Internet Use and Psychosomatic Symptoms among University Students: Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Measures
2.3. Data Analysis
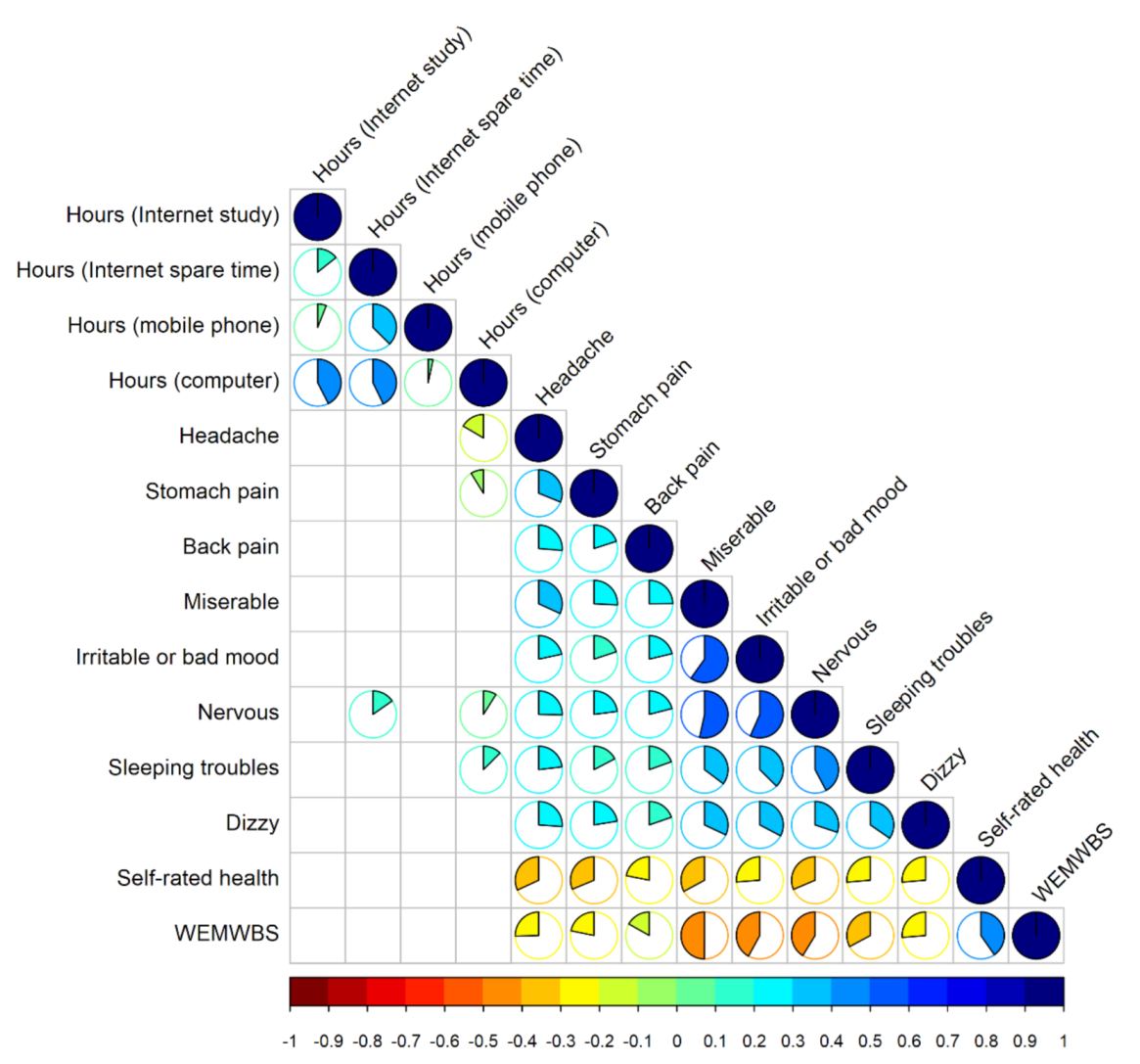
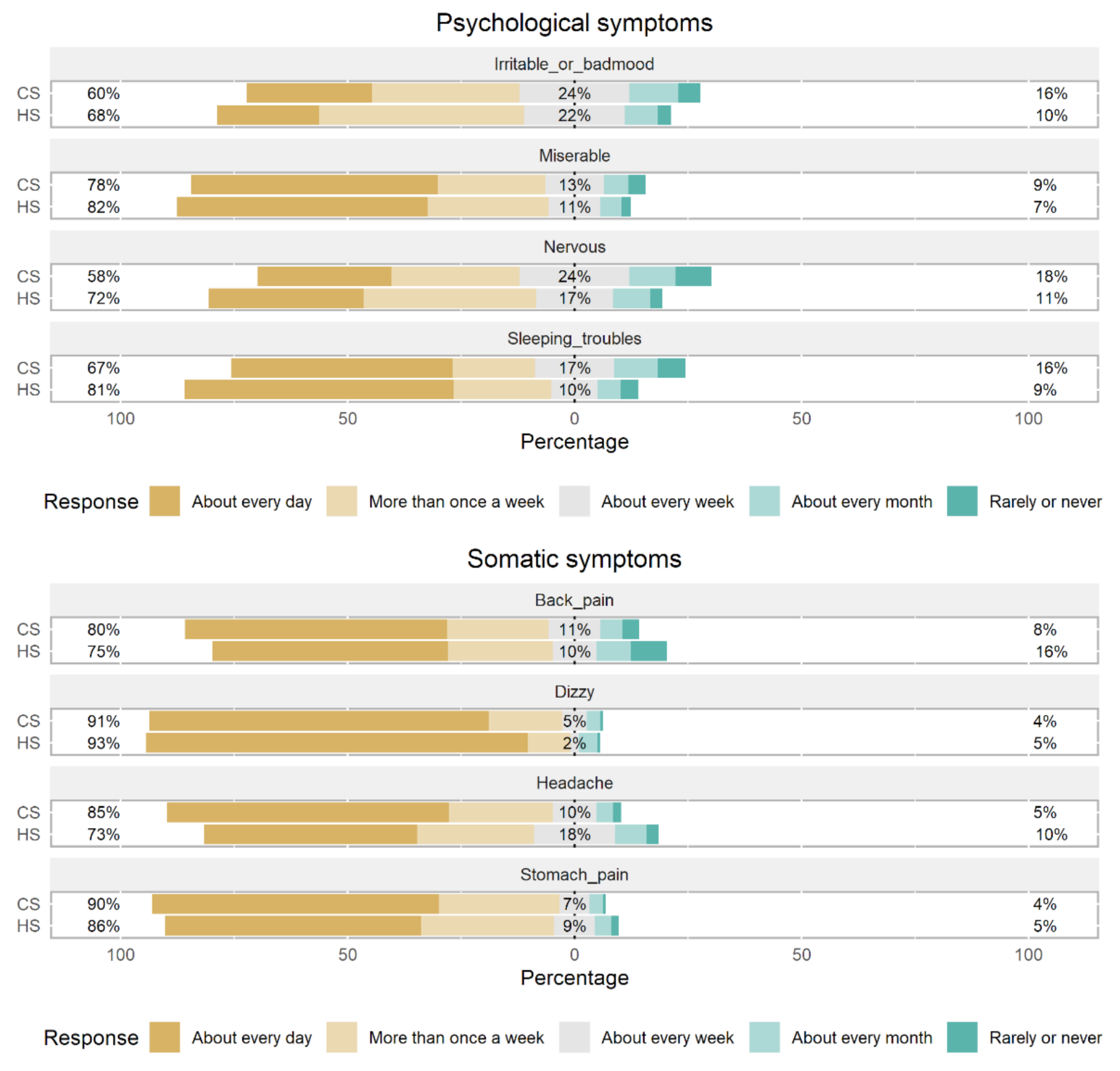
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shirazi, F.; Heidari, S.; Fard, S.J.; Ghodsbin, F. Pattern of internet use by iranian nursing students. Facilitators and barriers. Investig. Y Educ. Enferm. 2019, 37, e06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Oli, N.; Thapa, B. Electronic health–literacy skills among nursing students. Adv. Med. Educ. Pract. 2019, 10, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, S.; Wong, Y.K.; Wong, L.Y.; Hossain, L. The Internet and Facebook Usage on Academic Distraction of College Students. Comput. Educ. 2019, 134, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, D.D.K.; Bakliwal, M. A Study of Internet Usage and Study Habits among Students; ResearchGate: Berlin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Azeems, M.S. Use of social media and its perceived influence on the academic performance of university students. Anthropol. Bull. 2017, 9, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bener, A.; Yildirim, E.; Torun, P.; Çatan, F.; Bolat, E.; Alıç, S.; Akyel, S.; Griffiths, M.D. Internet Addiction, Fatigue, and Sleep Problems Among Adolescent Students: A Large-Scale Study. Int. J. Ment. Health Addict. 2018, 17, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baturay, M.H.; Toker, S. Internet addiction among college students: Some causes and effects. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 2863–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, K.S. Cognitive Behavior Therapy with Internet Addicts: Treatment Outcomes and Implications. Cyberpsychol. Behav. 2007, 10, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khamis, S.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M. A descriptive analytic model of internet usage and student performance. Technol. Manag. 2019, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, S.M.; Wong, H.C.; Lam, C.Y.; Shek, D. Common Mental Health Challenges in a University Context in Hong Kong: A Study Based on a Review of Medical Records. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2018, 15, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLafferty, M.; Lapsley, C.R.; Ennis, E.; Armour, C.; Murphy, S.; Bunting, B.P.; Bjourson, A.J.; Murray, E.K.; O’Neill, S.M. Mental health, behavioural problems and treatment seeking among students commencing university in Northern Ireland. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bruffaerts, R.; Mortier, P.; Kiekens, G.; Auerbach, R.P.; Cuijpers, P.; Demyttenaere, K.; Green, J.; Nock, M.K.; Kessler, R.C. Mental health problems in college freshmen: Prevalence and academic functioning. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 225, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pedrelli, P.; Nyer, M.; Yeung, A.; Zulauf, C.; Wilens, T. College Students: Mental Health Problems and Treatment Considerations. Acad. Psychiatry 2014, 39, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrer, M.; Adam, S.H.; Baumeister, H.; Cuijpers, P.; Karyotaki, E.; Auerbach, R.P.; Kessler, R.C.; Bruffaerts, R.; Berking, M.; Ebert, D.D. Internet interventions for mental health in university students: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 28, e1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cilar, L.; Barr, O.; Štiglic, G.; Pajnkihar, M. Mental well-being among nursing students in Slovenia and Northern Ireland: A survey. Nurse Educ. Pract. 2019, 39, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auerbach, R.P.; Mortier, P.; Bruffaerts, R.; Alonso, J.; Benjet, C.; Cuijpers, P.; Demyttenaere, K.; Ebert, D.D.; Green, J.G.; Hasking, P.; et al. WHO World Mental Health Surveys International College Student Project: Prevalence and distribution of mental disorders. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2018, 127, 623–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Internet addiction and psychosomatic symptoms in engineering students. Delhi Psychiatry J. 2014, 17, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Harerimana, A.; Mtshali, N.G. Internet usage among undergraduate nursing students: A case study of a selected university in South Africa. J. Nurs. Educ. Pract. 2018, 8, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Khan, A.M.; Rajoura, O.P.; Srivastava, S. Internet addiction and its mental health correlates among undergraduate college students of a university in North India. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2018, 7, 721–727. [Google Scholar]
- Barthakur, M.; Sharma, M. Problematic internet use and mental health problems. Asian J. Psychiatry 2012, 5, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisen, S.S.; Deshpande, Y.; Haridas, K. Does personality traits predict excessive use of internet technology among engineering students? Simple mediation analysis. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Educ. 2019, 0020720919894198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, N.; Jain, P.A.; Prabhu, S.; Thomas, C.; Bhat, A.; Prathyusha, P.V.; Bhat, S.U.; Young, K.; Cherian, A.V. Internet Use Patterns, Internet Addiction, and Psychological Distress Among Engineering University Students: A Study from India. Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2018, 40, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.I.; Alharbi, N.B.; Alhawasawi, H.Y.; Albander, A.B. Prevalence of Internet Addiction among Nursing Students and the Association with their Academic Performance and Mental Health. Athens J. Health 2016, 3, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, D.; Gerçeker, G..; Özdemir, E.Z.; Bektaş, M. The Effect of Problematic Internet Use, Social Appearance Anxiety, and Social Media Use on Nursing Students’ Nomophobia Levels. CIN Comput. Inform. Nurs. 2018, 36, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öksüz, E.; Guvenc, G.; Mumcu, S. Relationship between Problematic Internet Use and Time Management among Nursing Students. CIN Comput. Inform. Nurs. 2018, 36, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, F.; Friede, T.; Weich, S.; Clarke, A.; Johnson, M.; Stewart-Brown, S. Cross Cultural Evaluation of the Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (WEMWBS)—A Mixed Methods Study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2013, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taggart, F.; Stewart-Brown, S.; Parkinson, J. Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-Being Scale (WEMWBS): User Guide—Version 2; NHS Health Scotland: Edinburgh, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Tennant, R.; Hiller, L.; Fishwick, R.; Platt, S.; Joseph, S.; Weich, S.; Parkinson, J.; Secker, J.; Stewart-Brown, S. The Warwick-Edinburgh mental well-being scale (WEMWBS): Development and UK validation. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2007, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Currie, C.; van der Sluijs, W.; Whitehead, R.; Currie, D.; Rhodes, G.; Neville, F.; Inchley, J. Findings from the HSBC 2014 Survey in Scotland: Health Behaviour in School-Aged Children, World Health Organization Collaborative Cross-National Study (HSBC); University of Glasgow: Glasgow, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stiglic, G.; Watson, R.; Cilar, L. R you ready? Using the R programme for statistical analysis and graphics. Res. Nurs. Health 2019, 42, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. MissForest—non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, T.; Simko, V.; Levy, M.; Xie, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zemla, J. Package ‘corrplot’. Statistician 2017, 56, e24. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S.G.; Aiken, L.S. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinbinu, T.R.; Mashalla, Y.J. Impact of computer technology on health: Computer Vision Syndrome (CVS). Med. Pract. Preview 2014, 5, 20–30. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.; El-Massry, A.; Elagouz, M.; Elzembely, H. Computer Vision Syndrome Survey among the Medical Students in Sohag University Hospital, Egypt. Ophthalmol. Res. Int. J. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.K.; Pitangui, A.C.; Silva, G.R.; Oliveira, V.M.; Beltrão, N.B.; Araújo, R.C. Prevalence of headache in adolescents and association with use of computer and videogames. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2015, 20, 3477–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, C.; Straker, L.; Smith, A.; Pollock, C. A proposed model representing the relationships between user characteristics, computer exposure and musculoskeletal symptoms in children. Work 2012, 41, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harris, C.; Straker, L.; Pollock, C.; Smith, A. Children, computer exposure and musculoskeletal outcomes: The development of pathway models for school and home computer-related musculoskeletal outcomes. Ergonomics 2015, 58, 1611–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, T.; Roos, E.; Ray, C.; Villberg, J.; Välimaa, R.; Rasmussen, M.; Holstein, B.; Godeau, E.; Beck, F.; Léger, D.; et al. Computer use, sleep duration and health symptoms: A cross-sectional study of 15-year olds in three countries. Int. J. Public Health 2014, 59, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomée, S.; Härenstam, A.; Hagberg, M. Computer use and stress, sleep disturbances, and symptoms of depression among young adults–a prospective cohort study. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salehi, S.G.; Hassani, H.; Mortezapour, A.; Sadeghniiat-Haghighi, K. Assessing of sleepiness, insomnia and sleep quality among university students: Association between computer use and sleep quality. Ann. Mil. Health Sci. Res. 2015, 13, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Faridizad, R.; Ahadi, Z.; Heshmat, R.; Motlagh, M.E.; Sheidaei, A.; Ziaodini, H.; Taheri, M.; Qorbani, M.; Mahdavi, S.B.; Kelishadi, R. Association of screen time with subjective health complaints in Iranian school-aged children and adolescents: The CASPIAN-V study. J. Public Health 2019, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, A.; Bahadir-Yilmaz, E. Relationship between depression, anxiety, cognitive distortions, and psychological well-being among nursing students. Perspect. Psychiatr. Care 2019, 55, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.M.; Devis, K.; LeMoine, G.; Crouch, S.; South, N.; Hossain, R. First year nursing students use of social media within education: Results of a survey. Nurse Educ. Today 2018, 61, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Health Sciences (n = 300) | Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (n = 164) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 255 | 84.2 | 30 | 18.1 |
| Male | 48 | 15.8 | 136 | 81.9 |
| Level of study | ||||
| 1st (Undergraduate) | 245 | 80.6 | 125 | 75.3 |
| 2nd (Master) | 51 | 16.8 | 40 | 24.1 |
| 3rd (PhD) | 8 | 2.6 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Study year | ||||
| 1st | 128 | 42.1 | 152 | 92.1 |
| 2nd | 81 | 26.6 | 13 | 7.9 |
| 3rd | 95 | 31.3 | ||
| Study type | ||||
| Full time | 226 | 74.3 | 165 | 99.4 |
| Part time | 78 | 25.7 | 1 | 0.6 |
| Internet (Study) | Internet (Freetime) | Hours (Computer) | Hours (Phone) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Std. | Estimate | Std. | Estimate | Std. | Estimate | Std. | |
| (Intercept) | 1.378 | 0.072 | 1.490 | 0.083 | 1.323 | 0.107 | 1.784 | 0.114 |
| Female | 0.099 | 0.051 | 0.435 | 0.058 | 0.868 | 0.075 | −0.056 | 0.080 |
| Headache | −0.041 | 0.026 | 0.010 | 0.030 | −0.080 | 0.039 | 0.027 | 0.042 |
| Stomach pain | −0.021 | 0.030 | 0.048 | 0.035 | −0.013 | 0.044 | 0.060 | 0.048 |
| Back pain | 0.008 | 0.021 | −0.028 | 0.024 | 0.012 | 0.031 | −0.016 | 0.033 |
| Dizzy | 0.068 | 0.034 | 0.031 | 0.039 | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.049 | 0.054 |
| Internet (Study) | Internet (Freetime) | Hours (Computer) | Hours (Phone) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate | Std. | Estimate | Std. | Estimate | Std. | Estimate | Std. | |
| (Intercept) | 1.387 | 0.066 | 1.472 | 0.075 | 1.191 | 0.096 | 1.812 | 0.103 |
| Gender = Female | 0.117 | 0.050 | 0.420 | 0.057 | 0.877 | 0.074 | −0.080 | 0.079 |
| Miserable | −0.014 | 0.034 | 0.049 | 0.038 | −0.001 | 0.049 | −0.085 | 0.053 |
| Irritable or bad mood | −0.007 | 0.033 | −0.027 | 0.037 | −0.059 | 0.048 | 0.087 | 0.052 |
| Nervous | 0.012 | 0.029 | 0.055 | 0.033 | 0.071 | 0.042 | 0.054 | 0.045 |
| Sleeping troubles | −0.001 | 0.024 | −0.020 | 0.027 | 0.020 | 0.035 | −0.005 | 0.038 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stiglic, G.; Masterson Creber, R.; Cilar Budler, L. Internet Use and Psychosomatic Symptoms among University Students: Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031774
Stiglic G, Masterson Creber R, Cilar Budler L. Internet Use and Psychosomatic Symptoms among University Students: Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(3):1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031774
Chicago/Turabian StyleStiglic, Gregor, Ruth Masterson Creber, and Leona Cilar Budler. 2022. "Internet Use and Psychosomatic Symptoms among University Students: Cross-Sectional Study" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 3: 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031774
APA StyleStiglic, G., Masterson Creber, R., & Cilar Budler, L. (2022). Internet Use and Psychosomatic Symptoms among University Students: Cross-Sectional Study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(3), 1774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031774






