Professionals’ Perspectives on the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic among Child and Adolescent Victims of Domestic Violence Living in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System
Abstract
1. Introduction
Residential Foster Care System and DV in Portugal during the COVID-19 Pandemic
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Procedure
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis Techniques
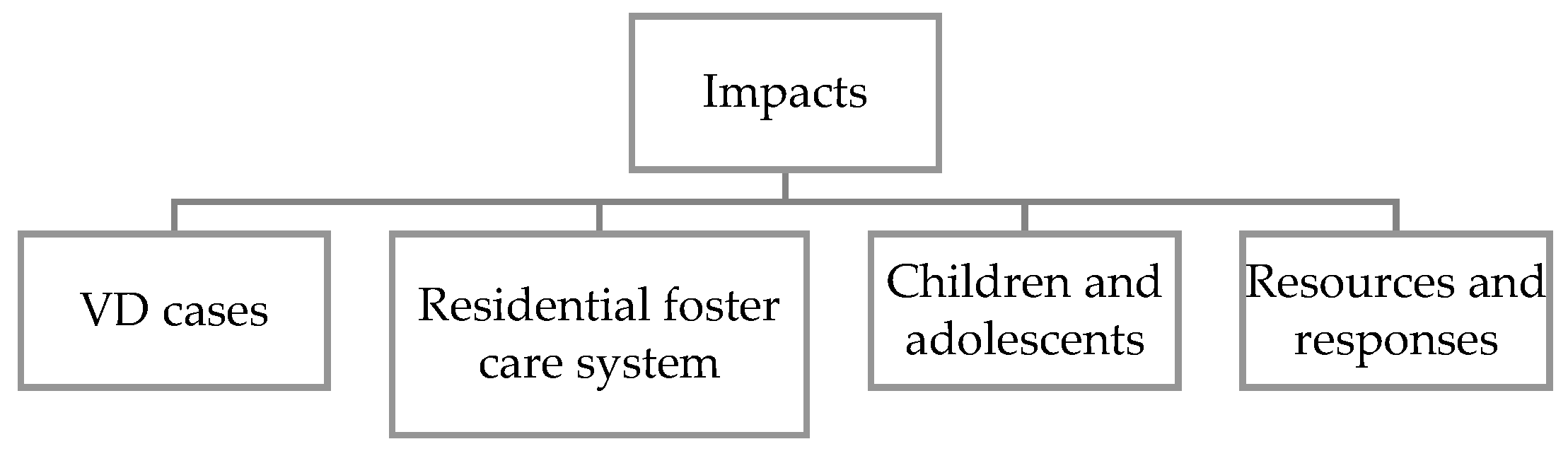
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative Data
3.2. Qualitative Data
3.2.1. The Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on DV Cases
“I think lockdown (…) has brought more domestic violence into homes (…). I believe that most of the cases were hidden (…). I would say that it was an atrocious increase. (…) “It brings a lot of frustration and I think it increased the level of domestic violence at home between parents and children because tolerance was much lower (…)”(I2-M-40)
“(…) but then there it is, the continuity, all those hours, 24 under 24 together ended up triggering even more.”(I1-M-49)
“The fact that we were all confined, there were no field teams that could prevent issues of domestic violence”(E2-M-40)
“(…) the children, if they are not at home, where are they? They’re in school! Therefore, if the school is closed and the children must be automatically at home, no one does this, this lookout and this, that take care of the child.”(I7-F-29)
3.2.2. The Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System
“(…) we are aware that these types of restrictions are not advantageous for children, because it limits the intervention a little bit and limits the interaction between family members and children.”(I7-F-29)
3.2.3. The Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Child and Adolescent Victims of Domestic Violence Living in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System
“(…) They are tired of being closed and together (…) it´s the same to us, adults, isn’t it? If we are too much time with the same people, we get tired, isn’t it? So, sometimes we need to be away for a while and the children need that too, isn’t it? They were 20 children living here daily (…).”(I6-F-46)
3.2.4. The Resources and Responses of the Professionals Working in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System during the COVID-19 Pandemic
“Here we always encourage contact to be maintained. (…) Always, the telephone contact, and the video calls, we promote here that contact should remain. (…) And to the youths themselves keep them abreast of the process and what’s happening, I think that’s fundamental”(I4-F-39)
“And then also, greatly increase the number of (…) playful-pedagogical activities (…) inside the house to keep them also active and distracted as well and fun (…)”(I3-F-36)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sá, A.F.; Lourenço, S.F.; Teixeira, R.D.; Barros, F.; Costa, A.; Lemos, P. Urgent/emergency surgery during COVID-19 State of Emergency in Portugal: A retrospective and observational study. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2021, 71, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgado, A.M.; Cruz, J.; Peixoto, M.M. Individual and community psychological experiences of the COVID-19 pandemic: The state of emergency in Portugal. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 42, 3213–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anurudran, A.; Yared, L.; Comrie, C.; Harrison, K.; Burke, T. Domestic violence amid COVID-19. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2020, 150, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, B.L.; Lu, L.Z.N.; MacFarlane, M.; Stark, L. Predictors of Interpersonal Violence in the Household in Humanitarian Settings: A Systematic Review. Trauma Violence Abus. 2020, 21, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourti, A.; Stavridou, A.; Panagouli, E.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Spiliopoulou, C.; Tsolia, M.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Tsitsika, A. Domestic Violence During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Systematic Review. Trauma Violence Abus. 2021, 24, 719–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gama, A.; Pedro, A.R.; De Carvalho, M.J.L.; Guerreiro, A.E.; Duarte, V.; Quintas, J.; Matias, A.; Keygnaert, I.; Dias, S. Domestic Violence during the COVID-19 Pandemic in Portugal. Port. J. Public Health 2021, 38, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorou, C.M.; Brown, E.G.; Jackson, J.E.; Beres, A.L. Child Abuse and the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Surg. Res. 2022, 276, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertan, D.; El-Hage, W.; Thierrée, S.; Javelot, H.; Hingray, C. COVID-19: Urgency for distancing from domestic violence. Eur. J. Psychotraumatol. 2020, 1, e1800245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.; Jijon, I. COVID-19 and violence against children: A review of early studies. Child Abus. Negl. 2021, 116, e105053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, H.; McLeigh, J.; Wolfe, K.; Conner, E.; Smith, V.; Greeley, C.S.; Keefe, R.J. Caring for children in foster and kinship care during a pandemic: Lessons learned and recommendations. J. Public Child Welf. 2023, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musser, E.D.; Riopelle, C.; Latham, R. Child maltreatment in the time of COVID-19: Changes in the Florida foster care system surrounding the COVID-19 safer-at-home order. Child Abus. Negl. 2021, 116, e104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.; Grise-Owens, E. Self-Care: An Imperative. Soc. Work 2020, 65, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheyden, C.; Van Holen, F.; West, D.; Vanderfaeillie, J. Secondary traumatic stress, burnout, and compassion satisfaction among Flemish foster care workers during the COVID-19 lockdown. Dev. Child Welf. 2020, 2, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilesanmi, O.S.; Ariyo, M.; Afolabi, A.A. Domestic violence amid the COVID-19 lockdown: A threat to individual safety. Glob. Biosecur. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.A.; Ming, D.; Maslow, G.; Gifford, E.J. Mitigating the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic response on At-risk children. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20200973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greeson, J.K.P.; Gyourko, J.R.; Jaffee, S.R.; Wasch, S. The Experiences of Older Youth in and Aged Out of Foster Care During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Material and Financial Well-Being by Foster Care Status, Gender Identity, Sexual Orientation, Ethnicity, and Race. Am. J. Orthopsychiatry 2022, 92, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitt-Woosley, A.; Sprang, G.; Eslinger, J. Foster care during the COVID-19 pandemic: A qualitative analysis of caregiver and professional experiences. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 124, e105444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, P. Risks to children and young people during covid-19 pandemic. BMJ 2020, 369, m1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shpiegel, S.; Aparicio, E.M.; Ventola, M.; Channell Doig, A.; Jasczynski, M.; Martínez-García, G.; Smith, R.; Sanchez, A.; Robinson, J.L. Experiences of young parents with foster care backgrounds during the COVID-19 pandemic. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 131, e105527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, R.; Sun, S.; Flannigan, A.; O’Meara, M. Impact of COVID-19 among young people currently and formerly in foster care. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 123, e105383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SSI—Sistema de Segurança Interna. Relatório anual de Segurança Interna—2021; Lisboa, SSI: Lisboa, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Delgado, J.P.F. O acolhimento familiar de crianças em Portugal—evidências e desafios. Polêmica 2020, 20, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, P.; Pinto, V.S.; Carvalho, J.M.S.; Gilligan, R. Family contact in foster care in Portugal. The views of children in foster care and other key actors. Child Fam. Soc. Work 2019, 24, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNPDPCJ—Comissão Nacional de Promoção dos Direitos e Proteção das Crianças e Jovens. Relatório Anual de Avaliação da Atividade das CPCJ 2020; CNPDPCJ: Lisboa, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- CNPDPCJ—Comissão Nacional de Promoção dos Direitos e Proteção das Crianças e Jovens. Relatório Anual de Avaliação da Atividade das CPCJ 2021; CNPDPCJ: Lisboa, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ISS—Instituto de Segurança Social. CASA 2021—Relatório de Caracterização Anual da Situação de Acolhimento das Crianças e Jovens; ISS: Lisboa, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ISS—Instituto de Segurança Social. CASA 2020—Relatório de Caracterização Anual da Situação de Acolhimento das Crianças e Jovens; ISS: Lisboa, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.; Matos, P.M.; Santos, B.; Carvalho, H.; Ferreira, T.; Mota, C.P. We stick together! COVID-19 and psychological adjustment in youth residential care. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 130, e105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machlin, L.; Gruhn, M.A.; Miller, A.B.; Milojevich, H.M.; Motton, S.; Findley, A.M.; Sheridan, M.A. Predictors of family violence in North Carolina following initial COVID-19 stay-at-home orders. Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 130, e105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, E.; Ritchie, H.; Rodés-Guirao, L.; Appel, C.; Giattino, C.; Ortiz-Ospina, E.; Hasell, J.; Macdonald, B.; Beltekian, D.; Roser, M. Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). Our World in Data. 2020. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus (accessed on 14 April 2023).
- da Silva Almeida, G.L.; Machado, G.G.; dos Santos, I.C.; Boldrini, L.F.F.; dos Reis, M.B.; Rebelin, M.S.; de Almeida Schittini, M.; Rizo, R.E.; da Silva, S.C.; de Oliveira Lourenço, A. A complexidade da violência doméstica durante a pandemia do COVID-19. RECIMA21 2021, 2, e28620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, P.A.; Carmo, R.M.; Cantante, F.; Cruz, C.; Estêvão, P.; Manso, L.; Pereira, T.S. Trabalho e desigualdades No Grande Confinamento; CoLABOR: Lisboa, Portugal, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury-Jones, C.; Isham, L. The pandemic paradox: The consequences of COVID-19 on domestic violence. J. Clin. Nurs. 2020, 29, 2047–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, A.K. Parental burnout and child maltreatment during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Fam. Violence 2020, 37, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Ward, K.P. Stress and Parenting during the Coronavírus Pandemic; Research Brief; University of Michigan, Parenting in Context Research Lab: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2020; Available online: https://bit.ly/2D3Fv2I (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Mikolajczak, M.; Gross, J.J.; Roskam, I. Parental burnout: What is it, and why does it matter? Clin. Psychol. Sci. 2019, 7, 1319–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordem dos Psicólogos Portugueses [OPP]. COVID-19. Isolamento com Direitos: Conter o vírus e a Violência Doméstica. 2020. Available online: https://www.ordemdospsicologos.pt/pt/noticia/2760 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Katz, I.; Priolo-Filho, S.; Katz, C.; Andresen, S.; Bérubé, A.; Yamaoka, Y. One year into COVID-19: What have we learned about child maltreatment reports and child protective service responses? Child Abus. Negl. 2022, 130, e105473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, E.S.; Moraes, C.L.; Hasselmann, M.H.; Deslandes, S.F.; Reichenheim, M.E. Violence against women, children, and adolescents during the COVID-19 pandemic: Overview, contributing factors, and mitigating measures. Cad. De Saúde Pública 2020, 36, e00074420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waksman, R.D.; Blank, D. A importância da violência doméstica em tempos de COVID-19. Residência Pediátrica 2020, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricoca Peixoto, V.; Vieira, A.; Aguiar, P.; Carvalho, C.; Rhys Thomas, D.; Abrantes, A. Initial Assessment of the Impact of the Emergency State Lockdown Measures on the 1st Wave of the COVID-19 Epidemic in Portugal. Acta Med. Port 2020, 33, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral, I.E.; Pestana-Santos, M.; Ciuffo, L.L.; Nunes, Y.R.; Lomba, M.L.L.F. Child health vulnerabilities during the COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil and Portugal. Rev. Lat. Am. De Enferm. 2021, 29, e3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callejas, L.M.; Davidson, A.; Ismajli, F. Rapid ethnographic assessment of pandemic restrictions in child welfare: Lessons from parent and Provider experiences. Human 2020, 79, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, E.; Copson, R.; Sorensen, P. Contact during Lockdown: How Are Children and Their Birth Families Keeping in Touch? Briefing Paper; Nuffield Family Justice Observatory: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mota, C.; Matos, P. Adolescentes institucionalizados: O papel das figuras significativas na predição da assertividade, empatia e autocontrolo. Análise Psicológica 2012, 28, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, D.C.F. Levantamento Nacional Sobre os Serviços de Acolhimento Para Crianças e Adolescentes em Tempos de COVID-19: Apresentação dos Resultados; NECA: São Paulo, Brasil, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, F.P.; Amaro, R.; Silva, F.M.; Pinto, S.V.; Barroca, I.; Sá, T.; Carvalho, R.F.; Cartaxo, T.; Boavida, J. Impacto do confinamento em crianças e adolescentes. Acta Médica Port. 2021, 34, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordem dos Psicólogos Portugueses [OPP]. Acolhimento Residencial de Crianças e Jovens. 2020. Available online: https://www.ordemdospsicologos.pt/pt/noticia/2758 (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- Montserrat, C.; Garcia-Molsosa, M.; Llosada-Gistau, J.; Sitjes-Figueras, R. The views of children in residential care on the COVID-19 lockdown: Implications for and their well-being and psychosocial intervention. Child Abus. Negl. 2021, 120, 105182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| n | % | M | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 38.39 | ||
| Gender | |||
| Male | 17 | 16.5% | |
| Female | 86 | 83.5% | |
| Nationality | |||
| Portuguese | 103 | 100% | |
| Education | |||
| Secondary school | 6 | 5.8% | |
| Bachelor’s degree | 70 | 68% | |
| Master’s degree | 25 | 24.3% | |
| Ph.D. | 1 | 1% | |
| Area | |||
| Social Service | 41 | 39.8% | |
| Psychology | 33 | 32% | |
| Others | 34 | 33% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salgado, M.; Neves, S.; Silva, E. Professionals’ Perspectives on the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic among Child and Adolescent Victims of Domestic Violence Living in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105826
Salgado M, Neves S, Silva E. Professionals’ Perspectives on the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic among Child and Adolescent Victims of Domestic Violence Living in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023; 20(10):5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105826
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalgado, Micaela, Sofia Neves, and Estefânia Silva. 2023. "Professionals’ Perspectives on the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic among Child and Adolescent Victims of Domestic Violence Living in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 20, no. 10: 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105826
APA StyleSalgado, M., Neves, S., & Silva, E. (2023). Professionals’ Perspectives on the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic among Child and Adolescent Victims of Domestic Violence Living in the Portuguese Residential Foster Care System. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 20(10), 5826. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20105826








