Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C Status
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Statistical Analysis
2.2. Missing Data and Sensitivity Analysis
2.3. Power Analysis
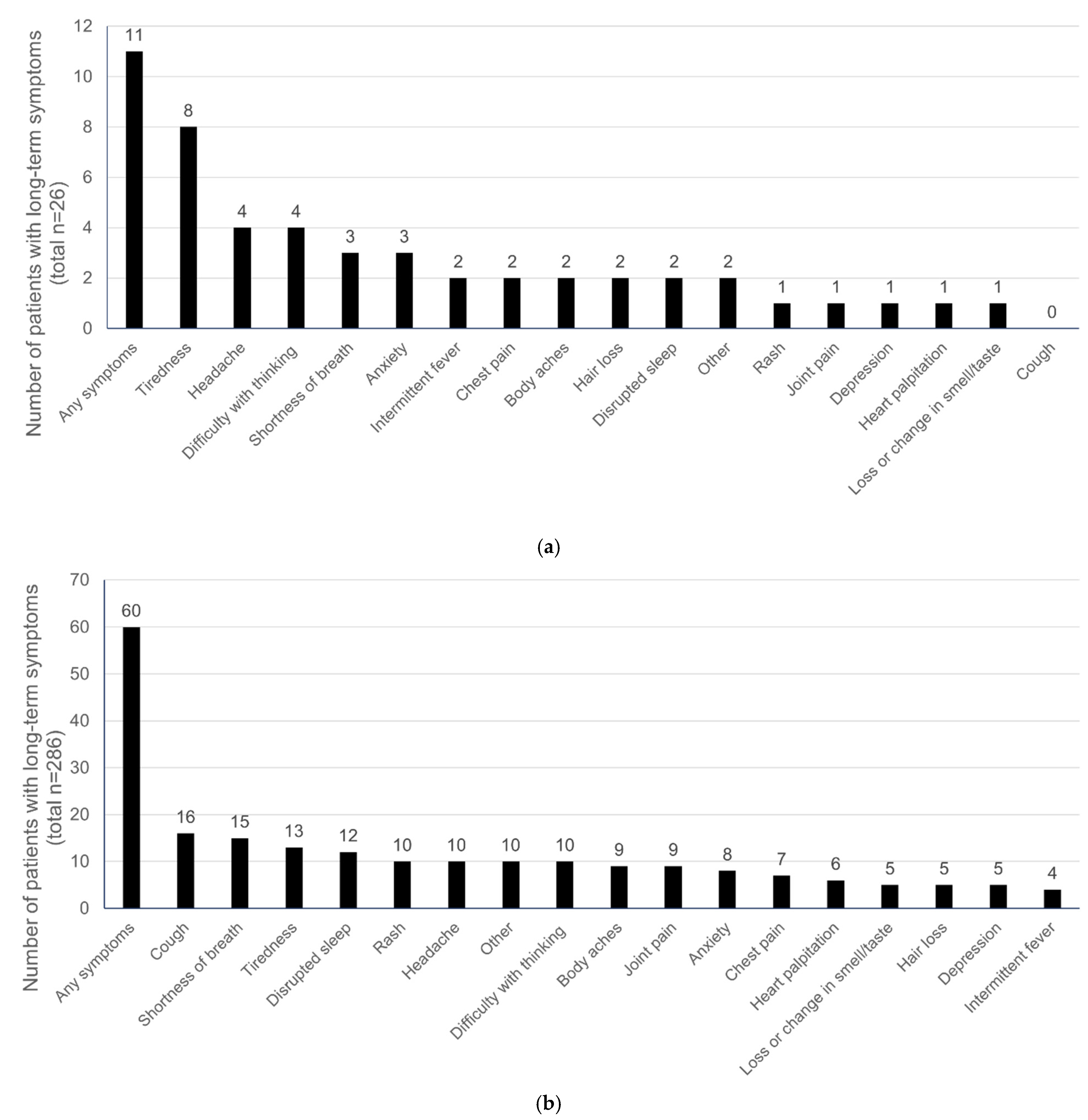
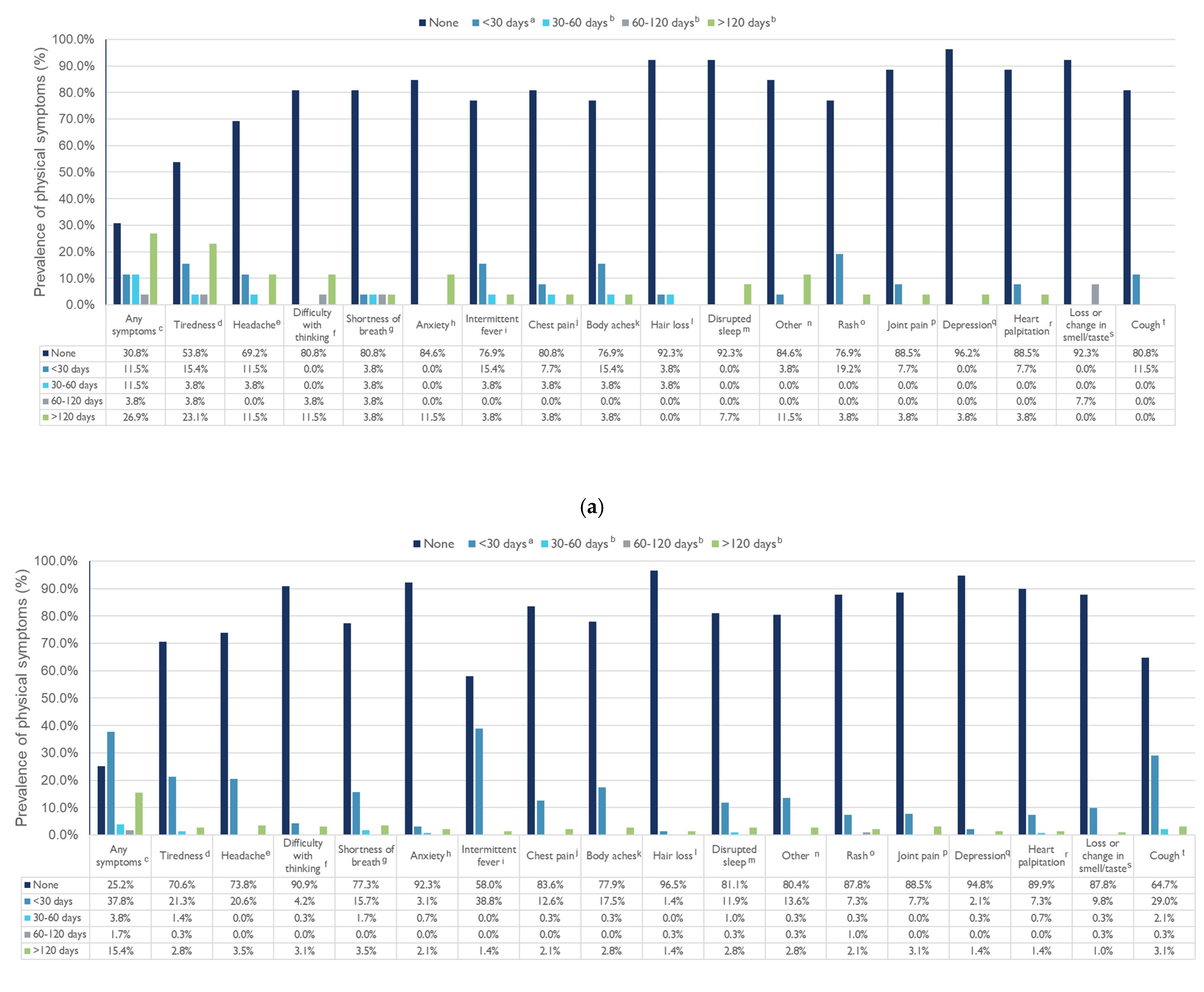
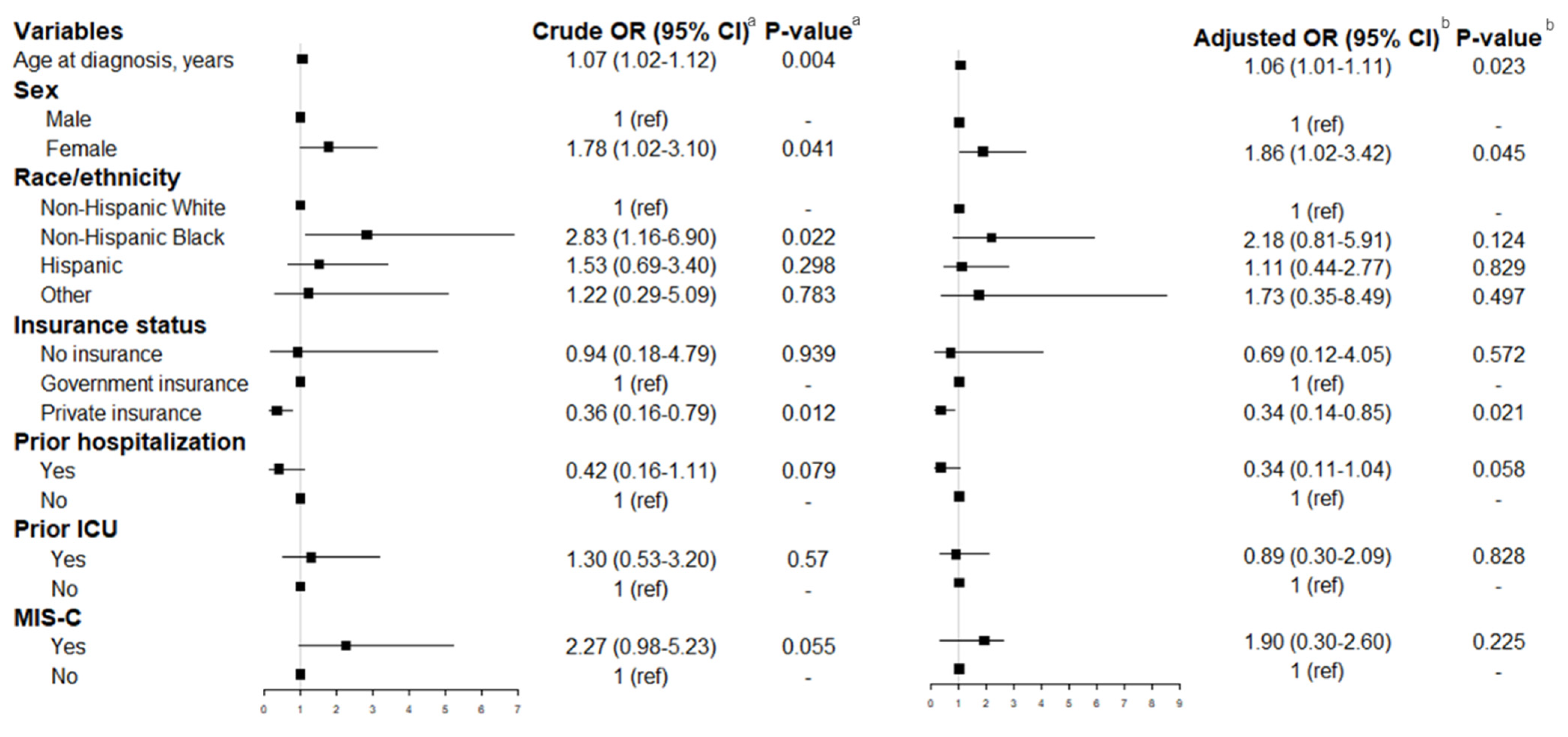
3. Results
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. Children and COVID-19: State Data Report. Available online: https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/AAP%20and%20CHA%20-%20Children%20and%20COVID-19%20State%20Data%20Report%202.3.22%20FINAL.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens. COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/children-teens.html (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health Department-Reported Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) in the United States. COVID Data Tracker. Available online: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#mis-national-surveillance (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Zimmermann, P.; Pittet, L.F.; Curtis, N. Long covid in children and adolescents. BMJ 2022, 376, o143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN) and Royal College of General Practitioners (RCGP). COVID-19 rapid guideline: Managing the longterm effects of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng188/resources/covid19-rapid-guideline-managing-the-longterm-effects-of-covid19-pdf-51035515742 (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Iqbal, F.M.; Lam, K.; Sounderajah, V.; Clarke, J.M.; Ashrafian, H.; Darzi, A. Characteristics and predictors of acute and chronic post-COVID syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine 2021, 36, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borch, L.; Holm, M.; Knudsen, M.; Ellermann-Eriksen, S.; Hagstroem, S. Long COVID symptoms and duration in SARS-CoV-2 positive children—A nationwide cohort study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long COVID and kids: More research is urgently needed. Nature 2022, 602, 183. [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, T.; Shafran, R.; De Stavola, B.; Rojas, N.; Aiano, F.; Amin-Chowdhury, Z.; McOwat, K.; Simmons, R.; Zavala, M.; CLoCk Consortium; et al. Long COVID and the mental and physical health of children and young people: National matched cohort study protocol (the CLoCk study). BMJ Open 2021, 11, e052838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borel, M.; Xie, L.; Kapera, O.; Mihalcea, A.; Kahn, J.; Messiah, S.E. Long-term physical, mental and social health effects of COVID-19 in the pediatric population: A scoping review. World J. Pediatr. 2022, 18, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeb, R.T.; Bitsko, R.H.; Radhakrishnan, L.; Martinez, P.; Njai, R.; Holland, K.M. Mental Health–Related Emergency Department Visits Among Children Aged <18 Years During the COVID-19 Pandemic—United States, January 1–October 17, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meherali, S.; Punjani, N.; Louie-Poon, S.; Abdul Rahim, K.; Das, J.K.; Salam, R.A.; Lassi, Z.S. Mental Health of Children and Adolescents Amidst COVID-19 and Past Pandemics: A Rapid Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Post-COVID Conditions. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO). COVID-19 Questionnaire—Child Parent-Report Version. ECHO-Wide Cohort Version 01.30. Available online: https://www.nlm.nih.gov/dr2/C19-cPR_COVID-19_Questionnaire-Child_Parent-Report_Version_20200409_v01.30.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Environmental Influences on Child Health Outcomes (ECHO). COVID-19 Questionnaire—Child Parent-Report Version. Available online: https://www.phenxtoolkit.org/toolkit_content/PDF/ECHO_Child_Self_Report_Primary_Impacts.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Pearlin, L.I.; Lieberman, M.A.; Menaghan, E.G.; Mullan, J.T. The stress process. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1981, 22, 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molteni, E.; Sudre, C.H.; Canas, L.S.; Bhopal, S.S.; Hughes, R.C.; Antonelli, M.; Murray, B.; Kläser, K.; Kerfoot, E.; Chen, L.; et al. Illness duration and symptom profile in symptomatic UK school-aged children tested for SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radtke, T.; Ulyte, A.; Puhan, M.A.; Kriemler, S. Long-term Symptoms After SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children and Adolescents. JAMA 2021, 326, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funk, A.L.; Kuppermann, N.; Florin, T.A.; Tancredi, D.J.; Xie, J.; Kim, K.; Finkelstein, Y.; Neuman, M.I.; Salvadori, M.I.; Yock-Corrales, A.; et al. Post-COVID-19 Conditions among Children 90 Days after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Netw Open 2022, 5, e2223253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi-Pooya, A.A.; Nemati, M.; Nemati, H. ‘Long COVID’: Symptom persistence in children hospitalised for COVID-19. J. Paediatr. Child Health 2022, 58, 1836–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterky, E.; Olsson-Åkefeldt, S.; Hertting, O.; Herlenius, E.; Alfven, T.; Rinder, M.R.; Rhedin, S.; Hildenwall, H. Persistent symptoms in Swedish children after hospitalisation due to COVID-19. Acta Paediatr. 2021, 110, 2578–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, R.; Berg, S.; Berntson, L.; Berthold, E.; Brodin, P.; Bäckström, F.; Compagno, M.; Fasth, A.; Lingman Framme, J.; Horne, A.; et al. Population-based study of multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19 found that 36% of children had persistent symptoms. Acta Paediatr. 2022, 111, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainardi, V.; Meoli, A.; Chiopris, G.; Motta, M.; Skenderaj, K.; Grandinetti, R.; Bergomi, A.; Antodaro, F.; Zona, S.; Esposito, S. Long COVID in Children and Adolescents. Life 2022, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Zheng, B.; Daines, L.; Sheikh, A. Long-Term Sequelae of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of One-Year Follow-Up Studies on Post-COVID Symptoms. Pathogens 2022, 11, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yao, Q.; Gu, X.; Wang, Q.; Ren, L.; Wang, Y.; Hu, P.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Xu, J.; et al. 1-year outcomes in hospital survivors with COVID-19: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet 2021, 398, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeßle, J.; Hippchen, T.; Lim AMerle, U.; Waterboer, T.; Simon, J.; Kirchner, M.; Muller, B. Persistent symptoms in adult patients one year after COVID-19: A prospective cohort study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cen, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, M.; et al. Symptoms and Health Outcomes Among Survivors of COVID-19 Infection 1 Year After Discharge from Hospitals in Wuhan, China. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2127403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.N.; Hoang, V.T.; Dao, T.L.; Dudouet, P.; Eldin, C.; Gautret, P. Clinical patterns of somatic symptoms in patients suffering from post-acute long COVID: A systematic review. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2022, 41, 515–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yomogida, K.; Zhu, S.; Rubino, F.; Figueroa, W.; Balanji, N.; Holman, E. Post-Acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Among Adults Aged ≥ 18 Years—Long Beach, California, April 1–December 10, 2020. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1274–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, N.; Park, I.W.; Robinson, J.R.; Jones, H.P. The perfect storm: COVID-19 health disparities in US blacks. J. Racial Ethn. Health Disparities 2020, 8, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messiah, S.E.; Hao, T.; DeSantis, S.M.; Swartz, M.D.; Talebi, Y.; Kohl, H.W., III; Zhang, S.; Valerio-Shewmaker, M.; Yaseen, A.; Kelder, S.H.; et al. Comparison of Persistent Symptoms Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Antibody Status in Nonhospitalized Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, e409–e417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 312) | MIS-C (n = 26) | Non-MISC (n = 286) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at diagnosis, years, mean (SD) | 6.65 (5.91) | 9.08 (4.86) | 6.43 (5.95) | 0.032 |
| Boys, n (%) | 165 (52.88) | 13 (50.0) | 152 (53.15) | 0.839 |
| Race/ethnicity, n (%) | 0.162 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | 64 (20.51) | 7 (26.92) | 57 (19.93) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 60 (19.23) | 7 (26.92) | 53 (18.53) | |
| Hispanic | 170 (54.49) | 9 (34.62) | 161 (56.29) | |
| Other/unknown | 18 (5.77) | 3 (11.54) | 15 (5.24) | |
| Education b | 0.001 | |||
| Preschool | 163 (52.41) | 5 (19.23) | 158 (55.44) | |
| Elementary school | 70 (22.51) | 13 (50.0) | 57 (20.0) | |
| Middle school | 29 (9.32) | 3 (11.54) | 26 (9.12) | |
| High school and above | 49 (15.76) | 5 (19.23) | 44 (15.44) | |
| Insurance status | 0.217 | |||
| No insurance | 8 (2.81) | 1 (3.85) | 7 (2.70) | |
| Government insurance | 206 (72.28) | 15 (57.69) | 191 (73.75) | |
| Private insurance | 71 (24.91) | 10 (38.46) | 61 (23.55) | |
| Hospitalization, n (%) b | 266 (85.26) | 25 (96.15) | 241 (84.27) | 0.146 |
| Hospital length of stay, days, mean (SD) | 5.77 (5.46) | 7.93 (3.79) | 5.12 (5.73) | 0.083 |
| ICU admission, n (%) | 28 (8.97) | 11 (42.31) | 17 (5.94) | <0.001 |
| ICU length of stay, days, mean (SD) | 11.0 (6.57) | 10.13 (3.76) | 11.58 (8.04) | 0.639 |
| Social and Behavioral Health | Total (n = 312) | MIS-C (n = 26) | Non-MISC (n = 286) | p-Value a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dietary intake b | Less | 27 (9.57) | 3 (11.54) | 24 (9.38) | 0.029 |
| Same | 208 (73.76) | 14 (53.85) | 194 (75.78) | ||
| More | 47 (16.67) | 38 (14.84) | 9 (34.62) | ||
| Sleep patterns b | Less | 29 (10.28) | 1 (4.0) | 28 (10.89) | 0.036 |
| Same | 219 (77.66) | 17 (68.0) | 202 (78.60) | ||
| More | 34 (12.06) | 7 (28.0) | 27 (10.51) | ||
| Physical activity c | Less | 37 (13.45) | 7 (26.92) | 30 (12.05) | 0.058 |
| Same | 216 (78.55) | 16 (61.54) | 200 (80.32) | ||
| More | 3 (11.54) | 3 (11.54) | 19 (7.63) | ||
| Spending time outside d | Less | 41 (15.30) | 6 (24.0) | 35 (14.4) | 0.326 |
| Same | 200 (74.63) | 16 (64.0) | 184 (75.72) | ||
| More | 27 (10.07) | 3 (12.0) | 24 (9.88) | ||
| In-person time with friends e | Less | 59 (22.10) | 9 (36.0) | 50 (20.66) | 0.016 |
| Same | 196 (73.41) | 13 (52.0) | 183 (75.62) | ||
| More | 12 (4.49) | 3 (12.0) | 9 (3.72) | ||
| Remote time with friends f | Less | 22 (8.66) | 0 (0) | 22 (9.57) | 0.013 |
| Same | 196 (77.17) | 16 (66.67) | 180 (78.26) | ||
| More | 36 (14.17) | 8 (33.33) | 28 (12.17) | ||
| Screen time for education purposes g | Less | 13 (4.98) | 0 (0) | 13 (5.51) | 0.053 |
| Same | 200 (76.63) | 16 (64.0) | 184 (77.97) | ||
| More | 48 (18.39) | 9 (36.0) | 39 (16.53) | ||
| Screen time for non-education purposes h | Less | 11 (4.15) | 0 (0) | 11 (4.58) | 0.036 |
| Same | 210 (79.25) | 16 (64.0) | 194 (80.83) | ||
| More | 44 (16.60) | 9 (36.0) | 35 (14.58) | ||
| Spending time participating in team activities i | Less | 26 (13.98) | 5 (22.73) | 21 (12.80) | 0.045 |
| Same | 145 (77.96) | 13 (59.09) | 132 (80.49) | ||
| More | 15 (8.06) | 4 (18.18) | 11 (6.71) | ||
| Social connections c | Less | 62 (22.55) | 9 (34.62) | 53 (21.29) | 0.045 |
| No difference | 184 (66.91) | 12 (46.15) | 172 (69.08) | ||
| More | 29 (10.55) | 5 (19.23) | 24 (9.64) | ||
| Difficulty sleeping c | Not at all | 186 (67.64) | 15 (62.64) | 171 (68.13) | 0.673 |
| Rarely/sometimes | 59 (21.45) | 7 (29.17) | 52 (20.72) | ||
| Often/very often | 30 (10.91) | 2 (8.33) | 28 (11.16) | ||
| Difficulty concentrating j | Not at all | 194 (75.19) | 14 (60.87) | 180 (76.60) | 0.019 |
| Rarely/sometimes | 46 (17.83) | 9 (39.13) | 37 (15.74) | ||
| Often/very often | 18 (6.98) | 0 (0) | 18 (7.66) | ||
| Startled easily k | Not at all | 211 (77.29) | 15 (62.50) | 196 (78.71) | 0.116 |
| Rarely/sometimes | 49 (17.95) | 8 (33.33) | 41 (16.47) | ||
| Often/very often | 13 (4.76) | 1 (4.17) | 12 (4.82) | ||
| Angry outbursts c | Not at all | 196 (71.27) | 12 (48.0) | 184 (73.60) | 0.021 |
| Rarely/sometimes | 58 (21.09) | 10 (40.0) | 48 (19.20) | ||
| Often/very often | 21 (7.64) | 3 (12.0) | 18 (7.20) | ||
| Slowing down l | Not at all | 206 (81.75) | 17 (70.83) | 189 (82.89) | 0.233 |
| Rarely/sometimes | 35 (13.89) | 5 (20.83) | 30 (13.16) | ||
| Often/very often | 11 (4.37) | 2 (8.33) | 9 (3.95) | ||
| Felt in a daze m | Not at all | 205 (80.39) | 18 (75.0) | 187 (80.95) | 0.233 |
| Rarely/sometimes | 38 (14.90) | 6 (25.0) | 32 (13.85) | ||
| Often/very often | 12 (4.71) | 0 (0) | 12 (5.19) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messiah, S.E.; Xie, L.; Mathew, M.S.; Shaikh, S.; Veeraswamy, A.; Rabi, A.; Francis, J.; Lozano, A.; Ronquillo, C.; Sanchez, V.; et al. Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C Status. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 13382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013382
Messiah SE, Xie L, Mathew MS, Shaikh S, Veeraswamy A, Rabi A, Francis J, Lozano A, Ronquillo C, Sanchez V, et al. Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C Status. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2022; 19(20):13382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013382
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessiah, Sarah E., Luyu Xie, M. Sunil Mathew, Sumbul Shaikh, Apurva Veeraswamy, Angela Rabi, Jackson Francis, Alejandra Lozano, Clarissa Ronquillo, Valeria Sanchez, and et al. 2022. "Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C Status" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19, no. 20: 13382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013382
APA StyleMessiah, S. E., Xie, L., Mathew, M. S., Shaikh, S., Veeraswamy, A., Rabi, A., Francis, J., Lozano, A., Ronquillo, C., Sanchez, V., He, W., Weerakoon, S. M., Srikanth, N., Borel, M., Kapera, O., & Kahn, J. (2022). Comparison of Long-Term Complications of COVID-19 Illness among a Diverse Sample of Children by MIS-C Status. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(20), 13382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013382







