outcomes from the GREAT2DO trial. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2372–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.J.; Banton, T.; Moncrief, M.; Conaway, M.; Diamond, A.; Holmes, V.; Green Pastors, J.; Wolf, A.; Fang, K.; Mccall, A. Glycemic excursion minimization in the management of type 2 diabetes: A novel intervention tested in a randomized clinical trial. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes, 2022. A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 2753–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumukadas, D.; Struthers, A.D.; McMurdo, M.E.T. Sarcopenia—A potential target for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition? Gerontology 2006, 52, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfik, V.L.; Quarta, M.; Paine, P.; Forman, T.E.; Pajarinen, J.; Takemura, Y.; Goodman, S.B.; Rando, T.A.; Clark, J.D. Angiotensin receptor blockade mimics the effect of exercise on recovery after orthopaedic trauma by decreasing pain and improving muscle regeneration. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campins, L.; Camps, M.; Riera, A.; Pleguezuelos, E.; Yebenes, J.C.; Serra-Prat, M. Oral drugs related with muscle wasting and sarcopenia. A review. Pharmacology 2017, 99, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.E.; Kosmac, K.; Dungan, C.M.; Bamman, M.M.; Peterson, C.A.; Kern, P.A. Potential Benefits of Combined Statin and Metformin Therapy on Resistance Training Response in Older Individuals. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 872745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, M.M.; Sumukadas, D.; Struthers, A.D.; Avenell, A.; Donnan, P.T.; Kemp, P.R.; Smith, K.T.; Hume, C.L.; Hapca, A.; Witham, M.D. Leucine and ACE inhibitors as therapies for sarcopenia (LACE trial): Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2018, 19, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Cao, L.; Liu, T.; Huang, T.; Wei, Q.; Ma, G.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Risk Factors for Sarcopenia in the Elderly with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Effect of Metformin. J. Diabetes Res. 2020, 2020, 3950404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Shao, H. Anti-diabetic drugs and sarcopenia: Emerging links, mechanistic insights, and clinical implications. J. Cachexia. Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, E.O.; Sheer, R.; Schmedt, N.; Evers, T.; Cockrell, M.; Tindal, M.; Pasquale, M.K.; Kovesdy, C.P. Glomerular filtration rate change and outcomes in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Manag. Care 2021, 27 (Suppl. S8), S160–S167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Protein M(SD) | Control M(SD) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| # Age (years) | 68.1 (4.5) | 68.9 (4.1) | 0.63 |
| # BMI (kg/m2) | 29.3 (2.6) | 26.8 (3.8) | 0.07 |
| # Education (years) | 11.5 (3.1) | 11.5 (3.1) | 0.39 |
| # Time since diagnosis (years) | 12.7 (3.8) | 12.8 (6.4) | 0.86 |
| # Other diseases (n) | 1.6 (1.4) | 1.2 (0.9) | 0.36 |
| # Medication (n) | 3.8 (2.0) | 3.4 (1.8) | 0.62 |
| § Ethnicity | n (%) | n (%) | χ2 (p) |
| Caucasian | 9/64.3 | 11/78.6 | 1.343(0.51) |
| Asian | 1/7.7 | 0/0 | |
| Black and Brown Skin | 4/28.6 | 3/21.4 | |
| § BMI (kg/m2) | n (%) | n (%) | χ2 (p) |
| Low weight | 1/7.1 | 1/7.1 | 0.650 (0.72) |
| Eutrophic | 6/42.9 | 4/28.6 | |
| Overweight | 7/50 | 9/64.3 | |
| * Oral Hypoglycemic Medication | n (%) | n (%) | Fischer’s exact (p) |
| Thiazolidinediones | 2/14.3 | 0/0 | 0.48 |
| Sulfonylureas | 8/57.1 | 8/57.1 | 1.00 |
| Biguanide | 8/57.1 | 9/64.3 | 1.00 |
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 2/14.3 | 3/21.4 | 1.00 |
| SGLT2 inhibitors | 2/14.3 | 2/14.3 | 1.00 |
| * Cardiovascular Medication | n (%) | n (%) | Fischer’s exact (p) |
| ARBs | 1/7.1 | 4/28.6 | 0.32 |
| ACE-Is | 2/14.3 | 1/7.1 | 1.00 |
| Statins | 5/35.7 | 3/21.4 | 0.67 |
| Parameters | Pre (sd) | Post (sd) | η2 | ANOVA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Effect | Group Effect | Group × Time Effect | |||||||
| F | p | F | p | F | p | ||||
| Lift Up left side | |||||||||
| Protein | 36.64 (9.90) | 36.82 (12.31) | 0.01 | 0.44 | 0.50 | 0.02 | 0.86 | 0.52 | 0.47 |
| Control | 35.1 (8.95) | 39.3 (10.68) | |||||||
| Lift Up right side | |||||||||
| Protein | 36.92 (7.23) | 38.00 (9.27) | 0.01 | 1.74 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.78 | 0.83 | 0.36 |
| Control | 33.8 (9.6) | 39.6 (11.3) | |||||||
| Moment Time left | |||||||||
| Protein | 1.51(0.19) | 1.69 (0.33) | 0.01 | 0.74 | 0.39 | 3.15 | 0.08 | 0.91 | 0.34 |
| Control | 1.78(0.35) | 1.77 (0.42) | |||||||
| Moment Time right | |||||||||
| Protein | 1.68 (0.30) | 1.76 (0.56) | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.85 | 0.004 | 0.95 | 0.84 | 0.36 |
| Control | 1.80 (0.42) | 1.67 (0.25) | |||||||
| Impact Index left | |||||||||
| Protein | 44.54 (13.58) | 38.10 (11.53) | 0.03 | 0.19 | 0.65 | 0.06 | 0.80 | 1.86 | 0.17 |
| Control | 40.57 (12.21) | 43.85 (13.0) | |||||||
| Impact Index right | |||||||||
| Protein | 40.00 (14.33) | 34.18 (12.66) | 0.01 | 0.47 | 0.49 | 5.74 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 0.50 |
| Control | 47.26 (17.13) | 47.23 (14.94) | |||||||
| Weight transfer | |||||||||
| Protein | 0.50 (0.19) | 0.52 (0.26) | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.95 | 0.03 | 0.86 | 0.05 | 0.82 |
| Control | 0.51 (0.32) | 0.48 (0.32) | |||||||
| Sway Velocity | |||||||||
| Protein | 3.50 (1.16) | 3.71 (0.88) | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.95 | 2.47 | 0.12 | 0.36 | 0.55 |
| Control | 4.08 (1.45) | 4.33 (1.72) | |||||||
| Turn Time-SND | |||||||||
| Protein | 2.20 (0.73) | 2.12 (0.58) | 0.007 | 0.95 | 0.33 | 1.29 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.57 |
| Control | 2.54 (0.87) | 2.23 (0.60) | |||||||
| Turn Time-SD | |||||||||
| Protein | 2.31 (0.74) | 1.85 (0.36) | 0.02 | 0.003 | 0.95 | 4.31 | 0.04 | 1.40 | 0.24 |
| Control | 2.34 (0.85) | 2.61 (1.10) | |||||||
| Turn Sway-SND | |||||||||
| Protein | 50.26 (13.10) | 45.21 (10.9) | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 1.31 | 0.25 |
| Control | 43.5 (13.1) | 46.7 (12.9) | |||||||
| Turn Sway-SD | |||||||||
| Protein | 50.26 (13.10) | 45.21 (12.62) | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.77 | 0.51 | 0.47 | 1.31 | 0.25 |
| Control | 43.71 (12.64) | 46.73 (12.72) | |||||||
| Pre (sd) | Post (sd) | η2 | ANOVA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time Effect | Group Effect | Group × Time Effect | |||||||
| F | p | F | p | F | p | ||||
| MDRD (mL/min/1.73 m2) | |||||||||
| Protein | 86.7 (32.4) | 90.1 (24.9) | 0.04 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 1.87 | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.71 |
| Control | 82.3 (17.6) | 79.2 (11.4) | |||||||
| FRUCTOSAMINE (µmol/L) | |||||||||
| Protein | 315.2 (75.0) | 285.0 (40.1) | 0.02 | 2.00 | 0.16 | 1.55 | 0.22 | 0.59 | 0.81 |
| Control | 281.6 (50.6) | 260.6 (30.8) | |||||||
| GLUCOSE (mg/dL) | |||||||||
| Protein | 140.1 (65.9) | 124.8 (37.7) | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 0.93 | 0.00 | 0.98 |
| Control | 141.2 (47.3) | 126.5 (17.8) | |||||||
| INSULIN (µU/mL) | |||||||||
| Protein | 11.0 (3.9) | 12.4 (9.0) | 0.02 | 0.16 | 0.68 | 1.82 | 0.18 | 0.73 | 0.39 |
| Control | 17.6 (9.1) | 14.3 (5.4) | |||||||
| HbA1c (%) | |||||||||
| Protein | 7.2 (1.1) | 6.9 (1.0) | 0.01 | 1.24 | 0.27 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.87 |
| Control | 7.0 (1.2) | 6.5 (0.6) | |||||||
| HOMA IR | |||||||||
| Protein | 4.1 (1.7) | 4.2 (2.6) | 0.03 | 1.50 | 0.21 | 2.50 | 0.11 | 1.7 | 0.20 |
| Control | 6.5 (3.9) | 4.1 (2.1) | |||||||
| Body Composition | |||||||||
| LEAN MASS (kg) | |||||||||
| Protein | 32.8 (5.3) | 32.5 (4.8) | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.67 | 0.84 | 0.36 | 0.20 | 0.65 |
| Control | 34.3 (5.4) | 34.4 (5.7) | |||||||
| FAT MASS (kg) | |||||||||
| Protein | 22.5 (7.8) | 21.9 (8.1) | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.86 | 3.00 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.93 |
| Control | 26.8 (10.3) | 26.6 (10.2) | |||||||
| Hand Grip Strength | |||||||||
| HGS–DS (kg/f) | |||||||||
| Protein | 36.7 (9.9) | 36.1 (8.7) | 0.01 | 0.34 | 0.55 | 0.20 | 0.65 | 068 | 0.41 |
| Control | 33.8 (8.7) | 37.0 (4.6) | |||||||
| HGS–NDS (kg/f) | |||||||||
| Protein | 33.7 (10.8) | 35.8 (10.3) | 0.001 | 1.20 | 0.27 | 0.25 | 0.61 | 0.05 | 0.82 |
| Control | 32.0 (7.4) | 35.1 (4.3) | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soares, A.L.d.S.; Machado-Lima, A.; Brech, G.C.; Greve, J.M.D.; dos Santos, J.R.; Inojossa, T.R.; Rogero, M.M.; Salles, J.E.N.; Santarem-Sobrinho, J.M.; Davis, C.L.; et al. The Influence of Whey Protein on Muscle Strength, Glycemic Control and Functional Tasks in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Resistance Exercise Program: Randomized and Triple Blind Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105891
Soares ALdS, Machado-Lima A, Brech GC, Greve JMD, dos Santos JR, Inojossa TR, Rogero MM, Salles JEN, Santarem-Sobrinho JM, Davis CL, et al. The Influence of Whey Protein on Muscle Strength, Glycemic Control and Functional Tasks in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Resistance Exercise Program: Randomized and Triple Blind Clinical Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(10):5891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105891
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoares, André Luiz de Seixas, Adriana Machado-Lima, Guilherme Carlos Brech, Júlia Maria D’Andréa Greve, Joselma Rodrigues dos Santos, Thiago Resende Inojossa, Marcelo Macedo Rogero, João Eduardo Nunes Salles, José Maria Santarem-Sobrinho, Catherine L. Davis, and et al. 2023. "The Influence of Whey Protein on Muscle Strength, Glycemic Control and Functional Tasks in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Resistance Exercise Program: Randomized and Triple Blind Clinical Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 10: 5891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105891
APA StyleSoares, A. L. d. S., Machado-Lima, A., Brech, G. C., Greve, J. M. D., dos Santos, J. R., Inojossa, T. R., Rogero, M. M., Salles, J. E. N., Santarem-Sobrinho, J. M., Davis, C. L., & Alonso, A. C. (2023). The Influence of Whey Protein on Muscle Strength, Glycemic Control and Functional Tasks in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Resistance Exercise Program: Randomized and Triple Blind Clinical Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(10), 5891. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105891











