High in Utero Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water and Birth Weight: A Cohort Study among Infants in Ronneby, Sweden
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Register Data
2.4. Exposure Assessment
2.5. Statistics
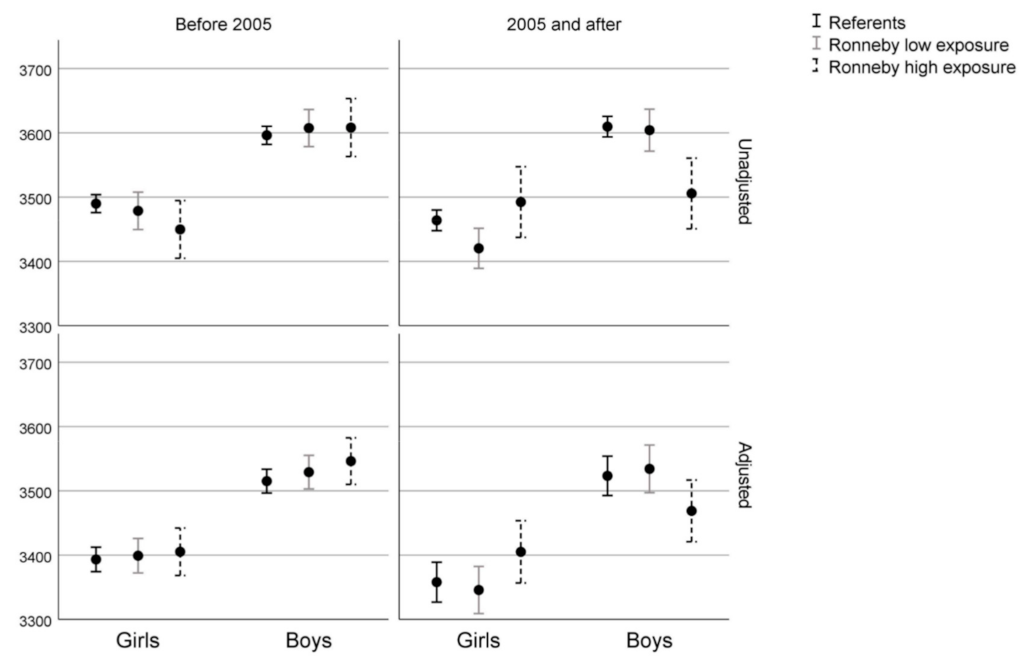
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, C.; Anitole, K.; Hodes, C.; Lai, D.; Pfahles-Hutchens, A.; Seed, J. Perfluoroalkyl Acids: A Review of Monitoring and Toxicological Findings. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 366–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Park, M.S.; Lee, H.S. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: Human Exposure and Health Risks. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2006, 24, 183–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, M.; Smurthwaite, K.; Braunig, J.; Trevenar, S.; D’Este, C.; Lucas, R.; Lal, A.; Korda, R.; Clements, A.; Mueller, J.; et al. Report: The PFAS Health Study: Systematic Literature Review; Australian National University: Canberra, ACT, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Risk to Human Health Related to the Presence of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, e06223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cot-trill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; et al. Risk to Human Health Related to the Presence of Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid and Perfluorooctanoic Acid in Food. EFSA J. 2018, 16, e05194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoeib, M.; Harner, T.; Wilford, B.H.; Jones, K.C.; Zhu, J. Perfluorinated Sulfonamides in In-door and Outdoor Air and Indoor Dust: Occurrence, Partitioning, and Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6599–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begley, T.H.; White, K.; Honigfort, P.; Twaroski, M.L.; Neches, R.; Walker, R.A. Perfluorochemicals: Potential Sources of and Migration from Food Packaging. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, J.L.; Nadal, M. Human Exposure to Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) through Drinking Water: A Review of the Recent Scientific Literature. Environ. Res. 2019, 177, 108648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.D.; Libelo, E.L.; Bugna, G.; Shelley, T.; Mayfield, H.; Stauffer, T.B. Biogeochemical Assessment of Natural Attenuation of JP-4-Contaminated Ground Water in the Presence of Fluorinated Surfactants. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 208, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.A.; Hebert, G.N.; Strauss, S.H.; Field, J.A. Occurrence and Persistence of Perfluorooctanesulfonate and Other Perfluorinated Surfactants in Groundwater at a Fire-Training Area at Wurtsmith Air Force Base, Michigan, USAElectronic Supplementary Information (ESI) Available: Map of Location of Wurtsmith. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, C.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Tarone, R.E.; Olsen, J. Perfluorinated Chemicals and Fetal Growth: A Study within the Danish National Birth Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, K.; Ji, K.; Seo, J.; Kho, Y.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Park, S.; Hwang, I.; Jeon, J.; et al. Trans-Placental Transfer of Thirteen Perfluorinated Compounds and Relations with Fetal Thyroid Hormones. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7465–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Mucs, D.; Scott, K.; Lindh, C.H.; Tallving, P.; Jakobsson, K. Half-Lives of PFOS, PFHxS and PFOA after End of Exposure to Contaminated Drinking Water. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendryx, M.; Chojenta, C.; Byles, J.E. Latent Class Analysis of Low Birth Weight and Preterm Delivery among Australian Women. J. Pediatrics 2020, 218, 42–48.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, E.J.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, B.M.; Shah-Kulkarni, S.; Park, H.; Kho, Y.L.; Park, E.A.; Kim, Y.J.; Ha, E.H. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluorinated Compounds Affects Birth Weight Through GSTM1 Polymorphism. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 2016, 58, e198–e205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.; Inoue, K.; Ritz, B.; Olsen, J.; Liew, Z. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Birth Outcomes; An Updated Analysis from the Danish National Birth Cohort. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonet, M.; Terrell, M.L.; McGeehin, M.A.; Christensen, K.Y.; Holmes, A.; Calafat, A.M.; Marcus, M. Maternal Concentrations of Polyfluoroalkyl Compounds during Pregnancy and Fetal and Postnatal Growth in British Girls. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apelberg, B.J.; Witter, F.R.; Herbstman, J.B.; Calafat, A.M.; Halden, R.U.; Needham, L.L.; Goldman, L.R. Cord Serum Concentrations of Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Perfluorooctanoate (PFOA) in Relation to Weight and Size at Birth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, E.M.; Yeung, E.H.; Ma, W.; Kannan, K.; Sundaram, R.; Smarr, M.M.; Louis, G.M.B. Concentrations of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals in Newborn Blood Spots and Infant Outcomes in the Upstate KIDS Study. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenters, V.; Portengen, L.; Rignell-Hydbom, A.; Jönsson, B.A.G.; Lindh, C.H.; Piersma, A.H.; Toft, G.; Bonde, J.P.; Heederik, D.; Rylander, L.; et al. Prenatal Phthalate, Perfluoroalkyl Acid, and Organochlorine Exposures and Term Birth Weight in Three Birth Cohorts: Multi-Pollutant Models Based on Elastic Net Regression. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Du, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, H.; Karmin, O.; Xu, L.; Liu, S.; Yi, J.; Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. PFOS, PFOA, Estrogen Homeostasis, and Birth Size in Chinese Infants. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Salgado, C.B.; Casas, M.; Lopez-Espinosa, M.-J.; Ballester, F.; Iñiguez, C.; Martinez, D.; Romaguera, D.; Fernández-Barrés, S.; Santa-Marina, L.; Basterretxea, M.; et al. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Cardiometabolic Risk in Children from the Spanish INMA Birth Cohort Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 097018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamm, M.P.; Cherry, N.M.; Chan, E.; Martin, J.W.; Burstyn, I. Maternal Exposure to Perfluorinated Acids and Fetal Growth. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2010, 20, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Lai, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y. Occurrence of Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Cord Serum and Association with Growth Indicators in Newborns from Beijing. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washino, N.; Saijo, Y.; Sasaki, S.; Kato, S.; Ban, S.; Konishi, K.; Ito, R.; Nakata, A.; Iwasaki, Y.; Saito, K.; et al. Correlations between Prenatal Exposure to Perfluorinated Chemicals and Reduced Fetal Growth. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darrow, L.A.; Stein, C.R.; Steenland, K. Serum Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Concentrations in Relation to Birth Outcomes in the Mid-Ohio Valley, 2005–2010. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, C.C.; Bech, B.H.; Nohr, E.A.; Olsen, J.; Matthiesen, N.B.; Bonefeld-Jørgensen, E.C.; Bossi, R.; Henriksen, T.B. Perfluoroalkyl Acids in Maternal Serum and Indices of Fetal Growth: The Aarhus Birth Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, K.W.; Haug, L.S.; Baird, D.D.; Becher, G.; Hoppin, J.A.; Skjaerven, R.; Thomsen, C.; Eggesbo, M.; Travlos, G.; Wilson, R.; et al. Perfluorinated Compounds in Relation to Birth Weight in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 175, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, K.J.; Cutler, A.J.; Jeddy, Z.; Northstone, K.; Kato, K.; Hartman, T.J. Maternal Serum Concentrations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Birth Size in British Boys. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2019, 222, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauritzen, H.B.; Larose, T.L.; Øien, T.; Sandanger, T.M.; Odland, J.Ø.; van de Bor, M.; Jacobsen, G.W. Maternal Serum Levels of Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Organochlorines and Indices of Fetal Growth: A Scandinavian Case–Cohort Study. Pediatric Res. 2017, 81, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.H.; Ha, E.H.; Wen, T.W.; Su, Y.N.; Lien, G.W.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, P.C.; Hsieh, W.S. Perfluorinated Compounds in Umbilical Cord Blood and Adverse Birth Outcomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, D.V.; Priskorn, L.; Lassen, T.H.; Nielsen, F.; Kyhl, H.B.; Kristensen, D.M.; Christesen, H.T.; Jørgensen, J.S.; Grandjean, P.; Jensen, T.K. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Anogenital Distance at 3 Months of Age in a Danish Mother-Child Cohort. Reprod. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.J.; Barr, D.B.; Ryan, P.B.; Panuwet, P.; Smarr, M.M.; Liu, K.; Kannan, K.; Yakimavets, V.; Tan, Y.; Ly, V.L.; et al. Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substance (PFAS) Exposure, Maternal Metabolomic Perturbation, and Fetal Growth in African American Women: A Meet-in-the-Middle Approach. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verner, M.A.; Loccisano, A.E.; Morken, N.H.; Yoon, M.; Wu, H.; McDougall, R.; Maisonet, M.; Marcus, M.; Kishi, R.; Miyashita, C.; et al. Assfociations of Perfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) with Lower Birth Weight: An Evaluation of Potential Confounding by Glomerular Filtration Rate Using a Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model (PBPK). Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, D.A. Guest Editorial: Biomarkers of Perfluorinated Chemicals and Birth Weight. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, A528–A529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Savitz, D.A.; Stein, C.R.; Elston, B.; Wellenius, G.A.; Bartell, S.M.; Shin, H.M.; Vieira, V.M.; Fletcher, T. Relationship of Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure to Pregnancy Outcome Based on Birth Records in the Mid-Ohio Valley. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savitz, D.A.; Stein, C.R.; Bartell, S.M.; Elston, B.; Gong, J.; Shin, H.M.; Wellenius, G.A. Perfluorooctanoic Acid Exposure and Pregnancy Outcome in a Highly Exposed Community. Epidemiology 2012, 23, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, L.A.; Nolan, J.M.; Shofer, F.S.; Rodway, N.V.; Emmett, E.A. The Relationship between Birth Weight, Gestational Age and Perfluorooctanoic Acid (PFOA)-Contaminated Public Drinking Water. Reprod. Toxicol. 2009, 27, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Nielsen, C.; Li, Y.; Hammarstrand, S.; Andersson, E.M.; Li, H.; Olsson, D.S.; Engström, K.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C.H.; et al. Serum Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Residents Following Long-Term Drinking Water Contamination from Firefighting Foam in Ronneby, Sweden. Environ. Int. 2021, 147, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enander, G. Spridning Av PFAS-Föroreningar i Dricksvatten. 2016 Rapport M2015B; Regeringskansliet: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobsson, K.; Georgellis, A.; Lilja, K.; Norström, K.; Nilsson, C.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C. Serum Levels of a Range of Perfluorinated Substances (PFAS) after Drinking Water Exposure in Three Populations Living around Military and Civil Airfields in Sweden. Environ. Epidemiol. 2019, 3, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Fletcher, T.; Pineda, D.; Lindh, C.H.; Nilsson, C.; Glynn, A.; Vogs, C.; Norström, K.; Lilja, K.; Jakobsson, K.; et al. Serum Half-Lives for Short-and Long-Chain Perfluoroalkyl Acids after Ceasing Exposure from Drinking Water Contaminated by Firefighting Foam. Environ. Health Perspect. 2020, 128, 077004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyllenhammar, I.; Berger, U.; Sundström, M.; McCleaf, P.; Eurén, K.; Eriksson, S.; Ahlgren, S.; Lignell, S.; Aune, M.; Kotova, N.; et al. Influence of Contaminated Drinking Water on Perfluoroalkyl Acid Levels in Human Serum—A Case Study from Uppsala, Sweden. Environ. Res. 2015, 140, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, K.E.; Starling, A.P.; Higgins, C.P.; McDonough, C.A.; Calafat, A.M.; Adgate, J.L. Sociodemographic and Behavioral Determinants of Serum Concentrations of Per- and Polyfluoro-alkyl Substances in a Community Highly Exposed to Aqueous FilmForming Foam Contaminants in Drinking Water. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 223, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.S.; Ma, Z.; Watkins, S.M.; Wood, S.S. Demographic and Exposure Characteristics as Predictors of Serum Per- and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFASs) Levels—A Community-Level Biomonitoring Project in Pennsylvania. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2021, 231, 113631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negri, E.; Metruccio, F.; Guercio, V.; Tosti, L.; Benfenati, E.; Bonzi, R.; La Vecchia, C.; Moretto, A. Exposure to PFOA and PFOS and Fetal Growth: A Critical Merging of Toxicological and Epidemiological Data. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2017, 47, 482–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzierlenga, M.W.; Crawford, L.; Longnecker, M.P. Birth Weight and Perfluorooctane Sulfonic Acid: A Random-Effects Meta-Regression Analysis. Environ. Epidemiol. 2020, 4, e095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenland, K.; Barry, V.; Savitz, D. Serum Perfluorooctanoic Acid and Birthweight. Epidemiology 2018, 29, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisch-Smith, J.I.; Simmons, D.G.; Dickinson, H.; Moritz, K.M. Review: Sexual Dimorphism in the Formation, Function and Adaptation of the Placenta. Placenta 2017, 54, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, R.; Nakajima, T.; Goudarzi, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Sasaki, S.; Okada, E.; Miyashita, C.; Itoh, S.; Araki, A.; Ikeno, T.; et al. The Association of Prenatal Exposure to Perfluorinated Chemicals with Maternal Essential and Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids during Pregnancy and the Birth Weight of Their Offspring: The Hokkaido Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1038–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, M.G.; Webster, T.F. Trade-Offs of Personal Versus More Proxy Exposure Measures in Environmental Epidemiology. Epidemiology 2017, 28, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables/Categories | Blekinge Referents | Ronneby Low Exposure | Ronneby High Exposure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before 2005 | 2005 and after | Before 2005 | 2005 and after | Before 2005 | 2005 and after | |
| n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | |
| Education | ||||||
| Pre-secondary (any) | 1482 (11) | 967 (10) | 339 (11) | 249 (10) | 236 (19) | 131 (16) |
| Secondary (up to 2 years) | 4368 (33) | 935 (10) | 977 (32) | 221 (9) | 520 (41) | 124 (15) |
| Secondary (3 years) | 2922 (22) | 3026 (31) | 692 (22) | 739 (30) | 284 (22) | 308 (37) |
| College/university (incl graduate) | 4275 (33) | 4764 (49) | 1068 (35) | 1243 (51) | 230 (18) | 260 (32) |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 6702 (51) | 5054 (52) | 1610 (52) | 1214 (50) | 656 (52) | 427 (52) |
| Female | 6345 (49) | 4638 (48) | 1466 (48) | 1238 (50) | 614 (48) | 396 (48) |
| Parity | ||||||
| 1 | 5323 (41) | 4082 (42) | 1373 (45) | 1171 (48) | 544 (43) | 367 (45) |
| 2 | 4937 (38) | 3683 (38) | 1103 (36) | 875 (36) | 475 (37) | 275 (33) |
| 3+ | 2787 (21) | 1927 (20) | 600 (20) | 406 (17) | 251 (20) | 181 (22) |
| Smoking | ||||||
| Non-smoker | 11,251 (86) | 8971 (93) | 2610 (85) | 2259 (92) | 974 (77) | 676 (82) |
| 1–9 cigarettes/day | 1243 (10) | 582 (6) | 308 (10) | 145 (6) | 186 (15) | 107 (13) |
| 10+ cigarettes/day | 553 (4) | 139 (1) | 158 (5) | 48 (2) | 110 (9) | 40 (5) |
| Variable/Values | Blekinge Referents | Ronneby Low Exposure | Ronneby High Exposure | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before 2005 (n = 13,047) | 2005 and after (n = 9692) | Before 2005 (n = 3076) | 2005 and after (n = 3452) | Before 2005 (n = 1270) | 2005 and after (n = 823) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||||
| Median | 23.42 | 24.22 | 23.11 | 24.03 | 23.48 | 25.04 |
| 25% | 21.45 | 21.89 | 21.16 | 21.72 | 21.48 | 22.05 |
| 75% | 26.23 | 27.55 | 25.54 | 27.34 | 26.50 | 29.02 |
| Maternal age | ||||||
| Median | 29 | 30 | 28 | 29 | 27 | 28 |
| 25% | 25 | 26 | 25 | 26 | 24 | 24 |
| 75% | 32 | 33 | 32 | 33 | 30 | 32 |
| Gestational age, days | ||||||
| Median | 280 | 279 | 280 | 279 | 279 | 278 |
| 25% | 272 | 272 | 272 | 272 | 271 | 270 |
| 75% | 286 | 286 | 286 | 286 | 285 | 285 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Engström, K.; Axmon, A.; Nielsen, C.; Rignell-Hydbom, A. High in Utero Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water and Birth Weight: A Cohort Study among Infants in Ronneby, Sweden. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042385
Engström K, Axmon A, Nielsen C, Rignell-Hydbom A. High in Utero Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water and Birth Weight: A Cohort Study among Infants in Ronneby, Sweden. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(4):2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042385
Chicago/Turabian StyleEngström, Karin, Anna Axmon, Christel Nielsen, and Anna Rignell-Hydbom. 2022. "High in Utero Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water and Birth Weight: A Cohort Study among Infants in Ronneby, Sweden" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 4: 2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042385
APA StyleEngström, K., Axmon, A., Nielsen, C., & Rignell-Hydbom, A. (2022). High in Utero Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl Substances from Drinking Water and Birth Weight: A Cohort Study among Infants in Ronneby, Sweden. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(4), 2385. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19042385







