Atherogenic Risk, Anthropometry, Diet and Physical Activity in a Sample of Spanish Commercial Airline Pilots
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Participants and Data Collection
2.3. Anthropometry and Bioimpedance
2.4. Physiometabolic Parameters and the Atherogenic Risk
2.5. Lifestyle Factors
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Professional Characteristics
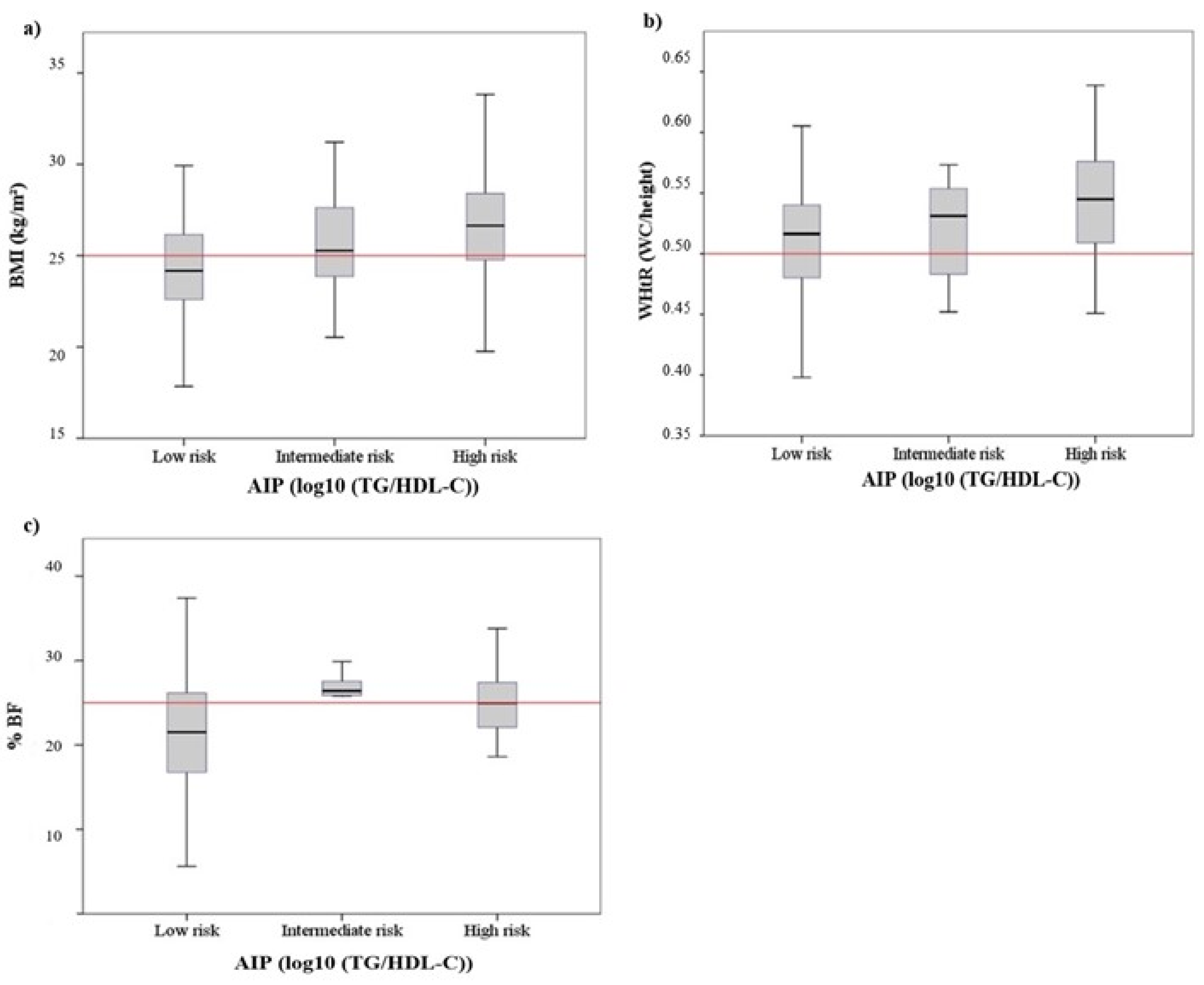
3.2. Anthropometry and Bioimpedance
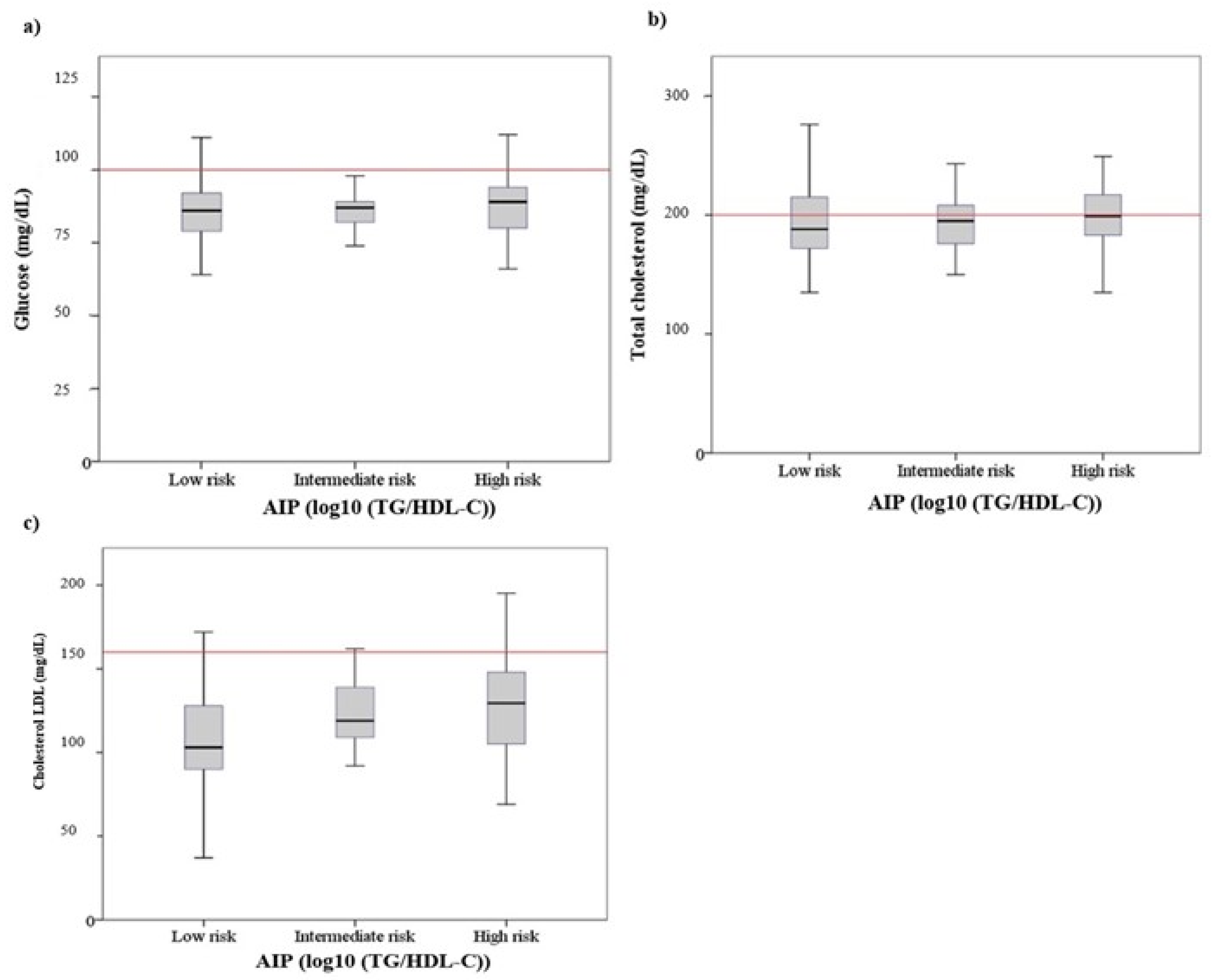
3.3. Physiometabolic Parameters and Atherogenic Index of Plasma
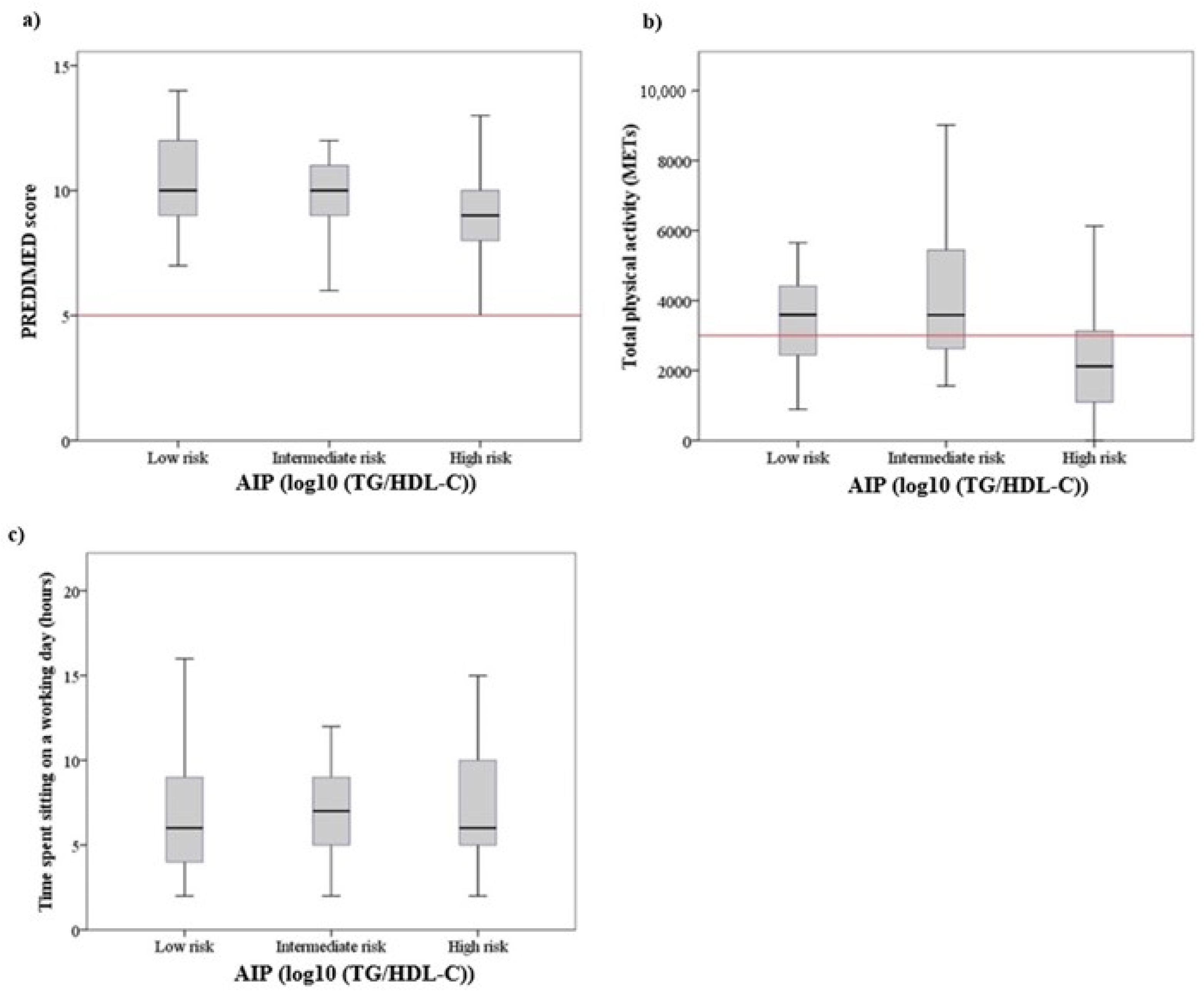
3.4. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet
3.5. Physical Activity and Sedentarism
3.6. AIP Interaction with Age, Cardiometabolic Profile and Lifestyle Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sallinen, M.; Sihvola, M.; Puttonen, S.; Ketola, K.; Tuori, A.; Härma, M.; Kecklund, G.; Akerstedt, T. Sleep, alertness and alertness management among commercial airline pilots on short-haul and long haul flights. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2017, 98, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrilli, R.M.; Roach, G.D.; Dawson, D.; Lamond, N. The Sleep, subjective fatigue, and sustained attention of commercial airline pilots during an international pattern. Chronobiol. Int. 2006, 23, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Civil Aviation Organization. Manual of Civil Aviation Medicine, 3rd ed.; International Civil Aviation Organization: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2012; ISBN 978-92-9231-959-5. Available online: https://www.icao.int/publications/documents/8984_cons_en.pdf (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Bennett, G. Pilot incapacitation and aircraft accidents. Eur. Heart J. 1988, 9, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeJohn, C.A.; Mills, W.D.; Hathaway, W.; Larcher, J. Cardiac inflight incapacitations of U.S. airline pilots: 1995–2015. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2018, 89, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, S.; Radcliffe, S.A. The annual incapacitation rate of commercial pilots. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2012, 83, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJohn, C.A.; Wolbrink, A.M.; Larcher, J.G. In-flight medical incapacitation and impairment of airline pilots. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2006, 77, 1077–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Wirawan, I.M.A.; Larsen, P.D.; Aldington, S.; Griffiths, R.F.; Ellis, C.J. Cardiovascular risk score and cardiovascular events among airline pilots: A case-control study. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2012, 83, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Fister, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines: A link between obesity and cardiovascular disease. J. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spyridaki, E.C.; Avgoustikani, P.D.; Margioris, A.N. Obesity, inflammation and cognition. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2016, 9, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubiak, G.K.; Osadnik, K.; Lejawa, M.; Osadnik, T.; Goławski, M.; Lewandowski, P.; Pawlas, N. “Obesity and Insulin Resistance” Is the Component of the Metabolic Syndrome Most Strongly Associated with Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H. Adipocytokines in obesity and metabolic disease. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 220, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giroud, M.; Jodeleit, H.; Prentice, K.; Bartelt, A. Adipocyte function and the development of cardiometabolic disease. J. Physiol. 2021, 600, 1189–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobiášová, M.; Frohlich, J. The plasma parameter log (TG/HDL-C) as an atherogenic index: Correlation with lipoprotein particle size and esterification rate in apoB-lipoprotein-depleted plasma (FER(HDL)). Clin. Biochem. 2001, 34, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiášová, M. AIP—Atherogenic index of plasma as a significant predictor of cardiovascular risk: From research to practice. Vnitr. Lek. 2006, 52, 64–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.J.; Yoon, J.; Lee, Y.-J.; Park, B.; Jung, D.-H. Predictive Value of the Atherogenic Index of Plasma (AIP) for the Risk of Incident Ischemic Heart Disease among Non-Diabetic Koreans. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Shi, G.; Xue, S.; Lu, W. The atherogenic index of plasma is a strong and independent predictor for coronary artery disease in the Chinese Han population. Medicine 2017, 96, e8058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, C.; Sundquist, J.; Winkleby, M.; Sundquist, K. Interactive effects of obesity and physical fitness on risk of ischemic heart disease. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina-Remón, A.; Kirwan, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Estruch, R. Dietary patterns and the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, asthma, and neurodegenerative diseases. Critical. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58, 262–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weiner, J.S.; Lourie, J.A. (Eds.) Practical Human Biology; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981; p. 439. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry; The Report of a WHO Expert Committee; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995; p. 452. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, S.D.; Muto, T. The superiority of waist-to-height ratio as an anthropometric index to evaluate clustering of coronary risk factors among non-obese men and women. Prev. Med. 2005, 40, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, D.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Heo, M.; Jebb, S.A.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Sakamoto, Y. Healthy percentage body fat ranges: An approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). The IDF Consensus Worldwide Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome. 2006. Available online: https://www.idf.org/our-activities/advocacy-awareness/resources-and-tools/60:idfconsensus-worldwide-definitionof-the-metabolic-syndrome.html (accessed on 20 January 2022).
- Fundación Española del Corazón (FEC). Available online: https://fundaciondelcorazon.com/prevencion/riesgo-cardiovascular.html (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Frohlich, J.; Dobiášová, M. Fractional esterification rate of cholesterol and ratio of triglycerides to HDL-cholesterol are powerful predictors of positive findings on coronary angiography. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobiásová, M. Atherogenic index of plasma log(triglycerides/HDL-cholesterol): Theoretical and practical implications. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 1113–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; García-Arellano, A.; Toledo, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Covas, M.I.; Schröder, H.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; et al. A 14-item Mediterranean diet assessment tool and obesity indexes among high-risk subjects: The PREDIMED trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Craig, C.L.; Marshall, A.L.; Sjöström, M.; Bauman, A.E.; Booth, M.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Pratt, M.; Ekelund, U.; Yngve, A.; Sallis, J.F.; et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 1381–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lear, S.A.; Hu, W.; Rangarajan, S.; Gasevic, D.; Leong, D.; Iqbal, R.; Casanova, A.; Swaminathan, S.; Anjana, R.M.; Kumar, R.; et al. The effect of physical activity on mortality and cardiovascular disease in 130,000 people from 17 high-income, middle-income, and low-income countries: The PURE study. Lancet 2017, 390, 2643–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenholm, S.; Head, J.; Aalto, V.; Kivimäki, M.; Kawachi, I.; Zins, M.; Goldberg, M.; Platts, L.G.; Zaninotto, P.; Magnusson Hanson, L.L.; et al. Body mass index as a predictor of healthy and disease-free life expectancy between ages 50 and 75: A multicohort study. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponce-Garcia, I.; Simarro-Rueda, M.; Carbayo-Herencia, J.A.; Divisón-Garrote, J.A.; Artigao-Ródenas, L.M.; Botella-Romero, F.; Palazón-Bru, A.; Martínez-St, J.D.R.; Gil-Guillén, V.F. Group of Vascular Diseases from Albacete. Prognostic value of obesity on both overall mortality and cardiovascular disease in the general population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Peralta, M.; Naia, A.; Loureiro, N.; de Matos, M.G. Prevalence of adult overweight and obesity in 20 European countries, 2014. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 28, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindgren, T.; Runeson, R.; Wahlstedt, K.; Wieslander, G.; Dammström, B.G.; Norbäck, D. Digestive functional symptoms among commercial pilots in relation to diet, insomnia, and lifestyle factors. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2012, 83, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, S.; Mitchell, S.; Evans, S. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease risk factors among UK commercial pilots. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 2011, 18, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez Pérez, M.D.C.; De León, A.C.; Aguirre-Jaime, A.; Domínguez Coello, S.; Brito Díaz, B.; Almeida González, D.; Borges Alamo, C.; Castillo Rodríguez, J.C.; Carrillo Fernández, L.; González Hernández, A.; et al. El cociente perímetro abdominal/estatura como índice antropométrico de riesgo cardiovascular y de diabetes The waist to height ratio as an index of cardiovascular risk and diabetes. Med. Clin. 2010, 134, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffetone, P.B.; Rivera-Dominguez, I.; Laursen, P.B. Overfat adults and children in developed countries: The public health importance of identifying excess body fat. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Browning, L.M.; Hsieh, S.D.; Ashwell, M. A systematic review of waist-to-height ratio as a screening tool for the prediction of cardiovascular disease and diabetes: 0.5 could be a suitable global boundary value. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2010, 23, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Rexrode, K.M.; Van Dam, R.M.; Li, T.Y.; Hu, F.B. Abdominal obesity and the risk of all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality: Sixteen years of follow-up in US women. Circulation 2008, 117, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Lu, Y.; Qi, H.; Li, F.; Shen, Z.; Wu, L.; Yang, C.; Wang, L.; Shui, K.; Wang, Y.; et al. Association between ideal cardiovascular health and the atherogenic index of plasma. Medicine 2016, 95, e3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.W.; Lu, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, C.J.; Feng, Y.B.; Li, H.W.; Yao, W.F.; Shen, Z.H. Atherogenic index of plasma is an effective index for estimating abdominal obesity. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.; Yu, L.; Zhou, H.; Ma, Q.; Zhou, X.; Lei, T.; Hu, J.; Xu, W.; Yi, N.; Lei, S. Atherogenic index of plasma is a novel and better biomarker associated with obesity: A population-based cross-sectional study in China. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aranceta, J.; Pérez Rodrigo, C.; Foz Sala, M.; Mantilla, T.; Serra Majem, L.; Moreno, B.; Monereo, S.; Millán, J.; Grupo Colaborativo para el estudio DORICA fase 2. Tablas de evaluación del riesgo coronario adaptadas a la población española. Estudio DORICA Tables of coronary risk evaluation adapted to the Spanish population: The DORICA study. Med. Clin. 2004, 123, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga-Arredondo, L.F.; Fajardo-Rodríguez, H.A. Prevalencia de factores de riesgo cardiovascular en pilotos de aviación civil en Colombia en el año 2005 Cardiovascular risk factor prevalence in civil aviation pilots in Colombia during 2005. Rev. Salud Públic 2010, 12, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linton, M.F.; Yancey, P.G.; Davies, S.S.; Jerome, W.G.; Linton, E.F.; Song, W.L.; Doran, A.C.; Vickers, K.C. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hershman, J.M., Hofland, J., Kalra, S., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Guallar-Castillón, P.; Gil-Montero, M.; León-Muñoz, L.M.; Graciani, A.; Bayán-Bravo, A.; Taboada, J.M.; Banegas, J.R.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Magnitude and management of hypercholesterolemia in the adult population of Spain, 2008-2010: The ENRICA Study. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2012, 65, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Chaparro, M.A.; Román-García, J.; Calvo-Bonacho, E.; Gómez-Larios, T.; Fernández-Meseguer, A.; Sáinz-Gutiérrez, J.C.; Cabrera-Sierra, M.; García-García, A.; Rueda-Vicente, J.; Gálvez-Moraleda, A.; et al. Prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors in the Spanish working population. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2006, 59, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, S.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; Soriguer, F. Evolución de la prevalencia de la diabetes tipo 2 en población adulta española. Evolution of prevalence of type 2 diabetes in adult Spanish population. Med. Clin. 2007, 129, 325–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriguer, F.; Goday, A.; Bosch-Comas, A.; Bordiú, E.; Calle-Pascual, A.; Carmena, R.; Casamitjana, R.; Castaño, L.; Castell, C.; Catalá, M.; et al. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and impaired glucose regulation in Spain: The Di@bet.es Study. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rincón-Mancheño, I. Prevalencia Del Síndrome Metabólico En Población Española Adulta Que Asiste A Consulta Dietética. Ph.D. Thesis, Complutense University of Madrid, Madrid, Spain, January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Godos, J.; Zappalà, G.; Bernardini, S.; Giambini, I.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Martínez-González, M. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is inversely associated with metabolic syndrome occurrence: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Gea, A.; Ruiz-Canela, M. The Mediterranean Diet and Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-López, P.; Lozano-Sanchez, J.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Emanuelli, T.; Menéndez, J.A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Structure–Biological Activity Relationships of Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds: Health Properties and Bioavailability. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-González, I.; López-Nicolás, R.; Rodríguez-Tadeo, A.; Ros Berruezo, G.; Martínez-Marín, M.; Doménech-Asensi, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet by nursing students of Murcia (Spain). Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnara, L.; Murillo, S.; Novials, A.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; Soriguer, F.; Goday, A.; Calle-Pascual, A.; Castaño, L.; Gaztambide, S.; Valdés, S.; et al. Low Physical Activity and Its Association with Diabetes and Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauman, A.; Bull, F.; Chey, T.; Craig, C.L.; Ainsworth, B.E.; Sallis, J.F.; Bowles, H.R.; Hagstromer, M.; Sjostrom, M.; Pratt, M. The International Prevalence Study on Physical Activity: Results from 20 countries. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2009, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niroumand, S.; Khajedaluee, M.; Khadem-Rezaiyan, M.; Abrishami, M.; Juya, M.; Khodaee, G.; Dadgarmoghaddam, M. Atherogenic Index of Plasma (AIP): A marker of cardiovascular disease. Med. J. Islam. Repub. 2015, 29, 240. [Google Scholar]
- Onat, A.; Can, G.; Kaya, H.; Hergenç, G. Atherogenic index of plasma (log10 triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein− cholesterol) predicts high blood pressure, diabetes, and vascular events. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2010, 4, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, M.K.; Loprinzi, P.D. Physical activity and diet on atherogenic index of plasma among adults in the United States: Mediation considerations by central adiposity. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Short/Medium-Haul Pilots | Long-Haul Pilots | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric Variables | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value (t-Test) |
| Height (cm) | 177.03 ± 7.64 | 176.99 ± 6.91 | 0.964 NS |
| Weight (kg) | 79.92 ± 11.66 | 80.57 ± 11.96 | 0.645 NS |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 92.09 ± 10.55 | 92.28 ± 10.99 | 0.901 NS |
| Body mass index (kg/cm2) | 25.45 ± 3.016 | 25.67 ± 3.17 | 0.540 NS |
| Waist-to-height ratio | 0.521 ± 0.0559 | 0.52 ± 0.059 | 0.982 NS |
| Body fat (%) | 23.94 ± 4.63 | 23.64 ± 7.75 | 0.813 NS |
| Short/Medium-Haul Pilots | Long-Haul Pilots | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic Variables | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value (t-Test) |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 87.77 ± 8.91 | 88.216 ± 13.024 | 0.799 NS |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 202.17 ± 36.87 | 195.21 ± 30.82 | 0.162 NS |
| HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 57.37 ± 15.26 | 60.38 ± 20.45 | 0.302 NS |
| LDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 122.64 ± 28.40 | 118.32 ± 29.24 | 0.348 NS |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 89.76 ± 37.25 | 95.24 ± 44.67 | 0.388 NS |
| Atherogenic index of plasma | 0.175 ± 0.245 | 0.181 ± 0.263 | 0.891 NS |
| Short/Medium-Haul Pilots | Long-Haul Pilots | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity Variables | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | p-Value (t-Test) |
| Low-intensity activity (MET) | 1011.69 ± 856.96 | 1184.83 ± 901.66 | 0.141 NS |
| Moderate-intensity activity (MET) | 706.85 ± 767.26 | 856.47 ± 856.48 | 0.180 NS |
| Vigorous activity (MET) | 1858.74 ± 1728.24 | 2190.24 ±2152.68 | 0.190 NS |
| Total activity (MET) | 3628.99 ± 2476.27 | 4292.21 ± 3165.59 | 0.090 NS |
| Time spent sitting in a working day (hours) | 6.20 ± 3.97 | 8.84 ± 13.88 | 0.007 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alaminos-Torres, A.; Martínez-Álvarez, J.R.; López-Ejeda, N.; Marrodán-Serrano, M.D. Atherogenic Risk, Anthropometry, Diet and Physical Activity in a Sample of Spanish Commercial Airline Pilots. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074128
Alaminos-Torres A, Martínez-Álvarez JR, López-Ejeda N, Marrodán-Serrano MD. Atherogenic Risk, Anthropometry, Diet and Physical Activity in a Sample of Spanish Commercial Airline Pilots. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(7):4128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074128
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlaminos-Torres, Ana, Jesús Román Martínez-Álvarez, Noemi López-Ejeda, and Maria Dolores Marrodán-Serrano. 2022. "Atherogenic Risk, Anthropometry, Diet and Physical Activity in a Sample of Spanish Commercial Airline Pilots" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 7: 4128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074128
APA StyleAlaminos-Torres, A., Martínez-Álvarez, J. R., López-Ejeda, N., & Marrodán-Serrano, M. D. (2022). Atherogenic Risk, Anthropometry, Diet and Physical Activity in a Sample of Spanish Commercial Airline Pilots. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(7), 4128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19074128






